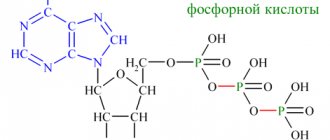
Norepinephrine (L-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-aminoethanol) belongs to the group of catecholamine compounds. Aka norepinephrine - international nonproprietary name. Typically, the term "norepinephrine" is used in relation to a substance created by the body itself. “Norepinephrine” is more often called an artificially synthesized hormone used as a medicine.
Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-SA 4.0. Photo by Mark Oniffrey.
Based on its functions in the body, norepinephrine can be called the “elixir of activity.” Moreover, norepinephrine plays a similar role in both of its guises: it is both a neurotransmitter and a hormone of the sympathoadrenal (adrenergic) system. Like its brother adrenaline, norepinephrine (NA) is produced abundantly during the fight-or-flight response to acute stress. The differences between them are that adrenaline is more responsible for flight, while norepinephrine is primarily an aggression substance. The topic of the difference between these hormones is described in more detail here: “Norepinephrine and adrenaline: differences.”
Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-SA 3.0
This photograph of an athlete best illustrates the role of norepinephrine in the body. Not only is the 196-centimeter Bob Sapp here in a frankly “offensive mood,” but in addition, norepinephrine is also necessary for the overall activity of the body: both physical and mental. There is no doubt that this athlete nicknamed “The Beast” in the photo is very….active.
How it is formed and how it works
Adrenaline and norepinephrine are synthesized from tyrosine. This is an amino acid that is included in the protein composition of any food. Every day a person absorbs a certain amount of tyrosine with food, this substance is transformed into norepinephrine. If the concentration is high, the amino acid, together with its derivatives, stimulates the CNS (central nervous system) and the functioning of many organs. Therefore, it is not advisable to eat such food before bed (for example, cheese) or when taking antidepressants as prescribed by a doctor.
When a neurite comes into contact with a cell and transmitters, it is called a synapse. Activation of the latter occurs after a signal impulse about an external stimulus passes through the neurite, for example, painful sensations, vivid emotions. In this case, the mediator acts on sensitive points. The neurotransmitter affects the state (excitation or inhibition) at different rates depending on the type of receptor: alpha or beta.
In the central nervous system it is one of the main mediators. It acts in the part of the brain responsible for controlling internal organs in stressful situations and during physical activity. It works as follows:
- strengthens the work of the heart muscle;
- constricts blood vessels;
- dilates the bronchi to enhance breathing;
- inhibits the digestion process in the gastrointestinal tract.
To launch different processes (simultaneously excitation and inhibition), adrenergic receptors are required, which are also used in the manifestation of adrenaline activity.
How to balance the presence of catecholamine
The building blocks of norepinephrine are phenylalanine and the amino acid tyrosine. For this reason, the rise in norepinephrine levels can be regulated by food consumption:
- Cheese;
- Seafood;
- Legumes;
- Eggs;
- Bananas;
- Chocolate;
- Chicken meat, etc.
In addition to food, you can increase norepinephrine readings by sleeping during the day.
If the natural balance of the hormone is insufficient, the doctor may prescribe an appropriate medication. Synthetic and natural medicines are widely used. Indications for use in this case are the following drugs:
- norepinephrine;
- norepinephrine agetan;
- norepinephrine hydrotartrate;
- serotonin.
It is important to follow the doctor's guidance and follow the instructions when using norepinephrine.
Impact on stress
Activation of the adrenal glands is one of the types of work of the sympathetic nervous system. As a result, adrenaline is capable of changing the activity of any organs; its influence is greater than that of a neurotransmitter. Its effect also extends to those cells that are not related to the sympathetic nervous system:
- in the liver;
- adipose tissue;
- in the blood (erythrocytes), etc.
When the adrenal medulla is activated, the effect is much stronger and its duration is much longer than that of norepinephrine. In the case of serious stressful conditions, adrenaline is actively produced, and stress in the chronic stage maintains an increased concentration constantly. As a result, the body begins to deplete due to excessive energy consumption, and disturbances in the functioning of the heart and gastrointestinal tract appear.
In a normal state, the short-term effect of norepinephrine is complemented by adrenaline, which ultimately results in the usual reaction (excitement, increased activity, surge of energy) to stress, physical activity, etc.
In the brain, the neurotransmitter is produced in a small area at the front of the surface of the brain. This is a kind of blue spot with several million NS cells, the neurites of which form a large number of branches. As a result: synapses can be found in various parts of the central nervous system.
