The adrenal glands are glands that are located above the upper pole of the kidneys. They are responsible for the production of a number of hormonal substances: testosterone, estrogen, cortisol, adrenaline, etc.
Situations often arise when a formation on the adrenal gland is detected. It is often benign and does not turn into cancer.
But a tumor on the gland interferes with the functioning of the organ, and the production of hormones is disrupted. This leads to the development of various diseases.
Adrenal tumors
The adrenal glands have a great influence on the functioning of the entire body.
They not only produce hormones, but also influence metabolic processes in the body: protein, water-salt, carbohydrate, and participate in the formation of secondary sexual characteristics.
The glands consist of two layers of tissue: external and internal. The outer layer is called the cortex, as it covers the adrenal gland, and the inner layer is the medulla.
A tumor on the adrenal gland can appear on both the outer and inner layers of the gland. This phenomenon occurs due to pathological proliferation of tissues of the endocrine system organ.
Formations on the gland are divided into benign and malignant. The difficulty in identifying pathology without special studies is that the symptoms when a tumor appears on the adrenal gland often coincide with a number of other diseases.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that computed tomography is a safe examination, there are also contraindications that the doctor must take into account before sending the patient for the procedure. The list of restrictions can include the following:
- pregnancy at any stage (especially in the first trimester);
- children under 3 years of age (for older children it is carried out only in case of emergency);
- mental disorder and claustrophobia;
- if there is a history of hyperkinesis or convulsive syndrome (due to the impossibility of being in a mandatory immobile state);
- the presence of implants, metal prostheses, implanted pacemaker, etc.;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- if the patient weighs more than 120-130 kg, it is not recommended (many tomographs cannot withstand the load more);
- increased levels of urea and creatinine in laboratory data;
- if another examination of internal organs using barium was performed less than a week ago.
Quite often, to obtain more reliable results, diagnostics are performed with contrast. However, this product contains iodine and that is why such a study is not recommended for the following persons:
- if there is renal or liver failure;
- in case of individual hypersensitivity to seafood and iodine;
- in the presence of diabetes mellitus.
If you are careful, the harm from radiation is unfounded.
Classification of adrenal tumors
Neoplasms arising in the adrenal gland are divided depending on the layer in which they appeared: medulla or cortex. Situations often arise when the tumor affects both layers, then this form is called mixed.
In addition, neoplasms are divided depending on the organ in which it developed:
- tumor of the right adrenal gland;
- tumor of the left adrenal gland;
- neoplasm on both adrenal glands.
But despite the location of the formations, they are all divided into benign and malignant. Benign tumors on the adrenal glands are usually small in diameter and do not contain cancer cells.
Such tumors usually do not produce pronounced symptoms and are often detected by chance during examination of internal organs.
Malignant neoplasms of the adrenal glands are dangerous to human health. They tend to rapidly grow altered cells in organ tissues and spread to other organs.
Malignant tumors include adrenal lymphoma. One of the symptoms of the disease is pathological enlargement of the lymph nodes. The disease is difficult to treat, especially if the metastases have penetrated into nearby organs.
Among primary gland tumors, hormonally active neoplasms are distinguished and hormonally inactive ones. Inactive formations of the adrenal gland are classified as benign.
This tumor can develop in any person, regardless of age and gender. Inactive formations are rarely of the malignant type and are better amenable to therapeutic treatment.
Why is a CT scan of the kidneys and adrenal glands prescribed?
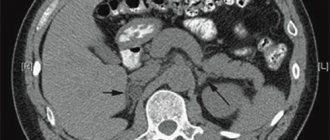
CT scan is most often prescribed for suspected tumors of the adrenal glands of malignant or benign etiology; the study allows us to determine their location and nature (adenoma, tumor, cyst, hyperplasia). Using computed tomography images, you can determine the shape (contour) of the adrenal glands, their location, structure and density, and see existing developmental anomalies. A contrast study with CT scans of the adrenal glands is aimed at the morphological differentiation of pathological formations.
A CT scan is usually prescribed after simpler studies (ultrasound, radiography, Dopplerography) in combination with laboratory tests.
Indications for CT may include:
- hormonal changes; progressive growth of body hair; causeless weight gain or sudden weight loss;
- back injuries;
- kidney diseases: urolithiasis, hydronephrosis, abscesses;
- suspicion of malignancy.
