Features and reasons
The right kidney is more often displaced than the left. Of the 91 cases described by Ebstein, displacement of the right kidney was observed 65 times, the left - 14 times; in other cases, both kidneys were displaced. Women are more susceptible to this disease: there are 1-18 men per 100 women. A wandering kidney is most often observed between 30 and 60 years of life, although there are indications in the literature that a wandering kidney was also observed in childhood: for example, Steiner saw wandering kidneys twice in girls aged 6-10 years and once in a boy, aged 9 years.
The appearance of this disease is attributed to relaxation of the abdominal walls as a result of repeated pregnancies or a decrease in perirenal adipose tissue due to rapid weight loss. Sometimes a wandering kidney appeared when carrying heavy weights, during severe coughing attacks, after heavy bowel movements, when walking long distances, etc. In some cases, the appearance of a wandering kidney was caused by a bruise in the lumbar region.
What complications can there be?
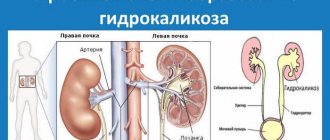
When the kidney moves downwards, the ureter begins to twist, making it difficult for a person to go to the toilet. When urinary retention occurs, stagnation occurs, urine becomes more and more, the outflow is poor, all this can end very badly until hydronephrotic transformation.
Pyolonephritis is another thing that this disease leads to in a large number of cases, that is, we are talking about an inflammatory process. The disease can be acute, the pain syndrome is akin to hepatic colic; naturally, emergency medical care is necessary here.
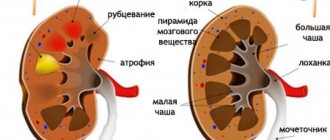
The renal artery can become very stretched; there are often cases when its length becomes 2 times greater, and at the same time it narrows. As a result, renal hypertension may develop, which is accompanied by blood pressure. The dangerous thing is that drug treatment here is difficult to help. There is a lack of blood, oxygen and essential nutrients, resulting in hypertensive crises.
Symptoms
One of the first symptoms, and sometimes the only one that arouses the patient’s attention, is pain localized in the ilium or hypochondrium. Sometimes the pain is replaced by a feeling of heaviness in one of the lumbar sides. The peculiarity of the pain is that when lying on the back, it weakens or completely disappears. During this physical examination of the abdomen, one can state in the lateral parts, under the free edge of the ribs, the presence of an elongated, ovoid, elastic formation that does not have any irregularities; the pressure on education is extremely painful. If the abdominal walls are very relaxed, then it is possible to cover the formation from all sides and accurately determine that the kidney itself is in the hands, that is, to distinguish its oval shape, convex edge, internal concave edge, etc. It is better to identify a mobile kidney in a standing position, since in a horizontal position the tumor most often disappears. Percussion of the area of the formation gives a dull sound, completely different from the tympanic tone of the intestines. In those cases where the formation cannot be accurately determined, information can be obtained by tapping the renal area from behind; then in place of the dull sound of the kidney one can easily ascertain intestinal tympanitis.
In addition, with a wandering kidney, a whole complex of various neuralgic pains in the area of the sciatic, femoral and other nerves has been repeatedly reported. Most patients suffering from a wandering kidney are extremely irritable, nervous, and quick-tempered; Men repeatedly develop symptoms of hypochondria, and women experience hysteria.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis can be made based on the patient's complaints; it must be carefully examined through palpation (when the kidney is palpated). Instrumental and laboratory studies are used.
Urine taken for analysis often contains protein and leukocytes. X-rays and ultrasound are the most effective diagnostic methods for this disease. X-ray of the urinary system, urography, and the pictures must be taken of both a lying patient and a standing one. Often there is a need to examine all organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Kidney strangulation
Prof. Dietl was the first to point out, under the name of infringement phenomena, a group of symptoms that is characterized by an increase in the volume of the displaced organ; in this case, the slightest touch to the kidney, even the lightest, causes sharp pain. These pains are accompanied by chills, fever, nausea, vomiting, signs of collapse, etc. This attack may end after several days with copious discharge of urine mixed with pus and mucus. The phenomena of strangulation and the seizures they cause are explained by the rotation of the displaced kidney around its axis and compression of the ureter, which, in turn, leads to acute hydrocele of the kidneys. The B. kidney itself very often undergoes very sharp and various changes. Most often, hydronephrosis (renal dropsy), kidney stones, diffuse inflammation of the kidneys, cancer, suppuration, etc. are observed.
The wandering kidney must be differentiated from tumors of the gallbladder, mobile spleen, fecal masses, peritiphlitis, local inflammation of the peritoneum, tumors of the adrenal glands, ovarian cysts, etc.
Stages of the disease
The wandering kidney can be classified into several stages. In its development, three stages of the pathological process are distinguished.
The first stage in which the wandering kidney can be identified by palpation.
The kidney is palpated on inspiration. As you exhale, it moves to the right hypochondrium. Usually seen in thin people!
At the second stage, the kidney can move from the hypochondrium. At the same time, in a lying position, it returns to the same place.
The third stage is characterized by the fact that the kidney descends. Namely - in the small pelvis.
go to top
conclusions
Treatment is usually palliative and should consist primarily of the application of a well-adapted renal band. Other symptoms are treated according to the existing seizures. In Russia, the school of S.P. Botkin worked especially hard on the issue of the wandering kidney.
