Warehouse relocation to Europe. We sell hepatitis C drugs in Russia at the purchase price - warehouse liquidation Go to website
Nephrectomy is an operation to remove a kidney. It is indicated in cases of severe disease of the organ, when it is not possible to save it. Life changes after kidney removal; health fundamentally depends on the patient’s behavior.
The kidney is removed in the presence of the following conditions:
- malignant tumor, when the second kidney is not affected;
- injuries leading to disruption of organ function;
- kidney stones, which cause tissue to fester and die;
- polycystic kidney disease, when medications do not have an effect;
- abnormal kidney development since childhood;
- hydronephrosis and other problems with urine drainage from the kidneys, which provokes tissue death.
Preparing for a nephrectomy
Having studied the indications for nephrectomy, the patient can imagine what awaits him with such a diagnosis, but the decision is made by the doctor. Initially, a diagnosis is carried out - the cause of organ dysfunction is identified, and the functioning of the organs is examined before surgery.
The range of diagnostic measures includes:
- assessment of respiratory function - nothing should interfere with lung function, general anesthesia depresses breathing;
- X-ray of the genitourinary organs to identify pathologies;
- creatinine test. If the blood level is elevated, they speak of kidney failure;
- CT, MRI of the kidney;
- Ultrasound and CT scan of vessels in the abdominal cavity for the presence of thrombosis in the veins.
For detailed information, blood and urine samples are taken and fluorography is performed. Until the day on which the kidney removal operation is scheduled, a person spends three weeks in the urology department, undergoes tests and is observed by doctors.
One day before surgery you should not eat. The patient is given an enema and the hair at the surgical site is shaved. You need to drink a lot of water.
Diagnosis before nephrectomy
Laboratory methods.
Patients operated on for kidney cancer are under clinical observation. The most frequent and accessible examination is tests. Even in the absence of symptoms, you should pay attention to:
- Decreased hemoglobin (anemia).
- Increase in ESR.
- Increased creatinine, urea, alkaline phosphatase, LDH, liver transaminases, bilirubin, calcium.
- Microhematuria (red blood cells in the urine).
Any deviation in these indicators is a reason for further examination. No specific oncological markers have been identified for kidney cancer.
- Ultrasound diagnostics. Ultrasound is a screening method; in 80-90% it can detect a tumor larger than 1 cm and enlarged lymph nodes.
- CT – computed tomography. Standard for diagnosing both primary tumors and recurrent tumors. It assesses size, prevalence, invasion of neighboring organs, and damage to lymph nodes with 100% accuracy.
- MRI is sometimes prescribed as a clarifying examination if tumor thrombosis is suspected, as well as if there is an allergy to contrast.
MRI scan of relapse in the bed of the left removed kidney
- Angiography is performed when planning surgery.
A blood test is used to detect elevated creatinine levels. CT, MRI and ultrasound of the peritoneal vessels are prescribed to detect vascular thrombosis. The first two manipulations are also carried out for the affected kidney, assessing its condition. Additional damage to organs is determined using x-rays.
It is important that respiratory function is normal, since anesthesia depresses breathing.
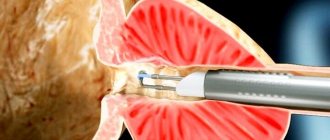
Kidney removal (classic abdominal surgery)
After preliminary preparation, on the day of the operation the person is taken to the operating room, placed on the table and secured with bandages (from spontaneous movements). After anesthesia, open surgery begins, which lasts about 3 hours. The procedure can be described as follows:
- incision;
- installing an expander;
- fixation of the duodenum and pancreas;
- sealing the veins leading to the kidney;
- clamping of the ureter from 2 sides, an incision is made on the clamped segment and the organ is sutured;
- suturing the renal pedicle to prevent bleeding;
- extraction of the removed kidney.
Sometimes removing a kidney leads to unpleasant consequences. These are the following states:
- bleeding;
- intestinal obstruction;
- vascular thrombosis;
- heart failure;
- disturbance of cerebral blood supply;
- respiratory failure.
Laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopy is a non-traumatic and technical option for organ removal compared to classical surgery. The bottom line comes down to this:
- the patient is placed face up on the table, a cushion is placed under his feet to make it easier for the patient to turn;
- laparoscopic nephrectomy of the kidney in the hospital is carried out under general anesthesia, so the patient is put under anesthesia after fixation with bandages;
- in the navel area, a puncture is made into the peritoneum and a trocar with a video camera is inserted, after which 2 other trocars with surgical instruments are inserted through other punctures. Upon completion of preparation, the patient is turned on one side and fixed;
- the surgeon compresses the vessels, removes the kidney, and stitches the wounds with self-absorbing threads.
As with classical surgery, laparoscopic radical nephrectomy can lead to complications, although they occur in only 16% of cases. These are the following problems:
- postoperative hematoma;
- gastrointestinal obstruction;
- postoperative hernia;
- pneumonia;
- nerve palsy in the shoulder;
- artery blockage.
Main complications of nephrectomy
With any type of operation, an inflammatory process is likely. An increased temperature will be a signal of deterioration. The presence of other consequences is associated with how well the preparation was carried out before the operation, what the qualifications of the surgeon are, as well as other pathologies in the patient.
Complications are possible due to prolonged immobilization or as a reaction to anesthesia. These consequences include the following conditions:
- congestive pneumonia, stroke;
- heart attack;
- thrombophlebitis.
After nephrectomy, patients develop renal failure. This happens because the kidney needs to take the entire load on itself. After time, the body will adapt, but some people undergo blood purification.
Why does the temperature rise after surgery?
With any surgical intervention, the patient’s body experiences enormous stress, so a slight increase in body temperature is considered a natural phenomenon. Even after a correctly performed operation, the patient has low-grade fever at the level of 37.2–37.7°. This is influenced by natural factors:
- If surgeons open a purulent wound or abscess, the decay products remain in the body and are gradually suppressed by the immune defense.
- On the first day, mild dehydration is often observed. This manifests itself in weakness, drowsiness and chills.
- In case of severe tissue damage (amputation, organ excision or intestinal resection), temperature is a protective reaction to installed drainages.
Postoperative period with one kidney
After surgery to remove a kidney, a catheter is inserted into the bladder, through which the bladder is emptied within a couple of days. The patient's condition in intensive care is constantly monitored.
When the attending physician is convinced that the intestines are functioning, the patient is allowed to drink and eat food. After surgery, pain occurs from coughing and changes in body position.
Despite the discomfort, doctors do not recommend staying in bed; moving is beneficial. On day 2-3 you can turn around and get up. To prevent the stitches from coming apart, the doctor recommends that the patient not make sudden movements. For those who have undergone surgery, rehabilitation after kidney removal is limited, among other things, to physical activity. Such actions are necessary to improve intestinal function and normalize blood flow.
After discharge, rehabilitation continues at home - the patient follows the recommendations received in the hospital. Full recovery lasts about 1.5 years, by which time the second kidney adapts to the load. It is more difficult for the body of people in old age to adapt. If you follow all medical instructions, the process will go faster.
How to deal with pain after surgery
Of course, no one other than a doctor can give an objective assessment of a specific situation, so it is best to contact your surgeon or nephrologist for help. But sometimes this opportunity does not present itself right away, so below are tips that will help reduce or eliminate discomfort.
Inflammatory processes
If inflammation occurs due to an infectious agent entering the organ, then antibiotics or antiviral drugs cannot be avoided. Under no circumstances prescribe them to yourself, because it can be dangerous to your health!
Teas made from anti-inflammatory components will help to slightly reduce the activity of microbes and the pain themselves:
- sage;
- chamomile;
- oak bark;
- rose hips;
- mulberry or raspberry leaves;
- horsetail;
- nettle and others.
To prepare such a decoction, you need to take a dried product of your choice (it is better to purchase it at a pharmacy) and boiling water in a ratio of 1:5. You can combine different ingredients, but the ratio of dry ingredients and water should not change. Brew tea for 20-30 minutes, sift it through a sieve and drink warm. You don’t have to prepare the decoction yourself, but buy a ready-made mixture of herbs for the kidneys at the pharmacy and brew it.
Therapeutic diet after nephrectomy
When treating any disease, much attention is paid to correcting nutrition. People left with one kidney need to help the body adapt and not overload the remaining organ.
The main factor in choosing dishes after kidney removal is their ease of digestibility. The diet includes low-calorie foods with low protein content. The daily menu includes:
- Rye bread;
- vegetable and fruit salads;
- pasta and cereals;
- dairy products.
