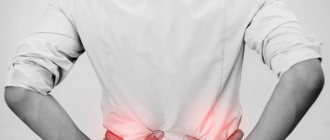
MCD is not considered an independent disease. This is a condition in which an excess of uric acid accumulates in the body of a sick person. This substance has a tendency to crystallize. At the same time, during the process of urination, small salt crystals are washed out of the body. Uric acid diathesis of the kidneys at the beginning of development does not cause any discomfort to the patient and is asymptomatic. In the urine you can notice a precipitate of uric acid salts, which looks like small grains of reddish sand. But such sediment can only be noticed when you empty your bladder into a special container.
What causes the disease
We have found out what MCD is, now let’s look at the most common causes of its occurrence:
- genetic predisposition;
- overweight, obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- lack of proper nutrition;
- alcohol abuse;
- prolonged hypothermia;
- kidney function problems;
- autoimmune, endocrine diseases;
- various types of injuries.
The development of pathology is also caused by a violation of the daily volume of fluid consumed, radiation therapy for cancer, and fasting for a long time. This is not a definitive list of all the factors that cause the accumulation of uric acid.
Signs of uric acid accumulation
Signs of urolithiasis are clearly expressed. The main one is severe pain in the lumbar back. When the stone moves, the pain spreads to the entire abdomen. Therefore, the pathology can be confused with an exacerbation of appendicitis or ulcers.
Symptoms accompanying the phenomenon:
- painful bowel movements;
- the presence of blood and urates in urine;
- lack of desire to eat and sudden weight loss;
- poor sleep;
- weakening of the body, nausea, constipation;
- colic in the kidney area, tachycardia;
- fever, severe headache.
With urolithiasis, a person does not control his emotions and is often irritated. If you do not see a doctor promptly, seizures may occur. Signs may not appear all the time, but only when the condition worsens.
Consequences of urolithiasis
If a person has kidney MCD, and what it is, how the condition manifests itself, he does not know, the disease may not be detected in time. This will lead to the development of complications: acute nephropathy, urolithiasis, problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract system, as well as the risk of developing uric acid infarction.
With advanced renal pathology, all organ systems suffer, especially the central nervous system, which is responsible for a person’s psychological health. The positive thing is that all consequences are eliminated without surgical treatment.
Possible complications
If MCD in adults or children is not treated for a long time, then this condition can lead to the development of the following diseases and problems with the functioning of the body:
- Since uric acid salts resemble sand at the beginning of their appearance, over time they can form large stones, that is, lead to the development of urolithiasis.
- The risk of kidney failure increases.
- Acute nephropathy may develop against the background of uric acid diathesis.
- There is a risk of uric acid infarction.
- Disturbances in the activity of the gastrointestinal tract.
Ways to detect uric acid accumulation
Before treating this pathology, the patient is fully examined. He is interviewed by a nephrologist and examined by a urologist. It is important that the person explains to the doctor exactly where it hurts and what other symptoms have appeared. Next, the patient is sent for an ultrasound of the kidneys, urine and blood tests, and, if necessary, an x-ray.
Ultrasound examination reveals the presence of sand or stones even at an early stage of the formation of this condition. Therefore, ultrasound is the main diagnostic method. Sometimes additional research is used to determine whether inflammatory processes are developing in other parts of the urinary organs.
Interpretation of results: norm and pathology
Normally, the renal arteries can be traced along their entire length: from the moment they branch from the aorta until they enter the portal of the kidney. The afferent vessel then branches into segmental arteries, which become arterioles. In a healthy kidney, blood flow is determined in all parts of the parenchyma of the organ, right down to the connective tissue capsule.
The diameter of the renal artery normally varies from 5 to 10 mm. Signs of stenosis of the afferent vessels of the kidney:
- blood flow velocity at the moment of cardiac contraction (PSV) is more than 180 cm/sec;
- acceleration time (AT) in intrarenal vessels is more than 70 ms;
- acceleration index PSV/AT less than 300 cm/sec2..
Ultrasound with color Doppler mapping allows identifying pathologies of the renal vascular system at an early stage. The non-invasiveness and complete safety of the method allows for regular monitoring of the condition of the vessels of the renal system in both adults and children.
Treatment for MCD
Urolithiasis is treated in three stages: symptomatic therapy, reducing the severity of symptoms, and correcting the diet.
To maintain metabolic processes, a saline solution (Regidron, Disol) is administered. Cleansing of the body is carried out using an enema, enterosorbents (Atoxil, Polysorb, activated carbon). For severe pain, No-Shpu and Novalgin are prescribed. Dissolve salt compounds with Canephron, Cyston, Urolesan. Anti-inflammatory drugs are also needed here: Hexicon, Betadine and the like.
