Urolithiasis is a chronic, recurrent metabolic disease characterized by the presence of stones in the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder), which is caused by various reasons.
The main cause of the occurrence and development of urolithiasis is considered to be a metabolic disorder, which leads to the formation of insoluble salts that form stones. The number of stones and their location can be very different.
The main predisposing factors for the development of urolithiasis include:
- food (drinking water, food, monotonous meals, etc.)
- climatic (hot climate)
- medications (cytostatics, glucocorticoids, antacids, acetylsalicylic acid, tetracyclines, etc.)
- developmental abnormalities of the urinary system, ureteral strictures
- hyperparathyroidism, A and D vitamin deficiency, idiopathic acidosis
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis)
- hereditary nephritis-like or nephrosis-like syndromes
Types of stones in the kidneys, ureters, bladder
It is important not only to diagnose the presence of kidney stones, but also to recognize the type as accurately as possible - the correct choice of method for treating urolithiasis or crushing stones depends on this. The effectiveness of the therapy chosen by the urologist directly depends on the composition and form of the solid formation.
- Oxalates and phosphates. This is the most common category of “stones” in urology, the basis of which is calcium salts. Diagnosed in 70% of patients with urolithiasis.
- Phosphate-ammonium-magnesium and struvite stones - arise due to infectious processes in the urinary tract. Another name is infection stones, diagnosed in 15% of patients.
- Urate - a uric acid stone in the kidney is diagnosed in 10% of patients, and its formation is explained by excess uric acid.
- Cystine stones - formations are rarely diagnosed, in 2-3% of patients. The causes are genetic and congenital pathologies of the urinary system.
To diagnose solid formations, you must make an appointment with a urologist at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Clinical manifestations of urolithiasis:
Depending on the location of the stone, the patient may complain of different symptoms, but the main ones for this disease are:
- Paroxysmal pain. Depending on the size and location of the stone, the pain is localized differently. A stone in the kidney or upper ureter is usually characterized by pain from the back or side just below the ribs. The pain can be sharp or dull, and the intensity can vary at intervals lasting from 20 to 60 minutes. This is often preceded by physical activity, taking large amounts of fluid or diuretics. As the stone moves along the ureter, the location of the pain changes, the pain moves from the lower back to the abdomen, radiating down the abdomen, into the perineum, inner thigh, and into the scrotum. These complaints are accompanied by a frequent urge to urinate. It is very important not to confuse renal colic with acute surgical diseases, such as acute appendicitis, acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, intestinal obstruction, strangulated hernia, ectopic pregnancy, perforated gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, so it is urgent to consult a doctor if the above symptoms occur.
- Patients often note blood in the urine. In urolithiasis, blood impurities are preceded by renal colic. Cloudy urine with sediment or a foul odor may also indicate a stone has passed.
- Deterioration in general health , nausea, vomiting. This is especially pronounced if, against the background of a violation of urine from the kidney, inflammation occurs in it - pyelonephritis.
- Passage of sand or stone
Diagnosis of the disease with the appointment of the necessary tests, examinations and treatment is carried out by doctors from the Urology Department.
Causes of kidney stones
CT or MRI of the kidneys: which is better?
What is better to use - CT or MRI of the kidneys depends on individual details. Magnetic resonance imaging will be appropriate in the following cases:
- suspicion of malignant neoplasm in the kidneys;
- the need to determine the extent of tumor spread in the kidney;
- congenital and acquired anomalies of the pyelocaliceal system;
- hydronephrosis;
- abscess;
- formation of cysts in the kidneys.
Computed tomography is performed for:
- suspected urolithiasis;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- injuries of the retroperitoneal space;
- the need to examine the shape of the kidney, its size, location, topographic relationship of organs.
Examination for urolithiasis
If you have the above complaints, you need to consult a urologist, who will conduct an additional examination and decide on further treatment.
Basic examination includes:
- Complaints, anamnesis, examination
- General clinical blood and urine tests.
