In recent decades, the ultrasound examination method has become an integral part of the examination for almost any pathology. A diagnostic search for pathology of the abdominal cavity and kidneys is also impossible without ultrasound.
In addition to assessing the structure and size of an organ with conventional ultrasound, the use of color Doppler mapping allows one to assess blood flow, its speed indicators, and detect areas with increased and decreased blood flow. This information is important in determining injuries and their consequences, and is also irreplaceable in oncological pathology.
Ultrasound examination with the use of contrast agents is a new stage in the development of this method. The information obtained as a result of such an examination makes it possible to differentiate benign and malignant formations without invasive intervention. However, the high cost of contrast still limits its widespread use.
Everything you need to know about ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands and bladder
In the modern diagnosis of kidney diseases, ultrasound occupies a large place, which is the most informative.
It is easily tolerated by patients, non-invasive, and does not require the administration of contrast agents. Using ultrasound, you can identify cysts, stones, tumors, and abnormalities in the location of the kidneys. Since ultrasound does not cause side effects, it can be performed repeatedly to monitor the dynamics of the patient's condition. A doctor usually gives you a referral for a kidney ultrasound.
However, if necessary, you can make an appointment for this procedure directly at the medical center or laboratory.
How does an abdominal ultrasound work?
General information revealed by ultrasound examination includes:
- organ size;
- tissue structure;
- organ location;
- the presence of an area of inflammation;
- presence or absence of neoplasms;
- deformation or developmental pathology;
- detection of free fluid, which should not normally be present.
Despite all the information content of the method, the ultrasound machine is not capable of assessing the functional state of organs. This means that with the help of ultrasound alone, it is impossible to say unambiguously whether an organ can cope with the load placed on it or not.
The result of this diagnosis is ultrasound images. When we look at the finished ultrasound images, we see how different organs and their parts are painted in different colors and shades. This is due to the fact that fabrics of different densities have different properties.
When and why is a kidney ultrasound performed?
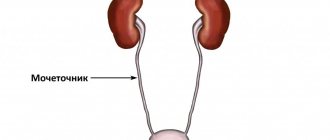
The kidneys, adrenal glands and bladder are the main organs of the urinary system, most susceptible to the formation of stones, polyps, cysts and other pathological formations that can be detected using ultrasound.
Kidney ultrasound is prescribed in the following cases:
- lower back pain;
- unusual color of urine;
- painful urination, abnormal urinalysis;
- the appearance of persistent edema;
- diagnosed inflammatory processes (pyelonephritis, cystitis);
- congenital anomalies or injuries of the urinary system;
- the need to study the renal arteries in hypertension;
- urolithiasis disease;
- metabolic diseases (diabetes, gout);
- diseases of the reproductive system;
- determining the presence and size of cysts and other focal formations in the kidneys.
The adrenal glands are endocrine glands responsible for the production of adrenaline. Their normal functioning is extremely important for maintaining a healthy physical and mental state of a person. However, ultrasound of the adrenal glands is prescribed only if tumors, cysts, or hemorrhages are suspected. The fact is that the adrenal glands are small in size and are visible on ultrasound only when they are enlarged due to illness.
Ultrasound of the bladder is prescribed in such cases as:
- suspicion of urolithiasis;
- the need to assess the shape of the bubble;
- inflammatory diseases;
- the need to assess the amount of residual urine in prostate adenoma.
As a rule, a comprehensive study is carried out. The fact is that all organs of the urinary system are interconnected, and if kidney inflammation is not detected today, it can be diagnosed tomorrow - if the source of inflammation was in the bladder.
Before the procedure
Preparation for an ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands and bladder involves following a diet. For three days before the procedure, you must refrain from spicy, fatty, fried, sweet foods, cabbage, legumes - anything that can increase inflammation, if any, or increase gas formation. You must stop eating eight hours before the procedure. An hour and a half after the last meal, it is useful to take activated charcoal at the rate of one tablet per ten kilograms of the patient’s weight (or its functional analogues). This is done to rid the intestines of accumulated gases and make the kidneys more clearly visible on ultrasound. An hour before the test, you need to drink half a liter of plain still water or unsweetened tea and try not to urinate.
How to do an ultrasound of the kidneys
The patient needs to lie on the couch and lift up clothes or undress to the waist to provide access to the abdomen, sides and lower back. A gel is applied to the skin to ensure better glide of the sensor. The sensor is moved over the patient's body, and ultrasonic waves, reflected from the kidneys and neighboring organs, form an image on the monitor. The doctor makes a printout of the image and deciphers the data. The duration of the procedure is 20-30 minutes.
Kidney ultrasound results
Ultrasound shows the location, shape, structure, size of the organs being examined. The results are printed, described and given to the patient immediately.
Normal kidney sizes on ultrasound in an adult are characterized by the following parameters:
- thickness: 40-50 mm;
- width: 50-60 mm;
- length: 100-120 mm;
- thickness of renal tissue (parenchyma): 11-23 mm.
During pregnancy, it is especially important to do an ultrasound on time if nagging pain appears in the lumbar region, urination is difficult or painful. Normally, the size of the kidneys in pregnant women should not deviate from the normal values for an adult.
In children, the size of the kidney depends on age and height. With a height of 50-80 cm, only the length and width of the bud are measured. On average, normal kidneys in children on ultrasound have the following characteristics:
- thickness: 40 mm;
- width: 22-25 mm;
- length: 45-62 mm;
- renal tissue thickness: 9-18 mm.
Normally, the transcript of an ultrasound of the kidneys reflects the following: the organ has the shape of a bean, the left kidney is slightly higher than the right, an even, clear outer contour, the sizes of the kidneys differ by no more than 2 cm. In pathologies, echo-positive formations are detected - it could be a stone or tumor, reflecting ultrasonic wave.
