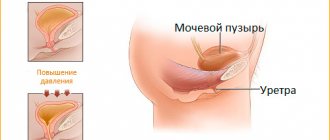
TUR of the prostate or transurethral resection is an endoscopic, least traumatic surgical operation used to remove prostate adenoma through the urethra. The purpose of TUR of the prostate is to restore adequate urination, while not the entire prostate is removed, but only the enlarged adenomatous tissue (prostate adenoma) compressing the urethra.
The advantage of TUR of the prostate over open adenomectomy is the absence of external incisions and, as a result, shorter recovery times for the patient and the ability to quickly return to normal life.
TUR of the prostate requires the surgeon to have specialized endoscopy skills and special equipment.
TUR of the prostate is the “gold standard” in the surgical treatment of prostate adenoma.
Indications for surgery
Outpatient treatment is carried out until the size of the prostate reaches 50 cm³. A third of patients note improvement from this method of treatment; surgery is not required for them. Otherwise, the size of the tumor continues to increase, and the man’s health deteriorates. It is worth thinking about surgery if there is no positive dynamics of recovery with drug restoration of the body, but on the contrary, indications for prostate cancer become clear:
- bladder pain;
- heaviness in the perineal area;
- constant urge to urinate;
- blood in urine;
- kidney diseases;
- cystitis;
- stones in the urethra.
Operation TUR in urology
A surgical method is used to remove part or all of an organ. Transurethral resection can be performed to eliminate lesions of the urinary system of varying severity caused by the proliferation of prostate tissue. During TURP of the prostate, the risk of complications is minimal.
A minimally invasive method of eliminating tumors allows you to remove the tumor layer by layer, preserving the surrounding tissues and organs. With innovative medical intervention, there is no bleeding and no need for a surgical incision, since the operation is performed through a perineal approach.
Types of iron operations
The operating method depends on the degree of prostate damage. If there are stones in the urinary system, large tumors, open surgery is used. Smaller tumors are removed using TUR. The following treatment methods are distinguished.
- Open surgery is the only alternative and effective way to remove a benign tumor. It belongs to the category of abdominal ones - the bladder is opened under general anesthesia. The main advantage is complete cutting off of the tumor, but the disadvantage is the likelihood of hemorrhage and blocking of the hole in the bladder along the outflow of urine by a blood clot.
- Prostate laparoscopy involves making small incisions in the abdomen using a resectoscope. With this low-traumatic method, prostate tissue or gland can be completely removed. Postoperative rehabilitation is significantly reduced.
- Prostate tour is used for small tumors, is easily tolerated by patients and has a short hospitalization period for the patient. However, the consequences of prostate tour are unpredictable, with possible complications.
Unfavorable development of events
Despite the fact that most often the operation for resection of the prostate gland goes well and the postoperative period does not have any complications, about 10% of patients still face some difficulties in rehabilitation after tumor removal. Thus, some men may experience an exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis; in approximately 30% of patients, azotemia occurs after surgery due to BPH. Infection of the bladder is also possible, which entails unpleasant consequences in the form of urinary incontinence and other problems with urination in the postoperative period, and the patient’s temperature rises. Other complications are also possible.
- Bleeding.
In terms of the severity of complications after transurethral resection of the prostate, massive bleeding after surgery is the most dangerous case. Sometimes bleeding after a TURP of the prostate can be so severe that a blood transfusion is required. These complications are a consequence of damage to large vessels that are invisible to the surgeon through the gland tissue. Bleeding can also be caused by a thrombus that has separated from a coagulated vessel. These complications are treated conservatively with hemostatic drugs. Sometimes surgery is required to rinse the bladder cavity to clear it of blood clots. If the bleeding does not stop, cauterization of the vessel is required.
- Water intoxication syndrome.
The postoperative period after TUR for adenoma can be accompanied by such a rare but unpleasant complication as TUR syndrome, when, after washing the bladder during surgery, water enters the vascular bed through the lumen of the vessels. This consequence is also called water intoxication syndrome and occurs in approximately 1% of patients. Symptoms of TUR syndrome are nausea, vomiting, some confusion, tachycardia, the patient’s blood pressure constantly fluctuates, and the temperature may rise. If the patient is not treated promptly, the syndrome can lead to kidney failure and shock. To relieve the syndrome, it is necessary to normalize the water and electrolyte balance in the body; for this, diuretics (furosemide) are prescribed or Lasix is added to a dropper with saline solutions.
