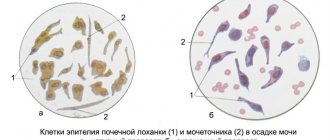
The emergence of new diagnostic methods has made it possible to detect rare pathologies of internal organs in humans. These primarily include anomalies of the genitourinary system. Before the advent of ultrasound, it was impossible to know whether a person had 3 kidneys. Now such a diagnosis is not surprising, and it is known for certain that the patient may have an accessory kidney.
In most cases, the presence of three kidneys in a person does not have a negative impact on the functioning of the body as a whole. But there are situations when an additional organ becomes the cause of dangerous conditions.
Features of the anomaly
During intrauterine development, the fetus develops two kidneys.
Therefore, the organ is considered a pair, and any deviations are classified as pathology. Three kidneys are an abnormality and require regular medical monitoring. Congenital defects also include duplication of the ureters and pelvis. The accessory organ is most often located in the pelvis or lumbar spine. The size and structure of the additional kidney may be complete and it may function normally.
But in some cases, the third kidney is passive and does not have any effect on the body. The worst thing is when a disease develops in this organ, which affects the patient’s health. This happens for various reasons.
Ureteral defects
This is most often discovered during examination due to enuresis. Due to the incorrect location of the ureter, which may not enter the bladder, but into the vagina or rectum, urination becomes uncontrollable.
This forces the child’s parents to consult a doctor with the problem, and then an additional organ is found. But the ureter may be normal and enter the main ureter or directly into the bladder. This pathology is more common for women than for men.
Hydronephrosis
An increase in the size of the organ due to inadequate urine drainage. With such a disorder, doctors do not save the kidney.
An additional organ is characterized by any inflammatory diseases that affect the main parts of the urinary system. Therefore, if unpleasant symptoms occur, doctors recommend removing an additional kidney.
People with three kidneys
Can a person have 3 kidneys? During a routine comprehensive examination, a physician may discover that a person has three kidneys. This anomaly of the urinary system develops even at the stage of intrauterine development.
The internal organs of the fetus are formed incorrectly, resulting in the formation of an additional kidney in the pelvis or lower back. In some patients it is completely healthy and functional, while in others it is completely inactive.
Patients with this feature should be constantly monitored by a doctor, as the risk of developing serious complications is high.
Pathology of fetal development, which leads to the formation of an additional kidney, is not considered dangerous, since it does not threaten the baby’s life. The child develops a third full-fledged organ with a capsule. Blood circulation occurs in the kidney, there are renal pelvises, a ureter that connects to the bladder.
In most cases, patients with three kidneys develop hydronephrosis, and the outflow of urine is impaired. When pathologies of an accessory organ negatively affect the patient’s health and cause discomfort to the person, the physician considers performing a surgical operation to remove the kidney.
In most cases, the patient does not even realize that he has 3 kidneys. The additional organ may not manifest itself at all. An anomaly is detected during an ultrasound.
A patient with such a deviation often develops diseases of the urinary system.
The ureter of the kidney is often embedded in the rectum or vagina, which is why the patient cannot control the outflow of urine.
Causes
Recently, many new diagnostic methods have appeared that can quickly identify deviations from the norm.
The third kidney can be found not only in newborns, but also in adult patients. However, most cases of anomaly formation are associated precisely with intrauterine development.
The exact reason for the formation of the deviation has not yet been found out. Provoking factors include:
- Bad habits (alcohol and cigarettes);
- Taking potent medications at different stages of pregnancy;
- Frequent treatment with analgesics, antispasmodics;
- Improper diet of a pregnant woman;
- Radiation of mother and fetus;
- Genetic disorders that are inherited.
An additional organ can simply be located in the body and function fully. It all depends on the size of the organ. Duplication of paired organs is a common diagnosis in modern urology. The patient may be diagnosed with additional renal pelvis, vessels, or a full-fledged organ.
Diagnostics
When the doctor tells the parents that the child has a 3rd kidney, they begin to panic. However, these worries are most often unfounded, because the pathology may not manifest itself in any way, and very rarely threatens the health or well-being of the baby.
However, in some cases, an accessory kidney leads to disruption of the functioning of the urinary system. In this case, you need to completely remove the organ, and then begin treatment for the disease. Patients with three kidneys may experience the following ailments.
- Pyelonephritis;
- Nephrosis;
- Organ prolapse;
- Enuresis;
- Formation of cysts on the kidneys;
- ICD;
- Kidney tuberculosis.
You can easily detect an additional organ, even by accident. However, a more thorough diagnosis is necessary to evaluate the condition of the abnormal kidney. For this purpose, ultrasound, x-rays, and laboratory testing of blood and urine are used.
The condition of all segments of the kidney can be studied using scintigraphy. The physician can quickly identify the negative impact of an additional organ on the patient’s health. If no abnormalities are found, therapy is not prescribed, but the patient should undergo regular examinations.
Therapy methods
If the kidneys are functioning without any problems, no treatment will be needed. If infectious diseases develop, the physician recommends that the patient undergo a course of drug antibacterial therapy. To eliminate inflammation, you need to take medications - Ciprolet, Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, etc. The dosage and duration of treatment is selected individually for each patient.
Urolithiasis can also be treated with potent medications (Canephron, Urolesan, etc.). If a tumor or dropsy has formed on an additional kidney, a surgical operation is prescribed, which involves resection of the organ.
Today it is possible to use a technique that is minimally traumatic and lacks any complications. This is laparoscopy. Doctors recommend this operation for the surgical treatment of children and elderly patients. During the procedure, the surgeon makes only a few incisions through which special equipment is inserted.
A patient with a healthy third kidney needs to submit urine for laboratory testing every 3 months.
