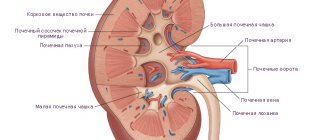
Acute pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the renal pelvis, which is characterized by fever, pain in the side and chills. Women are 3 times more likely to suffer from the disorder than men. The pathology can be unilateral or bilateral. The temperature with pyelonephritis does not always increase. Treatment methods depend on the clinical course and morphology of the disorder. In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10), the condition is designated by code N10. In this article we will look at how many days a high temperature lasts for pyelonephritis in adult patients.
Why is the temperature creeping up?
Human body temperature shows the degree of body heat and is an indicator of health.
The initial examination of patients with pathology begins with a measurement; this indicator is included in the sheet of a sick patient, even a dental one.
If the indicators are elevated, this means that the body has developed disorders that make normal functioning impossible.
This often happens during inflammatory processes when fighting an infection. The human body has a temperature amplitude of 5-6 degrees, which regulates life processes.
An increase in temperature is a natural reaction of the body to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and the onset of the inflammatory process.
The vital activity of pathogenic bacteria and the release of decay products require the body to eliminate toxins of this kind as quickly as possible.
Intoxication of the kidneys is extremely acutely perceived by the organ, so an increase illustrates this process like nothing better.
Therefore, for this purpose it is necessary to speed up metabolism so that processes proceed faster and more productively. An excellent mechanism for this is an increase in temperature.
Since a change in temperature is primarily a sign of ill health, patients should not self-medicate and regulate the temperature if they have inflammation of the renal pelvis. First of all, the indicator is assessed by a doctor who will draw conclusions about the body’s fight against the infectious process. If the temperature rises against the background of existing pyelonephritis, patients consult a doctor to consult about the changes - perhaps the pyelonephritis has become acute and emergency medical care will be needed.
Recommendations for patients who have had pyelonephritis
If inflammation of the renal pelvis is detected and treated in a timely manner, the prognosis is very favorable. After three days of treatment with antimicrobial medications, symptoms begin to gradually subside. Antibiotic therapy should be continued until the period agreed with the doctor to prevent a chronic course.
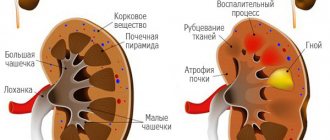
It is important to know! Chronic pyelonephritis does not disappear on its own. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly check the function of the organ. In rare cases, if the disease is diagnosed so late that the affected kidney is too inflamed and damaged, it should be removed.
There are no absolute measures to prevent pyelonephritis. In general, it is advisable to drink enough water and avoid nephrotoxic agents. Disturbances in urinary outflow (due to kidney stones or foreign bodies) must be promptly eliminated by conservative or surgical methods.
Stages of temperature symptoms in forms of pathology
With the development of acute pyelonephritis, the thermometer does not rise chaotically, haphazardly.
The activities of the human body are subject to the laws of physiology. There are three stages of increase:
- initial is the prodromal stage of the disease, in which the temperature does not rise sharply. The difference between the norm is half a degree, thus rising from 36.6-37.1˚С. Rarely does it exceed 37.2˚C in the initial stage. This indicates that the body’s functioning is disrupted, because the indicator is no longer 36.6˚C, which means that the body has begun to react to the presence of the pathogen. This condition persists for two days;
- progressive period - the indicator rises sharply and rises to 40˚С. In this state, the body fights the infectious process, the number of leukocytes in the blood increases, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate rapidly increases. The sharper and stronger the immune response, the more active the patient’s immunity. The indicator rises rapidly, does not last long, and also quickly decreases. If the patient’s immunity is weakened, then the readings will not exceed 37-38˚C. This indicator is not the norm and indicates a weak fight of the body against the pathogen. Any pathogenic microflora can cause deviations in the body, even if not so significant;
- regression of temperature indicators down to normal. The body fights infection, since an excessively elevated temperature, for example 39˚C, is already reduced with medication. Since pathogens still remain in the body and tissues, the body does not lower the temperature to normal, but fights them for several days. As soon as improvements occur, temperature indicators return to normal. This means that the cause of the patient's illness has been eliminated.
The subacute form of pyelonephritis is also characterized by an increase, but the values rarely exceed 38˚C. Fluctuations occur from 37.2 to 37.8˚С - this is how the body signals the fight against the pathogen. Since the subacute form of the pathology suppresses the immune system, strong jumps cannot be expected.
In chronic pyelonephritis, when the period of remission of the disease has begun, degrees are not a problem for the patient.
The temperature rises slightly, often not exceeding 37.3˚C. Occasionally, at night, patients' temperature rises from pyelonephritis, but by the middle of the day it returns to normal, and patients do not even feel such changes, so they do not measure it.
Doctors advise patients with pyelonephritis to take daily measurements as a rule, with the obligatory recording of the results in a temperature diary.
This diary records blood pressure and features of urination (small amount of urine, cloudy urine, urine with blood).
This will help track the dynamics of the disease. You should note when your temperature rises and how often it has happened recently.
For a doctor, such diagnostic data is extremely valuable, because an increase in temperature signals serious problems in the kidneys.
Why is the temperature rising?
When the infection enters the calyces and pelvis of the kidneys, it can multiply faster than causing acute inflammation. At the site of pathology, so-called mediators are formed - substances that support the process, the release of exudate. In response to this, the immune system, through complex mechanisms, releases antibodies - cells that can fight the pathogen.
So, temperature appears when the infection multiplies in the bladder, if the infection route is ascending (from bottom to top). If it is descending (from top to bottom), you can notice the temperature during the course of the primary disease.
