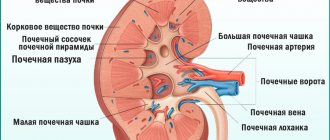
Causes of ICD
The immediate cause of urolithiasis is the increased content of salts in the urine and their crystallization, leading to the appearance of sand and stones.
There are many reasons for the development of ICD in a child:
- Often, stones appear as a result of inflammation of the kidney tissue or urinary tract. The composition of urine changes under the influence of many microbes, and stones are formed (usually phosphates and oxalates).
Urinary infection significantly aggravates the course of urolithiasis and can be a factor in the relapse of the disease, since the metabolic products of many microorganisms contribute to the alkalinization of urine and the rapid formation of phosphate stones. Infection of stones is observed in 68% of cases.
- A genetic predisposition to urolithiasis also plays a role due to the inheritance of changes in metabolic processes leading to increased absorption of calcium in the intestine.
- Poor nutrition of a child: frequent consumption of fast food, foods rich in purines; insufficient volume of fluid consumed.
- Anomalies of the urinary organs, leading to stagnation of urine, precipitation of salts, and the formation of foci of chronic infection. Anomalies are detected in 31.6% of children with urolithiasis in the form of underdevelopment of the ureters, narrowing of the pelvis, prolapse (dystopia) of the kidneys, incomplete duplication of the ureters or kidneys, horseshoe kidney and others.
- Calcium metabolism can also be affected by hormonal disorders due to pathology of the parathyroid gland.
- Lack of inhibitors in the body that should control and suppress the process of salt crystallization.
- Operations on the genitourinary organs.
- Severe injuries and prolonged immobilization as a result of immobilization.
Urolithiasis in children
The age of patients diagnosed with urolithiasis has decreased significantly. This is due to the current environment or poor heredity. The main symptom by which the disease can be recognized is attacks of acute pain. Urolithiasis in children is a dangerous disease that often causes serious complications.
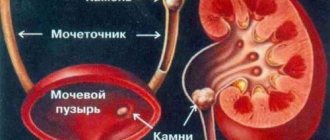
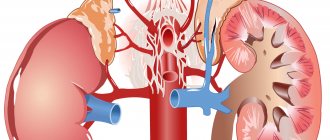
Pediatric urolithiasis is a renal pathology accompanied by the formation of stones and sand in the organs of the urinary system. When organs malfunction, certain chemical elements in urine form crystals.
They can be deposited on the walls of the renal pelvis, calyces and in the bladder itself, forming stones. If your child is diagnosed with a kidney stone, you should immediately begin medical or surgical treatment.
Source: zdorovyedetei.ru
The disease can be congenital or acquired. According to statistics, urolithiasis affects infants, as well as children aged 3 to 11 years. Girls are urologists' patients 2–3 times less often than boys. It is important to know that this disease can return at any moment; there is no 100% guarantee of recovery.
Causes
Urolithiasis is accompanied by the formation of stones. These are stones that are gradually formed from sand. Sand in the kidneys appears as a result of stagnation of harmful substances in the body. During normal kidney function, these substances are eliminated during urination.
There are two factors that provoke the crystallization of salts - general and local. The first includes:
- imbalance of acids and bases or acid-base balance;
- increased levels of calcium in the body;
- improper functioning of organs on which the level of fluid in the body depends;
- urine reaction;
- teenage hormonal changes;
- insufficient amount of vitamin A in the body and excess vitamin B.
The second factor, local, consists of four points:
- Inflammatory processes in the urethra.
- Pathology of the formation and functioning of the genitourinary organs.
- Increased or decreased amount of urine output per day.
- Hydronephrosis or stagnation of urine in the body.
The local factor is decisive in 90% of cases. This means that the risk of complications depends on the location of the stone. Most often, the formation of stones is observed in the right kidney and less often in the left. But sometimes, namely in 20% of cases, the disease affects both kidneys.