Complications
In some patients, the extra kidney is too large. This condition of the organ can harm human health and lead to hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, arterial stenosis or the formation of tumors.
Conservative drug therapy in this case is ineffective and provides only temporary relief. The patient may suffer from constant pain in the lower back, which intensifies when palpating the bulge. The urine becomes cloudy and its composition changes. Often the patient experiences chills and attacks of weakness.
Editor
Source: https://zdorovyisustav.ru/info/ljudi-s-tremja-pochkami/
Causes of accessory kidney
There may be nothing to indicate that a person has 3 kidneys. Typically, this pathology is detected during routine examinations or when the patient experiences discomfort. But modern medicine is able to detect fetal development abnormalities in the early stages of pregnancy. It is more difficult to determine the cause of their occurrence.
Doctors describe several factors that provoke deviations in fetal development:
- abuse of alcohol, smoking, toxic substances;
- use of systemic medications during pregnancy;
- uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs, pain relievers;
- deficiency of vitamins in the mother's diet;
- exposure to ionizing radiation;
- taking hormonal drugs;
- genetic predisposition.
There are two types of bifurcations:
- an increase in the number of certain parts of the kidney - pelvis, vessels, and so on;
- formation of a full-fledged functioning organ.
There are cases of a large organ being divided in half. In this case, one part does not function without the other.
In the case of complete doubling, the organ is formed with all structural parts, that is, it has a ureter and pelvis.
Causes
Over time, the diagnosis of three kidneys is made more often. Anomalies of this organ are common in both newborns and adults. But the percentage of intrauterine disorders is the highest. What causes mutations during fetal development has not been precisely established.
There are some factors during pregnancy in which such a deviation is detected:
- smoking, drinking alcohol;
- taking systemic medications in any trimester;
- uncontrolled use of antispasmodics, analgesics and painkillers;
- unbalanced diet with a lack of vitamins;
- radiation exposure;
- predisposition (if parents or close family members had such a pathology).
Regardless of the cause, the accessory kidney may or may not function in the overall functioning of the body. Its dimensions sometimes correspond to the main organs or are smaller.
In urology, different types of duplication of paired organs are classified - bifurcation of the renal pelvis, vessels or complete formation of the third kidney. The patient may have one large kidney divided into two parts that cannot function separately. With complete doubling, a separate organ is formed with its own pelvis and ureter.
Why is the anomaly dangerous?
Due to the fact that the accessory kidney often does not reach its normal size, the person does not feel discomfort. But in the case of a large organ or serious structural abnormalities, the patient experiences unusual symptoms.
Those with three kidneys may face a number of complications:
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis;
- stenosis of large vessels;
- neoplasms of various origins.
Each disease is accompanied by pain in the back, poor health and makes the patient dependent on medications and regular procedures. The course of treatment always includes antibiotics, the frequent use of which has an adverse effect on the human body as a whole.
Hydronephrosis with the development of the pathological process can even threaten the patient’s life. This condition develops very quickly and becomes chronic.
The surgical method of treatment is used in case of detection of pyelonephritis, stones, tumors, and so on. In such cases, an additional kidney can cause a disturbance in the outflow of urine, which leads to hypertension and anuria.
These diseases are difficult to respond to classical therapy. Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor at the slightest discomfort in the area where the additional organ is located.
Three kidneys instead of two: causes of abnormal development, symptoms, diagnosis, complications
The presence of an additional kidney can be detected almost immediately after the birth of the child, but if the baby is in good health, this is not necessary. The exact cause of the development of the anomaly is more difficult to determine.
The location of the additional organ is the lumbar zone or pelvic area. Its manifestation is full functioning or lack of activity.
The outline of the third kidney is similar to a normal paired organ. It is often smaller in size, and there are cases when it is no different from normal kidneys.
Characteristic features of the abnormal formation are the presence of a separate pelvis, calyx, fibrous capsule and ureter. Such an organ can function independently.
The urinary system of the additional kidney is equipped with an orifice that opens into the vagina, esophagus, or connects to the ureter of the main organ.
The pathology of the third kidney is often expressed by the presence of internal anomalies - double ureters or pelvises, although this defect is also observed in the main paired organ.
In contrast to kidney duplication, which is characterized by bifurcation of the pelvis and the likelihood of such deviations in the two main kidneys, the third is formed only on one side.
The discovery of a rare pathology leaves the patient bewildered. A natural question arises: is an additional kidney good or bad? There can be no clear answer.
The negative side of the abnormal formation is that the third kidney often provokes serious problems with the functioning of the urinary tract. But in most cases, the deviation does not affect the overall health.
If the third kidney brings discomfort and causes the development of pathological processes in the body, this is a direct indication for its removal.
You may be interested in the following article: “Kidney hydronephrosis: what is it? Outcome of the disease."
Causes
The percentage of detection of such pathology increases every year. Of the total number of congenital kidney malformations, it accounts for 20%.
the reason for the formation of the third kidney is disturbances in the intrauterine development of the unborn child that occur in the early stages of pregnancy.
The triggering mechanism for a renal anomaly is a disruption of the natural process during the formation of vital organs and systems.
A wide range of factors that can negatively affect this process have been identified.
Common reasons include:
- deviations inherited at the genetic level (abnormal structure and location of the kidneys in the parents);
- uncontrolled use of medications by a woman before conception or in the early stages of pregnancy;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- negative impact of radioactive rays;
- lack of a balanced diet, which requires a sufficient amount of vitamins, micro- and macroelements in a pregnant woman’s diet.
- alcohol, drugs, nicotine.
Important! When planning pregnancy and during pregnancy, risk factors must be taken into account. This will reduce the likelihood of the baby developing defects.
