Factors influencing the development of pain syndrome
Not only women, but also men are affected by pain in the lower abdomen. Moreover, they suffer from this much more often. If a man is suffering from pain, there is always a risk of serious danger. Causes of this symptom:
- inflammatory processes localized in the digestive system;
- appendicitis;
- diverticulitis;
- hernia;
- inflammation in the kidneys;
- damage to the genitourinary system;
- inflammation in the prostate gland;
- prostatitis.
Digestive system. Often, inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by pain of varying severity. This symptom on the left is characteristic of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Appendicitis. The pain syndrome is most often localized on the right, but can also radiate to the left side. Sometimes unbearable pain is recorded in the navel area. The process is accompanied by high fever and intestinal upset.
Diverticulitis. The pain is severe, observed in the lower abdomen on the left. The victim suffers only from mild nausea.
Hernia. This pathology is considered one of the most serious. It is characterized by a pinched nerve. The process is accompanied by acute pain with digestive disorders. In some cases, the person loses consciousness. Immediate surgery will help eliminate symptoms.
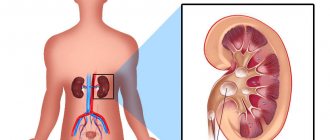
Inflammation in the kidneys. Pyelonephritis often causes pain in the lower abdomen. A similar symptom is recorded with damage to the testicles.
Damage to the genitourinary system. In the first stages, this process is asymptomatic. Over time, the first signs appear. More often, pain is recorded with cystitis and inflammation of the bladder. The man suffers from pain when urinating and there is urinary retention.
Inflammation in the prostate gland. This condition develops gradually and has virtually no symptoms. The clinical picture appears as the situation worsens. The man is plagued by aching pain that is quite bearable. Gradually the condition worsens.
Prostatitis. If it is not detected in time, the risk of developing severe complications, including adenoma, remains.
The appearance of pain requires identifying the underlying cause of this condition. This symptom can indicate both harmless inflammation and serious disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
For gastrointestinal disorders
Poor diet, lack of physical activity, hormonal imbalances and genetic predisposition can lead to problems with the functioning of the digestive system. The alarm bell of many diseases is pain in the lower left lobe of the abdomen.
Let's consider the possible causes of pain
Diverticulitis
This is a disease caused by inflammation in the colon due to dysbiosis or due to stagnation of food and feces. It is characterized by severe pain and cramping in the intestinal area on the left side, fever, diarrhea and the appearance of blood in the stool.
This disease can lead to dangerous complications. If an inflamed diverticulum (a protrusion in the intestinal wall) ruptures, the contents of the intestine will enter the abdominal cavity and cause peritonitis.
In addition, diverticulitis can affect the development of intestinal obstruction or even lead to cancer.
The disease is treated with medications; surgery should only be done in acute forms with a risk of complications.
IBS
Irritable bowel syndrome can develop against the background of various stressful situations. The disease occurs in the absence of regular physical activity, poor diet, dysbacteriosis and other factors.
It is characterized by diarrhea or frequent constipation, bloating, and a feeling of fullness in the intestines. Pain comes from the lower abdomen, in most cases on the left.
A person may experience different sensations: from mild internal discomfort to paroxysmal colic, which sometimes last for several hours in a row. However, signs of intestinal disorder do not appear when a person is sleeping.
This condition is not life-threatening, but if left untreated, it can lead to other pathologies. Medications are prescribed to treat the syndrome. In addition, the patient must adhere to a diet and try to avoid stressful situations.
Polyps
Sigmoid colon polyps are benign growths in the intestine. Some types can develop into malignant ones. They are caused by gastrointestinal diseases, as well as genetic predisposition, lack of fiber in food and poor physical activity.
The presence of polyps in the intestine may be indicated by colic in the lower part of the peritoneum, which occurs when squatting or any sudden movement.
In addition, blood or a large amount of mucus is found in the patient’s stool, constipation alternates with diarrhea, the person experiences a false urge to go to the toilet, suffers from bloating, heartburn and belching.
This disease is treated exclusively by surgery.
Sigmoitidae
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon. This disease can be caused by certain infections, including sexually transmitted infections, constipation and allergies.
This inflammation manifests itself as cramping pain in the left side of the abdomen, often shooting into the left leg and lower back, as well as vomiting, bloating and diarrhea. There is blood and mucus in the patient's stool, and his general condition worsens.
To treat sigmoitis, the patient must follow a special diet, take antibiotics and probiotics.
In addition to the cases described, a man may experience pain in the lower abdomen on the left side due to inflammation of the gallbladder, as well as gastritis or a stomach ulcer.
Pain syndrome in men: prostatitis
The acute form of the disease is characterized by unbearable pain. It is fixed in the perineum and extends to the anus. Prostatitis is often characterized by pain in the lower abdomen. The external genital organs are also affected in a certain way. Acute prostatitis is an inflammation localized in the prostate gland. It can be caused by unfavorable factors. More often, the development of prostatitis is caused by nonspecific microflora. Bacteria can enter the prostate gland through the urethra and provoke an inflammatory process in the urethra. Often, intestinal infections lead to inflammation of the prostate. It is extremely rare that the process develops due to infection as a result of medical procedures.
Prostatitis can be caused by disturbances in sexual activity. Prolonged abstinence or excessive sexual activity are especially dangerous. Sometimes the process is affected by sedentary work, excess weight and weak immunity.
The chronic form of prostatitis develops due to the lack of timely treatment at the early stage of inflammation.
The result is a periodic aggravation of the situation due to negative factors. Usually accompanied by abdominal pain, burning sensation when urinating and impaired sexual function.
Bladder cancer
Pain in the lower abdomen can be a symptom of bladder cancer. Malignant neoplasms quickly grow throughout the mucous membrane of the organ. Until now, the exact reasons for the development of this pathology have not been established. However, almost all doctors agree on one opinion: harmful working conditions are a predisposing factor for the development of bladder cancer. This disease is mainly diagnosed in miners, as well as in employees of plastic and rubber factories.
The development of bladder cancer is also influenced by genetic predisposition and past diseases such as prostatitis and urolithiasis.
At an early stage, the disease practically does not manifest itself. Only slight disturbances during urination are noticeable. Pain may radiate to the lower back. Such symptoms are also typical for cystitis. Therefore, a man cannot even suspect that his bladder cancer is actively developing.
Pain syndrome in men: malignant neoplasm and inflammation of the testicles
If the lower abdomen hurts, the cause may be hidden in the development of a malignant neoplasm. Typically, this symptom manifests itself in prostate cancer. In its clinical manifestations, it is similar to prostatitis in chronic form. The pain is localized in the lower abdomen and radiates to the external genital area. Cancer is most often diagnosed in men aged 50 years. This pathology is the most common. It is almost impossible to detect cancer at an early stage. This is due to the absence of any symptoms. Only a comprehensive examination will help in this matter.