Antibacterial medications are prescribed at the discretion of the treating doctor. With this pathological phenomenon, the use of Levomycetin, Erythromycin, and Penicillin will be effective. Your back should always be kept warm. To do this, use a heating pad or a warm scarf or belt. Warm baths are helpful.
Diet food
ICD of the kidneys can also be treated with proper nutrition. Chocolate, sausages, canned food, as well as meat, legumes, and offal are excluded from the diet. There is no need to eat mushrooms, processed foods, dairy products, pickles, or drink alcoholic beverages. It is worth removing fats and broths, hot and spicy snacks, and canned vegetables.
Eggs, prunes, potatoes, as well as nuts, citrus fruits, cabbage, including sea cabbage are recommended for consumption. Fill your daily diet with fruits, wheat bran, various cereals and eggplants, freshly prepared juices, fruit drinks, and compotes. Grapes, dried apricots, and vegetable oil will be useful. The standard drinking volume is two liters of liquid per day.
Alternative Treatments
MCD therapy with traditional methods will be effective only if you follow a diet and in addition to drug treatment. The patient should undergo ultrasound and other types of studies before starting treatment with alternative medicine methods.
A popular recipe is to prepare a mixture of 10 g of fennel and the same amount of juniper fruits. The ingredients are mixed, one large spoon of raw materials is separated, placed in 200 ml of just boiled water. Leave in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. After cooling, strain the broth and take 100 milliliters three times a day.
Celery is a good helper in getting rid of urolithiasis. You need to take 10 grams of the stems and rhizomes of the plant, pour 300 ml of it, which has just boiled, and leave to steam for 20 minutes. Then leave for 45 minutes. After straining, drink the infusion 100 milliliters in three doses per day. Time of use: 20 minutes before meals.
An effective method for normalizing kidney function and getting rid of accumulated uric acid is to drink apple infusion. To do this, cut half a kilogram of unpeeled fruit, boil it for 20 minutes, pour in a liter of liquid. Then leave for four hours. When the product is ready, it is consumed throughout the day as a compote.
Nettle, acting as a diuretic, quickly removes acid from the body. To prepare the medicine, place 50 g of dry herb in a glass of boiling water and boil for one minute. Leave the product for 10 minutes. You need to take 1 glass three times in 24 hours.
Preventive measures against MCD
The main preventive measure in the fight against uric acid deposits is dietary nutrition. The menu is individually selected for each patient by the attending physician. The patient must exercise daily, treat diseases of the genitourinary system in a timely manner, and maintain a drinking regime. An important point is to give up alcohol and follow a diet even after full recovery.
The development of urolithiasis does not pose a threat to human health with timely diagnosis and adequate therapy. The lack of treatment leads to the development of complications in the form of diseases of the urinary system.
Urolithiasis is not isolated as a separate disease. It can be characterized as a borderline state during which uric acid accumulates in the body.
Urolithiasis can provoke a number of ailments, such as gout, urolithiasis, etc. The risk group includes men over 40 years of age and women after menopause.
How to consolidate the result of treatment?
To prevent the recurrence of urolithiasis (relapse), it is necessary to adhere to the rules of dietary nutrition and drug therapy. It is recommended to lead an active lifestyle and try not to succumb to physical and emotional stress. If any diseases of the genitourinary system occur, you must consult a doctor and start therapy on time. If symptoms of the disease reoccur, you need to contact your doctor and undergo special examination methods.
Urolithiasis is not isolated as a separate disease. It can be characterized as a borderline state during which uric acid accumulates in the body.
Urolithiasis can provoke a number of ailments, such as gout, urolithiasis, etc. The risk group includes men over 40 years of age and women after menopause.
Symptoms of pathology
The most important symptom of urolithiasis is pain, which is localized in the lumbar region. As the stone moves toward the exit, there will be pain throughout the entire abdomen, and MCD is often mistaken for a symptom of another disease, such as appendicitis or an ulcer.
The disease is also accompanied by symptoms such as:
- frequent urge to urinate, which is also painful;
- blood in urine;
- excretion of urates in urine;
- sleep disturbance;
- frequent nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- rapid weight loss;
- weakness throughout the body;
- emotional instability and irritability;
- temperature increase;
- colic in the kidney area;
- Tachycardia may occur.
In advanced forms of the disease, convulsive syndrome may develop.
Diagnosis and treatment of MCD
Diagnosis of the disease begins with interviewing the patient, finding out where the pain is localized. Next, the patient is examined and a series of tests are prescribed. This is a blood and urine test, ultrasound of the kidneys, x-ray examination (in case of obstruction). If necessary, the patient can be referred for consultation to other specialists.
It is worth noting that ultrasound examination can detect sand and stones in the kidneys, subcutaneous fat or urinary tract at an early stage of the disease. Once a diagnosis of urolithiasis is made, therapeutic therapy is prescribed.