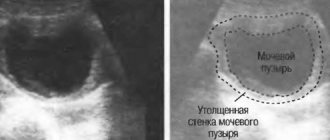
- Ultrasound of the urinary system, in which in most cases the diagnostician will see the location, number and size of the stones. This is a safe, painless and non-invasive examination method that can be repeated several times during the treatment process and for dynamic monitoring.
- Survey and excretory urography.
Additional examinations:
- Spiral computed tomography allows you to see the stone, calculate its density, volume, see the architectonics of the urinary system, and the condition of the surrounding tissues. If necessary, it is possible to perform 3-D reconstruction.
- Dynamic and static nephroscintigraphy allows one to assess renal function and, if present, the degree of their impairment.
- Culture of urine with sensitivity to antibiotics allows us to identify the presence of infection in the urinary tract and the degree of inflammation activity.
Principle of operation
Both computer and magnetic resonance techniques are expensive. They are carried out only on the recommendation of a doctor and when the ultrasound has completely exhausted itself.
When choosing which is better - CT or MRI of the kidneys, it is necessary to take into account the operating principle of the devices.
Computed tomography uses ionizing rays to produce images. Some of them are reflected by internal organs, the rest pass through the part of the body being examined and land on a sensitive matrix. The data is read by the device's analyzing system. Based on them, the computer builds an image.
MRI is based on the ability of hydrogen atoms to change their spatial orientation to the opposite one under the influence of a powerful magnetic field. The energy released during this process is recorded by a tomograph. The more protons that respond to the influence of the magnetic field, the brighter the area will look. Thus, with MRI of the kidneys, unlike CT, there is no negative impact of ionizing or X-ray radiation.
Treatment of urolithiasis
After receiving the examination results, the urologist will decide which treatment tactics should be used in a particular case.
Currently, a urologist has in his arsenal many different treatment methods:
- Drug treatment aimed at spontaneous stone passage
- Drug treatment aimed at dissolving the stone
- Open surgeries
- External shock wave lithotripsy
- Endoscopic contact lithotripsy
- Percutaneous nephrolithotripsy
- Endoscopic retroperitoneal surgery
Until recently, open operations in the treatment of urolithiasis were of leading importance, however, due to the development of medical technology, they fade into the background and are used according to strict indications. Increasing importance is being given to minimally invasive methods, such as: external shock wave lithotripsy, endoscopic methods (contact lithotripsy), percutaneous nephrolithotripsy. The “gold standard” for the treatment of urolithiasis is extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, which allows the removal of about 90% of urinary stones of any location. When performing remote shock wave lithotripsy, shock waves, penetrating through tissues and without injuring them, destroy the stone into small fragments (sand). Subsequently, the sand is gradually released in the urine when urinating. All existing treatment methods are complementary, and each patient with a stone of a certain location, size, volume, density, a certain anatomy of the urinary system, and the presence of concomitant diseases is selected with an individual treatment method. The issue of treatment tactics (operative, conservative, observation) should be decided by hospital urologists who have the appropriate certification, experience and qualifications, and equipment that allows them to use all types of treatment for urolithiasis.
CT or MRI of the kidneys: advantages and disadvantages
When choosing which method of renal imaging - CT or MRI - will be optimal, you need to consider the following nuances:
- duration of the examination;
- patient's age;
- presence of pregnancy;
- tolerance of contrast agents.
If the kidneys are injured, and results need to be obtained as soon as possible, preference is given to the computer method. If a pregnant woman is being examined, the choice is clearly magnetic resonance imaging. Over thirty years of use, no evidence of a negative effect of the magnetic field on young cells has been established. If the subject cannot tolerate iodine-containing drugs, he is also recommended to have a magnetic resonance imaging study.