Often, pain occurs as a result of an inflammatory process in the seminal vesicles. This is a paired organ, the main function of which is the formation of sperm and the maintenance of sperm vital activity. The inflammatory process often occurs against the background of prostatitis or urethritis. The pain syndrome is recorded in the suprapubic part and in the left side. The pain intensifies during the period of filling of the vesicles. This pathology is characterized by the development of spermatic colic. Acute pain affects the left side of the abdomen, perineum and testicular area. If the disorder becomes chronic, patients begin to complain of sexual problems.
In the absence of timely treatment, the risk of developing severe complications, in particular infertility, remains.
Abdominal pain, sexual dysfunction and urinary dysfunction are familiar to many people. And often such symptoms occur in combination.
What can be suspected in a man if he has pain in the lower abdomen on the left? What diseases of the genital organs are accompanied by this symptom? Is there a connection between the spine and abdominal pain? What diseases of the digestive system cause men to feel pain in the lower abdomen? Which doctors should I contact? Below we will answer all the questions.
Which doctor should I contact?
First of all, a man should consult a dermatologist, since pathology is often associated with damage to the skin. Once the cause is identified and after a thorough examination, treatment is prescribed.
If the burning sensation in the groin area is associated with sexually transmitted infections, then you will need to consult a venereologist. Renal pathologies that cause secondary burning of the skin are treated by a urologist, and gastrointestinal diseases fall under the purview of a gastroenterologist.
The appearance of pain or severe discomfort in the lower abdominal region in a man is an indicator of the development of a disease or inflammatory process. Pain is just a symptom that indicates the presence of pathology, but is never an independent disease.
Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you need to determine the cause and seek medical help. Timely differential diagnosis and correctly prescribed therapy are the key to quality treatment and preservation of health.
Causes
Localization of pain in the lower abdomen on the left in men indicates pathology of various organs:
- The most common cause is urological diseases - prostatitis, epididymitis, orchitis, urolithiasis, malignant tumors in the bladder and prostate, vesiculitis.
- Pathological changes in the spine.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
To identify the cause of pain, you may need to consult a urologist, neurologist or gastroenterologist.
Pain in the lower abdomen due to pathologies of the urinary system
When the primary diagnosis identifies the area of the problem – the genitourinary system. A urologist can diagnose:
- Urolithiasis disease. Often for many years he does not remind of himself. However, the movement of the stone within the system leads to a sharp attack of pain. In men, when a stone moves through the urinary tract, a sharp, unbearable pain is felt, shooting into the lower back. Treatment methods are aimed at pain relief and surgical elimination of the cause.
- Oncology of the bladder is accompanied by aching pain and difficult outflow of urine. The number of trips to the toilet per day increases sharply. The diagnosis requires additional tests and hardware diagnostics, which is accompanied by an oncologist.
- Urethritis - accompanied by pain and pain when passing urine. In case of infectious etiology, antibiotic therapy is necessary.
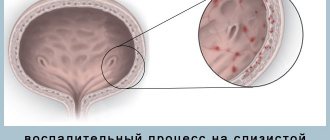
- Cystitis - the source of infection is localized in the bladder. In the case of a sudden, infectious process, it is accompanied by pain when passing urine and the appearance of blood. Requires identification of the source of the problem and treatment with NSAIDs, antimicrobial drugs and physical therapy.
When trips to the toilet become a problem or become more frequent than normal, you need to visit a urologist.
Prostatitis
The most common disease for pain in the lower left abdomen is prostatitis. The prostate gland is located deep in the pelvis, in close contact with the bladder in front, and with the rectum in the back. This inevitably leads to the spread of pain from the prostate to neighboring organs - the sacrum, penis and anterior surface of the thighs. Important! In men, pain is felt in the lower left abdomen because the rectum is projected here.
Other signs of prostatitis:
- The function of urination is impaired, up to urinary retention. But when trying to empty the bladder, pain occurs.
- There is difficulty in defecation.
- In the acute stage, signs of intoxication appear - an increase in temperature to 39.5 ° C, deterioration in health.
If treated incorrectly during this period, severe complications develop:
- prostate abscess;
- inflammation of the venous plexus and tissues around the gland.
In less severe cases, acute prostatitis becomes chronic with frequent relapses.
Causes of prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate can begin after hypothermia in the legs or pelvic area. The infection often spreads to the prostate from the bladder or urethra with cystitis. Bacteria can enter the prostate through the bloodstream from neighboring inflamed organs - the large intestine. In the same way, the infection penetrates from distant organs, for example, from the tonsils in chronic tonsillitis. Pathogens:
- E. coli is detected in 86% of cases;
- less often staphylococcus;
- streptococcus.
Prostatitis also develops after infection with sexually transmitted infections. In this case, the disease is caused by bacteria:
- Trichomonas;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasma;
- gonococci;
- mycoplasma;
- gardnerella;
- viruses;
- mushrooms of the genus Candida.
Prostatitis can develop due to congestion in the pelvis due to a sedentary lifestyle, with dysfunction of the genital organs. Sexual abstinence, sexual immoderation and interrupted sexual intercourse also provoke the development of prostatitis. Risk factors include alcohol consumption, obesity, and decreased immunity. Predisposing factors for the development of prostatitis are prolonged riding of a motorcycle or car.
Classification of peritoneal tumors
There are three main groups of peritoneal neoplasms:
- Benign peritoneal tumors (angiomas, neurofibromas, fibromas, lipomas, lymphangiomas)
- Primary malignant tumors of the peritoneum (mesotheliomas)
- Secondary malignant tumors of the peritoneum, which occur when malignant cells spread from another organ.
There are also mucus-forming neoplasms (pseudomyxomas), which some researchers consider as primary, and others as secondary peritoneal tumors of varying degrees of malignancy. In most cases, secondary peritoneal lesions develop as a result of aggressive local growth of neoplasms and implantation spread of cancer cells from organs located intraperitoneally, mesoperitoneally or extraperitoneally.
Peritoneal tumors resulting from implantation metastasis can be detected in cancer of the stomach, small and large intestines, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, kidney, uterine body, cervix, ovaries, prostate, anterior abdominal wall, etc. Less commonly lymphogenous spread of metastases of chest tumors (for example, lung cancer) is observed, caused by the retrograde movement of lymph along the lymphatic tract.
Urolithiasis disease
In men, pain in the lower abdomen on the left is also caused by kidney disease. Nephrolithiasis, kidney stones or urolithiasis, urolithiasis are names of the same disease. It is manifested by the formation of stones in the kidneys, ureters and bladder.
Nephrolithiasis is found in men aged 20 to 50 years. Stones are usually found in one kidney or ureter.
Important! The number of stones amounts to several hundred. And the sizes vary from grains of sand to 12 cm in diameter. Therefore, the disease is popularly known as “sand or salt in the kidneys.”
The main reason for stone formation is metabolic disorders, leading to the formation of insoluble salts of urates, oxalates, and phosphates. Over time, stones are formed from them. Risk factors for itch:
- insufficient fluid intake;
- hypovitaminosis;
- hereditary predisposition;
- diseases of the genitourinary system - prostate adenoma, cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis.
In most patients, pebbles and small crystals move up the ureter and are excreted in the urine. When passing sand, abdominal pain is felt.