Spleen and lymph nodes
The spleen, along with the kidneys and liver, is involved in blood purification. This organ produces antibodies, filters the blood from bacteria and protozoa, and destroys spent blood cells.
Disturbances in the functioning of this organ are less common and do not lead to such fatal consequences as disturbances in the functioning of the liver or pancreas. In its normal state, the organ will be approximately 12 cm in length and 8 cm in width. With inflammation and the appearance of neoplasms, the dimensions of the organ will increase, and the echostructure will be heterogeneous. If the transcript of the ultrasound results indicates that the spleen is enlarged, you should take a closer look at your health: often inflammation of this organ indicates an infectious disease or problems with blood circulation. If an ultrasound shows a heterogeneous echostructure, this may indicate the death of spleen tissue.
The conclusion describes the number of examined and pathologically changed lymph nodes, their location, shape, size and internal structure. As with the spleen, pathologies in the lymph nodes often indicate diseases of other organs.
Ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy
Content:
Ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy is not a mandatory examination procedure for all pregnant women, but it is done very often. This is due, first of all, to the high incidence of pathologies of the urinary system during pregnancy. The kidneys work more intensively during pregnancy, the load on them increases as the period increases, so during this period diseases of the urinary system often occur or their exacerbation in chronic forms.
Diagnosis of the pancreas using abdominal ultrasound
Using ultrasound diagnostics, both the body and the head of the pancreas are examined. This organ regulates metabolic processes and also secretes enzymes involved in the digestion of food. Without this organ, a person cannot live a day, and any disturbances in the functioning of the gland significantly reduce a person’s quality of life. Normally, the organ has the shape of the letter S. It is difficult to determine the entire pathology using an ultrasound machine. The specialist sees only isolated areas, as well as indirect signs of the problem. If they are noticed, the doctor refers the patient for a more detailed examination.
The gland is 14-22 cm long and weighs 70-80 grams. The main duct has a diameter of 1 mm, but with pancreatitis or neoplasm it increases, and with stones it decreases. Inflammation changes the size of the organ or its individual parts. In 60% of cases, malignant tumors are localized in the head of the gland; it reaches a length of up to 3.5 cm. Cysts also lead to an increase in size; they make the contours convex.
The contours of a healthy organ should be clear and uniform. Vagueness indicates inflammation, although reactive edema is sometimes a chain reaction to a stomach ulcer or gastritis. Stones and cysts have clear contours, and neoplasms have blurred boundaries. But only an experienced and attentive specialist can see this on the monitor screen of an ultrasound machine.
Increased echogenicity is typical for stones and chronic pancreatitis, and in acute pancreatitis it is reduced. White spots on the monitor screen indicate cysts and abscesses. Mixed echogenicity occurs when there is a change in the structure of the organ (for example, with pathology of the islets of Largehans, which produce insulin).
Indications for use
Ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy can be prescribed for the following indications:
- Deviations from the norm of a general urine test
(detection of protein, bacteria, red blood cells, leukocytes); - The patient complains of frequent nagging pain in the lumbar region;
- Various urination disorders
(pain, burning in the urethra, increased urination); - Unusual color of urine,
especially if there is blood in it
; - Increased blood pressure;
- Endocrine diseases;
- The appearance of persistent edema;
- Back injuries
(falling on your back, blows); - A history of any diseases of the urinary system
(pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, glomerulonephritis, neoplasms of the urinary system and others).
In what cases should it be done?
Indications for ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity are numerous, the main ones are:
- complaints of pain localized or radiating to the right hypochondrium
- feeling of heaviness after eating
- digestive disorders, dyspeptic disorders
- dynamic observation in the presence of chronic pathology of the organs of the hepato-biliary system and pancreas (hepatitis, pancreatitis, cirrhosis, portal hypertension, cholelithiasis)
- suspicion of the presence of a tumor formation
- search for metastases in the presence of a known primary site
- control of treatment
- abdominal injuries
Recently, ultrasound examination has become important in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis, intestinal diseases, including oncopathology. It is also possible to conduct research without indications, at the request of the patient, for the purpose of screening organic pathology.
Indications for kidney ultrasound:
- nagging pain in the lower back
- pain when urinating
- dysuric disorders
- routine examination for identified chronic diseases and developmental anomalies
- changes in urine tests
- arterial hypertension (especially in the absence of effect from antihypertensive therapy)
- traumatic injuries of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space
- oncological search for the primary focus and metastatic lesions
There are no absolute contraindications for ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys and, if necessary, the procedure can be performed multiple times even within a short period of time.
Preparation
remember Carrying out an ultrasound of the kidneys does not require special preparation, however, it should be remembered that bloating and increased gas formation can be an obstacle to the procedure.
To avoid this situation, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Diet 3 days before the test
. A woman should avoid foods that cause flatulence: legumes, cabbage, dairy products, brown bread, carbonated drinks; - Taking carminative drugs if necessary
(Espumizan, activated carbon and others).
In addition, kidney ultrasound is performed with a full bladder, so 1 hour before the procedure you need to drink several glasses of clean still water.
Lifestyle and diet
In addition to taking folk remedies, lifestyle is important in treating the disease. It is necessary to give up bad habits, lead an active lifestyle, and avoid hypothermia. It is very important to prevent the development of bacterial infections, as well as to detect and treat them promptly. A chronic infectious process is a potential source of infection in pyelonephritis.
The patient’s nutrition is important for prevention and treatment. Nutrition should be correct; it is best to eat home-cooked food. It is important to reduce the amount of animal protein. Preference should be given to vegetarian food, eat as many fruits and vegetables as possible as sources of vitamins and minerals. It is also important to reduce or completely eliminate salt intake. To cleanse the kidneys, it is useful to eat watermelon, celery, parsley, and asparagus.
