Kidney CT with contrast is a diagnostic method used in urology to identify various pathologies and is highly accurate. CT cannot be classified as “ordinary” studies, such as urine analysis or ultrasound, since it is more expensive and is prescribed as necessary, because it is not completely harmless.
In this article we will talk about the intricacies of the CT procedure, for which kidney diseases it is prescribed, what advantages this diagnostic method has, and also consider the existing contraindications and learn about the rules for preparing for the study.
CT even detects metastases
The principle of the method of computed tomography of the kidneys with contrast
Kidneys are organs on which the successful functioning of the body depends. They are endowed by nature with a special internal structure:
- With the help of nephrons, the kidney filters the blood, ridding it of waste and toxins. This process involves even smaller structures - vascular glomeruli and convoluted tubules;
Nephron is the basic structural unit of the kidney - renal calyces and pelvis - structures into which urine enters immediately upon exiting the tubules;
- the ureters are a kind of conductors through which urine passes from the pelvis to the bladder;
- The bladder is a round reservoir for the temporary storage of urine. For convenience, the latter is brought out in portions;
- The urethra is a narrow tube through which urine passes out. In men it is longer and curved, in women it is straight and short.
The urinary system consists of several organs
Kidney function - video
At the end of the last century, the method of X-ray diagnostics of renal diseases was popular. Conventional x-rays have limited information content, since the shadows of many organs overlap each other on the film. The image is distorted.
A conventional radiograph is the sum of all the shadows that appear on the film from the anatomical structures of the abdomen
Computed tomography does not have all these disadvantages. The developers of this method went their own way, improving the quality of x-ray images of the kidneys. During the examination, the tomograph produces many images from different angles. The movement of the table along the X-ray tube (gantry) is called stepwise tomography (CT). Combined with the movement of a single row of sensors inside the gantry, spiral images (SCT) are obtained. The more sensors there are in the tomograph, the clearer the images will be. Modern devices allow you to obtain 64, 128 and 256-slice images (multislice CT or MSCT). An important role is played by a computer program that processes images and builds a three-dimensional volumetric image of the studied area of the human body.
Spiral and multi-spiral shooting increases the information content of images
Computed tomography - video
The quality of CT images of the kidneys can be improved by preliminary introduction of special contrast agents into the bloodstream (Omnipak, Optirey, Vizipak, Ultravist). The kidneys capture it and pass it through their purification system. After the glomeruli and tubules, the substance sequentially enters the cups, pelvis, ureters and bladder. X-rays will show the drug in the pictures along with the contours of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Ultravist - X-ray contrast agent
Indications for use
A referral for a CT scan of the kidneys is given in case of a fairly wide range of diseases or when pathology is suspected in order to clarify the diagnosis and begin treatment:
- In case of urolithiasis, computed tomography will indicate the exact location of the stones, their size and possible disturbances caused by stones in the pyelocaliceal region of the kidney.
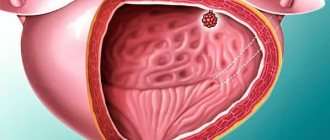
- In the presence of neoplasms in the kidney parenchyma or germination of foreign cells inside.
- For diagnostic purposes, to examine in detail the damage to the renal structure and adjacent organs.
- Determining the location of the kidney, to understand how much displacement or prolapse of the internal organ has occurred.
- Various congenital anomalies related to the shape, number or connection of organs.
- To understand the qualitative indicators of kidney function.
- Examine the renal blood vessels and determine whether they are abnormally narrowed or widened.
Additionally, computed tomography is used during a biopsy or after organ transplantation to understand the dynamics of its work.
Possibilities and limitations of the CT method
Computed tomography of the kidneys with contrast is currently used very often, since this study has a number of advantages compared to other diagnostic methods. However, CT, along with its obvious positive aspects, also has disadvantages that must be taken into account.
Possibilities and limitations of the kidney CT method with a contract - table
| Advantages of the CT method | Disadvantages of the CT method |
|
|
Features of diagnostic testing using CT
When examining using this method, layer-by-layer images (tomograms) of the examined organ are obtained in increments of 3-5 mm. Next, the images are digitized, transferred to the computer memory and displayed on the monitor. This allows the doctor to obtain the necessary information about what stage the disease is at and where the source of the disease is located. Thanks to this examination method, you can obtain images of bones, muscles and internal organs.
CT is a more informative diagnostic procedure than radiography.