Types of kidney duplication
Doctors are confident that the pathological condition of the internal organ does not pose a serious threat to the baby’s health, but nevertheless, an organ with pathology is more often susceptible to the development of diseases such as tuberculosis, urolithiasis, nephroptosis, tumors of various etiologies, etc.
There are 3 subtypes of pathology:
- Duplication of the left kidney. Most often, the pathological condition of an internal organ is determined unintentionally, that is, during a medical examination to identify a completely different disease.
- Duplication of the right kidney can be complete or incomplete. With incomplete doubling, the internal organ is visible in a larger size than usual. With complete doubling, 2 full-fledged kidneys appear, having their own ureters, but the pyelocaliceal system is underdeveloped. Often this pathology provokes spontaneous leakage of urine.
- The doubling of both kidneys does not cause the baby an uncomfortable physical condition, since the defective organ does not cause the manifestation of any negative processes in the body. But it is important to remember that doubling of both internal organs can provoke the development of diseases such as polycystic disease, nephrosis, pyelonephritis, and urine leakage.
Indications for ultrasound of the kidneys in children
An ultrasound scan of the kidneys as soon as possible (starting on days 3–5) is strongly recommended for all newborns who have undergone resuscitation during labor. Other indications for research in children:
- mandatory screening at the age of 1–1.5 months;
- poor heredity in terms of renal pathology (one of the parents has diseased kidneys);
- disturbances (especially difficulty) urination;
- changes in urine tests;
- swelling;
- prolonged increase in temperature for no apparent reason;
- pain in the abdomen and/or lower back;
- injury to the abdomen and/or lumbar region.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the kidneys in children
If you plan to perform only an ultrasound of the child’s kidneys, then preparation for the procedure is not necessary. A comprehensive ultrasound of the urinary system (kidneys + bladder) is performed with a full bladder.
When preparing, it is important to maintain a balance: if you drink less fluid than necessary, the doctor will not be able to get a clear “picture”, and if the bladder is too full, then the child will have residual urine and dilation of the renal pelvis (pyelectasia).
It would be optimal to drink 200 to 800 ml of liquid (strictly without gas) 30–40 minutes before the procedure. If it is difficult for a child to drink this amount of water at once, you can start drinking 1–1.5 hours before the ultrasound session and do it in small portions.
If you are planning an ultrasound of the kidneys for an infant, the task is simplified: it will be enough to feed or give the baby something to drink 15–20 minutes before the examination.
How is kidney ultrasound performed in children?
During the procedure, the child lies on the couch (on his stomach, on his side, on his back) or stands (if necessary, exclude nephroptosis), sometimes taking deep breaths and exhalations at the doctor’s request. The doctor moves the sensor over his skin, which has been previously lubricated with a light transparent gel.
The gel is odorless and does not irritate the skin; it is necessary for better glide of the sensor and increased conductivity of ultrasonic waves. In an ultrasound machine, these waves are converted into electrical waves and displayed on the monitor as an image.
Ultrasound is a type of sound that has a high frequency (1–12 MHz) and is inaudible to the human ear. In nature, ultrasound is found everywhere: in the noise of waves and wind, in the sounds made by dolphins, bats, some fish and insects. Ultrasound examination is safe for the body of a small patient.
Clinical manifestations
An accessory kidney may not make itself felt for a long time. But as the pathological process develops, discomfort begins to appear. For patients with three kidneys, the main complaints are:
- slight pain in the lumbar region, which occurs periodically, but does not become constant;
- feeling of heaviness in the lumbar region;
- cloudy urine;
- small compactions in the hypochondrium area, easily palpable, sometimes the patient experiences pain when touching them;
- fever;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- nausea and vomiting;
- arrhythmia;
- feeling tired even with minor physical activity.
Echinococcus kidneys
Kidney damage by echinococcus is rare, much less common than its localization in the liver, lungs, and spleen. Usually one kidney is affected. Women get sick slightly more often than men, which is probably due to greater contact with pets. Echinococcus kidney can be single-chambered (hydatid) and multi-chambered (alveolar). Hydatid echinococcus is a smooth-walled cyst covered with chitinous and fibrous membranes, inside which daughter blisters float in the liquid. Typically, echinococcus is located in the cortical part of the kidney, but, slowly growing, it compresses the parenchyma, penetrates to the pelvis and can open into it. Sometimes the cyst undergoes calcification; its contents may, in addition, become infected. Alveolar echinococcus kidney, even germinated from the liver, is an incidental rarity. The slow growth of echinococcus causes the disease to remain latent for a long time and go unnoticed. Some patients, even if they accidentally discover a tumor in the hypochondrium, do not consider it necessary to see a doctor. Over time, however, pain appears in the lumbar region. Sometimes, when a cyst breaks into the pelvis and secondary blisters pass through the ureter, attacks of renal colic occur. Dull pain is constant, it intensifies with movement and physical work.
Excretion of echinococcal blisters in the urine is a pathognomonic symptom of echinococcus of the urinary system. Suppuration of the contents of echinococcus is accompanied by an increase in temperature and a significant increase in pain.
Recognition of echinococcus presents significant difficulties even when the kidney with hydatid emerges from under the costal arch. Echinococcus kidney is palpated in the form of a smooth, spherical, elastic-elastic formation. The symptom of “trembling hydatid” is not always observed. The diagnosis is immediately made easier if the parasitic cyst has broken into the pelvis and thin-walled daughter blisters, reminiscent of small grapes, and echinococcus hooks are found in the urine.
If this pathognomonic symptom is not present, the diagnosis can be helped by medical history (contact with pets, living in an area with a high incidence of echinococcus), an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood, a positive complement rejection reaction (Weinberg), a positive intradermal Caizoni reaction, and radiography.
On a survey x-ray, when the echinococcal bladder is calcified, a ring-shaped shadow of the correspondingly calcified wall is visible.
