All over the world, babies are born every day with one kidney. Concerned parents do not always know how to behave in such a situation in order to make the life of a child with one kidney fulfilling. In cases where a pair of organs has not been formed, childhood will not be joyful and serene, like that of healthy peers, but such a disease should not be considered a disability. Modern medicine copes well with this pathology.
A child (fetus) has one kidney, should we sound the alarm?
Agenesis is a condition in which a child is diagnosed with the congenital absence of one or several organs. There are several types of the disease:
During the period of life when the fetus develops in the womb, the formation of all major organs occurs. It is during this period that there is a risk of all possible pathologies. In this case, expectant mothers are prescribed a screening procedure. An ultrasound of the kidneys shows signs of the presence or absence of a second one; it is recommended to carry out the procedure once a month. Doctors and geneticists have not found an exact answer to what exactly provokes the disease in a newborn child, but the disease is not associated with a predisposition at the genetic level. The pathology of the absence of a kidney in a child may be due to the following:
- developed infections in the first trimester;
- the mother who gave birth to the baby is sick with diabetes;
- uncontrolled use of medications occurred.
The critical period for the life of the unborn baby is the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy. It is during this period that a failure in the formation of organs may occur.
According to statistics, among people born with the pathology of the absence of a kidney, boys suffer from the disease more often than girls. During intrauterine development, the fetus may experience a stroke in the area of the ureter, which causes improper formation of the organ. With a bilateral type of disease, children die before birth or in the first hours after birth, which cannot be said about unilateral agenesis. In a fetus with unilateral organ absence, the disease is not diagnosed or visualized in any way, but with bilateral organ absence, the following symptoms may be observed on ultrasound:
- wide nose;
- wide eyes;
- swelling on the face;
- ear deformation;
- forehead prominence.
Return to contents
Among premature babies, congenital absence of a kidney is more common than among healthy children. The working kidney compensates for the work of the sick one. If an ultrasound examination did not reveal any prerequisites for the disease and the children live without problems, then it will make itself felt days and months after the birth of the baby. If one kidney is not functioning sufficiently, children have poor development of the genitourinary system, which is accompanied by constant urination, general dehydration and frequent regurgitation. Patients living with this disease experience symptoms of increased blood pressure, swelling and intoxication of the body from harmful substances.
As you grow older, the disease manifests itself in different ways: as a rule, the reproductive system is subject to harmful effects. In a boy, the disease manifests itself in the absence of a testicle and vas deferens, while in girls there are disruptions in the development of organs such as the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes. The disease of renal failure is completely incompatible with such a pathology as the absence of one kidney. Therefore, it is important to monitor the health of children to prevent the development of infections and diseases that can lead to deficiency.
It is very difficult to detect the disease before preliminary diagnosis. As children grow older, they do not develop any symptoms that would indicate the absence of a second kidney. When alarming symptoms appear, children are prescribed ultrasound diagnostics, which could visualize the diagnosis. There are cases when ultrasound doctors cannot always detect a problem, so they prescribe additional computer diagnostics and MRI so that specialists can see the full picture.
When examining the general condition in the womb, it is also important to observe the nature of the amniotic fluid and how the baby grows. If the kidney is not visible and the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor needs to collect all the information about the course of the mother’s pregnancy, hereditary diseases in the family and previous infections that could prevent the birth of a healthy baby. This will make it possible to formulate the correct treatment.
Therapeutic measures for kidney pathology are divided into two types: medication and surgery. The doctor may prescribe special antibacterial drugs that will help in the absence of a kidney. If parents are faced with the need for an organ transplant, with successful treatment, children grow up and lead a full life, like healthy peers. If a child was born with one kidney, but doctors did not find any abnormalities in its functioning, treatment may not be prescribed at all.
It is important to monitor the general lifestyle of the little patient. His health depends on nutrition and how the patient spends his free time. Therefore, a mother who has given birth to a special child needs to monitor her diet: the food should contain only healthy foods, strengthen the immune system, treat the disease in time so that the infection is detected in time, and eliminate the risk of injury. And also the child should drink the amount of water necessary daily to prevent dehydration and the kidneys from overexerting themselves.
If doctors find that the kidney is functioning properly, the child can lead a normal life, and the child is not diagnosed with a disability.
The workload of a person’s kidney is enormous, so the organ needs time to learn to work for two people; this usually takes up to six months. No one excludes the risk of complications developing, which obliges parents to closely monitor their children for the slightest deviations in well-being. Suspicion should be raised by:
- disturbances in the process of urination;
- pain in the area of a healthy kidney;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure.
Doctors do not recommend serious sports for children if one kidney is not visible, but it is worth including regular hardening exercises, walks in the fresh air, and a balanced diet. Only the diagnosis of the disease and life with one kidney does not make the baby disabled; the consequences of serious complications lead to a similar condition.
A healthy person has two kidneys in the body. This paired organ filters the blood from the remnants of metabolic processes and, together with urine, removes them from the body.
Sometimes (due to developmental defects) a person is born with only one bean-like organ. This occurs due to congenital anomalies such as aplasia (only one kidney is fully developed) or agenesis (one paired organ is completely absent).
At the same time, people with this pathology can live a full life. To do this, you must follow special rules to maintain health for many years. People with one organ should limit heavy physical labor, replace it with exercise, and follow a diet and drinking regime.
Summarizing
Women with one kidney carry the fetus for the same period as women with two. Having given birth to a child once without serious complications with one kidney, a woman can give birth again.
2pochki.com
- single at 32 years old. I'm not saying I'm perfect
- not a fleeting passion, but love. men are strangers and
- I didn’t have chickenpox as a child. what to do? vaccinations
- so scared for my son. I look for symptoms of illness in him.
- chemical peeling at home. who makes it at home? what acid
- I screwed up out of stupidity and I’m very ashamed. standing
- the body demands pregnancy. what age for birth
- They're trying to make me feel guilty. I have to quit
- What color is your coat this spring?
- The photos are pathetic! like going to the supermarket
- constantly talks about his ex-women, even
- wants to constantly sit down and crawl. what age
- my classmate died! extensive stroke, coma. Well
- Is it possible to take an advance at all? money is needed simply
- ugliness and bad taste. what color/shade of shadow is not
- Is hair extensions harmful?
- Do you need a gynecologist for mastopathy? mamologist said
- Do you like lemon with salt or do you prefer
- I blow my husband's mind. ready to melt away. husbands/boyfriends can
- My long labor is finally over! photo.
- He doesn’t need it, I’ll earn money alone. studio apartment
- and if a man is 40 years old and is not married and has no children,
- they drink, beat, disrespect, have a consumerist attitude,
- Is there a dish that has never been cooked?
- How do you like this figure? What do you like/dislike? Why?
- or a witch, or a temple keeper, or a librarian
- such a cutie! How do you like the socialite Andrey Shlyanin
- 2 looks for spring. what can I add? rate as a whole.