Carrying out the procedure
Before starting the procedure, a woman must remove all jewelry and clothing above the waist, because this may distort the resulting data.
information Ultrasound examinations are most often performed in the lateral, dorsal or abdominal decubitus position. In some cases, for example, if nephroptosis (prolapse of the kidney) is suspected, the procedure is performed in a standing position. When performing an ultrasound, it is important that the patient remains still.
A special gel is applied to the area being examined to improve the conductivity of ultrasonic waves, which is wiped off immediately after the examination is completed (for these purposes, the woman needs to take napkins or a towel with her).
Contraindications for liver ultrasound
This diagnostic method has no special contraindications. The study is carried out using ultrasound radiation and is an absolutely safe and painless way to obtain the necessary information about the organ being examined.
However, there are certain categories of patients to whom certain contraindications may apply:
- on the skin in the projection of the organ under study there are mechanical damage, inflammatory lesions and other dermatological diseases that can prevent close contact of the sensor with the skin;
- increased gas formation in the intestines;
- full stomach, examination is carried out on an empty stomach;
- taking medications that affect the organ being studied.
All of the above points are not capable of causing harm to the body when undergoing an ultrasound examination. Their presence helps to reduce the accuracy of the final results and their information content.
Decoding
During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor examines a number of parameters: the size of the kidneys, their location, mobility, structure, the presence of various formations (stones, sand, cysts, tumors) and others.
To decipher this examination method, you need to familiarize yourself with the list of normal indicators:
- Location
. Normally, the kidneys are located retroperitoneally on both sides of the spine at the level of the 12th thoracic and 1-2 lumbar vertebrae. The right kidney is most often located slightly lower than the left; - Mobility.
The kidneys can move very limitedly and only in a vertical position. Increased mobility is a pathological condition; - Dimensions
. Standard kidney sizes: length – 10-12 cm, width – 6 cm, thickness – 4-5 cm. This parameter is very important, because its change indirectly indicates a number of diseases of the urinary system. Thus, an enlargement of the organ is characteristic of inflammatory processes and the presence of various neoplasms in the kidneys. On the contrary, a decrease indicates severe chronic diseases that damage renal tissue or degenerative processes; - The thickness of the renal parenchyma
(kidney tissue itself): in young people is 1.5-2.5 cm. Normally, the parenchyma should have a homogeneous structure. Thickening of the renal tissue is often observed in inflammatory diseases, a decrease in long-term pyelonephritis, organ damage due to diabetes mellitus, degenerative processes, and with age; - Renal pelvis
(the free cavity in the kidney that collects urine). The pelvis should be free; the presence of sand or stones in it indicates urolithiasis; - Fibrous capsule
(the membrane that covers the outside of the kidney). Normally, the capsule is smooth and clearly identified during ultrasound examination.
On the ultrasound form, after a detailed description of the organs, the doctor writes a final conclusion, by which one can judge the condition of the urinary system.
Possible conclusions of ultrasound of the urinary system:
- Normal
(no gross kidney pathology detected); - Severe pneumatosis intestinalis
(the study is uninformative due to flatulence). In this case, the woman needs to repeat the ultrasound after following the diet; - Nephroptosis
(prolapse of one or both kidneys); - Kidney microcalculosis
: small stones or sand are detected in the renal pelvis; - Echogenic formations (echoshadow, nephrolithiasis):
stones more than 5 mm in the renal pelvis; - Pyelonephritis
(a common pathology during pregnancy, requiring urgent hospitalization of the woman); - Hydronephrosis
(enlargement of the renal pelvis as a result of impaired outflow of urine and its accumulation). This pathology also requires a thorough examination of the pregnant woman; - Kidney abscess;
- Tumor-like formations;
- Anomaly of the kidney structure;
- Kidney cyst(s).
It is important to note that most ultrasound diagnostic doctors rarely make an accurate diagnosis: they just describe what they see on the screen. The final diagnosis should be made only by your attending physician, taking into account not only ultrasound, but also other examination methods performed.
Digestive system
It includes the liver and gall bladder, intestines, stomach and pancreas.
The liver is responsible for breaking down fats and ridding the body of accumulated harmful substances. Therefore, for example, when taking potent drugs, doctors recommend taking hepatoprotectors, that is, drugs that protect the organ, improve its functioning and remove poison.
Normal liver values should be approximately as follows:
- The dimensions of the right lobe are up to 12 cm, the left lobe is up to 7 cm;
- The diameter of the portal vein is up to 13 mm, the vena cava is up to 15 mm;
- The diameter of the bile duct is up to 8 mm;
- The angle of the right lobe should be no more than 75 degrees, the angle of the left lobe should be no more than 45.
The edges should be smooth and clear. The liver should be equally dense in structure, without compactions and neoplasms. The ultrasound should show blood vessels and ligaments.
As a rule, the condition of the gallbladder is described together with data on the liver, since these organs are not only located nearby in the abdominal cavity, but also perform the same function: bile, necessary for the breakdown of fats that occurs in the liver, is produced and stored in gallbladder. Diseases such as cholecystitis and the formation of gallstones are associated with improper functioning of the gallbladder.
Normally, this organ should have the following parameters:
- Length – from 6 to 9 cm;
- Width – from 3 to 5 cm;
- The thickness of the organ walls is up to 4 mm;
- The lower edge of the bladder may protrude from the lower edge of the liver by 1 cm.
Ultrasound also shows the size of the gallbladder ducts, through which fluid enters the duodenum and liver. The diameter of the bile duct should be no more than 6 mm, the diameter of the hepatic duct should be no more than 5.
The pancreas produces digestive enzymes, as well as insulin and glucagon. Improper functioning of this organ is fraught not only with pancreatitis and stomach problems, but also with the appearance of diabetes.
A normal pancreas test result should be something like this:
- Head – no more than 32 mm;
- Body – no more than 21 mm;
- Tail – no more than 35 mm;
- Pancreatic duct – no more than 2 mm.