Types of stones
Stone formation in the human body is caused by an excessive amount of acids in the urine. Concretions are divided into types based on acid residues. There are 4 main types of kidney stones:
- Urate. Their appearance is promoted by uric acid. There is a lot of this element in foods such as fish, pork, chicken and beans.
- Cysteine deposits. This substance contains fermented milk, meat and fish products.
- Oxalate formations. They contain ethandic acid, found in many vegetables and fruits.
- Phosphate.
E338 is included in almost all taste and smell enhancers. Source: bestlaa.ru
Often the condition of a child who has been diagnosed with urolithiasis suddenly worsens. Exacerbation often occurs due to hypothermia, a virus or gastrointestinal infection.
Symptoms
Urolithiasis in children can develop without obvious symptoms. There are no acute pains in the kidney area, painful urination and fever. Small stones measuring 0.1 - 0.5 millimeters can leave the baby’s body unnoticed
But if a child complains of a nagging pain in the right side, you should listen to him. The pain may be accompanied by nausea and constipation, and the baby pees more often than usual. The urine will turn reddish due to blood in it, and the smell will be sour. This often means that stones are moving down the urethra.
Recognizing the signs of nephrolithiasis in infants is more difficult, but still possible. You should consult a specialist as soon as possible if the baby does not sleep well, is constantly capricious and cries. He is tormented by constipation or, on the contrary, diarrhea, as well as if the child begins to scream when the lower back is touched.
Complications
There are a number of complications of nephrolithiasis. These consequences can be quite serious:
- jade of varying complexity;
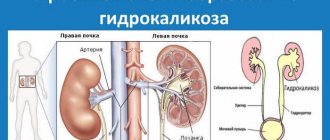
- hydronephrosis;
- renal failure;
- purulent formations inside the organ;
- kidney anemia (lack of red blood cells in the kidneys);
- kidney abscess.
Diagnostics
Having discovered symptoms of urolithiasis, parents should contact specialists such as a urologist and nephrologist. A urologist will examine your urethra, and a nephrologist will check your kidneys. Then the patient will have to undergo a series of studies:
- Ultrasound.
- CT scan of the urinary system.
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine.
- Urographic diagnostics.
- Retrograde pyelography. This is an x-ray method for examining the kidney.
Treatment
There are several treatment options. If stones have already appeared, then during treatment it is necessary to take certain medications. For example, “Eisenberg Mixture”, “Lidaza”, “Fitin” and “Magurlit”. No-shpa or Papaverine injection will help relieve pain. A strict diet also helps fight this dangerous disease.
Minimally invasive surgery in this case involves the installation of a catheter or stent. The catheter allows you to record the release of stone or sand and determine its nature. Using a stent, the ureter is widened, allowing stones to leave the body almost painlessly.
Complex surgical operations are performed extremely rarely in the modern world. But in some cases this procedure is necessary. Surgery may be prescribed in the presence of hydronephrosis (gradual death of the organs of the urinary system) and hematuria (the presence of blood in the urine is much higher than the permissible norm).
Traditional methods
Alternative therapy may well become an addition to the main prescriptions of a specialist. However, in order not to cause harm, you need to know exactly what residues of acids make up the crystals or sand in the kidneys. The following herbs will help fight certain types of stones:
- Urates - dill, lingonberries, birch branches and leaves.
- Oxalate - decoctions of strawberry leaves, horsetail and dill seeds will contribute to recovery.
- Phosphate and carbonate - infusions prepared from parsley, St. John's wort and lingonberries will help.
Symptoms
KSD in children can be asymptomatic and detected accidentally during examination. In other cases, the manifestation of the disease will be renal colic in the form of an attack. It can be triggered by physical overexertion, exposure to vibration, or a large amount of liquid drunk.
With colic, severe pain occurs in the lower back, spreading to the abdomen, groin and genitals. At the same time, the child is restless, rushes about, changes position to reduce pain, but this has no effect.
There is an increase in temperature and a decrease in the amount of urine in which blood can be observed. During an attack, nausea and repeated vomiting (or urges) appear, and sweating increases.
