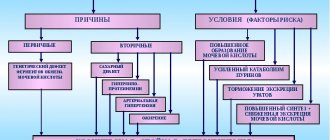
Etiology
The horseshoe bud is thought to form during organogenesis when the lower poles come into contact. The mechanical fusion theory is applicable to kidneys with a fibrous isthmus.
More recent studies suggest that abnormal tissue fusion occurs as a result of a teratogenic event involving abnormal migration of nephrogenic cells that subsequently fuse. The same mechanism may occur in the development of some neoplasias, for example, Wilms tumor.
Predisposing factors:
- previous infections during pregnancy;
- chronic intoxication of the body;
- genetic diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- environmental factor;
- mother's age over 40 years;
- exposure to radiation, etc.
Sometimes there may be several factors, but it is impossible to say which of them led to the development of the anomaly.
Causes of kidney fusion
Causes of kidney fusion - pathological formation in intrauterine development
It is quite difficult to determine the nature of the formation of kidney fusion, however, experts identify the reasons for the formation of pathology. The most common include:
- violation of the acid-base balance, which occurs due to the consumption of food products with GMOs, dirty water, and poor ecology;
- pathological formation in intrauterine development, the kidneys fuse at a period of 8-10 weeks, such an anomaly is caused by an infectious disease suffered by a pregnant woman, the treatment of which was accompanied by the use of chemical drugs;
- Severe bruises can also cause kidney fusion.
Types of pathology
- Asymmetric fusion (connection by opposite poles). The renal pelvis is turned in different directions.
- Disc-shaped fusion (connection by the upper and lower poles, middle parts).
- Galette-shaped (connected only by the middle parts).
The horseshoe kidney is asymptomatic, but due to the anatomical features of its structure, it is predisposed to inflammatory processes. The following also contribute to this:
- blood supply disorders;
- presence of an isthmus;
- abnormal location of the ureters.
All of the above increases the risk of hydronephrotic transformation, urolithiasis, inflammation and some oncological processes.
Narrowing of the ureteropelvic segment is a pathology that occurs in 35% of patients with this developmental anomaly.
Nephrolithiasis in the horseshoe kidney occurs, according to various sources, in 20 - 60% of cases. Urolithiasis develops against the background of hydronephrosis or obstruction of the ureteropelvic segment, which leads to impaired urine outflow and stone formation processes.
The inflammatory process in the horseshoe kidney develops in 27 - 41% of patients. Ascending infection from vesicoureteral reflux is another cause of acute inflammation.
An oncological process in a horseshoe kidney, most often renal cell carcinoma, is sometimes diagnosed, but its incidence is comparable to that in the normal structure of the urinary tract.
Transitional cell carcinoma accounts for 20% of cases, and sarcoma - 7%. The relative risk of developing transitional cell carcinoma increases 3-4 times. A certain role is assigned to long-term disturbance of urine passage, nephrolithiasis and infection.
Wilms tumor and carcinoid tumors are diagnosed more often in patients with horseshoe kidneys. Wilms tumor accounts for 28% of malignant neoplasms. The relative risk is increased by 2 times.
Renal carcinoids are detected much less frequently.
Important
The predominant location of malignant neoplasms is the isthmus.
Almost 35% of patients with a horseshoe kidney do not complain, and the developmental anomaly itself is diagnosed accidentally during an X-ray examination.
Symptoms appear when there are stones, urodynamic abnormalities, or infection.
In children, an infectious inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system is the most common symptom.
The clinical picture of the disease is similar to the symptoms that would be present in patients without the developmental anomaly.
Features of the anomaly
A horseshoe kidney may not manifest itself in any way, becoming a diagnostic finding, but this rarely happens. Typically, all symptoms of pathology that occur in a child or adult are caused by the following features of the abnormal relationship:
- dystopic or lowered position of the organs of the urinary system;
- lack of mobility (due to the peculiar shape and many fixing vessels);
- the fused parts of the kidneys are located in front of the large vascular trunks (aorta, vena cava, iliac arteries);
- with severe dystopia, blood flow through the renal vessels is almost always impaired;
- With any injury, due to immobility, the renal parenchyma is much more damaged.