Pyelonephritis is rarely caused by independent factors. The non-infectious etiology of the disease consists of congenital anomalies of the urinary system, in which urine can be thrown back into the kidneys.
Each infectious pathogen behaves differently. If it moves with the lymph flow and is not retained by the lymph nodes, and at the same time multiplies on the way to the kidneys, the temperature will rise already at the beginning of the development of pyelonephritis.
Symptoms accompanying fever
With a slight increase in body temperature, a patient with pyelonephritis is unlikely to visit a doctor. Doctors give strict instructions when a visit to them is indispensable, even if the numbers on the thermometer have changed slightly. This:
- the appearance of chills or fever;
- abnormal behavioral response - drowsiness, overexcitation;
- dysfunction of the respiratory system;
- increased sweating;
- drop in blood pressure and increased heart rate;
- severe headaches, vomiting and nausea;
- convulsions.
If a patient with a fever experiences such symptoms, a visit to the doctor is required.
Danger of condition
Complications are more common in patients with diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, sickle cell disease, double organ transplantation (especially within the first 4 months), AIDS, and other immunodeficiencies. Sometimes it can be difficult to identify complications that have arisen.
Main adverse outcomes of the disease:
- acute kidney injury
- chronic kidney disease leading to hypertension and kidney failure;
- sepsis;
- papillary necrosis;
- xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis;
- abscesses.
Patients often develop renal cortical, corticomedullary, or perinephric abscesses. Older people have a higher incidence of developing the second type. Pathology occurs equally in both men and women.
Patients with corticomedullary abscesses often present with chills, fever, flank or abdominal pain, dysuria, nausea, and vomiting. Leukocytosis may be present. Bacteriuria, pyuria, hematuria, or proteinuria do not occur in all people. Urinalysis results are normal in 30% of patients. Bacteremia may be seen in acute focal or multifocal bacterial nephritis.
In emphysematous pyelonephritis, a purulent abscess is located between the renal capsule and the surrounding fascia. It is secondary to chronic or recurrent disease, tissue rupture, or expansion of the purulent process from within the kidney.
Attention! Although the abscess is usually limited to the perinephric space, it can extend to the colon, groin, lungs, paracervical area, peritoneal cavity, psoas muscle, and skin surface.
The following symptoms are characteristic:
- fever;
- chills;
- unilateral lateral (70%);
- dysuria (40%);
- nausea;
- decreased concentration;
- low blood pressure;
- vomit;
- sweating at night, which lasts until the morning;
- weight loss (25%);
- poor sleep;
- abdominal pressure (60%);
- pyuria (70%);
- rachiocampsis.
In 1/3 of patients the diagnosis is detected upon admission to the hospital, in the other third at autopsy. A perinephric abscess usually does not cause clinically significant symptoms.
Duration of temperature rise
During the course of pyelonephritis, it is impossible to clearly say how long the increase in temperature will last. Depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and immunity.
There are cases when pyelonephritis occurs without fever. Long-term low-grade fever is possible when the figure does not exceed 37.5˚C. And this will happen for more than one day. And some patients stay at 38˚C or higher for a long time.
In the acute form or exacerbation of pyelonephritis, the indicator will rise to 39-40˚C, and in the morning it is not felt, and it is lowered, but in the evening it rises.
Therapy reduces the temperature to normal within two weeks, and with chronic sluggish pyelonephritis, the thermometer will not show high numbers for a couple of months.
You can’t lower your temperature when you’re sick—this won’t eliminate the disease, but it can harm your body. Antipyretics are taken when the indicators approach critical numbers. For adults it is 40˚С, and for children - 38˚С. The doctor will tell you how to reduce the temperature of a patient with pyelonephritis in critical condition.
Do not use drugs containing paracetamol, metamizole sodium. Use Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Ibufen, Viburkol.
In such crises, after normalization of indicators, patients visit the clinic and find out the reasons for the jump. It may be necessary to change therapeutic measures and medications.
Similar article - Treatment of papillomas on the eyelid
Is it possible to lower the temperature and how to do it?
In acute pyelonephritis, you can take medications for fever, but this is a short-term solution to the problem. Until the source of infection or reflux is eliminated, the temperature in acute pyelonephritis will not completely go away.
In the chronic form of pyelonephritis, the temperature does not reach such levels as to require the use of analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs. Therefore, taking medications is not advisable. It is better to consult a doctor and undergo extensive diagnostics to determine the pathogen.
In acute pyelonephritis, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs if the cause is infection. In case of reflux, when urine is thrown back into the kidneys, surgery is indicated. In parallel with antibiotics, the urologist can prescribe medications that will help reduce the temperature during pyelonephritis:
- Paracetamol.
- Efferalgan.
- Panadol.
- Nurofen.
- Ibuprom.
- Theraflu.
- Flukold.
- Nimesulide et al.
Using antipyretics, you can lower your temperature only for 1-2 days. Such drugs should not be taken for more than 3-5 days without consulting a doctor, and acute pyelonephritis requires treatment in a hospital. Therefore, it is advisable to take the drugs only 1 or 2 times, and this is even if the exacerbation began at night and it is not possible to immediately go to the hospital.
Video
Blurred signs of pyelonephritis do not always allow you to consult a doctor on time. This disease is asymptomatic until a certain time. Only severe pain in the kidney area can signal the presence of a disease and the need to urgently consult a doctor. An infectious disease that causes kidney damage must be treated in a hospital. It is impossible to get rid of it yourself at home.
Prevention and prognosis
To prevent complications, you need to closely monitor your health and promptly begin treatment for inflammation.