Prolactin, stress and pregnancy
In women, stress hormones cause increased secretion of prolactin. This hormone is associated with reproductive function. As the concentration of the active substance rises, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, ovulation does not occur, and problems arise with conceiving a child.
Prolactin levels increase during pregnancy. This is a normal physiological reaction, since one of the functions of the substance is to ensure lactation. Hormonal imbalance leads not only to emotional swings, but also to problems with pregnancy, and subsequently, with breastfeeding.
Main functions
In short, norepinephrine is responsible for the mental state of stress. Moreover, its functions are not limited to the psychological side; other aspects are affected:
- brain activity;
- mobility;
- tactile sensations;
- emotional condition;
- memory, etc.
The mediator is responsible for activating the central nervous system by inhibiting sleep. Therefore, when stressed, a person is active, falls asleep worse, and suffers from insomnia due to endless worries.
The next function is to inhibit sensory sensations, as a result we can focus on important signals. The substance serves as a pain reliever in case of extreme conditions. In a state of passion, serious tissue damage and injury may not be noticed.
The neurotransmitter is involved in the regulation of motor activity, which is expressed in increased mobility and increased running speed. Therefore, during stress, a person constantly moves and is unable to sit still for a long time.
Norepinephrine plays an important role in controlling and regulating the dynamics of various needs and motivations for action. The centers of activity are located in the hypothalamus and tonsils. By influencing these points it reduces anxiety and aggressiveness. The more active the locus coeruleus is, the more pronounced the temperamental traits inherent in choleric people are; in emergency situations, the choice falls on the option of solving the problem at any cost. The brain is susceptible to more impulsive actions, characterized by sudden outbursts of aggression.
Ultimately, the hormone actively regulates emotional behavior, namely a positive mood during stress (the joy of victory, excitement, a portion of emotions from a sense of risk, etc.).
Norepinephrine is a hormone of what?
But norepinephrine is more commonly called the “stress hormone.” Indeed, norepinephrine is one of the body’s humoral tools for the physiological support of “fight or flight” reactions, but to a lesser extent than adrenaline. Its concentration in the blood increases in all stressful situations: fear, anxiety, nervous and emotional stress, injuries, burns, blood loss.
The fight-or-flight response involves the body's readiness to confront or flee from danger. Accordingly, norepinephrine causes a number of corresponding, mobilizing changes in the body.
If we consider norepinephrine in terms of purely somatic reactions, then norepinephrine is a hormone of what, what changes in the body? These are the following physiological changes:
- The force of skeletal muscle contraction increases.
- The speed (frequency) of heart contractions increases.
- In addition, NA modulates the function of certain types of immune cells (for example, T lymphocytes), which play a major role in acquired immunity.
- The concentration of glucose and free (non-esterified) fatty acids in the blood increases (norepinephrine promotes the breakdown of fats).
- Blood pressure increases. This happens in two ways. The first is through narrowing the lumen of blood vessels (vasoconstriction). Second, due to an increase in cardiac output, the heart muscle pushes blood out of the heart with greater force. Due to these changes, there is an increase in perfusion pressure in the coronary and cerebral arteries. But at the same time, peripheral vascular resistance and central venous pressure increase significantly. Instructions for using the drug norepinephrine in the very first lines of the description of the pharmacological action state:
The need to strengthen muscle function to ensure “fight” or flight is obvious. Increasing blood pressure has the same purpose - supplying tissues and cells with oxygen. An increase in blood glucose levels is necessary to improve the nutrition of muscles and organs - this is energy for the body (in fairness, it is worth noting that adrenaline causes a much greater rise in blood glucose levels).
In general, norepinephrine is a hormone of what? Mobilization of the body in the face of danger: “everything for the front, everything for victory”!
Balance in the body
To increase the release of adrenaline, and with it norepinephrine, humanity has come up with a lot of ways. These are mainly extreme sports:
- descent along mountain rivers;
- parachuting;
- attractions;
- video games;
- casino games, etc.
However, it is important that the person emerges victorious, otherwise the result will be negative, that is, the feeling of euphoria is replaced by the annoyance of defeat. A portion of adrenaline makes you experience a feeling of joy and excitement again and again, which is actually why people become addicted to gambling and computer games.
For harmony, concentration should be average, no more and no less. Excessive content of the mediator or its deficiency leads to the manifestation of:
- hyperactivity;
- outbursts of aggression;
- irritability;
- apathy and depression;
- decreased concentration;
- memory impairment.
You can adjust the balance with the help of antidepressants and other drugs, but it should be taken into account that other hormones, such as endorphin and serotonin, are also involved in the process of regulating emotions.