The final decision on whether to choose a CT or MRI of the kidneys as a diagnostic procedure is made by the attending physician. Only he can take into account all the features of the disease and recommend the examination that will be as informative as possible.
testpuls.ru
Get a consultation at the urology department
In our clinic, for remote crushing of stones, a device of the latest generation from the German company DORNIER MEDTECH is installed. The DORIE company developed and introduced this type of treatment into clinical practice in 1983 and is currently a leader in the implementation of advanced medical technologies. The DORNIER GEMINI device is a set of equipment for the urological X-ray operating room, which allows for remote crushing of stones of any composition, size and location. When conducting a lithotripsy session, positioning on the stone can be performed using both X-ray and ultrasound methods, which significantly reduces the radiation dose at the entire stage of examination, treatment and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment, and also eliminates the harmful effects of the shock wave on the tissue surrounding the stone. Low pain and high efficiency from crushing allow treatment to be carried out on an outpatient basis. The undeniable advantage of this device is the presence of a built-in electrocardiograph, which allows synchronizing the frequency of the lithotripter with the heart rate in patients with severe cardiovascular diseases.
In the urology department of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, consultations with patients with urolithiasis are provided by appointment on weekdays from 9:30 to 19:00.
CT or MRI of the kidneys: contraindications
The presence of contraindications to CT or MRI of the kidneys also plays a significant role in choosing the correct diagnostic method.
Computed tomography is contraindicated in the following cases:
- expecting a child;
- early childhood;
- intolerance to iodine preparations (if the kidneys are examined with contrast).
Magnetic resonance imaging is absolutely contraindicated if the patient has a pacemaker, middle ear implants, wires and plates that were used to treat fractures, hemostatic clips in the vessels of the brain, or metal fragments.
Both procedures are contraindicated in case of convulsive syndrome and mental disorders in the patient.
Presence of contraindications
During a CT scan, the doctor administers an iodine-containing drug to the patient. If an allergy to iodine or seafood is detected, such an examination should be done without the use of contrast. The procedure is also contraindicated for pregnant women and young children aged 0 to 14 years.
Other possible contraindications:
- the presence of a metal implant or prosthesis in the examined area;
- body weight is greater than what the tomograph table can support;
- renal failure;
- leukemia;
- bleeding;
- thyroid diseases.
If a tomography is performed on a nursing mother, the baby should not be fed breast milk for 48 hours after the procedure. It needs to be expressed and replaced with formula during this period. Also, during the study, diabetics will need to stop taking glucose-lowering pills.
Possible complications
Computed tomography of the kidneys is a safe method for human health. However, when a contrast agent is introduced into the body, there is the possibility of some complications:
- Allergic manifestations in the form of rash, lip swelling.
- For some period, the taste of metal may be felt in the mouth.
- Kidney failure. Patients with severe diabetes are the main ones at risk. The contrast solution is excreted by the kidneys. The dye becomes toxic to the organ, which provokes the development of this complication. It can also be caused by incorrectly selected combinations of drugs.
- Sometimes there is difficulty breathing or a decrease in blood pressure.
Complications occur extremely rarely. However, there are also methods to eliminate them. The allergy goes away after taking antihistamines (Lomilana, Tavegila, etc.). The metallic taste goes away on its own within a day. In case of kidney failure and difficulty breathing, urgent medical attention is required. Blood pressure is returned to normal with the help of medications.
What are the contraindications to CT and MRI of the kidneys?
Contraindications to CT scan of the kidneys:
- pregnancy - radiation negatively affects the development of the fetus, in addition, the use of a contrast agent is strictly prohibited due to its ability to pass through the hematoplacental barrier;
- allergy to iodine during CT scanning with contrast;
- renal failure during CT scanning with contrast;
- diabetic nephropathy during CT scan with contrast;
- the weight of the subject is more than 120 kg - in this case, CT must be performed in a specially adapted apparatus with an open top;
- The patient's age is up to 14 years.
Contraindications for MRI of the kidneys:
- the patient has a pacemaker, metal implants, stents and clips on blood vessels;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- epilepsy;
- the presence of an allergy to iodine during MRI with contrast.
The choice of diagnostic method is a complex issue; it requires the participation of the attending physician, who, taking into account the above-described indications and contraindications for CT and MRI of the kidneys, will help prescribe a plan for examining the disease.
urolog-msk.ru