Metabolism (metabolism) is a complex biochemical process during which nutrients, vitamins, micro- and macroelements entering the gastrointestinal tract are used with maximum efficiency for the needs of the body. When this mechanism fails, multiple dysfunctions of internal organs occur, most of which are accompanied by the development of the disease. For example, nephrocalcinosis of the kidneys, associated with impaired calcium metabolism, can lead to serious health consequences. The causes, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and complications of this condition are reviewed below.
What is nephrocalcinosis
Nephrocalcinosis is a pathological condition characterized by the accumulation of calcium salts in the kidney tissue. This disease is accompanied by morphofunctional restructuring of the organ and leads to a gradual disruption of its structure. Most often, men and women over 50 years of age are susceptible to developing the disease, but in rare cases, the pathology can also occur in children.
Calcifications disrupt the normal flow of urine
The second name for nephrocalcinosis is renal calcinosis. In some cases, the disease is mistakenly confused with urolithiasis (with this type of damage, stones can contain not only calcium, but also other salts, as well as organic substances).
Features of the course of the disease in children
The urinary system of a child is significantly different from that of an adult. The kidneys are much smaller in size, as well as extremely vulnerable vascular bundles. This explains the high probability of bleeding even with the formation of small calcifications.
In 90% of cases, children have congenital nephrocalcinosis, which occurs against the background of the incorrect lifestyle that the mother led.
Symptoms of the disease in children, unlike adults, begin extremely acutely. Nephrocalcinosis often begins with an intense bursting attack of pain, which ends with copious discharge of blood in urine. Older children may experience seizures or irregular heart rhythms caused by excess calcium ions in the body. All children with a similar diagnosis must be hospitalized in the urology department of a children's hospital.
Existing classifications of pathology
Types of the disease due to their occurrence:
- congenital (formed even before the baby is born in the womb and may be caused by genetic abnormalities);
- acquired (occurs under the influence of external environmental factors).
Classification of the disease according to the affected layer of renal tissue:
- medullary (the medulla that forms the pyelocaliceal system is involved);
- cortical (calcifications are deposited in the cortical layer that forms the renal glomeruli);
- perinodular (located next to the lymph nodes);
- papillary (the renal papillae are damaged, which open with their apices into small cups).
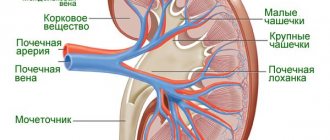
To understand the area of damage, you need to know the structure of the organ
Types of nephrocalcinosis according to the nature of changes in organ tissue:
- primary (develops in a previously healthy organ that does not have systemic pathologies);
- secondary (formed as a result of inflammatory processes in the kidneys).
Features of diet therapy
For calcifications in the kidneys, therapeutic diet No. 7 is prescribed, in which it is necessary to strictly control nutrition.
It is recommended to consume the following products: low-fat broths, boiled or baked meat and fish, foods with a high magnesium content, which are beneficial for metabolism. You should limit your salt intake to 3-4 grams per day.
It is necessary to exclude alcohol, coffee, foods with a high content of vitamin D (fatty, fried and smoked foods, baked goods, hard cheeses, legumes). You need to eat little and often so as not to burden the digestive tract and urinary system.
Why does nephrocalcinosis develop?
Such a disease can occur both as a result of hereditary anomalies and genetic mutations (more typical for children), and under the influence of environmental factors. The main reasons for the development of nephrocalcinosis include:
- drinking low-quality contaminated water with a lot of salts;
- excess calcium in food;
- unauthorized use of medications and vitamin and mineral supplements;
- destruction of bone tissue due to external and internal processes;
- burn disease;
- infectious pathologies (HIV, tuberculosis, syphilis);
- disturbances in the exchange of phosphorus and calcium in the body;
- malignant neoplasms of bone tissue;
- frequent contact with ultraviolet radiation;
- hypervitaminosis D;
- tumors of the urinary system;
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis);
- traumatic injury to the lower back.
Treatment
It is necessary to promptly eliminate the cause of calcium metabolism disorders. In case of severe dehydration, infusion of a solution of sodium bicarbonate or citrate, potassium citrate and aspartate for acidosis, and sodium and ammonium chloride for alkalosis is indicated. For moderately severe hypercalcemia, a diet with a limited calcium content, an infusion of magnesium sulfate solution, and vitamin B6 are prescribed. For acute hypercalcemia, solutions of sodium phosphate, magnesium sulfate, and sodium EDTA are infused; prednisolone, thyrocalcitonin are administered; with progressive renal failure, hemodialysis is performed (see). Particular attention is paid to the treatment of pyelonephritis, which contributes to the progression of renal failure. In addition, with secondary N., measures are taken to treat the underlying process.