- Infection and inflammation.
Despite all the antiseptic measures used during TUR of the prostate for adenoma and in the postoperative period, approximately a fifth of patients may experience infectious and inflammatory complications after surgery. The consequences can manifest themselves in the form of prostatitis, acute pyelonephritis, cystitis, acute inflammation of the testicles and appendages (orchiepididymitis) and others. The patient's temperature rises. Inflammation can be caused both by the patient’s own microflora, the activation of which was facilitated by surgical intervention, and by an infection that entered the body from the outside during the operation. Such complications are usually treated with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs, but surgical measures such as urinary diversion or opening of purulent formations may also be required.
- Dysuria.
The majority of patients who have undergone TUR for prostate adenoma continue to have dysuria for about six months after the operation, which is difficult to respond to conservative treatment. From the point of view of urologists, these complications are most often a consequence of incorrect surgical tactics, since dysuria is most often caused by remnants of prostatic hyperplasia tissue, which disrupt the normal outflow of urine. Sometimes, to eliminate the consequences, the TUR operation is repeated.
- Impotence.
There is no reliable data in the scientific literature on the relationship between TUR surgery for prostate adenoma and subsequent impotence, however, these complications are observed in a small percentage of men. From the point of view of doctors, this complication is most often caused by the psycho-emotional state of the patient, as well as some hormonal changes in the postoperative period. A serious factor in the occurrence of impotence is the patient's age. Also, impotence is more often observed in patients who have undergone several operations other than TUR for BPH.
- Narrowing of the urethra.
Urethral stricture is a stable complication after resection of the prostate for adenoma, which, along with sclerosis of the bladder neck, is observed on average in 2-10% of patients. These complications are most often caused by mechanical injuries during surgery, as well as incomplete removal of pathological tissue. The cost of such a medical error can be high. Treatment can be carried out with anti-inflammatory drugs, and if they are insufficiently effective, repeated endoscopic surgery is recommended.
- Problems with urination.
Urinary incontinence occurs in approximately 2% of patients after TUR for prostate adenoma. Most often, the cause of its occurrence is injury to the external sphincter of the bladder, but sometimes these symptoms can also appear due to neurogenic disorders. Treatment of this disorder is carried out both with medications that affect muscle tone, and with acupuncture and other physiotherapeutic procedures.
Preparatory stage
Surgery requires a preliminary examination of the patient. General blood and urine tests are taken. A coagulogram is required, which will show the percentage of blood clotting. This examination will help assess the likelihood of bleeding during surgery. In addition to these tests, an ultrasound examination is performed to determine the size of the adenoma. A urodynamic test will show the volume of residual urine. Doctors advise patients to stop smoking, as nicotine affects the full recovery after a prostate cancer. The patient undergoes a consultation with a doctor about the presence of allergic reactions and chronic diseases, then a decision is made on the method of treatment.
Consequences and possible complications
In some cases, postoperative complications may occur in the form of:
- difficulty urinating (pain may bother you in the first days after resection, but this phenomenon goes away after 3-5 days);
- urinary incontinence with weakened muscle tone;
- discomfort when urinating (when the condition lasts for several days and does not go away, a technical error was made by the surgeon);
- retrograde ejaculation, in which sperm does not come out, but enters the bladder, a condition in which there is a need to repeat the procedure.
Due to surgical treatment of the prostate, the patient may experience impaired sexual function, for the treatment of which phosphodiestrase type 5 inhibitors are used.
How is a prostate tour performed?
Before surgery, the man must empty his bladder. The anesthesiologist administers anesthesia and observes its effect on the patient's body. On the operating table, the patient's lower limbs are placed on footrests. The operation is performed in the following sequence:
- when the anesthesia has taken effect, the surgeon inserts an endoscope into the urethra through the urinary canal;
- an instrument is brought to the gland to remove the tumor;
- they remove tissues that obstruct the outflow of urine;
- the prostate gland is constantly irrigated with a special liquid;
- After the procedure, the endoscope is removed;
- In order to prevent stagnation of urine during the postoperative period of the prostate, a urinary catheter is used.