The structure of the pancreas should be homogeneous, and the density should correspond to the density of the liver or be slightly higher. The contours of the organ must be clear. As in other cases, blurred contours and increased sizes indicate tissue inflammation and swelling. Cysts, tumors and stones in the ducts will also be noticeable during an ultrasound examination.
Ultrasound of the intestines and stomach is rarely done, since these are hollow organs through which ultrasound passes poorly, making it impossible to detect mucosal lesions. But the test shows the presence of fluid or foreign bodies in the cavities, which can be useful in making a diagnosis.
Description
Abdominal ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic technique for human organs and tissues, which is based on the use of ultrasonic waves. During this procedure, a sensor is placed on the pregnant woman's stomach, which produces high-frequency sound waves.
They are not audible to the ordinary human ear, but penetrate well through the anatomical structures of the body. Depending on the density of the fabric, some of the waves are reflected back and are captured by the same sensor. The received signal is transmitted to a computer, where it is processed and displayed on the screen as a picture.
In some cases, contrast is used or ultrasound is performed with additional stress.
Ultrasound diagnostics has the highest information content for dense organs that are created from homogeneous tissue (liver, spleen, pancreas), vessels (abdominal aorta, portal, renal, splenic veins) and lymph nodes. Among the advantages of the technique are also accessibility (ultrasound can be performed in almost any hospital or clinic) and moderate cost.
Why do you need to prepare for the instrumental examination procedure?
The ultrasound method has many advantages over other diagnostic techniques, such as:
- high information content - the examination result shows in detail the features of the morphological structure of organs;
- low time consumption - the procedure takes no more than half an hour, including a description of the research results;
- painless – the method excludes penetration into the body;
- safety – the equipment does not emit waves dangerous to the human body.
However, there are many different factors that can influence the outcome of the examination. The main one is considered to be improper preparation. In such cases, ultrasonic waves are scattered and the image is distorted. The sonologist cannot accurately identify the pathology, and the research data becomes uninformative. That is why, to perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, careful preliminary preparation of the patient is required.
Is it possible to do?
An important question that worries many patients is whether it is possible to do an ultrasound during pregnancy?
You can often hear the statement that ultrasonic waves (especially when ultrasound is frequently prescribed) can lead to disruption of fetal development, the occurrence of mutations or the formation of malformations. Fortunately, this is all nothing more than a pseudoscientific myth.
Ultrasound examination in pregnant women has been used in clinical practice for many decades. And during this time, there was no increase in the incidence of diseases or developmental defects in children.
Ultrasound is a safer diagnostic method than computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. International recommendations recommend using it in pregnant patients.
Diagnosis of pathology.
With iliac and lumbar dystopia, the abnormally located organ is palpated during a medical examination. If the kidney is located in the pelvic region, this is determined using a gynecological or rectal examination. When the organ is located thoracically, tools are used for diagnosis: fluorography or radiography.
Ultrasound examination, urography, renal angiography to study the renal vessels and magnetic resonance imaging are also performed. When diagnosing, make a differential diagnosis between dystopia and tumors of internal organs.
Peculiarities
The main feature of ultrasound diagnostics is that the topographic location of organs changes in pregnant patients. In the second, and especially the third trimester, the enlarged uterus displaces other anatomical structures upward and to the sides. Therefore, the doctor must be prepared for the fact that conventional approaches and positions of the sensor lose their relevance.
In the third trimester, the information content of the study also decreases, due to the fact that the uterus and fetus block access to a significant part of the abdominal cavity. This should always be understood when prescribing this diagnostic technique. Typically, the upper part of the uterus is at the following level (depending on the week of pregnancy):
- 12 week – upper edge of the pubic bone;
- 16 week – at the level of the line drawn between the crests of the iliac bones;
- Week 22 – navel;
- 26 week – at the level of the lower edge of the costal arch;
- 32-24 weeks – epigastric region.
During multiple pregnancies, the uterus grows in size even faster. Therefore, it is rational to routinely carry out ultrasound diagnostics until 18-22 weeks.
Reasons for displacement of paired organs
The causes of dystopia may be the following factors:
- intrauterine anomalies caused by infectious diseases, smoking and intoxication of the mother’s body;
- genetic factors.
The formation of the fetus is influenced by the mental state - stressful situations and psychological trauma.
Renal dysfunction depends on the stage of development at which the process of descent of the organ into the small pelvis has stopped - the lower the dystopic organ is, the more pronounced the process of rotation.
The position of the kidney is considered disturbed not only due to displacement, but also when rotated relative to the normal position. Dystopia is also diagnosed when the sinus and pelvis are in the lateral plane or turned forward.
Pathology options
In 57% of cases, lumbar dystopia of the right kidney is diagnosed, and only in 33% of cases - of the left. All other identified variants of the disease are included in the remaining 10%.
In lumbar pathology, the arteries of the organ are located at the level of the lumbar region, II-III vertebrae, the renal pelvis is turned towards the abdominal cavity.
On palpation, the kidney can be felt in the hypochondrium area; the condition can be mistaken for the appearance of a neoplasm or nephroptosis. Symptoms may appear: dull pain in the hypochondrium, periodic difficulty urinating.
Pelvic dystopia of the left kidney is more often diagnosed, although the anomaly itself is very rare. The pathologically altered organ is located between the rectum and uterus in women, and the rectum and bladder in men.
The condition causes displacement of surrounding organs - severe pain occurs in them due to compression and partial dysfunction. By palpation through the rectum, you can feel a lump, which is previously determined to be a neoplasm. This diagnosis is made for the following reasons: palpation makes it clear that the body of the seal is dense, and when you try to move it from its place, painful sensations occur.
Ileal dystopia
Ileal dystopia of both kidneys is not uncommon. The multiple renal arteries are supplied by the common large iliac artery.