Clinical picture of the disease
In adult patients, the symptoms of the pathology develop and increase gradually. This is due to the body’s adaptation to decreased kidney function and the active work of decompensation mechanisms. Small calcifications may not produce a clinical picture for a long time and go unnoticed. Large pathological formations in thin patients can be felt in the lower back.
Clinical symptoms of the disease include:
- pulling, bursting and pressing pain in the lumbar region (may intensify with physical activity, stressful situations);
- periodic increases in blood pressure several times higher than normal values (up to 220/120 mmHg);
- the appearance of blood impurities in urine;
- severe discomfort and pain when urinating (sometimes there is a disturbance in the outflow of urine);
- spastic contractions of various muscle groups;
- headaches in the temporal and occipital areas;
- sleep disturbances (frequent awakenings);
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- tendency to infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract.
How is nephrocalcinosis diagnosed?
If you suspect the development of such a kidney pathology, you should consult a urologist. The doctor will ask you to describe in detail the symptoms of the disease and the time of their onset, and will also need to talk about your diet, lifestyle and bad habits. This will help to get an overall picture and partially facilitate diagnosis.
One of my patients tried to be treated for pyelonephritis on his own for a long time, which did not bring the desired effect. The man went to a private clinic and underwent an ultrasound examination, as a result of which it was possible to detect salt deposits in the kidneys and begin specific therapy.
Nephrocalcinosis must be differentiated from the following ailments:
- kidney cancer;
- glomerular pathology (glomerulonephritis);
- inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system.
What methods are used to identify the disease:
- general urinalysis (with nephrocalcinosis, blood cells, epithelium and casts are detected, as a result of which the urine acquires a brick tint and becomes cloudy);
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys (the images reveal stretching of the collecting system and the presence of pathological formations);
Ultrasound also allows you to determine changes in the structure of the organ
- plain radiography of the abdominal cavity (calcifications are X-ray positive stones, so they are visible on the images).
The image shows bilateral deposition of calcifications
Diagnostic methods
Calcifications in the kidney parenchyma are foreign inclusions that lead to various diseases of the urinary and other organs.
Therefore, it is necessary to consult a urologist in a timely manner to examine the kidney tissue in detail. He conducts a medical history and prescribes an examination:
- laboratory tests of urine and blood for levels of parathyroid hormone and vitamin D;
- instrumental diagnosis of calcifications and formations in the kidneys (ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging).
Various ways to get rid of the disease
If the patient is in satisfactory condition, treatment of nephrocalcinosis can be carried out at home. The patient is prescribed a special diet, as well as the use of medications. To assess the general condition of the body and the dynamics of the pathological process, it is necessary to regularly see a doctor and undergo tests. In case of a more severe and life-threatening course of the disease, the patient is hospitalized in the urology department and prepared for surgery. In this case, you also need to adhere to proper nutrition and drink more fluids. During the recovery stage, the victim is prescribed regular visits to physical therapy and therapeutic exercises.
It is extremely rare to completely get rid of nephrocalcinosis. Most patients have minor residual effects after completion of treatment.
Main goals of therapy:
- normalization of urine outflow;
- prevention of infectious complications;
- protection against relapse;
- stabilization of blood pressure levels;
- reducing the severity of pain;
- removal of excess fluid from the body.
Table: use of medications to combat nephrocalcinosis
| Name of drug group | Main active ingredients and preparations | Effects of the appointment |
| Diuretics |
| Prevents the formation of edema, removes water accumulated in tissues from the patient’s body, and indirectly reduces blood pressure |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Relieves pain in the lumbar region; if necessary, can be used as an antipyretic |
| Detoxification solutions |
| Restore water-salt balance and remove toxic substances from the bloodstream |
| Antihypertensive drugs |
| Normalize blood pressure levels, promote relaxation of the vascular wall |
| Immunostimulants |
| Protect the body from the penetration of bacterial, viral and fungal microflora by increasing the activity of bone marrow cells responsible for the immune system. |
Photo gallery: drugs for the treatment of pathology
Polyoxidonium strengthens the immune system
Lorista normalizes blood pressure
Veroshpiron removes excess fluid
Reopoliglucin cleanses the blood of toxins
Dietary recommendations for patients with nephrocalcinosis
To get rid of unwanted manifestations of the disease and ensure the prevention of the appearance of new formations in the kidney tissue, doctors advise carefully monitoring the quality of food consumed. Most calcium enters the systemic circulation with food: therefore, you need to limit some foods. All dishes should be boiled, stewed or baked so that they retain as many vitamins as possible.
