Types of pathology
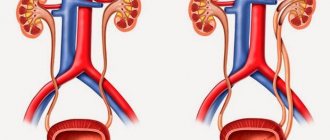
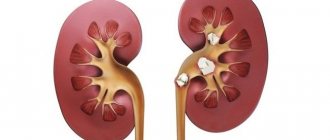
The defect is manifested by two fused organs and can be complete or incomplete (formed much more often). In the first case, there is a connection between two pyelocaliceal systems and ureters, which deepen into the bladder.
Incomplete doubling occurs when there is a pronounced change in the size of the kidney area. Most often, the upper half of the organ is enlarged. Cases when it is either proportional to or larger than the lower one are extremely rare.
If there is an anomaly, ectopia of the ureter of the daughter kidney is possible. It opens into another organ: intestines, vagina, urethra. Urine leakage occurs after urination.
An atypical process can be one-sided (left, right) or two-sided. An organ that has an irregular structure is able to function (cleanse blood and remove excess fluid).
Prices
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for examination and treatment for testicular cancer | 3 730 — 39 940 |
| Prices for vaporization of prostate adenoma with a “green laser” | 16 050 |
| Prices for diagnosis and treatment of impotence | 1 320 — 50 000 |
| Prices for diagnostics of the genitourinary system in men | 5 630 |
| Testicular cancer treatment prices | 15 410 |
| Prices for the treatment of urolithiasis | 11 760 — 16 180 |
| Bladder cancer treatment prices | 21 280 — 59 930 |
| Prices for diagnosing prostatitis | 2 720 |
| Prices for diagnosing male infertility | 6 300 |
| Prices for prostate cancer treatment | 23 490 — 66 010 |
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for kidney cancer treatment | 28 720 — 32 720 |
Causes of the disease
The formation of anomalies in the fetus during pregnancy can be facilitated by:
- avitaminosis;
- influence of ionizing radiation;
- unfavorable environmental conditions in the place of residence;
- radiation exposure;
- work in a specific production;
- prescription of certain medications;
- diseases of bacterial or viral origin;
- bad habits (drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking).
The developmental defect can be inherited. The baby receives the altered genome from his father or mother.
Causal factors of the defect
Until now, experts have not identified the exact reasons contributing to the formation of the defect, however, according to research data, some factors have been identified that influence the pathological development of internal organs.
The most common causes of abnormal kidney development include:
- Heredity. A pathological gene is passed on to a child from one of the parents who has anomalies in kidney development.
- Mutations. Mutagenic causes can have a variety of origins.
It is unfortunate, but it is the mutagenic factor that ranks first among the causes of pathology.
The provocateur becomes:
- smoking of the expectant mother;
- abuse of alcohol-containing drinks by a pregnant woman;
- drug addiction of both parents;
- uncontrolled use of medications by a pregnant woman;
- finding the expectant mother in conditions of increased danger, for example, in areas where chemical substances predominate;
- radioactive radiation, for example, CT or X-ray exposure during pregnancy
In addition to the above factors, pathology is caused by a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body.
The bad habits of the expectant mother negatively affect not only her health, but also the health of her baby.
Manifestation of symptoms
There are no typical symptoms that would indicate kidney duplication. The defect is often asymptomatic until changes appear in the organs.
Then general symptoms appear: increased body temperature, fatigue, swelling.
A person may also be bothered by pain in the lumbar region, cephalalgia, discomfort during urination, nausea, vomiting, and changes in blood pressure.
People with an atypical organ structure are more susceptible to various diseases of the genitourinary system, which often degenerate into chronic ones.
Duplication of the right organ due to the physiological characteristics of its location is less often burdened by concomitant pathologies.
With complete doubling, nephrolithiasis is diagnosed much more often. Abnormal formation of an organ can cause pyelonephritis, nephroptosis, tuberculosis, benign or malignant neoplasms, hydronephrosis.
Signs
Bifurcation of the kidney, as such, occurs without any special symptoms. In some cases, an intrauterine anomaly is detected completely by accident.
Some people live with this diagnosis and do not even know they have it. And everything would be fine, but sometimes such a defect can cause other diseases that have their own symptoms.
In this case, the signs may vary differently for each patient. General list of signs:
- Hydronephrosis. The pelvis is stretched and disruptions occur in contractile work. This condition causes disturbances associated with urine excretion.