- holiday at sea in June (in Ros). where would you recommend
- not counting fast food and alcohol, 20% off for 2
- Does dye really damage your hair?
- we are shocked. My sister was diagnosed with this disease. mastopathy
- temporary filling. I understand that I came without an appointment, but
- How do you like Tatyana Kurylenko - the most beautiful participant
- Do you have a lot of cosmetics? what do you use to make up, what do you eat?
- late virginity. She became very nervous and apathetic.
- I get pimples on my legs after shaving! What
- Disgustingly elderly chicks dye their hair purple
- What are your favorite beauty treatments?
- expensive sunlight jewelry. how do they even wear and
- If you don’t like him outwardly, will you be attracted to him as a man?
- hips of 10 cm are considered beautiful if the waist is at the same time
- How do you like this figurine?
- How can I recover deleted audio recordings? I can not
- 24 is old. do you feel what life is like
- Is it normal to go to another city to study by correspondence?
- marry people who are masculine or who look like them,
- Have you ever worked in companies like Sharashmontazh?
- stupid brother! Even flowers for your girlfriend on March 8th
- if a woman becomes pregnant and works at 0.5 times the rate, then
- people get married to gain material benefits.
- How do you like this jumpsuit?
- What clothes would you never wear?
- I baked pies in the morning. At least they wouldn’t boast about evil!
- the child cannot walk on his own?! It’s unpleasant to put food in
- who does Nordic walking? how much did you lose?
- I've never been to the USA. how to get a visa, what kind of visa
- you are a woman, you must give birth! what nonsense?! ourselves
- where can you make money on the Internet? how do you earn
- costume jewelry ala silver for a wedding, and all the rings are from
- What's for dinner?
- my sister told me that he molested her as a child
- she won’t go around like a husbandmaid and spoon feed me.
- How long did it take you to wean yourself off your husband? 2.5 passed
- stinky sneakers! I don't want to hang myself from the smell
- can I get pregnant? was unprotected, got on the genitals
- bright pink wedding dress. beautiful or
- I try to dodge, but they shout at me to get married! ready,
- who helped children's tenoten? Is it worth giving it to a child?
- Do your pets eat chocolates? not dangerous
- her beauty is admired by the whole world and only by her compatriot
- it is possible to get rid of genital warts with medication
- How do my husband and I look like as a couple? there's a big difference between us
- completely deflated at the end of winter. no strength or motivation.
- I am Ukrainian, he is Georgian. is there a possibility that
- left his pregnant wife and went to another, who also
- showed that it was sticking out. boy, but it seems otherwise. are wrong
- do you like the name Arkady? Would you name your son that? Now
- appearance without makeup. your opinion about age. photo.
- fulfills all my wishes. you don't have to worry about him
- Looking for a slender wife. you can meet at
- some kind of moron. even dirty things are not enough brains
- How much does a big bucket of popcorn cost in movie theaters now?
- in bars there are minors or married men. girls from small
- you will still get married and give birth! higher education
- How do you like this appearance? What do you like/dislike?
- I sent my resume on Friday at lunchtime. after what time
- Is it normal to wear a leather jacket at +10? I won't be ridiculous
- take a million and immediately repay 60 thousand so as not to overpay
- Tell me successful, tasty recipes for a multi-baker.
- doesn't sound very reliable. have you tried to earn money
- do you like neck kisses?
- what affects the vaginal microflora in the absence of intimate
- How do you like this figure?
- do you know a singer named indila? the voice was amazing
- Diana Shurygina is going to start a solo career as a singer.
- Loboda is pregnant from the lead singer of the ramstein group? went
- I'm looking for a friend to go to the cinema, theater together,
- I want to marry a military officer. where to meet
- We won't be able to see each other for 7 months. how long have you not seen each other?
galya.ru
The compensatory capabilities of paired organs are such that the absence of one of them does not interfere with the performance of basic body functions. Currently, it is safe to say that pregnancy develops normally in women with one ovary, one adrenal gland, one lung or one kidney.
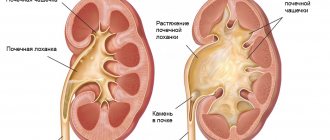
A single kidney is a congenital malformation or a consequence of the removal of another kidney affected by a pathological process.
In the second case, the adaptation period occurs in 2 stages. First, there is a relative functional failure of the organ, since the function of the remaining kidney has not yet increased significantly; there is a loss of functional reserve, since all nephrons are functioning; hyperemia of the kidney and its beginning hypertrophy appear. At the second stage, complete functional compensation is noted, characterized by an increase in kidney function, restoration of the functional reserve, moderate but stable hyperemia and hypertrophy increasing to a certain limit.
The reserve capacity of the kidney is mobilized from the first days after nephrectomy and is aimed primarily at removing water and sodium chloride. Nitrogenous wastes are not fully excreted, but this has a beneficial effect, since, accumulating in the blood, nitrogenous substances stimulate compensatory hypertrophy of the kidney. Morphological and functional hypertrophy of the glomerular-tubular apparatus occurs. Compensation for the function of the lost kidney is completed 1-1.5 years after nephrectomy . The large reserve capacity of the kidney can be judged by the fact that normally only 1/4 of the nephrons function at the same time. After nephrectomy, blood flow in the kidney increases 1.5 times, and its functional capacity remains at the level of the body's needs.
Women with one kidney cannot be considered absolutely healthy; their kidney has a limited reserve of functional activity. The nephrons of the remaining kidney are forced to bear a double load, and therefore, over time, their functional failure may occur. Therefore, the most favorable period for pregnancy occurs 2 years after nephrectomy, when the functional restructuring of the organ is completed and the kidney reserves have not yet been depleted. This can be determined by examining a woman in the first trimester of pregnancy. With one kidney, renal blood flow and glomerular filtration increase to the same extent as in healthy women with two kidneys. The physiological functions of the remaining kidney during pregnancy are usually normal, excretory function is not impaired. Blood pressure is not elevated, there is no proteinuria, and urea clearance is normal.
A woman’s condition during pregnancy depends on the reason for the removal or absence of one kidney. A congenital single ectopically located kidney copes with its functions worse than a healthy, normally located kidney remaining after removal of its pair. If the cause of nephrectomy was pyonephrosis, tuberculosis or urolithiasis, then the woman’s condition improves, since the source of intoxication in the body is eliminated along with the kidney.
It is not so important which kidney is removed, although with a right nephrectomy the prognosis for pregnancy is better, since the right kidney and ureter are more likely to undergo changes during pregnancy.
Women who have undergone nephrectomy are more likely to suffer from pyelonephritis during pregnancy; it is possible that a latent disease is activated. However, according to our observations, kidney function suffers little; it does not worsen significantly either during pregnancy or after childbirth.
