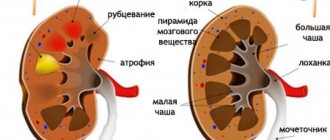
When a person's kidneys are healthy, the difference in size between them will be insignificant. Much more dangerous are situations when one kidney turns out to be smaller than the other or when kidney hypertrophy occurs. The difference between the internal organs is a sign of severe renal pathologies, incurable and chronic. However, with the right therapeutic measures, sleep and wakefulness, and a balanced diet, the consequences and complications of ailments that affect changes in the size of the kidneys can be significantly reduced.
Signs
First of all, the presence of pathology is indicated by renal colic - pain in the lumbar region.
At the same time, newborns become capricious and restless. Parents need to be extremely careful, as it is difficult to identify problems in children. At the first latent stage, which all diseases go through, the problem can only be recognized during palpation or instrumental examination. When an inflammatory process occurs, the patient’s body temperature rises, while appetite worsens and the functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted, nausea and vomiting occur. Gastrointestinal disorders accompany almost every kidney disease.
The next sign is impaired diuresis. During the process of emptying the bladder, the patient may experience pain and burning in the perineum, as well as pain in the pelvic area. Also, depending on the reason for the change in the size of the organ, the volume of urine excreted may increase or decrease.
The presence of pathological processes in organs is indicated by changes in general clinical indicators. With an infectious-inflammatory lesion in the urine, the level of leukocytes increases. With urolithiasis, the number of red blood cells, protein and salts increases.
Attention! With renal hyperplasia, the severity of symptoms is usually lower. A characteristic feature of a small kidney is the absence of pain.
Life after nephrectomy
Sometimes one of the two kidneys has to be removed. This operation is called nephrectomy. In this case, a person can also lead a full life, with the exception of some restrictions. In the postoperative period, rest and bed rest are necessary. All food should be gentle.
The remaining kidney will increase slightly in volume, which will be accompanied by slight discomfort, which will pass over time. After nephrectomy, a person should adhere to gentle physical activity and carry out hardening procedures.
Food should be high in calories, but easy to digest. Preference should be given to:
Symptoms of poor kidney function
- Dishes of vegetables and fruits.
- Rye bread.
- Fermented milk products.
- Dishes made from lean meat or fish.
Fatty, canned, and spicy foods can be consumed in limited quantities. Maintain drinking regime. Sharp restriction of fluid and salt is undesirable.
Why can one kidney be larger than the other in children?
Hydronephrosis is a common cause of pathologies in children.
Sometimes children experience changes over time, when one kidney is smaller than the other, this indicates a problem in the genitourinary system. Significant changes in the size of the kidneys indicate the development of pathologies within the body. Among the causes of pathologies in a child are hydronephrosis and hypoplasia. With hypoplasia, one kidney does not develop like the other; this pathology is often congenital. Hypoplasia can develop simultaneously with dysplasia or mental retardation.
Hydronephrosis can be congenital or acquired. The peculiarity of the disease is that it can pass without pain. Pathology is determined by pain symptoms, finding out where the discomfort is localized. The enlargement of the kidney is explained by the constant filling of the pelvis. Most often, girls over 25 years old suffer from hydronephrosis. Another reason for the increase is an additional vessel that compresses the ureter, making the normal outflow of urine impossible. No less dangerous is the narrowing of the urinary system, which also prevents the normal flow of urine. The narrowing becomes a consequence of injury to the organ.
- Diagnosis: hypoplasia
- About hydronephrosis and hypertrophy
- Are there any chances to save the baby’s life and maintain health?
- What can you do?
When a person's kidneys are healthy, the difference in size between them will be insignificant. Much more dangerous are situations when one kidney turns out to be smaller than the other or when kidney hypertrophy occurs. The difference between the internal organs is a sign of severe renal pathologies, incurable and chronic. However, with the right therapeutic measures, sleep and wakefulness, and a balanced diet, the consequences and complications of ailments that affect changes in the size of the kidneys can be significantly reduced.
Hypoplasia
With hypoplasia, one kidney is smaller than the other because it develops too slowly. This condition is most often congenital; the pathology spreads to one kidney. But there is evidence of cases where both kidneys were affected.
This disease begins to form in the mother's womb. It can develop according to one of the following scenarios:
Even if the disease occurs in a simple form, pyelonephritis often develops in a pathologically small kidney.
