Every tenth person on Earth has kidney disease. Even in Ancient Egypt they knew what kidney stones were. Many suffer from kidney failure and wait a long time for dialysis or organ transplantation. Therefore, it is necessary to know what the functions of the kidneys are in the body and measures to prevent diseases associated with this organ.
Human kidneys
Structure
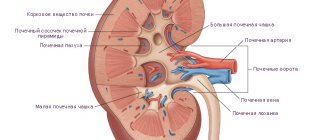
The kidneys are made up of nephrons. In a healthy person, there may be almost 2 million nephrons in the body, which produce urine. Inside each of them there is a renal corpuscle with tangles of capillaries. They are surrounded by a two-layer capsule, lined with epithelium on the inside. On the outside, this entire “structure” is protected by a membrane and surrounded by tubules.
Nephrons are of 3 types. They are distinguished by the structure and location of the tubules:
- superficial;
- intracortical;
- juxtamedullary.
How the kidneys work
This organ is constantly in action. Those who are interested in the structure and functions of the kidneys should know that blood circulation in them does not stop all the time. Blood is supplied by an artery, which divides into many arterioles. They bring it to each ball. As a result, urine is produced in the kidneys.
It happens like this:
- in the first stage, plasma and fluid contained in the blood are filtered in the glomeruli;
- the resulting primary urine is collected in special reservoirs, where the body absorbs all useful substances from it;
- Thanks to tubular secretion, excess substances move into the urine.
Over the course of 24 hours, the body repeatedly pumps all the blood present in the body. And this process does not stop. Every minute the body processes 1 liter of blood.
Prevention of kidney diseases
Symptoms of kidney disease may not appear for a long time, but gradually they eventually make themselves known. By adhering to the simplest and most basic rules, you can significantly improve and facilitate the functioning of your kidneys. This:
- active lifestyle (improves blood circulation and prevents congestion in the kidneys);
- proper nutrition;
- sufficient amount of water per day;
- drafts and prolonged exposure to cold should be avoided.
To optimize kidney function, Zdravie Oil will be an excellent assistant. These are capsules with a mixture of unrefined natural vegetable oils: pine nut kernels, watermelon and sesame seeds.
Health oil is suitable for adults and children. It normalizes the functioning of the kidneys, genitourinary system, urinary tract, and has no contraindications for kidney diseases. Zdravie oil is intended for general health promotion and prevention of kidney diseases.
What is the function of the kidneys?
This organ plays the role of a kind of filter. The main function performed by the kidneys is urination. She is extremely important. That is why nature provided a person with 2 kidneys, and in rare cases there may even be 3. If one of the kidneys fails, the human body can function normally even with one kidney.
The main functions of the kidneys also include:
- excretory;
- ion-regulating;
- metabolic;
- endocrine;
- blood creation function;
- osmoregulatory;
- concentration.
Excretory capabilities of the kidneys
The main function of this organ is to remove excess fluid and metabolic products. It is called excretory or excretory. The kidneys pass through a huge volume of blood per day (up to 1500 liters), filtering from it first about 180 liters of primary urine, and eventually from 0.5 to 2 liters of secondary urine.
This function is based on two stages: filtration and reabsorption. At the exit from the bladder, urine must have a certain composition and density. This is necessary to remove all unnecessary and harmful waste products from the body, but at the same time, filter out and leave everything useful and necessary.
To perform the excretory function, the kidneys use abilities such as filtration and concentration. Thanks to filtration, the blood is divided into fractions, and thanks to concentration, the relative density of urine and the optimal content of excreted substances are ensured.
How urine is formed
The blood entering the organ is filtered by passing through the renal corpuscle, that is, the initial part of the nephron, which is the main functional unit of the kidney. Nephrons originate in the cortex of the organ, so filtration is one of the functions of the cortex. Next, the filtered fluid enters the nephron capsule. This is primary urine, which is water in which various substances are dissolved. Primary urine contains amino acids, vitamins, salts, and glucose. The next stage is reabsorption, that is, reverse absorption. Primary urine is sent to the renal tubules, where nutrients are absorbed into the blood. Substances that need to be removed from the body remain in the urine. Its concentration is regulated by the nephron loop.