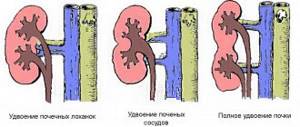
In severe cases, nephropexy is performed - (from the Greek nephros
- kidney and
pexia
- fixation, fastening) - a surgical operation to fix the kidney in its physiological state (to eliminate pathological mobility during nephroptosis).
In our country, the Rivoire method, modified by Pytel and Lopatkin, is more often used, the essence of which is to cut out a flap from the lumbar muscles and suture it not to the rib, as with the Rivoire method, but to the kidney itself. This preserves the physiological mobility of the kidney, which is important for its good function. In recent years, laparoscopic methods have begun to be used for nephropexy.
In what cases is wearing a bandage contraindicated?
When the kidney prolapses, it is contraindicated in cases where there are mechanical damage to the body in the form of abrasions and scratches that are located in the area where the belt is fixed. It is also not recommended to use a renal band if the organ is significantly displaced from the correct anatomical location, specifically the renal bed. In case of severe pain, experts also do not recommend wearing a bandage. In this case, it is better to undergo a comprehensive examination so that the doctor can identify the cause of severe pain and prescribe a different treatment algorithm.
In fairness, it should be noted that there are cases when patients do not comply with all the instructions and recommendations of doctors regarding wearing. As a result, wearing the belt incorrectly does not give the expected results. On the contrary, during the next examination by the doctor, even more aggravated problems are revealed, often leading to surgical intervention.
Today in pharmacies there is a wide selection of models and sizes of belts, so each patient can easily choose a bandage that will correspond to the waist circumference. However, before purchasing a bandage, you must first consult with your doctor.
In adults
Nephroptosis can appear at any age. This pathological condition of the kidney is observed mainly in women. Although there are cases of manifestation in men.
According to statistics, in 2% of cases the disease affects women of childbearing age. More often during pregnancy. Or under the influence of infections or injuries.
What else could cause the process? The disease can develop due to an anatomical predisposition. Let’s say that the structure of the female organs, one way or another, contributes to the wandering of the kidney.
It is known that women have a certain pelvic structure. Wider pelvis and decreased abdominal wall tone.
In adults, the kidneys are in a mobile state. When you inhale and exhale, they move a certain number of centimeters. This directly contributes to the physiological excretion of urine.
The insidiousness of the disease is that with the duration of the location of the kidney. It can be fixed in a certain place for a long time.
Treatment methods
A wandering kidney cannot be cured with medication. Taking medications only relieves the symptoms of the pathology. The main purpose of medications is aimed at:
- normalization of blood pressure;
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- suppressing the risk of development and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms.
Conservative
At the early stage of nephroptosis, wearing a special bandage is indicated. The belt is put on the patient when he is in a supine position and is fixed while inhaling. It is recommended to wear the bandage during the day and remove it at night. The best option is to select a bandage according to the patient’s individual body size, but modern medicine offers belts with adjustable fasteners that can be easily adjusted to fit the body shape.
The main disadvantage of the bandage is the weakening of the muscles of the lumbar and abdominal regions. To prevent this process, it is recommended to perform special physical exercises that help return the displaced organ to its place.
Wearing a bandage is contraindicated for patients whose internal organ is in a displaced position due to the presence of adhesions in the surrounding tissues.
Physical therapy exercises
A course of special exercise therapy provides a positive effect of therapy for nephroptosis. At the initial stage, the exercises are performed under the supervision of a specialist; subsequently, the physical warm-up complex can be continued independently.
Together with therapeutic exercises, the patient should adhere to a gentle salt-free diet, and also limit any physical activity.
Possible consequences and prevention
Complications of nephroptosis:
- Recurrent pyelonephritis.
- Venous hypertension of the kidney vessels.
- Hydronephrosis.
- Urolithiasis disease.
To prevent kidney nephroptosis, it is recommended:
- strengthen the abdominal press;
- get rid of excess weight;
- wear a bandage during pregnancy;
- monitor children's posture;
- strengthen the immune system.
In the first degree of nephroptosis, contraindications include heavy lifting, hypothermia, and sudden weight loss. Your kidneys should be checked annually (ultrasound, urine test). These measures will help prevent the progression of the disease.
Symptoms
If the kidney has become wandering, and its deviation from the natural bed is great, the patient will definitely notice this, since the pathology in this case is accompanied by certain symptoms.
Unfortunately, stage 1 nephroptosis is quite difficult to recognize and visually diagnose, since there are no obvious symptoms, the person simply does not worry about anything.
It is most often possible to identify a grade 1 vagus organ only by chance, when a person is sent for ultrasound diagnostics for other reasons.
However, each person is unique, so the body can perceive individual internal pathological processes differently.
As a result, a wandering kidney can be suspected based on the individual symptoms that appear. In particular, pain in the lumbar region indicates renal pathologies.
If pain is eliminated after changing body position, it is quite possible that the organ has become overly mobile and wandering. It is no secret that a wandering kidney can be returned to the renal bed, indeed occupying a horizontal position.
Symptoms of a wandering kidney can also include increased heartbeat, as well as an excessive increase in blood pressure.
In some cases, the vagus organ manages to affect the nerve endings, squeezing them, resulting in neuralgia, excessive irritability and hot temper.
Nephroptosis is also characterized by loss of appetite and intestinal disorders.
In addition, the patient feels a clear loss of strength, dizziness, and often experiences insomnia.