The fact that hypoplasia is developing in the body is indicated by the following signs:
- Frequent hyperthermia for no apparent reason.
- Diarrhea and vomiting.
- The appearance of rickets.
- Paleness of the skin.
Diagnostics
In order to determine pathological changes in paired organs and the cause of their occurrence, it is necessary to seek help from a specialist - a nephrologist. During the examination, the doctor will conduct a survey, examine the patient and refer him for clinical and instrumental examinations.
- One kidney from birth: causes of anomaly, how to live with such a pathology
The process of kidney enlargement
Throughout life, the volume of the kidney constantly changes, this is due to various reasons; they can be divided into acquired and congenital. The latter can be diagnosed during intrauterine development; ultrasound diagnostics are used for this. Congenital factors are characterized by anatomical defects, defects of the body, in which the child is immediately born with a pathology. Acquired causes lead to the development of various diseases, and are also provoked by exogenous factors.
Kidney health is negatively affected by problems with urine excretion, which provokes urine retention; this also applies to increased vasodilation, which impairs blood circulation. The following reasons for the increase in kidney volume can be identified:
- taking hormonal drugs;
- self-medication;
- a lot of fluid in the body;
- poor nutrition;
- bad heredity;
- bad habits such as alcohol and smoking;
- pyelonephritis;
- hydronephrosis.
When some causes are eliminated, the kidneys quickly return to normal. It is enough to improve your diet, get rid of bad habits, make your life more active and give up self-medication. But the last reasons should be dealt with in more detail.
Pyelonephritis contributes to the expansion of the calyces and changes in the pelvis. On the 5th day of illness, the kidney increases in size, becoming particularly painful when palpated by a doctor. At the same time, the presence of pus in the urine and a large number of bacteria are determined.
With urolithiasis, the pelvis is filled with medium or large stones. The reasons for organ enlargement due to illness depend on the factors causing the disease:
- environmental;
- genetic predisposition of the patient.
Coral stones in an enlarged organ contribute to its subsequent atrophy. Enlargement of the organ occurs during an acute inflammatory process. The patient needs to remove obstacles to free outflow:
- urine;
- stones;
- formed narrowings in the ureters;
- malignant neoplasms.
A sharp increase in the presence of creatine in the blood indicates the formation of renal failure.
- Three kidneys in humans: symptoms and diagnosis of anomalies
Partial blockage of the ureter contributes to the formation of an infected process in the pelvis. The patient is bothered by pain in the lumbar region, aching, prolonged, with bouts of vomiting and increased blood pressure. The kidney can be easily palpated by the doctor during examination. With bilateral enlargement of the organ after interstitial nephritis, the amount of residual nitrogen in the blood increases. With glamerulonephritis, numerous changes lead to the development of chronic diffuse processes with the formation of a shriveled organ.
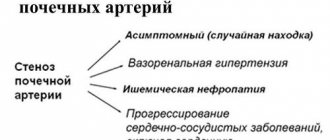
The main reasons for the development of hydronephrosis
Conservative treatment involves symptomatic therapy organized in the first stages of the disease. It consists of taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, medications to reduce blood pressure, as well as other drugs depending on the signs of damage. In case of infection, antibacterial treatment is required. As a rule, conservative treatment is carried out before surgery.
As for surgical intervention in the disease process, organ-saving surgery is mainly organized to eliminate the cause of hydronephrosis and restore kidney function. It is best to perform surgery in the early stages of the disease, when changes in the organ are still reversible, especially in situations with congenital disorders.
It is important!
Surgical intervention involves the resumption of patency of the urinary canals, and in advanced stages of the disease - plastic surgery of the renal pelvis and restoration of its normal size.
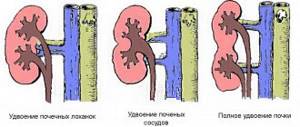
Nephrectomy is performed only if the process is severely advanced, when the kidney has completely lost the ability to function, and its preservation can cause inflammation and, as a result, other serious complications.
Hydronephrosis refers to the reason why one kidney is smaller than the other. This disease develops due to functional failures in the genitourinary system. Gradually, urine begins to fill the renal pelvis.
The phenomenon when one kidney is larger than the other is not uncommon. Nobody pays much attention to it if the difference is insignificant. This feature is common to many people when the kidneys increase in size over the years.