The final urine contains a high concentration of substances unnecessary for the body, and normally there are absolutely no vitamins, amino acids and glucose.
The excretory function of the kidneys is also called nitrogen excretion, since the removal of end products resulting from nitrogen metabolism is the most important part of human life. Substances such as purines, indican, and especially creatinine and urea are toxic to our body, so it is necessary to ensure their isolation and elimination from the body.
How does filtering work?
The kidneys are not limited to pumping blood. In parallel with this process, they remove from it microbes, toxins, waste and other harmful substances that pose a danger to the normal functioning of organs and systems of the human body.
Then the breakdown products end up in the blood plasma, which carries them to the ureters, and from where to the bladder. During urination, all harmful substances are removed from the human body. To prevent released toxins from getting back in, the ureters are equipped with a special valve that opens only in one direction.
Regulation of homeostasis
Thanks to the homeostatic function of the kidneys, we have a stable state of the body, maintain balance and ensure the formation of substances necessary for the body.
What does the homeostatic function provide?
- Maintains fluid and salt balance.
- Regulates pH.
- Participates in the production of glucose.
- Provides ammoniogenesis.
Water-salt balance depends on the ionic composition of liquids both inside and outside cells. The work of the kidneys is aimed at maintaining a constant quantity and composition of these fluids. The main “participants” in this process are ions of chlorine, sodium and water. About two-thirds of these ions are reabsorbed in the proximal tubules of the renal glomeruli.
The value of the ratio of acids and alkalis in the blood, that is, the pH value, is regulated at the first stage by special blood systems. However, this regulation occurs over a very large range. The kidneys, as it were, refine it; they remove either acidic or alkaline elements to ensure their normal ratio.
Acidosis, that is, a shift in the acid-base balance towards increasing acidity (decreasing pH), is dangerous for our body. The homeostatic function of the kidneys provides a special system for combating this undesirable phenomenon. In cases of imbalance and increased acidity in the body, the kidneys increase the production and entry into the blood of ions, which alkalize the blood, restoring the balance of acids and alkalis. Such balance is important for the normal functioning of all organs and systems, maintaining the body in a vigorous working state.
The participation of kidney tissue in the production of glucose ensures normal sugar concentrations while the balance shifts towards acidity. The kidney enzyme is more active in an acidic environment, which cannot be said about the liver enzyme involved in glucogenesis. This function is especially important during acidosis due to fasting or lack of carbohydrates. Increased acidity due to ketone bodies stimulates glycogenesis in the kidney tissue. As a result, acidic substances are converted into glucose, and the pH changes towards an increased alkaline reaction. With alkalosis (the predominance of an alkaline reaction), glycogenesis in the kidneys is inhibited, and the reverse reaction is activated, which reduces the concentration of glucose and increases acidity. In this way, a balance is achieved both in the acid-base composition of the blood and in the concentration of glucose.
Ammoniogenesis provides an additional tool. This is necessary because adjusting the ionic composition is not enough to maintain equilibrium and optimal pH. Ammonia is formed from amino acids in the epithelium of the renal tubules, after which it interacts with hydrogen ions in the lumen of the tubules, as a result of which ammonium ions are excreted. Thus, ammoniogenesis makes it possible to remove excess acids.
Metabolism regulation
The body processes substances ingested with food and liquid not only by the digestive organs, but also by the kidneys. The metabolic function of this organ ensures metabolism: the absorption and breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
Homeostatic and metabolic functions
This organ effectively regulates the volume of intercellular fluid and blood. This is achieved by ensuring the balance of ions contained in the cells. The metabolic function of the kidneys is no less important. It manifests itself in the form of metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. This organ is also directly involved in the process of gluconeogenesis, which is triggered by fasting.
In addition, it is in the kidneys that “regular” vitamin D is transformed into its more effective form - D3 and enters the body through the so-called skin cholesterol, produced under the influence of the sun's rays.
This organ is also responsible for the active synthesis of proteins necessary as building materials for the formation of new cells.
How is kidney function regulated in the body?