After transmitting the signal to the receptors, the neurotransmitter is destroyed and gradually absorbed into the nerve endings with the help of special proteins. Then it is released again and transmits signals to receptors.
Drug treatment
Dozens of different drugs have indications for treating depression. The main class is antidepressants, which come in several types. Their main difference is the method of influencing neurotransmitters - chemicals that are produced by the brain.
Antidepressants are classified as follows: first-line, second-line and third-line drugs. Most often, specialists begin by prescribing first-line medications. Particular preference is given to antidepressants of the SSRI class. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are quite effective and have a small list of possible side effects. This class includes:
- paroxetine;
- escitalopram;
- fluoxetine;
- citalopram;
- sertraline.
The most powerful blocker that inhibits the actions of adrenergic neurons is the first drug.
The next class of first-line medications - selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors - affect 2 types of receptors. Duloxetine, milnacipran and venlafaxine are often used. This therapy may be effective for those for whom previous class of medications have failed.
The first line also includes the following inhibitors, antagonists and stimulants:
- OIMAO-A;
- SYZNAN;
- AASR;
- IOSSAS;
- Tianeptine (Coaxil).
Second- and third-line drugs are also quite effective. The non-selective class of tricyclic antidepressants was among the first to be developed, and until recently was widely used. However, these drugs have more pronounced side effects. For this reason, their use is used less frequently.
Research methods
Since the discovery of hormones, scientists have been trying to synthesize substances similar to them or, on the contrary, action blockers. Skillful direction of influence helps to control blood pressure, treat rhinitis, bronchial asthma, etc. For older people, drugs based on the functions of the mediator are indispensable in the treatment of hypertension, because they prevent strokes and heart attacks.
Until a few decades ago, research was carried out on animals. With the development of technology, it was possible to see how the system works on the human body under conditions of different manifestations of emotions. These methods make it possible to clearly show reactions in people depending on their character, age, living conditions, etc.
Stress management
The development of depression and other negative consequences of stress can be prevented if you learn to manage your internal state. There are many ways and special techniques to increase stress resistance. They will help you stay calm and “take the hit” in a stressful situation. In this list:
- relaxing practices;
- physical exercise;
- walks in the open air;
- listening to music;
- nice talking;
- good sleep;
- planning and time allocation.
The human body responds to stress with a chain of biochemical reactions, which are accompanied by the release of adrenaline, norepinephrine, and cortisol into the blood. They are called stress hormones. Their role is to increase the adaptive capabilities of the body. If a person is exposed to constant stress factors, pathological changes occur.
- Routes of drug administration during patient resuscitation.
- Norepinephrine in ampoules
About the unexplored
The human body is a complex of complex systems, one of which is the cardiovascular system. It controls tens of thousands of kilometers of blood vessels in all organs and tissues affected by adrenaline and norepinephrine. Little is still known about the variety of mediator effects due to research limitations. Moreover, laboratory mice, snails and fruit flies do not provide a complete picture of its impact on the behavior of other creatures on the planet. However, the research that has already been carried out is enough to confirm: man is not the only unique creature on the planet.
How to reduce norepinephrine levels
Normalization of norepinephrine in a “nutritional” way - by drinking green tea and its extracts. They contain the compound epigallocatechin gallate (and norepinephrine is a catecholamine). Of course, green tea also contains caffeine, which helps increase norepinephrine levels. But other components of green tea reduce this effect of caffeine.
Losing weight can reduce norepinephrine levels. In men, a relationship has been noted between the distribution of adipose tissue and the level of norepinephrine. If fat is deposited mainly around the abdomen, then norepinephrine levels are increased. The authors of this study hypothesized that reducing belly fat would reduce norepinephrine levels.
Psychotherapy, specifically the use of cognitive behavioral therapy. The benefit of CBT is that it allows you to get rid of maladaptive coping mechanisms. These are the so-called psychological defenses that are developed to overcome negative experiences. Not all of them are good ways to counteract psycho-emotional problems. Psychotherapy is designed to help people identify these maladaptive mechanisms and replace them with healthier thinking patterns. This method allows you to reduce the level of anxiety and aggressive feelings. Accordingly, the level of norepinephrine in the body decreases.
Important. If you have been given prescriptions or advice from a doctor, then all of the above methods do not replace medical advice.
As you can see, norepinephrine is a very “multifaceted personality” among the hormones of the human body. I hope you found this article useful and interesting.