Hormonally active neoplasms
An adrenal tumor is a neoplasm in the adrenal glands that causes excessive production of one of the hormones, which leads to malfunctions in the functioning of the body.
Such formations cause pronounced changes in the body, which can often be seen with the naked eye.
Hormonally active tumors include:
- aldosteroma;
- androsteroma;
- corticoestroma;
- corticosteroma;
- pheochromocytoma.
Aldosteroma is a tumor of the adrenal gland that produces the hormone aldosterone. The formation develops in the cortical zone of the adrenal glands. Aldosteroma causes disruption of the water-salt balance in the body. This leads to muscle weakness, headaches, interruptions in heart function, hypoglycemia, and increased blood pH.
If the level of the hormone sharply increases in the body, then a crisis occurs, which is manifested by vomiting, shallow breathing, blurred vision, and the onset of flaccid paralysis. Neoplasms of this type can be single or multiple, but most often they are benign. Malignant aldosteroma occurs in only 2-5% of all patients.
Androsteroma is a formation that develops in the cortical layer of the gland and produces an excess amount of androgens. When androsteroma appears, early maturation begins in boys, signs of hermaphroditism appear in girls, and male-type changes in appearance are observed in women.
If the tumor is malignant, it quickly metastasizes to other organs: liver, lungs and lymph nodes. This disease is quite rare, accounting for no more than 3% of all neoplasms. But the probability of a malignant process in this case is 50%.
Corticosteroma, or glucosteroma, is a formation that develops in the cortical layer of the gland and produces glucocorticoids. This type of neoplasm is the most common. With glucosteroma, patients experience obesity, frequent headaches, increased fatigue and muscle weakness, early puberty or, conversely, premature decline of sexual function.
Hemorrhages and stretch marks appear on the abdomen and chest; in women, male-pattern hair growth begins and the timbre of the voice decreases. Such tumors can be either benign or malignant. A benign neoplasm is called “adenoma”, and a malignant one is called “corticoblastoma”, “adenocarcinoma”.
Corticoestroma is a neoplasm that produces an excessive amount of estrogen, which leads to the development of a man’s body according to the female type (increase in fat mass in the abdomen, hips and chest), sexual impotence. This neoplasm develops in the adrenal cortex and is common mainly in men. Most often it is malignant.
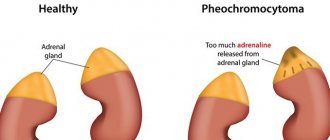
Pheochromocytoma is a neoplasm in the adrenal medulla that produces catecholamines. This type of tumor is most often benign; signs of malignancy are observed in only 10% of patients.
Volumetric formations of the adrenal cortex
Most often, neoplasms of the adrenal cortex are benign, but they pose a danger to humans, since the production of hormones is hazardous to health to a large or small extent. Let's look at the most common neoplasms.
Clinical manifestations depend to one degree or another on the hormone secreted by the tumor.
Corticosteroma (glucosteroma) is the most common tumor of the adrenal cortex. Synthesizes glucocorticoids - biologically active substances that regulate metabolic processes, especially fat and carbohydrate metabolism, have a high degree of anti-inflammatory effect in the body, and are directly involved in the regulation of blood pressure. Excessive release of glucocorticoids leads to disruption of these functions in the body.
Adrenal corticosteroma causes characteristic Itsenko–Cushing syndrome
Cortisol (hydrocortisone), a substance synthesized by this tumor uncontrollably, leads to the gradual development of Itsenko-Cushing syndrome (hypercortisolism) in the body. This syndrome is characterized by female-type deposition of adipose tissue typical of this disease, sexual dysfunction in both men and women, and an uncontrolled increase in blood pressure. By disrupting carbohydrate metabolism, it can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, even leading to the formation of diabetes mellitus.
Changes occur in the patient's appearance. The face changes, acquiring rounded shapes, due to deposited fat, the skin becomes red. The skin changes, areas of hyperpigmentation appear in the folds and folds. A characteristic “widow’s hump” forms on the back of the neck.