The volume and composition of urine excreted by the body per day is greatly influenced by hormones:
- adrenaline secreted by the adrenal glands reduces urine formation;
- estradiol regulates the level of phosphorus and calcium salts in the blood;
- aldosterone, synthesized by the adrenal cortex, with excessive secretion causes sodium and fluid retention in the body, and with its deficiency, a lot of urine is released, which leads to a decrease in blood volume;
- parathyroid hormone - stabilizes the excretion of salts from the body;
- vasopressin - regulates the level of fluid absorption in the kidneys;
The amount of fluid consumed during the day affects the activity of the central osmoreceptors of the hypothalamus. With excess water, it decreases, which leads to an increase in the volume of urine excreted by the kidneys. If the body becomes dehydrated, activity increases and the amount of fluid leaving the body decreases. A very dangerous situation can arise when the hypothalamus is damaged, when the volume of urine can reach 4-5 liters per day.
It's not just hormones that regulate kidney function. Their activity is greatly influenced by the vagus nerve and sympathetic fibers.
Causes of kidney diseases
The most insignificant factors turn out to be detrimental to the kidney. These include:
- hypothermia can lead to an inflammatory process in the kidneys, which subsequently manifests itself as nagging pain;
- promiscuity in sexual relations can lead to sexually transmitted diseases, which affects kidney function;
- poor nutrition;
- formation of kidney stones;
- ecology;
- heredity.
It is important to follow some preventative and health measures. If you treat this with disdain, then with age the consequences will appear on their own.
What symptoms should you consult a doctor for?
Kidney problems are a very serious health threat, so if they occur, you should not delay visiting your doctor.
And the fact that there may be a violation of kidney function may be indicated by the presence of several symptoms from the following list:
- increased fatigue;
- reduced immunity (successive infectious and cold diseases);
- high temperature, which ranges from 37–37.5 degrees Celsius and rises slightly in the evening;
- frequent and painful urination;
- change in urine color;
- polyuria (excretion of too much urine that becomes excessively light in color);
- the presence of blood clots in the urine;
- the appearance of swelling around the eyes, on the feet, legs, fingers;
- the occurrence of frequent, aching pain in the lower back, aggravated by being in an upright position.
Why you shouldn’t neglect medical care
Many people put off visiting a doctor, hoping that everything will “resolve” on its own. Such hopes are futile, since this can only aggravate your problems and lead to complete disruption of the kidney functions in the body. At first, the disease can become chronic, and then lead to kidney failure. In this case, the cardiovascular, neurological, musculoskeletal, endocrinological systems and gastrointestinal tract will be affected. Serious treatment will be required, and in advanced cases, hemodialysis. In this procedure, the patient's blood is pumped many times through a filter in an artificial kidney machine. Each hemodialysis session lasts several hours. The patient requires 2-3 similar procedures per week, so the patient is deprived of freedom of movement, as he must visit the medical facility where he is being treated every 2-3 days. And so on until the end of life, at least until medicine comes up with an alternative to hemodialysis.
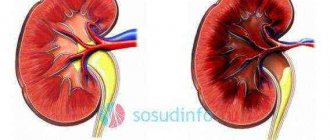
What determines the size of the kidney?
The human kidney, like all other organs, grows as long as the body grows. Changes occur proportionally, but sometimes failures occur and then one or two grow too small or large.
Need to know! For the kidneys to function properly, they must be the normal size according to the anatomy of the kidney. If at least one of them has non-standard sizes, this will lead to their inferior functioning, which will affect the health of the whole organism.
What sizes are considered normal? A healthy organ meets the following parameters: length - 100-130 mm, width - 50-75 mm, thickness - 20-25 mm, weight - 150-200 g. These are average data, since parameters may vary depending on gender, weight and human growth. Mature men and women experience a decrease in size.
It is very difficult to talk about standards in children, since their development occurs too individually. Urologists have been conducting research for a long time to come to some average figures. The length of the organ depends on the specific age of the child:
- up to 2 months – 49 mm;
- from 3 to 12 months – 62 mm;
- from one to 5 years – 73 mm;
- from 5 to 10 years – 84 mm;
- from 10 to 15 years – 98 mm;
- from 15 to 18 years – 106 mm.
