What is a disease?
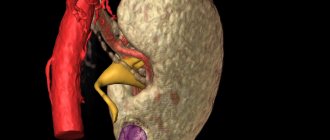
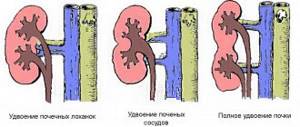
Spongy kidney belongs to the category of cystic diseases, since the tissue of the organ is damaged by the formation of a large number of cysts. Their diameter is small - from 1 to 5 mm. However, closer to the center of the organ there are also larger ones, the size of which reaches 7.5 mm. The appearance remains the same: regular structure, smooth edges and healthy solid color, but the size is slightly increased. Pathology is found in the area of the Malpighian pyramids and urinary tubules, which greatly expand, thereby creating cysts. They do not accumulate in one place, but are scattered throughout the organ and filled with dead cells, fluid, sand and stones. The name of the disease appeared due to the resemblance of the damaged organ in cross-section to a sponge with small pores.
Description of the disease
Spongy kidney is a pathology that is usually bilateral. Cysts can affect the renal papillae to varying degrees. Unlike polycystic disease, the spongy kidney has a regular shape, its surface is smooth, and its contours are clear. In a section of the affected kidney, one can see dilated terminal tubules and many small cysts with cavities in the pyramids.
The diameter of the cysts varies between 1-5 mm. The increase is directed towards the center. Inside the formations there is a transparent yellowish exudate (if they are not inflamed), calcium stones or grains of sand, and desquamated cells. Small pebbles from cysts can be washed out and enter the collecting system.
The tissues in the pyramidal region mainly have a dense structure and fibrous changes. If the anomaly is accompanied by pyelonephritis, changes associated with the inflammatory process appear. Due to stasis of urine, the renal parenchyma becomes overgrown with calcium salts, which settle in the cystic cavities, and a secondary disease develops - nephrocalcinosis.
For a long time, with a spongy kidney, the organ functions normally. Disruption of its functioning usually occurs in the event of an infectious process, stone deposition, or deterioration in the capacity of the upper urinary tract.
Find out about the causes of flakes in the urine in women and the treatment of possible diseases.
Read about how to collect a urine test for a three-glass sample and how to interpret the results on this page.
What are the causes of spongy bud?
Medullary spongy kidney is often hereditary, but it cannot be said that a child will definitely inherit it.
The appearance of the disease is characteristic of the last stages of fetal development in the womb, when kidney formation occurs. At this time, cysts begin to appear in the kidney tissue, as a result of a failure or anomaly in the development of the embryo. Later, after birth and in the first months of life, the tubules expand, the defect provokes inflammation. As a rule, diagnosis is impossible in childhood due to the latent and quiet course of the disease. At approximately 30-40 years old, the first “bells” appear.
Sponge kidney: what are the chances of a favorable prognosis?
Unlike most other renal pathologies, spongy kidney is a disease that always appears at the stage of intrauterine development.
Despite this, after the child is born, the symptoms and consequences of such an illness may not appear in any way, and the pathology can only be diagnosed in adulthood.
What it is?
In a normal state, the kidney tissues in cross-section are dense structures. When diagnosed with “spongy kidney” (ICD-10 code – Q61), the organ has a spongy, porous structure. This pathology is also called cystic kidney disease or medullary kidney .
In the human kidneys there is a medullary (medullary) substance, which, due to certain disorders begins to grow , and this leads to the expansion of the renal tubules. As a result, cysts appear in the organ in the area of the Malpighian pyramids.
The functions of the kidneys are not impaired, and externally the organs look healthy and do not change either size or color.
The resulting cysts are filled with fluid and dead cells; deposits in the form of sand or calculi can also accumulate in such cavities, which, when subsequently entering the renal pelvis, turn into stones . Some cysts may eventually merge into one formation.
Why is this dangerous?
The disease develops over a long period of time and in the first years there may be no alarming symptoms at all. Diagnosis is also complicated by the fact that external disorders in the kidney tissues practically do not appear. When the disease can be identified (and this can happen at the age of 20, 30 years and later), treatment becomes problematic.
If left untreated, the pathology can cause the following serious complications :
- The development of inflammatory processes that can spread not only to the kidneys, but also to other internal organs.
