Nephropathy in pregnant women refers to late toxicosis and is a complication of dropsy. Nephropathy in pregnant women is observed in the second half of pregnancy and disappears completely after childbirth. The transition from dropsy to nephropathy in pregnant women can occur either gradually, with a constant worsening of symptoms, or extremely quickly, almost with lightning speed. There are two types of nephropathy: primary and secondary. Primary nephropathy occurs in pregnant women with uncomplicated toxicosis. Secondary nephropathy develops against the background of other diseases, such as hypertension, pyelonephritis, heart disease and glomerulonephritis.
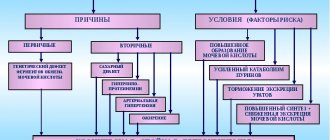
Causes of occurrence and mechanism of development
The exact causes of the pathology have not been established. Existing hypotheses allow us to formulate a list of significant risk factors.
The development of nephropathy is due to:
- Accumulation of toxins, harmful products of metabolic processes in the placenta and uterus.
- Deterioration of blood clotting indicators.
- Complications of hypertension, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis.
- Heart defects.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Hyperthyroidism and other endocrine diseases.
- Malfunctions affecting the functioning of the nervous system.
- Overwork, stress overload.
- Diseases that affect the immune system.
- Immune conflicts between mother and baby.
- Chronic forms of infections.
- Hepatitis.
- Cholecystitis.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Obesity.
- Diabetes.
- Early (before 17 years) or late (after 35 years) pregnancy.
- Multiple pregnancy (development of two or more fetuses).
- Nephropathy suffered during a previous pregnancy.
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle.
- Vitamin deficiency.
- Unfavorable heredity.
- Tobacco smoking and other bad habits.
Stages of the hypothetical development of pathology: arterial spasm leads to venous expansion, increased permeability of vascular walls, penetration of plasma into the intercellular space, changes in blood composition, destabilization of the uterine and placental circulation, fetal hypoxia, hypertensive manifestations in the mother.
As nephropathy progresses, vascular spasm intensifies and serum creatinine concentration increases. The enlarged uterus puts pressure on the internal organs, which leads to fluid stagnation and increased swelling, aggravated by renal sodium retention. Blood circulation worsens, platelet concentration increases, the liver, brain, placenta, and nervous system are affected.
According to some hypotheses, the key risk factor is uterine ischemia, the accumulation of waste products in the placenta with the production of substances that negatively affect the functioning of the kidneys and contribute to circulatory disorders.
Causes of the disease
Nephropathy in pregnant women, what it is and how it manifests itself, is of interest not only to expectant mothers, but also to future grandparents. A condition that does not have a completely positive result alarms all family members who are concerned about the health of the pregnant woman and her baby.
You should sound the alarm if a woman:
- first pregnancy - the body’s reaction to hormonal changes is unknown, the risk of a diagnosis of “nephropathy in pregnancy” increases tenfold;
- hereditary diseases of the urinary tract, vascular diseases, allergies, the manifestation of gestosis on the maternal side and the predisposition of the pregnant woman to endocrine diseases;
- crisis periods of age for the first birth - up to 18 years and over 35;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the expectant mother - pyelonephritis, adnexitis, heart disease, diabetes mellitus, II and III degrees of obesity;
- manifestation of gestosis during the first and second pregnancy;
- chronic ToRCH infections - herpes, cytomegalovirus, human papillomavirus;
- bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol during pregnancy;
- Rh conflict between fetus and mother.
In most cases, the cause of a disease such as nephropathy in pregnant women is changes in the concentration of hormones entering the blood. Such hormonal imbalances are a consequence of renal dysfunction.
Often, nephropathy in pregnant women manifests itself when expecting the first child and carrying twins. Expectant mothers suffering from chronic pyelonephritis, hypertension, and obesity are at risk.
Classification of the disease
There are three stages of the disease (according to severity).