- Very often the body suffers from inflammatory outbreaks. However, they are prone to relapse.
- Urine through the ducts should only go down to the outlet. If there are any failures in the structure, its reverse flow is noted.
- High body temperature.
- The person may have difficulty urinating.
- Pain in the back area where the kidneys are located.
- General malaise.
- High blood pressure.
- Incontinence.
- Renal colic may appear.
- Edema.
These symptoms are among the most common. Depending on the complications, the list may decrease or expand.
Each organism is individual, therefore both the course of diseases and their symptoms vary.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of the anomaly is carried out mainly during the ultrasound procedure.
With complete bifurcation, the specialist sees two independently functioning pyelocaliceal systems.
To confirm abnormalities in the structure of the organ, the patient is referred to cystoscopy (examination of the surface of the bladder from the inside with an endoscope) or excretory urography (x-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent).
When performing cystoscopy, the specialist can examine the orifice of the ureters.
Urogram is able to determine the structure of the urinary tract.
Retrograde pyeloureterography helps obtain x-ray images of the ureters after injecting a special marker into the patient's pelvis.
Organ duplication is not a disease. If the patient has no complaints, then it is enough for him to be observed by a nephrologist: take a urine test every year and perform an ultrasound of the kidneys.
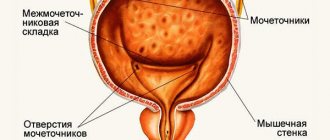
What is duplication of one or both kidneys?
An important part in the structure of the entire kidney.
It has the shape of a funnel, obtained as a result of the separation of 2 cups of the organ. It is in the pelvis that all urine is located. Inside, it is lined with a special mucous membrane, which prevents fluid from escaping into the abdominal cavity.
Its main function is to contract and push urine out through the drainage pipes.
As already mentioned, kidney duplication is usually observed in newborns. The causes of kidney duplication are usually:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Taking hormonal drugs by the expectant mother during pregnancy;
- Exposure to ionizing radiation;
- Vitamin deficiency during pregnancy, lack of some important minerals.
- Drug poisoning;
- The future mother's use of alcohol and cigarettes.
With incomplete doubling of the right or left kidney, a situation is usually observed when a person lives with a double kidney all his life and does not suspect it, and the pathology is discovered by chance during an examination.
Treatment options
Treatment of a double kidney is carried out if a pathological process has developed in the organ (pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, hydronephrosis).
Pyelonephritis resolves with increased temperature and renal colic. The urine produced becomes cloudy and flakes appear in it.
Antibiotics, antispasmodic and painkillers are effective for the inflammatory process.
Urolithiasis may not bother you until the stones begin to move along the ureter. If they are small in size, then the person experiences painful and frequent urination.
With larger stones, signs of renal colic appear: severe paroxysmal pain. The discomfort goes away with a rise in temperature, nausea or vomiting, and increased sweating.
For urolithiasis, antispasmodics, anti-inflammatory and diuretic drugs, and warm baths are prescribed. It is important to adjust your diet by eliminating fatty, fried, spicy foods and spices.
Kidney tea and herbal infusions may be recommended. Hydronephrosis is a pathological change in the size of the collecting system.
For a long time, the disease may not bother you with its manifestations, only sometimes causing moderate pain in the lumbar area.
This pathology is dangerous due to atrophy of kidney cells.
As a result, the likelihood of chronic renal failure increases.
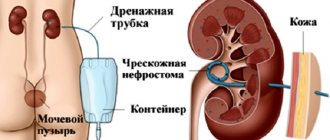
For hydronephrosis, surgery is performed. The changed organ is completely removed.
Surgery is also performed for vesicoureteral reflux, urethrocele, cancer, and urolithiasis that does not respond to conservative therapy. Can be done:
- nephrectomy (heminefrureterectomy) – cutting out some fragments of the kidney;
- ureterouretero- or pyelopyeloanastomosis - creation of artificial connections for reflux;
- Unnelization of the ureters - the formation of a lumen for the passage of urine.
Organ duplication is not considered a serious health threat, but it does increase the risk of inflammation.
Complications may occur: hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, vesicoureteral reflux.
When following specialist recommendations and correcting nutrition, a person’s quality of life remains at a comfortable level for many years.
Before conception, you will need to take blood and urine tests and perform an ultrasound of the kidneys. In the absence of deviations from normal values, planning a child is allowed.