The only possible and at the same time radical method of treatment is surgical intervention in the form of resection of the cyst or total nephrectomy.
Diagnostics
It is easy to identify 3 kidneys in a person with a high level of modern medical technology. Diagnostic methods used in pathology:
- palpation;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray examination;
- laboratory tests of urine and blood;
- scintigraphy.
The anomaly is detected during a comprehensive examination, and doctors receive information about the functioning of all segments of the organ and its impact on the functioning of the body as a whole. Systematic monitoring helps to identify disorders in time and begin treatment.
How does pathology manifest itself?
When a person has three kidneys, this may not manifest itself in any way. The presence of three kidneys is discovered in this case absolutely by accident. But sometimes an additional organ brings discomfort and even pain. The pain is explained by the fact that with an additional kidney, urodynamic processes change due to the peculiarities of the structure of the renal structures.
Urinary incontinence is one of the most common signs of accessory kidney disease in people of all ages. This happens if the ureter of the accessory kidney ends in the vagina or final intestine. In this case, urine will constantly leak. The female part of the population suffers from this disease more often.
When is treatment needed and how to treat
A person does not require treatment if the accessory kidney works normally and does not cause problems. Treatment is necessary only when an inflammatory process develops in the organ. After identifying problems, the doctor makes a decision on the patient’s treatment regimen and methods.
In many cases, it is possible to cope with the infection with the help of antibacterial agents; drugs from the fluoroquinol group are prescribed. If stones are detected in the accessory kidney, the doctor recommends taking specific medications that help dissolve the stones and remove them.
Such patients are recommended to undergo examination at least once every three months. If the condition changes for the worse and research indicators confirm this, then the question of removing the kidney is raised.
Doctors try to avoid surgical treatment when the organ is functioning normally. Removal is indicated only in cases where the patient has severe urolithiasis or hydronephrosis, which provoke chronic renal failure. The patient is operated on as planned, having carried out preliminary examinations and preparation.
One of the modern methods of kidney removal is laparoscopy. This method is less traumatic for the body and allows you to reduce the rehabilitation period. The entire process is carried out with special instruments inserted into the abdominal cavity through small incisions. This method is indicated in the absence of vascular lesions.
To monitor the condition of the additional organ, you need to be regularly examined, and if problems are detected, follow the doctor’s recommendations in order to avoid surgical intervention.
Is it normal for a person to have three kidneys?
The formation of three kidneys in the body is a rare anomaly. An uninformed patient may think that this makes the organs function even better. In fact, in 20% of cases, the defect causes some complications in the functioning of the genitourinary system.
Peculiarities
In origin, the pathology resembles doubling, but during division the processes are accelerated, which leads to the appearance of a third full-fledged organ. The development of cells and tissues occurs only in a one-sided manner.
The accessory kidney has a capsule formed of connective or fibrous tissue. And also the system through which blood circulation occurs. The third organ consists of the calyx of the pelvis. The proper ureter enters the bladder through the orifice or merges with the main ureter.
Typically, the development of the third kidney is accompanied by hydronephrosis (enlargement of the kidney elements due to improper outflow of urine). If the pathological process in the third kidney worsens the state of health and causes discomfort, the question of its removal is raised.
The additional kidney may not manifest itself for some time. Sometimes the patient does not suspect the deviation. During a routine examination of organs using ultrasound, the doctor immediately sees the pathology.
In other cases, people deliberately go for examination when they discover unpleasant symptoms, such as urinary incontinence.
In this case, the pathology openly declares itself, which is noticeable by the malfunction of the urinary system. The ureter at the third kidney is formed with insertion into the rectum or vaginal wall.
Urine output is not controlled and cannot be corrected on its own without medical assistance.
When is treatment necessary and how to treat?
Taking medications is not required if all kidneys are functioning normally. If the duplicated organ causes the development of infectious diseases, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics before further treatment tactics.
To eliminate bacterial influence, fluoroquinolone agents are prescribed.
- Ciprofloxacin (from 80 rubles).
- Ofloxacin (from 100 rubles).
- Tsiprolet (60-120 rubles).
- Ceftriaxone (100-250 rubles).
To eliminate the symptoms of urolithiasis, it is recommended to use special drugs that affect the formation of stones.
- Canephron (350-400 rubles).
- Phytolysin (300-350 rubles).
- Urolesan (320-400 rubles).
Tumors, severe urolithiasis or hydrops associated with the third kidney must be treated surgically. The indicator for surgical intervention is failure of the main organ. Usually this is a planned operation, before which all the necessary studies have been carried out.
If there are no deviations, then experts recommend saving the third kidney. The patient needs to monitor his health by taking urine tests. This can be done every three months.
Removal (laparoscopy)
Thanks to modern techniques, the third kidney is removed with minimal tissue trauma. The use of this type of surgery is mandatory for the elderly and children with severe complications.
The rehabilitation period after laparoscopic treatment is reduced by several days compared to abdominal surgery. The patient makes incisions in the abdomen, where special tubes are inserted. Through them, the instruments necessary for the operation enter the abdominal cavity.
This method is suitable if the patient’s main vessels are not affected.
Possible complications
Too large a size of the third kidney can lead to the development of pathologies that threaten the patient’s health.
Among them are identified:
- hydronephrosis;
- arterial stenosis;
- tumors;
- chronic pyelonephritis.
Usually the disease is severe and leads to hospitalization. Conservative treatment for such pathologies is unsuccessful and gives a temporary effect. Symptoms appear intensely and progress quickly:
- lower back pain;
- turbidity and changes in urine composition;
- a bulge under the rib, sometimes painful when palpated;
- feeling unwell, chills.