First degree - pressure does not exceed 150/90 mm Hg. Art., proteinuria - less than 1 g/l, swelling appears in the legs.
During pregnancy, the patient’s blood pressure is constantly monitored, urine and blood are examined
The second stage (preeclampsia) – the pressure reaches 170/110 mm Hg. Art. (pulse difference - at least 40), protein concentration - up to 3 g/l. Hyaline casts appear in the urine, swelling spreads to the anterior abdominal wall, diuresis is at least 40 ml/hour.
The third degree (eclampsia) is accompanied by pressure readings above 170/110 mm Hg. Art. with a pulse amplitude of less than 40, proteinuria more than 3 g/l. When diagnosed, a high concentration of granular cylinders is detected, and generalized swelling is observed. The diuresis rate does not reach 40 ml/hour. Urgent hospitalization is required.
Primary nephropathy, which manifests itself in healthy kidneys, progresses during pregnancy, disappearing without a trace after childbirth. The secondary form is aggravated by kidney diseases, hypertension, heart defects, vascular insufficiency, and pathologies affecting the functioning of other body systems.
Subtleties of terminology and a little theory
Nephropathy in pregnant women is a rather unpleasant complication of the second half of pregnancy, which is popularly called late toxicosis. It occurs quite rarely (according to various sources, from 20 to 150 cases per 1000 pregnancies), but due to the severity of symptoms and the progressive nature of development, it is considered one of the main causes of child and maternal mortality. However, here it is worth clearly understanding that with timely and qualified medical care, such a scenario can usually be avoided.
However, nephropathy in pregnant women (or, to put it simply, diffuse kidney damage) is an exclusively domestic “invention,” since abroad such a condition is usually called preeclampsia or proteinuric hypertension. And if in our country the disease is considered one of the stages of gestosis, then in Western Europe it is recognized as an independent nosological unit.
Almost always, nephropathy in pregnant women occurs after 34 weeks (that is, almost at the finish line), but begins to develop from about 20 weeks. From the first symptoms (more about them below) to the development of severe and very dangerous complications (eclampsia, preeclampsia) it takes from 2 days to 2-3 weeks, so at the first symptoms you need to immediately (!) consult a doctor.
Symptoms and manifestations
Nephropathic manifestations are detected after the 4-6th month of pregnancy. Swelling of varying intensity (dropsy), increased blood pressure (diastolic, systolic), and increasing proteinuria are observed.
Patients complain of worsening sleep, headache, overexcitation, frequent mood swings, apathy, dizziness, and thirst. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fever, weakness, nausea, flatulence, and dyspepsia. Painful sensations in the lumbar region, visual, speech, and auditory disturbances are detected.
Pain spreading to the right hypochondrium indicates liver damage. The second and third stages are accompanied by an increase in the concentration of uric acid in urine, a decrease in renal blood flow, convulsions, neurological disorders, impaired blood clotting, hoarseness, coughing, difficulty in nasal breathing, and skin itching.
Nephropathy in pregnant women: the dangers that diagnosis poses for the pregnant woman and the fetus
In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, moderate preeclampsia is called nephropathy of pregnancy. In the Russian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, this pathology is called gestosis.
Symptoms of nephropathy in pregnant women develop after the 20th week of gestation.
The pathology is based on widespread spasm of microvessels and impaired blood supply to internal organs, which entails their failure.
What leads to the development of nephropathy?
An increase in the number of patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension and overweight women leads to an increase in the frequency of gestosis during pregnancy. It is the main etiological factor in the morbidity of newborns and ranks 3rd among the causes of maternal mortality.
Two factors play a role in the development of nephropathy:
- Placental. If, at the time of formation of the placenta, it incompletely grows into the spiral arteries of the uterus, then insufficient blood supply and ischemia develop. To compensate for this condition, vascular active substances (inflammatory mediators, interleukins, tumor necrosis factor) are released. But gradually they damage the blood vessels and pass into the mother’s blood. This leads to the development of vascular dysfunction in other organs.