Particular attention should be paid to the manifestations of urolithiasis and other kidney pathologies. Doctors recommend avoiding the following conditions and factors that can lead to pathologies of the bean-shaped organs:
- hypothermia;
- overwork;
- lack of sleep;
- stress.
In most cases, the patient recovers within 1-2 months. Of course, there are exceptions. In this case, we are talking about the chronic stage and the occurrence of various complications.
Kidney disease or nephritis is an unpleasant illness that can last from a week to a month, sometimes more. It is accompanied by many symptoms, including fever, so it is often confused with a common cold. Depending on the form of the disease, the temperature ranges between 37 and 40 °C, so timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment are required.
Pyelonephritis: can it cause fever?
In addition to pain in the kidney area, the disease brings a lot of other unpleasant moments. It is expressed by a frequent urge to urinate and an increase in body temperature. An advanced form of pyelonephritis is accompanied by blood in the urine. Hyperthermia of the body indicates that the body's immune system has entered the fight against a pathogenic infection. The inflammatory process in the renal pelvis is accompanied by:
- chills;
- fever;
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- increased sweating;
- headaches;
- weakness;
- shortness of breath.
Temperature during pyelonephritis is an indicator of the inflammatory process in the body. It is important that the higher the body temperature, the more serious the inflammatory process. When hyperthermia is severe, protein metabolism is disrupted. Loss of consciousness and dehydration are possible.
Symptoms of hyperthermia
An elevated temperature during pyelonephritis indicates an increase in inflammation in the body, provoked by harmful microorganisms.
Hyperthermia turns out to be a kind of protective reaction of the body, activating the immune system. But more often this symptom is explained by bacterial intoxication.
With hyperthermia, the following symptoms occur:
- fever with chills, body aches;
- fatigue or nervous overexcitation;
- changes in respiratory function, tachycardia;
- increased sweating;
- headache, nausea;
- In children, convulsions, fainting, and vomiting are not excluded.
In addition to a sharp jump in temperature, additional striking symptoms of pyelonephritis are lumbar pain and dysuric syndrome with obvious physiological disturbance of urination.
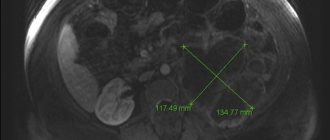
This is frequent or difficult urination with pain and burning in the urinary canal. Diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests of blood and urine, as well as ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
What temperature occurs with pyelonephritis. And how long can she hold on?
Body temperature with pyelonephritis can rise to thirty-nine to forty degrees. Its fluctuations are possible for fourteen days. If the disease is not advanced, body hyperthermia is possible for a couple of days. During the acute period of the disease, the temperature reaches its highest levels. Then there is a decline.
It is impossible to say for sure how long the temperature lasts for pyelonephritis. If an elevated body temperature lasts more than two weeks, this is an indicator of a complication of the disease. Typically, its increase is observed in the evening and at night, and in the morning and daytime it decreases.
The initial phase of the disease is characterized by a deviation in body temperature towards an increase of one or two degrees. This means that the body has begun to fight the infection. With significant spasmodic hyperthermia, we can talk about strong immunity, which began to sharply counteract the infection. The higher the hyperthermia, the stronger the immunity. A decrease in body temperature to thirty-seven degrees indicates that the patient’s critical condition is over.
The long-term form of the disease, which has become chronic, is no less dangerous. This process usually results in a low-grade fever. Chronic pyelonephritis also must be treated, despite the sluggish state of the disease and not a high temperature. A temperature of 37 with chronic pyelonephritis is normal. With this form of the disease, a person gets used to mild hyperthermia. In this case, he doesn’t even notice her anymore. It is impossible to say exactly how many days the temperature lasts for pyelonephritis.
Treatment of the chronic form of pyelonephritis is mandatory, since the transition of the disease to this phase with structural changes in the kidney tissue contributes to purulent complications.
Pyelonephritis without fever is a fairly rare occurrence. It is clear that identifying it will be very difficult. Usually, only laboratory tests can show the nonspecific manifestation of this disease. A general urine test is required. Next, the attending physician draws conclusions based on the research and adds additional diagnostics.
Symptoms
Temperature indicators depend on the nature and severity of the inflammatory process.
Kidney pain is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- change in the amount of urine;
- pain when urinating;
- change in color or smell of urine;
- swelling on the face, hands;
- temperature increase.
The fever lasts for several days, then a low-grade fever persists for a long time.
With pyelonephritis, predominantly the tubular system of the kidneys becomes inflamed. Most often the disease is of bacterial origin.
Women suffer from pyelonephritis much more often due to the anatomical features of their body: it is easier for infection to enter the bladder through the urethra.
In men, pyelonephritis is mainly secondary in nature: it is a consequence of urolithiasis, chronic prostatitis. Older people are much more susceptible to this disease due to problematic urine flow caused by adenoma of the paraurethral glands.
With exacerbation of pyelonephritis, in addition to pain in the kidneys, weakness, periodic increases in temperature (up to 39°C), attacks of fever, chills, and rapid pulse are observed.
In the morning the temperature is normal, but increases sharply in the evening. Herpetic-like rashes are often observed.
Severe, aching pains radiate to the abdomen, they increase when walking, but disappear in a horizontal position on the side.
What causes an increase in body temperature
Infectious inflammation that accompanies the disease causes an increase in human body temperature.
The development of pyelonephritis is accompanied by several factors:
- presence of uropathogenic flora;
- an environment favorable for the development of microbes.