Fat deposition occurs on the upper surface of the body, while the lower limbs remain thin, and the muscles gradually atrophy. The skin on the body becomes thinner, it is covered with stretch marks, and there is a pustular rash on the face. In addition, constant, uncontrollable synthesis of cortisol leads to changes in the musculoskeletal system, causing muscle weakness and frequent fractures.
Manifestations of Itsenko-Cushing syndrome are possible with pituitary tumors, therefore, when making a diagnosis, differential diagnosis should be carried out.
Aldosteroma - a neoplasm releases the hormone aldosterone in very large quantities, which leads to the following disorders:
- disrupts the regulation of microelements in body tissues;
- increases sodium content in the blood;
- removes excess potassium and magnesium from the body;
- lowers renin levels.
The so-called, according to the author, Conn's syndrome develops. Clinical manifestations of this syndrome, provoked by increased production of aldosterone, lead to irreversible changes in the heart muscle, renal parenchyma, vascular wall, and muscle tissue.
All manifestations of aldosteroma will develop in accordance with which organs and systems are affected. The symptom complex is extensive, characterized by hypertrophy of the heart muscle, then its complete dystrophy, damage to the vascular wall due to narrowing of the lumen in the vessels, which can close some of them completely. On the part of the excretory system, there is a violation of the concentration of urine excreted, profuse urination, especially frequent at night.
Reduced potassium levels and increased excretion in the urine gradually lead to electrolyte changes in the heart muscle. Which, accordingly, is reflected on the ECG in the form of electrolyte dissociation. And cramps occur in the skeletal muscles.
It is impossible to describe in full the full list of disorders that can occur as a result of a mass formation in the adrenal cortex. All disorders that occur during the formation of tumors are interconnected. A decrease or increase in hormone production will lead to sometimes unpredictable disorders in the body.
Causes of the disease
The appearance of a tumor on the adrenal glands cannot always be explained by a specific cause. Scientists have not yet established the causes of tumor development, but have identified factors that increase the likelihood of their occurrence:
- congenital pathologies in the structure of the organs of the endocrine system;
- cases of detection of malignant neoplasms in close relatives;
- history of cancer;
- chronic pathologies of the liver or kidneys;
- constant stress;
- high blood pressure.
People at risk should periodically check their adrenal glands and undergo examinations in a medical facility. Then there is a high probability of detecting the development of a tumor at the initial stage and promptly starting treatment.
Procedure
Many people are concerned about questions: how is tomography of the adrenal glands performed? What to expect when undergoing this examination?
- The patient takes a comfortable position on the table. The medical worker is in the next room at this time.
- During the procedure, the subject holds his breath for a while and does not move in order to avoid distortion of the result.
- A contrast agent is injected using an injection.
- Before starting the diagnosis, the specialist needs to take several pictures.
- The patient may feel a slight crackling or noise. Pain and various kinds of discomfort should not occur.
Complications of adrenal tumors
When the adrenal glands develop, serious disturbances occur in the body, which often lead to crises, expressed in a sharp increase in blood pressure, dizziness, the skin becomes pale, the heartbeat quickens, sweating increases, attacks of vomiting, panic attacks, and increased body temperature begin.
The main complications of tumors depend on their type. For benign tumors, this is the probability of their degeneration into malignant ones. And with a malignant neoplasm, metastases that affect healthy organs pose a greater threat.
They primarily affect the bones, uterus, liver and lungs.
Preparatory stage
CT scan does not require special preparation. It is enough to follow simple recommendations. You should completely stop eating for 5-6 hours. Typically, the examination is scheduled for the first half of the day. In the morning you can drink only clean water without gas in small quantities.
See also: basic rules for preparing for a CT scan.
It is not advisable to eat before a CT scan; you can drink water
During a comprehensive examination of the kidneys and adrenal glands, you should not defecate an hour before diagnosis. You must come to the examination in comfortable clothes without metal elements. It is better to leave any jewelry at home. Otherwise, the pictures will be overexposed.
First you need to lay out all electronic devices. You must inform your doctor about any implants or stimulators installed.
You need to have a referral for the procedure with you. It is best to arrive 10 minutes before your scheduled time to fill out the paperwork. People enter the office wearing shoe covers or clean, replaceable shoes.