In children under 3 years of age, a typical attack of colic does not occur: only fever, severe anxiety, crying, vomiting, and a decrease in the amount of urine are noted.
Outside of an attack, children with ICD may periodically be bothered by unilateral pain in the lower back of a dull, aching nature.
Of particular danger are coral stones that completely fill the renal pelvis. Their formation is asymptomatic until the function of the affected kidney is impaired.
In young children, a secondary infection (chronic pyelonephritis, pyelocystitis, etc.) often develops against the background of urolithiasis; when examined in this regard, the presence of stones is also revealed.
DETAILS: Brief outline of the history of Russian urology
Coxitis according to microbial 10
Inflammatory damage to joint formations occurs in people of all ages and is accompanied by a number of unpleasant manifestations leading to impaired movement in the affected limb.
Symptoms and treatment of coxitis of the hip joint in children and adults are closely related, since the effectiveness of therapy is determined by the timeliness of a person seeking medical help.
The first symptoms of the pathology are pain in the hip joint, which intensifies during any movements. An external examination of the patient and instrumental research methods: radiography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging help to make an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Clinical diagnosis of KSD is carried out when a typical attack of renal colic occurs. In this case, additional research methods are also used.
Hardware diagnostic methods for ICD include:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- X-ray studies: urography, survey of the kidneys, intravenous pyelography, retrograde pyelography (but urate stones are not determined in this way);
- CT and MRI to exclude malignant kidney disease.
Most often in pediatrics, KSD is diagnosed using ultrasound. Hardware research methods not only confirm the diagnosis, but also determine the position of the stone, which is very important when choosing treatment tactics. They also make it possible to monitor the dynamics of the process and the progress of the stone.
The following laboratory methods are used:
- Urinalysis (clinical), which notes: an increased number of leukocytes and salts (urates, phosphates, oxalates). With renal colic, red blood cells may be found in increased numbers. In some cases, bacteria may be found with a urinary tract infection.
- Bacteriological urine analysis to determine the causative agent of urinary tract inflammation and its sensitivity to antibacterial agents.
- Clinical blood test - changes may be noted (leukocytosis and accelerated ESR) in case of infection.
- A biochemical blood test to determine the functional capacity of the kidneys and the electrolyte composition of the blood.
- Blood test for parathyroid and thyroid hormones, since in children ICD may be caused by impaired calcium metabolism.
- Crystallography during the passage of a stone (its spectral analysis).
Surgical treatment for kidney stones
Surgical intervention is allowed only if there are certain indications, which include:
- constant pain that is felt despite the fact that the child takes painkillers;
- severe renal impairment;
- growth of the stone in size;
- development of secondary infection;
- hematuria, that is, the appearance of blood in the urine, which indicates damage to the walls of the urinary system.
Both the age of the child and the “age” of the kidney stones matter. If they were identified 2-3 years ago, and during this time they could not be dissolved, then they will have to be dealt with by more radical methods.
Various surgical methods are used.
Treatment
Many specialists - urologists, nephrologists, pediatricians, surgeons - take part in the treatment of urolithiasis in children.
Treatment of urolithiasis is practiced conservatively and surgically. Conservative therapy is carried out in the absence of complications, when there are no obstacles to the outflow of urine. The purpose of this treatment is to relieve pain, dissolve and remove stones, and eliminate infections in the urinary tract.
Long-term therapy is carried out with combined herbal remedies (Cyston, Phytolysin, Cystenal). They have an analgesic, antimicrobial effect, relieve spasm and inflammation.
For uric acid urolithiasis, children are prescribed Allopurinol, Eisenberg's citrate mixture, and Uralit-U.
For calcium urolithiasis, methylene blue and lidase are used.
For oxalate stones, children can be prescribed vitamin B6 and phytin. For oxalate-urate stones, therapy is carried out with Magurlit, Blemaren.