Escherichia coli, enterococci, Proteus, and enterobacteria are the main causative agents of the disease. Various fungi and chlamydia cause pyelonephritis much less frequently. Infection occurs quite often along the urinary tract. Microbes penetrate from the large intestine or from the surface of the skin in the urogenital area.
The waste products of harmful organisms cause a high temperature, which can be very difficult to bring down. Taking antibacterial agents promotes an even greater release of toxins, and as a result, an increase in body temperature.
Can the temperature rise?
To understand whether pyelonephritis is accompanied by temperature and why it rises, you need to know the etiology of the disease. The cause of inflammation in most cases is bacteria that affect the interstitial renal tissue, calyces and pelvis, and the mouth of the ureter.
The infection either enters the bladder and rises to the kidneys through the ureters, or is carried by blood and lymph, reaching the kidneys. The causative agents of the disease are:
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- enterococcus;
- staphylococcus;
- enterobacter;
- pseudomonas;
- Klebsiella etc.
Regardless of how the infectious agent penetrates the tissues of the kidneys and ureters, it actively multiplies and thereby provokes inflammation. This disrupts urinary and excretory function and causes a reaction from the immune system. That is why with pyelonephritis the body temperature reaches 37 o C before the acute phase begins. This is a sign that the bacteria are gradually moving towards the kidneys, multiplying along the way, and the immune system already detects their presence.
How to lower the temperature correctly
The high temperature that accompanies pyelonephritis must be reduced. Attention should be paid to the fact that this must be done correctly. Treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and according to his instructions. Therapy is determined only by a specialist with appropriate medical education. Self-medication in case of pyelonephritis is fraught with bad consequences. The disease can occur with complications in both children and adults.
It is impossible to say for sure how long the temperature lasts during pyelonephritis in adults compared to children. It is known that in children the immune system works more actively than in adults. Due to this, sharp hyperthermia and its longer presence are achieved. This is an indicator of the active functioning of the immune system.
If different symptoms of the disease are detected, you must go to the hospital to undergo the necessary examinations and tests. Pyelonephritis cannot always occur with fever. Based on the examination results, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. Therapy involves taking medications that will ensure the destruction of pathogenic flora. The doctor will prescribe a suitable antibiotic and antipyretic. With the correct selection and administration of medications, harmful microorganisms will be suppressed and, as a result, inflammation will decrease and the temperature will decrease.
During treatment, you must adhere to the correct drinking regime. It is important to focus on the amount of fluid you take and your diet. At the acute stage of the disease, you need to exclude foods rich in protein: meat, fish. It is worth giving up pickles, marinades, spicy and fried foods, canned food, and chocolate. Alcohol is completely excluded.
The chronic form of pyelonephritis in the remission stage allows the consumption of a variety of dairy products, cereals, and baked goods. You can eat fruits, vegetables, berries. Watermelons, melons, and pumpkins are very useful. You should drink cranberry fruit drinks, rosehip drinks, special herbal infusions, and weak tea. Drinking alcohol is not recommended.
During treatment of the disease it is necessary:
- adhere to bed rest;
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- apply cool compresses.
It often happens that with pyelonephritis the temperature does not subside. Thus, an advanced form of the disease and an acute inflammatory process may require an integrated approach in the treatment of pyelonephritis:
- normalization of the free outflow of urine (installation of stents, catheters);
- taking antibiotics aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease;
- taking antispasmodics and antipyretics;
- prescription of additional anti-inflammatory drugs;
- correction of hypertension;
- preventing anemia;
- herbal therapy to prevent relapses;
- restriction of physical activity;
- compliance with the drinking regime;
- food according to the diet.
Development of pyelonephritis
In acute pyelonephritis, there is weakness, the pulse quickens, and the kidney area hurts. Temperature rises periodically, sudden fever and chills occur. Most often, the acute form of pyelonephritis is combined with a temperature of 39 degrees. Low-grade symptoms are more typical for the chronic course of inflammation.
At the same time, the temperature curve itself has a serious range. In the morning the values are normal, but in the evening there is an increase. You may notice rashes similar to herpes. The pain is mostly unilateral. This may be an aching sensation with strong irradiation into the abdomen. When walking, the pain usually intensifies, and disappears if you lie on your side.
For chronic pyelonephritis, the presence of pain is not typical. Elderly people often experience atypical pyelonephritis. In this case, the main signs of the disease are acute pain in the lumbar region and high temperatures. At the same time, constant chills are added to the temperature, and the urine acquires a pungent odor of ammonia.
Kidney diseases often resolve with a significant increase in temperature, up to forty degrees. In this case, vomiting and other signs of intoxication are recorded. If we talk about children, then with pyelonephritis, lower back pain is not as noticeable as in adults. However, there is an additional combination with abdominal colic.
If your diagnosis is urosepsis, then in the second stage the temperature rise is insignificant. This is usually observed twice or thrice a day. Progression leads to fever without chills; this condition can persist from a month to three.
Causes of fever during pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is a disease caused by the penetration of various microorganisms (mainly bacteria) into the kidney tissue. Types of pyelonephritis:
- primary - an independent disease that occurs through the spread of infection from the urinary tract;
- secondary - is the result of previously suffered viral diseases.
Staphylococcus most often causes inflammatory processes in the kidneys
Pyelonephritis can occur in two forms:
- acute - characterized by pronounced symptoms of the disease;
- chronic - appears as a result of inadequate or untimely treatment of the acute form, characterized by regular relapses.
Elevated temperature is the main sign that an inflammatory process is occurring in the body. This is a protective reaction of a person fighting germs. It involves the immune system, which seeks to recognize and destroy incoming microbes. This process is the cause of fever in pyelonephritis. Intoxication caused by gram-negative bacteria is the second source of this symptom.