The location of a person's kidneys also matters. The left is always larger than the right, and this is explained by the fact that the right organ is prevented from growing by the liver, which is also located on the right side of the person.
An important point: experts say that size is not as important as the ratio between the sizes of the left and right kidneys. The norm is considered to be a difference in values of no more than 15 mm.
What are the consequences of deviation from the norm?
Due to the different sizes, there may not be any special problems and the kidneys may function quite normally, but there are not many such cases. Mainly due to existing human anatomy, abnormal kidneys can cause a wide variety of diseases.
Kidney ultrasound
Note! Such a popular study today as ultrasound perfectly assesses the size of human organs. Thanks to the data obtained, the doctor will be able to potentially identify problems that do not yet exist, but which have a high chance of appearing in the near future.
A kidney with dimensions smaller than normal can provoke:
- renal failure;
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- renal artery stenosis;
- renal obstruction.
A kidney that is larger than the standard one can cause:
- renal polycystic disease;
- acute pyelonephritis;
- kidney doubling;
- renal thrombosis;
- renal infarction.
It is important to know! Existing urological diseases in humans can occur without visible symptoms. This is dangerous because time is lost to begin an effective fight against the disease. Another point is that kidney diseases often mimic the symptoms of other diseases. Muscle spasms, fatigue, loss of appetite, pale skin are the most common ones.
Who should take care of prevention?
Those whose immediate relatives have had or have impaired renal function should be especially attentive to their health. Frequently recurring sore throats and/or unstable blood pressure should cause caution. The best place to start is by visiting a qualified therapist. Most likely, he will suggest taking urine and blood tests, and will also prescribe an ultrasound examination. If the results are “suspicious,” you will need to consult a nephrologist and/or urologist. In general, it is believed that people over 40 years old should have an ultrasound of their kidneys every year.
What's useful
Knowing the structure and functions of the kidneys is not enough. It will also be useful to get acquainted with the recommendations of specialists who will help avoid problems in the activities of this body.
To prevent kidney function from being impaired, you need to drink at least 2 liters of water daily. This amount is optimal for the normal functioning of the human body. In addition, with this drinking regime, the blood will be sufficiently thin, which will facilitate its filtration by the kidneys.
Drinking cranberry or lingonberry juice will also be beneficial for this organ, as it helps remove excess fluid from the body and reduces the concentration of urine, which prevents the formation of stones.
Eating watermelons, pumpkins, zucchini and melons, which have an excellent diuretic effect and contain many vitamins and microelements, is very beneficial for kidney health.
An active lifestyle and sports are encouraged, which prevent the occurrence of blood stagnation in the pelvis. However, the load should be moderate, and when in the fresh air, you should dress for the weather so as not to chill your internal organs. For the same reason, girls, and even boys, are not recommended to wear “transparent” underwear during severe frosts.
Your kidneys will thank you if you sleep on your stomach more often. If you don’t get enough sleep in this position, then try to lie down like this for 20 minutes between 17:00 and 19:00, since it is at this time that the kidneys work most actively.
Diet during kidney recovery
To maintain the normal condition of the kidney organ, you should review your diet. For better kidney function, each person is recommended to eat a healthy and balanced diet. A dietary regimen will not only restore kidney function, but also improve a person’s overall health. Thus, the patient’s menu should not contain fatty and salty foods, but should be dominated by foods that help the kidneys work at the same intensity. Vegetables and fruits, dairy products, pumpkin seeds, and various cereals will restore the paired organ.
Diet is a guarantee of the health of the whole body, and in case of illness, it is a condition for a speedy recovery.
To improve kidney function, you should definitely eat asparagus, cauliflower, onions, red peppers and cranberries. To keep the organ responsible for urine production in good condition, you need to consume these foods regularly. In addition, it is important to adhere to the diet, namely, eat often and in small portions, at least 5 meals a day. In order not to overload the digestive system, portions should be the size of a fist, then the kidneys will not have to work at full capacity. Normalizing renal imbalance includes eating dietary foods that have undergone proper heat treatment - steaming, boiling or baking.