- Maternal factor is diseases that a woman had before pregnancy and aggravate microvascular damage. These include diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, kidney pathologies, and fat metabolism disorders.
In some women, the formation of nephropathy can be predicted. The following conditions increase your risk:
- chronic stress leads to frequent release of substances that affect vascular tone, while the body’s adaptive abilities are disrupted;
- pregnancy with existing diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, endocrine pathologies (including hyperthyroidism), cholecystitis, hepatitis, vegetative-vascular dystonia and obesity;
- hereditary predisposition, maternal gestosis;
- for diseases of the immune system, increased allergization;
- the age of the pregnant woman is up to 17 years;
- in women who suffered nephropathy during a previous pregnancy;
- chronic infections;
- smoking;
- malnutrition.
Vitamin deficiency and a sedentary lifestyle of a pregnant woman have a great influence on the formation of pathology.
The mechanism of pathology formation
The pathogenesis of nephropathy is based on the release of vasoactive substances by the placenta, which leads to generalized vasospasm. In the kidneys, blood flow and glomerular filtration are reduced. At the same time, serum creatinine increases. Sodium is retained by the kidneys, but does not allow water to leave. Permeability to protein increases and it is excreted in the urine.
The kidney senses ischemia and, to eliminate the problem, releases substances that further increase vascular spasm. The amount of aldosterone decreases, but vascular permeability increases, which leads to the release of fluid into the tissue and the formation of edema. The volume of circulating fluid decreases.
All kidney functions are gradually disrupted: hormonal, excretory, filtration, resorption and regulatory, the amount of protein in the urine increases.
Classification
A classification of nephropathy is based on clinical manifestations. It is characterized by edema of varying severity. Dropsy of pregnant women can be hidden or visible.
Obvious swelling is divided into 4 degrees:
- Swelling of the legs.
- Lower limbs + abdomen.
- Attachment of facial edema.
- Anasarca, total swelling.
The severity of nephropathy itself is assessed using the Savelyeva scale. Each pathological condition is assigned its own number of points, their sum is an indicator of severity. Pregnant nephropathy of the 1st degree - up to 7 points, moderate severity - 8-11 points, severe nephropathy - 12 or more.
Concomitant diseases are those that worsen the condition and increase the risk of developing pathology.
Manifestations of nephropathy
The main clinical signs that distinguish nephropathy in pregnant women from mild gestosis are the classic triad:
- Edema.
- Proteinuria.
- Arterial hypertension.
Symptoms do not appear all at once, usually there is a gradual addition of signs of nephropathy. Swelling is often the first to appear. Sometimes this is a latent form of dropsy, which can be suspected by pathological weight gain.
The weight increases by 600 g or more per week. Systolic pressure rises by 20-30 mmHg. Art. from the original, and diastolic by 15 mm Hg. Art. After some time, proteinuria joins the first symptoms.
Sometimes the classic triad of signs is not observed; the pregnant woman develops one or two of them.
During normal pregnancy progression, blood pressure remains virtually unchanged. In women with gestosis, a significant increase in pressure can lead to overload of the left ventricle of the heart and the development of pulmonary edema.
Symptoms accompanying nephropathy in pregnant women
If nephropathy develops against the background of pre-existing hypertension, then its course is more aggressive and quickly reaches grade 3. An isolated increase in only diastolic pressure with low systolic pressure is considered an unfavorable phenomenon that deserves special attention.
Increased pressure leads to characteristic changes in the fundus of the eye. In this case, the following signs are observed:
- swelling of the optic nerve nipple;
- spasm of arterioles;
- traces of hemorrhages.
Sometimes, with pronounced pathological conditions of the fundus, a decision may be made about early delivery. But if the pressure returns to normal, then the pathological changes disappear. Preservation of signs of eye pathology persists with existing chronic pyelonephritis or hypertension.