Similar article - Do I need a prescription for Postinor?
The mechanism of temperature increase can be traced when considering the periods of the infectious process:
- Incubation (hidden) period. Characterized by the reproduction and accumulation of pathogens in tissues. Defense forces are mobilizing to begin the fight against them. This period lasts from 1–7 days (acute form of the disease) to several months (chronic pyelonephritis).
- Prodromal period. This is the period of warning signs of the disease. Patients notice the first signs of the disease with the appearance of low-grade fever. The immune system begins to respond to the infection.
- High period. There is a rapid jump in temperature to 38–40°C. This value depends on the state of the human immune system. When it weakens, the reaction will not be so pronounced.
- Recovery period. It is characterized by ridding the body of intoxication. If there are no complications, the temperature goes down.
Pyelonephritis without fever
A latent form of chronic pyelonephritis is possible, resulting from insufficient treatment of an acute disease. It is characterized by an asymptomatic course, which makes diagnosis difficult. Laboratory tests for other diseases help to identify this condition.
A person does not pay attention to a slight increase in temperature to 37–37.3°C. This does not happen all the time, but periodically. Associated symptoms also appear:
- reduced performance and fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- slight increase in urination;
- periodic abdominal pain;
- increase in pressure.
Weak immunity, unable to fight microbes, is the main reason for the occurrence of the disease without fever.
With increased fatigue and decreased performance, one should suspect the presence of a latent (latent) form of the disease
Treatment options
After correct diagnosis of kidney disease, therapy is prescribed, aimed not only at suppressing symptoms, but also at eliminating the causes of the disease. The main methods of treatment include medication and surgery. Some people rush to take the advice of traditional medicine, but in advanced cases and during the acute phase it is necessary to use traditional therapeutic methods.
Drug treatment
The most common method used for kidney diseases. Medicines are divided into painkillers (Baralgin, Ketanov, Analgin, Toradol), antispasmodics (Spazmalgon, Noshpa, Nurofen) and antibiotics. The latter are prescribed strictly by a specialist and are used to prevent the development of secondary infections. More often than others, drugs of the fluoroquinolone and nitrofuran series are recommended. There is a strict contraindication to their use - renal failure.
Surgical intervention
Conservative treatment methods are the most preferable, but sometimes drug therapy alone cannot cure a person. The operation is prescribed after thorough examinations; the indications for it are as follows:
- pain in the kidneys that cannot be relieved with medications;
- attacks of colic in the lumbar region;
- purulent inflammation, threat of peritonitis;
- tumors of any type;
- multiple exacerbations of pyelonephritis;
- severe obstruction of urine flow or inability to urinate.
The surgical method is used in cases of advanced disease of the patient. The type of surgery is individual for each patient.
Physiotherapy
This method of treatment is used for rehabilitation and elimination of symptoms in the initial or chronic stage. It is relevant after removing stones from the kidneys, during inflammatory processes, and disturbances in the functioning of the collecting and pelvic region.
Types of therapy vary for each disease, but its arsenal is limited: dry-air heat baths, UHF, paraffin applications and electrophoresis. The procedures are carried out in courses over several months.
How high can the temperature be?
Temperature is an indicator of a person’s well-being. An increase in its level to 40°C indicates the presence of inflammatory processes and is associated with increased immune activity. The number of leukocytes in the blood increases sharply. Even an organism with a weakened immune system is forced to fight the microbes that have entered it. But then the temperature will be lower.
For acute pyelonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis begins instantly. Suddenly the patient develops severe chills. More than 80% of patients experience an increase in temperature to 39–40°C with fluctuations throughout the day (increases in the evening). The temperature persists for up to 14 days with the highest numbers at the apogee of the inflammatory process. If there are complications, the duration of this period may be increased.
The duration of the disease depends on the causative agent of the infection. On average, it lasts from 10 to 20 days. Proper treatment contributes to the patient's full recovery.
In chronic form
Chronic pyelonephritis is characterized by a sluggish form with periodic exacerbations and a not very pronounced temperature reaction. This indicator fluctuates between 37–37.5°C, in the evening and night hours – 37.5–37.7°C. It persists for a long time and sometimes does not cause concern to the patient. During an exacerbation, the disease is characterized by a rapid rise in temperature.
Failure to comply with medical recommendations during treatment of acute pyelonephritis threatens the occurrence of a chronic form of the disease.
What kidney pathologies are accompanied by fever?
Temperature for lower back pain is a very important symptom. During the diagnostic process, it is necessary to establish the root cause of the pathology, since the treatment regimen will depend on this in the future.
The main thing is to correctly identify the disease and determine the causative agent. This will allow the attending physician to prescribe effective treatment that will lead to the desired result.
Of course, it is worth noting that body temperature can increase with various pathologies of the bean-shaped organs.
Pyelonephritis
This disease is characterized by an infection of the kidneys. If proper assistance is not provided in time, the patient’s general condition worsens significantly, and the temperature rises to 40 degrees. Among the main symptoms it is worth highlighting:
- difficulty urinating;
- lower back pain;
- unpleasant smell of urine and the presence of a dark color;
- the presence of bloody and purulent veins in the urine.
In the chronic form of pyelonephritis, the temperature remains at 37 - 37.3 divisions. In this case, the symptoms are mild. This form is especially dangerous for young patients. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you need to seek help from specialists.
Urolithiasis disease
Stones in paired organs are a fairly common ailment. The main symptoms of the pathology are pain in the kidneys and high fever. In addition, the patient has:
- stomach ache;
- blood in urine;
- the presence of sand particles in the urine.