If you have mild claustrophobia, you will need to take a sedative. If it is impossible to remain motionless due to fear of a closed space, then preference should be given to a procedure with an open tomograph.
Diagnostics
To identify a tumor, different types of examinations are used:
- Ultrasound is suitable for diagnosing tumors whose size exceeds 1 centimeter.
- MRI can detect the presence of even small tumors.
- The CT method allows you to evaluate the density of the tumor and make a conclusion whether the tumor is malignant or not.
- X-ray examination is carried out to detect metastases in other organs.
- Urinalysis - to determine hormone levels.
- Phlebography – blood sampling for analysis is carried out directly from the vessels of the adrenal glands.
- Histological examination - determines what cells the tumor consists of.
Based on the data obtained as a result of the examination, the doctor will make a diagnosis and select effective treatment.
Features of the tomography procedure
After entering the X-ray room, the patient is placed on a movable tomograph couch. Then the laboratory assistant leaves the room and observes the procedure through a special window in the computer room. The tomography machine is equipped with an intercom, and in case of discomfort or deterioration of the condition, the patient can always report this. At the doctor's command, the patient will need to hold his breath for a few seconds during the scan.
The examination is carried out painlessly, quickly and comfortably. Native scanning takes 3-5 minutes. Contrast increases the duration of screening by 20 minutes. The results are delivered in most medical centers in St. Petersburg on the same day within 30-60 minutes. The conclusion obtained in the process of describing the results of a CT scan of the adrenal glands is taken into account by the attending physician to establish a diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Leading radiologists of St. Petersburg
specialization: MRI doctor, candidate of medical sciences, radiologist of the highest category. Recording - MC RIORIT and Federal State Budgetary Institution DNACIB
medical experience - 25 years
Online registration
specialization MRI Doctor Professor of the Department of Radiation Diagnostics Northwestern State Medical University Appointment - CMRT Staraya Derevnya, CMRT Petrogradskaya
medical experience - 35 years
Online registration
specialization MRI doctor, MD, professor. Recording - Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center named after. V. A. Almazova"
medical experience - 35 years
Online registration
specialization: MRI doctor, radiologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences. Registration - at MC Scandinavia
medical experience - 20 years
Online registration
General symptoms
Symptoms of tumor diseases of the adrenal glands can be divided into two types:
- Primary.
- Secondary.
Primary symptoms of the development of a tumor in the adrenal glands appear in the form of:
- external signs of hormonal disorders, which differ depending on the type of tumor;
- deterioration of conductivity in nerve endings;
- increased blood pressure;
- panic attacks;
- increased urge to urinate;
- pressing, painful sensations in the chest.
Secondary symptoms appear as the disease progresses due to changes in hormonal levels and are expressed in the following disorders:
- renal failure;
- decreased sex drive;
- increased blood sugar levels.
The manifestation of secondary symptoms indicates progression of the disease. It is better for the patient to consult a doctor at the stage of the appearance of primary signs, then the consequences of the disease will be less severe.
Indications
Due to radiation exposure of up to 7 mSv, which is present during the examination, CT scanning requires the patient to have clear indications for diagnosis. Typically, a referral for tomography is issued in the following cases:
- suspicion of a tumor of malignant and benign type;
- traumatism of the lumbar region to prevent hemorrhages;
- disorders of the kidneys and adrenal glands;
- hormonal imbalance, which manifests itself as weight fluctuations, hair growth and problems with reproductive and sexual function;
- deciding on the need for surgical manipulations and constructing an operation plan.
Treatment
If a patient has been diagnosed with a tumor in the adrenal glands, then it is necessary to conduct medical tests to determine the exact diagnosis and the extent of damage to the gland and other organs.
Treatment for tumors on the adrenal gland depends on the type of tumor.
The main type of treatment for tumor pathologies is surgery. The operation is performed if the size of the tumor is more than 3 cm, it is hormonally active and has signs of malignancy.
After surgery, the patient is prescribed a course of hormonal therapy to restore the functioning of the gland and normalize hormone levels.
But this type of treatment is not suitable for all categories of patients. The operation is not performed if:
- the patient has pathologies for which surgical intervention is contraindicated;
- the disease has progressed so much that metastases have appeared in organs distant from the lesion;
- Due to his advanced age, the patient may not be able to tolerate the intervention.