For mixed urolithiasis, treatment is carried out using drugs such as Fitolysin, Nephrolit, Enatin, Nieron, Olimethin, tableted madder extract, Cystenal.
You can also use the recommendations of traditional medicine in the treatment of urolithiasis in children:
- for carbonate and phosphate stones, it will be useful to use parsley, lingonberries, decoctions of St. John's wort and lingonberry leaves;
- To remove oxalate stones, it is recommended to use decoctions of horsetail, strawberry leaves, and dill seeds;
- for urate stones, it is necessary to use lingonberries, dill, and a decoction of birch leaves.
DETAILS: Pediatric urology opening of the head || Pediatric urology opening of the head
If an attack of renal colic occurs, antispasmodics are prescribed (Baralgin, No-shpa is administered intravenously). Physiotherapeutic procedures are used (pulse magnetic therapy, inductothermy). When an infection in the urinary tract is detected, uroseptics (nitrofuran drugs) and antibiotics are used.
If the effect of conservative therapy is not obtained, the issue of choosing a surgical treatment method (non-invasive or invasive) is decided.
A number of modern technologies have been developed and are used in the treatment of urolithiasis in children, replacing open surgical intervention. These include:
- shock wave extracorporeal lithotripsy (ESLT), or stone crushing;
- endoscopic methods of surgical treatment - transurethral and percutaneous contact lithotripsy and lithoextraction.
Each of these methods is performed under anesthesia. To select the optimal treatment method for each child, a thorough examination is carried out, since each method, like open surgery to remove stones, has indications and contraindications.
The choice of treatment tactics is influenced by the following data:
- size and chemical composition of the stone;
- renal function and stage of renal failure;
- presence and type of infection in the urinary tract;
- condition of the urinary tract.
EBRT is the least traumatic non-invasive treatment method. Since in children the kidneys are closer to the surface of the body and the process of their formation has not yet been completed, stones during DLT are destroyed faster and easier than in adults. It is possible to use the minimum mode of the lithotripter apparatus and a smaller number of pulses.
The duration of the procedure (with intravenous anesthesia) is about 25 minutes. The elasticity of the urinary tract facilitates the removal of fragments of crushed stones with less severe pain compared to adults.
In second place in importance are endoscopic operations - they allow you to remove stones up to 2 cm in size. They are performed under general anesthesia, like open operations, which are still practiced in 1-5% of cases.
Regardless of the method used to remove stones, comprehensive postoperative treatment is required. This stage is extremely important for preventing relapse of urolithiasis.
It should include:
- active treatment of urinary tract infections (especially with phosphate stones) with regular bacteriological monitoring;
- treatment of any concomitant diseases;
- litholytic therapy, that is, the breakdown of salts (especially with urate stones) with herbal remedies;
- measures to restore kidney function.
Complications
Urolithiasis is a very serious disease that can lead to serious complications. Possible complications of ICD:
- hydronephrosis (progressive damage to the renal parenchyma, accumulation of urine in the dilated renal pelvis);
- chronic renal failure;
- abscesses (ulcers) in the kidney tissue;
- urosepsis (spread of infection from the kidney through the bloodstream, damage to many organs).
DETAILS: Qualifying tests in urology (Omsk Diagnostic Center). (*correct answers are marked) Potencia.com || Medicine questions and answers urology
Types of stones
Stone formation in the human body is caused by an excessive amount of acids in the urine. Concretions are divided into types based on acid residues. There are 4 main types of kidney stones:
- Urate. Their appearance is promoted by uric acid. There is a lot of this element in foods such as fish, pork, chicken and beans.
- Cysteine deposits. This substance contains fermented milk, meat and fish products.
- Oxalate formations. They contain ethandic acid, found in many vegetables and fruits.
- Phosphate. E338 is included in almost all taste and smell enhancers.
Source: bestlavka.ru
Often the condition of a child who has been diagnosed with urolithiasis suddenly worsens. Exacerbation often occurs due to hypothermia, a virus or gastrointestinal infection.