Protein in the urine may be combined with traces of red blood cells (microhematuria) or cylindruria. If hematuria is significantly pronounced, then nephropathy is combined with glomerulonephritis.
Mild nephropathy in pregnant women can worsen its course, and additional symptoms appear:
- headache;
- drowsiness or state of agitation;
- dyspeptic disorders in the form of nausea, vomiting;
- behavioral disorder, irritability, tearfulness, frequent mood swings;
- impairment of vision, hearing, speech;
- feeling of heat.
The appearance of hoarseness, difficulty in nasal breathing, and coughing indicates widespread edema and is an unfavorable sign. Skin itching, the appearance of pain rashes in the right hypochondrium are evidence of liver damage.
The following symptoms indicate that the condition of grade 2 severity is progressing and risks developing into eclampsia:
- impaired consciousness of varying severity, the extreme state is coma;
- retinal detachment and sudden loss of vision;
- acute renal failure;
- respiratory failure and signs of pulmonary edema;
- acute liver failure and HELLP syndrome;
- premature placental abruption;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- convulsions.
Nephropathy after childbirth, if it does not occur against the background of pre-existing hypertension and kidney disease, usually resolves and does not lead to the persistence of severe symptoms. Otherwise, the disease may worsen its course.
Complications due to nephropathy
Pathological conditions that arise during pregnancy affect the condition of the fetus. Complications may be as follows:
- intrauterine growth retardation in combination with feto-placental insufficiency;
- asphyxia and hypoxia of the fetus, which can result in antenatal loss of the child;
- premature detachment of a normally located placenta;
- premature delivery or spontaneous termination of gestation before 22 weeks.
The consequences of nephropathy in pregnant women manifest themselves in labor disturbances. Blood pressure may begin to increase during labor, leading to labor abnormalities. During childbirth and the postpartum period, the risk of bleeding increases.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
At each visit to the gynecologist, a pregnant woman is prescribed a urine test, blood pressure is measured and the presence of swelling in the legs is checked. Weighing is mandatory. These simple techniques allow you to notice pathological symptoms at an early stage and carry out appropriate treatment.
The results of all measurements are entered into the pregnant woman’s chart. This allows you to dynamically monitor the progress of pregnancy.
When the first symptoms of nephropathy appear, additional examination is carried out to identify the extent of pathological changes:
- coagulogram;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, liver;
- blood chemistry;
- measurement of daily diuresis;
- fetal cardiotocography after 27 weeks of gestation;
- Ultrasound of the fetus and determination of uteroplacental blood flow;
- ECG.
In many cases, an examination by an ophthalmologist is prescribed, who assesses the condition of the fundus. According to indications, a consultation with a nephrologist, endocrinologist, or cardiologist is carried out. Other diagnostic methods may be used, depending on the individual case.
Treatment options
Treatment of nephropathy in pregnant women is determined by the severity. For grades 1-2, hospitalization in the pregnancy pathology department is required. Severe nephropathy is treated in the intensive care unit.
In the maternity hospital, a therapeutic and protective regime is created, which reduces the load on the nervous system. Bed rest and a general reduction in physical activity are mandatory. A woman needs proper sleep and rest.
The diet should be balanced. The daily salt intake must be limited to 3 g, the amount of liquid is reduced to 1.3-1.5 liters. This includes all drinks, soups, and juicy fruits.
Drug treatment includes drugs aimed at lowering blood pressure. To do this, intravenous drip infusions of magnesium sulfate solution are performed. It has a hypotensive effect, reduces uterine tone, and improves placental blood flow.
To reduce vascular spasm, antispasmodics are prescribed: Drotaverine, Papaverine, Platyphylline. Diuretics that are administered after a drip, for example, Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide, help reduce swelling.
Under the control of a coagulogram, disaggregants and anticoagulants are prescribed to improve the rheological properties of blood. This can be Aspirin in small doses, Dipyridamole, Pentoxifylline. The duration of their use is determined individually.