But sometimes unexpected “surprises” arise when one kidney differs significantly in size from the other. Such changes can cause functional disorders in the body. Such problems provoke a deterioration in a person’s condition, and the consequences can lead to serious illnesses.
Manifestations in children
When an ultrasound diagnosis was made of hypoplasia, it is necessary to find out why one kidney is larger than the other.
During the first years of life, children grow very quickly. The body is under enormous stress. Therefore, you should carefully monitor the baby’s condition. As already mentioned, in such cases, quite often the child lags behind in development.
There are no drugs that can restore the kidney to its correct size. To maintain normal health, you should lead a healthy lifestyle. A balanced diet and moderate physical activity will help you avoid noticing this diagnosis, renal hypoplasia in adults.
Preventive measures
If a person knows that he has been missing 1 kidney since birth or has had a nephrectomy, then his lifestyle may be somewhat different from other people. Although preventive measures will not hurt everyone else, as they provide recommendations for maintaining general health:
- Infectious diseases should be prevented.
- In the presence of chronic ailments, promptly eliminate the source of inflammation.
- Avoid hypothermia of the body.
- Periodically visit a urologist to monitor kidney function.
In general, we can say that the life of a person with one kidney is not much different from the life of other people. Many young women are concerned about how they will be able to give birth to a child with one kidney, and whether this is acceptable.
There are many examples of such women giving birth to completely healthy babies. This circumstance is not a contraindication for childbirth. In medical practice, of course, there are cases of unsuccessful pregnancies in women with one kidney; it all depends on the characteristics of each specific situation.
Symptoms and treatment
An enlarged kidney sometimes does not affect the patient’s condition in any way, and can only be detected after an outbreak of infection or injury at the time of palpation.
Symptoms of pathology
A symptom of the disease is an increase or decrease in the amount of urine in relation to painful attacks. Most urine is released immediately after the pain disappears.
Feeling places in the hypochondrium and comparing them reveals that one kidney is enlarged. The presence of blood in the urine also indicates such an anomaly.
When one kidney is large, the patient feels:
- Reasons for the development of hydronephrosis transformation of the kidneys, symptoms, diagnostic methods and treatment
pain, discomfort in the side; temperature increase; painful or frequent urination; presence of blood in the urine.
Symptoms of hypoplasia practically duplicate the symptoms of hydronephrosis. However, in most cases they occur without pain.
Hematuria
Unfortunately, this pathology has an extremely negative impact on the general condition, since it inhibits both the physical and mental development of a person.
If you discover a fact indicating that one kidney is large, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The medical institution will prescribe comprehensive treatment to restore the normal functioning of the organ or at least somewhat mitigate its pathological condition.
Drug treatment
When making a decision, doctors must take into account the degree of damage, the causes of the disease, as well as the speed with which this anomaly develops.
In the treatment of hydronephrosis, the use of anti-inflammatory, analgesic and blood pressure-lowering drugs is indicated. If there is a developing infection, antibacterial treatment must be carried out.
In advanced forms, surgical intervention is indicated to return the organ to its normal size.
If you have a small kidney, a certain diet is indicated, excluding salt consumption and limiting foods high in protein.
Since the second kidney compensates for the work of the affected hypoplasia, surgical intervention is used only when additional lesions are present in the form of:
urinary tract infections; urodynamic abnormalities; changes in hemodynamics; manifestations of nephrosclerosis.
How to cure the disease
As for the increase, at the beginning the doctor must conduct a thorough examination of the patient, take into account complaints and analyze the clinical picture. Once the diagnosis of hydronephrosis is confirmed, the specialist is required to select an individual treatment regimen.
Therapy should be aimed at improving kidney function and completely eliminating the pathological condition. In some cases, it is necessary to take into account the manifestation of symptoms and whether the organ is much enlarged. We must not lose sight of the speed of development of the disease. The main goal of treatment is to completely eliminate hydronephrosis.
It is generally assumed that a conservative treatment method will be used, especially if the kidney has increased slightly. Therapy includes taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. The patient is also prescribed medications that can lower blood pressure.
2pochki.com
Possible complications
If the disease becomes advanced, a person can experience very serious complications. If the kidney enlarges due to the accumulation of fluid in its cavities, sooner or later the walls of the organ rupture. The rupture provokes very severe bleeding - if surgery is not performed immediately, the patient dies.
