Pus in urine: reasons
If a significant number of leukocytes are found in the urine, the reasons for this may be the following:
- Urinary tract infection. The causative agent of the infection can be hidden both in the bladder and in the urethra. It is also possible that the infection originated from the kidneys. To identify the pathogen, it is necessary to perform a culture
- Diseases of internal organs:
- Tuberculosis of the urinary tract. This condition is not very common, but tests are necessary to rule it out.
- Prostatitis. Pus in the urine is one of the symptoms of a male illness - inflammation of the prostate gland.
- Kidney or bladder cancer. Progressive oncological diseases of the kidneys or urinary tract lead not only to an increase in leukocytes in the urine, but also to the appearance of blood in it
- Stones in the kidneys. They provoke irritation of the urinary system, promoting the formation of pus in the urine. The analysis will also show the presence of red blood cells in it.
- Specific kidney diseases. Kidney diseases such as pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, and polycystic kidney disease will certainly manifest themselves as pyuria.
Pyuria and pregnancy
A pregnant woman always has an increased risk of developing a genitourinary tract infection, when bacteria that enter there progress to pyuria. The reason for this is intense hormonal changes during pregnancy, which create favorable conditions for infection to enter the genitourinary system.
You should be especially wary if mucus appears in the urine during pregnancy, since it indicates inflammation of the urinary system, in which the outflow of urine is disrupted, causing epithelial cells to increase mucus synthesis, which makes itself felt as white threads. The reason for this may be cystitis, inflammation of the kidneys, the appearance of stones in them and other factors.
Sometimes the cause may be a lack of hygiene, which leads to increased mucus production. Therefore, so that a urine test does not show mucus, it is very important to thoroughly clean the genitals (without soap) before the analysis, and collect the urine in a sterile jar.
UTI, pyuria and bacteriuria in pregnant women should be treated without fail, regardless of the presence of symptoms. This is necessary, since not only the health of the pregnant woman, but also the baby is at risk. The danger is so great that even with asymptomatic pyuria, pregnant women take antibiotics.
Reasons for violation
Since pus in the urine is not a diagnosis, but a sign of inflammatory processes, various causes can be provocateurs of this condition. With leukocyturia in the urine, it is important to correctly identify provoking factors, take a urine test on time, using a modern diagnostic method, and treat the identified disease only under the supervision of a qualified specialist.
There is also asymptomatic leukocyturia, which often occurs without bacterial infections, but indicates extrarenal pathological processes. One of them is helminthic infestation. We are talking about latent leukocyturia, when pathology can be detected in the bladder by performing appropriate tests.
If we talk about pus in the urine, there are many factors influencing its appearance. Therefore, with leukocyturia, the causes have to be looked for individually. Much depends on what the urogram shows. Excessive accumulation of leukocytes in the urine acts as evidence of disorders, undesirable processes that can lead to a number of serious consequences. Sometimes there is blood in the urine, which should cause even more concern for patients. Therefore, diagnosis is an important component in identifying disorders and their timely treatment. If you find urine with pus, be sure to do all the necessary tests. Particular attention should be paid to such phenomena as abundant leukocytes in the urine of a child, pyuria in an infant, purulent discharge from the urethra in women during pregnancy.
Urogram indicators may be as follows:
- neutrophilic pyuria, when neutrophils are detected in a urine test, indicates a high probability of tuberculosis or pyelonephritis;
- with the pononuclear type of urogram, there is suspicion of interstitial nephritis or glomerulonephritis;
- lymphocytes, that is, blood, indicates potential systemic pathologies, such as lupus or arthritis with rheumatoid etiology;
- Having detected eosinophils in the urogram, we can talk about possible allergosis.
Leukocyturia in pyelonephritis and other diseases is a fairly characteristic sign. But only a specialist should accurately diagnose and identify the causes of pyuria.
The doctor should pay attention to the presence of pus at one or another level of the genitourinary system, as well as its quantity. This speaks volumes about what kind of disease caused the pus in the urine:
- Kidney level. Indicates the likelihood of developing glomerulonephritis, as well as nephritis affecting interstitial tissues.