Late toxicosis, for unknown reasons, rarely develops in women with one kidney. Polyhydramnios and weakness of labor occur somewhat more often. Children are born healthy, with normal body weight and height. Perinatal mortality is less than 100%.
The most unfavorable obstetric prognosis is for women with congenital aplasia of one kidney. A single kidney may not be completely functional, although this was not evident before pregnancy. During pregnancy, with anomalies in the development of the urinary tract, including renal aplasia, pyelonephritis often occurs, perinatal mortality and the frequency of births of immature children increase significantly. There is often a combination of abnormal development of the genital and urinary organs. The detection of some (usually on one side) structural defects of the genital organs (unicornuate uterus, etc.) gives reason to suspect abnormalities in the development of the urinary organs on the same side. However, it is not possible to prove the presence of congenital pathology of the kidneys and ureters, including the absence of a kidney, without X-ray examination.
Childbirth in women with congenital renal aplasia proceeds safely. However, if the kidney is located in the pelvis, the fetus may take an incorrect position; in this case, a caesarean section becomes necessary.
In the pregnant women we observed with one kidney, the most common reason for nephrectomy was tuberculosis. Apparently, this group of women will decline in the future, since conservative methods of treating renal tuberculosis have prevailed in recent years. After nephrectomy for tuberculosis in the bladder, residual effects caused by intoxication (toxic effects of kidney tuberculosis or specific cystitis) may remain in the other kidney. Intensive anti-tuberculosis therapy, against the background of which nephrectomy is performed, eliminates intoxication within several months. However, pregnancy should not be allowed before postoperative complications and intoxication disappear. Pregnancy is permissible if, for several years after the operation, the causative agent of tuberculosis is not detected in the urine, there are no specific changes in the urinary tract and the woman does not need treatment for tuberculosis (deregistered from the anti-tuberculosis dispensary) Pregnancy and childbirth in this case proceed well Some observed our women gave birth twice Since tuberculosis affects not only the kidneys, it is necessary to make sure that there is no specific process in other organs. To do this, in addition to a thorough study of the anamnesis and an objective examination, you should obtain a conclusion from a TB doctor at an anti-tuberculosis dispensary.
If the kidney, preserved after nephrectomy for hydronephrosis, is not affected by the same disease, its function during pregnancy remains sufficient and pyelonephritis rarely occurs. Other observations existing in the literature refer, presumably, to cases of nephrectomy for bilateral hydronephrosis. Such patients may develop hypertension, renal failure, and pyelonephritis during pregnancy.
Great care is required when deciding whether pregnancy is permissible in women who have undergone nephrectomy for pyelonephritis. The remaining kidney can be completely healthy, and then the pregnancy proceeds safely. These are the majority of observations. But the inflammatory process in the kidney can occur latently, without being detected and treated in a timely manner, it threatens to worsen during pregnancy, which is not always amenable to conservative therapy. This also applies to a large extent to women with obvious pyelonephritis of a single kidney; the condition of such patients, as a rule, worsens during pregnancy. This affects both the course of pregnancy and the health of the fetus, leading to azotemia, premature birth, malnutrition or intrauterine death of the fetus.
Pregnancy in women after nephrectomy for kidney stones usually proceeds normally. The condition may worsen in the presence of stones or pyelonephritis of a single kidney.
Successful diagnosis and treatment of renovascular hypertension has led to the emergence of pregnant women whose kidneys have been removed due to this disease. Renovascular hypertension is caused by damage to the renal artery or its branches by a stenotic process. A decrease in renal blood flow serves as a trigger for the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone hypertensive system. The only radical treatment for such patients is surgery (reconstructive surgery on the renal artery or nephrectomy). After surgery, high and stable blood pressure returns to normal fairly quickly. Our observations show that if pregnancy occurs a year or more after nephrectomy, when blood pressure is normal and the kidney is adapted to the changed operating conditions, the gestational period proceeds without complications. If pregnancy occurs in the first months after surgery, it often ends in spontaneous abortion.
Pregnancy and childbirth after removal of a kidney affected by a tumor are rare. Only 20% of women live longer than 5 years, since 80-85% of kidney tumors are malignant. Kidney tumors often recur. The prognosis for pregnancy is unfavorable. Pregnancy is contraindicated. Only in some cases is it permissible if more than 5 years have passed after nephrectomy and no recurrence of the tumor has been detected.
Whatever the reason for nephrectomy, the possibility of maintaining pregnancy depends primarily on the condition of the remaining kidney. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully check all functions (excretory, concentration, filtration). The most thorough examination of pregnant women with one kidney carried out by us, including, in addition to the specified minimum tests, also a study of the cardiovascular system (ECG, indicators of general hemodynamics, condition of the fundus vessels), electrolytes in plasma and urine, acid-base status of blood, total protein and protein fractions of blood, indicators of renal hemodynamics and kidney function showed that 2/3 of women had no significant impairments. Only in some patients were signs of severe dysfunction of the remaining kidney found.
In every patient with one kidney, it is imperative to find out the presence of a urinary tract infection. Pyelonephritis significantly worsens the prognosis of the disease and casts doubt on the possibility of carrying the pregnancy to term. We diagnosed pyelonephritis in 15% of pregnant women who underwent nephrectomy. Other researchers found it much more often.
If nephrectomy was a consequence of kidney tuberculosis, it is necessary to do a urine test for the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The absence of one kidney does not affect the duration of pregnancy. In all the women we observed, labor occurred on time, with the exception of those few cases when they were induced ahead of schedule due to the severity of the patients' condition. Childbirth and cesarean section in all women proceeded without complications. The postpartum period was rarely complicated by endometritis or deterioration of the urinary organs.
In conclusion, it should be noted that most women with one congenital kidney or who have undergone nephrectomy can proceed through pregnancy and childbirth without harm to their health. Repeated births do not worsen the condition. Pregnancy is contraindicated if kidney function is sharply reduced, especially in the presence of azotemia or arterial hypertension, as well as with tuberculosis and pyelonephritis of a single kidney.
auno.kz
The causes of this pathology
There are two types of agenesis of a paired organ: bilateral and unilateral.
In the first case, the child dies immediately after birth or while still in the mother’s womb, since he has no kidneys. Unilateral agenesis implies the presence of one organ and in most cases is a completely safe condition for life. There is no main reason for this anomaly. Parents may not even suspect that their child has any developmental disabilities.
To compensate for the absence of the second organ, the size of the remaining one increases. This recovery feature allows you to increase its performance by 45%. In this case, one kidney is not much inferior to the normal functioning of two.
During the period of bearing a child, a woman’s body and her fetus are very vulnerable because their immune system is weakened. The etiological factors for the development of agenesis include:
- Severe viral illnesses in a pregnant woman. These include measles and rubella.
- Oligohydramnios during pregnancy.
- Alcohol abuse or drug use during pregnancy.
- Exposure of the fetus to toxic substances or ionizing radiation.