Treatment of the disease is carried out in 3 stages. The first stage is symptomatic treatment, the second is the easing of acute symptoms, the third is nutritional correction.
Related article - Drug resistance in tuberculosis
Drug therapy begins with administering to the patient such saline solutions as Disol, Regidron, Gidrovit. This is necessary to maintain the normal functioning of metabolic processes.
Cleansing enemas and enterosorbents are also prescribed. The most popular and effective of them are Polysorb, Atoxil, Enterosgel, and activated carbon.
To relieve pain, painkillers are prescribed: Novalgin, No-shpa, Novagra.
To dissolve salt conglomerates, Cyston, Canephron, Urolesan, etc. are prescribed. Anti-inflammatory drugs also play an important role: Betadine, Hexicon, Terzhinan, etc.
Uroseptics are prescribed only for small kidney stones. If the doctor deems it necessary, he will prescribe antibiotics to the patient. Effective antibiotics for the disease include Levomycetin, Penicillin, Erythromycin.
It is very important for the patient to keep the lower back warm during the treatment process. For this, medicinal baths are prescribed, a hot heating pad on the lumbar region or wearing a warm woolen scarf is recommended.
As for adjusting your diet, there is a whole list of prohibited foods for consumption. These include:
- chocolate;
- meat;
- canned food;
- sausage and frankfurters;
- offal;
- legumes;
- spicy snacks and spices;
- mushrooms;
- canned vegetables;
- semi-finished products;
- dairy products;
- alcohol;
- pickles;
- broths and fat.
It is recommended to include in the patient’s diet in sufficient quantities:
- eggs;
- cabbage;
- fruits;
- potato;
- prunes;
- wheat bran;
- seaweed;
- vegetable and butter;
- dried apricots and grapes;
- rice, millet, oat and buckwheat cereals;
- nuts;
- citrus;
- natural compotes and juices;
- eggplants.
As for the fluid consumed, the patient needs at least 2 liters per day.
Hydronephrosis and abscess
Hydronephrosis is an obstructive uropathy with dilatation of the pelvis (calicoectasia). Obstruction may be due to the presence of kidney stones, external pressure, narrowing of the ureter, or acute urinary retention.
The following stages of hydronephrosis are distinguished:
- dilatation of the pelvis and/or calyces (calicoectasia) without fusion. Separation of the renal sinus;
- dilatation of the pelvis and calyces with a decrease in the thickness of the parenchyma;
- disappearance of sinus echogenicity, thinning of the parenchyma, disappearance of the renal pelvis;
- hydronephrotic sac – structures cannot be visualized.
An abscess is a variation of pyelonephritis. But, unlike the latter, which has a widespread process, the abscess is limited in its spread. Simply put, an abscess is an abscess on the surface or deep in an organ. Most often, in non-medical circles, this condition is described as the presence of a “spot” on the kidney.
As a result of sonography, a lesion is identified, usually with a thick capsule and increased blood flow (due to inflammation), the contents of which are heterogeneous, often layered.
Treatment of urolithiasis with traditional medicine
Treatment of the disease with folk remedies gives quite good results, but only if the patient follows all the recommendations for traditional treatment and nutrition. In folk medicine, for the treatment of MCD, medicinal herbs and plants are used that have diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic effects, which increase the release of uric acid salts.
A positive effect of treatment can be achieved by consuming the following herbal mixture. For preparation you will need 10 g of fennel fruits and 10 g of common juniper fruits. The herbs are thoroughly mixed.
Next take 1 tbsp. l. mixture and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Cover the mixture with a lid and place in a water bath for 20 minutes. Next, the broth is cooled for 45 minutes at room temperature and filtered. Drink the decoction 3 times a day, 100 ml.
An infusion is prepared from the roots and herbs of celery. Take 10 g of herbs and roots. Pour 300 ml of boiling water, cover the composition with a lid and place in a water bath for 20 minutes. Cool the infusion at room temperature for 45 minutes.
Next, filter and bring the infusion with boiled water to its original volume. Drink the infusion 3 times a day, 100 ml, 20 minutes before meals.
Apples are used for normal kidney function and treatment of urolithiasis. An infusion is prepared from apples. To prepare the infusion you will need half a kilo of unpeeled apples. Chop the apples, place them in a saucepan, cover with a lid and boil in one liter of water for 20 minutes.
After the time has passed, the infusion is removed from the heat and left for 4 hours. Drink the infusion warm throughout the day.
Everyone knows that nettle is very beneficial for the kidneys, while it has a diuretic effect and perfectly removes uric acid salts. To prepare a medicinal decoction you will need 50 g of dry nettle and a glass of boiling water. The grass is poured with boiling water and cooked for 1 minute. After 10 minutes, filter the broth and take 3 glasses a day in small sips.