- Pelvis and calyces. Suppuration is present at the renal level. With a qualitative assessment of leukocyturia, one can detect pyelonephritis in chronic or acute form, renal carbuncle, abnormal location of the kidneys, hydronephrosis, polycystic disease, tuberculosis, etc.
- Extrarenal level. What does it mean? This suggests that the causes of pus in the urine are a kink, a duplication of the ureter, or a diverticulum of the patient’s ureters.
- Urethral level. Indicates pathological processes in the urethra or phimosis.
Problems with urine and pus are typical for many diseases. A similar pathology can manifest itself in the urine of men, women or children, regardless of age. Therefore, to identify abnormalities in the bladder in the form of pus, it is recommended that everyone carry out an analysis at the first suspicion. One of the main symptoms is an unpleasant smell of urine, it smells like pus. A sharp putrid odor should be a reason to immediately seek help from a doctor.
Pyuria affecting the male body may indicate a complication of prostatitis. The symptoms that appear in the female body potentially indicate cystitis and problems with the course of pregnancy. And in childhood, the symptoms of pyuria often indicate phimosis. Therefore, it will be useful to know what pyuria looks like, what features leukocyturia has during pregnancy, and how the patient should act in certain situations.
How to cure pyuria?
The appearance of any symptoms of pyuria, the appearance of characteristic flakes in the urine, changes in its color and smell are all reasons to immediately consult a doctor. He will prescribe tests and examinations and, based on their results, determine the place where the pus is concentrated and the reason for its accumulation. After this, antibiotics are prescribed. Their course and composition depends on the bacteria that caused the disease.
If an infection was introduced into the bladder by a catheter during medical procedures, then properly selected antibiotics will help get rid of pus in the urine in just a week. If the disease has already become chronic, then curing it is much more difficult. Especially if the patient is a child. Treatment should be gentle and comprehensive. Antibiotics are supplemented with a complex of vitamins, herbal medicine, and a special diet.
In case of exacerbation of the disease, both in men, women and children, the doctor prescribes strict bed rest for the patient, drinking plenty of fluids, and diet. The more carefully and responsibly the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, the faster the disease will recede.
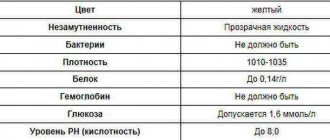
In medical terminology, pus in the urine is called pyuria. This condition is diagnosed when more than 10 white blood cells, which are classified as neutrophils, are visible in a urine sample under a microscope at 400x magnification in the laboratory. Pus in the urine is not a disease, but only a symptom. Therefore, in order to make a diagnosis, the attending physician must find the cause of pyuria, for which additional examination is prescribed.
The cause of pyuria is often a bacterial infection of the genitourinary system: the human body reacts to tissue irritation by causing an inflammatory reaction, which is manifested by a rush of blood to the area of irritation and swelling of the tissue. This is caused by the fact that the blood delivers an increased number of leukocytes to this area of the body to combat irritants. Therefore, inflammation of the urinary system leads to an increase in white blood cells in urine. In this case, neutrophils are the first to react to the pathogen. If they die in the fight, they form pus, calling new leukocytes to the site of the lesion.
Some people confuse the concepts of pyuria and bacteriuria, although there are differences. Pyuria is the appearance of white blood cells (more than 10) in a urine sample under a microscope
. This number of leukocytes is quite enough for the urine to become cloudy or whitish. But the presence of bacteria in the urine (bacteriuria) may either not be observed or be within low limits: with bacteriuria, the number of bacteria must exceed 105 units per milliliter.
In pyuria, the cause of the presence of neutrophils, from which pus is formed, is an inflammatory process, primarily in the genitourinary system. White blood cells act as fighting units of the immune system that attack infectious agents and substances that can harm the body. When this natural reaction of the body occurs, the mucous membrane is also included in this process. The cause of inflammation of the mucous membrane is the presence of too many leukocytes, which are excreted in the urine.