In most cases, symptoms indicating the presence of a horseshoe kidney are caused by compression of neighboring organs, large vessels or nerve trunks. Immobility of the kidney becomes a serious problem for a person with constant pressure on the inferior vena cava.
Symptoms of a horseshoe kidney
Symptoms can be vague - instead of pain in the lumbar region, pain will appear in the abdomen, and sometimes dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, bloating, distension) occur. In addition to these complaints, pay attention to the following symptoms:
- increased pain in the abdomen during physical activity;
- weakness, fatigue;
- increased blood pressure;
- change in the quality of urine excreted (hematuria, unpleasant odor, turbidity, etc.).
Some patients develop signs of varicose veins due to prolonged compression of the inferior vena cava by the dystopic kidney.
The horseshoe kidney is prone to injury because it does not have rib protection.
Additional developmental anomalies, in addition to the horseshoe kidney, occur in 67% of patients:
- vesicoureteral reflux - 50%;
- duplication of the ureter - 10%;
- hypospadias - 4%;
- pathologies of the uterus or vagina (bicornuate uterus, vaginal septum) - 7%.
There is evidence that there may be developmental anomalies not only in the organs of the urogenital tract, but also in the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and skeletal systems.
Horseshoe kidney is associated with known genetic syndromes, such as Turner syndrome and trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome).
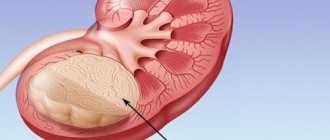
The horseshoe kidney can be located both in the pelvic region and in the middle parts of the abdomen; this localization occurs due to the fact that the isthmus can be fused to the mesenteric artery during the renal rise during embryogenesis. The isthmus, as a rule, is located anterior to the great vessels, at the level of the 3rd - 5th lumbar vertebra.
Kidney shape after fusion
When an organ is united into one whole, it takes on a certain shape.
When an organ is united into one whole, it takes on a certain shape, and the kidney can grow together in several ways. In medicine, there is a certain classification, which includes the following types:
- I-shaped kidney - unilateral fusion;
- biscuit-shaped kidney - bilateral fusion, in which the patient does not feel painful attacks; as a rule, they are located vertically and can fuse in the same position.
For information! An S-shaped kidney refers to a unilateral fusion of an organ that does not have a pronounced symptom complex.
The kidney structure is divided into two types:
- asymmetrical - the organ fuses along the upper poles;
- symmetrical - the organ fuses along the lower poles.
The most complex fusions of organs are lumpy and biscuit-shaped; such fusions are characterized by complete attachment to the internal part.
How to find a kidney recipient and who can become a donor?
Diagnostic tests
With instrumental confirmation of a horseshoe kidney, laboratory tests are performed to assess the functional capacity of the kidneys and identify concomitant pathologies:
- general urine analysis, Nechiporenko test;
- urine culture for flora and antibiotic sensitivity;
- general blood analysis;
- urea, creatinine.
Instrumental diagnostics include CT, MRI, ultrasound, excretory urography, renal arteriography, and radioisotope scintigraphy.
Treatment of pathology and prevention during pregnancy
Correction of the kidney structure and elimination of pathology is performed surgically or conservatively. Conservative treatment includes:
- drug treatment;
- performing preventive procedures;
- Spa treatment;
- dietary food.
The surgical method consists of direct intervention in the human body, however, the main task of this method is to minimize injuries. Kidney surgery is quite complex and requires great practical skills and knowledge.
For information! Nephrectomy is prescribed only if one organ fails.
Surgery
In some cases, the issue of surgical treatment is considered.
In the presence of obstruction of the ureteropelvic segment, pyeloplasty can be performed, which is performed to improve the outflow of urine.
Surgery for a horseshoe kidney is associated with an increased risk of bleeding, fistulas, and renal infarction.
Some patients ask: “Can lithotripsy be used to treat urolithiasis if there is a horseshoe kidney?”
This question cannot be answered unequivocally. Everything is decided on an individual basis, but contraindications to ESWLT are hydronephrosis, concomitant inflammatory process, and stricture.