Over time, meat dishes are carefully added to the menu - no more than 100 g of boiled chicken, rabbit or calf meat. Fish is allowed, and chicken eggs can be eaten as an omelet. You should not drink a lot of milk, since the calcium it contains can potentially lead to the formation of kidney stones. It is better to avoid legumes, as they contribute to flatulence.
During the day you need to eat little by little, but often - about 6 times. Fluid consumption is discussed with the doctor separately, and soup, juices, and liquids from fruits and vegetables are taken into account.
Recommended for consumption are dishes that are steamed, baked or boiled. Salt should be consumed up to 5 g per day, bread - up to 400 g. The diet prescribed by the doctor must be strictly followed - the only kidney must be protected.
urologia.expert
Indications for kidney removal surgery
Indications for nephrectomy (removal of the left or right kidney) include a group of pathological manifestations affecting the organ:
- tumors of a malignant nature, if one kidney is not affected or functions partially;
- traumatic damage to the kidney, in which the organ stops working normally and it is impossible to restore its functions;
- kidney stones, which provoked suppuration of the kidney tissues and their death;
- polycystic kidney disease, developing against the background of renal failure (nephrectomy is used if drug therapy does not help);
- pathologies of kidney development in childhood;
- problems with urine excretion from the kidney (hydronephrosis), which provoke tissue atrophy.
Return to contents
How is ureteral stenting performed and possible complications?
The method allows you to prevent or stop the development of such a serious complication as kidney hydronephrosis.
What is stenting and why is it necessary?
Stenting, or stent installation, is the insertion of a special tube into a hollow organ that has a narrowing, allowing the contents of the organ to move unhindered. Stents are installed in various organs and systems. For example, in the coronary (supplying the heart muscle) arteries with coronary heart disease, bile ducts when they are narrowed or blocked by a stone, intestines, etc.
Preparing for a nephrectomy
Before the procedure, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination.
Before performing a nephrectomy, you need to do a thorough examination of the patient. The doctor must find out why the organ stopped working, that is, identify the reasons for removing the kidney, and find out everything about the condition of both kidneys. In addition, the importance of the examination is due to the fact that the operation is performed under general anesthesia, which poses some danger for a patient in serious condition.
Return to contents
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures include:
- Assessing the patient's respiratory function - nothing should interfere with the functioning of the lungs, since respiratory depression occurs during general anesthesia.
- X-ray examination of the organs of the genitourinary system - the condition and possible additional damage to the organs are determined.
- Taking a blood test for creatinine - indicates kidney failure if the indicator is elevated.
- Computer (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the affected kidney.
- Ultrasound, CT or MRI of the peritoneal vessels reveals the presence of venous thrombosis.
If clarification of information about the patient’s condition is required, additional urine and blood tests are taken to identify infections, and fluorography is performed. Before the kidney is removed, the patient must spend about 3 weeks in the urology department. During this period, the entire diagnostic range of studies and careful monitoring of the patient are carried out.
Return to contents
Preoperative preparation
The day before surgery you need to completely stop eating.
The day before surgery, final preparations are carried out. The patient is given an enema to cleanse the intestines and the hair is shaved in the place where further manipulations by the surgeon are expected. It is forbidden to eat for the whole day before the nephrectomy. You should drink a minimum amount of water, and if possible, avoid liquids altogether.
Return to contents
Hydronephrosis of the kidney - proper treatment guarantees the health of your kidneys
A whole group of serious diseases is associated with the kidneys. One of these pathologies is hydronephrosis of the kidney.
The disease consists of expansion of the cups of the kidney and pelvis due to stagnation or disruption of the outflow of urine.
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
There are several stages of this disease, and its symptoms may be absent at the first stage.
Treatment methods can be medicinal or surgical.
Alternative treatment is widely used, but only after consultation with the treating doctor.
What is hydronephrosis of the kidney?
During the day, the kidneys process up to two thousand liters of fluid, while producing from one to two liters of urine. This helps the body get rid of metabolic products, water, waste, toxic and harmful elements.
If there are malfunctions in the functioning of the kidneys or one kidney, then the whole body suffers. Therefore, it is better not to delay the diagnosis of hydronephrosis.
There are three stages of this disease and the first stage cannot always be diagnosed by symptoms alone.
But, if the disease has reached the second stage, then with a high probability it will go to the third, when the kidney can no longer perform its functions. Hydronephrosis is often a consequence of urolithiasis.
Most often, hydronephrosis of the kidney occurs in people from 18 to 45 years old; women are affected one and a half times more often than men. The disease can affect both the left and right kidney. Disease of this type in both kidneys is quite rare, only in 5-9% of cases.
Signs and stages of disease development
At the first stage of hydronephrosis, a person most often does not complain of any specific symptoms. Because the clinical picture of the early stage is determined by the cause that caused the disease. For example, if it is urolithiasis, then attacks of renal colic with severe acute pain occur.
Constant dull aching pain, which is localized in the lower back, is the most severe symptom of hydronephrosis. The pain does not depend in any way on the position of the body and can occur at any time of the day. The localization of the pain syndrome depends on which kidney is affected.
Transformation of the right kidney is often manifested by pain in the right side of the abdomen (pain syndrome is similar to cholecystitis and liver diseases). Sometimes the pain is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and bloating. A less commonly described symptom contributes to increased blood pressure.
Sometimes the only sign of illness is blood in the urine. It occurs in 20% of patients. Often this symptom occurs if the cause of hydronephrosis is urolithiasis (stones injure the walls of the urinary tract).
In the final stage of the disease, especially if it manifests itself on both sides, signs of chronic renal failure are often observed. There is also less urine, swelling and anemia appear.
Main degrees of hydronephrosis:
- The first stage, when only the pelvis system is dilated, but there is no dysfunction of the organ.
- The second stage is characterized by a large expansion of the pelvis. There is a slow thinning of its walls. Kidney function is impaired by 20%.
- The third stage turns the kidney into a large multi-chambered organ that is filled with urine. Kidney function is reduced by 80%.
Diagnostic measures
Hydronephrosis often develops latently and does not have symptoms of inflammation, impaired filtering or excretory function. Thus, the disease may not manifest itself until the initial form of renal failure occurs. Therefore, if the amount of urine has decreased, its color or consistency has changed, you should seek a laboratory and hardware examination from a urologist.
The most accurate diagnostic methods:
- Laboratory testing includes urine and blood tests. Including a biochemical blood test, and a urine test is done according to Zimnitsky, Nechiporenko.
- Ultrasound of both kidneys, as well as the bladder and ureter. If necessary, an ultrasound examination of other internal organs is performed.
- X-ray using contrast agents;
- MRI.
The devices help in diagnosis very much. With their help, you can determine on which side the kidneys are damaged.
Hydronephrosis of the right kidney always has a large size of the pelvis area when compared with a healthy left kidney. Conversely, if the left kidney is diseased, there will be a larger pelvis compared to a healthy right kidney.
Treatment methods
You can get by with drug treatment in the early stages. The doctor must find the cause of hydronephrosis and try to eliminate it. Sometimes there is abnormal congenital development, then treatment requires surgical intervention.
Drug treatment
If hydronephrosis is acquired, then there are different treatment options.
The doctor conducts hospitalization in order to do a thorough examination of the body. When the diagnosis is confirmed, it is necessary to cure the disease that led to the development of the disease.
If this is only the first stage of the disease and the diagnosis was made on time, then kidney function is not yet impaired. Therefore, the patient, under constant supervision, takes certain medications.
Antibacterial therapy is often prescribed (if an infection occurs, pyelonephritis develops). If urates (stones consisting of uric acid) are present, the doctor will prescribe alkalizing therapy.
Hormonal treatment is required if hydronephrosis leads to retroperitoneal fibrosis.
Surgical treatment
In advanced stages of the disease, surgery is indispensable. Often, if severe renal dysfunction is observed, surgery is the only option. There are several methods of surgical intervention:
- An anastomosis is made between the pelvis and the ureter. An additional pathway is created for urine, which helps relieve pressure on the kidney.
- The cause of narrowing of the area of the calyx and pelvis is eliminated. To do this, the kidney is dissected longitudinally and then sutured transversely.
In 99.9% of cases, after surgery, the described pathology is completely cured. The recovery period also does not last long: from three to five days. You can return to your normal life after two weeks.
Traditional methods
Suitable only for the treatment of the first stage of hydronephrosis and only after consultation with a doctor. Otherwise, self-medication can cause great harm and cause active further development of the disease.
