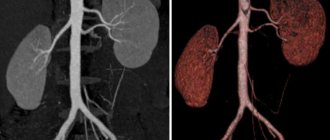
X-ray of the kidneys is an examination of the organ, which helps determine the condition of its structural elements. Another name for this type of diagnosis in relation to the kidneys is urography. Urography is considered the most effective way to detect kidney disease, as well as other urinary tract diseases.
It is worth noting that when the body is exposed to a large dose of x-rays, it can be harmed, up to the occurrence of various types of mutations. It is for this reason that doctors use low-frequency rays, which are safe for the urinary system and do not cause side effects.
Types of X-ray
X-rays with contrast are divided into several types:
- Intravenous urography. A contrast liquid is injected into a person's vein. It moves through the bloodstream and enters the kidneys, from where it is then excreted naturally.
- Excretory helps evaluate kidney function and take clear pictures of blood vessels.
- Retrograde is prescribed if it is necessary to check the urinary tract.
- Percutaneous is done using the puncture method. It is used if it is impossible to carry out retrograde or excretory.
- Antegrade helps to examine the upper region of the urinary system.
- Cystography helps detect tumors.
Angiography is used when other types of x-ray cannot be used.
Contrast urography
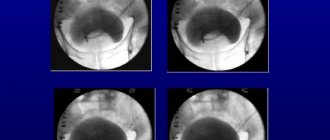
An X-ray of the kidneys using a contrast agent allows you to see pathological changes in the structure of the organ, tumors, soft tissue ruptures, various cysts and stones. This is one of the most reliable methods for identifying pathologies of the urinary tract. Intravenous urography is carried out by introducing iodine-containing substances into a vein (Urografin, Ultravist, Omnipaque). In order to study the condition of the organs, pictures are taken at certain time intervals - at 6, 15 and 21 minutes. The specialist monitors the functioning of the kidneys, the rate of filtration of blood plasma and the ability to convert it into urine.
Contrast pyeloureterography involves the administration of sterile iodine-based drugs using a urinary catheter. Only a doctor can prescribe a kidney x-ray with contrast after reviewing the patient’s medical history. The method has some contraindications, so before the procedure the patient must undergo laboratory tests. A few days before urography with a contrast agent, you need to start preparing the body.
What does it show
Examination with contrast reveals anatomical features and failures in the excretion of fluid by the kidneys. Stones located in the urethra and pelvis are easily identified. X-ray helps diagnose:
- neoplasms (even in their infancy);
- cysts;
- tuberculosis;
- vascular system;
- duplication of the ureter or kidney;
- nephroptosis;
- abnormal position of the kidney (dystopia);
- hydronephrosis;
- check the patency, shape and operation of the channels;
- examine the bladder, its volume, size, and evaluate possible pathologies.
X-ray with contrast helps determine the presence or absence of atherosclerosis or thrombosis. Excretory urography helps identify damage that appears after kidney rupture.
What will a kidney x-ray show?
A kidney x-ray is the first step in diagnosing various pathological conditions of the urinary system. The procedure helps to detect the following deviations from the norm:
- Congenital developmental anomalies - the absence of one kidney.
- An increase in kidney size is observed in hydronephrosis, polycystic disease, and diabetes mellitus.
- Uneven contours of the organ indicate polycystic disease, pyelonephritis.
- Kidney prolapse.
- A decrease in the size of the kidneys indicates chronic pyelonephritis, while one kidney indicates congenital hypoplasia.
- Rupture of the soft tissues of the organ.
- Presence of kidney stones.
- Tumor.
For diagnosing various diseases of the urinary system, the most accurate method is x-ray. Kidney stones of the oxalate and phosphate type are clearly visible on the image. You can find out their size, shape and exact location. Urography with contrast gives a complete picture of the condition of the entire urinary system. Urate formations are practically invisible on conventional radiography, so they are diagnosed using ultrasound examination.
Preparation
Preparation for the examination begins with reducing the formation of gases. They reduce the accuracy of the results. To avoid this, three days before the procedure, foods that cause gas (apples, black bread, cabbage, pastries, etc.) are removed from the menu.
The last meal is 8 hours before the examination. An enema is given the night before and repeated in the morning. This frees up the intestines. The bladder is emptied immediately before the examination.
This is necessary because when urine is mixed with a contrast liquid, it is diluted, and the information content is greatly reduced. Stop taking glucophage within two days. Urea and creatinine tests are done. The procedure cannot be done if you have kidney failure.
X-ray with contrast helps determine the presence or absence of atherosclerosis or thrombosis. Excretory urography helps identify damage that appears after kidney rupture.