Favorable scenario
In 90% of men, the postoperative period after TUR for prostate adenoma proceeds without any complications; this operation has good reviews from patients. After the catheter is removed from the bladder, which usually occurs 2-4 days after surgery, the patient can urinate on his own and is discharged from the hospital. Before discharge, doctors warn the patient that for some period of time after a TUR with prostate adenoma, he will continue to experience certain negative sensations, such as frequent and painful urination. But these symptoms, from the point of view of surgeons, are not associated with the prostate itself, but are the consequences of instrumental influence on it. There is a wound in the surgical area that causes severe postoperative discomfort. Unpleasant consequences of transurethral resection are also caused by the presence of a catheter in the urethra for quite a long time. These sensations, including urinary incontinence, pass fairly quickly. To speed up the rehabilitation process, physiotherapeutic treatment using acupuncture is used. But it is worth keeping in mind that any operation, including transurethral resection of prostate adenoma, is stressful for the male body, since it causes changes in microcirculation in the kidneys. In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed a number of drugs to prevent the onset of inflammatory processes in the prostate from the point of view of general provisions:
- Antibiotics.
- Alpha adrenergic blockers.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
Certain restrictions must be observed for at least a month after TUR for prostate adenoma, since stress can cause consequences such as bleeding from the surgical wound and urinary incontinence. Normal urination in patients is usually restored within two months.
Almost all men experience retrograde ejaculation after surgery, i.e., during sexual intercourse, sperm enters the bladder and does not come out. From the point of view of urology, this is the result of a TUR for prostate adenoma, but is not considered a complication. Treatment of retrograde ejaculation is carried out using acupuncture and electrical stimulation, and in some cases urethroplasty is used.
During a TUR for prostate adenoma, only the prostate tumor is removed, and the prostate gland itself remains and continues to function normally, so even if the operation was successful, the patient is recommended to undergo regular examinations for standard prostate diseases. It is necessary periodically:
- Undergo a rectal examination of the prostate.
- Get tested for PSA.
- Do an ultrasound.
In some cases, it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the prostate gland; for this, points for taking tissue samples are selected under ultrasound guidance and a histological examination is performed. The cost of the operation varies depending on the region, the range starts from 20,000 rubles.
Recovery
After prostate surgery, water is allowed to be drunk in small portions. In the evening, you should eat a light meal; eating before that is prohibited. You should remember about the diet after a prostate tour. You can only get out of bed the next day. Catheters are removed after two to three days. While damaged tissues are healing, blood enters the urine after a prostate tour; this is an acceptable consequence. To ensure that rehabilitation after a prostate tour occurs as quickly as possible, you should:
- drink liquid;
- give up alcohol and coffee;
- monitor bowel movements and avoid constipation;
- exclude physical activity;
- perform kegel exercises after a tour of prostate adenoma.
Contraindications to TUR of prostate adenoma.
Taking into account the extensive experience of such operations, from a urological point of view, a contraindication to performing TUR of prostate adenoma can only be technical issues, for example, the inability to place the patient on a gynecological chair (this is the operating position required by the TUR of prostate adenoma technique) due to severe arthrosis of the hip joints , prostate volume more than 110 cm.
Contraindications to TUR of prostate adenoma (any operation), for which anesthesiologists will refuse surgery, can actually be from:
-cardiovascular system (thrombosis of the veins of the neck, legs, severe heart failure, multiple heart attacks in history, etc.),
-respiratory system (pneumonia, severe respiratory failure, etc.),
— nervous system (stroke, epilepsy, etc.),
- musculoskeletal system (coxarthrosis of the hip joints, severe osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, etc.),
-blood clotting disorders (coagulopathies of various origins),
-infectious or inflammatory diseases (influenza, ARVI, etc.),
- gastrointestinal diseases (acute gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer).
Therefore, before the TUR operation for prostate adenoma, all our patients undergo examination and consultation with related specialists.