If the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms, the doctor recommends monitoring your diet and drinking regimen. If the condition worsens, then surgical removal of the formations is performed using laser exposure.
Oncological formations
Temperature and pain in the bean-shaped organs may indicate the development of an oncological process in these organs. Initially, the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms.
Subsequently, as a result of tumor growth, pressure occurs on the tissues and nerve fibers of the organ. This is accompanied by pain. In addition, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- weight loss;
- dysfunction of neighboring organs;
- elevated temperature;
- cough with bloody mucus;
- acute headache;
In such cases, it is important to quickly diagnose the disease and begin treatment. This will significantly increase the chances of successful treatment.
Glomerulonephritis
As a result of the development of pathology, organ dysfunction and damage to the renal glomeruli occur. Impaired fluid filtration leads to infectious exacerbation. This process is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased blood pressure;
- intoxication;
- the occurrence of edema;
- Oliguria appears.
During the development of glomerulonephritis, body temperature rapidly increases. If treatment is not started in time, the patient will experience swelling of the lung tissue and difficulty breathing. As a result, kidney failure develops.
Other organ diseases
In addition to the above ailments, increased temperature occurs with nephroptosis, hydronephrosis, renal failure and other pathologies of paired organs.
If the first symptoms occur, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. This will allow you to diagnose and prescribe the correct treatment.
If treatment of the disease is not started in time, this can lead to serious consequences, including complete organ dysfunction.
How long does the temperature last for pyelonephritis?
If treatment for acute pyelonephritis is started in time, the temperature can last up to 1–2 weeks. In the presence of a purulent process, the period may be increased to 2 months. From 2 to 4 weeks, an increase in temperature is observed with a sluggish form of the disease.
Bed rest of the patient contributes to an earlier decrease in temperature.
Chronic pyelonephritis can be accompanied by constant low-grade fever, and during periods of relapse, lasting 7–14 days, approaching 38°C. Such exacerbations occur 1–2 times a year.
Treatment
Acute pyelonephritis requires complex treatment. Patients are required to be prescribed antibiotics. These drugs can quickly relieve inflammation and improve the patient’s well-being. The result may appear within 2-3 days, but the course of treatment must be completed to the end.
Amoxicillin has a wide spectrum of action, therefore it is very popular among doctors.
At the same time as taking antibiotics, it is necessary to maintain normal intestinal microflora.
You should drink Linex, Hilak-Forte or other similar drugs, eat kefir and yogurt.
The antimicrobial drug 5-NOK belongs to the class of uroseptics. It is effective for pyelonephritis, but has contraindications, so it is available with a prescription.
If the disease is severe and the patient is in the hospital, he is prescribed Cifran.
Treatment of the kidneys takes time: after the acute inflammation has resolved, it must be continued for another month. After 6 months, you should repeat the course, take all tests, and undergo an ultrasound.
Treatment of hyperthermia
A sick person is faced with the question: “Is it necessary to lower the temperature?” Yes, only if it goes beyond 38°C for a child, and 38.5°C for an adult. If hyperthermia persists for more than three days or exceeds acceptable limits, measures must be taken to restore normal values. An increase in temperature above 40°C poses a threat to the patient’s life, so it should be reduced immediately.
A decrease in fever leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of the immune system. At elevated temperatures, the number of bacteria does not change, the blood vessels dilate, which promotes better penetration of immune cells to the site of infection and a faster recovery of the patient.
Medication
It is better not to use antipyretics without medical advice. Firstly, these drugs have contraindications and side effects that have an adverse effect on kidney function. For example, in this case, you cannot use medications that contain paracetamol, metamizole sodium (Panadol, Analgin, Coldrex). Secondly, a decrease in temperature blurs the overall picture of the course of the disease.
However, there may be cases when it is impossible to quickly consult a doctor and you have to bring down the temperature yourself. Then you can use several drugs: Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Ibufen, Viburkol.
After taking Ibuprofen, the fever decreases quickly and for a long time (up to 8 hours)
Ibuprofen and other drugs based on it can be taken by children and pregnant women.
Children under 12 years of age and pregnant women are contraindicated to use Aspirin . There may be cases of toxic liver damage and adverse effects on the central nervous system of the child or fetus. Adults with problems in the gastrointestinal tract also need to be careful when taking it.
Video: what is important to know about temperature
Traditional ways
It is better to use alternative remedies without resorting to medications. Folk recipes will come to the rescue.
Cool compresses on the forehead help relieve fever. You can wipe the body with water at room temperature or using liquids that evaporate quickly (alcohol, vinegar). Prepare a warm solution with water in a 1:1 ratio. For children under 3 years old, it is better to use plain water.
The use of herbal medicines individually and in mixture with several components will help achieve antipyretic effects.
Photo gallery: antipyretic medicinal plants
A few recipes for use at high temperatures:
- Prepare a collection that includes elderberry and linden flowers in equal quantities. Take one tablespoon of this mixture, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave to brew for 20 minutes. Drink in one go.
- Squeeze juice from mashed 300 g cranberries. Pour one liter of boiling water over the remaining cake and boil over low heat for 5 minutes. Add berry juice and 3 tablespoons of honey to the cooled broth. Drink several times throughout the day. Course - 7 days. Contraindicated for people with stomach and intestinal diseases.
- Pour one teaspoon of a mixture of chamomile, linden and thyme, taken equally, into 200 ml of boiling water for five minutes. Strain. Drink during the day.
- The honey content enhances the effect of any folk remedies for fever.