- The presence of various infections in the genitourinary system in a pregnant woman.
- The use of hormonal contraceptives during pregnancy.
- The presence of infections transmitted through sexual intercourse. Women infected with syphilis are most susceptible to giving birth to a child with an anomaly.
According to statistics, boys are more often born with renal agenesis. For every 10 thousand newborns, 1–3 children are identified with this anomaly. In the absence of a kidney, most often it is the left organ.
Symptoms of pathology in a child
The presence of an anomaly of the filtering organs in a baby does not initially manifest itself with any symptoms if the baby is healthy.
Pathology is often detected by chance during preventive examinations. Sometimes a child may experience aching pain in the groin, moving to the sacral area. Girls with the presence of an anomaly have pathologies of the reproductive system. Vaginal underdevelopment and uterine hypoplasia are often detected.
Another manifestation of the clinical picture:
- swelling of the face;
- dry skin, mucous membranes;
- frequent regurgitation;
- excessive urination;
- lethargy;
- deformation of the ears and skull;
- high blood pressure;
- increased distance between the eyes;
- protruding forehead;
- macrognathia – underdevelopment of the jaw;
- flat and wide nose.
Boys exhibit specific symptoms. They do not have a duct that removes seminal fluid.
Quite often, children with agenesis are born prematurely, and their filtering organ is increased in size. If the kidney does not cope with the functions assigned to it, symptoms appear almost immediately after the birth of the baby.
Diagnostic methods
In those days when the ultrasound machine had not yet been developed, many people lived with an anomaly without knowing it.
Nowadays, the absence of an organ in a child is sometimes determined while the fetus is still in the womb. However, this is quite difficult to detect. The adrenal gland can be identified as a kidney. After the baby is born, the diagnosis is confirmed by:
- CT scan;
- cystoscopy;
- nephroscytingraphy (determines the accumulation of radioisotopes in the kidney area);
- angiography (detects the absence of organ vessels in the area of the affected side).
A urologist may prescribe excretory urography. Taking an anamnesis is of great importance. The doctor finds out not only the possible reasons for the development of agenesis, but also learns all the features of the course of pregnancy.
How to live with one organ
People with the anomaly from birth must observe dietary restrictions.
It is necessary to maintain a certain diet, sleep and wakefulness. It is required to lead a healthy lifestyle, giving up alcohol-containing drinks and smoking. The lives of people with this anomaly are full and practically no different from others.
In case of nephrectomy (surgery to remove one of the kidneys), a person can also lead a normal life. Immediately after the operation he needs bed rest and rest. In the first days you should only eat a gentle diet. Rehabilitation can take a long time.
However, in the normal condition of the patient, approximately ten days after nephrectomy, the person returns to the workplace. This happens if his profession is not related to physical labor.
There is a risk of organ dysfunction. Women with this pathology experience difficulties during pregnancy. However, there are many known cases of the birth of normally developed children from mothers with one kidney.
To avoid various complications, patients should be examined by a doctor at least once a year. Recommendations from a specialist will help support the organ and improve its performance.
Recommended Diet
Diet is an important factor in the healthy and fulfilling life of such special people. The diet should be rich in foods such as sour cream, honey, eggs, vegetables and fruits.
It is better to eat boiled meat, as well as fish, and preferably rye bread. The quantity of products should be determined by an experienced nutritionist. High-calorie foods are recommended, but not protein foods.
If you decide to eat vegetarian foods, then you should not rely on legumes and pasta; it is better to replace them with potatoes or vegetables. One kidney already has a double load, so you should limit the intake of large amounts of mineral salts into the body.
They are found in canned foods, smoked foods, pickles, and carbonated drinks. Caffeine and alcohol are contraindicated; you can drink fruit drink, compote or juice. Such nutrition will not allow the only kidney to lose its functionality, otherwise you will have to register for disability.
To smoothly transition from protein foods to others, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Eat boiled meat or fish, but not more than 3 times a week.
- Eat foods rich in carbohydrates. This includes buckwheat, oatmeal and other porridges, rye bread; from white varieties, choose grain bread. Other baked goods are excluded or reduced to a minimum.
- For dairy products, sour cream and cream are recommended. It is better to reduce the consumption of other fermented milk products.
Methods of therapeutic action
Therapy for such patients depends mainly on the condition of the kidney. If it is healthy and performs all the functions of the second organ, then special treatment is not required. It is necessary to see a urologist and follow all his recommendations (follow proper nutrition and drinking regimen).
Specific therapy for the treatment of patients with one kidney is not prescribed. For hypertension, medications to lower blood pressure are usually prescribed. In most cases, it is necessary to use means to enhance immunity.
This is facilitated by the incorrect behavior of the patient himself - the requirements of the attending physician are not followed, the body is subjected to increased stress and stress, and a strict diet is not maintained.
If a violation of even one of the basic functions of the kidney is detected, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment prescribed by a nephrologist. The choice of drugs depends on the patient’s condition, the interpretation of his tests and the identified pathology.
Patients living with one kidney should undergo regular blood and urine tests, as well as instrumental examinations. Maintenance therapy includes the use of antibacterial agents.
In the event of renal failure, the goal of treatment is to slow the rate of progression of the pathology.
In some cases, a kidney transplant is necessary. Transplantation is the most effective way to get rid of kidney failure.
Connection to the device is made strictly in the mode prescribed by the attending physician. Failure to do so increases the risk of death.
A fundamental factor for a full and active life is dietary nutrition. Some foods must be present in the diet: black bread, vegetables, eggs, honey, sour cream. Fish and meat should only be boiled.
In what quantities they should be on the menu depends on the body. An experienced nutritionist will tell each patient individually how much and what foods to consume.
Complications and contraindications
Patients' concerns are associated only with kidney pathologies. After all, they have only one organ, so attention to its condition is doubled. The most dangerous manifestations of agenesis are:
- Urinary dysfunction. The volume of urine may decrease or even be completely absent.
- Renal colic is an attack of pain accompanied by urination problems.
- High blood pressure that cannot be treated with conventional medications. Indicators can reach very high numbers.
If the above manifestations occur, you should immediately contact a nephrologist. If there are no such violations, then it is necessary to conduct an examination at least once a year and take urine and blood tests. The doctor can give different recommendations for each patient individually.
Restrictions after kidney loss
In the case of sudden loss of one of the kidneys, we can only talk about potential danger in the case of kidney diseases that can damage the remaining organ. This applies equally to people with two kidneys, but extreme care must be taken with the only remaining kidney. It is necessary to urgently seek medical help if:
- Single or constant attacks of pain in the lumbar region, groin area and genitals;
- Decreased volume, lack of urine, or irregular urination rhythm with unchanged diet and drinking;
- High blood pressure, uncorrectable with medications. With high numbers we can talk about renal hypertension.