Correction of metabolic and electrolyte disturbances, restoration of organ blood flow, and the amount of protein is carried out through infusion therapy.
Blood plasma infusion helps maintain sufficient amounts of blood clotting factors, which prevents bleeding.
Correction of the electrolyte composition occurs due to solutions of Poliglyukin, Reopoliglyukin, Ringer, dextrose, and saline solutions.
Treatment of nephropathy in pregnant women with herbs is a supportive and distracting method. Traditional methods are not able to influence pathological changes in blood vessels. When using only herbal medicine, the risk of the disease progressing to a serious condition increases.
The choice of delivery date depends on the effectiveness of the treatment. For mild nephropathy, treatment is carried out for 2 weeks. If it does not have a significant effect, then termination of pregnancy is indicated.
Treatment of moderate nephropathy lasts 5-6 days. Severe nephropathy requires emergency treatment in the intensive care unit. If there is no effect of treatment within 3-12 hours, then emergency delivery is indicated. To do this, a cesarean section is performed, during which endotracheal anesthesia is used.
Prevention of gestosis and its complications
To prevent the symptoms of nephropathy from becoming a surprise, timely prevention is necessary. It should begin before conception with examination and elimination of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, treatment of chronic kidney diseases, and diabetes mellitus. It is necessary to achieve stable remission of these pathologies. For overweight women, a diet to reduce it is recommended.
During pregnancy, a woman should get enough rest and not go to bed too late. But at the same time we must not forget about physical activity. You can perform some gymnastic exercises on your own or in schools for pregnant women.
Nutrition for the period of bearing a child should be balanced in terms of essential nutrients. Additionally, take multivitamin complexes. Be sure to limit table salt. It is recommended to cook dishes without salt, and add salt directly on your plate.
Women at risk for the development of nephropathy during critical periods are prescribed drugs that improve placental blood flow and reduce tone. This is Curantil, Magne B6.
Pregnant women must follow all doctor's instructions. If the therapy is effective, then the pregnancy is prolonged until fetal maturity.
After suffering severe nephropathy, a woman should be observed by a therapist for a year. This is necessary to promptly treat the consequences of the pathology in the form of a persistent increase in pressure, kidney damage, and changes in the fundus.
If you follow your doctor's instructions and receive proper treatment, the prognosis for nephropathy is favorable.
Source: https://ginekolog-i-ya.ru/nefropatiya-beremennyh.html
Diagnostic methods
From the point of view of potential risks of complications, regular measurement of pressure, body weight, diuresis monitoring, laboratory tests of blood, urine, hormonal tests, and fundus examinations are of great importance.
High-precision diagnostic methods include Dopplerography, phonocardiography, cardiotocography, ultrasound, electrocardiogram, study of uteroplacental blood flow, biopsy, and magnetic resonance imaging of the kidneys.
To organize the most effective treatment and preventive procedures, additional consultations are held with highly experienced specialists in the field of cardiology, neurology, endocrinology, nephrology, and ophthalmology.
The mechanism of pathology formation
The pathogenesis of nephropathy is based on the release of vasoactive substances by the placenta, which leads to generalized vasospasm. In the kidneys, blood flow and glomerular filtration are reduced. At the same time, serum creatinine increases. Sodium is retained by the kidneys, but does not allow water to leave. Permeability to protein increases and it is excreted in the urine.
The kidney senses ischemia and, to eliminate the problem, releases substances that further increase vascular spasm. The amount of aldosterone decreases, but vascular permeability increases, which leads to the release of fluid into the tissue and the formation of edema. The volume of circulating fluid decreases.
All kidney functions are gradually disrupted: hormonal, excretory, filtration, resorption and regulatory, the amount of protein in the urine increases.
Treatment and prognosis
Therapy carried out in a hospital setting, taking into account the severity of the disease, involves the use of specialized drugs, but also correction of the daily regimen aimed at eliminating any types of overload.
