Kidney adenoma is a benign disease. In most cases, it is small, does not create problems in the functioning of organs and does not manifest itself in any way.
In case of growth or large size, there is a risk of disruption of the affected tissues and the formation of oncological pathology, therefore, in this case, surgical removal of the pathological focus is required. As a rule, therapy is successful, relapses are rare.
Kidney adenoma
Causes
The real causes of the tumor remain unknown today. However, numerous cases of the disease are systematized by pathological anatomy, on the basis of which certain statistics are built. Thus, there are a number of factors that can affect the process of tumor development:
- Smoking. It is among smokers that adenoma occurs most often.
- Contact with chemicals. Constant interaction with chemicals, for example, in hazardous industries, can contribute to the development of various tumors.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Presence of chronic diseases. Pyelonephritis, polycystic disease and other kidney diseases can have a significant impact on the occurrence of other diseases. This occurs due to a decrease in the functionality of the organ and changes in tissue structure.
- Age-related changes. Kidney adenoma in men is more common than in women. This is especially true for men whose age exceeds 40 years.
Despite the fact that the disease most often affects older people, the development of oncology can also occur in children. Thus, the metanephrogenic blastema, responsible for the formation of kidneys, gradually disappears even during the embryonic development of the fetus. But in rare cases, part of it remains functional, resulting in the formation of a nephrogenic area. Such a place is considered to be at increased risk of developing cancer. The adenoma itself is not life-threatening.
An increase in its size is dangerous, which increases pressure on the kidney tissue, ureter and blood vessels. In addition, patients should be wary of the adenoma developing into cancer.
What it is?
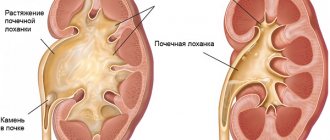
Kidney adenoma is a benign tumor . It is characterized by slow growth, clearly defined edges and dense consistency. Its diameter varies from 1 to 30 millimeters.
The neoplasm is a single tumor in the superficial layer of the kidney.
Often damage occurs in only one organ. The structure resembles a malignant formation of glandular cell carcinoma. This disease develops in several stages:
- Initiation. Disruption of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid under the influence of external factors. This provokes a disruption in cell division.
- Promotion. Changes in the structure of cells, their uncontrolled division.
- Progression. Tumor growth in kidney tissue.
There is an opinion that this type of tumor is a precancerous condition. However, research does not confirm this.
The following forms are distinguished depending on the structure of the tumor:
- acinar;
- solid;
- cystic;
- tubular;
- trabecular;
- papillary.
According to statistics, adenoma occurs in 10% of the population ; middle-aged people are most susceptible to it, women to a lesser extent.
Symptoms
The course of the disease is rarely marked by any signs, especially in the initial stages. The tumor sends its first warning signals only when it significantly increases in size. With kidney adenoma, the following symptoms are possible:
- The appearance of blood in the urine. Blood impurities can be so minor that it is difficult to notice on your own. The color of the urine rarely changes, but sometimes it may become a little richer.
- Pain during urination.
- Increased blood pressure. Blood pressure may remain constant or rise intermittently.
- Stitching pain in the lower back. This symptom is caused by the pressure that a large tumor puts on the blood vessels. Typically, such discomfort leads the patient to be examined by a doctor. If a person is diagnosed with an adenoma of the right kidney, he is bothered by pain in the right lumbar region, and vice versa.
- Renal colic. The pain is usually pronounced and intense. The pain may radiate to the groin or abdominal area.
- The appearance of edema in the extremities.
All of these symptoms are not unique and are characteristic of many diseases. Therefore, it is possible to detect the presence of an adenoma only with the help of special diagnostics.
Prevention
The formation of adenoma, like other kidney diseases and tumors, is provoked by bad habits, unbalanced nutrition, closed organ injury, hypothermia and other factors. Therefore, the recommendations of specialists for tumor prevention boil down to the following:
- Abstinence from smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Diet : exclude fatty foods with a high protein content. Be sure to include watermelon, grapes, pumpkin and its seeds, cranberries, and bee products in your diet. Oatmeal and wheat porridge will have a beneficial effect;
- Elimination of water deficiency in the body . You need to consume high-quality liquid in sufficient quantities (at the rate of approximately 35 milliliters per kilogram of weight);
- Periodically cleanse the kidneys with kidney teas and diuretic herbs;
- Physical exercise , especially in the lumbar and hip area, will improve blood flow in this area;
- Avoiding hypothermia , because only heat helps increase blood flow to organs, and therefore improves their functioning;
- Timely treatment of kidney diseases , preventing their transformation into tumor growths.
To identify and treat adenoma in the early stages, it is necessary to undergo an annual ultrasound examination, this is especially true for men who are over 40 years old.
Which doctor should I contact?