Even if there are no such violations, it is still necessary to undergo an annual preventive examination, including laboratory tests and instrumental methods of examination (ultrasound) of the condition of the kidney.
After nephrectomy
After removing one of the organs, the following rules and recommendations must be observed:
- Avoid severe overheating or hypothermia of the body. This is reasonable especially in the postoperative period, when a sharp drop in immunity occurs, as a result of which an infectious disease can develop;
- Maintaining a special diet. At the same time, liquid intake is limited (up to 1 liter per day), the diet consists only of easily digestible food, and restrictions on protein, salt, spices, and sour foods are introduced. Diet table No. 7 is very suitable for these purposes;
- Avoid intense physical activity (sports, heavy lifting), stress;
- Completely eliminate the use of alcohol and other potentially hazardous substances.
3 months after the operation, with normal recovery processes, restrictions are either partially or completely removed. However, the risk always remains, so it would be best if such a lifestyle becomes a habit.
Preventive measures
For prevention purposes, doctors recommend:
- Healthy food;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- undergo a medical examination once a year;
- exercise moderately;
- treat all diseases in a timely manner.
Pregnant women should lead a healthy lifestyle and give up bad habits.
An important point in prevention is measures aimed at preventing the development of any kidney pathologies. To perform them, patients must stop drinking alcohol and avoid hypothermia. It is also necessary to promptly treat all infectious diseases. After all, their complicated course can provoke organ damage.
In this case, blood pressure is constantly monitored. Attention! It should be remembered that in collisions that occur in contact sports, falls from a bicycle or accidents, there is a possibility of internal injuries.
However, having only one kidney is not a contraindication for sports. Moderate physical activity is an urgent need.
The kidneys in the human body are a paired organ of the urinary system. In addition to filtering the blood and removing waste products, as well as drugs, toxins and other harmful substances, they perform many other vital functions.
Among them are regulation of osmotic pressure, blood volume, level of intercellular fluid, ion exchange, maintaining acid-base balance.
They are also involved in the synthesis of glucose and physiologically active substances (vitamin D, renin, erythropoietin, etc.). As a result of intrauterine developmental disorders, a child from birth may have only one kidney or two kidneys missing at once.
Pregnancy, active life and habits
Despite the possibility of a normal lifestyle, if a person has one kidney, then he should still take care. During physical work and sports, you need to monitor your well-being. It is advisable to avoid contact sports: hockey, football, boxing, wrestling, etc.
If a woman with one kidney decides to become pregnant, then she must first undergo a full examination and discuss all the features of bearing a child and childbirth with a gynecologist, and attend a consultation with a nephrologist. If the organ is healthy, then no problems will arise during pregnancy.
If there is an anomaly such as a congenital one kidney or the organ has been removed, then the person must stop drinking any drinks containing alcohol and caffeine and refrain from smoking.
To exclude diseases of the urinary system, it is recommended to maintain a good level of immunity and prevent hypothermia.
What is renal agenesis
The absence of one or two kidneys at once is called agenesis. This is an abnormal condition that occurs as a result of disturbances in the embryonic development of the fetus. It manifests itself either in the absence of one kidney and its stem, or in the absence of both kidneys.
In the latter case, the child dies before being born, or in the early postpartum period from kidney failure, if he was not urgently provided with assistance in the form of connecting to an artificial kidney and further transplantation of a donor organ.
If agenesis is unilateral, and the only kidney functions without disturbances, then there will be no clinical manifestations of this pathology. The diagnosis in this case is most often made only after an ultrasound scan.
Classification of Potter syndrome
The classic form of Potter syndrome is accompanied by bilateral congenital renal agenesis. This symptom may occur on its own, but may be part of a larger brachio-otorrenal syndrome.
Bilateral renal agenesis is usually incompatible with life - the child dies before birth. But in practice, it happened that such children were born alive and full-term, but died a few days later as a result of severe renal failure.
Now modern medicine has stepped far forward, so it is possible to transplant a kidney into a sick child and develop a system of subsequent hemodialysis.
In this case, it is extremely important to identify bilateral agenesis in time in order to try to take measures for the survival of the newborn baby.
Causes of pathology
Currently, renal agenesis is not recognized as a genetically determined disease. This means that if one of the parents does not have a kidney, then this fact does not affect the likelihood of having a child with agenesis.
Why children are born with one kidney is still not known exactly. The probable causes of agenesis are associated with disturbances in embryogenesis during the formation of internal organs due to the effect of the following factors on the body of a pregnant woman:
- viral diseases. Measles and rubella viruses are especially dangerous;
- oligohydramnios during gestation;
- long-term use of alcohol and drugs;
- the effect of toxic substances, medications and radiation on the fetus, high levels of glucose in the blood of a pregnant woman;
- genitourinary system infections;
- taking hormonal medications;
- STIs, the most dangerous is syphilis.
This was the first victory
I’ll say right away that my first pregnancy proceeded with excellent urine tests and everything was fine. The only thing is that by the 37th week, swelling began and the pressure rose, and at exactly 37 weeks the water broke. The birth took place naturally. Everything was stable with the kidney.
In general, the story about the first pregnancy is quite positive. But with the second pregnancy, everything happened exactly the opposite.
I started having problems with my kidney not during my second pregnancy, but my second pregnancy happened during an exacerbation of pyelonephritis. My temperature rose, my urine looked very cloudy and scary.
I decide to start taking antibiotics and since my period was about to start, I take a pregnancy test just in case.
And having pulled out the test from the cloudy and scary urine, after a few minutes I examined a clear second strip.
What did I experience? Wild paralyzing fear...
I imagined being referred for an abortion or how they would stuff me with antibiotics for such a short period of time, which could harm my very tiny Baby...
The next morning I propped open the door of that very woman nephrologist, who, as it seemed to me then, was my Guardian Angel. Thanks to her for everything. She calmed me down again. She prescribed cranberry, Canephron and other drugs that are suitable for pregnant women.
She said that ideally, wait until 12 weeks, when the baby is fully formed, and then take a course of antibiotics. Or, if it gets really bad, and she told me the worst case scenario, then start treatment earlier.
When I came to the local gynecologist, I listened to what a “bomb” I was, a fool, and a complete description of how I would die in agony.
Then I already knew that I couldn’t trust one doctor and I moved on. I went to a paid gynecologist and heard that even those who weren’t like that were able to carry a pregnancy to term, but healthy people might not even be able to carry it to term. I went to the head of gynecology and asked to register with him. He took me in and supported the nephrologist’s advice to hold off on antibiotics.
Canephron with herbs did not help me... I took urine tests constantly, but there was no improvement. Either the entire field of view is covered with leukocytes, or half. Bacterial culture of urine did not reveal the causative agent of infection. This is how week after week passed. I was scared. I was afraid for the child because he was developing under conditions of infection.
I was afraid for myself. I was afraid to leave the eldest child without a Mother. In general, it was morally difficult...