Symptoms of the condition are abdominal pain, equally pronounced on the right and left sides. Displaced paired organs put pressure on surrounding tissues, and the nerve plexuses react to this. The pain is inconsistent and in women it often coincides with the menstrual cycle. An additional symptom is a violation of urodynamics.
The condition causes disease of the gastrointestinal tract, provokes nausea, vomiting, and frequent signs of enterocolitis. The deterioration of health cannot be explained only by rotation - general malaise appears due to inflammatory processes in the most altered organ: urolithiasis, hydronephrosis, the introduction of pathogenic microflora.
The position of the kidneys in the absence of ultrasound examination often led to serious errors.
Mistaking it for a neoplasm, it was removed surgically, mistaking it for a cyst or even a cancerous tumor of gynecological organs - the ovary or fallopian tube.
Rotational dystopia
Rotational dystopia of both kidneys is also called cross dystopia. In this case, the paired organs are located on one side and - in most cases - are connected to each other; one might say, they work like a common organ.
It is impossible to detect an anomaly during an ultrasound examination; the following methods are used to identify a rare anomaly:
- scintigraphy;
- radioisotope scanning;
- excretory urography.
Thoracic dystopia
Thoracic dystopia is more often detected on the left side. It has other names - subdiaphragmatic or thoracic. During the formation of the embryo's body, the kidney is displaced through the Bogdalek fissure into the thoracic cavity extrapleurally.
An open hole remains in the diaphragm through which the ureter and vessels pass - in this case they are significantly elongated. The pathology is detected by chance: when the patient complains of pain in the chest, worsening after eating.
To determine the nature of the pain, a chest x-ray is prescribed, which shows a shadow on the diaphragm or a faint lump. Only an experienced diagnostician can read the image correctly. The anomaly is mistaken for pleurisy, aneurysm, cystic neoplasm or diaphragmatic hernia and a decision is made to remove it. Currently, if the X-ray picture is unclear, a kidney scan or excretory urography is performed, thanks to which the correct diagnosis is established.
When dystopia is detected, operations are performed only in cases of organ damage - urolithiasis, hydronephrosis, persistent inflammatory processes - pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. If no pathology is observed and there is no excessive mobility, the kidney is not removed.
Dystopia is diagnosed in diseases of the urinary system - in a healthy state, organs that have changed their normal position do not show themselves in any way - however, like those that are in their place.
Treatment and preventive measures
Since dystopia is detected due to the appearance of symptoms indicating inflammatory processes, treatment is carried out in exactly the same way as for diseases of the urinary system according to the standard regimen.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- antispasmodics;
- diuretics;
- antibiotics or antiviral drugs;
- vitamins;
- immunity correctors;
- extended drinking regime.
The surgical method is used only in emergency cases - if the displaced kidney puts pressure on the surrounding tissues. Most often, the organ is expelled to the renal pelvis. The organ is removed only if there is complete necrosis, after first conducting a thorough examination. Patients with renal rotation have a high risk of detecting the absence of a paired organ.
Patients with dystopia should lead a special lifestyle that imposes significant restrictions.
Recommended diet according to Pevzner, table No. 7. It is necessary to exclude smoked, spicy, alcohol, fried and fatty foods from the diet - and for life, in order to avoid exacerbation of urinary system diseases.
You should monitor the water-electrolyte balance, limit the water regime, and refuse mineral waters - dissolved minerals are not completely removed from the body and provoke the onset of urolithiasis.
You should dress according to the weather and take care of yourself - if you are hypothermic, the risk of inflammatory diseases of the urinary system is too high. Streptococcal tonsillitis is especially dangerous - its complications adversely affect renal function.
Kidney dystopia during pregnancy is dangerous only when the kidneys are located deep in the pelvis, between the uterus and rectum. This condition causes acute painful sensations; disturbances in urodynamics provoke severe toxicosis.
Pregnancy is rarely carried to the end of the third trimester; delivery is carried out only by cesarean section.
Natural labor in this case cannot proceed without complications and causes a risk of death after childbirth due to compression of the vessels supplying the kidney.
The location of the kidney outside the pelvis does not affect the course of pregnancy in any way. In the absence of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, it proceeds according to the usual pattern and delivery is carried out naturally.
Thanks to the level of modern medicine and the latest diagnostic methods, kidney dystopia is diagnosed at the stage of the appearance of painful symptoms, which makes it possible to choose the optimal treatment method.
Fetal examinations are carried out during the prenatal period. When rotation is detected after the baby is born, if necessary, the necessary adjustments are made.
Kidney dystopia is a pathological placement in an uncharacteristic area, as a result of a developmental defect. The kidneys initially develop in the small pelvis and then rise to the level of the XI-XII thoracic - I-III lumbar vertebrae. Dystopia occurs when this process is disrupted. The kidney is tightly fixed to the pathological site and is immobile.
Indications
Regardless of the period of pregnancy, a situation may arise when ultrasound diagnostics is performed. The expectant mother is not immune from the occurrence of acute inflammatory processes, injuries or exacerbation of chronic diseases. We have separately identified several groups of pathologies, which tell us why an abdominal ultrasound may be prescribed.
Acute stomach
This term refers to the sudden onset of abdominal pain of moderate or severe intensity.
It may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, severe weakness, paralysis of intestinal motility and muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall.
The occurrence of these symptoms in a pregnant woman requires immediate hospitalization in a specialized hospital and examination by a gynecologist and surgeon. After laboratory tests, an immediate ultrasound examination is also necessary. It allows you to detect signs of appendicitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, which are the most common causes of acute abdomen.
Are you worried about high acidity in your stomach? In this article you can find 10 proven methods of treating gastritis with folk remedies.
After an abdominal ultrasound, a decision is made on the further management of the patient: immediate surgery, observation, or prescribing other examination methods.