Typical signs of kidney stone disease:
- Abdominal pain of varying intensity either subsides or intensifies, but does not completely disappear. A severe attack of renal colic requires medical attention. If it moves along the ureter, a stone larger than the width of the ureter gets stuck, causing severe pain in the lower abdomen on the left or right, where the lower part of the ureters is located.
- During an attack, patients experience nausea, vomiting, and painful urination.
- Small stones or salts in the urine are not uncommon in people with urolithiasis.
- Red blood cells in the urine are a typical sign of kidney stones, especially after an attack of colic. In this case, the urine turns pink, reddish, or the color of “meat slop.” In other cases, hematuria can be detected microscopically or using special test strips.
Urolithiasis can be hidden for years and is discovered by chance.
Diagnosis of urolithiasis
Stones in the urinary tract and kidneys are detected by instrumental examination methods:
- Ultrasound is the most accessible, safe and reliable method for detecting stones.
- In doubtful cases or in preparation for surgery, a highly accurate diagnostic method is done: MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or CT (computed tomography).
Instrumental examination methods are carried out after laboratory detection of blood, salts, and leukocytes in the urine.
Treatment of kidney stones
For frequent attacks, urologists use methods to destroy or remove stones:
- SWL (shock wave lithotripsy) is used for stones in the kidneys and upper ureters. After destruction, the stones come out naturally.
- URS – ureteroscopy. The device with the camera is inserted through the bladder and advanced along the ureter to the kidney. It is equipped with tools for crushing and extracting stones.
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy is an endoscopic method for removing large stones. A device with a camera is inserted into the kidney through a small puncture in the abdomen. It is used to crush and remove kidney stones.
During a moderate attack of abdominal and lower back pain, urologists prescribe outpatient treatment - painkillers and antispasmodics Ibuprofen, Baralgin. Doctors prescribe Tamsulosin, Nifedipine to speed up the passage of stones.
Types of tumor lesions of the peritoneum
Benign peritoneal tumors
They are a very rare pathology. The reasons for the development are unknown. The disease can be asymptomatic for years. In some cases, peritoneal tumors reach enormous sizes without significantly affecting the patient’s condition. The literature describes a case of removal of an omental lipoma weighing 22 kilograms. With large nodes, an enlarged abdomen is detected. Sometimes benign tumors of the peritoneum cause compression of nearby organs. Pain is uncharacteristic. Ascites occurs extremely rarely. The diagnosis is made based on the results of laparoscopy. The indication for surgery is the compressive effect of the tumor on neighboring organs.
Primary malignant tumors of the peritoneum
Peritoneal mesotheliomas are rare. Usually found in men over 50 years of age. A risk factor is prolonged contact with asbestos. They manifest themselves as pain, weight loss and symptoms of compression of nearby organs. With sufficiently large peritoneal tumors, an asymmetric protrusion in the abdominal area may be detected. On palpation, single or multiple tumor-like formations of various sizes are detected.
Characterized by rapid progression of symptoms. When the portal vein is compressed, ascites develops. Due to the lack of specific signs, the diagnosis of malignant peritoneal tumors is difficult. Often, the diagnosis is made only after excision of the tumor and subsequent histological examination of the removed tissue. The prognosis is unfavorable. Radical removal is possible only with limited processes. In other cases, patients with peritoneal tumors die from cachexia or from complications caused by dysfunction of the abdominal organs.
Pseudomyxoma peritonei
Occurs when an ovarian cystadenoma, pseudomucinous cyst of the appendix, or intestinal diverticulum ruptures. Mucus-producing epithelial cells spread across the surface of the peritoneum and begin to produce a thick, jelly-like fluid that fills the abdominal cavity. Typically, the rate of development of this peritoneal tumor corresponds to a low degree of malignancy. The disease progresses over several years. The jelly-like liquid gradually causes fibrotic changes in tissue. The presence of mucus and tumor formation interferes with the activity of internal organs.
Less commonly, high-grade peritoneal tumors are detected that are capable of lymphogenous and hematogenous metastasis. If left untreated, death occurs in all cases. The cause of death of patients is intestinal obstruction, exhaustion and other complications. The presence of a mucus-forming tumor of the peritoneum is indicated by an increase in the size of the abdomen with a decrease in body weight, digestive disorders and jelly-like discharge from the navel.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of CT, laparoscopy, histological and immunohistochemical studies. For malignant tumors of the peritoneum, positron emission tomography can be used. For a benign variant of the disease, this study is not informative. Treatment tactics for peritoneal tumors are determined individually. In some cases, surgical excision of the affected areas in combination with intraperitoneal intracavitary chemotherapy is possible. With timely initiation of treatment, the prognosis is quite favorable, especially for low-grade peritoneal tumors.
Single secondary malignant tumors of the peritoneum
The lesion occurs when the germination of malignant tumors located in organs partially or completely covered by the peritoneum. The appearance of peritoneal tumors is accompanied by increased pain and deterioration of the patient's condition. Palpation of the abdomen may reveal tumor-like formations. When a lesion in a hollow organ (stomach, intestine) disintegrates, the phenomena of perforated peritonitis are observed. In some cases, the primary tumor simultaneously grows into the wall of a hollow organ, the layers of the peritoneum and the anterior abdominal wall. When the resulting conglomerate disintegrates, soft tissue phlegmon occurs.
Peritoneal tumors are diagnosed based on medical history (there is a malignant neoplasm of an organ covered by the peritoneum), clinical manifestations, abdominal ultrasound data and other studies. With a limited process, radical excision of the primary tumor along with the affected area of the peritoneum is possible. In the presence of distant metastases, symptomatic therapy is carried out. Patients with peritoneal tumors are prescribed painkillers; if fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, laparocentesis is performed, etc. The prognosis depends on the extent of the process.
Peritoneal carcinomatosis
Malignant cells entering the abdominal cavity quickly spread throughout the peritoneum and form multiple small foci. At the time of diagnosis of stomach cancer, peritoneal carcinomatosis is detected in 30-40% of patients. In ovarian cancer, secondary peritoneal tumors are found in 70% of patients. The pathology is accompanied by the appearance of profuse effusion in the abdominal cavity. Patients are exhausted, weakness, fatigue, stool disorders, nausea and vomiting are detected. Large peritoneal tumors may be palpable through the abdominal wall.
There are three degrees of carcinomatosis: local (one affected area is detected), with damage to several areas (the affected areas alternate with areas of unchanged peritoneum) and widespread (multiple secondary peritoneal tumors are detected). With an undiagnosed primary tumor and multiple peritoneal nodes, clinical diagnosis in some cases is difficult due to the similarity with the picture of tuberculous peritonitis. Secondary tumors of the peritoneum are supported by the hemorrhagic nature of the effusion and the rapid reappearance of ascites after laparocentesis.
Epididymitis
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, in which pain is felt in the lower left abdomen. Anatomically, this small formation is located in the upper part of this organ. The seed comes out of it through the tubules of the appendage.
The infection usually penetrates the epididymis through the blood flow from the prostate. The causative agents of the disease are Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, chlamydia, gonococcus. Epididymitis develops with urogenital chlamydia, tuberculosis and gonorrhea. The development of the disease is facilitated by hypothermia, hypovitaminosis, and placement of a catheter for urination.