Drink at least 2 liters of clean water throughout the day. Mineral water, soda and packaged juices should be excluded: the additives they contain can provoke the growth of calcifications and their compaction.
What should be excluded from the diet:
- sesame and garlic;
- hot spices;
- dairy products;
- bakery products;
- coffee and strong black tea;
- nuts (especially almonds);
- chips and crackers.
Photo gallery: junk food for patients with nephrocalcinosis
Dairy products contain a lot of calcium: their consumption should be limited
Chips contain a lot of salt
Coffee increases blood pressure
What to add to your daily diet:
- porridge and cereals;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- homemade berry fruit drinks;
- lean soups;
- lean meat and fish;
- honey.
Photo gallery: healthy food
Cereals are rich in healthy carbohydrates
Berry fruit drinks remove toxins from the body
Vegetables and fruits are the best source of vitamins
Physiotherapy for nephrocalcinosis
To quickly restore kidney function, doctors resort to physiotherapy. They are indicated for almost all patients suffering from nephrocalcinosis for a long time. The course of therapy is selected based on the individual age and gender characteristics of each person. The duration of treatment is determined by the urologist.
Physiotherapy to combat the symptoms of nephrocalcinosis:
- Acupuncture. Thin needles are inserted into certain areas of the subcutaneous fat. This promotes the activation of sensitive nerve fibers, resulting in accelerated healing processes of soft tissues. Do not forget that a specially trained person must carry out the procedure, otherwise damage to blood vessels and nerves may occur.
- Drug electrophoresis. This treatment is carried out even for children, as it is completely harmless to the body. Through a drip system, the patient receives the drug prescribed to him, and at the peak of its concentration, an electric field acts on the body. This promotes faster and more efficient distribution of the drug in tissues.
- Baths with medicinal gases. The patient, under the supervision of a doctor, is immersed up to his neck in water, where he remains for half an hour. This procedure reduces the severity of discomfort, relieves spasm and pain in the lumbar region.
Photo gallery: physiotherapy for illness
Acupuncture stimulates blood circulation
A bath with medicinal gases relieves pain and spasms
Electrophoresis ensures better distribution of the substance in tissues
Therapeutic exercises not only help strengthen the body and help build muscle mass, but also break up venous congestion in the lower half of the body. You can exercise at home (if you have free space and a gymnastics mat) or in the gym with an experienced trainer. Exercises used to strengthen the muscle groups of the lower back and perineum:
- Lie on your back on a gymnastics mat. Stretch your arms along your body, alternately lift your right and left legs at an angle of at least 45 degrees, hold them in this position for about 30 seconds. The recommended number of repetitions is 20 times.
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart. Make consistent bends forward and down, trying to touch your toes or at least your ankles. This will help stretch the necessary muscles. The exercise should be repeated about 10–15 times.
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and your arms along your body. Raise and lower your buttocks until they touch the floor. The recommended number of repetitions is 12.
Video: therapeutic exercises for the kidneys
Surgery to eliminate pathology
If conservative therapy does not bring the expected results within several months, doctors decide on the need for surgical removal of calcifications. The operation is indicated under the following conditions:
- the appearance of an infectious-inflammatory process;
- difficulty in urine flow;
- intense pain syndrome;
- damage to more than 1/2 of the organ by calcifications.
Calcifications may have jagged, sharp edges
Stages of surgery:
- Conducting spinal or general anesthesia and preparing the surgical field. The patient is put into a medicated sleep while the surgeon treats the skin of the lumbar region with an alcohol-containing solution.
- Sequential soft tissue incision. The skin and fat layer are cut, and the muscles are separated using blunt instruments. The damaged kidney is removed into the wound canal and then carefully opened.
- Removal of pathological formations. The surgeon performs an inspection of the organ, at the same time cutting off altered areas of tissue with calcifications. They are sent to the laboratory for further examination, and then kidney plastic surgery and wound suturing are performed. If necessary, a drainage tube is installed to drain the contents.
Folk remedies to combat symptoms of the disease
It is extremely difficult to get rid of nephrocalcinosis at home, since 90% of all cases of the disease require medical intervention. However, natural recipes based on medicinal herbs and plants can also be useful: they help cope with unpleasant symptoms, strengthen the immune system and partially protect against the development of adverse consequences. But do not forget that many folk remedies can cause an allergic reaction: you need to consult a doctor before taking it.
One of my colleagues, who was faced with nephrocalcinosis in her mother-in-law, selected her not only the optimal drug treatment, but also a course of natural recipes. This partially reduced the load on the liver and prevented other toxic effects of pharmaceuticals. For several months, the woman was treated with traditional and alternative medicine, as a result of which she was able to completely get rid of the symptoms of nephrocalcinosis and prepare for surgery to remove pathological calcium deposits.