Clinical manifestations
Provided that the only kidney is functioning normally and there are no concomitant diseases, agenesis does not have clinical manifestations for a long period of time.
In this case, it becomes possible to establish a diagnosis only after an instrumental examination.
Symptoms will appear if the only kidney ceases to perform its functions to the required extent. Then the clinical picture will be characterized by the following signs:
- symptoms of intoxication (general weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, headache, hyperthermia over 38 0C, tachycardia);
- increased blood pressure;
- in children of the first year of life - frequent regurgitation, similar to vomiting;
- polyuria;
- symptoms of dehydration (dry mucous membranes and skin, decreased turgor, retraction of the large fontanelle in children under one year old, tachycardia).
In severe intrauterine conditions, agenesis often provokes premature birth. Congenital absence of a kidney in a newborn can be detected by the following symptoms:
In case of anomalies in the development of the genitourinary system in the clinic, in addition to the above symptoms, pain occurs in the groin area and in the lower abdomen.
Doctors diagnose renal agenesis during the second scheduled ultrasound of the fetus, at about 5 months of pregnancy.
In addition to the visual absence of one kidney, the fetus has the following ultrasound signs:
- wide nasal bone;
- wide-set eyes;
- forehead prominence;
- anomalies in the location of the ears and their shape;
- puffiness of the face.
The gestation period for a child with one kidney is shorter than during normal pregnancy.
The clinical picture usually does not appear in the first year of life, provided that the only kidney performs its functions in full.
Complications during pregnancy
During pregnancy, due to the increased load on all organs and decreased immunity, complications are possible both in women with two kidneys and in those who have undergone nephretomy or were born with agenesis. The most common complications are:
- Infections: pyelonephritis. This complication occurs in 50% of pregnant women. Fortunately, the functional abilities of a single kidney, as a rule, do not decrease. But if past unilateral pyelonephritis became the reason for nephrectomy, the risk of its occurrence on a healthy organ during pregnancy increases even more.
- Late toxicosis, or gestosis. This complication occurs in pregnant women with one kidney with a significantly higher frequency than in those who give birth with two. Preeclampsia is manifested by increased blood pressure, edema, and increased protein content in the urine. Under the supervision of a doctor, in 50% of cases, gestosis does not become severe and allows you to give birth to a healthy baby without serious consequences for the mother’s health. In the remaining 50% of cases, gestosis becomes the cause of intrauterine infection or insufficient body weight, which can later be cured. The risk of death of a newborn from gestosis in women with one kidney is not much higher.
- Pregnant women with nephrectomy, the cause of which was tuberculosis, kidney stones, or a purulent process, feel even better after removal, since the source of infection is no longer present in the body, and the performance of functions is easier.
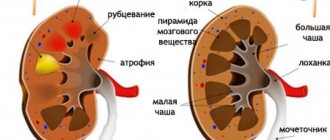
- Expectant mothers who have had a nephrectomy due to unilateral hydronephrosis (dilated renal pelvis, partially atrophied renal medulla and, as a result, renal failure) have a high chance of a successful birth if the remaining organ functions well.
- Women with nephrectomy due to unilateral pyelonephritis can give birth to a healthy child without complications during childbirth and pregnancy. If purulent lesions have formed in the remaining kidney, then the risk of various complications increases significantly. However, proper treatment will increase the chances of success.
- Serious complications of pregnancy and childbirth can be caused by a single kidney affected by tuberculosis. Often after nephrectomy, foci of infection are observed first in the bladder, and then in the previously healthy organ. It is necessary to conduct diagnostic studies over several years, since renal tuberculosis is characterized by frequent relapses.
- The prognosis is also favorable during pregnancy with one kidney, if nephrectomy was performed due to kidney stones that did not cause complications on the remaining healthy organ.
- Complications of pregnancy and childbirth occur more often in pregnant women with one kidney due to nephrectomy for renal cystosis. Doctor's permission to continue pregnancy is given on an individual basis.
- Complications during pregnancy appear in women born with unilateral agenesis if the only kidney cannot fully adapt to working for two. Clinical data indicate that such mothers are more likely to give birth to children with improperly developed organs of the genitourinary system. Also, in such a situation, there is a higher risk of pyelonephritis, and in the worst case, intrauterine fetal death.
- A negative prognosis is given to pregnant women with one kidney due to a tumor on the other. A initially healthy organ can have metastases without showing significant symptoms. In such cases, pregnancy is either prohibited or allowed after a certain time.
What is the danger of renal agenesis?
The absence of one organ is not life-threatening if you follow the recommendations of a nephrologist, undergo all prescribed examinations and adhere to a gentle regimen.
If possible, it is necessary to prevent urinary tract infections and other infectious diseases.
Children born with one kidney require more attention from their parents to their health.
When nonspecific preventive measures are performed, such patients live a full life, no different from a person with two kidneys. The prognosis for a child with one kidney is often good.
If a single organ cannot cope with the increased load or the doctor’s instructions are not followed, the risk of complications increases, such as:
- association with infectious pathology. The course of the disease will then be longer and more severe, with a greater risk of complications;
- development of renal arterial hypertension. In this case, the blood pressure level is high and is poorly reduced by antihypertensive drugs;
- formation of chronic renal failure. Occurs more often with left-sided pathology.
In terms of prognosis, the absence of the right kidney is considered more favorable, since it bears less functional load and is smaller in size than the left.
In addition, left-sided pathology is often accompanied by the absence of the ureter and abnormal development of the genital organs.
Possible consequences
One kidney is a pathology either hereditary or acquired. There is evidence indicating that 5 out of 1000 people suffer from it. The congenital absence of an organ is called agenesis. It occurs due to disturbances during intrauterine development.
More often, agenesis is unilateral; if it is bilateral (both kidneys are absent at once), the death of the born child is almost instantaneous. But sometimes one-sided ones are not even discovered right away. If the only organ functions normally, then there are no visible symptoms of pathology. And only during preventive diagnostic studies is agenesis detected.
A kidney is removed (nephrectomy) when diseases such as pyelonephritis, kidney stones, tumor, polycystic disease, etc., do not respond to conservative (with the help of drugs) treatment. It is reliably known that one kidney can perform the functions of both by 75%; this is ensured by the high compensatory abilities of the paired organ.
To perform the necessary functions, a single organ can increase almost 2 times in size. Each healthy kidney has reserve nephrons (cells), which begin to work only if the constantly functioning nephrons fail. Immediately after nephrectomy, these reserves are put to work, the organ becomes hyperemic (reddened) and increases in size (hypertrophy).
The work of the removed organ will be fully compensated in a year and a half. And even in one normally functioning kidney, over time, some of the nephrons become reserve, since the subsequent loss of kidney cell function is possible due to constant work with a double load.
Given these facts, women who want to give birth should plan a pregnancy 2 (or more) years after the loss of one of the kidneys. During this time, compensatory functions will be fully restored, and the functional reserve of one working organ will not be exhausted.