Methodology
The examination of the kidneys and urinary system is carried out in several positions: lying, on the side, standing or sitting. The sonologist applies a hypoallergenic water-based gel to the patient’s skin to ensure the most complete contact of the sensor with the surface of the patient’s body and increase the level of transmission of ultrasonic waves.
First, the kidneys are examined in the longitudinal direction (lumbar region), then transverse and oblique sections are studied, moving the sensor to the anterior and lateral surfaces of the abdomen. In this case, the patient is asked to alternately turn on the right and left sides. This technique allows you to determine the localization (location) of the kidneys, their size and shape, and assess the condition of the parenchyma, renal sinuses, calyces and pelvis.
To determine the mobility of the kidneys and improve visualization of the organs, with each change in body position, the doctor asks the patient to inhale and hold his breath for a few seconds. As you inhale, the kidneys descend from under the costal arch and are much more visible. A standing ultrasound of the kidneys is done if nephroptosis (prolapse of one or both kidneys) is suspected.
Doppler ultrasound (ultrasound of renal vessels) is performed with the patient lying on his side or sitting. This procedure does not have any special features. The doctor also moves the sensor over the surface of the patient's skin, carefully studying the constantly changing images on the monitor.
The duration of the entire procedure is about half an hour.
Interpretation of ultrasound
Best doctors by rating
Varenitsa Anna Nikolaevna
16 years of experience. Candidate of Medical Sciences
Pertskhelia Liya Chichikovna
Maykov Anatoly Nikolaevich
The ultrasound procedure performed does not yet provide a clear picture of the disease. Therefore, the next step for the doctor is to interpret the results obtained from the study. As a rule, the doctor performing the ultrasound does not explain to the patient what exactly he sees in the results and, having issued a conclusion, refers the patient to the attending physician
However, it often happens that the ultrasound was done today, and the attending physician will be at the appointment the day after tomorrow. Two days of waiting and uncertainty can be simply unbearable for the patient. Therefore, you need to learn to understand the diagnostic results and decipher kidney ultrasound.
Normal indicators and possible deviations from the norm
What does a doctor determine during an ultrasound examination of the kidneys? First of all, these are the size and location of the organ, the structure of the tissue, the presence of all kinds of formations and inclusions, including sand, stones, cysts and tumors.
Renal ultrasound interpretation always begins with determining the exact location of the kidneys. In normal condition, the kidneys are located on both sides of the spine at the level of the XII thoracic, I and II lumbar vertebrae. Usually the right kidney is located slightly lower than the left one and both can migrate to a limited extent in the vertical direction. The kidneys are surrounded by a layer of fatty tissue.
The size of a healthy adult organ can vary in the following ranges:
- length from 10 to 12 cm;
- the width should not exceed 6 cm;
- the thickness is usually between 4 and 5 cm.
In a healthy adult, the size of the kidneys is a constant, so an increase or decrease in the size of the organ indicates the occurrence of certain problems. If the kidney has increased more than normal, this may indicate inflammatory processes, the presence of neoplasms, and congestion.
A decrease in kidney size signals a degenerative process in the kidneys, destruction of organ tissue due to various chronic diseases.
The age of the patient is important when interpreting the results of ultrasound diagnostics. Ultrasound of the kidneys and normal indicators are not identical for different categories of people. Each age group of patients has its own norms - what is normal for an elderly person will be a pathology for a young person, what is normal for an adult will be a pathology for a child.
For example, for a healthy adult, the thickness of the renal parenchyma (tissue) should be from 1.5 to 2.5 cm. At the same time, for patients over 60 years of age, this figure in normal condition will be 1.1 cm or even less. This fact is explained very simply - with age, the renal parenchyma gradually decreases.
This factor must be taken into account.
A very important sign of a healthy kidney is the uniformity of its tissue, as well as a clean kidney cavity (pelvis). If, during ultrasound diagnostics, sand or stones are found in the renal pelvis, then most likely the patient suffers from urolithiasis.
In this case, the size of the stones found in the kidney cavity is of decisive importance. If they are not large, then there is a chance that they will be able to come out of the kidney on their own.
If the size of the stone is large enough, then certain procedures will have to be used to get rid of them.
Special terms in the conclusion
Let us separately dwell on special medical terms that are incomprehensible to most patients, which are often found in ultrasound diagnostic reports. So, what do we encounter most often and what does all this gobbledygook mean?
Sometimes in the conclusion you can read the phrase “increased pneumatosis intestinalis.” There is no need to be afraid of this. Simply put, this means that there is high gas production in your intestines. Most likely, you simply did not follow the recommendations for preparing for the study.
Another incomprehensible phrase is “fibrous capsule.” This is the membrane of the kidney, which in a healthy person should be smooth.
Pelvis. We have already mentioned this term briefly above. This is the cavity of the kidney into which urine flows from the renal calyces. From the renal pelvis, urine moves to the ureter and is then excreted from the body.