What folk remedies are used to combat the disease:
- Take a liter of boiling water and throw in 10 grams of oak bark and the same amount of calamus. Leave for an hour, then take a bath of warm water and pour the product into it. Immerse yourself in water up to your waist and spend at least 20 minutes in this position. Oak bark and calamus reduce the severity of pain and swelling. After the procedure, immediately go to bed. You can take a bath only if you are completely sure that there is no inflammatory process, so as not to harm yourself. It is recommended to be treated in this way once a week.
- Place 50 grams of chopped plantain in a saucepan with 1.5 liters of boiling water, cook for about 20 minutes. After cooling, add 6 tablespoons of honey and 20 drops of lemon juice. Drink 1 glass of the product every 4 hours. This helps remove excess calcium from the body, as well as cleanse the kidney tissue of foreign impurities. To achieve the desired result, you need to be treated with this method once every 3 days.
- Pour 2 teaspoons of oatmeal with a glass of boiling water and leave for 24 hours. The next morning, before breakfast, drink the resulting remedy. Oatmeal helps effectively cleanse the kidneys of excess calcium and is also an essential source of healthy carbohydrates. This procedure must be carried out daily to prevent relapse.
Photo gallery: folk treatment of nephrocalcinosis
Calamus reduces pain
Plantain helps cleanse the kidneys
Oatmeal removes excess calcium
Video: kidney therapy at home
Prognosis for recovery and undesirable consequences of nephrocalcinosis
Treatment of the disease lasts on average from 1 to 12 months. The peculiarity of this pathology is that even after surgery, the patient may experience a relapse due to a diet disorder, stress, physical or mental strain, or hormonal imbalance.
Often pregnancy is a provoking factor in women.
Nephrocalcinosis is also characterized by the development of secondary complications that form against the background of impaired renal function. The likelihood of their occurrence is influenced by age, gender, and the presence of congenital pathologies.
Many patients do not realize that the lifestyle choices they make may also contribute to the progression of nephrocalcinosis. One of my patients was successfully operated on, after which the doctors discharged him home, strictly ordering him to follow a diet and give up alcoholic beverages and smoking. Immediately after returning to work, the man decided to celebrate this event with friends over several glasses of beer and eating fatty and fried snacks. This contributed to the development of an acute pain attack in the lumbar region, as a result of which the patient was urgently hospitalized in the intensive care unit, where doctors fought for his life for several hours. It turned out that due to the consumption of large amounts of alcohol and fatty foods, the victim’s postoperative sutures came apart. The man underwent repeated surgery with lavage of the retroperitoneal space. Doctors believe that if the patient had followed all the recommendations, this could have been avoided.
What complications may arise due to nephrocalcinosis:
- vessel damage and massive bleeding;
- development of acute and chronic kidney failure, accompanied by symptoms of uremia (due to deposition of urea and ammonia in the mucous membranes);
- the addition of infection and the development of inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system (pyelonephritis);
- difficulties with conceiving and bearing a child (for the fair sex);
- purulent lesions of the organ: multiple abscesses, phlegmon, kidney carbuncles;
- the occurrence of benign and malignant neoplasms;
- acute disturbances of water-salt balance until the patient falls into a coma;
- wrinkling and death of the kidneys;
- constant need for dialysis (artificial blood purification through the membrane of a special apparatus).
Photo gallery: undesirable consequences of the disease
Purulent foci in the kidney are a sign of generalized development of the infectious process
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the pyelocaliceal system
A kidney tumor often occurs against the background of inflammatory tissue changes
Elimination of calcifications
If small calcifications are detected in the kidneys, the patient will not require complex treatment. However, it is important to listen to your doctor's recommendations. If there is calcification of the parenchyma of the right or left kidney, it will be enough for the patient to get rid of bad habits: stop drinking alcoholic beverages, stop smoking and drink exclusively purified water.
Sources used:
- https://propochki.info/bolezni-pochek/kaltsinaty-v-pochkah
- https://kardiobit.ru/pochki/lechenie/kaltsinaty-v-pochkah-chto-eto-takoe-prichiny-poyavleniya-i-lechenie
- https://vseopochkah.com/bolezni/drugie/nefrokaltsinoz.html
- https://simptom.info/nefrologiya/kalcinaty-v-pochkah
- https://fb.ru/article/410562/kaltsinatyi-v-pochkah-chto-eto-takoe-prichinyi-poyavleniya-simptomyi-diagnostika-i-lechenie
- https://tvoyapochka.ru/prochee/kaltsinaty-v-pochkah
- https://1pochki.ru/mkb/lechenie/kalcinaty-v-pochkah-html.html