However, even if the patient scrupulously follows the instructions of the attending physician, hydronephrosis can provoke illnesses such as kidney stones, pyelonephritis and nephrolithiasis.
Pathologies associated with kidney size
Hypoplasia can affect a person from both sides at once. Traditional therapy is not used for treatment and it is believed that it does not bring significant results. If this disease is detected, surgery is recommended. Hypoplasia forms in children in the womb. The affected organ does not differ in appearance from a healthy one.
It is believed that hypoplasia occurs in children without any symptoms. But you need to know that pyelonephritis can develop in a damaged kidney. This will cause increased pressure in the smaller organ.
The disease can affect two organs at the same time. This is its most severe form. It can be diagnosed in the first months of a child’s life. Children suffering from this disease develop unevenly and differ in development from their peers. Hypoplasia is indicated by the following signs:
- Pale skin;
- frequent high body temperature;
- diarrhea.
Also, due to the damaged organ, the baby often vomits. Blood pressure remains normal, but if kidney failure develops, it will rise.
This disease is easily detected with the help of modern medicine. The symptoms of hypoplasia and pyelonephritis are believed to be similar because both diseases cause irreversible kidney damage.
If the different size of the kidneys does not cause any special problems in the child’s health, then treatment is not necessary. A healthy organ is able to compensate for the work of a sick one. Medical intervention will be required in cases where secondary lesions begin to develop.
In the absence of treatment or advanced hypoplasia, nephrectomy is prescribed.
Diagnosis: hypoplasia
The appearance of a difference in the size of the kidneys in a child is most often a consequence of a congenital anomaly.
This deviation from the norm is observed in 8-11% of newborns. Hypoplasia can affect one or two kidneys. Traditional therapy in treating the disease is considered ineffective, and if an anomaly is detected, doctors recommend surgery. The formation of hypoplasia in children occurs when they are still in the mother's womb. Externally, the larger kidney is no different from the smaller one. Hypoplasia can:
- proceed in a simple form;
- combined with oligonephronia or dysplasia.
It is generally accepted that hypoplasia in children is asymptomatic. But it is necessary to take into account the fact that pyelonephritis usually develops in a reduced kidney. Doctors say one of the reasons for the latter disease is higher internal pressure in a smaller kidney.
The disease can affect one or both organs at the same time. The most severe condition in children is bilateral hypoplasia. It is usually detected in babies in the first year of life. Children who have this anomaly usually lag behind their peers in physical development. The following signs will indicate the presence of hypoplasia in a baby:
- pale skin;
- frequent fever;
- diarrhea;
- manifestations of rickets.
Impaired functioning of the affected kidney causes frequent vomiting. Blood pressure readings, as a rule, are normal, but if the baby’s hypoplasia provokes the appearance of renal failure, blood pressure will rise.
A deviation from the norm, when one kidney is larger than the other, is quite easily diagnosed by modern medicine through ultrasound, excretory urography and radioisotope examination. It is generally accepted that the signs of hypoplasia and pyelonephritis are similar. This is true because both diseases involve irreversible damage to the kidney tissue. However, the renal calyces with hypoplasia do not undergo deformation, but if this process occurs, it indicates the presence of pyelonephritis in the affected kidney.
When hypoplasia does not clearly show its symptoms and there is no significant impairment in the functioning of the reduced kidney, the child may not require treatment. The second kidney, the size of which corresponds to the norm, compensates for the incomplete functioning of the reduced organ. Surgical intervention will be required if secondary lesions begin to develop:
- changes in hemodynamics;
- urodynamic disorders;
- urinary tract infections;
- nephrosclerosis.
When the baby’s kidneys are functioning within normal limits, parents should make sure that the concentration of salt and foods containing animal proteins in the little patient’s diet is strictly limited. Successful non-surgical treatment of hypoplasia is possible if even in the baby the third part of the organ has retained its functioning. When his kidney failure progresses, doctors prescribe embolization of the arteries in the kidney or nephrectomy - removal of the reduced organ.
Return to contents
Polycystic kidney disease
Another disease that can lead to enlarged kidneys is polycystic disease, in which multiple fluid-filled cysts appear in the organ. If there are several of them (one or two), it’s usually not a big deal. But if there are a lot of them or they become too large, destructive changes begin in the kidneys: the cysts slowly replace healthy kidney tissue, greatly reducing their functions and leading to kidney failure.