Kidneys and genitourinary system
Ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system and kidneys is very informative even in late periods of pregnancy. Among the indications it is necessary to highlight:
- the occurrence of attacks of renal colic (sharp pain in the back, side, which radiates to the groin area, and does not subside when changing position);
- deterioration in the results of urine tests, which pregnant women must undergo periodically;
- frequent painful urge to urinate;
- change in urine consistency, cloudiness, appearance of blood or pus;
- pain in the transverse region with increased temperature;
- development of a kidney failure clinic.
Liver diseases
Ultrasound of the liver allows you to verify tissue changes, visualize the development of benign or malignant processes, and also determine the presence of cirrhosis and secondary signs of portal hypertension (increased pressure in the portal vein).
Which organs need training?
Diagnosis using ultrasound allows a specialist to carefully examine all abdominal organs (abdominal organs) - liver, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, circulatory and genitourinary systems. It is also possible to study the condition of the kidneys, adrenal glands and retroperitoneal space. A successful ultrasound examination can reveal many pathologies or abnormalities in the development of the above organs.
Ultrasound allows:
- assess the condition and structure of the liver and kidneys;
- examine the gallbladder and its ducts;
- study the pancreas;
- identify inflammatory processes and ascites (fluid accumulation in organs).
The procedure makes it possible to determine the presence of calculi (stones) in the ureters, bladder, kidneys, gallbladder and its ducts, and to thoroughly examine the aorta, the largest vessel in the abdominal space. For children, ultrasound is one of the fastest and most painless ways to quickly detect appendicitis, which allows you to take the necessary measures as soon as possible. Also, during the diagnostic process, violations of the integrity of organs due to injury or other damage are quite easily determined.
All of the above research opportunities provide identification of the causes of unexplained pain in the abdominal region and various dysfunctions of its organs and systems. In some cases, ultrasound is used for monitoring after taking a biopsy or for preparation for surgical operations.
When is research required?
Ultrasound diagnostics is used as a screening examination of the condition of the fetus during pregnancy. After the expectant mother registers with a gynecologist at the antenatal clinic, she is required to undergo fetal ultrasound several times:
– the age of the fetus is clarified, gross developmental anomalies are excluded;
11-13 weeks- 20-24 weeks – the baby is measured, the volume of water is assessed, the condition of the placenta is assessed;
- 32-34 weeks – assessment of the location of the fetus, exclusion of placental insufficiency.
Ultrasound examinations of other organs and systems (digestive, cardiovascular, urinary) are performed when their pathologies occur.
Why is ultrasound examination of internal organs necessary?
In order to prevent various diseases, practicing doctors advise patients to undergo an instrumental examination of the abdominal cavity and kidneys once a year. This will allow you to monitor the condition of the organs, identify pathological changes in time and begin rational treatment at the earliest stage of the development of the disease.
The medical diagnostic industry is equipped with modern equipment, thanks to which the possibilities for informative and high-quality examination of the abdominal organs and kidneys are expanded.
During ultrasound diagnostics, patients may be diagnosed with:
- stones (stones, sand), which are localized in the bladder, kidneys, bile ducts and gall bladder;
- benign changes in the structural elements of organ tissues;
- malignant neoplasms;
- inflammatory processes.
You need to undergo an ultrasound when the first signs of the development of a pathological condition appear, such as:
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- constant or periodic nausea;
- bowel disorders;
- vomit;
- bleeding;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- acute or chronic pain;
- peritoneal injuries.
Preparation
When prescribing an ultrasound examination, the doctor is obliged to tell you what preparation for it should look like. Usually it does not differ from that in other adult patients, and consists of 3 components:
- diets;
- drinking regimen;
- medicinal preparation.
If there is a planned study, it is advisable to remove from the diet for a few days foods that contribute to the development of gas formation in the intestines:
- all legumes;
- butter cookies, as well as products with chocolate;
- fresh bread and bakery products;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- grapes, apples, pears, apricots, peaches;
- cabbage, radish, turnip, Chinese salad, onion;
- mushrooms;
- ice cream;
- canned or pickled foods;
- fatty meats.
Moreover, if the patient was admitted to a medical facility due to an acute pathology (for example, suspected appendicitis), then special preparation with food is not required.
Drink
to exclude all carbonated drinks and juices (especially homemade ones)
from the diet for a day or two If you plan to exclusively examine the digestive system or the vessels of the abdominal cavity, then there are no other special features. But if you need to diagnose the bladder, then within 10-15 minutes the pregnant woman is given about 1-1.5 liters of still table water to drink. This makes it possible to increase the information content of diagnostics.
Medicines
Typically, drug preparation is not required before an ultrasound scan. The patient also takes her previously prescribed medications as usual.
Some patients experience increased intestinal gas formation during pregnancy. To reduce it, in addition to diet, the following medications are prescribed:
- sorbents (activated carbon, white carbon, Smecta) - absorb part of the formed gases, but can contribute to the development of constipation;
- antispasmodics (drotaverine) - relax the smooth muscle muscles of the intestines, are prescribed with caution during pregnancy;
- simethicone preparations (Espumizan) - leads to a decrease in the surface tension of gas bubbles, which promotes their elimination.
Important components of preparing for an ABP examination
In order to properly prepare for an ultrasound scan of the OBP, and nothing interferes with the process, the patient should strictly adhere to all the recommendations that he will receive in the diagnostic room. These include:
- adherence to a special diet and a certain diet;
- correct timing, taking into account certain examinations;
- prohibition of bad habits - drinking alcohol, smoking;
- use of medications only as prescribed by a specialist;
- taking into account the characteristics of organs and their appropriate preparation.
Basic diet rules for preparation
The most important rule of the diet is to differentiate which foods you can eat and which are prohibited. The diet consists of completely abstaining from food that leads to flatulence in the stomach and intestines, which will prevent a quality examination of the organs. It must be started at least 3 days before the planned study.