Diet therapy is an important component of treatment. Patients need to limit the consumption of fatty foods, salt (less than 1.5-2.5 g/day), liquids (up to 1000 ml/day, taking into account all types of liquid foods). It is advisable to supplement the personal menu with vegetable, fruit dishes, dried fruits, protein, foods high in carbohydrates and potassium compounds. It is useful to organize fasting days with a predominance of lactic acid products. Alcoholic drinks are strictly contraindicated.
Drug treatment is aimed at replenishing protein deficiency and normalizing macro- and microhemodynamics. Therapy includes the use of:
- Antispasmodic complexes (drotaverine, platyphylline, papaverine).
- Antihypertensive drugs (magnesium sulfate).
- Potassium drugs.
- Diuretics.
- Herbal medicines
- Antiplatelet agents.
- Protein preparations (albumin).
- Calming agents.
- Antihistamine complexes.
- Thiol drugs (unithiol).
- Tranquilizers.
- Multivitamins.
- Drugs that help restore cellular metabolism.
- Special solutions for correcting electrolyte blood parameters.
If necessary, hirudotherapy sessions are performed. In severe stages, with low effectiveness of drug treatment, the threat of placental abruption, hypoxia, there is a need for urgent delivery (caesarean section).
Self-medication poses a significant threat to the health of mother and baby.
With timely, highly effective therapy, symptomatic manifestations are eliminated after several days in the hospital, and pregnancy continues. In addition to painkillers and other therapeutic procedures, measures are organized aimed at reducing the risk of fetal hypoxia.
Newborns are observed by a neonatologist. The mother's blood pressure normalizes, the concentration of protein in the urine decreases, swelling is eliminated, and kidney function is normalized.
Preventive actions
Measures to prevent nephropathy are standard; it is important to inform your doctor about changes, concerns, and observations. When collecting anamnesis, indicate hereditary, chronic diseases so that the gynecologist can get an accurate picture of the patient and possible complications during pregnancy. Strictly follow all doctor’s recommendations regarding nutrition, amount of drink, physical and psychological stress. Take all tests and undergo the necessary studies in a timely manner. To summarize all of the above, do not interfere with medical workers who, like a woman during pregnancy, are interested in a successful and easy completion of pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby.
Nutrition rules
During pregnancy, diet is very important for both mother and baby. If we add nephropathy to this, it turns out that a mother should think a hundred times before violating the doctor’s recommendations regarding food. A special diet is prescribed. Since a lot of protein is excreted from the body in urine, its amount should be replenished. It is responsible for the normal development of the entire fetus, and it will not be superfluous for the mother, because protein is necessary for the proper functioning of organs and systems. But the amount of salt should be reduced. Products with a high salt content will only aggravate the situation with nephropathy, which is extremely undesirable for the mother. That is, you should absolutely not eat any salty, smoked or spicy delicacies. It is better to replace them with fresh vegetables and fruits, healthy berries, natural juices and fruit drinks. But you should not get carried away with a large amount of liquid, as this is also fraught with the appearance of edema. For each individual case, the attending physician draws up an approximate menu, which the mother must strictly follow.
Sleeping mode
Pregnant women are familiar with the constant feeling of drowsiness when they want to sleep at any time of the day or night. You shouldn't indulge your body. You need to adhere to a normal, physiological daily routine, with an 8-9 hour interval for sleep. It must be remembered that sleep from 22.00 is more useful as a rest than sleep from 24.00 and later.
To ensure that you feel good during pregnancy and that your baby is born healthy, you must follow the recommendations and instructions of specialists. After timely and correct treatment, nephropathy completely disappears, as does the range of unpleasant symptoms, and childbirth proceeds normally for the woman, without complications.
Complications and consequences
Long-term pathology that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods is accompanied by a high risk of:
- Delayed fetal development.
- Premature placental abruption.