Dysuria or obstruction of urine flow can cause serious problems. Due to the increased work of the third kidney, substances are released into the blood that increase blood pressure. If left untreated, the patient is at risk of developing a stroke.
If a third kidney is discovered in a child or other patient, it is recommended to coordinate all further actions with a urologist and nephrologist. Treatment tactics are determined only by a specialist. Folk remedies should not be used until the danger of such an anomaly is clarified.
You can watch a video where they will tell you how a kidney was transplanted, and the patient now has three kidneys.
Source: https://bolyatpochki.ru/anatomia/tri-pochki-u-cheloveka.html
3rd kidney - uniqueness or problem?
Cause and symptoms of the condition
The third kidney is formed due to a failure in the natural formation of internal organs in the fetus. The main influence on the development of renal pathology is exerted by the following factors:
- genetic predisposition, especially if there are disorders in one or both parents;
- regular use of hormonal medications;
- use of medications in large quantities;
- exposure to radioactive radiation on the fetus during pregnancy;
- lack of nutrients and vitamins for the proper development of the embryo;
- drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking.
Main reasons
Recently, the incidence of three kidneys has increased. It is impossible to say with 100% certainty that this or that factor led to such a pathology, since its formation occurs in utero. But you need to know about those points that can give impetus to the development of the third kidney.
Among the main reasons are:
- maternal smoking, drug addiction and alcohol consumption;
- taking hormonal drugs;
- uncontrolled and irrational use of medications;
- deficiency of vitamins in the mother's diet;
- the effect of radiation on the fetus located in the mother’s body;
- heredity (the presence of pathology in one or both parents).
Treatment of the disease
After carrying out diagnostic measures, the attending physician assesses the effect of the accessory organ on the patient’s body. If no abnormalities or diseases are detected, regular preventive monitoring of the condition of the organs is carried out. If a child is in good health and has no symptoms of disease, constant medical monitoring and periodic testing are required.
Therapeutic treatment is carried out in case of development of urological diseases with deterioration of health. The following drugs are used:
- Antispasmodics. Relieves spasms, relieves pain.
- Antibiotics. Kill pathogens and eliminate infections.
- Analgesics. They have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Diuretics. Helps improve urination and remove harmful substances from the body.
Surgical removal of an accessory organ is carried out in the event of the development of progressive urological diseases of a complicated nature, ineffectiveness of therapeutic treatment or complete cessation of kidney function. In this case, a nephrectomy is performed - surgical removal of the entire kidney.
Among the numerous anomalies of intrauterine development of the body, the most common are unusual structures of the urinary system. In particular, over time, a person is diagnosed with 3 kidneys or even doubling them. Often such an anomaly remains undetected and is diagnosed solely by chance when examining a patient for other diseases. We will discuss below how people with three or four kidneys live, and whether this condition is dangerous for their health.
Important: the abnormal structure of the urinary organs accounts for 30% of all possible renal pathologies in the world.
Kidney duplication: how dangerous the disease is, causes, treatment
Recently, diseases associated with genetic abnormalities that occur even before a person’s birth, so-called developmental defects, are often diagnosed. They are a consequence of the deterioration of the environmental situation and many other unfavorable factors.
General information
Kidney duplication is a congenital change in the genitourinary system (MS), manifested by the development of an additional kidney on one or both sides. The anomaly may take the form of a separate organ, growth or section in a healthy kidney.
Often this malformation is discovered by chance during an ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
Causes and factors of education
During the study of the disease, it was found that kidney doubling occurs for two main reasons:
- genetic mutations;
- heredity.
It can develop under the influence of the following factors on the fetus:
- alcohol;
- nicotine;
- radiation;
- chemical substances;
- medicines.
If a similar condition is observed in one of the parents, there is a high probability of it occurring in the child. If the disease is present in both the father and mother, the risk of transmission increases.
Age and gender differences
Of all MS defects, kidney duplication is the most common. Moreover, in females the likelihood of development is 2 times higher. Scientists suggest that this fact is somehow related to the characteristics of the body, but the exact reason is not clear.
The anomaly can be diagnosed at any age. This often happens after 25-30 years of age. For most women during this period, the load on the kidneys caused by pregnancy and childbirth increases. Unstable hormonal levels are also an impetus for the development of new diseases or exacerbation of existing ones.
For males, the picture is slightly different. Their development of kidney diseases is often associated with:
- bad habits (smoking and drinking alcohol);
- an abundance of heavy food (spicy, salty, smoked, etc.
); - neglect of one’s health (refusal to visit a doctor, hypothermia, heavy lifting, etc.).
In children, as a rule, the anomaly is detected accidentally and is asymptomatic.
But even in this case there are exceptions.
Kidney problems in babies may be associated with:
- abundance of medications;
- hypothermia;
- not drinking enough;
- infections.
Damage to two kidneys at once makes them very vulnerable, regardless of age.
If the congenital feature was identified early enough, then if medical recommendations are followed, the likelihood of problems in the future is significantly reduced.
Characteristic symptoms
As medical practice shows, the disease has no characteristic symptoms when all the kidneys are healthy. However, people with double kidneys need to know that such organs are more susceptible to the development of various pathologies, so they should be protected.
If complications occur, the defect may be accompanied by:
- painful urination;
- disruption of the flow;
- nagging pain in the lower back;
- increased pain when tapping the lower back (right or left);
- retention of urine inside the pelvis;
- high body temperature;
- increased blood pressure;
- swelling;
- weakness;
- dark circles under the eyes.
Forms
Depending on the nature, the following types of illness can be distinguished:
- Incomplete doubling. With this type of pathology, the kidney has an increased size. Its two formed sections are combined into a common collecting-pelvic system (PCS). The ureters join together and empty into the bladder.
- Full doubling. It is distinguished by the development of additional organs, each of which has its own CLS. One kidney is often complete, while the other is underdeveloped. Two ureters arise from each organ.