It is important to give up bad habits and balance your diet. These measures will help reduce the likelihood of developing kidney disease. It is possible to find out about pathology in the fetus by ultrasound in the second half of pregnancy.
Symptoms
Regardless of whether the doubling of the left kidney or the right one occurs, this does not in any way affect the condition of the body and its performance. Therefore, in most cases, this developmental anomaly is discovered completely by accident, for example, during examination for other diseases, during pregnancy, etc.
But still, sometimes a double kidney can cause pain in the complete absence of any pathological processes. This is explained by the fact that, due to structural anomalies, urodynamics are distorted in it or interureteral reflux may be present. The patient may also have a positive Pasternatsky sign.
Possible dangers
Incomplete doubling of the left or right kidney is associated with a lower risk of developing other diseases than with complete doubling, since urodynamic disturbances in this case are minor. However, the risk of kidney pathologies in people with both types of anomalies is still high. Therefore, they often suffer from:
- pyelonephritis;
- urolithiasis;
- hydronephrosis;
- tuberculosis;
- nephroptosis;
- tumor formation.
Important: the presence of vesicoureteral reflux significantly increases the risk of developing pyelonephritis during kidney duplication.
At the same time, diseases of the upper urinary tract very often occur in a severe form and poison the lives of patients for a long time. They stubbornly resist treatment, and antibiotic therapy provides only temporary results. Therefore, usually patients with complete duplication of the right kidney suffer from chronic diseases and frequent exacerbations.
Features of pregnancy
Pregnancies in the presence of such a developmental anomaly must be planned in advance so that the expectant mother can undergo all the necessary examinations and, if necessary, sanitize detected foci of infection. Throughout pregnancy, the woman is observed by a general practitioner, and also visits a urologist or nephrologist several times, but in general, kidney duplication does not interfere with the normal bearing of the child and is not a contraindication to pregnancy, except in cases where the patient is indicated for surgical intervention or she has renal failure . If, however, the expectant mother encounters some kind of kidney disease, she is sent to a urological hospital, where she is provided with the necessary assistance and prescribed treatment appropriate to the situation.
What is the essence of the double kidney problem?
Double kidney is the most common congenital disorder. In children, kidney duplication is often detected completely by accident during the diagnosis of another pathology and an ultrasound scan. Double kidney - what is it? Organ duplication occurs in the prenatal period. The kidneys are a paired organ. Doubling is more often observed on one side. Medical practice shows that this pathology is most common on the left, and girls are more susceptible to it.
Bilateral doubling, according to statistics, occurs in only 10% of cases of this pathology. The kidney can be doubled completely or partially. A pathological kidney is significantly larger in size compared to a normal one.
Each part of such a kidney has a separate blood supply system, but most often a single pyelocaliceal system. The pathological structure of the kidney does not physically and functionally create any problems, and people often learn about this fact by accident. However, during life, such features of the organ can provoke a number of diseases.
Diagnostics
It is not difficult to detect such a pathology. To do this, it is enough to conduct a kidney examination using:
- Ultrasound;
- cystoscopy;
- excretory urography;
- CT;
- magnetic resonance urography;
- radiography.
In addition, standard tests are prescribed, such as a general blood and urine test.
Often hardware testing alone is not enough. So, x-rays do not make it possible to see whether this is a complete doubling or not. Then additional studies are prescribed.
During an ultrasound, a specialist often makes an unambiguous conclusion and identifies two separate CLs of both kidneys or one. This makes it possible to suspect a complete bifurcation of the organ.
Cystoscopic examination allows you to see the orifice of the ureters. If one or both kidneys are completely doubled, there will be more than two. For example, when a child’s right kidney is doubled, a pair of ureters will enter the bladder on the right, and one on the left.
Ascending urography involves the use of a contrast agent, which is clearly visible on x-rays.
All these research methods allow you to accurately make a diagnosis.
Prevention and prognosis
The only possible measure to prevent congenital malformations is to protect the pregnant woman as much as possible from any teratogenic environmental factors (the most dangerous time is the 1st trimester of pregnancy). You can try to exclude the genetic factor: by contacting a geneticist, preferably based on family history and the presence of risk factors, calculate the likelihood of having a sick child.
The prognosis is always individual, and largely depends on the functional state of the urinary system. You can live your whole life without problems with bilateral kidney duplication. Or, starting from childhood, constantly be observed and treated by a nephrologist for pathology on one side.