- It is good to use green tea (brew at the rate of 1 teaspoon per glass of boiling water) with the addition of raspberries, linden blossom, lemon, currants or lingonberries.
Video: how to lower a high temperature without medication
Kidney inflammation and fever
Kidney disease or nephritis is an unpleasant illness that can last from a week to a month, sometimes more. It is accompanied by many symptoms, including fever, so it is often confused with a common cold. Depending on the form of the disease, the temperature ranges between 37 and 40 °C, so timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment are required.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Kidney inflammation develops after infectious bacteria enter the renal system.
The disease can develop independently, or it can be part of complications of other diseases (female and male genital organs, urinary system, acute renal failure). The most common causes of infection are:
- hypothermia, weak immunity after illness, constant temperature changes;
- constant abstinence from going to the toilet on time;
- poor nutrition, eating too spicy and salty foods;
- long period of taking antibiotics;
- smoking and alcohol;
- blood stasis.
A sign of nephritis can be considered an aching feeling in the lumbar region.
The first symptom of nephritis is an aching feeling in the lower back. Often the back hurts on only one side. Sometimes the pain is confused with radiculitis or other back inflammations.
Further, nephritis manifests itself in increased temperature, general weakness, dizziness, and nausea. Because of this, it can be confused with a cold or poisoning. There is swelling of the face or swelling of the entire body.
The process of urination is also disrupted, sweating increases, and blood pressure increases.
Does inflammation of the kidneys cause fever?
When the kidneys become inflamed, the temperature most often rises. This occurs as a result of the body's reaction to the presence of an infection in it. This is a defensive reaction with which the body tries to protect itself and get rid of the pathogen.
With nephritis, the temperature stays between 37-37.5 °C. This condition is called low-grade fever.
In more severe conditions - complications, inflammatory lesions, the temperature rises to 39 ° C, the condition resembles a fever, accompanied by dizziness, pain, chills.
How long does the temperature last?
The length of time during which the temperature can persist depends on the form of the disease. In acute nephritis, it rises to 38-39 °C and can last for several days until quality treatment is provided.
In the morning and afternoon the condition is normal, but in the evening the temperature usually rises.
In the chronic form, the so-called low-grade fever persists, which has a debilitating effect on the patient - it stays at around 37 °C and may not subside for a week.
Markings for different forms of the disease
With different forms of the disease, temperature indicators fluctuate in different ranges:
The temperature can rise to 40 degrees with purulent kidney damage.
- for varieties of jade - from 37 to 37.5-38 °C;
- if acute inflammation develops, it reaches 38-39 °C;
- with chronic inflammation, the temperature can rise to 38 °C, sometimes weakness is observed, the mark drops to 35 °C;
- purulent disease causes a mark of 40-41 ° C;
- infection of the renal pelvis - a complex disease in which the temperature rises to 40 ° C;
- In men and women, the disease occurs under similar conditions; the level can rise to 39 °C.
What to do?
Kidney disease requires an individual approach. Complications require urgent hospitalization and medical observation. But even in the initial forms of the disease, the patient requires calm and bed rest. At home, bring down the temperature with the help of medications and the right regimen. This should happen under the supervision of a doctor.
Among the drugs that are necessary to treat the urinary system:
- antibiotics have an anti-inflammatory effect - “Furadonin”, “Ciprofloxacin”, “Norfloxacin”;
- uroseptics act directly on the kidneys, destroying infections - “Furazidin”, “Nitroxoline”, “Ercefuril”;
- drugs aimed at symptomatic treatment - vitamins, immunostimulants, antihistamines, calcium, drugs for better blood circulation, cytostatics and others.
It is necessary to take antibiotics for 7-10 days, in especially severe cases - for several weeks. Noticeable improvement is observed within a week, and complete recovery usually occurs within a month. Treatment will be complete only if you follow a special diet.
It excludes excessive consumption of protein foods, salty, spicy, spicy foods, alcohol, carbonated water, canned food, and meat. The diet consists mainly of fruits, cereals, bread, and vegetables. Be sure to drink a lot of liquid; healing decoctions of rose hips and dried fruits will be very useful; you can drink tea. Dairy products are gradually allowed to be consumed.
With a noticeable improvement, protein products are returned to the menu. Chronic diseases completely exclude smoked, spicy and salty foods.
Complications of hyperthermia
With prolonged or improper treatment, there is a risk of developing purulent complications. Inflammatory processes in the body intensify, so the temperature does not subside.
The load on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems increases. The viscosity and coagulability of blood increases, which leads to impaired circulation in the internal organs. The body becomes dehydrated. If the high temperature does not subside for a long time, it becomes life-threatening.
Pregnant women and people with diabetes are most at risk of worsening the condition.
Urolithiasis disease
If combined with high fever, pain can act as a sure sign of kidney stones. In this case, the temperature is associated with an infection. Severe pain may indicate the onset of stone movement, which causes injury to the mucous membrane lining the area of the ureters.
Urolithiasis is dangerous for patients due to paroxysmal colic. Most often this manifests itself as severe pain and fever. Most often, the duration of the attack does not exceed a day. In this case, the condition can become very serious when the patient does not understand what is happening around. This is due to severe pain, which often does not even respond to painkillers.
Other symptoms of an attack of KSD include frequent urination, which is painful for the patient, nausea and vomiting. At the same time, the amount of urine is reduced, and its waste may stop altogether. Urine tests show excessive amounts of protein, red blood cells and white blood cells. Chronic renal failure is a complication of ICD.
Kidney pain and fever
If a person of any age begins to hurt their kidneys, they should definitely consult a doctor. Especially if a child complains of pain. Kidney fever in adults and children is an alarming sign that cannot be ignored, otherwise there is a risk not only to health, but also to life.