Treatment of adenoma is usually carried out under the supervision of a nephrologist. In some cases, for example, when blood appears in the urine, joint work with a urologist is necessary. If the development of the tumor has continued for a long time, and the attending physician suspects cancer, a consultation with an oncologist is necessary.
Forecast
Adenoma, as a benign neoplasm, does not affect kidney function. When large in size, it can put pressure on nearby tissues. The prognosis for recovery with such a growth is positive and amounts to 95%.
When an adenoma of benign origin transformed into a malignant one and was surgically removed, then, taking into account its nature, rate of formation and metastasis, there was a 53% survival rate over a 5-year period and 43% over a 10-year period.
During this period, the occurrence of relapses is minimized. Strict adherence to preventive measures and constant monitoring by a urologist ensure a lasting therapeutic effect.
Diagnostics
If a patient is seen unintentionally, the development of a neoplasm is usually discovered by chance. This often happens during a kidney ultrasound procedure. However, at high magnification, the tumor can be obvious even with normal palpation. To diagnose the disease, the following procedures are performed:
- Blood analysis. The patient's hormone levels are checked if the doctor suspects problems in the renal cortex or adrenal glands.
- General urine analysis. Able to show the functioning of the entire genitourinary system and indicate an excess of red blood cells in the body.
- Ultrasound. A more accurate diagnostic method. Thanks to the study, you can see the size of the tumor, determine its exact location, and also assess the damage to neighboring organs.
- Computed tomography to detect renal adenoma. CT helps to see the tumor layer by layer and note even minor changes in tissue. Thanks to this procedure, it is also possible to trace the presence of metastases.
- MRI. Usually used if the patient has contraindications for CT scanning. The study helps to see the location of the tumor, the size and consequences of its presence in the body. Prescribed if there are contraindications to CT. Helps determine the degree of damage to adjacent organs.
- Biopsy. It is carried out to determine the benign quality of the existing tumor. A tissue fragment is torn from the growth and sent for histology, which reveals the nature of the disease.
Not all of these methods are used for diagnosis, but a biopsy is considered mandatory before any surgical intervention.
What causes tumor formation?
The causes of adenoma are not fully understood. But there are factors that influence the development of the tumor:
- smoking;
- development of the initial stage of renal cell cancer;
- drinking alcohol in large quantities;
- the presence of junk food in the diet;
- reducing the amount of fluid you drink per day.
Return to contents
Sources used:
- https://orake.info/adenoma-pochki/
- https://kistateka.ru/pochki/adenoma-pochek
- https://fb.ru/article/391614/adenoma-pochek-simptomyi-diagnostika-i-lechenie
- https://prourinu.ru/zabolevaniya/novoobrazovaniya/adenoma-pochki.html
- https://kcson-sp.ru/adenoma-pravoy-pochki-u-zhenschin-simptomy-lechenie.html
- https://opochke.com/nefrologiya/adenoma.html
Treatment
Growths up to 3 cm in size are considered small, so they are usually suggested simply for observation. If no further development occurs, the neoplasm is left without specific treatment. However, in cases where the size of the tumor rapidly increases, the patient will have to be treated more actively. The main direction of treatment for kidney adenoma is surgery. There are two main methods of therapy:
- Partial resection is an operation to remove part of an organ and affected tissue with an existing tumor.
- Complete resection (nephrectomy) - during the operation, the entire organ is removed, after which the patient receives supportive care.
It is recommended to completely remove the kidney only in the case of a large adenoma that has managed to cause significant damage to the kidney tissues and neighboring organs. Surgical intervention can prevent the process of magnetization and the occurrence of metastases. Kidney adenoma in women can cause additional concerns. Sometimes growths can also appear on the adrenal glands, which are responsible for hormonal balance. In this case, the woman will need to additionally correct her weight, skin, blood pressure and, of course, hormonal levels.
Clinical picture
Symptoms will vary greatly depending on the location of the tumor. The adenoma itself cannot cause pain or discomfort - so the patient may not be aware of it for many years. Then the tumor reaches a large size and begins to compress tissues, blood vessels, branches of nerves and the urinary tract.
Clinically this is expressed as:
- pain or discomfort when urinating (feeling of incomplete emptying, excessive tension of the peritoneum);
- causeless pressure surges or stable increases (“renal” hypertension);
- lower back pain caused by compression of blood vessels and nerves. The intensity of the pain syndrome “grows” along with the pain;
- colic - circulatory disorders of the kidney with unbearable pain in the lower back, radiating to the diaphragm or groin, pubic area or inner thighs. Colic can last from a few minutes to a day;
- darkening/clouding of urine;
- hematuria - from noticeable inclusions of blood in the urine to microinclusions detected during laboratory testing;
- proteinuria – loss of protein in the urine;
- reducing the daily volume of urine excreted;
- swelling of the face and limbs;
- signs of intoxication (nausea, fever).
In men, kidney adenoma is often accompanied by testicular varicose veins.
Pain in the absence of other signs is characteristic of the early stages of the tumor.