The presence of bacteria in the urine may not indicate the presence of a disease at all. A small amount of them in a sample from healthy people is allowed. This is a normal phenomenon, since the internal environment of the urinary system is saturated with moisture, which is ideal for bacteria to develop and reproduce. But if the number of bacteria is outside the normal range, they can cause infection of the genitourinary system. Bacteriuria can occur with or without symptoms. At the same time, symptomatic bacteriuria can be treated with antibiotics, while asymptomatic bacteriuria often goes away on its own without treatment.
Symptoms of pyuria
We figured out what the causes of pyuria are.
Now, before the doctor prescribes treatment to influence the provocateurs of pyuria, it is necessary to give patients with such a disorder recommendations on identifying the disease. That is, tell why an unpleasant smell of urine occurs in an infant or an adult, as well as how leukocyturia manifests itself, indicating various pathologies.
Any diseases of an infectious nature, such as urethritis (or urethral infection), for example, often manifest themselves in the form of intoxication, pain, leukocytosis, etc.
When examining a healthy person who does not complain of unpleasant symptoms, red and white blood cells may also be present in the urine. There is a certain norm, which is from 2 to 4 units in the visual field for men and from 2 to 6 units in the visual field for women.
Forms of violation
If you find urine containing pus, you should immediately consult a doctor. An unpleasant smell of urine, discomfort in the genitourinary organs and pain should be a strong argument in favor of finding the causes of the symptoms as quickly as possible.
Treatment of pyuria is prescribed individually, depending on the patient’s symptoms and complaints, as well as test results. In a situation where leukocytes cover the entire field of view, pronounced leukocyturia is often observed, in which whole flakes of purulent impurities come out during urination. When leukocytes are completely present, treatment must be started promptly.
According to experts, depending on the duration and nature of the inflammatory processes, pyuria is divided into two main forms:
- Infectious. Its obligatory feature is the presence of bacteria in urine samples. Children may have a transient form, when pathogenic bacteria penetrate the genitourinary system, but they do not find conditions for existence, therefore they leave the body without harm to health.
- Aseptic. With aseptic pyuria, eosinophils and lymphocytes are detected. At the same time, a large number of bacteria are absent, which is why the form causes such a disease. Often referred to as sterile.
Using modern diagnostic methods, doctors are able to timely detect pus in women’s urine during pregnancy and find diseases in men and children. This way the disease can be cured at a relatively early stage.
Symptoms
The presence of a significant number of blood cells in urine does not always cause discomfort. However, this phenomenon is mainly accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the form of:
- pain and burning when urinating;
- constant urges;
- feeling of aching in the lower back;
- heaviness in the pubis;
- a decrease in the amount of fluid released.
The temperature often rises, weakness and painful headache occur. Urine becomes cloudy and changes color. She gives off a disgusting smell. With pyelonephritis, anemia develops and appetite disappears.
If stones begin to leave the kidneys, the paths along which they move are injured, and not only pus, but also blood appears in the urine. The pain can radiate to the perineum, rectum, and be felt on the surface of the thighs. The process of excreting urine becomes more difficult.
All these symptoms, which are the same in children, men, and the fairer sex, warn of a serious pathological process that requires immediate treatment.
Treatment
Having discovered a symptom such as leukocyturia, the doctor prescribes treatment on an individual basis. First, the specialist determines what concomitant symptoms of pyuria the patient has and selects a diagnostic method to identify the possible causes of pus in the urine. It is extremely important to choose an effective method that will allow you to determine the form of the disorder, infectious agents and other significant components.
Leukocyturia in pregnant women occurs in every tenth case. A woman is faced with the fact that bacteria appear in the urinary tract, cloudy urine comes out and sometimes mucus is detected. In some situations, this means that the woman is dealing with quite serious violations.
Removal of symptoms such as leukocyturia, cylinduria or hematuria is based on the treatment of the disease itself that provoked the corresponding symptoms. If a patient has pus covering the internal surfaces of the urinary tract, most likely it is an infectious form. In this case, a general blood and urine test may be required. After the doctor prescribes treatment, the patient must strictly adhere to the recommendations.