In critical cases, when tumor removal is impossible, only courses of chemotherapy are used. With this method of treatment, the tumor is treated with drugs that kill cancer cells.
Preparing for a CT scan of the adrenal glands
Before the procedure, the patient should not eat or drink for six hours. If the patient has an increased content of gases in the intestines, then preparation consists of taking gas-removing drugs. In case of constipation, a cleansing enema is used.
If you are planning a procedure using contrast, you should take Urografin a day before the procedure. This drug is sold at any pharmacy. The ampoule with the solution is diluted in two liters of water. The first liter of solution must be drunk a day before the procedure, the second liter before the study itself.
Forecast
The prognosis for an adrenal tumor largely depends on its type and the patient’s health status. If the formation is benign, the likelihood of a complete cure for the patient will be much higher than with cancer.
In the absence of cancer cells, removal of a high-grade adrenal tumor results in a complete cure for the patient. But even in this case, complications are possible: disturbances in the functioning of the heart, slowing of growth in children.
If the formation is malignant, then the treatment prognosis is much worse. Even in the absence of metastases, survival is about 2%. And if metastases have managed to affect neighboring organs, then the prognosis is disappointing.
Frequently asked questions about CT scans
- Which is better - MRI or CT scan of the adrenal glands?
The purpose of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging depends on the purpose of the study. The information content of the methods is similar; the optimal type of examination is determined by the doctor. Computed tomography of the adrenal glands allows you to exclude or confirm the presence of tumor lesions of the adrenal glands, determine further tactics and the possibility of surgical treatment.
- Is the CT procedure safe?
The CT examination technique involves the use of X-rays, but modern tomographs, due to their design, emit small doses of radiation, so CT is not hazardous to health and can be prescribed many times.
- What equipment is used at the center for CT scanning of the adrenal glands?
Our center has modern 16-slice computed tomographs from GE:
— in the branch on Engels Ave. — GE Healthcare Brightspeed 16;
— in the branch on Leninsky Prospect — GE-Optima CT 520; Thanks to the radiation dose reduction function, the CT 520 system allows you to reduce the radiation dose without compromising diagnostic information.
- When is a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast prescribed?
The use of a contrast agent is indicated (as prescribed by a doctor) if a malignant tumor in the adrenal glands is suspected. In the absence of an allergy to iodine, the contrast is safe for health and is eliminated from the body in 1.5–2 days.
Contrast improves the clarity of the resulting images and makes it possible to accurately assess the vascularization of the organs and formations being studied.
What to do before the procedure itself
Before diagnosis, the patient is placed on a special moving table and then sent to a tomography machine. During the examination, in order to avoid obtaining unclear images, it is forbidden to move. Sometimes (for mental disorders or if necessary) the patient is secured with belts. At the doctor's command, the person must not breathe for several seconds. During a CT scan, a specialist examines the condition of the kidneys and adrenal glands on the monitor and assesses the extent of their damage.
Afterwards, the result can be transferred to disk and decrypted on your doctor’s computer. In any case, the doctor evaluates the image and, taking into account the information received, confirms or refutes the diagnosis.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 1544 Date of publication: 08/21/2018
Urologists - search service and appointment with urologists in Moscow
What does a CT scan show?
A unique scanning makes it possible to accurately determine pathological foci on organs, assess their size and localization areas. The image is obtained in three-dimensional format, which allows you to analyze the entire gland, rather than individual sections.
The reliability of the data is more than 97%, so CT is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods. Tomography provides clear information about the structural changes in the tissue, which is important to do if there is a suspicion of oncology; it is necessary to identify the formation.
Obtaining accurate data is facilitated by the use of a special substance or contrast, which is administered intravenously and is not chemically active in tissues. More often, a solution containing iodine in specially selected concentrations is used for these purposes.
Features of CT
Computed tomography is considered one of the modern and information diagnostic methods. The technique is based on the specificity of X-ray radiation to penetrate and scan tissue, and all attenuation differences are recorded by a particularly accurate computer system.
The equipment makes it possible to visualize the adrenal glands in 3D format and view structural and shaped changes in organs. To maximize data collection, contrast-enhanced CT is used, which is most often practiced for diagnostic purposes.