Authorized products include:
- boiled or steamed lean meat - quail, beef, chicken, veal;
- lean fish – boiled, baked, steamed;
- hard-boiled eggs - no more than 1 per day;
- porridge – pearl barley, oatmeal, buckwheat;
- low-fat types of cheeses.
You need to eat often - every 3-4 hours, but in small portions. It is not recommended to drink food with food; you can drink unsweetened and weak tea and still water an hour before a meal or an hour after it. The volume of liquid drunk per day should not be less than 1.5 liters. Products that should be completely excluded:
- legumes - peas, lentils, beans, beans;
- carbonated and caffeinated drinks;
- sweets, bakery products, black bread;
- fermented milk products (including cottage cheese);
- fatty meats, fish and cheeses;
- raw vegetables and fruits.
This diet should be followed until dinner on the eve of the procedure - no later than 18-19 hours, and if the study is scheduled for the next morning, then you can no longer eat or drink. And if the examination is scheduled for the afternoon, then at 8–9 o’clock in the morning you can eat a light breakfast, so that in any case the diagnosis is carried out on an empty stomach.
Diet for children
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys in adults and children is in many ways similar, but still has some differences. Infants have to skip one feeding so that at least 3 hours pass before the procedure and they should not be given anything to drink for at least one hour. Older children - from 1 to 3 years old - take a break between meals, since it is easier for them not to eat for 4 hours, and this is enough to digest leftover food.
You will also have to abstain from liquids for an hour before diagnosis. From 3 to 14 years, when children already understand what is needed from them and can tolerate 6–8 hours without food and an hour without drinking, the procedure is carried out with exactly this feeding interval. Children over 3 years old already understand that research needs to be done and can refrain from eating and drinking for the necessary time.
Recommended drugs
Patients of any age will be helped to prepare for the study by drugs that reduce gas formation - “Espumizan” and its analogues: “Bobotik”, “Kuplaton”, “Infacol”. They are prescribed for 3 days before the study, taking into account the age of the subject. If these medications do not give the required effect or are poorly tolerated (in infants, colic does not go away, and in adults the feeling of bloating remains), then it is recommended to take adsorbents. These are the well-known “Smecta” and “White Coal”.
Previously, “Activated carbon” was used, but it is less effective and now, with the creation of new drugs, it has been successfully replaced by more effective drugs. They do not need to be taken within 3 days - 2 doses are enough, the evening before the procedure and in the morning 3 hours before it starts. Adult patients who do not have a history of pancreatitis can drink Mezim or Festal 3 times a day, one tablet with meals, to improve digestive processes.
Purgation
The intestinal lumen filled with feces can become a significant obstacle to examination, so preparation for the procedure must be thorough. You can use the old method using an Esmarch mug and 1–1.5 liters of water at room temperature. The enema must be done in the evening no later than 16-18 hours.
After cleaning, you should take adsorbents or anti-flatulence medications - 1-2 doses. New and effective drugs that can perfectly cleanse the colon in a few hours have become an excellent alternative to the enema method. One of the most commonly used is Fortrans.
It is diluted with 1 liter of water at the rate of 1 sachet per 25 kg of a person’s weight and drunk over 1 hour, that is, if the body weight is 75 kg, then 3 liters of solution is taken in 3 hours. This cleaning should be carried out on the eve of the examination in the afternoon - from 16 to 19 hours. Preparations based on lactulose - Duphalac, Normaze, Prelaxan - should not be taken, as they can cause bloating, which will interfere with obtaining quality results.
What to take with you?
Don't forget to take the following things with you to your ultrasound examination :
- referral from the attending physician;
- compulsory health insurance policy;
- medical card and exchange card for a pregnant woman;
- a bottle of still mineral water (during an ultrasound of the genitourinary system);
- a towel (especially if the study will be carried out in public medical institutions) in order to remove any remaining gel from the skin of the abdomen.
If you wish, you can bring food (such as a croissant or sandwiches) with you to snack on after completing the study.
What can affect the results of the examination?
There are plenty of reasons that can negatively affect an ultrasound examination, and the patient can avoid some if they take the examination responsibly. These include:
- spasm of the intestinal muscles due to recent smoking or endoscopy;
- increased flatulence due to poor preparation;
- remnants of contrast agent in the intestinal lumen;
- excessive weight of the patient, preventing the penetration of ultrasound;
- a large wound surface that does not allow placement of a sensor;
- increased patient activity during the examination.
The patient cannot influence some factors, but he can easily take care of excluding others. Therefore, it is better to immediately tune in and properly prepare for an ultrasound so as not to waste time and money on repeated diagnostics.
diametod.ru
What to do after?
After completing the ultrasound, a conclusion is prepared within 10-15 minutes , which indicates all the detected changes (with standard indicators).
It is important to note that the doctor who conducts the study cannot make a final diagnosis. The results are issued (by hand, sent to the electronic kidney) to the patient or the doctor who referred him.
a special diet after the examination (unless there are other restrictions). Since patients come hungry for diagnostics, they can eat immediately after completion. Also, no additional medications are prescribed.
With the results of the ultrasound examination, the pregnant patient returns to her doctor. Based on them, he makes a final diagnosis and prescribes treatment, or prescribes additional examination methods.
It is allowed to be prescribed in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, when the formation of the main organs of the child has already completed. It is strongly recommended that the use of CT and other radiological methods be avoided.
Diagnosis of lymph nodes using abdominal ultrasound
Ultrasound does not normally visualize lymph nodes. If they are visible on the monitor screen, this indicates the development of such a terrible disease as myeloid leukemia or lymphocytic leukemia. With this disease, the spleen also increases in size.
If lymph nodes are visible on ultrasound, but other organs are normal in size, the person may be developing an infection. The spleen filters the blood from bacteria and produces antibodies, so during an infectious infection, it is the internal lymph nodes that will increase in size. Depending on their location, the doctor identifies disturbances in the functioning of neighboring organs. The heterogeneous echostructure of the spleen indicates the destruction of its tissues, blood diseases and damage to the organ by pathogenic microbes and viruses.