The infectious transient form is treated mainly with an antibacterial method. The doctor prescribes cephalosporin antibiotics, and the course of treatment lasts about two weeks.
If the smell of urine is normal, but tests show leukocyturia, then most likely it is an aseptic form. It is treated locally by douching or irrigation with special antiseptic medications. At the same time, the doctor prescribes immunomodulators, vitamins, and ascorbic acid.
Regardless of the reasons for pus in the urine, each patient must strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene. Without this, treatment may be ineffective or may not achieve the best possible results. Therefore, devote enough time and attention to your genitourinary system, form the habit of carefully caring for your own body, not only during treatment, but also in the process of everyday life.
analiztut.ru
Where does pus come from in urinary sediment?
In order to understand the main reasons for the appearance of “purulent” urine, it is necessary to understand the questions of what pus is and how it is formed.
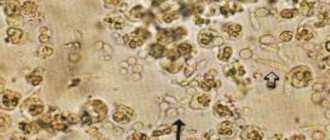
When an infectious agent penetrates the organs of the urinary system, the patient’s body launches mechanisms aimed at combating the pathogenic microorganism and its complete elimination. Leukocytes (neutrophils), macrophages and other immune-active cells (cytokines, tumor necrosis factor, etc.) are sent to the site of pathogen penetration. They secrete substances that can destroy and inactivate it. The appearance of pus is nothing more than dead “defender” cells of the body and infectious agents.
Main causes of pyuria
Leukocyturia is observed in men and women of all ages, which is associated with a large list of factors that can lead to this.
Among the main causes of the pathological symptom, the following are worth highlighting:
- Inflammatory processes in the kidneys (acute and chronic pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis, tuberculosis, abscess and others). One or both kidneys may be affected; penetration of the pathogenic microorganism most often occurs from the lower parts of the urinary tract (bladder or urethra), as well as from other infectious foci of distant localization. During pregnancy, a disease such as gestational pyelonephritis may appear.
- Inflammatory processes in the tissues of the bladder (acute or chronic cystitis). Most often, the disease is registered in females, with pyuria being a characteristic and pathognomonic symptom of the disease.
- Inflammatory process in the tissues of the urethra (acute or chronic urethritis). The disease has extremely unpleasant manifestations and, as a rule, it is associated with infectious processes of sexually transmitted origin (STIs).
- Inflammatory process in the tissues of the prostate gland (acute or chronic prostatitis). The disease is limited to representatives of the stronger sex, with the disease occurring in approximately every second man over 40 years of age.
- Inflammation in the tissues of the penis and foreskin (acute and chronic balanoposthitis). Most often, this diagnosis is made to a child who has a congenital narrowing of the foreskin, which leads to a constant accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms there.
- Urolithiasis disease. If pyuria is observed against the background of urolithiasis, this is direct evidence that the patient has complications in the form of inflammatory processes in the lower parts of the urinary tract (in the ureters, bladder or urethra).
- The appearance of purulent discharge in women can be caused by diseases such as candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, salpingoophoritis, vulvovaginitis and other processes in which leukocytes may enter the urine.
- Failure to maintain personal hygiene before collecting a urine test. Insufficient treatment of the genitals or its complete absence, improper washing of the woman (from the anus towards the vagina), etc. It is incorrect preparation for the study that quite often becomes the cause of false leukocyturia, since the genitals and vaginal lumen contain opportunistic microorganisms and leukocyte cells that can enter urine.
- Using a container that is known to be non-sterile, the walls of which may contain infectious agents (we are talking about food containers or containers that have been in contact with open air for a long time). Therefore, it is important to collect urine only in a special container, purchased at any pharmacy.
Forms of pyuria
Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, the following forms of pyuria are distinguished:
- Aseptic form
, characterized by the content of a huge number of leukocytes without pathological microorganisms. It is noted in cases of kidney tuberculosis, dehydration of the child’s body due to poisoning. - The initial form
is noted in the inflammatory process of the lower urinary tract. - The terminal form
occurs in diseases of the seminal vesicles and prostate, and is characterized by an increased content of leukocytes in the urine. - The total form
indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the kidney itself, the renal pelvis and the bladder.