The most effective recipes:
- A collection is made from bud tea, string grass and knotweed, meadowsweet flowers, raspberry and currant leaves, chamomile, and calamus root. Two tablespoons of the mixture are poured into 250 ml of boiling water. Drink the product three times a day in a dosage of 50 ml;
- Another good collection consists of knotweed and mint herbs, fireweed, and celandine. Add marshmallow root, alder cones and coriander fruits. Prepare and treat as indicated in the recommendations for the first collection.
These preparations should be taken one at a time over a course of about two to three weeks. After treatment with one collection, a break is taken for two weeks, and then you can start taking the second collection.
About the importance of proper nutrition
The diet should be such as to help restore the flow of urine and kidneys. The menu should include a lot of fiber, which is found in black bread, raw and steamed vegetables, lean fish and veal, beets, and cabbages. You need to avoid foods that are fatty and very salty.
You also need to drink two liters of water per day, eat as many fresh berries and fruits as possible. You should consume approximately 3000 kcal per day, but the food should not be fatty.
If it is possible to eliminate the causes of hydronephrosis in time, then it will be possible to quickly and without consequences restore kidney function. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to periodically perform an ultrasound of the kidneys and undergo a laboratory urine test.
Video: How to overcome kidney hydronephrosis - recommendations from doctors
Abdominal surgery (open)
How do they do it?
Patients are placed on the operating table and secured with elastic bandages so that they do not make involuntary movements. Next, they are put under anesthesia, and the operation to remove the kidney begins. There are several options for making the incision: in the front in the area of the lower border of the ribs or on the side between the 10th and 11th ribs. The second technique of nephrectomy is considered less traumatic, since the doctor has direct access to the kidney.
The operation to remove a kidney using the open method lasts about three hours.
After making the incision, it is necessary to install a dilator and fix the pancreas and duodenum so that when working with the kidney they do not harm them and prevent displacement. The connective and fatty membranes are separated from the kidney to be removed. If there are blood vessels in the tissues, they are blocked with clamps. The veins approaching the kidney are sealed, disrupting the original structure of the kidney protein.
The ureter is compressed on both sides. An incision is made between the installed clamps. Next, the organ is sutured with absorbable threads. If cancer has metastasized from the kidney to the ureter, it is removed along its entire length. Before removing the kidney, the surgeon sutures the renal pedicle. Through it, arteries, veins and the ureter enter the kidney. To prevent the development of bleeding, the vessels are sutured. The separated kidney is removed from the peritoneum.
Return to contentReturn to content
Possible problems
The most common complications after abdominal surgery are:
- Bleeding caused by an undetected blood vessel or insufficient occlusion of large veins or arteries.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Heart failure caused by patient predisposition or taking the wrong dose of anesthetics.
- Thrombosis of large vessels.
- Problems with the blood supply to the brain, usually caused by bleeding or a blood clot.
- Respiratory failure caused by anesthesia. If breathing problems go away over time, the patient’s life and health are not in danger.
Return to contents
Increase in temperature after tooth extraction procedure
November 25, 2020 Last revised: January 10, 2020 Dental diseases
Many people are scared when the temperature rises sharply after tooth extraction. To reassure patients, you need to have certain information, which we will now try to present to you.
When is fever normal?
By removing a tooth from the hole, the dentist willy-nilly injures the soft tissue. As a result, bleeding begins. The body is a smart system.
It reacts to injury with inflammation with some signs: pain, redness, swelling and temperature. In such cases, temperature after tooth extraction is a completely justified phenomenon.
The immune system responded correctly. There's no need to worry. There is no need to swallow antibiotics.
The temperature rises on the day of removal. The temperature value may fluctuate. Usually it varies in the range from 36.6ºС to 37ºС. In the evening it always rises, that is, it becomes larger. Sometimes it can reach up to 38ºС.
If a person feels exhausted and very ill, you can take an antipyretic pill.
Painkillers can be taken only in case of severe pain, which is usually absent with simple removal.
To alleviate the condition, you will have to wait some time (sometimes 2-3 days is enough) until the temperature returns to normal. But there are other more serious cases of complications when its increase is a dangerous signal. We'll talk about them further.
Cold
Know that the more damage the dentist caused to the patient during removal, the higher the risk of fever. If after three days the temperature does not subside, then you need to take this more carefully.
The person may have a cold or flu. In this case, the disease can be caused by hypothermia or a viral infection. In this case, the temperature must be accompanied by a sore throat, cough, runny nose and red eyes.
A therapist can help treat these symptoms.
Temperature after wisdom tooth removal
It is after the removal of the named tooth that fever most often occurs.
Typically you should look out for the following signs:
- The temperature lasts for more than 3 days and increases in height in the evening, its value is early 38ºС and above.
- There is pain in the tooth socket.
- Swelling and redness are visible at the removal site.
- There is no blood clot in the socket.
- Strong headache.
Signs may appear sequentially. Others may be absent altogether (for example, headache). Increasing pain in the socket, high temperature and pain always indicate an abnormal process. The ongoing inflammation must be treated.
Temperature after removal of the figure eight is a common occurrence. The body reacts violently to the removal of the third molar. Removal is considered quite difficult. The difficulty is associated with the distant and hard-to-reach location of the figure-eight tooth. It becomes even more complicated if the tooth is retracted or dystopic.
The removal procedure looks like this:
- Injection of local anesthesia.
- Gum cutting.
- Drilling out bone tissue.
- Sawing (if necessary) and removal of the tooth from the oral cavity.
- Suturing and final treatment of the wound.
Patients are also often tormented by soft tissue swelling, sharp pain and swelling of the cheek.
Baby teeth
If the child’s temperature increases after tooth extraction, parents should consult a doctor. The spontaneous loss of baby teeth is intended by nature. Even tooth extraction by a doctor should not cause complications. You should not wait (as in the adult case) 3 days for the temperature to normalize. Your actions: visit the doctor.
Reasons for a rise in temperature after the removal of a baby tooth:
- The body received severe stress and therefore reacted sharply.
- An inflammatory process has begun in the gum.
Possible complications
A complication is a rather dangerous case. A high temperature after tooth extraction is a serious warning sign. Complications occur when:
- the root or part of the tooth remains in the socket;
- alveolitis;
- hematoma;
- chronic periodontitis;
- sinusitis.
The root or part of the tooth remains in the socket
It is clear that this complication occurs due to the fault of the doctor who performed the removal. The human body works like a clock here. Over time, tissue forms around the root or part of the tooth (tooth root granuloma). Granuloma initially does not have a cavity. Over time, it turns into the form of cystogranuloma, and then into a cyst. The cyst cavity already contains products of fatty and protein tissue.
There are cases when the cyst is destroyed. This usually occurs against the background of periodontitis, trauma, ARVI, and sinusitis. In this case, the body temperature rises sharply to 39 ºС. In addition, there is poor physical condition, swelling of the gums, swelling of the cheeks and unpleasant pain. This frightening picture can last for several days.
Alveolitis
Alveolitis is an inflammation of the walls of the socket. Often occurs after the removal procedure. Causes of alveolitis:
- Improper care after surgery.
- Decomposition of a blood clot.
- No blood clot in the socket.
- Injury resulting from surgery.
- Heavy bleeding from the removal site.
- Caries.
- Purulent inflammation of the throat.
- Pushing infected tissue into the hole during surgery.
- Weak immunity.
If at least one of the listed factors is present on the face, then alveolitis develops in 1-3 days. In addition, the patient experiences nauseating breath, poor physical condition, general malaise, paroxysmal acute pain in the gums and, of course, fever.
In case of delay, alveolitis will go into the purulent-necrotic stage. Subsequently, osteomyelitis will begin in the socket. You should know the symptoms of osteomyelitis:
- The mouth is difficult to open (when lower teeth are removed).
- The temperature is closer to 40ºС.
- Lack of strength and performance.
- Throbbing pain.
- My mouth smells bad.
- Night sleep is disturbed.
Subsequently, osteomyelitis develops into an abscess and phlegmon. The outcome could be fatal.
Hematoma
After removal, a hematoma may form in the soft tissue. The cause of its formation is a burst vessel, increased capillary fragility, and hypertension.
Hematoma can be identified by enlarged gums, pain, redness and elevated body temperature.
Chronic periodontitis
A tooth with periodontitis often leaves pathogenic microflora in the socket. As a result, the temperature reaches 37.5ºC, severe swelling is visible and pain is felt.