Ultrasound of the liver for adults
Before undergoing a liver ultrasound, an adult patient is required to obtain a doctor’s referral, which is issued if certain symptoms are present:
- general malaise and weakness throughout the body, accompanied by acute pain in the area where the organ is located;
- bitterness in the mouth and constant heartburn;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- increased gas formation;
- sudden weight gain and the appearance of a bulging belly.
During diagnostic measures, liver diseases will be identified that contribute to the manifestation of characteristic symptoms indicating improper functioning of the internal organ.
Unlike other imaging methods, liver ultrasound does not cause harm to health, while having maximum information content.
The procedure makes it possible to detect the presence of cancer in the early stages of development, which facilitates timely completion of the therapeutic course. Repeated studies are completely harmless and can be carried out an unlimited number of times.
Sign up for an ultrasound diagnostic by phone or by filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | All types of analyzes | Ultrasound at home | Calling a doctor to your home |
Ultrasound of the liver at home
It is not always possible to visit the clinic on your own. In this case, the modern method of ultrasound diagnostics of the liver at home will allow you to undergo the examination in a comfortable home environment and significantly save time.
This method will be useful for certain categories of patients:
- elderly people who, due to their physical capabilities, have difficulty traveling on public transport;
- patients with limited mobility due to serious injuries of various types or who are undergoing a rehabilitation period after undergoing surgery;
- busy people who have limited time or who simply do not like visiting medical centers and spending time in queues.
Most often, patients experiencing ailments associated with liver disease postpone a visit to the clinic until the last moment. This is due to various personal reasons or simply lack of time. This attitude towards one’s own health contributes to the unfavorable state of the body later, when the developing pathology enters the chronic stage and threatens with serious complications.
Equipment for performing ultrasound of the liver at home is identical to stationary units, but has a more compact size.
The sequence of actions during diagnostics is identical to outpatient examination:
- the patient takes a horizontal position on a flat surface;
- the skin in the examination area is covered with a special gel to ensure the best glide of the scanner;
- upon completion, the remaining gel is removed with wet wipes;
- all information received is entered into the patient's record.
Based on the results obtained, a diagnosis is made and an individual therapeutic course is developed, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Where to do an ultrasound of the liver
At the “Your Doctor” clinic, doctors with extensive experience in various medical fields take care of patients. You should also choose our medical center due to the availability of all the necessary modern equipment for undergoing an ultrasound of the liver and subsequent specialized examinations if necessary:
- Ultrasound examinations of the liver are carried out in separate rooms, which are equipped with all the necessary equipment for comfortable placement of the patient and obtain extremely accurate and most informative results;
- doctors have at their disposal all the necessary tools for effective and safe interaction with the patient;
- It is possible to perform an ultrasound of the liver at home.
The ultrasound diagnostic specialist’s office is equipped with special furniture for the most comfortable stay for the patient. In cases where there is a need for additional procedures, the doctor can use an additional set of tools to achieve the desired results.
What factors can distort liver ultrasound
In order to obtain the most accurate ultrasound results, which will subsequently lead to the correct diagnosis, you need to follow generally accepted recommendations for preparing for the event.
Certain factors can distort the readings:
- excessive accumulation of gases that interfere with the normal reflection of the transmitted signal;
- uncontrolled use of medications, without prior agreement with the therapist;
- non-compliance with the prescribed diet before diagnosis;
- mechanical damage to the skin at the point of contact of the sensor.
The accurate results obtained after ultrasound of the liver help to make the correct diagnosis, which in turn helps to prescribe the most effective course of therapy in each specific case.
Ultrasound of the liver for pregnant women
During pregnancy, a woman’s body is exposed to certain dangers that require timely detection in order to eliminate the possibility of harm to the developing fetus. Ultrasound of the liver during pregnancy is an absolutely harmless diagnostic method that is not capable of causing harm to the body of the mother and child.
Indications for this procedure include discomfort in the abdomen and right side. Complaints of pain and heaviness are also prerequisites for performing an ultrasound of the liver.
The procedure is prescribed after examination by a doctor, and among the main symptoms associated with it are:
- severe intoxication;
- unnatural yellowness of the skin;
- mechanical injuries;
- vomiting that appears in the later stages;
- a sharp increase in internal organs in the abdominal cavity;
- suspicion of the development of cholelithiasis;
- manifestation of symptoms indicating a possible tumor lesion.
The diagnostic method by undergoing an ultrasound of the liver is completely harmless and does not cause any harm to the pregnant woman and the fetus developing in the womb. Based on the results, an accurate diagnosis is made, which facilitates immediate treatment to eliminate the causes of the discomfort.
Which doctor performs liver ultrasound
An ultrasound specialist examines internal organs, in particular the liver, using ultrasonic waves. During the diagnostic procedure, a picture of the liver is displayed. This method of examination is the most accurate and safe; thanks to the results obtained, it is possible to make the correct diagnosis and formulate an effective therapeutic course.
The doctor’s responsibilities include carrying out the procedure and all accompanying manipulations. The specialist must understand the image displayed on the monitor and correctly describe what he saw in the reporting documentation and patient’s card.
To effectively perform the work, the doctor must understand topographic anatomy and know:
- norms of liver size;
- natural structure of tissue connections;
- possible pathological manifestations;
- the size of the organ with developing pathology.
After the procedure is completed, the ultrasound specialist does not make a final diagnosis. It only deciphers the received data from the monitor screen, analyzing and comparing the current indicators with the norms for the organ being examined.
If, during diagnosis, there are signs indicating a specific disease, it is indicated in the patient’s card. But the final diagnosis, based on the information received, is made by the attending physician.