In children, the presence of pus in the urine is most often associated with infectious inflammation of the kidneys and can manifest itself in acute and chronic forms. The chronic form of the disease is observed in congenital diseases of the genitourinary system or its pathologies. The acute form is observed in acute infectious kidney lesions.
In case of pyuria, a urological examination is required. For treatment, bed rest, a balanced diet, plenty of fluids, and vitamin supplementation are prescribed.
Pus in the urine is always an alarming sign. The presence of purulent masses in biological fluids is never normal. Therefore, at the first sign of the appearance of such impurities in the urine, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Let us consider the mechanism of formation of such a phenomenon.
Symptoms to watch out for
Pyuria may be asymptomatic, or it may be accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms, such as:
- pain in the lumbar region on one or both sides, which can radiate to the perineum, rectum or thighs;
- the appearance of dysuric disorders (pain or cramping when urinating, unpleasant or uncomfortable sensations, etc.);
- increased urge to urinate, including at night, scanty urine output, etc.;
- increased body temperature, general weakness, malaise, etc.;
- change in the color or shade of urine (it looks cloudy, various inclusions, traces of pus or blood appear in it).
Symptoms
Symptoms of leukocyturia usually coincide with the symptoms of those pathologies that are the provoking factor for the formation of pus in urine. Leukocyturia is accompanied by bacteriuria - the presence of bacteria and microorganisms in the urine. Due to the increase in the number of colonies of microorganisms and the exacerbation of the inflammatory process, a typical symptom of leukocyturia is:
- painful act of urination;
- increased urge to urinate;
- reduction in the amount of urine excreted;
- aching pain in the lumbar region;
- headache;
- increased body temperature – hyperthermia;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- burning in the urinary duct;
- uncharacteristic odor of urine.
Leukocyturia is also characterized by a change in the color of urine. Due to the increased content of leukocytes in the form of purulent inclusions, the urine acquires a more cloudy yellow-green hue. If, during the act of urination, urine is released along with blood (hematuria), the color of the urine becomes reddish. Signs of dysuria, a disorder of natural urination, may also appear. Has the following types:
- Frequent urination (pollakiuria) - signs of a frequent urge to urinate, especially at night, can serve as symptoms of diseases such as diabetes, cystitis, urethritis and other inflammatory processes affecting the lower parts of the genitourinary system.
- Difficulty urinating (stranguria) - can be a clear sign of urolithiasis, phimosis, or exacerbation of prostatitis.
Pyuria exhibits symptoms typical of the pathologies that accompany it. Experts also observe cases of the development of hidden or asymptomatic pyuria. This type is detected only during laboratory tests, mainly in the initial stages of disease development.
yamuzhchina.ru
Diagnostic methods
Laboratory and instrumental examination of the patient consists of the following procedures:
- general blood and urine analysis (the severity of the inflammatory process is assessed);
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko (provides the most information about the number of leukocytes in the urinary sediment, as well as the concentration of red blood cells and casts);
- culture of urine on nutrient media and determination of antibacterial sensitivity of the infectious agent;
- the three-glass sample method, the essence of which is to simultaneously collect urine in three containers;
- X-ray diagnostics (general X-ray and excretory urography);
- Ultrasound of the urinary system;
- CT and MRI (if indicated).
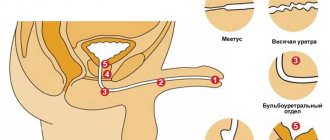
The three-glass analysis allows, even at the stage of primary diagnosis, to determine the localization of the inflammatory focus at different levels of the urinary system:
- if pus is released exclusively in the first portion of urine, then this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the urethra (urethra);
- if pyuria is observed only in the third portion, then prostatitis should be excluded in the patient;
- if leukocyturia is observed in all three portions at once, then it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis between pyelonephritis and cystitis.
Treatment of pyuria
Treatment for pyuria depends on the cause of the disease. For example, antibiotic therapy is indicated for urinary tract infections. If treatment does not bring positive results, additional diagnostic studies are needed to clarify the diagnosis.