Sinusitis
Sometimes after removal a runny nose and nosebleeds appear. A common culprit is the upper incisor. The integrity of the bottom of the maxillary sinus is disrupted, and a hole is formed into which food easily enters.
As a result, inflammation begins with a sharp rise in temperature. In addition to a runny nose with pus and high fever, the patient experiences pain in the area of the bridge of the nose, nose and forehead.
The patient constantly suffers from headaches.
Other reasons
The temperature after tooth extraction may also rise due to:
- Allergies to painkillers (anaesthesia).
- If an infection has entered the wound cavity.
- If the doctor touched the root of a neighboring tooth during the intervention.
- If a foreign object remains in the hole: cotton wool or a foreign body.
When to lower the temperature
Every single doctor believes that no matter how the process progresses, it’s worth bringing down the temperature. A high value causes disruption of the functioning of the main organs of the body. But there are certain subtleties in lowering the temperature:
- At a temperature of 37.2ºC-38ºC, you should not take tablets and lower the temperature. The body must fight off the infection on its own.
- If the value is above 38ºC, you need to take an antipyretic tablet. This is worth doing regardless of the reason for the increase. For reduction purposes, paracetamol and ibuprofen are good drugs.
- If fever occurs in children, then they need to use an antipyretic suppository, which is inserted rectally. Adults can use suppositories if nausea or vomiting occurs due to poor condition.
Visit doctor
The time to see a doctor should not depend on when the fever started: today or has already lasted 3 days.
If side symptoms are present, help should be provided immediately. Symptoms include:
- Nauseating odor from the mouth.
- Temperature above 38ºС.
- The pain is constantly increasing.
- The gums swelled and became red.
- The cheek is swollen.
- The lymph nodes are inflamed.
- The removal site festers.
The doctor will conduct a survey and order an x-ray, which will show the reason for such a long high temperature.
If a root was left behind, the dentist will remove it and thereby remove the inflammation. Typically, after surgery, an antiseptic is treated and a course of antibiotics is prescribed. For granuloma and cyst, the actions taken by doctors are similar.
If, after a previous visit to the dentist, the patient’s cheek or gum is torn, the doctor will make stitches and apply a sterile bandage.
If sharp edges of the bone were left, the doctor will smooth them with a special tool.
Be aware that repeated intervention will lead to a rise in temperature again. But this will already be a completely normal and encouraging phenomenon.
Postoperative actions
Preventive measures consist of the following actions:
- Antiseptic treatment (for example, Rotokan or Burana 400 solution).
- Sanitation.
- Carrying out regular hygiene procedures.
- Using traditional methods.
In folk medicine, calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort, sage and calamus are used. They use traditional methods in parallel with medications.
On the day of removal, you should not visit the bathhouse or eat hot or cold food. It is necessary to thoroughly avoid contact with sick people, beware of winds and drafts. You should not eat too hard foods, so as not to damage your painful gums. Do not drink alcohol or consume hot spices.
Reviews from patients
I had my wisdom tooth removed. After the procedure, I was exhausted, and in the evening my temperature rose sharply, but not much. My doctor told me everything and explained what this could be. I didn't take the pill.
My husband had no fever at all after the removal. I thought that this was not a terrible phenomenon. I only ate liquid porridge. Surprisingly, the next day everything went away for me.
All that remained was an unpleasant feeling at the removal site.
I've always been afraid of dentists. I haven't visited these doctors for a long time. Accordingly, my teeth were in critical condition. When my cheek suddenly became swollen, I was seriously scared. There was nothing to do, I ran to the hospital, to the doctors who were terrible for me. The doctor was dismayed by my condition.
Unfortunately (and for obvious reasons), my tooth was not saved. I felt calm in the dentist's chair. It didn't hurt very much. The injection worked well. I left the office and started shaking.
Probably due to an emotional background and due to the difficulty of removal (it was a distant tooth), my temperature jumped sharply in the evening. I was pounding, the fever was intense, about forty degrees. I took antipyretic tablets (2 pieces). I feel a little better. I drank another one at night.
Maybe someone will say a lot, but I felt bad. The next day made my life easier, my temperature was 37ºC. The condition is more or less normal. However, for some reason the removal site ached. On the first day, amid the heat, I didn’t notice it. On the third day I experienced significant relief.
There was no temperature, the pain did not bother me. Thank God, but everything is fine now. I will now try to take more responsible care of my teeth. After all, temperature is not a very serious problem, but it is still a dangerous signal.
Sources used:
- Colgate 32%, 27501 votes27501 votes 32%27501 votes – 32% of all
- Splat 24%, 2073020730 24%20730 – 24% of all
- ROCS 16%, 14293 votes14293 votes 16%14293 votes – 16% of all
- Sensodyne 11%, 96809680 11%9680 – 11% of all
- New pearls 11%, 93009300 11%9300 – 11% of all
- President 6%, 54875487 6%5487 – 6% of all
Laparoscopic surgery
Progress of the operation
Laparoscopy is a more modern method of removing a kidney, requiring a highly qualified doctor.
The patient lies on his back. A bean-shaped cushion is placed under the legs to make it easier for doctors to turn the patient over. The body of the person being operated on is fixed with elastic bandages. As in the previous case, laparoscopic nephrectomy is performed under general anesthesia. A surgical instrument called a trocar is inserted near the navel. It is represented by a tube with a stylet at the end, which is used to pierce tissue. A camera is attached to it, with the help of which the surgeon can control the insertion of the remaining trocars, providing access to the organ from all sides. After all the necessary preparations have been made, the patient is turned on his side, deflating the pillow under his feet. The body is fixed again.
The vessels approaching the kidney and the ureter are clamped with staples of a laparoscopic stapler. They cannot be sutured until the kidney is removed from the body. The damaged organ is removed with the largest trocar, measuring 11 millimeters, after the patient is turned onto his back again. The edges of a plastic bag and a laparoscope are placed in the middle of the instrument, which is used to directly trunce the organ. Next, the trocars are removed from the patient’s peritoneum. The wound and damaged tissues are sutured with self-absorbing thread. The excised kidney is examined histologically.
Possible problems
The hematoma usually goes away on its own some time after surgery.
Laparoscopic nephrectomy is considered a gentle method of kidney removal, so the risk of complications after it does not exceed 16%. The most common problems:
- A hematoma that develops during surgery is a collection of blood of limited size, which will resolve on its own after some time.
- Obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract. Problems with intestinal motility occur due to drugs that relax the muscles or accidental squeezing of the intestine during a nephrectomy.
- Postoperative hernia at the site where the trocar enters most often occurs in overweight people who have had their kidneys removed urgently.
- The development of an inflammatory process in the lungs, unrelated to an infectious infection, is the reaction of the immune system to a surgical procedure.
- Blockage of the pulmonary artery by a blood clot or gas. Occurs if an artery is damaged during surgery.
- Paralysis of the brachial nerve if it was touched by the surgeon. Given the severity of the lesion, the patient may feel a tingling sensation in the arm, and in some cases, be unable to move it.
Return to contents
Causes of pain in the kidney after surgery
Various renal pathologies are very often treated with surgical methods. Surgical intervention is needed when conservative treatment methods do not give the desired result, for example, with inflammatory diseases or urolithiasis. Some problems with this organ can only be eliminated through surgery, for example, benign and malignant tumors. In this case, during the operation, removal of a tumor, calculus, resection of an organ or its complete removal (nephrectomy) can occur. After any operation, the patient may experience pain. In our article we will try to understand the reasons for their occurrence and ways to eliminate them.
Postoperative complications and consequences
High temperature after surgery is observed during inflammatory processes.
The consequences of kidney removal directly depend on the quality of preparation for surgery, the actions of the surgeon during nephrectomy, how successful the operation was, and the presence of additional diseases in the patient. Removal of an organ is associated with the risk of developing nonspecific complications. Most often, such problems are caused by anesthesia and the fact that the patient lay motionless for a long time (kidney removal lasts 2-4 hours). These include:
- congestive pneumonia - secondary inflammation of the lungs, provoked by problems with ventilation or hemodynamic disorders;
- stroke - a violation of blood circulation in the brain;
- infarction - ischemic necrosis of a portion of the myocardium;
- thrombophlebitis - thrombosis that develops against the background of inflammation of the vein wall.