Contraindications and side effects
Before you begin preparing for the study, you need to understand what prohibitions on performing diagnostics exist. The study should not be carried out on pregnant women and nursing mothers. Other contraindications can be identified:
You should not prescribe such a diagnostic method to a patient with Graves' disease. It is also dangerous for those people who periodically have high blood pressure. As for possible side effects, they are as follows:
We recommend reading: Olive oil for constipation: how to take it for adults, children and pregnant women
- feeling of heat in the body;
- dizziness;
- dysfunction of the respiratory system;
- skin rash, allergies;
- nephropathy (in this case the reagent will be poorly excreted from the body);
- swelling of the lips;
- hematoma at the injection site;
- phlebitis;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- Often a patient’s sleep after urography is disturbed:
- hemodynamic disorder.
Side effects usually go away on their own within a few days. In complex cases, hospitalization and symptomatic treatment are required.
X-ray of the kidneys in children
Radiography can be used in pediatrics according to strict indications. Examinations using this method can be carried out at any age, even in newborns. When prescribing an x-ray, the doctor talks about the need for this type of diagnosis and the possible consequences if the parents refuse. Indeed, not everyone is ready to expose a child to radiation, but modern medical X-ray machines can reduce the negative consequences of the procedure.
X-rays of the kidneys and genitourinary system with contrast are not performed on children in the first week of life, with developmental anomalies and impaired renal function.
Process description
The procedure is permitted only after the feasibility of the method has been established and contraindications have been taken into account. A study is being conducted in a hospital. The service is paid, but its price is not very high. The following drugs can be used for diagnosis: Urografin, Fortrans.
Reason for holding
Before doing a survey x-ray, you need to find out in what cases it is prescribed. Indications for using the technique are as follows:
- the presence of infection in the organs of the excretory system;
- pain in the lower abdomen or lumbar region;
- pathological changes in the formula of biological fluid;
- suspicion of the presence of a malignant or benign formation;
- hydronephrosis, kidney prolapse, pyelonephritis;
- blood in urine;
- state of shock or collapse;
- persistent increase in blood pressure and temperature;
- tuberculosis in the active phase;
- glomerulonephritis in chronic form;
- presence of stones;
- congenital pathology of system development;
- cystitis of various etiologies;
- prolonged presence of edema;
- postoperative complication;
- obstructive pathologies.
Prescribing urography is a doctor’s decision, which is made if other diagnostic methods are ineffective. The examination is also carried out in preparation for surgery, during the expansion of the collecting apparatus. In the latter case, atrophic processes develop in the excretory system.
- feeling of heat in the body;
- dizziness;
- dysfunction of the respiratory system;
- skin rash, allergies;
- nephropathy (in this case the reagent will be poorly excreted from the body);
- swelling of the lips;
- hematoma at the injection site;
- phlebitis;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- Often a patient’s sleep after urography is disturbed:
- hemodynamic disorder.
The most reliable and accurate method for examining the kidneys and urinary tract today remains x-rays of the kidneys with a contrast agent. This examination method includes several types of x-rays, with the help of which it is possible to obtain information about the kidneys, renal pelvis, bladder and urethra (urine excretion channel).
Indications for testing
In fact, an X-ray examination of the kidneys has a large number of indications.
Diagnostics can be prescribed for 8 main indications:
- pathological changes identified during an ultrasound examination;
- pain in the lumbar region, if neurological pathologies are excluded;
- pain during urination with an unpleasant odor;
- changes in urinalysis indicators, indicating the presence of an inflammatory process;
- the presence of purulent, bloody or mucous discharge in the urine;
- congenital malformations of the urinary system;
- injuries to soft tissues located near the kidneys;
- ureteral rupture, bladder damage.
How to prepare?
How to prepare for a kidney x-ray? The most common preparation of a patient for a survey x-ray of the kidneys is as follows:
- 2 days before the scheduled examination, the patient is prescribed a diet that excludes the consumption of foods that contribute to intestinal gas formation: baked goods, milk, fruits, legumes, etc.
- The intestines are cleansed. The procedure can be performed in the evening and in the morning (2 hours before the scheduled examination). You can use the drug Fortrans (the dose must be prescribed by a doctor). It is suitable for people for whom giving an enema is problematic. In fact, it is very important that the intestines are free and clean; this will increase the diagnostic information several times.
- From the evening of the previous day, limit fluid intake. This is necessary so that the density of urine increases and the contrast of the study increases. Contrast agents have a diuretic effect, so water intake should be limited.