Signs of acute epididymitis:
- The disease begins acutely – within 3–4 hours. Acute pain in the scrotum radiates down the abdomen with left-sided epididymitis.
- Temperature rise to 38.0°
- Swelling of the scrotum.
Chronic inflammation develops gradually. Pain in the testicle increases, and swelling of the scrotum appears. Acute chronic epididymitis can be treated with antibiotics. But with untreated inflammation, the infection spreads to neighboring organs. In this case, complications arise:
- orchitis - inflammation of the testicle, spreading to the scrotum;
- sepsis – blood poisoning;
- infertility.
Urologists make a diagnosis by external examination and palpation of the scrotum.
- Antibiotics Unidox Solutab 100 mg twice a day or Ofloxacin 200 mg 2 times a day for 2 weeks.
- Applying a suspension bandage with ice to the scrotum to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Diclofenac rectal suppositories to relieve inflammation and pain.
Important! Self-medication leads to complications or chronicity of epididymitis. Bilateral inflammation of the epididymis is the cause of male infertility.
Abdominal cancer: diagnosis, symptoms, treatment and life prognosis
Abdominal cancer is a pathological condition of uncontrolled growth of atypical, previously healthy cells (neoplasms) by the body, life-threatening, arising from the cells of the abdominal cavity. The ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision) code for the disease is assigned to C48.
The abdominal cavity is a space in the human body. The upper part of the abdominal cavity is marked by the diaphragm, and below by the pelvic organs. The entire peritoneal space is filled with digestive organs.
The walls are lined with serous substance (serous membrane), which consists of fibrous and epithelial tissue and separates the peritoneum from the retroperitoneal space, beginning to line the peritoneal walls with epithelium from the diaphragm and below.
These tissues are present to cover the walls of the cavity:
- upper (diaphragm);
- lower (pelvic diaphragm);
- left and right (three broad abdominal muscles);
- anterior and posterior (anterior abdominal wall and lumbar spine).
The organs located in the abdominal cavity include:
- stomach;
- parts of the large and small intestines;
- spleen;
- gallbladder;
- liver.
Also in the peritoneum there are ligaments, blood vessels, and lymph nodes.
Due to the large number of organs and varieties of cells and tissues in the abdominal cavity, malignant oncology can develop. The disease can occur for various reasons, under the influence of a number of negative factors.
Classification of abdominal cancer
Cancer is usually classified according to the method of its formation. In the case when the oncological process begins in the abdominal cavity, there are two types:
- Peritoneal mesothelioma (primary cancer - formed in the tissues of the cavity itself). This type of malignant oncology, in which science remains unknown to the main trigger causes of the appearance of tumors. However, statistical studies have revealed the main predisposition to this type of cancer in people who, due to the nature of their employment, constantly deal with asbestos dust. For example, during construction and production work, labor activities with chemical reagents of increased toxicity to the body. In this regard, this type is more common in men; for women this type is rare.
- Epithelial cancer (carcinoma). Statistically, women have a greater predisposition to it. Primary localization is the ovary. The neoplasm retains its histological predisposition and does not mutate beyond recognition. The ovary and peritoneal epithelium are histologically similar and located nearby. Pathology begins to develop in the ovary. Then, in the process of growth or metastasis, it begins to affect healthy peritoneal epithelial cells. The same type of cancer occurs if there is a history of gastrointestinal cancer.
Causes of peritoneal cancer
The reason that triggers the oncological process is not known to science today. In the case of epithelial cancer, the main factor is the presence of oncology in the ovaries.
Given the increased risk, abdominal cancer prevention is used in the treatment of ovarian cancer. In the case of mesothelioma, it is the influence of building materials and chemistry. There are also other factors that lead to the occurrence of cancer.
The main factors influencing the occurrence of neoplasms in the peritoneum include the following:
- Genetic predisposition - the influence of the factor is noticeable when people in the immediate blood relatives suffered from oncological pathologies, in particular abdominal oncology.
- Non-compliance with the diet and incorrectly selected diet of foods, leading to the occurrence of chronic pathologies of the stomach, gastrointestinal tract and other pathologies of the digestive system of a chronic nature.
- Hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Endocrine pathologies (for example, type 2 diabetes mellitus, inflammatory processes in the thyroid gland).
- Increased body mass index (obesity 2 and 3 degrees).
- Chronic pathologies of internal organs.
- Use of tobacco products in unlimited quantities.
- Alcoholism and drug addiction of the patient.
- Violation of the development of organs and skeletal bones in the body.
- Degenerated benign neoplasms of the abdominal cavity.
- Constantly being in a state of increased nervousness and stress.
There are also other possible causes.
Stages of the disease
As in most cases, abdominal cancer goes through 4 main stages in its development:
| Stage No. | Characteristics of the stage |
| Stage 1 | The neoplasm does not have multiple foci. Localization is clearly visible. There is no metastasis. |
| Stage 2 | There is a sharp increase in tumor size. Signs of invasion into nearby organs and tissues of the abdominal cavity appear. |
| Stage 3 | The tumor begins to spread throughout the peritoneum. |
| Stage 4 | Metastases begin to damage vital organs. Both nearby and distant. Ascites (peritoneal dropsy) may develop. This term refers to the pathological accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. The abdomen increases in volume. The patient begins to gain weight quickly. In advanced forms, the volume of liquid can reach values of more than 25 liters. In addition to peritoneal oncology, liver cirrhosis becomes the cause of pathology. |
The above-mentioned features of the pathology are characteristic of mesothelioma, when the oncology in the primary focus is formed in the abdominal cavity. For epithelial cancer in the early stages, the disease will not differ from the development of ovarian cancer, where the original site is located.
Symptoms of abdominal cancer
Oncological pathologies cause increased danger when they are detected in late stages. Often the reason for delayed diagnosis is the asymptomatic onset of the process. The first signs appear when the size of the tumor becomes large (5 centimeters or more).
The main symptoms and clinical picture of the development of peritoneal cancer are as follows:
- An increase in abdominal volume, especially with the development of ascites. Due to this, body weight gain occurs.
- Painful sensations with constantly increasing intensity (the symptom is associated with irritation of pain receptors located in the peritoneum).
- Swelling of the lower extremities, genitals, abdomen.
- Intestinal obstruction is a deadly symptom in the absence of timely medical intervention. The intestine is an internal organ that performs many digestive functions. As the tumor grows, a blockage occurs.
- With sarcoma of the retroperitoneum, rapid loss of body weight occurs (on average, in two to three months the patient loses up to 10 kilograms in weight).
- Chronic fatigue syndrome due to disruption of the normal functioning of the liver. Pathologies of the organ cause disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, resulting in inhibition. A person does not feel rested, even after a long period of rest. Discoordination and psychosomatic disorders are present.
- Changes in body temperature with the possibility of low-grade fever.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Decreased appetite.