- Asphyxia.
- Hypoxia.
- Miscarriage.
- Bleeding, labor abnormalities.
- Cerebral edema, stroke (ischemic, hemorrhagic).
- Cardiac asthma.
- Liver necrosis.
- Acute renal failure.
- Mental disorders.
- Stopping breathing.
- Impaired consciousness.
- Eclamptic (convulsive) seizures.
- Retinal detachments.
- Sudden deterioration of vision.
- Pulmonary edema.
Early nephropathy is extremely unfavorable for the health of the pregnant woman and the fetus. High risk of fatal consequences.
Why does nephropathy form during pregnancy?
Doctors are confident that such a disease is based on several active factors. The most important of them is pregnancy - the body changes completely, protective barriers become extremely vulnerable. As the pathology develops, the normal blood supply to all vital organs is disrupted due to massive spasm of the venous and arterial vessels.
This may be caused by the following reasons:
- stress and mental stress;
- intense physical activity;
- the presence of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- congenital and acquired heart and vascular defects;
- recent infections, colds or flu;
- insufficiency of the immune system;
- injuries and surgical interventions;
- poor nutrition (consuming small amounts of liquid and salt more than 5 grams per day);
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drugs);
- unauthorized use of pharmaceuticals;
- overwork at work;
- exposure to adverse environmental factors (air, water, soil pollution).
Prevention
During the entire period of pregnancy, blood pressure, body weight, kidney function, and urinary system should be monitored, toxicosis should be identified and eliminated in the initial stages.
You can reduce the risk of nephropathy and its consequences by:
- Timely treatment of chronic forms of renal and cardiovascular diseases.
- Regular walks in the fresh air help improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Maintaining a sufficient level of physical activity.
- Optimization of the daily routine, proper rest.
- Increasing stress resistance.
- Use of vitamin complexes.
- Limit the amount of salty foods you consume.
- Compliance with the drinking regime prescribed by the doctor.
Maximum attention to well-being and health status should be paid to patients with a predisposition to nephropathy.
Prognosis for nephropathy
If signs of nephropathy were detected at an early stage, then the condition, dangerous for mother and child, can be treated quickly and effectively. In the future, only enhanced control and compliance with preventive measures are required.
More serious stages of nephropathy with the risk of developing preeclampsia, eclampsia and gestosis require long-term treatment and constant monitoring by doctors. In complex cases, if drug treatment is ineffective, emergency delivery may be required. This fact is due to the fact that severe forms of gestosis threaten not only the health, but also the life of a woman.
With effective treatment of nephropathy, pregnancy can be preserved and safely brought to natural birth. During labor, special attention is paid to the condition of the child and monitoring the development of intrauterine hypoxia. In the postpartum period, additional examination of the woman is required with a thorough check of renal function and the cardiovascular system.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: Date of publication:
Gynecologists - search service and appointment with gynecologists in Moscow
Features of pregnancy
The correct tactics for managing pregnant patients with gestosis allows you to prolong pregnancy until the natural date of birth or at least until the period when the life of the woman and the fetus is not in danger.
If pregnancy proceeds with complications, from the second trimester it is necessary to constantly check blood pressure levels, do blood and urine tests.
If gestosis is established in the second half of pregnancy, the following preventive measures are used:
- Salt-free diet with a reduced volume of liquid (daily portion of calories - up to 3500 kcal, salt - 6-8 g per day, liquid - 1.3-1.5 l).
- Special bed rest (you need to lie on your left side from 10 to 13 and from 14 to 17 hours, at this time the peak of blood pressure is recorded).
- Mandatory multivitamin intake to prevent consequences for the unborn child.
- Herbal infusions: diuretic, sedative, renal, to normalize vascular tone.
- Preparations for restoring cellular metabolism (“Asparkam”, etc.).
In some cases, drug therapy is prescribed in the first days after childbirth to prevent relapse of gestosis.