Surgical treatment depends on the disease process and standard surgical indications. When planning a surgical approach, abnormal vascular supply to the kidneys is examined using angiography . Typically, a midline abdominal incision provides access to both sides of the kidney and vessels.
Important
If there are no concomitant urological diseases or renal failure, surgical treatment is not indicated.
Methods for diagnosing horseshoe anomalies
Diagnostic studies are based on several procedures:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys - ultrasound examination;
- Intravenous pyelography - a contrast solution is infused into the veins, and then, under the influence of X-rays, the genitourinary structures are visualized;
- Cystourethrography – study of the genitourinary tract using X-rays;
- MRI or CT;
- Urine, blood tests, etc. etc.
Based on the data obtained from nephroscintigraphy, urography, echography and aortography, the specialist determines the exact location, limitation of mobility and isthmus. A retrograde pyelographic study allows you to see the low localization of the renal pelvis and the abnormal location of the cup system.
Modern innovative technologies and diagnostic methods make it possible to establish an accurate clinical picture of the anomaly. And with the help of an angiographic study, the condition of the vascular system is revealed; such a procedure often becomes decisive for surgical intervention.
As often happens, in the absence of any manifestations from the horseshoe renal anomaly, there is no need for treatment. But if the pathology is complicated by any additional abnormal processes, then they resort to diagnosis and treatment.
Indications for surgery
Surgical intervention is used in the following cases:
- Obstruction of the ureteropelvic junction. Obstruction of the ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) is usually treated with an open approach. It should be noted that data have emerged on robotic pyeloplasty using the da Vinci surgical system, but so far its success rates are lower than with open operations.
- Stones in the kidneys. Kidney stones can be treated with external shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), endoscopy, or open surgery.
- Treatment decisions and indications are similar to those for normal kidney. The presence of obstruction or hydronephrosis excludes ESWL. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy with endopyelotomy is successfully used for urolithiasis due to obstruction.
Important
Studies have been conducted that have shown that with a horseshoe kidney complicated by nephrolithiasis, it is possible to use endoscopic interventions (percutaneous nephrolithotomy, ESWLT), but there is a possibility of repeated manipulations. The success rate of interventions is about 67%.
- Kidney transplant. A horseshoe kidney can be used for transplantation. It can be transplanted into one recipient or divided into two. Isthmus separation increases the risk of urinary fistula formation.
Important
We are talking about transplanting a functional organ, without other urological pathologies.
- Loss of function of one of the kidneys. After an examination in which the function of one of the fused kidneys is absent, or there is significant hydronephrotic transformation, heminephrectomy is performed.
- Kidney tumor. The peculiarities of the blood supply to the horseshoe kidney complicate surgical intervention to remove tumors. The choice of access in each case is determined individually. The principles of the operation are similar to those for conventional kidneys, but whenever possible, organ-sparing surgery is preferable.
A horseshoe-shaped kidney without dysfunction and in the absence of inflammation or stones does not complicate pregnancy or childbirth . It is important to note that the presence of an abnormal kidney alone does not affect the length and quality of life. But, since there is a risk of complications, the prognosis depends on the background pathological process or its absence.
Periodic renal ultrasound examinations in children with horseshoe kidneys are used for early detection of Wilms tumor. Dynamic ultrasound in adults may also be useful, especially in patients with hydronephrosis.
If horseshoe kidney is diagnosed in adulthood, and there is no previous urological history, there is nothing to worry about. In this case, it is necessary to undergo an examination and tests to ensure the normal function of the urinary organs.
How to live with a horseshoe kidney
It is necessary to exclude spicy, sour, salty, smoked, and marinades from the diet.
You should visit a urologist for a preventive examination 2 times a year.
In spring - autumn, uroseptics (Palin, Furomag, 5-NOK) are taken for preventive purposes in 10-day courses and herbal medicines (Canephron, Fitolysin, etc.). It will not be superfluous to avoid hypothermia, lifting heavy objects, it is important to exclude activities in those sports where it is possible to receive a direct blow to the abdominal area.
Mishina Victoria, doctor, medical columnist
just today
( 60 votes, average: 4.90 out of 5)
Interstitial cystitis - symptoms and treatment
Kidney cancer: first symptoms, stages, treatment, prognosis