If a person’s fever does not go away for a long time after surgery, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. The consequences of nephrectomy are usually associated with the development of renal failure. The cause of the pathology may be compression of the contralateral vein if the patient had a thrombus consisting of pathological cells in the kidney with a tumor. Since the patient has only one working organ left, he needs to take on the entire load. After some time, normal functioning is restored, but sometimes it is necessary to carry out extrarenal blood purification.
Return to contents
Clinical picture
In 40% of cases, relapses are asymptomatic and are detected only during the next follow-up. The appearance of complaints and clinical signs is considered a poor prognostic criterion.
Local recurrence after partial nephrectomy will behave in the same way as the primary tumor. It may present with pain, hematuria, general and neoplastic signs.
With locoregional growth, there will be no renal symptoms, since the kidney itself has been removed. Clinical signs are possible when the tumor grows into surrounding tissues, generalization of the process (relapse can metastasize in the same way as the primary tumor). Return of the disease is manifested by paraneoplastic symptoms.
In the operated organ.
- Hematuria (the appearance of blood in the urine).
- Pain in the lumbar region or hypochondrium of an aching nature, sometimes like renal colic.
- Unreasonable arterial hypertension.
- Weakness, loss of appetite.
- Increased body temperature.
- Swelling of the legs.
- Varicocele in men.
Locoregional relapse at the site of the removed organ.
- The appearance of back pain due to invasion of the psoas muscle and nerve receptors.
- When it grows into the organs of the pancreaticoduodenal zone, the pain is localized in the abdomen or hypochondrium, simulating pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and the development of jaundice is possible.
- Just like the primary tumor, relapse is associated with the risk of developing thrombosis of the inferior vena cava, which will manifest itself as swelling of the legs, thrombophlebitis, and dilation of the scrotal veins in men.
- Invasion of the spleen is manifested by pain and heaviness in the left half of the abdomen.
- Germination of the intestinal wall can cause blood in the stool or bleeding, causing intestinal obstruction.
- Paraneoplastic syndromes - weakness, fatigue, low-grade fever, weight loss, numbness of the extremities.
Early postoperative period
After removal of the kidney, catheterization of the bladder is performed.
Immediately after surgery to remove a kidney, the person undergoing surgery is placed in the intensive care unit for constant monitoring of the condition. For the first and next few days, the operated patient has a catheter to remove urine. The patient is allowed to drink and eat not immediately, but only after the doctor confirms the presence of intestinal motility. Water is consumed in small quantities, and food is ground.
Among the unpleasant symptoms, pain occurs after removal when taking a deep breath or coughing. It also hurts when moving the body. Despite this, breathing exercises are recommended to speed up recovery and prevent pneumonia. Under the supervision of a doctor, the patient needs to gradually increase physical activity. From the 2-3rd day it is allowed to roll over to one side and stand up. There is no need to make sudden movements so that the seams do not come apart. Physical activity prevents problems with the intestines and blood circulation from developing.
Return to contents
Treatment
Therapy for any inflammatory process that occurs after surgery is prescribed by the doctor. He will also select a pain reliever and an antibacterial drug. To reduce the activity of pathogenic microorganisms and reduce pain, you can drink teas made from anti-inflammatory herbs:
- oak bark;
- chamomile;
- sage;
- rose hips;
- lingonberry, raspberry and mulberry leaves;
- nettle;
- horsetail.
An important role in eliminating discomfort and pain is played by proper nutrition and adherence to the drinking regime prescribed by the doctor. It is necessary to exclude everything salty, spicy, fatty and fried.
Rehabilitation upon returning home
The main rehabilitation after kidney removal begins at home, since the patient is now responsible for his own condition. People with a removed kidney need at least 1.5 years to recover after surgery. Over time, the kidney gets used to the stress and works on a compensatory principle. It is more difficult for older people to recover.
Return to contents
Nutrition rules
During home rehabilitation, you need to adhere to a special diet.
The rehabilitation period for people who now live with one kidney begins with a change in diet. The main condition for selecting dishes is the easy digestibility of the food consumed. The diet includes foods with moderate calorie content and low protein concentration. The daily menu must include:
- bread based on rye flour;
- vegetable and fruit salads;
- cereal porridges and pasta;
- dairy products.
Meat is included in the diet with caution. You can eat no more than 100 g of boiled veal, chicken or rabbit per day. It is allowed to eat low-fat fish and chicken eggs in the form of an omelet. It is forbidden to consume milk in large quantities because of the calcium it contains, which provokes stone formation. It is not recommended to eat legumes, as they increase gas formation in the intestines.
The diet is divided into 5-6 small meals. The amount of water per day is agreed upon with the attending physician, taking into account the consumption of liquid from soups, diluted juices, vegetables and fruits. All dishes are steamed, boiled or baked. The dose of salt per day is 5 g, and bread - no more than 400 g. The diet developed by the doctor must be adhered to in full.
Return to contents
Physical activity
Low physical activity is indicated for those undergoing surgery.
A physically active life with one kidney means little stress on the body for the first 2-3 months. Those undergoing surgery are required to walk for about half an hour in the mornings and evenings. Over time, you can walk up to 3 hours every day. Heavy lifting is excluded. You are allowed to lift no more than 3 kilograms. The back is fixed with a special bandage. Once a week, the kidneys are unloaded - bath procedures are performed.
Return to contents
Prevention of complications and lifestyle precautions
Restoring a normal lifestyle in the postoperative period is associated with maintaining the health of the remaining one kidney. Necessary:
- prevent the development of infection;
- if inflammation occurs in any organ, do not hesitate to start treatment;
- Have your kidney examined regularly.
Life after kidney removal is closely related to being attentive to your own health. Those who have undergone nephrectomy should not overexert themselves and allow the body to become hypothermic. If you have any suspicions or symptoms of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. If before the operation the patient’s work was associated with harmful or toxic production or severe physical activity, the field of activity should be changed.
Return to contents
What are the consequences of removing a kidney with a tumor?
- 4 minutes to read
Kidney cancer is a serious disease, the only effective treatment is to remove the affected organ. According to statistics, this type of oncological pathology is diagnosed in 3% of all cases of malignant tumor. In addition, unlike women, men are most often affected by the disease. The risk of complications will directly depend on the methods of therapeutic measures, the degree of the disease and care in the postoperative period.
Content
Rehabilitation and disability
If the patient has no complications after nephrectomy and the body quickly adapts to the new lifestyle, working capacity is fully restored in 1.5-2 months. Sick leave will be required for this period. But the question often arises whether a person with one kidney becomes disabled. Nephrectomy is not considered as a basis for assigning disability. Disability after kidney removal is determined by the only authority - the medical and social commission. The commission members are authorized to find out how much the remaining kidney is able to compensate for the absence of the second and take into account the presence of concomitant diseases to make a decision.
etopochki.ru
Postoperative complications
After surgery, kidney removal, the consequences depend on the patient’s concomitant diseases, the experience of the specialists and preoperative preparation. In the postoperative period, nonspecific complications mainly occur due to general anesthesia and prolonged immobility.
These include:
- congestive pneumonia,
- pulmonary embolism,
- thrombophlebitis,
- myocardial infarction,
- stroke.
The listed complications are observed quite rarely. To prevent them, proper preoperative preparation of the patient and early activation after surgery are important.
Early postoperative period
1. Physical activity
Immediately after the intervention, the patient should lie on his back and not make sudden movements to avoid complications in the form of sutures slipping off the renal pedicle. By the end of the first day, with the help of medical staff, you can carefully turn onto your side. If there are no complications, you can sit up in bed on the 2-3rd day, and get up on the 4th day. During the early postoperative period, it is necessary to activate the operated patient within reasonable limits:
- breathing exercises,
- limb movements,
- turns to the side.
2. Nutrition after nephrectomy
A few hours after the operation, the patient is allowed to drink some water or rinse his mouth. You can eat food the next day. Sometimes the postoperative period after kidney removal is complicated by intestinal paresis. Sluggish peristalsis may be due to irritation of the peritoneum during surgery and is manifested by bloating, delayed passage of gas and stool. In these cases, a gas tube is used, an enema is given, and drugs are prescribed that enhance intestinal motility.
Causes of pain
Normally, immediately after any surgical procedure, the patient may feel pain. To eliminate it, the patient is prescribed analgesics in the first few days after the operation. Such pain and discomfort immediately after surgery is normal and does not indicate any problems.
The reason for such pain lies in the fact that during the operation not only muscle tissue and blood vessels are cut, but also nerve endings. However, you should be alert to pain that occurs in the area of the operated organ a few days after the operation, when the pain and discomfort from the incision should subside. There may be several reasons for this pain syndrome.