Polycystic disease is the fourth leading cause of kidney failure (5% of cases). In many patients, polycystic disease does not appear until the age of thirty or forty. The first symptoms of this disease are:
- High blood pressure is the most common symptom of polycystic disease, which can be accompanied by headaches. High blood pressure causes the destruction of kidney tissue, so timely treatment of hypertension can prevent or slow down the onset of kidney failure.
- Pain in the side or back.
- Abdominal enlargement.
- Blood in urine.
- Frequent kidney or bladder infections.
- Fluttering or gurgling sensations in the chest. Twenty-five percent of people with polycystic disease suffer from relaxation of the heart valves, which is accompanied by chest pain.
It is possible to accurately diagnose polycystic disease using ultrasound. Sometimes CT scans and magnetic resonance scans can identify small cysts that ultrasound cannot detect. MRI can measure the volume and size of kidneys and cysts. In some cases, genetic testing is performed using a blood test.
The main cause of polycystic disease is heredity, namely abnormal genes. Polycystic kidney disease is transmitted by both dominant and recessive types. With autosomal dominant polycystic disease, a child only needs to receive the defective gene from one parent to develop polycystic kidney disease. Symptoms usually appear after the age of forty, but the disease can also develop in childhood.
Infantile or autosomal recessive polycystic disease is rare (in 1 case per 25 thousand people) and occurs in newborns or infants. For this disease to occur in infants, pathological genes are needed from both parents. Symptoms of pathology appear already in the womb.
Chances of recovery
First, we note that the most severe form of the disease is bilateral. Because of it, children may develop kidney failure, which will only worsen the situation. The disease itself occurs in several stages, each of which has its own effective treatment. At stage 1, the use of non-surgical methods is allowed, and at stage 3, only nephrectomy can save lives.
Another reason for different organ sizes is hypertrophy. It is not dangerous in all cases. It depends on how the baby develops in the future. This disease does not have clearly identified symptoms, but in some cases it is similar to various tumors.
The first type is characterized by an adaptive function. And the second is that the organ enlarges due to a large amount of fatty tissue. It is especially dangerous for patients.
Why do the kidneys become different sizes?
When prolapsed, the ligamentous apparatus is unable to hold the kidneys in their normal place. This situation can be caused by the following factors:
- Hematomas, injuries and bruises - when tears occur, the ligaments lengthen and the organ is not fixed securely.
- Strong physical activity - when pressure increases in the abdominal cavity, the ligaments stretch and the kidneys drop.
- Sharp weight loss leads to depletion of the fat capsule.
- Postpartum period - during the birth of a child, the muscles are greatly weakened, as a result of which the kidney may prolapse.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Low motor activity - the tone in the abdominal muscles decreases, causing the pressure to drop and the organ to descend.
- Chronic diseases - liver cirrhosis, tumors and other infections.
- Congenital pathologies of the location of one or both kidneys.
A slight difference in kidney size is normal. This state of affairs does not pose a danger, so doctors are in no hurry to sound the alarm. But a significant deviation in the size of organs is already dangerous to health.
A situation where one kidney is larger than the other to a significant extent signals the development of a very dangerous pathology in the body. Moreover, this pathology often takes on a chronic nature and cannot be completely cured. But you shouldn’t despair in advance: if you carefully follow all the doctors’ recommendations, the risk of possible complications will be minimal.
So why does one kidney become larger or smaller than another? This is due to hydronephrosis or hypoplasia.
Adrenal parameters
The adrenal gland of an adult weighs at least 12 g, length – 40–60 mm, width – up to 30 mm, thickness – 4–7 mm. Some people are born with only one adrenal gland. The adrenal gland of a newborn weighs a maximum of 7 g, and this is almost twice as much as the mass of the organ of a one-year-old child.
This is explained by the fact that the mass of the organ has decreased due to the thinning of the cortex, which is in the process of restructuring. By the age of five, the mass of the adrenal glands returns to the initial value, after which it gradually increases. The cortex of the organ is formed by the age of 12.
By the age of 20, the weight of the adrenal gland becomes greater, the maximum size indicators are reached - up to 13 g. In the future, neither the size nor the mass of the adrenal tissue undergoes changes. Women's adrenal glands are slightly larger in size compared to men's. During pregnancy, the adrenal gland enlarges by 2 g.
In the eighth decade, there is a decrease in the mass and size of the organ. The adrenal glands are located asymmetrically: the left one is slightly behind the right in size and weight