Decoding the results
With normal functioning of the urinary system, a survey x-ray will show the correct bean-shaped shape of the organ, outline the shadow of the lumbar muscles, and confirm the absence of tumors and bone damage in the lumbar spine. Excretory urography with normal indicators confirms the normal functioning of the kidneys: the calyces and pelvis are filled with contrast evenly, there are no abnormal formations, “Urografin” is evenly distributed along the ureters and accumulates in the bladder.
Deviation from the norm should be immediately noticed. For example, the contrast is not released in one of the ureters or is poorly visible, the pyelocaliceal system is filled unevenly - this indicates urolithiasis. If a shadow is visible in the parenchyma, this indicates pyelonephritis. With a survey x-ray, it is possible to immediately determine the cause of nagging pain in the lower back - it could be incipient vertebral cancer.
As mentioned earlier, when taking an X-ray of the kidneys, it is important to properly prepare the patient, otherwise the image may show inaccurate information. Possible reasons include outdated medical equipment and non-compliance with the algorithm. In children, poor image quality is possible due to active breathing.
Who is it prescribed to?
There are several ways to perform an x-ray. Some of them involve the introduction of the contrast agent Urografin or Omnipaque into a vein or through a urinary catheter. It is necessary to consider which radiographic techniques are used.
The contrast agent contains iodine. The drug is intended for administration into the cavity and blood vessels. When introduced into the bloodstream, it enhances visualization of the vascular bed.
Survey radiography. This x-ray examination of the kidneys is performed without the introduction of contrast. The area of the entire urinary system is projected onto a film on which the following information will be available to the specialist:
- stones in the renal pelvis and urinary canal;
- position of the kidneys (prolapse or displacement);
- kidney development (doubling or underdevelopment);
- bladder condition;
- passages of the urinary canal;
- condition of the intestinal walls, which is indicated by increased gas formation (perforation of the intestinal walls).
A survey radiography of the kidneys will allow the doctor to decide whether surgical intervention is necessary to remove kidney stones or treat the patient conservatively.
How to prepare for a kidney x-ray? The most common preparation of a patient for a survey x-ray of the kidneys is as follows:
How is the procedure done?
The patient is injected with a contrast agent, after which 3 pictures are taken at strictly defined time intervals: the first - 5-7 minutes after injection, the second - after 15-17 minutes, the third - after 20-23. In this way, the image captures the contrast in the collecting system, then in the ureter and, finally, in the bladder.
We recommend reading: Diarrhea due to rotavirus infection - Treatment of diarrhea
X-ray of the kidneys: indications for examination
- Urolithiasis or suspicion of it
- Chronic kidney diseases (for monitoring and treatment control purposes)
- Diagnosis of tumors, metastases
- Injuries of the pelvic and lumbar region
- Postoperative control
- Significant abnormalities in urine analysis: hematuria (blood in the urine), proteinuria (protein), pathological changes in odor, color, density and clarity of urine
- Pain of characteristic localization (lumbar region and lower abdomen), renal colic
- Painful urination
- Suspicion of obstruction (obstruction) of the urinary tract, urinary retention, swelling of the eyelids and face
- Hypertension
- Clarification of ultrasound examination
How to prepare for a kidney x-ray
- Before being referred for testing, the doctor prescribes tests to rule out renal failure; Some medications should not be taken
- 3 days before the procedure, gas-forming foods are excluded from the diet.
- On the eve of the procedure in the morning on an empty stomach in the presence of constipation, a cleansing enema and taking carminatives are recommended; the study is carried out on an empty stomach
- Immediately before the procedure, an allergy test for a contrast agent is performed.
- Then the patient removes metal jewelry, watches, dentures, and a belt and is placed on the couch in light clothing without fasteners; areas not involved in the study are covered with a lead apron
What does it represent?
The method is based on the ability of X-rays to pass through body tissues, the degree of density of which determines the degree of darkening (the so-called “shadow”) in the finished image. Considering the harmful effects of ionizing radiation on the body, the intensity of the rays is strictly dosed, and the procedure is carried out only for medical reasons.
Contraindications to x-rays are only pregnancy and some cancers; other restrictions relate to the administration of contrast:
How is X-ray contrast examination of the urinary tract done?
Excretory urography: a slight decrease in the tone of the urinary tract.
Urostereoradiography is rarely used. The method involves taking a series of consecutive photographs at a distance of 6-7 cm from the previous one. The exposure produces an animated image that is easy to view with stereo binoculars.
Obtaining ideal radiographs during urostereoradiographic examination is complicated by the constant movement of urine through the urinary tract, so the method is not widely used.