In the body of a pregnant woman, a single organ experiences even greater stress due to the increased volume of fluid in the body. Accordingly, the organ filters more fluid and excretes more urine.
Monitoring the entire pregnancy is very important, since chronic renal failure can occur at any time. During a normal pregnancy, a woman with one kidney does not experience a significant increase in protein in the urine and urinary disorders.
It does not matter which kidney remains (right or left). However, this statement is relative, since in pregnant women with both kidneys, complications most often arise in the right organ and ureter.
Diagnostics
For the first time, agenesis can be diagnosed in a child by performing an ultrasound of the fetus, which is performed on a pregnant woman at about 20 weeks.
Subsequently, after birth, the diagnosis is confirmed using ultrasound of the urinary system, CT, MRI, excretory urography, renal angiography and cystoscopy.
As a rule, a nephrologist makes the diagnosis.
What to do if your child has one kidney
If a child was born with one kidney, it is necessary to consult a nephrologist. He will order additional studies to assess your health status and decide on recommendations.
He will explain what needs to be done so that this pathology does not lead to complications and a decrease in quality of life.
Treatment is not prescribed for newborns with one kidney if there are no manifestations of this defect.
If the patient develops arterial hypertension as a result of this anomaly, then treatment is carried out with antihypertensive drugs.
When symptoms of chronic renal failure appear, medications are prescribed whose action is aimed at preventing the progression of the pathology.
If chronic renal failure is severe (terminal stage), the patient is indicated for an organ transplant or hemodialysis. Kidney transplantation is currently the most effective method of treating this pathology.
Many parents are interested in the answer to the question of whether a child with one kidney is given disability. This defect, in the absence of signs of renal failure, is not a reason for registration of disability.
Disability is considered if chronic renal failure develops. Disability groups are distributed depending on the stage of the disease.
Treatment of the disease
The development of the disease in newborns poses a huge risk to life. Currently, there are two types of treatment for renal agenesis, namely: antibacterial treatment and surgery, that is, donor kidney transplantation. Doctors often come to perform an operation because an organ transplant is the most effective treatment method, despite the high risks for the health and life of the child.
With successful treatment of renal agenesis, children have a chance to lead full life activities in the future.
Unfortunately, doctors are forced to admit that they cannot change the situation. The baby will have to live his entire life with one kidney. But even one healthy kidney can cope with filtering blood and removing toxins from the body. The main thing is to keep it in good condition. To do this, you should not overstrain the body with concentrated foods, salt, preservatives, and the like, and also avoid inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system and the entire body. Life expectancy can be affected by complications from any other diseases - diabetes, urolithiasis, and even furunculosis, tonsillitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, pneumonia, etc. You should also be careful about training, since physical overload with a sharp increase (from overexertion) of intra-abdominal pressure or jumping can cause the kidney to move. If displacement occurs - prolapse of the kidney, this will provoke stagnation of urine and ascending inflammatory diseases of the kidney. This situation can lead to chronic renal failure. In general, doctors recognize that congenital defects in kidney development are quite common. There are doubling, displacement, fusion and absence of one organ. All these changes are, in principle, not life-threatening and do not require treatment. Children's doctors advise simply to regularly conduct urine tests in order to promptly identify diseases if they arise. After all, the kidney tissue does not perceive pain. Only in cases where the process affects the capsule or pelvis will pain occur. Therefore, after any infection, check your urine test several times. Try to avoid hypothermia and any inflammatory diseases. In general, a child who was born with one kidney is healthy, but has some peculiarities.
Nature has established the development of the kidneys as paired organs of our body. If a child was born with one kidney, the diagnosis usually sounds like a death sentence. But this does not mean that a child with such a congenital anomaly will not be able to live a full life and will be disabled. What is the cause of such abnormal development, what is the diagnosis and clinical formation of the pathology?
Lifestyle with one kidney
Every person born with one kidney needs to know how to live to prevent unwanted manifestations of this pathology.
If it is detected in a child, then his parents should know these rules. Namely:
- observe the frequency of visits to the nephrologist, take all recommended tests;
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle, follow the principles of proper nutrition (avoid excessively salty, sweet, fried and smoked foods);
- observe the drinking regime: drink clean drinking water in the required quantity;
- If possible, avoid contact with patients with acute respiratory infections;
- exclude the use of alcoholic beverages, tobacco, and drugs;
- avoid both overheating and hypothermia;
- in case of any diseases requiring medication, treatment should be carried out with drugs that do not have a nephrotoxic effect and are not excreted in the urine.
Preparation for kidney removal and prognosis for the patient
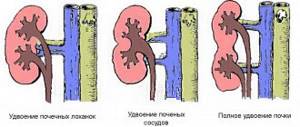
In some cases, removing a kidney is the only way to save a person’s life and relative health. The operation is called nephrectomy. It is carried out regardless of how old the patient is - if there are no contraindications to surgery, the intervention is performed even in infancy or in old age.
On the eve of a nephrectomy, patients are concerned about whether it is possible to live with one kidney. As many years of medical experience show, the answer is positive, but subject to compliance with medical recommendations.
Over time, the remaining organ takes over all excretory functions, and if you do not burden the body, you can live fully, quite actively, including physically.
Many people live with one kidney initially, due to congenital pathology. A person who voluntarily decides to become a donor also does not condemn himself to complete disability. Therefore, radical nephrectomy is not an operation that should be feared. The sooner it is carried out, the greater the patient’s chances of recovering faster and returning to normal life. The only question is what method is used to remove the kidney. There are two of them:
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
- open;
- laparoscopic.
The open method is a classic surgical procedure performed through an incision in the lumbar region. The advantages of the operation include relative technical simplicity - the technique is many years old, its protocol has been worked out to the smallest detail. The disadvantage is blood loss, slow healing of the suture, and a long rehabilitation period.
Laparoscopic method - excision of vessels, ureter, separation and removal of the kidney is carried out using a laparoscope and other instruments inserted through three punctures in the abdominal wall. The advantages of laparoscopic removal: it is less traumatic, little blood loss and quick recovery. The disadvantage can be considered the high complexity of manipulations that require appropriate experience.
Regardless of the method used, general anesthesia is always used.
Indications and contraindications for nephrectomy
In all cases, the need for surgery arises when the kidney completely loses its functions and the patient’s life is threatened. Medicine is developing rapidly, for many diseases it is possible to develop an organ-preserving treatment protocol, but there are also unconditional indications for nephrectomy.
The operation is performed for a malignant tumor of an organ whose size exceeds 7 cm. The intervention is indicated when conservative therapy is ineffective in the case of renal failure, as a treatment for purulent-necrotic pyelonephritis, urolithiasis with formations that cannot be crushed. Indications for nephrectomy are polycystic disease, loss of excretory functions due to hydronephrosis, congenital anatomical abnormalities and defects, complete tissue destruction (due to a gunshot wound or other trauma).