Microcalculosis is a less safe term than all of the above. It signals that small stones or sand have been found in the kidney.
Other terms are also used to refer to sand or stones found in the kidneys, including “echoshadow” or “echoic formations.”
Ultrasound diagnostics is today the most accessible method for examining the kidneys for the vast majority of patients. Ultrasound is performed in almost all government medical institutions, as well as in commercial organizations. If something is bothering you and you want to get diagnosed, then you shouldn’t have any obstacles.
All you need is the desire to do this, and the diagnosis can be carried out either with or without a referral from a doctor. As a result of the examination, the diagnostician will give you a conclusion. Having received it, we learn to understand the diagnostic results and decipher the kidney ultrasound. But, for an accurate interpretation, it is still better to contact a specialized ultrasound specialist.
Deciphering kidney ultrasound results is not at all an easy task, as you might think. Separately, it should be noted that good ultrasound diagnostic results do not at all guarantee the absence of organ pathology. If something still worries you, then for a more accurate diagnosis you should conduct laboratory tests, and in some cases even a computed tomography scan of the kidneys.
examples of ultrasound diagnostics of kidneys
The administration of the portal categorically does not recommend self-medication and advises consulting a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease.
Similar article - Full diagram of human organs
Our portal presents the best medical specialists with whom you can make an appointment online or by phone. You can choose the right doctor yourself or we will select one for you absolutely free
.
Also, only when you make an appointment through us, the price for a consultation will be lower than in the clinic itself.
This is our little gift for our visitors.
Parameters and indicators studied
During an ultrasound examination, characteristics such as the number of kidneys, location in the abdominal cavity, contours and shape are determined. The specialist also checks their dimensions - length, thickness and width. In addition, it is necessary to assess the condition of the tissue structure of the organ under study, the thickness of the parenchyma, pelvis, calyx, check the existence of benign or malignant neoplasms, diffuse diseases, and the presence of calculi (stones). Ultrasound is also designed to detect signs of inflammation and help assess the state of blood flow in the vessels of the organ. The bladder must be examined - its dimensions in a filled and empty state, volume, wall thickness. In addition, the adrenal glands are examined, their size and the presence of pathological formations.
What is kidney stones (urolithiasis)
Urolithiasis is not isolated as a separate disease. It can be characterized as a borderline state during which uric acid accumulates in the body.
Urolithiasis can provoke a number of ailments, such as gout, urolithiasis, etc. The risk group includes men over 40 years of age and women after menopause.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are many reasons for the development of MCD. Below are just some of them:
- hereditary factor;
- poor nutrition;
- obesity or overweight;
- kidney dysfunction;
- passive lifestyle;
- injuries;
- endocrine diseases;
- autoimmune diseases;
- alcoholism;
- hypothermia of the body;
- long-term use of medications.
Symptoms of pathology
The most important symptom of urolithiasis is pain, which is localized in the lumbar region. As the stone moves toward the exit, there will be pain throughout the entire abdomen, and MCD is often mistaken for a symptom of another disease, such as appendicitis or an ulcer.
The disease is also accompanied by symptoms such as:
- frequent urge to urinate, which is also painful;
- blood in urine;
- excretion of urates in urine;
- sleep disturbance;
- frequent nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- rapid weight loss;
- weakness throughout the body;
- emotional instability and irritability;
- temperature increase;
- colic in the kidney area;
- Tachycardia may occur.
In advanced forms of the disease, convulsive syndrome may develop.
Diagnosis and treatment of MCD
Diagnosis of the disease begins with interviewing the patient, finding out where the pain is localized. Next, the patient is examined and a series of tests are prescribed. This is a blood and urine test, ultrasound of the kidneys, x-ray examination (in case of obstruction). If necessary, the patient can be referred for consultation to other specialists.
It is worth noting that ultrasound examination can detect sand and stones in the kidneys, subcutaneous fat or urinary tract at an early stage of the disease. Once a diagnosis of urolithiasis is made, therapeutic therapy is prescribed.
Treatment of the disease is carried out in 3 stages. The first stage is symptomatic treatment, the second is the easing of acute symptoms, the third is nutritional correction.
Drug therapy begins with administering to the patient such saline solutions as Disol, Regidron, Gidrovit. This is necessary to maintain the normal functioning of metabolic processes.
Cleansing enemas and enterosorbents are also prescribed. The most popular and effective of them are Polysorb, Atoxil, Enterosgel, and activated carbon.
To relieve pain, painkillers are prescribed: Novalgin, No-shpa, Novagra.
To dissolve salt conglomerates, Cyston, Canephron, Urolesan, etc. are prescribed. Anti-inflammatory drugs also play an important role: Betadine, Hexicon, Terzhinan, etc.