What does urostereoradiography show:
- stones;
- enlargement of the pelvis (pyelectasia) and calyces (hydrocalicosis);
- tumors and kidney tuberculosis.
What is retrograde ureterography
Retrograde ureterography is an x-ray method for diagnosing urinary tract diseases in cases of suspected calculi (stones), tumors
or other formations along the urethra (urinary canal).
How is retrograde ureterography done:
- the catheter is inserted through the urinary tract;
- a contrast agent is supplied through it;
- the patient assumes the Fowler position (lying on his back);
- After 30 seconds, an x-ray is taken.
25-30 seconds is enough to fill the ureter with contrast. With longer exposure to the “luminous” substance, the diagnostic value of the examination decreases.
What is contrast pyeloureterography?
Contrast pyeloureterography is an X-ray diagnostic method that allows you to assess the condition of the pelvis and urethra during the administration of contrast. The procedure involves the introduction of a contrast agent through urological catheters No. 4, 5, 6 (Charriere scale).
It is preferable to use catheter No. 5 for contrast pyeloureterography. Its caliber is sufficient for normal outflow of urine when the pelvis is full. Before administering Urografin or Omnipaque, a survey of the kidneys should be taken. It will show the location of the distal catheter fragment. It shows whether a contrast X-ray of the urinary tract should be done.
Urografin is administered in its pure form, which prevents the occurrence of spasms of the pyelocaliceal structure of the urinary system.
Features of X-ray contrast examination of the urinary tract:
- urografin is used in low concentration;
- the substance creates “metallic” shadows at high intensity;
- intense darkening increases the number of diagnostic errors;
- for X-ray contrast examination, a 20% solution is sufficient;
- ideal if gaseous or liquid contrasts are used for urography - triyotrast, sergozine, cardiotrast.
Modern contrast agents contain three or more iodide groups. They form clear shadows. The polyatomic structure creates a contrasting image of the urinary structures.
Contraindications to radiography with contrast and possible complications
This type of diagnosis has many contraindications. Depending on the area being examined and the type of contrast agent, restrictions may vary.
- Hypersensitivity to drugs that contain iodine.
- Kidney, heart or liver failure.
- Acute inflammatory processes in the area where they plan to inject a contrast agent.
- Serious mental disorders.
- Thrombosis, which is accompanied by inflammation in the vascular walls.
- Disorders associated with blood clotting - in the case of examination of the genitourinary system.
The main contraindications for this procedure are
- the presence of an allergy to iodine-containing substances - the main complication will be an allergic reaction, which can cause skin itching or anaphylactic shock;
- pregnancy – radiation received during diagnostics can negatively affect the overall development of the fetus;
- renal failure - to remove the contrast agent from the body, full functioning of the organs is necessary, since the contrast agent puts a strong load on the kidneys;
- hypothyroidism (thyroid disease) – a decrease in the functional capacity of the thyroid gland may occur, which will be reflected in a decrease in hormone production.
Preparing for an x-ray with a contrast agent - recommendations for patients before and after the examination
Before coronary angiography, the patient should undergo some tests:
- General and detailed blood test.
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
- Testing the body for the presence of hepatitis B and C.
- Electro- and echocardiogram.
- Blood test for AIDS and syphilis.
According to statistics, the popularity of this type of x-ray diagnostics is increasing every year. Over the past 15 years, contrast agents have begun to be used 5 times more often when studying certain internal organs and systems.
Through this type of examination, you can obtain more accurate information about what is happening inside the body. The patient is injected with a certain dose of a coloring substance, after which the diagnosis begins.
This type of diagnosis has many contraindications. Depending on the area being examined and the type of contrast agent, restrictions may vary.
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
What is an X-ray?
X-ray exposure is a procedure in which short electromagnetic waves are passed through the body. “X-ray” allows you to see any pathological abnormalities - displacements and fractures of bones, neoplasms in soft tissues. The result is displayed on a special film (radiography) or on a screen (fluoroscopy).
Irradiation in large doses is dangerous for the body and can cause mutations and abnormal development. In medical practice, low-energy rays are used, which are safe and do not cause side effects. The required dose for an x-ray examination is calculated depending on the part of the body (organ) being diagnosed and the device used.
What are the features of examining children?
X-ray of the kidneys in adults has significant differences from a similar examination in children. Before deciding on the need for an x-ray examination, the child is first sent for an ultrasound examination. Only after an ultrasound, according to the doctor’s indications, can a decision be made to send a small patient for an x-ray.
To avoid unnecessary anxiety on the part of the child, he is given sedatives or light anesthesia is used. During the examination, the presence of a doctor and an anesthesiologist is mandatory. To secure the child in a certain position, the procedure also requires the presence of parents who wear special protective aprons.