There are also contraindications. The operation is not performed if you have poor blood clotting or are taking blood thinning medications. In the latter case, such treatment is stopped, surgery is prescribed a week after stopping the medications.
Diabetes mellitus and decompensated heart disease are also absolute contraindications for surgery. If a person has only one kidney, no intervention is performed. The same applies to cases with serious damage to the second organ. The exception is nephrectomy followed by transplantation.
How to prepare for surgery
In order for the intervention to proceed without complications and rehabilitation after kidney removal to be shorter, a preliminary examination is mandatory. The patient donates blood for a coagulogram, tumor markers, biochemical, general analysis. Ultrasonography, MRI or CT, and excretory urography are indicated. Ultrasound of the abdominal vessels is necessary if venous thrombosis is suspected.
When acute conditions or exacerbations of a chronic disease are detected, preparation includes preoperative therapy aimed at stabilizing the patient's condition.
Respiratory function is carefully studied - there should be no disturbances in the functioning of the lungs, since the anesthesia used inhibits their functioning.
On the day of surgery, the patient is given a cleansing enema and the hair at the site of future incisions is shaved. On the eve of nephrectomy, complete abstinence from food and minimal water consumption are required.
Carrying out the operation
As mentioned above, the intervention is carried out either open or laparoscopically.
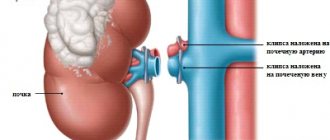
When performing abdominal surgery, the patient should lie on his side, on the side on which the healthy kidney is located. The leg should be bent at the knee. An incision is made on the opposite side - directly under the ribs or between the 10th and 11th ribs. The skin, fatty tissue, and muscles are dissected to provide access to the diseased organ. The kidney is carefully removed from the fat capsule and brought to the surface of the wound. Using surgical clamps, the ureter and the blood vessels of the organ are closed - after which they are excised along with the kidney pedicle. Next, the clamps are removed and the kidney is completely removed. After this, sequential suturing of the wound is carried out. On average, the operation lasts no more than 3 hours. The length of the cut is 12 cm.
During laparoscopic nephrectomy, the patient lies on his back. A catheter with a special balloon is installed in the ureter - with its help you can control the degree of expansion of the pelvis and fix the lumen of the organ. Instruments are inserted through 3 or 4 holes in the abdominal cavity: endoscope, laparoscope. The length of each incision does not exceed 2 cm, so laparoscopy is considered a minimally invasive intervention. To improve vision, carbon dioxide is pumped into the abdominal cavity. Excision of organs is carried out using electric scissors; the ureter and blood vessels are clamped with a special device (called a stapler).
The wounds are sutured with self-absorbing threads, the catheters are removed in the ward, after the operation. After removing a kidney using this method, the patient can eat the very next day; the postoperative period is reduced to several days.
Complications after surgery
Abdominal intervention is fraught with the following complications:
- bleeding due to vascular damage;
- heart failure, heart attack;
- intestinal obstruction;
- thrombosis;
- respiratory failure;
- stroke;
- damage to the spleen or pancreas;
- infectious purulent inflammation;
- hernia;
- stomach ulcer;
- venous bleeding from the esophagus.
Such complications after kidney removal occur due to insufficient preparation for the operation or violation of recommendations in the postoperative period.
The laparoscopic method is less traumatic, but there may be consequences after such an intervention. Most often, a non-threatening hematoma occurs that resolves over time. If during rehabilitation the doctor’s recommendations regarding nutrition are violated, intestinal obstruction occurs.
During emergency surgery or in obese people, there is a risk of a hernia at the insertion site.
Thromboembolism does not develop so often, and it is treated with resuscitation methods. Complications such as pneumonitis and brachial nerve palsy occur rarely and are easily managed.
Possible consequences include disability. It is assigned to persons who have lost the ability to live, if long-term rehabilitation is necessary, or if frequent disorders occur after surgery. In most cases, the patient manages without disability. Moreover, after removing one kidney from a woman, she can carry and give birth to a healthy child.
Rehabilitation
Life after kidney removal largely depends on the recovery period, which begins in the hospital. Its duration is from six months. At this time, it is necessary to carefully observe the drinking regime, and a diet is required.
Any self-medication is strictly prohibited, if pain bothers you or other disorders occur; drugs are prescribed only by a doctor. Moderate physical activity is recommended: light exercise, regular walks.
Recovery will come faster, and you can live a long, full life if you strictly follow all instructions. After a kidney has been removed, it is necessary to give the second organ time to adapt to new conditions.
Preventive measures
To date, there is no exact answer to the question of why children are born with one kidney.
To prevent developmental abnormalities in the child, the expectant mother is recommended:
- exclude alcohol, smoking, drugs, taking drugs with teratogenic effects;
- before conception, achieve remission of chronic diseases, cure possible STIs;
- get vaccinated against measles and rubella;
- take measures to prevent acute respiratory infections;
- carry out the orders of the obstetrician-gynecologist
Sometimes compliance with the listed rules can prevent not only kidney agenesis, but also a number of other fetal malformations.
Planning pregnancy: contraindications, precautions
Childbirth is possible in most cases . The patient’s age, nature and history of the disease, and treatment results are taken into account. If nephrectomy was performed, the course of the operation and recovery period is of no small importance. Much depends on the initial diagnosis.
It is not recommended to become pregnant:
- After kidney removal due to cancer. Due to hormonal changes in the body, the risk of disease relapse and late metastasis increases.
- After nephrectomy for tuberculosis, the full course of treatment with antibacterial drugs has not yet been completed. They negatively affect the fetus.
When deciding to become pregnant, the patient is primarily responsible for her health. Pregnancy in women with a single kidney is prohibited in the presence of pyelonephritis and renovascular hypertension.
Possible complications of the gestational period with these diseases:
- Severe gestosis.
- Acute or chronic renal failure.
- Malignant arterial hypertension.
- Stroke.
- Infection, malnutrition, fetal malformations.
- Intrauterine fetal death, spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
- Death of mother.
The course of pregnancy will be more favorable after removal of the organ due to pyonephrosis, tuberculosis (subject to completion of the course of treatment), and urolithiasis than before the operation. A kidney with a huge cyst does not function; its absence does not impair the functioning of the urinary system at any stage of gestation.
With a congenital malformation - a single ectopic kidney, pregnancy becomes a serious burden on the excretory organs.
The daily filtration process is joined by the removal of fetal waste products entering the mother’s body via the transplacental route. But, nevertheless, successful pregnancy and childbirth are possible.
The most optimal period for pregnancy is the second to fourth year after nephrectomy . This is the time the body needs to adapt and fully restore the functionality of the urinary system. For approximately two years, the single kidney is rebuilt to work with double load.