If metastasis and concomitant pathologies occur, additional symptoms characteristic of the symptoms of a particular pathology are likely to appear. These may include:
- swelling of the right hypochondrium;
- jaundice (change in skin color);
- urine color is deep yellow;
- color of stool – discolored;
- itching of the skin;
- bloody diarrhea;
- flatulence.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, doctors need to perform a series of diagnostic procedures on the patient. The most informative for this type of oncology is ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs. It can show the size of the tumor and its exact location in the abdominal cavity.
As additional diagnostic procedures, the patient is given:
- General and biochemical blood tests, biomaterial are checked for the presence of appropriate tumor markers.
- Analysis of abdominal fluid (used in case of ascites).
- Laparoscopy may be prescribed, collecting material for histological examination and establishing the nature of the neoplasm.
- Contrast computed tomography – to determine the structure of the tumor.
- Transvaginal ultrasound for primary tumor localization in a woman’s ovary.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (analogous to computed tomography in cases where there is intolerance to contrast agents or other contraindications to the use of CT for diagnostics).
- Electrocardiogram - to determine the involvement of the heart in the oncological process.
- General tests (urine, feces).
Abdominal cancer treatment
Cancer treatment depends on the diagnostic data obtained during diagnosis. To select the necessary treatment methods, the doctor takes into account the general health condition, the patient’s age, type of cancer, stage of development, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
The most common methods of treating any cancer are:
- surgical intervention;
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy.
If it is impossible to perform abdominal surgery to remove oncology according to indications, chemotherapy or radiation therapy can be used as independent methods. The most effective is a combination of all three types of treatment. This is due to the fact that initially these types of cancer treatment are designed to consolidate the success of the surgical operation.
If a decision is made to perform surgery, during the procedure the surgeon removes both the body of the tumor and the damaged tissue around it. Additionally, regional lymph nodes must be removed.
The remaining foci of pathology will be destroyed during the use of radiation exposure during radiation therapy and the effects of pharmacological drugs introduced into the patient’s body intravenously during chemotherapy.
In the case of abdominal oncology, the method of thermal chemotherapy has been developed, in which drugs are administered to the patient after exposure to temperature.
When the tumor is in a complicated position, radiosurgery is used. Each of these methods can cause a temporary deterioration in the patient’s health and lead to chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
If other organs are damaged during the development of oncology, they are subject to partial or complete amputation, depending on the nature of the damage. In the case of ascites, a drain is inserted to remove excess fluid from the abdominal cavity.
General therapy consists of the patient using fortifying fortified medications, diet, physical therapy, and maintaining a sleep-wake schedule.
Life forecast
An individual survival prognosis for peritoneal oncology is created taking into account the stage of the process, the level of tumor growth, health indicators, and the patient’s age.
Statistical studies indicate the importance of early diagnosis of pathology. If detected in the early stages, the prognosis is favorable.
For the second stage, with proper treatment, remission occurs in 85% of patients when calculating a five-year survival rate. In this case, the patient will live without loss of quality of life and risk of relapse.
During the thermal stage of the oncological process, patients live no more than two years.
Source: https://onko.guru/organ/rak-bryushnoj-polosti.html
Urethritis
Urethritis is another disease in which pain is localized in the lower abdomen on the left or right. Even with acute illness, there is no increase in temperature.
- Stinging and pain spreads along the entire length of the urethra. Anatomically, its lower part goes down the abdomen on the left and right, where pain is felt on one or both sides.
- Copious mucous discharge from the urethra in the morning.
- Cloudy urine sometimes with drops of blood at the end of urination.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Redness of the glans penis with sticky lips of the urethral opening.
- Pain during erection.
- A common cause of the disease is sexually transmitted infection.
- Urethritis also appears after hypothermia. The causative agents of the disease are staphylococci, streptococci, and E. coli, which ascend into the urethra through the ascending route from the bladder during cystitis. Bacteria spread from neighboring (intestines) and distant organs (tonsils) through the bloodstream.
- Allergic urethritis occurs after using condoms, soaps, and shampoos. Medicinal substances also cause allergic reactions.
- Non-infectious urethritis develops after the passage of salts or stones through the urethra.
Congestion in the pelvis with a sedentary lifestyle contributes to the development of urethritis.
Diagnosis and treatment of urethritis in men
The diagnosis of the disease is established by collecting anamnesis, palpation of the abdomen and examination of the external genitalia.
Laboratory testing is aimed at identifying infection:
- A general urine test determines a large number of leukocytes.
- To determine the type of pathogen in men, a culture of discharge from the urethra or the first portion of urine is done. Bacterial culture also determines the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics.
- antibiotics are prescribed by a doctor after determining the type of pathogen;
- drugs to restore normal intestinal flora;
- antiallergic drugs;
- immunostimulants and vitamins.
Diagnostics
If the presence of fibroma or other neoplasms formed in the abdominal cavity is suspected, the specialist conducts an examination, palpation examination and carefully studies the patient’s medical history. To establish an accurate diagnosis, a number of studies are prescribed:
- Ultrasound . The technique allows us to identify the location and size of the tumor.
- analysis . It is carried out to determine the presence of tumor markers.
- CT scan . One of the informative methods for diagnosing many diseases. Allows you to determine the degree of development, location and size of the formation.
- X-ray examination. Prescribed to detect metastases in the lungs.
- Cytological examination. Indicated in cases where the abdominal volume is increased
- Diagnostic laparoscopy . Necessary for the procedure of collecting an image of biological material. The biopath is sent to the laboratory for a cytological study, which confirms or denies the malignancy of the neoplasm.
If a tumor is detected in the ovarian area, women are advised to undergo a transvaginal ultrasound examination. The method allows you to study the condition of the internal genital organs.
Digestive system diseases
A common cause of pain in the lower abdomen is pathology of the digestive system. Anatomically, in men, the rectum and sigmoid colon are projected in the lower abdomen on the left. Therefore, when they become inflamed, pain is felt here. In addition, the nerve plexus of the rectum and sigmoid colon are interconnected with the prostate gland and urethra.
Intestinal diseases extending down the abdomen:
- proctitis (proctosigmoiditis);
- constipation due to colitis;
- bowel obstruction, diverticula, or tumor;
- hernia;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- colon tumor.
Let's look at some of those diseases.
Prevention
To prevent the development of conditions that cause pain in the left side and lower abdomen, men should:
- Pay attention to personal hygiene.
- Lead an orderly sex life - without casual sexual intercourse.
- Avoid hypothermia and prolonged stay in humid climates.
- Avoid chaotic eating and consumption of low-quality foods.
- Change working and living conditions in favor of a safe option - move away from sources of intoxication.
- Avoid body damage.
- Limit yourself from stress.
Additional preventive measures are seasonal vitamin therapy, regular medical examinations for hereditary predisposition to pathologies.
Pain in the left side extending to the lower abdomen is an important sign that indicates the need to consult a specialist. Diseases that lead to abdominal discomfort are numerous. Without hardware and instrumental diagnostics, it is impossible to accurately determine the root cause of the condition. Therefore, a visit to a specialist is an indispensable condition for maintaining the integrity of the affected organ.
Proctitis
Proctitis (proctosigmoiditis) is an inflammation of the inner lining of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
- Pain in the lower abdomen spreads to the perineum, bladder, groin area, and sometimes the buttocks and the front of the thighs.