When conducting a standard examination of a patient using radiography, a plate is placed under the organ being studied, with the help of which it is recorded how the energy of the beam has changed after it has passed through the structures of the body.
CT scanning is performed using a narrow beam of X-rays moving around the body. The data is sent directly to the computer. After which the received information is converted into a two-dimensional form and shown on the monitor.
A special feature of a CT scan of the kidneys is that it can be performed with or without a contrast agent.
The first CT scans appeared in the twentieth century. However, since then the tomograph installations have been somewhat modified and improved. The following types of procedures are common in modern medicine:
- SCT or spiral computed tomography;
- MSCT or multislice computed tomography.
When conducting spiral tomography, as the name implies, the images are cut not in layers, but in a spiral. This examination makes it possible to obtain layer-by-layer images of the structure of individual parts of the body in just a couple of seconds.
The installation of a multislice tomograph differs in that the detectors on its circumference are placed in 2 rows. Accordingly, examination of a patient using a 16-spiral tomograph is performed 32 times faster.
There are other types of diagnostic measures that are used if it is necessary to examine the condition of the kidneys: urography, examination of the kidneys using ultrasound, MRI of the kidneys, biopsy, angiography and venography of the renal vessels.
Measures to prepare for the study
Successful research is necessarily preceded by careful preparation. It usually includes a number of activities:
- two days before the test, it is advisable to exclude all foods that increase the formation of gas in the intestines: white cabbage, rye bread, carbonated drinks, all legumes. The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach;
- To reduce the risk of allergies, it is advisable not to consume chocolate, alcohol and citrus fruits the day before. These products themselves contribute to the release of the biologically active substance histamine, the main participant in all allergic reactions;
All allergic phenomena are caused by histamine - It is necessary to donate blood for a biochemical analysis in advance. High levels of urea and creatinine give the doctor a signal to cancel the study using contrast;
- For infants, the pediatrician often additionally prescribes Espumisan, a medicine to eliminate excess gas in the intestines.
How to prepare for a kidney CT scan
Preparation for a kidney CT scan begins a few days before the examination. The patient must follow a special diet for 2-3 days, excluding foods and dishes made from legumes. Also on these days you should not drink carbonated drinks, fermented milk products, or foods that contain yeast and contribute to increased gas formation in the intestines.
If a CT scan of the bladder is prescribed, then you should come to the diagnosis with a full bladder. The examination is performed on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 5 hours before the start of the procedure. In the morning before the examination, you can drink water or weak tea.
People who have previously had allergic reactions to medications are recommended to undergo a contrast sensitivity test. If the test is positive for the drug chosen by the doctor, the doctor can either replace the marker during diagnosis or conduct a study without contrast.
Carrying out the procedure
A CT examination begins with the patient laying on the machine table and attaching a system for automatically injecting contrast into a vein. The drug is administered through a regular plastic cannula installed into the lumen of the vessel. After the procedure is completed, it is removed from the vein without any problems. The following is the approved research algorithm:
- The abdominal organs are scanned before contrast is administered;
- automatic injection of the drug into the vein is started. The dose is calculated per kilogram of patient weight;
Contrast is injected into a vein using a machine - The process of scanning the kidneys and urinary tract starts. The study is repeated at the fifteenth and twenty-fifth minutes after contrast administration.
For infants, the examination is performed under general anesthesia in the presence of an anesthesiologist. When the drug is administered into a vein, a feeling of fever and nausea may occur, which disappear without external intervention and are not considered side effects.
Decoding the results
Deciphering and evaluating the results of the received images takes from 1 to 1.5 hours. The results of the computed tomography scan are entered into the patient’s chart, and a series of images, at the patient’s request, can be recorded on a disk and given to them.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor will be able to accurately diagnose the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. If a certain disease is suspected, specialists can refer the patient to a specialized doctor. The presence of tumors requires a visit to an oncologist, and the formation of stones in the urinary system requires a visit to a nephrologist or urologist.
Normal kidney indicators on CT images are assessed by the shape, structure and location of the internal organs. The parameters of adjacent organs are compared to obtain an accurate diagnostic picture.
Deviations from the norm in photographs can be very diverse. The growths on or inside the kidney will have a different tissue density, which will be visible in a completely different color scheme, thanks to the contrast agent. The structure of the renal vessels with damage is clearly visible and leaves no doubt for doctors in making a diagnosis.
Examination of the kidneys and the entire urinary system using computed tomography is the most effective way to identify abnormal processes and damage, which will allow timely initiation of adequate treatment.