- Urolithiasis disease. This pathology develops due to the fact that, with a spongy structure, the kidney tissue better absorbs toxins and harmful deposits, which subsequently form pathogenic formations in the form of stones.
- Kidney failure.
Such consequences arise in the absence of treatment or in case of untimely contact with a nephrologist. In other cases, treatment prognosis is favorable.
Causes of the disease
Medullary kidney is a congenital pathology that is inherited, but this does not always happen: often, even if both parents have such a disease, the disease may not be transmitted to the child.
The main cause of a spongy kidney is considered to be a failure at certain stages of embryo development. The risk of developing the disease increases with a renal abnormality such as dilated tubules.
Symptoms
Clinically, such a disease may not manifest itself for many years, and some signs of pathology can be detected in people in the age range of 20-40 years, and, as a rule, the disease makes itself felt by developing complications. Experts include common signs
- the presence of purulent discharge in the urine;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- attacks of dull or sharp pain in the lumbar region;
- deposition of calcium salts in the parenchyma (nephrocalcinosis), manifests itself in approximately half of the cases;
- in rare cases, death of the parenchyma as a result of purulent melting.
The presence of a spongy kidney can also be determined during an examination: when performing diagnostics, cysts up to 5-7 millimeters in size , which are located in the central region of the kidneys.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis of “medullary kidney” or excluding it is possible only after performing the following diagnostic procedures :
How to treat?
As long as the disease is asymptomatic and is not accompanied by the development of complications, no specific treatment is prescribed, but the patient is prescribed to follow preventive recommendations that eliminate the development of consequences.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, drugs are prescribed to eliminate disturbances in metabolic processes and treat secondary associated infections affecting the urinary tract.
Basically, with a spongy kidney, associated pyelonephritis is observed. In such situations, the patient is recommended to limit the consumption of foods containing calcium, and prolonged antibacterial therapy is additionally prescribed.
If the disease is advanced and the patient develops urolithiasis, conservative therapy may be powerless and nephrostomy .
In case of complicated unilateral organ damage, nephrectomy (removal of the diseased kidney) may be necessary, but this happens extremely rarely. Of the surgical treatment methods, the most commonly used method is resection , in which individual areas where foci of cystic deformation develop are removed.
If the disease is diagnosed in time and regularly examined for the development of symptoms, we can talk about favorable prognosis for treatment.
The disease may not manifest itself in any way throughout life and may not affect health. But if a spongy kidney makes itself felt, immediate contact with specialists is required to exclude complications and the development of irreversible processes in tissues.
How the kidney resection operation is performed - watch the video:
Source: https://opochke.com/nefrologiya/kista/gubchataya.html
Symptoms caused by internal pathologies
The pathology may be complicated by pyelonephritis.
A spongy kidney is considered a benign phenomenon that does not cause significant deviations in the functioning of the organ. However, the presence of an anomaly in the body leads to diseases such as pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), accumulation of sand and stones, kidney failure, as a result of which the following symptoms appear:
- colic in the kidneys;
- the presence of blood, pus and leukocytes in the urine (hematuria, pyuria, leukocyturia);
- aching constant pain in the lumbar region;
- cystitis and difficulty urinating;
- urolithiasis disease;
- increased body temperature and blood pressure due to inflammation of the kidneys and bladder.
Symptoms
In children, the medullary spongy kidney does not manifest itself in any way; the disease is latent and is discovered either when complications develop, or becomes an accidental finding during a kidney examination. Most often, the disease makes itself felt in patients aged 40 to 50 years with the following manifestations:
- hematuria – the presence of blood in the urine;
- pyuria - detection of pus in urine;
- dysuria - a violation of the process of urine excretion;
- renal colic, which occurs when stones penetrate the pelvis or calyx of the kidney;
- constant aching pain in the lumbar region;
- increase in body temperature due to associated infection
Such symptoms indicate that a urinary tract infection has been added to the congenital pathology. Sometimes a doctor may suspect the presence of a spongy kidney in a patient with long-term recurrent stone formation. In the event of a secondary infection or stones entering the cavity of the renal pelvis, its function is impaired, which requires constant medical supervision and urgent hospitalization.