Inflammatory process
If your kidney hurts after surgery, most often the cause lies in inflammation. Although the operation is performed under sterile conditions, the risk of infection still remains. Sometimes the infection does not enter the tissue during surgery, but the chronic infectious process in the patient’s body is activated against the backdrop of a weakening of the defenses.
Causes of pain during inflammation:
- Pyelonephritis. This is the most common cause of pain after kidney surgery. Moreover, according to statistics, pyelonephritis more often affects the right kidney, since physiologically this organ is located lower than the left one and is more mobile.
- The inflammatory process can develop not only in the kidney itself, but also in the ureter - the duct through which urine flows into the bladder. In this case, the pain will be localized a little lower, not under the ribs, but in the central part of the lower back.
Tissue damage
If stones were removed during surgery, damage to organ tissue could occur, which would subsequently cause pain. At the same time, cracks and microcuts appear in the kidney tissues, which give stabbing and aching pain.
Moreover, such damage can occur not only due to the careless actions of the surgeon or the use of low-quality instruments. A person by nature may have very delicate tissues that are easily injured and take a long time to heal. In this case, after the stone removal operation, microcuts and cracks will take a long time to heal, causing pain.
Wrong diet
A fairly common cause of pain in the postoperative period is the patient’s failure to comply with the diet and proper drinking regimen. Excess glucose, protein and minerals can cause organ dysfunction after surgery. As a result, the operated kidney will hurt.
Important: after surgery, you need to adhere to a diet for the first couple of weeks. It is forbidden to immediately return to the usual menu.
Psychological factor
The psychological factor plays a significant role in the appearance of pain syndrome. In this case, the nervous system is influenced at a subconscious level. At the same time, some people have such a strong fear of pain that they begin to feel it for no apparent reason.
In this case, proper psychological preparation of the patient for surgery is of great importance. He needs to be explained that there is no risk and the procedure is completely safe.
Problems with neighboring organs
The operated organ is not always the cause of pain. Often during surgery, neighboring tissues and even organs are damaged, so the inflammatory process can occur in them:
- If the pain is localized in the area of the left kidney, then the cause may lie in damage to the lymph nodes or spleen.
- If the pain is localized on the right, it is worth examining the condition of the small intestine or liver, since they are located not far from the left kidney.
Rehabilitation after nephrectomy
For people who have had a kidney removed, rehabilitation can take about 1-1.5 years. During this period, the remaining kidney begins to perform more work and can fully compensate for the absence of the second kidney. During the adaptation process, the kidney increases in size (hypertrophies), so for a year, those operated on are bothered by a mild dull pain in the area of the remaining kidney. This symptom is not dangerous and disappears on its own over time. After discharge from the hospital, excessive physical activity should be avoided.
Recommended:
- walking in the morning and evening,
- hardening water procedures (wiping with a wet towel, then shower).
It is known that the skin, along with the kidneys, performs an excretory function, so it is necessary to ensure its cleanliness.
Nutrition in the absence of one kidney involves taking easily digestible food. The diet should be sufficiently high in calories. Protein intake should be limited.
The basis of nutrition is:
- dishes from vegetables and fruits,
- Rye bread,
- fermented milk products (in small quantities),
- lean meat and fish (200-300 g per week).
All dishes are steamed, boiled or stewed. Fried, smoked and canned foods are excluded.
You should not sharply limit the amount of liquid and salt, as this can only cause harm. You can drink clean water without gas, fruit juices diluted with water, weak tea, lingonberry and cranberry juice. The exact diet can be drawn up by your doctor or nutritionist.
Rehabilitation after kidney removal includes measures to preserve the second kidney in a healthy state. To do this you need:
- avoid various infections (genitourinary, food, respiratory);
- timely treat chronic and acute inflammatory diseases (tonsillitis, otitis, caries, sinusitis, sore throat, etc.);
- avoid hypothermia,
- regularly visit a urologist to assess the functional state of the second kidney.
Important: if you get sick, do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor. Untreated infectious diseases can cause pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis of the second kidney and lead to loss of its function.
Life after kidney removal is not much different from the life of other people. With adequate physical activity, good nutrition and proper work and rest schedule, the life expectancy of people with one kidney is almost the same as that of healthy people. Many young women with one kidney can give birth to a child, although this issue is decided individually in each case.
How much does a kidney transplant cost?
Millions of people are diagnosed with acute chronic renal failure, which practically signs the patient's death warrant. A kidney that has been reduced several times in size and is not able to function fully must be replaced as soon as possible with an artificial organ or an organ transplanted from a living donor.
However, if an artificial kidney helps to survive by tying a person to a hemodialysis machine, then organ transplantation will not only extend the patient’s life by 15-20 years, but will also provide the opportunity to lead an almost full life. True, a happy and long life will cost at least $20,000.
Briefly about the operation
Transplantation procedures increase a person’s life expectancy, improve its quality, while simultaneously relieving the patient of concomitant diseases.
A kidney transplant is a lengthy process and begins with a doctor diagnosing “acute renal failure” and deciding on the need for surgery. The patient is immediately examined for contraindications to transplantation: malignant cancers, tuberculosis, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), cardiovascular failure, post-infarction condition, coronary artery disease and other diseases in the thermal stage.
After “admission” to the operation and the appearance of a kidney suitable for weight, age and other parameters, the donor material is implanted into the patient’s body, connecting the corresponding vessels. The old organ remains in its previous position, and the new one is placed in an uncharacteristic place in the iliac fossa in the pelvic area.
The peculiarity of the ongoing operation is that both the donor and the patient undergo surgical intervention at the same time, for which two teams of transplantologists are involved.
If the outcome is successful, the full functioning of the new organ in the patient is established within 7-10 days, and the donor is discharged on the second day.
Competent rehabilitation prevents rejection of the transplanted kidney and stimulates the body's adaptation to the new organ. Therapy is aimed at taking immunosuppressants, activating the circulatory system and eliminating the risk of blood clots.
Who can become a donor
The wait for a suitable kidney can last for many years, because in the absence of a living donor, organs are removed from those who die from brain death, and only from those who made the appropriate decision during their lifetime or, if a similar choice was made by relatives after his death.
Ideally, the donor and the patient should have the same age, weight, blood type, Rh factor and histocompatibility as much as possible, so it is advisable for a living donor to be a relative: parents, children, grandparents, grandchildren, brothers and sisters aged 18 to 60 years. Among other things, a related kidney has a number of advantages:
- There is no need to wait for an organ;
- Possibility of urgent surgery;
- The planned nature of the operation, strictly scheduled time;
- High organ compatibility;
- Better survival rate and minimal risk of rejection.
Removal of a kidney is possible only with voluntary consent and free of charge.
Risks and complications
Even a brilliantly performed operation can ultimately lead to complications and rejection of the transplanted organ. A failed kidney transplant is signaled by alarming symptoms:
- Acute pain in the lumbar region;
- Heat;
- Hematuria is the presence of blood in urine;
- Problems with urination.
These signs indicate adverse consequences: bleeding, separation of sutured vessels, infections, blockage of veins or arteries.
To promptly identify symptoms of poor kidney function, the patient is regularly examined at a medical facility, undergoes an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, and undergoes the necessary tests.
However, the donor also risks his health, because the operation is technically very complex and unpredictable, and life with one kidney is risky, incomplete and shortened by 15-20 years. It is very rare, but it happens that during surgery a neighboring kidney is damaged, which leads to the donor being moved to the category of those in need of an organ transplant.
It is also worth considering that the body fully recovers after the operation after 2 months, and for 3 months after kidney removal it is recommended to be under constant supervision and monitoring by doctors.
Where and how long does it take to get a kidney transplant?
Kidney transplantation operations are carried out both in Russia and abroad. Moreover, every citizen of the Russian Federation can count on a free transplant in a budget institution, and all medical expenses amount to about 1 million rubles. are paid from the state treasury. True, not everyone waits their turn.
In private clinics you don’t have to wait for months or years, but you will have to pay for all the amenities, especially since the price depends on a number of conditions:
- Urgency of the operation;
- Patient's health status;
- Availability of a suitable donor;
- Fame and qualifications of the surgeon;
- Conditions of stay in the clinic;
On average, the cost of an operation in a Russian private institution ranges from $30,000 to $120,000.
Transplantation will cost more in the United States and Germany, where the price for the operation starts at $150,000, but the mortality rate is much lower. The price tag is lower in Pakistani and Indian clinics, where the cost of the procedure does not exceed $30,000.