- In acute proctitis, there is a frequent urge to stool or the discharge of a small amount of crumbly feces with particles of blood and mucus.
- Chronic proctosigmoiditis is accompanied by frequent mucus discharge from the intestines, causing itching and irritation of the skin around the anus.
- Dyspeptic disorders - diarrhea, less often constipation.
The doctor makes a diagnosis of proctitis based on the following criteria:
- Palpation of the abdomen is painful in the lower abdomen on the left.
- The skin around the anus is irritated.
- When palpated with a finger, sphincter spasm and pain are noted.
Instrumental and laboratory research methods:
- Rectoscopy shows hyperemic mucous membrane with erosions and ulcers.
- A scatological examination of stool reveals an increase in the number of leukocytes. Red blood cells and fungi are also visible. With protozoal infection, amoebas, lamblia, and worm eggs are detected.
- The bacteriological method (culture) identifies gonococci, dysentery and paratyphoid bacteria.
If sexually transmitted diseases are suspected, the Wasserman and Koch reaction is performed, as well as a blood test using PCR and ELISA.
Causes of proctitis
Several reasons contribute to the development of the disease:
- Infections – bacterial and amoebic dysentery, typhoid fever. In homosexuals, proctitis is caused by syphilis and gonorrhea bacteria.
- A common cause of proctitis is constipation, when dried feces linger for a long time in the rectum, mechanically and chemically irritating its walls. The same effect on the rectum is exerted by potent laxatives and the administration of hypertonic and essential oil mixtures and glycerin with an enema.
- Allergic proctitis after eating crayfish, mushrooms, squid.
Proctitis is a manifestation of general intestinal inflammation.
Treatment of proctitis
After the examination, the proctologist prescribes a set of therapeutic measures depending on the cause and causative agent of the disease. The action of the drugs is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, which relieves men of pain in the lower left abdomen. For this purpose medications are prescribed:
- Antibiotics. For giardiasis, Intestopan is prescribed.
- Rectal anti-inflammatory suppositories.
- Warm therapeutic enemas with Protargol or rosehip decoction.
- After the acute process has subsided, physiotherapy and balneotherapy are used - diathermy currents, mud panties.
During an exacerbation, proctologists recommend bed rest and a gentle diet.
Treatment methods for detected pathologies
Since the left or right side of the abdomen can be larger for various reasons, treatment differs significantly. The severity of the pathologies accompanied by this symptom also depends on the nature of the course and the characteristics of organ damage. There are 2 groups of treatment methods – surgical and non-surgical:
- in case of severe pathologies, such as appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy or intestinal obstruction, emergency surgery is required;
- a hernia is not considered a serious medical disorder, but in most cases requires surgical removal;
- after surgery, antibiotic therapy is prescribed to prevent inflammation and infections;
- during the rehabilitation period, the patient takes medications prescribed to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and accelerate recovery: immunomodulators, probiotics, vitamins, NSAIDs and antispasmodics to prevent pain, as well as specific groups of drugs (hormones, diuretics, proton pump inhibitors);
- if an enlarged abdomen is caused by flatulence, gas formation or intestinal distension, most often conservative methods of therapy are sufficient: diet correction, taking antispasmodics and carminatives, exercise.
More severe forms of diseases, for example, ovarian cancer, abdominal wall tumors, require complex treatment. Radiation or chemotherapy is often used, followed by surgery and rehabilitation measures.
Diseases of the peripheral nervous system
A common cause of lower abdominal pain in men is inflammation of the sciatic nerve. With this disease, the roots of the lumbosacral spine are infringed. The cause of compression is a herniated intervertebral disc.
Symptoms of a herniated disc:
- The most common early sign is lower back pain associated with movement. A displaced disc impinges on the roots coming out of the spine.
- One of the signs of a hernia is pain in the lower abdomen on the left or right. In neurosurgery there is a term “cauda equina syndrome”. It means impaired sensation and movement of the limbs, as well as urination and defecation. The cauda equina is a continuation of 40 nerve roots that emerge from the lumbar region and descend in the form of a bundle to the tailbone. The tail is responsible for innervation of the lower extremities, as well as the pelvic organs - rectum, bladder. When the cauda equina is affected, pain appears along the course of the cauda equina - in the limb, perineum, buttocks, lower abdomen on the left or right, depending on the side of the lesion. In the later stage of cauda equina syndrome, urination and defecation are impaired. After all, the transmission of nerve impulses to the rectum and bladder is disrupted during a hernia. More often, pain in the lower abdomen appears later than in the lower back, but there are exceptions.
Signs of bladder dysfunction are difficulty starting to urinate and lack of urge. The functioning of the rectum is also disrupted in the form of constipation and difficulties in passing gases. In the advanced stage of cauda equina syndrome, the urge to urinate and defecate is completely absent. The patient suffers from urinary and fecal incontinence.
Causes of intervertebral hernia:
- The lumbosacral spine is the most vulnerable part of the spinal column. It carries the greatest load and is more likely to be injured when falling. Regular lifting of weights over the years can trigger the development of a hernia.
- Hereditary predisposition – the structure of the bones and ligaments of the spine – contributes to the formation of the disease.
- Osteochondrosis is also a provoking factor.
- Weakness of the back muscles.
- Curvature of the spinal column.
- Insufficient nutrition of vertebral tissues.
A neurologist and vertebrologist are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of hernia. After the examination, doctors use instrumental examination methods:
- X-ray of the spine.
- CT (computed tomography).
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
- Myelography (lumbar function using contrast).
Therapy for cauda equina syndrome consists of conservative and surgical treatment. If the disease is caused by inflammatory diseases of the spine (spondylitis or Paget's disease), then conservative methods are used. For intervertebral hernia, surgical intervention is performed.
Based on the above, we note. Most often, pain in the lower left abdomen in men is caused by inflammation of the genitourinary system. If the urologist does not identify the disease, most likely the cause of the disease is proctitis or another intestinal disease. In this case, the diagnosis is carried out by a proctologist or gastroenterologist. Less commonly, the cause of abdominal pain is caused by spinal pathology, which is dealt with by a neurologist.
If pain in the lower abdomen appears in men, then comparing it with women’s problems in this area is pointless. The structure of organisms has significant differences. And above all, it is in the hip area. There are only a few diseases that both women and men can have. The female body is complex, unlike the male one. The stronger sex will not suffer from unpleasant cyclical disorders or inflammation in the later stages. But this does not mean that pain is a sign of minor or harmless illnesses. They are caused by problems with the anatomical structure or parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Regarding diseases that are unique to the stronger sex, men rarely experience pain in the lower abdomen. To understand why cutting or aching symptoms occur, it is best to become familiar with all types of pain and lesions closely associated with them.
Treatment methods
When an abdominal tumor is identified, the only treatment option is surgery. Depending on the size, nature of the course, the presence of indications and contraindications, the operation can be performed in various ways.
Radiation therapy
Performed before and after abdominal surgery. The method is based on the impact on the tumor with a special device. When rays influence a neoplasm, a slowdown in the growth of pathogenic cells is observed.