At the first signs of illness, you should understand what is causing it. The doctor will do this. Laboratory tests and ultrasound diagnostics are usually prescribed. Often, such a disease is caused by inflammatory pathologies, urolithiasis or neoplasms.
It is worth noting that if a bacterial infection is superimposed on the inflammation, the temperature from the kidneys does not drop when using the usual means to bring it down.
In addition to pain, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- headache;
- disturbance of well-being;
- nausea (sometimes vomiting).
Deterioration in general health occurs due to intoxication. In addition, the urinary system is of concern:
- pain and burning when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- urine turns reddish.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, renal failure develops, which can lead to irreversible consequences.
Diseases
Kidney temperature in an adult has its own reasons. The urologist’s task is to conduct a differential diagnosis in order to understand which disease is to blame for the discomfort. If everything is done immediately after the onset of symptoms, you can avoid the chronic form of the disease.
Pyelonephritis
The more severe the patient's condition, the higher the numbers on the thermometer. If the infection has affected the kidneys, the values will be at least 38°C, or even reach 40°C.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis are as follows:
- difficulty passing urine;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- change in urine - the color becomes dark, the smell is unpleasant;
- the pain is felt more strongly from the side of the kidney, which is affected by the inflammatory process.
The extreme degree of the disease is characterized by the appearance of pus, mucus and blood in the urine.
In the case of the chronic form, the temperature does not rise above 37-37.2°C. The symptoms are not so acute, the pain is not constant. The urine may not change.
The disease is very dangerous for pediatric patients. That’s why you should definitely call a doctor if, apart from fever and pain, there are no symptoms of ARVI.
Glomerulonephritis
This disease affects the kidney glomeruli, called glomeruli. With their help, the kidneys filter the blood. If the function of the glomeruli is impaired, a diagnosis of glomerulonephritis is made.
The symptoms will be as follows:
- blood pressure increases;
- urine flow is impaired;
- swelling appears;
- intoxication.
The disease is dangerous and also requires urgent care to prevent kidney failure. Edema can take over the lungs, and it is not so easy to reduce the pressure, which is also life-threatening.
Urolithiasis disease
When your kidneys hurt and the temperature is 37°C, you need to rule out the presence of stones in them. Stones form in organs if metabolism is disrupted or if their function is impaired. When the size of the stones is quite large, the following symptoms may occur:
- periodic pain in the abdominal region of varying intensity;
- blood in urine if formations scratch the mucous membrane;
- There is a sediment in the urine - small particles called sand.
For the time being, kidney stones practically do not interfere with everyday life. If there is any discomfort, it especially affects your overall well-being.
If stones are accidentally detected on an ultrasound, the doctor does not prescribe medications. To begin with, it is determined by the urine sediment which type of stones is formed. Based on the results obtained, a diet will be selected, and the specialist will also give recommendations regarding the drinking regime.
If the kidneys hurt and the temperature persists, then surgical treatment is indicated. This is how renal colic can manifest itself. Thanks to laser treatment, you can get rid of stones.
Tumors
The initial stages of the tumor process do not manifest themselves in any way. When the tumor becomes larger, it will put pressure on the tissues and nerve fibers of the organs. And then the temperature will begin to rise. The kidneys often hurt because the tumor is growing.
At the same time, the state of health is disturbed, a constant feeling of fatigue appears, and the patient loses weight. The work of neighboring organs may be disrupted. The pain will be felt more clearly on the side where the affected organ is located. Hematuria cannot be ruled out. The thermometer will constantly be at 37.1-37.4°C. Sometimes the temperature will rise even more.
In advanced cases, when metastases occur, a cough with blood, a persistent headache, and yellowing of the skin will appear if the liver is damaged. It is important to undergo regular examinations to detect the disease at an early stage. Then the prognosis is more favorable.
general information
When the kidneys hurt and the temperature rises above normal limits, the most common problem is an infection in the kidneys.
It is infections that give rise to inflammation processes. With the blood, microbes and their metabolic products penetrate into the kidney blood, which gives a powerful effect of inflammation in the urinary system. The development of such diseases can be:
- venereal infection;
- problems with alcohol;
- smoking abuse;
- taking medications that are harmful to the kidneys.
Most often there is cystitis or pyelonephritis. Moreover, for this pathological series, elevated temperature is a constant companion, since inflammation is present. However, one infection can lead to low-grade fever, while another can leave a person with a fever.
It is worth noting that kidney problems often occur in women. They are, in principle, at risk, especially if they have gynecological problems. Often in this case, pain and fever are considered symptoms.
Additionally, it is important to note that kidney pain is not the only symptom. Most often, the pain is combined with a change in the amount of urine excreted, and going to the toilet can cause discomfort or pain. The urine itself may change color and smell. Against the background of increased body temperature, swelling can be noticed. Kidney ailments often result in swelling of the face and hands.
Today, kidney pathologies are classified according to many parameters. It is difficult to list them accurately. But, speaking in general terms, the list looks something like this:
- Glomerulopathy. In this case, we are talking about diseases that are accompanied by damage to the glomerular apparatus of the bean-shaped organs. Pathology can be acquired or congenital, as well as inflammatory and non-inflammatory.
- Tubulopathy. This category includes diseases that affect tubular structures. They are also divided into congenital and acquired pathologies.
- Abnormal development and injury of the organ.
- Oncological pathologies developing in the kidneys.
In fact, the list of these diseases is quite extensive. Therefore, it is so important to undergo a timely diagnosis from a qualified doctor who can prescribe the correct treatment based on this.