How much does a kidney cost?
In almost all countries of the world, the sale and purchase of donor organs is prohibited by criminal penalties at the state level. However, people often break the law in order to correct a difficult financial situation. Thus, a kidney donor in Russia can receive from $3,000 to $20,000, while the price depends on the health of the seller, urgency, rarity of the blood type, the number of intermediaries and the financial capabilities of the customer.
Also, the answers to the question “how much does a kidney transplant cost” vary in different localities: in the center of Russia, Moscow, a potential donor will hear a price of $30,000-40,000, and in the provinces they will have to sell a kidney for the same amount, but only in rubles.
In some countries, the kidney trade has turned into a whole business, with special “donor farms” being created in Pakistan and India, where physically healthy patients are kept in comfort so that, if necessary, they can sell the kidney to a rich buyer.
Iranian transplant model
Iran is one of the few countries where it is legal to engage in donor business. The decision of the authorities to promote the development of transplantation arose after the complication of the hemodialysis procedure and the increase in the number of people in need of a kidney transplant. The end result of a number of events and bills was the creation of a special Fund, financed jointly by the state and citizens of the country.
Donor services are paid for by a third of the total cost of donation and amount to about $2,500. Foreign citizens cannot act as either buyers or sellers.
A kidney transplant becomes a real salvation for a person whose one of the kidneys does not function, and the hope for a full, healthy and long life. The price of an operation for future happiness is measured in tens of thousands of dollars from private surgeons or constantly sitting by the phone waiting for a call from a public clinic.
Work ability after kidney removal
In the absence of complications and good adaptation of the body, working capacity is restored 1.5-2 months after nephrectomy.
Advice: if your profession involves heavy physical labor or constant intoxication, then you should change your place of work. Don't forget about additional good rest.
Many people are concerned about the question of whether kidney removal will result in disability after surgery. Nephrectomy in itself is not grounds for recognizing a person as disabled. The issue of ability to work is decided by a medical and social commission. The decision depends on the compensatory capabilities of the remaining kidney and concomitant diseases.
lechim-pochki.ru
Information for patients undergoing kidney removal (radical nephrectomy)
What is a kidney?
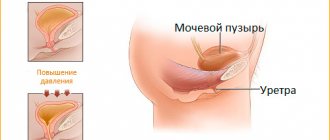
The kidney is an organ that plays the role of a “filter” that helps cleanse the blood of various metabolic products (“waste” from the body). Typically, each person has two kidneys, located retroperitoneally below the diaphragm to the right and left of the spine. The kidneys produce urine, which then travels through the ureters to the bladder, where it is stored between urinations. For normal functioning of the body, the function of a single kidney is sufficient.
What is radical nephrectomy?
The operation proposed to you is to remove the kidney in which a tumor is found. The doctor will explain to you why it is impossible to save at least part of the kidney. The type of tumor (benign or malignant) will be finally determined after surgery by microscopic examination. The operation is necessary because, if left untreated, the existing tumor may begin to manifest itself with pain, the appearance of blood in the urine, and fever. If the tumor is malignant, then only surgical treatment will avoid progression of the disease.
Are there other treatments?
Only the operation offered to you allows us to simultaneously establish a final diagnosis, carry out treatment and determine the nature of further monitoring of you.
How to prepare for surgery to remove a kidney?
To perform the operation, you will have to spend 2-3 weeks in a urological hospital. Before surgery, all patients must undergo blood tests (including for syphilis, HIV and hepatitis) and urine, electrocardiography (ECG), and chest x-ray. Special examination methods include ultrasound examination of the urinary system, computed tomography of the kidneys, etc. Patients are also examined by a therapist and an anesthesiologist, who determines the type of anesthesia (in most cases, general anesthesia). The evening before the operation, a cleansing enema is performed and the hair on the anterior abdominal wall is shaved. From 0 o'clock on the day on which the operation is scheduled, you are not allowed to eat or drink. On the morning of the day of surgical treatment, antibacterial therapy begins (intramuscular or intravenous antibiotics).
How is kidney removal surgery performed?
The incision can be located in the hypochondrium or in the lumbar region on the corresponding side. The choice of surgical approach depends on the size and location of the tumor, your general condition and concomitant diseases, as well as the preferences of the operating urologist. The length of the skin incision is about 20 cm. During the operation, not only the kidney is removed, but also the perinephric fat along with the lymph nodes, and, if necessary, the adrenal gland. At the end of the operation, one or more drainage tubes are installed to the bed of the removed kidney: their presence makes it possible to assess the course of the postoperative period. A bandage is applied to the skin. To control the amount of urine excreted by the remaining kidney, a catheter (a hollow latex or silicone tube through which urine flows into a urinal bag) is installed into the bladder through the urethra.
How does the postoperative period proceed?
Almost always, after surgery to remove a kidney, the patient spends one day in the intensive care unit, from where, if the course is favorable, the next day he returns to the urology department. If you have pain in the area of the postoperative wound, you will be regularly administered painkillers, including narcotics. 1.5-2 hours after the operation, in the absence of nausea and vomiting, you can rinse your mouth and take a few sips of water (drink in small portions; until the evening you are allowed to drink about 500 ml of still water). You can usually resume eating the next day: meat broth, boiled meat, low-fat cottage cheese or yogurt are allowed. The food ration is usually expanded after independent bowel movements (if there is no bowel movement, a cleansing enema is performed on the third day). For 7-10 days after surgery, avoid eating salty, fried, smoked foods, try to drink at least 2000-3000 ml of liquid per day (water, tea, fruit drink, juice, etc.). In any case, it is better to check your diet and fluid intake with your attending physician: it is possible that, due to any concomitant diseases you have or features of the operation, the doctor will give recommendations that differ from the above. The next day after the operation, you can get up and walk around the room, and the next day - along the corridor. Be careful when you get up for the first time: after spending a day in a horizontal position, your vision may darken and your head will spin. The catheter is removed from the bladder 1-2 days after surgery. The timing of removal of the safety drainage tubes is determined by the attending physician. You will undergo regular dressing changes until the stitches or staples are removed from the postoperative wound (usually on days 7-12). Antibacterial therapy lasts 10-15 days. A conclusion from a morphologist on the results of a microscopic examination of the tissue removed during surgery can be expected in 5-7 days. You can find out the histological conclusion and final diagnosis from your attending physician.
How to behave at home?
Avoid sports and strenuous physical activity for 3 months after surgery; the first month - wear a bandage. Try not to lift heavy objects (more than 3 kg). Try not to get too cold and drink alcohol. You can walk as much as you want and be in the fresh air. As a rule, 7-10 days after discharge from the hospital, if you feel well, you can resume work (if it does not involve physical labor). You can be sexually active after 4-6 weeks.
What are the possible risks and complications of the surgery?
Any operation, as well as anesthesia, is always associated with a certain risk of complications, including life-threatening ones, associated not only with your disease, but also with the individual characteristics and reactions of the body, which are not always possible to foresee. The anesthesiologist will explain the possible risks of anesthesia to you. Complications of your disease and surgery include:
During surgery: • Damage to neighboring organs (spleen, intestines, pancreas, pleura), which may require their removal, resection (partial removal) or suturing of defects; • Damage to blood vessels (arteries and veins) and bleeding, necessitating the need for blood transfusions or blood substitutes.
In the immediate postoperative period: • Bleeding, which may require reoperation; • Thromboembolism; • Infectious complications, including purulent-inflammatory process in the area of the postoperative wound; • Formation of acute ulcers of the stomach and (or) duodenum, bleeding from the veins of the esophagus; • Impaired intestinal evacuation function, up to intestinal obstruction.
After a few months or years: • As with any open operation – the formation of a deformity (hernia) of the abdominal wall or lumbar region; • Formation of abdominal adhesions; • Recurrence of kidney tumor.
Do I need to see a urologist after surgery?
The purpose of monitoring by a urologist after kidney removal surgery is to assess the function of the only remaining kidney and monitor for recurrence of the disease in case of malignant kidney disease. In most cases, after surgery to remove a kidney, after 6 months you should contact a urologist for a follow-up examination, which usually includes, in addition to a conversation with you, a computed tomography scan of the retroperitoneum. In the future, computed tomography is performed once a year. In addition, you will have to have a biochemical blood test and a chest x-ray every year. In any case, it is advisable to check the timing of control examinations with your doctor.