Evaluation of the information received
The analysis of tomographic images is carried out by a radiologist. In this case, medical documentation must be studied: medical history, extracts and results of other studies. The information is also assessed by the attending physician, who makes a diagnosis based on the totality of examination data.
Interpretation of CT examination results - table
| Normal indicators | Possible deviations |
| Position of the kidneys at the level of the first two lumbar vertebrae | Prolapse of the kidneys (nephroptosis) |
| Correspondence of the sizes of the dense part of the kidney (parenchyma) and pelvis to gender and age |
|
| Absence of pathological structures in the kidneys |
|
| Presence of two kidneys with a system of 4 cups and pelvis |
|
|
|
| The bladder is round in shape without foreign components in the lumen |
|
CT images of the kidneys - photo gallery
Hydronephrosis - excessive dilation of the renal pelvis
CT scan is a method for diagnosing urolithiasis
Cyst - a kidney formation containing fluid
A horseshoe kidney is formed by the fusion of two organs
Kidney tumor is diagnosed using CT scan
CT scan is a method for diagnosing bladder tumors
Alternative Methods
Because of the above-mentioned risks, the treating physician must weigh whether the benefits of CT scan outweigh the potential risks. Depending on the problem, ultrasound diagnostics and magnetic resonance imaging may be used.
The difference between CT and MRI is that the latter does not use ionizing radiation, so there are no long-term negative effects. Before starting examinations, it is recommended to consult with your doctor. The doctor will choose the most appropriate test procedure based on the potential risks and benefits.
It is strictly forbidden to independently interpret the research results. All research data must be given to the doctor. Self-medication or self-diagnosis may cause more harm than potential benefit. Therefore, if you have any symptoms or suspicions, you should seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional.
Side effects
Because CT scans are performed using contrast, there may be side effects. Most are caused by hypersensitivity to iodine, the main component of the pharmacological drug. The type of symptoms determines the severity of the allergic reaction:
- in the mildest case, the allergy will manifest itself as dry mouth, a feeling of dizziness, nausea and headache. One-time vomiting is possible, as well as the appearance of an itchy rash on the skin (urticaria);
Urticaria - allergic skin rash - Repeated vomiting can lead to dehydration, so it is considered a moderate allergy;
- Severe forms include angioedema and anaphylactic shock. In the first case, swelling of the face, tongue and neck can cause significant difficulty breathing and oxygen deficiency in the body (hypoxia). The second case leads to a sharp disturbance in vital signs: pulse, blood pressure.
Quincke's edema is a form of allergic reaction to contrast
Quincke's edema - video
The likelihood of allergic symptoms occurring can be anticipated. The risk increases sharply in the following situations:
- if there have been similar reactions to contrast in the past;
- with a general tendency to various kinds of allergic reactions: urticaria, food allergies, etc.;
- with symptoms of exacerbation of chronic diseases.
In this case, you can take certain measures in advance and introduce antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil) and steroid hormonal drugs (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone). If symptoms of severe allergic reactions appear, hospitalization and intensive care in the intensive care unit are required.
Prednisolone is a powerful antiallergic drug
Side effects and contraindications
Because a CT scan is an x-ray, it can cause damage to genetic material. The more frequently a patient undergoes CT and X-ray examinations, the greater the risk of radiation damage. It is preferable for pregnant women not to have x-rays because too much radiation can cause birth defects in the baby. Relative contraindication – age under 18 years. In one session, the patient receives up to 20 mSv of radiation.
The use of contrast agents (iodine) may cause allergic reactions in some patients. Often during CT scanning it is necessary to inject a contrast agent, which accumulates in blood vessels, as well as in heavily perfused tumors or areas of inflammation. Although allergies to contrast agents have become rare, such reactions can still occur today. Some people may experience asthma, hay fever, food allergies or atopic dermatitis.
The most common reactions are nausea and vomiting, skin blisters and itching, which disappear quickly. Sometimes dangerous swelling of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract occurs with suffocation, asthma attacks and cardiovascular reactions up to shock. However, a slight feeling of warmth during the injection or a "metallic taste" are harmless side effects.
Multislice CT (MSCT) with contrast may impair renal function in patients. Contrast interacts with certain medications and causes kidney damage in a rare bone marrow disease called plasmacytoma.
Like any injection, a needle with a syringe of contrast agent can “get into the wrong place” and accumulate contrast in the tissue. It is painful and can cause bruising and an inflammatory reaction. Another possible risk concerns the way contrast media are released from the blood through the kidneys: in people with certain kidney diseases, kidney function may deteriorate. For healthy people, contrast agents in normal quantities are harmless.