Uroseptics are prescribed only for small kidney stones. If the doctor deems it necessary, he will prescribe antibiotics to the patient. Effective antibiotics for the disease include Levomycetin, Penicillin, Erythromycin.
It is very important for the patient to keep the lower back warm during the treatment process. For this, medicinal baths are prescribed, a hot heating pad on the lumbar region or wearing a warm woolen scarf is recommended.
As for adjusting your diet, there is a whole list of prohibited foods for consumption. These include:
Where are the kidneys and how do they hurt?
- chocolate;
- meat;
- canned food;
- sausage and frankfurters;
- offal;
- legumes;
- spicy snacks and spices;
- mushrooms;
- canned vegetables;
- semi-finished products;
- dairy products;
- alcohol;
- pickles;
- broths and fat.
It is recommended to include in the patient’s diet in sufficient quantities:
- eggs;
- cabbage;
- fruits;
- potato;
- prunes;
- wheat bran;
- seaweed;
- vegetable and butter;
- dried apricots and grapes;
- rice, millet, oat and buckwheat cereals;
- nuts;
- citrus;
- natural compotes and juices;
- eggplants.
As for the fluid consumed, the patient needs at least 2 liters per day.
Treatment of the disease with folk remedies gives quite good results, but only if the patient follows all the recommendations for traditional treatment and nutrition. In folk medicine, for the treatment of MCD, medicinal herbs and plants are used that have diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic effects, which increase the release of uric acid salts.
A positive effect of treatment can be achieved by consuming the following herbal mixture. For preparation you will need 10 g of fennel fruits and 10 g of common juniper fruits. The herbs are thoroughly mixed.
Next take 1 tbsp. l. mixture and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Cover the mixture with a lid and place in a water bath for 20 minutes. Next, the broth is cooled for 45 minutes at room temperature and filtered. Drink the decoction 3 times a day, 100 ml.
You can treat diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, including urolithiasis, with celery. It has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and choleretic effect.
An infusion is prepared from the roots and herbs of celery. Take 10 g of herbs and roots. Pour 300 ml of boiling water, cover the composition with a lid and place in a water bath for 20 minutes. Cool the infusion at room temperature for 45 minutes.
Next, filter and bring the infusion with boiled water to its original volume. Drink the infusion 3 times a day, 100 ml, 20 minutes before meals.
Apples are used for normal kidney function and treatment of urolithiasis. An infusion is prepared from apples. To prepare the infusion you will need half a kilo of unpeeled apples. Chop the apples, place them in a saucepan, cover with a lid and boil in one liter of water for 20 minutes.
After the time has passed, the infusion is removed from the heat and left for 4 hours. Drink the infusion warm throughout the day.
Everyone knows that nettle is very beneficial for the kidneys, while it has a diuretic effect and perfectly removes uric acid salts. To prepare a medicinal decoction you will need 50 g of dry nettle and a glass of boiling water. The grass is poured with boiling water and cooked for 1 minute. After 10 minutes, filter the broth and take 3 glasses a day in small sips.
How to recognize kidney cancer in the early stages
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
Kidney cancer is the proliferation of atypical cells from the kidney tissue, which leads to dysfunction of the organ, anorexia, and the spread of metastatic screenings to other organs and tissues. At the moment, according to statistics, kidney carcinoma ranks 10th among all cancer pathologies. The incidence in men is twice as high as in women. The article describes the symptoms and treatment of kidney cancer at different stages.
Classification
There are several types of classification that are included in the diagnosis and are the main marker when choosing treatment methods. One type of classification is based on the study of cells from puncture or surgical material of the kidney. Depending on which cells initiated the growth of a cancerous tumor, the following are distinguished:
- Clear cell kidney cancer. It ranks first in frequency of occurrence among kidney cancers, frequency - up to 85% of cases. Formed from atypical cells lining the proximal tubules of the nephron.
- Chromophobic cancer. The cancer grows from cells located in the collecting ducts, a rare form of cancer, diagnosis is possible in the early stages before metastasis.
- Chromophilic cancer. The development of pathology occurs from the cortical layer of the collecting system of the kidney.
- Papillary cancer. Carcinoma has spread to the pelvicalyceal apparatus. Aggressive course with rapid spread of metastases to internal organs.
- Undifferentiated kidney cancer. The most rapidly progressing and aggressive malignant kidney cancer is characterized by the fourth stage.
Carcinomatosis of the excretory system, like all oncological nosologies, is divided into four stages of kidney cancer according to its activity:
- Stage I. It is characterized by a tumor up to 5 cm in size, which does not extend beyond the organ, without screening out metastases. The most favorable prognosis, but is rarely diagnosed due to the paucity of symptoms.
- Stage II. It is characterized by carcinoma exceeding 5 cm, but not more than 10 cm, which already affects the kidney capsule and does not metastasize.