In the case of oncology, treatment depends on the situation. Surgery, chemotherapy, or laser therapy may be indicated. A benign tumor or kidney stones must be removed. For the treatment of tuberculosis and viral infections, appropriate therapy is also prescribed. If the problem is caused by medications, they should be discontinued.
Prevention of pyuria involves observing the rules of personal hygiene.
After emptying the bladder and bowel, you need to wipe the area of the urethra, vagina and anus with antiseptic wipes. In this case, women must strictly adhere to the direction of movements, which should only be from front to back, in order to avoid bacteria that came out of the intestines from entering the vagina. You should also shower frequently using special detergents for intimate hygiene.
Drinking plenty of fluids daily is also a good prevention of urinary system diseases. Water accelerates the removal of pathogens, sand and other harmful substances from the body.
Pyuria is a condition in which purulent impurities are found in the urine. In medicine there is another name for this pathology -. However, many experts say that it is not correct to combine these terms, because pyuria is one of the stages (and a very acute one) of leukocyturia. Pyuria is detected through tests. However, a more accurate judgment about the extent of the disease is provided by special tests - Nechiporenko-Almeida, Amburge and other tests.
By the way, leukocytes are constantly present in the urine of a healthy person; in adults they range from 0 to 3, in children – from 0 to 6.
There is a clinical division of pyuria into three main types:
- Initial
- it can be determined by the three-glass test and is detected in the first portion of urine. Based on the test results, they judge the inflammatory processes of the urinary system (its lower parts) - Terminal
- determined by the third portion of tests and indicates that there is inflammation deeper. - Total
- leukocytes are present in all three portions, this indicates that urea is also present.
Purulent impurities in the urine are the first sign of pyuria
Pyuria develops for many reasons, but most often it is a consequence of inflammation of the urinary and reproductive systems:
- pyelonephritis
- exacerbations of the prostate
- hydronephrosis and so on.
In all these cases, pyuria is a specific symptom that requires additional examination to make an accurate diagnosis and identify the true causes that led to an increase in leukocyte counts.
Antibiotic therapy is the main principle of treating the inflammatory process
Help for patients with pus in the urine
Therapy for the patient begins only after the cause of the appearance of pus in the urine is finally established; such treatment is called etiological. If pyuria is diagnosed completely by chance, the patient’s health remains satisfactory and there are no complaints, it is necessary to re-examine the urine test.
The main role in the treatment of inflammatory processes of any localization (in the kidneys, bladder or urethra) belongs to antibacterial drugs. Penicillins (including protected ones), latest generation cephalosporins, macrolides and others are widely used in treatment.
In complex treatment he uses drugs from different pharmacological groups:
- painkillers and antispasmodics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diuretics and others.
Symptoms of pyuria
The appearance of pus in the urine can be judged by its color (cloudy or milky), the strong and foul odor of the urine. You should be wary of frequent urge to urinate, discomfort when urinating, or elevated body temperature. For men, there is an alarm signal if white threads appear. Pyuria without symptoms is the result of chronic urinary incontinence or chronic catheter insertion.
The older the patient's age, the more likely it is to develop asymptomatic pyuria. In this case, one of the main causes of the pathology is urinary incontinence, which appears and intensifies as the body ages. This is explained by the fact that the muscular system ages along with the body, including the smooth muscles of the urinary system.
Since pus in the urine is only a symptom of the disease, it is imperative to determine the cause: if the problem is not treated, serious complications can occur. For example, if pyuria is caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI), it can lead to serious kidney problems. If the cause is cystitis, the infection can spread to the upper urinary tract, ureters and kidneys. If you have infected kidneys (pyelonephritis), blood poisoning (sepsis) and irreversible kidney damage may occur.
In medical terminology, pus in the urine is called pyuria.
This condition is diagnosed when more than 10 white blood cells, which are classified as neutrophils, are visible in a urine sample under a microscope at 400x magnification in the laboratory.
Pus in the urine is not a disease, but only a symptom. Therefore, in order to make a diagnosis, the attending physician must find the cause of pyuria, for which additional examination is prescribed.