More than half of all patients diagnosed with medullary spongy kidney have concomitant papillary nephrocalcinosis, which manifests itself in a large number of small stones distributed throughout the renal parenchyma, which is clearly visible on x-ray.
Nephrocalcinosis on radiograph
Diagnosis of the disease
Detection of the disease is also possible by chance, during a routine examination in a hospital. But standard tests are not enough to diagnose congenital pathology. The doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis of “spongy kidney” only after a complete urological examination, which includes the mandatory tests and procedures outlined in the table below:
| Type of diagnostic event | What determines? |
| Excretory urography | Accurately shows the presence of cysts and the width of the tubules |
| Ultrasonography | Does not show microcysts, but ultrasound clearly shows the general condition of the organ structure |
| Laboratory research | Provide information about foreign elements in blood and urine |
| Tomography with contrast agents | Makes it possible to see disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys |
Diagnostics
In addition to the traditional ultrasound of the kidneys, which, by the way, is not always informative in the case of such a diagnosis, the patient must undergo a series of studies that help the doctor accurately determine whether the cystic formation in the kidneys is a medullary spongy kidney.
The examination includes:
- Excretory urography as the main method for diagnosing spongy kidney. When a contrast agent is injected, cystic cavities in the form of clusters and dilated tubules are clearly visible in the structure of the kidneys.
- X-ray. This type of study is mainly used in the presence of stones or complications such as nephrocalcinosis.
- Computed tomography used to select the area where tissue will be taken for histological examination, as well as in the case of possible surgical intervention for the purpose of postoperative monitoring.
- Blood and urine tests to help identify pyuria, hematuria, hypercalciuria.
Treatment of a spongy paired organ
As a rule, nephrologists do not treat the pathology itself, since it does not provoke malfunctions of the kidneys.
A surgical solution to the problem is possible in case of serious complications of the disease, that is, renal colic, stones and pyelonephritis. In case of ineffectiveness of drug treatment and frequent recurrences of inflammation, a decision is made to remove it to prevent the disease. At earlier stages, in case of disturbances in the functioning of the bean-shaped organ, basic therapy is prescribed in the form of drinking large amounts of water, using diuretics, and a diet low in calcium.
Treatment
Treatment for spongy kidney is not required in the following cases:
- asymptomatic;
- no complications.
If the first symptoms appear, then the prescriptions are based on:
- diet low in calcium - you should reduce the consumption of milk, cottage cheese and other dairy products;
- drinking in sufficient quantities - to stimulate urine formation and sufficient passage of urine in the kidneys (to prevent urinary stagnation);
- Antibacterial therapy - to prevent the addition of an infectious agent.
Surgical treatment methods can also be used, namely:
- nephrostomy - the formation of an artificial connection between the renal pelvis and the external environment to facilitate the outflow of urine. It is used if the spongy kidney is complicated by urolithiasis or pyelonephritis, as well as in cases where the effectiveness of conservative treatment does not live up to expectations;
- resection (partial removal) of the kidney - practiced if the cysts have grown to such an extent that they deform the kidney;
- in the presence of stones - pyelolithotomy (dissection of the calyces and pelvis, removal of stones), nephrotomy (dissection of the kidney parenchyma, removal of stones), various methods of crushing stones (lithotripsy) with their subsequent removal from the kidneys;
- nephrectomy (kidney removal) - rarely performed, indicated in case of massive damage to this organ and provided that the other kidney is healthy.
Signs of the disease
The main manifestations are:
- Dull or sharp pain, which can be aching or paroxysmal.
- The appearance of blood in the urine (micro- or macrohematuria).
- The addition of a pronounced inflammatory process in the form of pyelonephritis leads to the detection of pus and epithelial cells in urine. Body temperature may rise.
Colic develops when small stones begin to migrate into the pelvis and calyces. This is accompanied by the development of inflammation, fever, and difficulty urinating. Cases of hypertension with spongy kidney are no more common than with other
A severe form of the disease develops rarely, occurs during a long-term infectious process, resulting in purulent melting of the kidney parenchyma, and chronic renal failure develops.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with kidney tuberculosis and papillary necrotic changes.