Often, symptoms are completely absent until the tumor becomes malignant.
How to treat kidney adenoma with a folk remedy
As additional help to the body, you can try traditional medicine. For these purposes, herbal medicine has proven itself well, suggesting combining different herbs. Among them:
- containing many vitamins: rowan, rose hips, black currant;
- good for the kidneys: bearberry, birch buds, strawberries;
- having a calming effect: mint, lemon balm.
The recipe for making the decoction is very simple. Take a few herbs and pour 2 tablespoons into 0.5 liters of hot water. After this, keep the liquid in a closed container or thermos for 1.5-2 hours. The resulting product should be strained and drunk before meals several times a day.
general information
Kidney adenoma is a benign neoplasm; it has a dense consistency and clear outlines. It is characterized by slow growth, as a rule, sizes vary from 0.2 cm to 3 cm.
Unfortunately, for a long time the symptoms of the disease are completely absent, and later the adenoma has the ability to degenerate into a malignant tumor; such suspicion arises if the tumor size exceeds 3 cm.
The disease is usually diagnosed in people over 40 years of age, and the male population suffers from the pathology three times more often than the female population. As a rule, the pathology affects one kidney, but two at the same time is very rare.
Among all renal tumors, adenoma accounts for about 8% of all tumors.
The disease is classified depending on the histological structure of the tumor, and the type of formation determines subsequent treatment tactics. There are three types of adenoma:
- clear cell;
- metonephrogenic;
- oncocytoma.
When examining a tumor under a microscope, histologists note the similarity of its cellular composition with adenocarcinoma, which is why some doctors call adenoma a precancerous condition.
The true causes of the disease are unknown. Doctors call the following provoking factors for the development of pathology:
- poor nutrition;
- nicotine addiction;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- organ trauma;
- endocrine disorders;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- polycystic disease;
- constant interaction with toxic substances.
Urologists also point to a genetic factor as the cause of the disease.
Complications
The consequences of the development of adenoma, as a rule, occur with untimely treatment, when the disease has progressed greatly. Possible complications include the following pathologies:
- Inability to urinate independently. At the same time, the bladder is greatly stretched, causing the patient significant pain. In this case, the patient needs a catheter.
- Urinary tract infection. May result from stagnation of urine in the bladder.
- Bladder stones. They are also formed due to prolonged standing of urine and its subsequent infection. All this causes the precipitation of salt, which gradually turns into stone.
- Deterioration of the bladder. Without proper urination, the walls of the organ gradually weaken and stretch due to constant tension. As a result, the ability to contract decreases, and the bladder holds urine less well.
- Changes in the kidneys. Long-term stagnation of urine can provoke hydronephrosis, as a result of which the kidney tissue becomes thinner.
- Cancer.
It is possible to prevent the onset of undesirable consequences by promptly consulting a doctor.
Video: Resection of renal adenoma
What is the danger?
Despite the slow growth of tumor formation and the gradual progression of the disease, you need to understand that as its size increases, normal organ tissue will be increasingly affected.
As a result, renal dysfunction is observed, increasing in parallel with the diameter of the tumor focus.
In addition, it should be emphasized that the morphology of adenoma is similar to renal cell carcinoma, on the basis of which some scientists consider it a precancerous process.
Considering this fact, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor when the first signs of kidney damage appear.
Methods of therapy
The choice of treatment method depends on the diagnostic results, that is, on the nature and size of the kidney adenoma and the general condition of the patient.
If its size is no more than 3 cm and it grows slowly, then surgical intervention can be postponed. The patient will remain under the doctor's supervision to monitor the growth of the adenoma.
Conservative methods
Kidney adenoma cannot be treated with medications, since there are no drugs that could resolve the tumor or stop its growth.
Drug therapy can be symptomatic or be a preparatory step for surgery.
The decision to undergo surgical intervention is made if the formation grows too quickly and has a negative impact on neighboring tissues and organs, or tends to transform. The operation can be performed using several methods.
Laparoscopy - the adenoma is removed through a small hole in the peritoneum or pelvis. This type of operation is minimally invasive and gentle, it allows you to maintain the integrity of organs and systems and does not leave scars. Patients recover quickly and are discharged from the hospital after 5-7 days.
Classic resection - during this operation, the adenoma and affected tissue are removed through a deep incision, a scar appears at the site of the operation, the patient needs the help of medical personnel for the first few days.
Nephrectomy – performed in severe cases, if the neoplasm has reached a large size and degenerates into a malignant formation.
When choosing a method of surgical intervention, the doctor tries to preserve the organ as much as possible, therefore, during the operation, as much healthy kidney tissue as possible is isolated and preserved.
If, after surgery, histology shows the presence of cancer cells, then the patient undergoes radiation and chemotherapy
Relapses of the disease occur extremely rarely.
ethnoscience
There are no effective traditional methods for treating renal adenoma.