CT scans work with X-rays, just like other X-ray techniques. Differences exist because the radiation fades very quickly and the load is therefore largely limited to the body part being examined. Radiation exposure involves many more factors than conventional X-rays: thickness and number of slices, sensitivity of the CT detector, patient weight, desired image quality. Thus, the radiation exposure in a CT scan is greater than in other x-ray studies.
The disadvantage of CT is the exposure to the same ionizing radiation as conventional X-rays, but in slightly higher doses. The radiation dose depends on the volume of the area being examined, the physical characteristics of the patient, the number and type of scans, and the required accuracy and quality of the image.
Newly purchased CT scanners are more powerful, have sensitive detectors, and typically have a variety of hardware and software utilities that result in a significant reduction in overall dose. However, it is also necessary to understand that the exposure described is always taken for a single data collection.
The BMJ study found the risk of cancer in 680,000 people who had CT scans in childhood or adolescence. The study, published in the BMJ on May 22, 2013, looked at 700,000 children aged 0 to 19 years. It confirmed an increase in the incidence of cancer (brain cancer and leukemia) by 24% compared to a healthy population of similar age.
Results: norm and deviations
It will take about 2 hours for the radiologist to write down what the kidney examination shows. The results with a report, photographs and a CD are made available to the attending physician, who makes the final diagnosis.
- Kidney tissue is comparable in density to liver and bone structures. It should be denser than the liver, but looser than the bones. In the image, healthy kidneys appear lighter than the liver, but darker than the surrounding skeletal bones.
- Dense areas: inflammation, cancerous tumors, sand and stones appear as light zones in the pictures.
- Cystic formations are less dense, look darker, and have clear boundaries.
- After being enhanced with a contrast agent, the boundaries of cancer tumors expand, which makes it possible to accurately diagnose the disease.
Thus, CT scan of the kidneys, adrenal glands and urinary tract is especially informative and relevant in the diagnosis of urolithiasis and cancer. If there are contraindications, CT can successfully replace the equally informative, but more expensive MRI method.
What are the dangers of kidney pathologies?
Few people know that kidney pathologies can cause heart attacks and strokes. When they are damaged, a disturbance in the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus occurs. Calcium is deposited in the walls of blood vessels, causing thrombosis.
There are other dangers:
- Nephroptosis or displacement of the kidney. If left untreated, it leads to chronic inflammation, hypertension and kidney failure, which threatens organ loss.
- Pyelonephritis refers to inflammatory diseases. It is often asymptomatic or “masked” as an acute respiratory infection. In severe cases, a purulent focus appears in the body, which can lead to sepsis or removal of the kidney.
- Kidney stones are a common pathology that often requires emergency medical care and surgical intervention. In a kidney blocked by a stone, acute inflammation occurs, threatening urosepsis.
This is not the entire list of diseases with serious consequences. This is why it is so important not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor and regularly take blood and urine tests.
Kidney MRI: what does it show?
MRI of the kidneys: A-polycystic kidney disease, B-tumor of the left kidney, B-arrow indicates hydronephrotic transformation of the right kidney, D-complete duplication of the ureters
Magnetic resonance imaging shows all pathological processes in the area under study, the condition of adjacent tissues, bone structures, and blood vessels. MRI of the kidneys allows you to determine:
- acute and chronic pyelonephritis;
- narrowing of the pyelocaliceal segment;
- hydronephrotic transformation of the kidneys;
- developmental anomalies of the upper urinary tract: absence of an organ, duplication, fusion (horseshoe kidney), organ hypoplasia, etc.;
- incorrect discharge of the ureter, its bend through an accessory vessel, doubling, etc.;
- megacalycosis (expansion of the pyelocaliceal system, not associated with urinary stasis);
- ureteral valves, its deformation, strictures;
- benign kidney tumors: cyst, angiomyolipoma, hemangioma, etc.;
- polycystic and multicystic;
- malignant processes, their prevalence;
- secondary damage to the kidney and ureters (for example, with retroperitoneal fibrosis);
- infectious process: urogenital tuberculosis, echinococcosis, etc.;
- secondary shrinkage of the kidney;
- nephroptosis, pelvic dystopia;
- vascular pathologies: stenosis, embolism, malformations (allows us to determine the cause of tissue ischemia or renal infarction);
- post-traumatic injuries (consequences);
- nephrolithiasis.