Complications and consequences
The most common complications observed are:
- stones in the cavity of renal tubular cysts;
- acute urinary retention, it is formed as a result of blocking the urinary tract with stones formed in the kidney tubules;
- pyelonephritis in acute and chronic phases;
- chronic renal failure - characterized by impaired renal function of varying degrees;
- renal encephalopathy - pronounced disturbances in the functioning of the brain resulting from the toxic effects of the breakdown products of residual urine that is not excreted;
- renal coma - loss of consciousness is observed as a result of intoxication of the body.
Causes
A number of medical studies have confirmed the fact that a spongy kidney, which may have a pattern of abnormal development even at the stage of intrauterine development, is very similar in its etiology to polycystic kidney disease. The manifestation of the disease is often caused by both late disruptions of embryogenesis and significant changes in the renal collecting ducts already during the postnatal period. At the same time, the heredity of the disease has been scientifically proven, but the type of heredity itself in many cases is sporadic.
Colic is one of the main manifestations of the disease
Treatment and prognosis
Therapy for such a renal anomaly is not carried out due to the lack of symptoms. The main therapy should be aimed at preventing or eliminating complications and exacerbation of the formation of stones or pyelonephritis. In the treatment of inflammation, they resort to well-known methods, however, treatment with antibacterial agents does not always bring results, as a result of which therapy can take a very long time. Sponge kidney without complications practically does not appear and, therefore, treatment is not necessary. But a person with identified renal deformity should be systematically observed by a doctor and carefully monitor his internal state.
Therapy with surgical intervention is recommended when large stones form or pyelonephritis lasts for a long time, then, if treatment is ineffective, nephrostomy is prescribed; if partial cystic deformations are detected on ultrasound, the deformed area is removed; if there is regular movement of stones, nephrolithotripsy, nephrolithotomy and pyelolithotomy are used. Positive results are shown by the elimination of deforming parenchyma. The absence of complications is a positive prognosis for spongiform renal anomaly. However, to prevent the diagnosed pathology, a special diet is recommended, which includes foods with low calcium levels, sufficient fluid intake, and in some cases it is prescribed to take thiazide diuretics.
Source: EtoPochki.ru
How is the treatment carried out?
The asymptomatic course of the disease in the absence of complications does not require treatment. Therapy is aimed only at eliminating and preventing stone formation and inflammatory phenomena. Possible treatment measures:
- Therapeutic diet with limitation of salty, fatty, fried, spicy foods, foods with calcium to reduce the load on the kidneys.
- Consume only clean, high-quality water.
- Taking diuretics to eliminate edema and normalize blood pressure.
- Taking antibiotics, uroantiseptics, herbal preparations for pyelonephritis.
Lithotripsy or surgery is prescribed for the formation of kidney stones. Nephrostomy is done when treatment of pyelonephritis is ineffective. Local areas with cysts need to be removed. A person diagnosed with a spongy kidney should be regularly monitored by a doctor in order to detect complications in time and completely eliminate them.
General information about the disease
Unfortunately, quite often the pathological process is diagnosed late, which is explained by the absence of impairment of the functional capacity of organs over a long period of time.
There are cases of carriage of this anomaly for several years; the disease manifests itself only after the addition of concomitant pathological conditions, for example:
- infectious process;
- rapid formation of stones;
- deterioration of the patency of the upper segments of the urinary tract.
As for children, this pathological condition manifests itself in rare cases, because it has the ability to occur in a latent form.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you experience pain in the lumbar region, cloudy or red urine, or signs of urinary disturbances, you should consult a nephrologist. After conducting a line of research (excretory urography, CT, MRI, radiography, blood tests, urine tests, etc.) and if a medullary kidney is suspected, the doctor will refer the patient to a urologist for further observation or treatment.
With a medullary spongy kidney, the dense structure of the renal material changes to porous, in cross section it looks like a sponge. These changes result in the formation of many cystic cavities with liquid contents in the kidney. This pathology is congenital and often affects both organs. For a long time or throughout life, the anomaly may not manifest itself in any way, but in a number of cases its course leads to the occurrence of inflammatory processes (pyelonephritis) and urolithiasis, which significantly aggravate the patient’s condition and subsequently can lead to the development of many serious consequences - chronic renal failure, renal encephalopathy and renal coma.
Loading…