In addition, radiation therapy helps reduce the risk of complications.
Chemotherapy
Also prescribed before or after surgery to remove a tumor. It is carried out using chemicals, the active substances of which have a negative effect on pathogenic cells.
As a result, the tumor slows down its growth, reducing the risk of metastases in neighboring tissues or various organs.
Radiosurgery
It is prescribed in cases where there are metastases in hard-to-reach places. The impact on education is carried out using radio waves, which have a negative effect directly on cancer cells.
Abdominal surgery
The classical method of resection of tumors formed in the abdominal region is rarely used today. During the procedure, the specialist uses a surgical scalpel. After resection of the tumor, the abdominal cavity is washed with antiseptic solutions.
Cryodestruction or laser removal is prescribed only in cases where the neoplasm is not large and there are no contraindications. The advantages of these removal methods are a short recovery period, the absence of large scars and bleeding during the procedure.
Pain and discomfort on the right
If you experience pain that can be described as nagging or aching, you should contact specialists who can deal with chronic inflammation. The peritoneal organs suffer, but there are cases that are exceptions:
- urological diseases;
- perhaps this is how the adhesions formed after the operation make themselves felt;
- a hernia formed in the groin area. Its treatment and diagnosis are simple. The formation of a tubercle is not only noticeable, but also palpable;
- appendicitis. Discomfort may indicate a deceptive appendix;
- there are problems in the colon.
Folk remedies for eliminating pain in the testicles
Some illnesses require immediate medical attention. Others can be dealt with using effective folk remedies. To maintain men's health, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Include fresh vegetables, fruits, and natural juices in your daily diet.
- Take decoctions based on black currant.
- Take chopped parsley with melted milk.
- Drink a decoction of cornflower flowers daily.
When a person is sensitive to his body, the quality of life significantly improves and many health problems are eliminated. Men should not neglect regular examinations by a urologist, and if alarming symptoms appear, they should immediately make an appointment with a doctor.
Vermiform appendix and diseases
Why does a man's lower abdomen hurt? The reasons are varied. In 80% of cases it is attributed to appendicitis. But there is another 20 percent. These include life-threatening violations. They require mandatory immediate treatment, which will consist of a complex.
One such lesion is carcenoid. This is a cancerous tumor that arises on the appendix. It appears from cells, namely neuroendocrine ones. But nagging pain in the lower abdomen in men is not the only sign:
- connective tissue quickly grows and reaches the endocardium of the heart muscle, which causes rapid heartbeat and severe shortness of breath. Blood pressure also decreases;
- During the initial development of the disease, many people confuse it with intestinal infections. This is exactly the kind of cutting pain in the lower abdomen that occurs in men;
- frequent vomiting and nausea after eating and at rest;
- diarrhea is characterized by wateriness and frequency;
- the skin begins to itch very much. When you scratch the area, redness occurs and the itching intensifies 2-3 times;
- heaviness when breathing resembles bronchial asthma in the acute stage;
- the front part often burns and heat occurs.
All signs are due to the fact that the neoplasm promotes the production of large amounts of serotonin, prostaglandin, histamine and bradykinin. Traditional medicinal medicine and traditional methods of treatment are powerless here. Therefore, there is only one way out - surgery. In the last stages of development, intensive anesthesia is required, and surgical intervention should be abandoned.
Testicular cancer
This disease is one of the most common. Testicular cancer manifests itself with the following symptomatic signs:
- noticeable compaction in the structure of the organ;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- sharp pain due to tissue necrosis;
- inflammation of the appendages.
The specific method of therapy depends on the specific type of tumor. Often, the doctor uses a complex treatment method that includes radiation, surgery, tumor removal and chemotherapy.
Bowel prolapse or hernia
Hernia most often occurs in the male population of the globe. The fat layer and mesh in women are stronger and more difficult to tear. It is characterized by elasticity. This is due to the fact that the body and structure are created in such a way that it is always possible to bear a child. As you know, the increase in the size of the abdomen varies, but the mesh also stretches, but without being damaged.
In the case of the male sex, the walls of the abdominal cavity are weaker, and the ligamentous apparatus, instead of stretching, simply breaks. A hernia occurs anywhere, but most often in the groin area. If the lower abdomen hurts on the left in men or on the right, at the same time there is a noticeable lump that is movable and should be palpated. It disappears when lying down. It’s possible to discover and explore on your own. But it won’t be possible to straighten or cure it. The hand of a professional surgeon is needed here. Since during the operation, in addition to setting the organs in place, it is necessary to install new connective tissue and fat mesh.
A hernia can settle anywhere in the inguinal canal. There is enough space for her here, since the testicles descend into the scrotum during intrauterine development and the spermatic cords are located along it. But, despite the fact that there is enough space, the prolapse can be found near or in the scrotum. There is no increase in temperature or other persistent symptoms other than discomfort. When coughing or lifting heavy objects, men experience a burning sensation in the lower abdomen or sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
In addition to the operation, wearing a bandage or a special bandage is recommended. But it’s still better to trust the doctor. The disease is not as simple as it seems at first glance. The longer you delay, the more problems you get. For example, poor stool and urine passage. As well as prostatitis and other inflammatory processes in the pelvic region.
When an injury occurs, resuscitation must be carried out. Discomfort in a man’s lower abdomen develops into other moments:
- a sharp rise in temperature;
- nausea and gag reflex;
- when touching the convex area there is severe pain;
- the outflow of urine and bowel movements stops.
General information
Peritoneal tumors are neoplasms of various origins, localized in the area of the visceral and parietal layers of the peritoneum, lesser omentum, greater omentum and mesenteries of hollow organs. Benign and primary malignant neoplasms of the peritoneum are rarely diagnosed. Secondary peritoneal tumors are a more common pathology; they occur with cancer of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space, internal female and male genital organs. The prognosis for benign lesions is usually favorable, and for malignant lesions it is unfavorable. Treatment is carried out by specialists in the field of oncology and abdominal surgery.
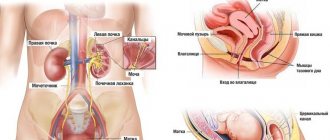
Anatomy of the left abdomen
To understand why the lower abdomen on the left side may hurt, you need to understand a little the anatomy of this part of the body. From an anatomical point of view, the following organs and anatomical formations are located on the left side of the abdomen:
- Abdominal wall. Consists of soft tissue (skin and muscle), which is a seal that holds the contents of the cavity. It has several sections: lower, upper, posterior and anterior. Pain is most often associated with damage to the anterior wall.
- Left lower ribs. The two lower pairs of ribs are called “floating” ribs because they are not attached to the spine. When they become inflamed, they can bulge, causing discomfort. It is also possible to break rib bones after certain injuries.
- Spleen. The largest organ in the abdominal cavity, consisting of lymphoid tissue. Located between the ninth and eleventh left rib.
- Stomach. The digestive organ, which is a section of the intestine. The microflora of the stomach is quite aggressive, so inflammation is not uncommon.
- Duodenum. This is a section of the small intestine. The main task is to normalize the acid-base balance.