Regardless of the form, a second renal artery is necessarily formed at the daughter kidney or department, providing a separate blood supply.
Based on location, the anomaly is divided into:
- one-sided;
- two-sided.
Sometimes one of the ureters may open into the colon or vagina rather than into the bladder. In this case, a person may feel urine leaking in the corresponding places. This phenomenon is most often observed in children.
When is treatment required and what kind?
Drug therapy is not effective for kidney duplication. Treatment can be carried out to eliminate complications, relieve pain and improve organ function.
The patient may be prescribed the following medications:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antispasmodics;
- analgesic;
- antibiotics;
- stone dissolving agents;
- diuretics.
A prolonged absence of positive dynamics and deterioration in well-being is a reason for emergency or planned kidney surgery:
- removal of the entire affected kidney or part of it (nephrectomy);
- creation of passages for the outflow of urine (anti-reflux surgery);
- connection of the bladder and ureters using a suture (excision of ureterocele);
- the use of anastomoses (artificial connections between organs) for reverse reflux of urine (pyelopyeloanastomosis).
The type of operation is selected by the attending physician, based on the test results.
The diet has no therapeutic effect, but it reduces the load on the kidneys, so patients are advised to limit certain foods throughout their lives.
Namely:
- alcoholic beverages;
- everything smoked, salted and spicy;
- sweets (sweets, cakes, pastries);
- greens (dill, parsley, cilantro);
- mineral water;
- instant products (semi-finished products);
- mushrooms and legumes.
Alternative therapy
To cope with the exacerbation of certain MS diseases or to maintain renal function, it is possible to take folk remedies. Before use, you need to consult your doctor, who, based on the test results, will select the optimal prescription.
The following remedies can be used to prevent kidney diseases:
- Rose hip decoction. Fresh rose hips are cut in half; dry ones can be crushed in a blender.
100 gr. raw materials are poured with a liter of water and brought to a boil. Leave for about 4 hours, filter. Drink half a glass, 3 times a day, regardless of meals. Duration 2 weeks. After 7 days, the procedure can be repeated. - Apple diet. This recipe is quite simple.
It has a beneficial effect on kidney function and promotes weight loss. For 3 days you need to eat only apples or freshly squeezed juice. Please note that inflammatory and ulcerative diseases of the digestive system are an absolute contraindication to eating fresh apples. - Diuretic infusions. Raspberry, elderberry and coltsfoot flowers are mixed in equal proportions.
Then a teaspoon of raw material is poured with boiling water and left for 15 minutes. Drink in one go. Use up to 5-6 times a day. The ingredients can be used separately.
What to do as a preventive measure
When you discover a daughter kidney, you should not fall into despair. You can live a full life with this anomaly without constantly visiting the hospital.
To do this you need:
- keep the kidneys warm;
- reduce the consumption of salt and products containing it;
- get rid of bad habits (drinking alcohol and smoking);
- drink enough fluid (at least 1.5 liters per day);
- stop eating unhealthy foods (burgers, processed foods, spicy foods, smoked foods, etc.);
- do not drink mineral water without consulting a doctor;
- visit a medical facility if new symptoms appear;
- undergo a kidney examination at least once a year;
- wash your hands after visiting public places;
- carry out hardening;
- walk more;
- have a good rest;
- avoid stress and other emotional stress;
- take a course of vitamins and minerals once a year.
Possible anomalies of the kidney structure: types
In addition to tripling the urinary organs, it is useful to know that other variants of abnormal intrauterine development of the urinary organs are also abnormal. So, there are these types of kidney structure that differ from normal ones:
- Aplasia. Simply put, this is interpreted as the complete absence of one kidney. In most cases, this pathology occurs in female embryos (3 times more often than in male embryos). Moreover, against the background of the absence of one organ in boys, there is also an absence of the ureter and testicle on the side of the missing organ. Both may be absent at once, or selectively (either the testicle or the ureter). As for girls, against the background of aplasia, they may develop a bicornuate uterus, dysplasia (underdevelopment) or there will be no uterus at all.
Important: it is worth knowing that bilateral aplasia is incompatible with life.
- Duplication of urinary organs. That is, if normally a person develops two urinary organs, then when the person doubles, he has 4 kidneys. With this structure of the urinary system, people live quite fully, provided that all four organs function normally. However, it also happens that in people with four kidneys, additional ureters form incorrectly and find their way into the vagina (in girls) or into the rectum (in both sexes). In this case, there is constant leakage of urine, which requires surgical intervention. Also, when the kidneys are doubled, a person may experience pathologies in the form of pyelonephritis (54% - chronic, 20% - acute), kidney stones (31% of cases), or hydronephrosis (almost 20% of cases).
- Accessory kidney. The rarest of all possible anomalies in the structure of the urinary organs. In most cases, this defect is one-sided. Typically, people with a third kidney have a completely separate third collecting system, ureter, circulatory system, and fibrous capsule. That is, the third kidney is a completely independent organ. Sometimes it may have a smaller size than paired organs, or be of a standard size. It is worth remembering that in some cases the third organ is completely inactive.
Important: often people who have an additional third kidney voluntarily become donors, giving an additional organ to those who need it (children, seriously ill people, etc.). However, if the third organ is susceptible to pathology (most often hydronephrosis), then it is simply removed.
Kidney duplication - what is it? Signs and causes of kidney duplication
Double kidneys are a congenital pathology, which in most cases is observed in girls and is often unilateral. The reasons for this phenomenon are very different. The duplication of the kidney begins to form and develop in the child while still in the womb.
Double kidneys. What it is?
The kidneys in the human body are a paired organ. They perform the function of removing toxins from the body. Everyone knows about this. But not everyone has heard that kidney doubling occurs.