Decrease in indicator
A reduction in norepinephrine synthesis occurs against the background of degenerative changes in nervous tissue. The reasons for the decrease in study values are:
- Neuropathies
. Deviations from the norm are detected in patients with diabetic neuropathy, parkinsonism, Alzheimer's disease, and Riley-Day syndrome. - Taking medications
. Catecholamine levels decrease when taking clonidine, imipramine, reserpine, and MAO inhibitors. A decrease in value against the background of pheochromocytoma confirms the success of treatment.
Normal values
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
The normal level of serum norepinephrine for adults is 70-150 pg/ml. For children under 14 years of age, reference values have not been determined - the vein puncture procedure is stressful, increases the level of the hormone, which neutralizes pathological changes in its secretion. Urine analysis standards for different ages are (in mcg/day):
- 0-1 year – 0-10.
- 1-2 years – 1-17.
- 2-4 years – 4-29.
- 4-7 years – 8-45.
- 7-10 years – 13-65.
- 10-15 years – 15-80.
- After 15 years – 0-97.
If the training rules are not followed, there is a high risk of a physiological increase in performance. The concentration of catecholamine increases with emotional stress, physical activity, smoking, consumption of foods/drinks with caffeine, vanillin, and alcohol.
Norepinephrine and adrenaline: what is the difference
Hormone and neurotransmitter
Although epinephrine and norepinephrine act as both hormones and neurotransmitters in the body, adrenaline plays more of a hormone role. Norepinephrine is primarily a neurotransmitter.
Hormone
A hormone is a substance that is released into the blood by specialized cells. Often they are collected in a gland. Hormones travel through the bloodstream throughout the body and affect many tissues and organs. Moreover, their effect is long-lasting – minutes and hours.
Neurotransmitter
The neurotransmitter is produced in the axon (the outgrowth of the neuron). This process forms contact with the target cell in which mediators work: another neuron, a muscle cell, a gland cell. The action of the mediator is strictly selective - only on this target cell. The action is very short - no more than a few seconds.
The contact between a neuron's axon and another cell is called a synapse. A synapse is triggered when an electrical impulse arrives along the axon, which represents a signal about a sensory stimulus: an emotion, pain, a decision made by the brain. Released from the end of the axon, the mediator acts on sensitive proteins located on the surface of the target cell: receptors. For norepinephrine, these adrenergic system receptors are divided into two types: alpha and beta. They differ either in the speed of operation or in the nature of the effect that appears on the next cell: excitation or inhibition.
The action of norepinephrine is associated with a predominant effect on α-adrenergic receptors.
Norepinephrine and adrenaline: differences in appearance
The Great Medical Encyclopedia reports that physiologically the effect of norepinephrine is very similar to the effect of stimulation of the adrenergic system (i.e., the effect of adrenaline). At the same time, there is, as they say, a “fat BUT ”:
For example, the following situations cause the release of predominantly norepinephrine:
- Aggressive, active emotions,
- compression of the carotid arteries.
The predominant release of adrenaline occurs:
- with hypoglycemia,
- in response to pain
- with irritation of the sciatic nerve, injury and other factors that cause a metabolic reaction.
Norepinephrine and adrenaline: differences in action on the body
Norepinephrine primarily affects the cardiovascular system. The release of NA occurs when there is a need for changes in hemodynamics: in response to a change in posture, during physical activity, during bleeding. But at the same time, the stimulating effect of norepinephrine on heart contractions is weaker than that of adrenaline.
NA differs from adrenaline by a much more pronounced vasoconstrictor effect (norepinephrine is a strong vasoconstrictor).
Norepinephrine has a stronger pressor effect. It causes an increase in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, which can reflexively lead to severe bradycardia.
The effect of norepinephrine on the smooth muscles of the bronchi and intestines is less. Epinephrine is a more potent smooth muscle inhibitor than HA.
Norepinephrine increases the need for oxygen in the myocardium and other tissues to a lesser extent.
The effect of norepinephrine on metabolism is also weaker than that of adrenaline: there is no pronounced hyperglycemic, lipolytic and general catabolic effect.
Catecholamine content analysis
The effect of catecholamines on the body is very specific. When the above pathological conditions occur, a blood test is performed to determine the level of these substances. To obtain an accurate result, the patient’s venous blood is taken in the morning, when the main amount of catecholamines is in the initial concentration.
For 3-4 days, coffee, citrus fruits, chocolate, and bananas are completely excluded from the diet. During the period of preparation for the analysis, you should not take Aspirin. You should refuse to donate blood for analysis if the patient suffered stress the day before.