- Pancreas. One of the most important digestive organs. Synthesizes enzymes and gastric juice necessary for complete digestion of food.
- Small intestine. The intestine where digestion takes place. Located between the stomach and large intestine. It is divided into three sections: jejunum, ileum and duodenum.
- Colon. Here the digestive process is completed and feces are excreted.
- Peritoneum. This is the membrane that covers the inside of the abdominal wall. Includes elastic fibers, collagen and endothelium. The peritoneum has high sensitivity and many nerve endings, and minimal inflammation can provoke pain.
- Left kidney. This organ is in contact with the back of the cavity, and is fixed by ligaments and fatty tissue. Because of this, it can sink and cause pain.
- Left ureter. It is a tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder. In men, it is located in front of the rectum. It looks like a hollow organ that consists of muscles.
- Vessels. Provide blood supply to the abdominal cavity.
- Nerves. They are located near blood vessels and arteries and are part of the autonomic system. They are bundles and nodes of nerve fibers.
IMPORTANT! It is worth understanding that each of these anatomical formations and organs can cause pain, so making a diagnosis on your own is almost impossible.
Causes of a lump in the groin
The inflammatory process can affect any one lymph node or several at once, which indicates the extensiveness of the inflammation process.
Lymphadenitis leads to a deterioration in general health, and body temperature rises. The lump in the groin is painful and causes discomfort upon palpation. When examined, inflamed lymph nodes appear as small, hard lumps the size of peas or beans.
If we are talking about lymphadenitis, then the bumps can be located in any part of the groin area; the neglect of the process is indicated by the appearance of new seals.
inflammation of the lymph nodes
There may be redness on the skin around the bump, a concomitant sign of inflammation. If you let the disease take its course, you may encounter a process of suppuration, and then you will need the help of a surgeon. Therefore, if you detect any lump in the groin area, it is recommended to visit a specialist.
Lymphadenitis
occurs for various reasons, usually these are diseases:
- colds;
- infectious,
- genitourinary system,
- fungal.
A man's lymph nodes become inflamed if he has prostatitis. Diseases transmitted through sexual contact can cause lumps in the groin. It could be:
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea;
- infection with trichomoniasis.
inguinal hernia
Helminths,
settled in the human body can also become the culprits of lymphadenitis. Their waste products are very toxic and their habitats are unpredictable. Therefore, it is necessary to periodically test feces for the presence of helminthiasis in order to protect your body and clean it in time if a problem is detected.
Hernia
- another cause of a lump in the groin in women and men can be. Its appearance can be triggered by either a normal cough or lifting heavy objects. The lump can be localized in any part of the groin area.
Men are more likely to experience this type of hernia, because their work involves heavy physical labor. In women, inguinal hernia is rarely diagnosed; it mainly affects those who lift heavy objects.
Blockage of the sebaceous gland duct
may be accompanied by the formation of a lump in the groin. Wen most often occurs due to improper body hygiene. Its appearance is facilitated by:
- profuse sweating;
- excess weight;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- impaired metabolism in the body;
- excessive greasiness of the skin or injury to it.
Vitamin deficiency and weakness of the immune system also contribute to the appearance of wen in the groin area.
There are other reasons
formation of a lump in the groin area.
- Cryptorchidism. This is a disease when, during the development of a boy in the womb, the testicle does not enter the scrotum. In this case, a lump appears in the groin area. If a lump is noticed in a newborn, you should show it to your pediatrician.
- Vesiculitis. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the seminal vesicles in men. As the disease progresses, painful lumps appear in the groin area.
- Varicose veins. If you feel the lump of varicose veins, it will appear to be pulsating.
Root causes of manifestation
A lump in the groin is most often a sign of the development of inflammatory processes directly in the lymph nodes. It can also appear due to an inguinal hernia. To correctly diagnose the disease, it is important to pay attention to the location of the growth and its size.
If the lymph node is inflamed, the lump resembles a small bean, both in size and shape. With the development of a hernia, the dimensions of the growth are much larger. They can range from a medium-sized walnut to a very large tumor located in the upper part of the groin.
A lump in the groin area sometimes occurs due to swelling of the scrotum caused by injury or hydrocele. However, such a growth may occur due to the fact that the testicle has not descended into the scrotum from the peritoneum, which is important for little boys and teenagers.
When the lymph nodes are inflamed, that is, lymphadenitis, the lump is small. When it occurs, body temperature rises. There is pain in the groin area, and sometimes purulent formations appear. This is due to infection of the male genitalia, penetration of pathogenic viruses into the groin area, fungus of the lower extremities, colds, reaction to toxins, infection with syphilis, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, gonorrhea, development of prostatitis or testicular diseases, and the occurrence of benign or malignant tumors.
If the skin in the groin area above the lump turns red, the nodes begin to hurt. Their compaction may be caused by mechanical trauma to the abdomen, the formation of wen, sarcoma, or the development of inguinal lymphogranulomatosis. Such ailments are initially treated with conservative methods, and at a later stage - with the help of surgery.
A lump in the groin area can also occur when the abdominal muscles are weakened. With physical effort or severe coughing, the intestines drop under the skin, causing the appearance of a hernial sac. This growth is manifested by pain, which intensifies as the disease develops. Swelling of the skin occurs at the location of the lump. Over time, the lump turns red. This pathology can only be eliminated surgically.
Sometimes a growth that appears on the right in the groin area radiates pain even to the leg. The pain is most noticeable when moving. This phenomenon is called radiating pain. That is, discomfort is transmitted to distant areas from the base lesion. Such a lump can be caused by injuries to the groin area, urological, fungal, viral diseases, hernia, spinal diseases or cancer. Only a qualified doctor can accurately diagnose and prescribe treatment.
However, a lump can occur on the right side of the groin for other reasons. So, it can be triggered by the presence of stones in the ureter, a dense lump descending from the kidney, or inflammation of appendicitis.
If the lump is accompanied by sudden and sharp pain that lasts from two minutes to several days, then most likely this is due to the passage of stones. The main focus can even be transmitted to the bladder, external genitalia, under the ribs and in the groin.
When the appendix is inflamed, pain occurs in the epigastric region. Over time, they move to the lower organs of a person. The right leg may be pulled back when walking. At the same time, pain spreads across the entire right side of the groin and can even spread to the rectum.
In addition, a growth on the right in the groin area sometimes provokes the following pathological conditions:
- cryptorchidism (the testicle simply did not descend into the scrotum and was localized in the inguinal duct);
- development of herpes;
- vesiculitis;
- spermatic cord lipoma;
- oncological tumors in the pelvis;
- epididymitis;
- mechanical groin injury;
- formation of varicose veins in the veins of the lower extremities;
- proptosis and colliculitis;
- cystitis - accompanied by frequent urination, pain occurs, blood is observed in the urine, intestinal function is disrupted - the disease often precedes the formation of prostatitis;
- disorders in the male genitourinary organs (may manifest as pain in the groin, growth in this area, bleeding from the penis).
Of course, each case requires a special approach. Having found out the root cause of the pathology, the doctor will explain what causes the pain in the groin area on the right. The above disorders usually require long-term therapy.