What it is? This is the division of an organ into two halves, fused at the poles. Each part is equipped with its own blood supply system. Externally, such a kidney is much larger in size.
The development of pathology occurs during intrauterine development.
Double kidneys in children are the most common congenital anomaly of the urinary system. An altered kidney does not pose a threat to human life, but is often the cause of other diseases.
The structure of the renal pelvis
This funnel-shaped structure is formed by the fusion of the major and minor calyces of the kidney. It is in the pelvis that urine accumulates. The surface of the inner part of the pelvis is covered with mucous membrane. In the wall of the pelvis there are fibers that perform peristaltic contractions, as a result of which urine flows down the urinary tract.
Due to the impermeability of the walls of the pelvis and ureters, the liquid with the substances dissolved in it never enters the peritoneal cavity, but always remains within the urinary system.
Complete kidney doubling
Sometimes a person is diagnosed with complete kidney duplication. What it is? This is an abnormal phenomenon when the kidney is divided into two parts by a groove. The upper and lower lobules are distinguished, and the upper one is most often underdeveloped and smaller in size.
Each of them has its own artery and its own renal pelvis, which is usually underdeveloped in the upper half. They also have their own ureters. Each goes separately and ends in the bladder with its own mouth.
It is possible that one ureter flows into another.
So, instead of one, there are two separate buds. In itself, complete doubling of the kidney does not bother a person, so there is no need to treat it. But it leads to other diseases.
Problems that arise when a kidney doubles
Often, some kind of disease may begin to develop in one half of the doubled organ. Complete doubling of the kidney can provoke pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, nephrosis, and polycystic disease.
It happens that the mouth does not flow into the ureter, but into some other organ. It can be the rectum, cervix, vagina.
In this case, a person may feel urine constantly leaking from the ureter.
Incomplete bud duplication
This pathology is observed when a person develops one large kidney with clearly defined upper and lower sections. Each of them has its own renal artery. N, each part of the doubled organ does not have its own pyelocaliceal system; they have one for two sections. There are two ureters, but they are connected to each other and flow into the bladder with a single trunk, like one.
In medical practice, cases have been recorded where incomplete doubling of the left kidney is more often observed, rather than the right. Most people with this anomaly live until old age, unaware of its existence. Incomplete doubling of the kidney does not cause inflammatory processes in the organ.
Causes of kidney duplication
If the pathology does not manifest itself in any way, which happens when a person has incomplete duplication of the left or right kidney, it does not matter, you may not even know about the abnormal development of this organ.
It is discovered by chance, during an ultrasound examination of some other organ located next to the kidney. Doctors often diagnose a double kidney in a newborn child.
The reasons for this phenomenon can be very different. Let's look at some of them:
- Radioactive exposure of the fetus in the womb, if her work activity during the entire period of pregnancy takes place at an enterprise whose production cycle is associated with radiation.
- The predisposition is inherited if one or both parents have a double kidney. What it is is described above in this article.
- Poisoning with drugs during pregnancy, including hormonal drugs.
- Presence of bad habits in a pregnant woman: abuse of alcohol, drugs, etc.
- Vitamin deficiency occurs frequently and regularly during pregnancy. There are many places on our planet where vegetables and fruits do not grow due to harsh climatic conditions. But women live and give birth to children there too. So the expectant mother suffers from a lack of vitamins and minerals. It’s good if everything works out and the child does not have a disease such as kidney duplication. Of course, there may be other reasons, but this one can be ruled out for the sake of the health of the unborn baby.
Diagnostics
If no examination was carried out when the person was a child, kidney duplication is diagnosed, as a rule, after an inflammatory disease of the organ begins or accidentally, during a preventive examination using diagnostic devices. First you need to do an ultrasound examination. If this is not enough, the doctor prescribes other methods.
When a person does not have pathology, there are only two ureteric orifices in his body: one for each kidney. If the doctor suspects kidney duplication, the patient is prescribed a cystoscopy.
With its help, it is determined how many orifices the ureter has: if there are three, then the diagnosis of “double kidney” is confirmed.
To determine the size of the enlarged kidney and identify the presence or absence of the third calyceal pelvis and additional ureter, the doctor prescribes excretory urography.
Symptoms
Kidney duplication does not manifest itself in any way. It does not need to be treated until it causes some other disease in this organ. Signs of kidney duplication vary. Typically, inflammatory processes are characterized by:
- Increasing temperature.
- Weakness and swelling.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Regular headaches.
- Increased pressure.
- Cloudy urine.
- Reverse flow of urine.
- Discomfort and pain in the lumbar region.
- Urinary incontinence.
- Unpleasant sensations when urinating.
- Renal colic.
- The occurrence of infection in the urinary canal.
Whether all signs appear at once or each one separately will depend on the disease.
Treatment
Kidney duplication is characterized by complete or incomplete division of the organ into two parts. If it doesn't bother the person, nothing needs to be done. It is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle and undergo regular preventive examinations.
This pathology provokes inflammatory processes in the kidney when it completely doubles. Even in this case, there is no point in doing a complex operation to correct the defect.
It may not cause trouble to a person throughout his life.
Therapeutic treatment is usually used when diagnosing some serious disease, for example, pyelonephritis, if it was caused by this anomaly.
When the disease becomes chronic and cannot be treated using conservative methods, then they resort to surgical intervention, which is aimed at correcting the cause that caused the complication.
But they always try to save the kidney. It is removed only when it has completely lost its functionality.
Prevention
If during the examination a doubling of the kidney is discovered, there is no need to panic. This diagnosis is not fatal. When the pathology of an organ does not bother you, it will not affect a person’s quality of life in any way. You need to take a closer look at your health:
- Give up bad habits, if any: stop drinking, smoking, taking drugs.