If after reading the above information you still have questions, please contact your doctor.
If you need advice, please call +7 or at the address indicated on the contacts page.
www.urocon.ru
Source: pochki5.ru
Possible consequences
The risk of potential complications after removal of a diseased kidney always exists, but it is small - only 3-10%. Much, if not everything, depends on the qualifications of the surgeon, his experience, and assistants. Consequences are rare, but they can occur both after abdominal surgery and after laparoscopic intervention.
Open nephrectomy can provoke:
- respiratory failure;
- bleeding, sepsis;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- intestinal obstruction;
- heart failure;
- injury to the pancreas, spleen;
- thrombus formation.
When one kidney is removed using a laparoscope, the following consequences are possible:
- hernias that form at the trocar entry site;
- blockage of arteries in the lungs;
- pneumonia;
- damage to nerve endings.
Removing a diseased kidney affected by cancer provokes its relapse. This consequence is being combated with new targeted drugs that target certain proteins of the cancer cell.
The only effective treatment for a malignant tumor in the kidney is its surgical removal. The operation is performed at the first, second and third stages of the disease. In the future, it turns out to be useless, since metastases form in nearby organs.
If kidney cancer is diagnosed, the prognosis after removal is of primary concern to patients. Therefore, it is important to understand the characteristics of this disease and the rules of behavior after surgical treatment.
A malignant kidney tumor can appear at any age, but it is more often diagnosed in people over 40 years of age. The problem mainly affects men. Experts cannot say for sure what the reasons for the development of such a problem are. There are only a few provoking factors:
- Overweight.
- Alcohol abuse. According to statistics, beer often provokes illness.
- Regular smoking.
- Long-term uncontrolled use of diuretics.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Diabetes.
- Kidney injury.
- Hereditary predisposition.
A tumor can be detected by palpation only in the late stages of its development. A person lives for a long time without knowing about his illness.
It is possible to make a diagnosis after carrying out diagnostic measures: ultrasound, CT, MRI and others. You should suspect a problem if blood appears in the urine. It is very viscous and gathers into large clumps.
It happens that such a lump blocks the ureter. In this case, the person feels a sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
Kidney removal
Kidney resection for cancer is becoming the most effective treatment method. The tumor must be removed along with the entire affected organ or part of it.
This treatment is used at stages 1, 2 and 3 of cancer, in the presence of Wilms tumor or transitional cell carcinoma. They operate after undergoing a full examination.
The specialist must accurately determine the location of the tumor and develop a surgical intervention program.
The oncologist makes the decision to have surgery based on the results of the examination. If the patient doubts the correctness of the diagnosis, several specialists can be consulted.
It is important to remember that the earlier the fight against cancer is started, the greater the chances of a successful outcome. Each patient has the right to decide for himself who exactly will operate, and where it is best to do it.
Kidney removal is successfully performed by both Russian and foreign specialists.
Unforeseen situations may occur during the operation. The body's response to anesthesia is in most cases unpredictable.
Sometimes, when excision of affected tissues, large vessels are damaged, which leads to serious complications. During the postoperative period, the patient may experience spontaneous bleeding.
Other dangers of such treatment include: pneumothorax, wound infection, and the development of hernias.
If a tumor is found in only one kidney, then the organ is completely removed. In case of bilateral damage, resection of the neoplasm itself and nearby tissues is limited.
The prognosis after surgery for a malignant neoplasm directly depends on the timeliness of diagnosis. Oncology detected at an early stage requires urgent treatment. Chromophobe cancer responds well to therapy. It rarely metastasizes, and therefore removal of the tumor leads to a complete cure.
At stage 1, the tumor size is minimal. It does not exceed 2.5 cm in diameter. The neoplasm does not spread beyond the borders of the kidney. It cannot be felt upon palpation. There are no characteristic symptoms at all, which makes diagnosis much more difficult. More often, the disease is discovered accidentally during a routine examination.
Complete removal of a kidney for cancer at an early stage is carried out only in exceptional cases. More often, doctors limit themselves to resection of the tumor itself. The surgical program is developed individually for each patient. Other treatment methods, such as chemotherapy or radiation, are not used because they do not have the desired therapeutic effect in this situation.
Upon completion of therapy and rehabilitation, a person can return to a full life.
Adverse effects of cancer treatment are observed in people suffering from diabetes, heart disease and hypertension.
At the second stage, the size of the tumor may exceed 7 cm, but the tumor does not extend beyond the kidney. In this case, a characteristic triad of symptoms appears:
- The appearance of blood in urine.
- Pain in the area of the affected organ.
- When palpating the kidney, you can feel the lump.
There is a general deterioration in health. Performance decreases sharply, body temperature rises to 38 degrees. A person constantly feels overwhelmed and tired.
Life expectancy is high. More than 74% of all patients live longer than five years after therapy. Cancer rarely metastasizes. The lymphatic system is not affected. The absence of concomitant diseases improves the prognosis.
Stage 3 kidney cancer is characterized by a large tumor size. The tumor spreads to large veins without affecting the adrenal glands. It remains within the fascial sheets. In 25% of cases, metastases appear, which significantly worsens the survival prognosis.
Only 50% of all patients live more than five years after kidney removal. In addition to surgery, chemotherapy is performed. This allows you to eliminate the remaining cancer cells and prolong a person’s life.
Cancer therapy at stage 3 cannot give a 100% result, since cancer can metastasize. In this case, the lungs, liver, and bone marrow are affected.
The fourth stage of cancer is considered the most severe, and it is impossible to completely defeat it. Statistics say that the number of surviving patients does not exceed 5%. However, they live no more than 5 years after a course of therapy.
Surgeries to completely remove a kidney with a tumor do not allow one to cope with the disease, since a large number of metastases are formed. The oncological process spreads throughout the body.
The digestive organs, lungs, and bone marrow are affected.
For stage 4 kidney cancer, surgery is aimed at prolonging the patient's life. Maintenance therapy is required. Chemistry helps improve the prognosis. Interferon and interleukin preparations are also used.
How long people live after surgery, and what the consequences will be, depends on the characteristics of the body and compliance with all rehabilitation rules. The following factors can worsen the prognosis:
- Presence of chronic diseases.
- Reduction of body weight by more than 10%.
- Diagnosis too late. The third stage of cancer is much more difficult to treat than the first.
- Increased blood ESR. High values of erythrocyte sedimentation rate worsen the results of surgery.
It is difficult to completely cope with malignant tumors. In 30% of cases, a relapse is observed, and the tumor appears again. To improve your prognosis, you need to constantly monitor your health. People who have had cancer should be observed not only by an oncologist, but also by an endocrinologist, urologist, psychotherapist and other specialists.
Proper patient care helps improve the prognosis after surgery to remove a tumor on the kidney. Rehabilitation turns out to be lengthy and requires strict adherence to all specialist recommendations. At first, a person will not be able to cope without the help of strangers. The help of loved ones is extremely important to him. During the recovery period it is necessary:
- Follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle.
- Strengthen the immune system. To do this, it is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air, avoid stress, mental and psychological stress.
- Avoid contact with people suffering from infectious or viral diseases.
- As the person recovers, it is recommended to increase physical activity. Physical therapy, long walks, and breathing exercises are indicated.
- Spa treatment is indicated. Effective health programs are offered in Russia, Kazakhstan and other countries.
How long patients who have undergone surgery to remove kidney cancer live will also depend on the correctness of the rehabilitation period. To avoid psychological problems, you should not leave a person alone.
Proper nutrition
Kidney cancer is a disease that negatively affects the condition of all organs and systems of the body. To reduce negative health consequences after a patient has had a tumor removed, it is necessary to maintain a proper diet. The menu is compiled in accordance with the following recommendations:
- Eating can be started on the second day after kidney resection. The best option would be light chicken broth or liquid vegetable puree.
- A complete rejection of excessively salty, fatty and fried foods, smoked meats, canned food, as well as semi-finished products, which are very common today, is required.
- Mushrooms, cheeses, sausages, legumes, and confectionery products should not be included in the diet.
- It is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol, strong coffee, or carbonated drinks.
- The list of permitted foods includes: boiled lean meat, dairy products, cereals, vegetables, herbs and fruits.
- If there are no direct contraindications, then you should drink at least 2.5 liters of clean water per day. You can also use dried fruit compotes, rosehip infusion, and unsweetened fruit drinks.
- It is important to consume enough vitamins and minerals. If it is not possible to obtain the daily dose of these substances from food, it is necessary to take specialized medications.