If a repeat examination is necessary, it is done after a decent break, so you should try to get everything right the first time. To do this, parents are advised to give their children a cleansing enema before the procedure. It would also be a good idea to take Espumisan a couple of days before the x-ray.
To make the child less worried, you can take with you a pacifier or a toy that does not contain metal parts. With familiar objects, any child feels more comfortable and calm.
Varieties
There are several types of urographic diagnostics:
- Infusion (intravenous with the use of a contrast agent);
- Observatory;
- Excretory.
Infusion (contrast) urography involves intravenous administration of a contrast agent using a dropper. Typically, in such a study, contrast is slowly introduced during the procedure, and images are taken at different stages of the diagnosis.
Overview
Survey urographic diagnosis is a standard x-ray examination and is carried out without the use of contrast. As a result of the study, a rather meager picture of the disease is usually produced, although the doctor, based on the results of survey urography, is able to detect large stones and determine the general structure of the kidneys.
Typically, such a procedure is always prescribed before contrast urography.
excretory
This method is also called intravenous or contrast urography, since the procedure is performed using a radiopaque agent. Typically, Cardiotrast, Urografin, Vizipak, Triombrast, etc. are used as contrast. The method is based on the use of renal filtration function, excretion of processed materials and release of metabolic substances.
Infusion
The absolute indications for intravenous urographic examination are:
- Urinary abnormalities;
- Chronic inflammatory renal lesions;
- Tumor processes in the kidneys;
- Functional bladder changes;
- Urolithiasis;
- Prolapse of the kidneys, etc.
Also, contrast urography is often prescribed before surgery.
Experts distinguish three types of urography:
- survey urography. It is a regular image of the kidney area. Such a study helps to detect the presence of tumors and stones in a paired organ;
- excretory urography of the kidneys. In this case, a contrast agent is used, and diagnosis is based on the excretory function of the kidneys. The patient is injected with a special drug, and a picture is taken during its removal;
- intravenous urography. It also requires the use of a contrast agent, but doctors take several pictures. The study helps determine the rate of excretion of the drug by the kidneys. Diagnostics detects the following diseases: cysts, neoplasms, hydronephrosis, wrinkling and stretching of the kidneys.
Depending on the patient’s condition and clinical signs of the disease, doctors select a specific type of urography.
How and what to treat for cystitis? Look at the list of effective treatment options. Read about the causes of acute urinary retention in women and the treatment of the pathology at this address.
In medical practice, the following types of urography are distinguished:
- intravenous (excretory);
- overview;
- retrograde.
Intravenous (using contrast)
The essence of the procedure is the introduction of a contrast agent through a vein. Some time after the injection, an x-ray is taken, in which, thanks to this substance, the internal organs are clearly visible.
The following contrasts are used for the study:
- Visipack;
- urografin;
- triomblast;
- Cardiotrust.
Medical practice uses several types of x-rays that are used to diagnose kidneys. The choice of technique remains with the doctor, who knows what results this or that procedure will show. This is taken into account when it is advisable to confirm a particular diagnosis.
Survey radiography
Among the simple types of examination is digital x-ray. This is a common type of procedure, it is performed quickly and is available in almost every medical institution.
The irradiation area is placed in front of an X-ray screen, and the rest of the body is protected by a lead apron. The procedure is painless.
A survey X-ray examination makes it possible to see the organ as a whole and determine deviations. The disadvantage of such an image is that not all pathologies can be examined and identified.
CT scan
A modern examination for kidney diagnostics is computed tomography. The research is carried out using special high-precision equipment.
With a CT scan, the image is displayed on a computer monitor. Using a special program, they work with images that are of high quality.
Therefore, when an X-ray image is enlarged, the doctor sees those pathologies that are hidden from the view of a specialist with a regular X-ray. Layer-by-layer imaging is extremely effective for identifying pathologies - tumors, cysts, stones.
The doctor receives not only the image itself with the localization of the pathology, but also data on the size of the tumors, their structure and other characteristics.
X-ray with contrast
Another type of examination is an x-ray of the kidneys with a contrast agent. The patient is specially injected with a substance that transmits rays through itself differently than tissues and organs.
Once in the cavities and vessels, the contrast agent is distributed into them and displayed on an x-ray. This helps the doctor to see pathologically enlarged cavities, places of protrusion of vascular walls, thrombosed vessels and other results.
For each type of examination, with the exception of computed tomography, preparation is made for radiography of the kidneys. The doctor tells the patient about this when he gives a referral for diagnostics.