- Change your job if it involves toxic chemicals.
- Urgently switch to a properly balanced diet.
- Strictly monitor the work and rest schedule.
If one of your relatives has a doubling of the kidney, what it is is known to the whole family. Therefore, when a woman from your family is bearing a child, you need to treat this period with double attention.
The child in the womb must develop, receiving the necessary vitamins. A woman is obliged to take care of her health and not take alcohol, drugs, or medications that can cause poisoning to the child.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/165131/udvoenie-pochki—chto-eto-takoe-priznaki-i-prichinyi-udvoeniya-pochki
Symptoms of the third kidney
It is worth knowing that the accessory urinary organ does not manifest itself in any way. That is, if there are three kidneys, in most cases, if pathological processes do not occur in it (the third), a person lives a completely normal and familiar life. And the anomaly is detected during an ultrasound of the kidneys or abdominal organs to identify other possible diseases. However, enuresis (urinary incontinence) may still be a clear suspicious clinical symptom of the anomaly. In this case, there is reason to believe that a possible ureter of a possible third kidney penetrated into the vagina or rectum during the formation of the embryo.
Possible complications
Complete or incomplete kidney duplication becomes a serious problem in most cases, since the incidence of complications is quite high. This situation is explained by anatomical features and functional disorders: if there are three underdeveloped kidneys, then this is sometimes much worse than the absence of one of the organs.
Two CHLS in a double kidney work worse than one in a normal one. The main complications that have an extremely negative impact on the functional state of the urinary tract are:
- chronic pyelonephritis against the background of stagnant processes;
- hydronephrosis due to disruption of normal outflow;
- nephroptosis - due to duality, the organ is larger and heavier;
- benign or malignant neoplasm (as the cause of structural disorders of the renal parenchyma).
Duplication of the right kidney with severe nephroptosis is more common, this is due to the fact that the right-sided organ is initially located lower. In other cases, the most common complications will be inflammation and hydronephrotic transformation.
Diagnosis of pathology
Identifying a problem called an “accessory kidney” is not at all difficult. Fortunately, modern medicine has many hardware diagnostic methods for assessing the condition of the urinary system. So, the following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Ultrasound. In this case, the number of organs, their size and possible functionality are assessed.
- X-ray using a contrast agent. This diagnostic method allows us to identify the possible presence of kidney stones.
- Dynamic scintigraphy. In this case, the method is as informative as possible. The use of the isotope substance hippuran makes it possible to fully assess the condition of all three organs (their size, functionality, the presence of pathological processes occurring in them). If reduced functionality of an accessory organ or pathologies occurring in it is detected, the attending physician decides to remove the third kidney.
It is worth knowing that if during the examination no pathologies were identified in all three organs, then treatment is not required. However, periodic monitoring of the health of the patient’s urinary organs is indicated. If, during observation, dilation of the pelvis, hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, stones or other pathologies is diagnosed in the third organ, the additional organ is removed.
Diagnostics are carried out on an outpatient basis in diagnostic centers or in hospitals equipped with the necessary equipment. At the same time, to perform all the necessary tests, you need a referral from a specialist.
Important: if you or your child have received a diagnosis (additional kidney), then do not be alarmed. People live quite normally with such an anomaly. If the baby is very small, the only thing parents can do for him is to monitor the baby’s health and observe all its changes. Regular examinations with a doctor, ultrasound and laboratory tests will give you an idea of the functionality of the third kidney.
What anomaly?
An additional kidney is still a relatively rare defect of internal organs. It is most often located either in the pelvis or in the lumbar region. Sometimes this organ works at full capacity, there are cases when it was completely inoperative. As a rule, such a kidney is smaller in size compared to a regular one. However, there are cases of normal organ parameters.
There are many defects in its structure: double ureters, two pelvises. Also, structural changes are possible in the other two kidneys. It is worth noting that the third kidney is a separate anomaly, which differs from the double kidney. This defect is always located on one side. In the overwhelming majority of cases, such an organ is equipped with its own pelvicalyceal system, has its own fibrous capsule, and its own ureteral system.
Reasons for the development of pathology?
The development of pathology can be caused by a number of factors affecting the body:
- Irradiation.
- Use of certain medications during pregnancy.
- Hereditary genetic pathologies.
- External mutagenic factors.
- Drinking alcohol or other toxic substances during pregnancy.
The biggest role in the formation of this organ defect is given to the genetic factor, since kidney doubling is most often inherited. However, one should not discount the poor lifestyle of the mother, who abuses alcohol, medications and other substances that poison the fetus. There is also a possibility of developing the disease in the presence of radiation, which often occurs at specific enterprises or in a specific area. Under the influence of radiation, there may be settlements in which such a pathology develops in the majority of people. At the same time, they feel normal, but in another place a person with a double kidney suffers from constant exacerbations of genitourinary diseases.
Removal (laparoscopy)
Thanks to modern techniques, the third kidney is removed with minimal tissue trauma. The use of this type of surgery is mandatory for the elderly and children with severe complications.
The rehabilitation period after laparoscopic treatment is reduced by several days compared to abdominal surgery. The patient makes incisions in the abdomen, where special tubes are inserted. Through them, the instruments necessary for the operation enter the abdominal cavity.
This method is suitable if the patient’s main vessels are not affected.
Description of the anomaly
Accessory kidney is a rare congenital disorder of the structure of internal organs. In addition to the two well-known kidneys, there is another one, located mainly either in the lumbar region or in the pelvic region. Cases of both ordinary work and complete inactivity of the additional organ have been recorded. In most cases, it is smaller in size than ordinary kidneys, but there are also identical ones. Cases of anomalies in the accessory organ are often recorded. These include duplication of the ureters and pelvis.
Return to contents