- Stage III. It is a tumor more than 10 cm, which grows into adjacent organs and tissues, metastasizing to the lymph nodes through the lymphogenous route. A clear clinical picture allows you to quickly diagnose the pathology.
- Stage IV. The most unfavorable option for prognosis is undifferentiated cytosis in the histogram of punctate or postoperative material. Rapid growth, multiple metastasis by hematogenous and lymphogenous routes.
Clinical manifestations
Manifestations of kidney cancer in the early stages are nonspecific. In the first and second stages, there may be a slight deterioration in general well-being: increased fatigue, drowsiness, appetite decreases slightly, and the person loses weight. In the initial stages, the following symptoms of kidney cancer are possible:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- hyperhidrosis (increased sweating);
- chronic fatigue and the manifestation of other nonspecific markers.
At later stages - the third and fourth stages - the main signs of kidney cancer appear:
- Hematuria. The appearance of blood in the urine is the most important clinical landmark, which makes the patient alert and consult a doctor. Blood discharge occurs in the form of clots and may be accompanied by hepatic colic. In women, this clinical criterion is less informative than in men. So, in women, according to statistics, cancer is detected more often at later stages.
- Pain syndrome. It manifests itself as pronounced spasms in the lumbar region, simulating urolithiasis, but sometimes the pain is a constant pulling or pressing encircling character in the area of the right or left kidney. May radiate to the thigh on the affected side.
- Volumetric education. It is most often found in kidney cancer in children (Williams cancer is a malignant tumor of the kidney). The formation is most often lumpy on palpation, dense, can bulge, but more often it is motionless, rarely painful. There is asymmetry of the abdomen, most often the process is unilateral, but even with bilateral damage, asymmetry is observed due to uneven growth.
- Cachexia. A cancer patient quickly loses weight due to a sharp decrease in appetite.
- Intoxication syndrome. Increased body temperature, weakness, accompanied by drowsiness, apathy, chronic fatigue syndrome. The fourth stage is characterized by necrosis and severe inflammatory processes in the affected organ due to a decrease in the reactive properties of the body, infection occurs.
- Inferior vena cava compression syndrome. A volumetric formation in the retroperitoneal region can block the outflow of blood through the inferior vena cava, which leads to severe swelling in the legs and provokes the development of varicose veins in women and varicocele in men. It is possible to develop thrombosis in the lower extremities, often deep; upon palpation, an increase in parenchymal organs is observed: liver, spleen. On the anterior abdominal wall, a “jellyfish head” may be observed - dilated veins of the anterior abdominal wall protruding above the surface of the skin.
Diagnostic methods
Based on clinical data, a thorough history of the disease, life history and hereditary predisposition, additional research methods are prescribed to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis of kidney oncology:
- Clinical blood test. Nonspecific study, possible registration of anemia, slight lymphocytosis, significant increase in ESR.
- General urine analysis. Macrohematuria, macroproteinuria, leukocyturia, cylindruria.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. Detection of space-occupying formations in the retroperitoneal space; it is possible to detect oncological nodes at an early stage.
- CT or MRI. It is carried out not only in the area of the abdominal organs. A tomography of the chest organs is recommended to exclude metastatic lesions.
- Renal angiography. The method is necessary for visualizing the blood supply to the tumor process.
- Excretory urography. Allows you to visualize a volumetric formation.
- Biochemical parameters. Renal parameters (urea, creatinine, glomerular filtration rate) reveal the degree of functional impairment of the kidney, chronic renal failure.
- Needle biopsy. An invasive method for diagnosing the histological structure of carcinoma, carried out under ultrasound control.
Treatment methods
Recently, progressive methods have been developed for the treatment of kidney cancer; the most effective regimens are selected individually, depending on the stage and type of cancer pathology. Most often, therapy is carried out by a combination of several types of therapeutic measures:
- Surgery;
- Chemotherapy treatment;
- Immunological treatment;
- Hormonal therapy;
- Targeted therapy for kidney cancer;
- Radioisotope radiation therapy, etc.
Surgery
Today it remains the most effective therapeutic method. At the first and second stages, radical operations are performed:
- Kidney resection for stage 1 cancer (partial removal);
- Removal of a kidney for stage 2–3 cancer with revision and excision of regional lymph nodes;
Palliative intervention at the fourth stage is carried out to reduce symptoms of urinary tract obstruction and compression of nearby organs, to prolong the patient’s life.
The prognosis after removal of kidney cancer at the first - second stages is relatively favorable: the first stage survival rate is about 90% of patients, the second - up to 70%. In parallel, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or other innovative treatment methods are carried out according to indications, which allow patients with cancer to live.
Of course, with stage 4 kidney cancer, how long patients live is impossible to predict; the five-year survival rate is no more than 4%. The main task of medicine in this case is to maximize their quality of life.
Chemotherapy treatment
Chemotherapy is based on the use of drugs that can suppress the growth of atypical cells, reduce the blood supply to the cancerous tumor (the drug Nexvar - used in palliative therapy to prevent the appearance of new vessels that feed kidney cancer) and other drugs.
It is recommended to carry out several courses, depending on the stage and histological structure of the tumor. In fact, chemotherapy drugs are not able to cure cancer, but are used to reduce the volume of the tumor. This method is often performed before surgery. After surgery, chemotherapeutic cytostatic drugs are prescribed to prevent recurrence of tumor growth.
Polychemotherapy is carried out during palliative treatment at the terminal stage to reduce the volume of formation and alleviate the patient's condition.
Radiation therapy
It is carried out as palliative treatment to reduce pain, thereby improving the quality of life.
Widely used for metastasis of cancer cells to bones, it causes a reduction in the volume of metastases, reduces pain and reduces the risk of developing many possible complications. It is carried out in courses of 7-14 days, the dose is calculated individually.
Often, to reduce the volume of a malignant neoplasm, a preoperative course of radiation therapy is performed. In this case, surgery must be performed within the next 48 hours.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is an innovative method of treatment, hypothetically capable of curing patients even at the fourth stage of cancer. Selectively affects cancer cells, while leaving healthy tissue untouched.
Allows you to transfer oncological pathology into remission, especially in the initial stages of the disease. The method can be used as monotherapy. The method is new, and the consequences of using targeted therapy drugs have not yet been studied.
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
Kidney ultrasound mkd what is it
Urolithiasis is not isolated as a separate disease. It can be characterized as a borderline state during which uric acid accumulates in the body.
Urolithiasis can provoke a number of ailments, such as gout, urolithiasis, etc. The risk group includes men over 40 years of age and women after menopause.
Treatment of urolithiasis with traditional medicine
Treatment of the disease with folk remedies gives quite good results, but only if the patient follows all the recommendations for traditional treatment and nutrition. In folk medicine, for the treatment of MCD, medicinal herbs and plants are used that have diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic effects, which increase the release of uric acid salts.
A positive effect of treatment can be achieved by consuming the following herbal mixture. For preparation you will need 10 g of fennel fruits and 10 g of common juniper fruits. The herbs are thoroughly mixed.
Next take 1 tbsp. l. mixture and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Cover the mixture with a lid and place in a water bath for 20 minutes. Next, the broth is cooled for 45 minutes at room temperature and filtered. Drink the decoction 3 times a day, 100 ml.
You can treat diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, including urolithiasis, with celery. It has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and choleretic effect.
An infusion is prepared from the roots and herbs of celery. Take 10 g of herbs and roots. Pour 300 ml of boiling water, cover the composition with a lid and place in a water bath for 20 minutes. Cool the infusion at room temperature for 45 minutes.
Next, filter and bring the infusion with boiled water to its original volume. Drink the infusion 3 times a day, 100 ml, 20 minutes before meals.
Apples are used for normal kidney function and treatment of urolithiasis. An infusion is prepared from apples. To prepare the infusion you will need half a kilo of unpeeled apples. Chop the apples, place them in a saucepan, cover with a lid and boil in one liter of water for 20 minutes.
After the time has passed, the infusion is removed from the heat and left for 4 hours. Drink the infusion warm throughout the day.
Everyone knows that nettle is very beneficial for the kidneys, while it has a diuretic effect and perfectly removes uric acid salts. To prepare a medicinal decoction you will need 50 g of dry nettle and a glass of boiling water. The grass is poured with boiling water and cooked for 1 minute. After 10 minutes, filter the broth and take 3 glasses a day in small sips.
Features of examination of men, women and children
There are no differences in preparation for kidney ultrasound between men and women. Before the study, you must fast for 8–10 hours. During the day before the procedure, you should not eat foods that increase gas formation in the intestines. Before the procedure, smoking and chewing gum are prohibited; it is advisable to observe a “silence regime” to reduce the accumulation of gas in the intestines. Sonography is performed on a full bladder, preferably in the morning.
To the question “Is it possible to do an ultrasound of the kidneys during menstruation?” The unequivocal answer is yes! Menstruation will not affect the woman’s body or the results of the study in any way. During the menstrual period, no changes occur in the examined organ that could interfere with sonography. Thus, women can undergo ultrasound examination at any time of the month.
It also happens that sonography is prescribed to women during pregnancy. Naturally, many are concerned about the possible impact of ultrasound on the fetus. It is worth noting that during the entire period of use of ultrasound technology, its effect on the child in the womb has not been identified.
If a child needs an ultrasound of the kidneys, no special preparation is required; it can be done even on a newborn. This is due to the baby’s thinner abdominal wall and, accordingly, better visualization of the internal organs. However, just like adults, children need to fill their bladder.