Possible complications
Complications depend not only on the experience and skills of the surgeon, but also on the patient’s compliance with the recommended advice. In the early stages of recovery, urination problems and blood in the urine may occur for more than two weeks. Although unlikely, urinary tract infection and prostate inflammation may occur. Late complications after prostate adenoma are much more dangerous. They arise from a narrowing of the urethra. Some patients require repeat surgery.
At the slightest symptoms and pain, you should seek help to protect yourself from deterioration and the development of pathologies. The cost of a prostate surgery tour is the price of health, on which it is unacceptable to save.
| Code | Our prices | Price |
| 03.67 | Transurethral resection of the prostate | 100,000 rub. |
Recovery after surgery
Recovery is an important stage that occurs after removal of prostate hyperplasia. Hospitalization lasts about a week. In the hospital, the man is flushed with a urinary catheter, which is inserted before resection and removed 3 days after surgery. For 2 days the patient is in a supine position. To prevent inflammatory processes from occurring, the specialist prescribes antibiotics.
Subsequent rehabilitation takes place at home for 1-2 months. This period is difficult, because there is no doctor nearby to monitor the recovery. At this time, the man faces difficulties, which include dietary nutrition. The patient will need to reduce portion sizes and consume only approved products. Among the prohibited products:
- salty food;
- sour and spicy dishes;
- smoked meats;
- alcohol;
- diuretic drinks.
During recovery, it is necessary to take medications prescribed by the doctor, reduce physical activity, avoid playing sports and lifting heavy objects, drink enough fluids in the morning and afternoon, and also avoid sexual activity until complete recovery. After removing the catheter, you need to monitor the quality of your urine.
For about 2 weeks, a man may be bothered by a burning sensation in the urethra, a strong urge to empty the bladder, and fractional urine output.
If the discomfort does not go away for more than 14 days, it is recommended to consult a specialist. In this case, blood clots in urine may appear for 3 weeks after surgery. Transurethral resection of prostate adenoma, which may result in urinary incontinence, has a positive prognosis in most cases if the doctor’s advice is followed.
Kegel exercises are used to combat urine incontinence. To perform the first exercise, you need to tense and relax your pelvic floor muscles. The procedure is allowed to be carried out several times a day, 10 repetitions. To perform the second exercise, you must repeat the same steps as in the first case, but the tension must be maintained for 5 seconds. A positive effect is observed after several sessions.
FAQ
What is the postoperative period?
— Upon completion of the operation, observation by a doctor in a hospital setting is required for 1-3 days. The rehabilitation period at home is from 2 to 3 weeks.
When should you avoid surgery?
— The operation is not performed in cases where, for certain reasons, the patient has difficulty abducting the lower limbs. This usually occurs due to damage and immobility of the hip joints due to the tuberculosis process, arthritis and the consequences of previous injuries. Inflammatory processes of the urinary tract in acute form. In such cases, operations are indicated only after the exacerbation has been eliminated.
Ask a Question
Indications and contraindications
Indications for TUR are prostate diseases. In addition, the doctor prescribes surgery if:
- frequent urination with painful sensations;
- urinary incontinence and frequent urge to micturate at night;
- the formation of excess cavities leading to sagging of the organ;
- problems with urination (urine does not come out in full, part of it remains in the bladder);
- carcinoma at an early stage.
TUR is also performed for pathological changes in the bladder, when the outflow of urine is disrupted.
Surgical intervention should be abandoned when the patient has poor blood clotting, exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the body, heart disease and vascular pathologies.
A TOUR of the prostate gland is not performed if the patient suffers from:
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- carcinoma in an advanced form, when nearby organs or most of the prostate are affected;
- renal and heart failure;
- aortic aneurysm;
- varicose veins on the scrotum;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- immobility of the hip joint due to tissue fusion.
Reviews from doctors about TOUR
Experts call TUR the most effective surgical operation among those with a similar goal. After all, suprapubic and laparoscopic approaches have a more negative impact on men's health.
According to doctors, it is preferable to carry out a TOUR in the following cases:
- if it is necessary to preserve sexual function;
- with prostate size less than 80 cm3;
- in the presence of parallel diseases of the urinary tract, problems in the functioning of the endocrine and cardiovascular systems;
- with a diagnosis of chronic prostatitis;
- if adenocarcinoma is suspected;
- for all patients with previous abdominal surgeries.
In addition, urological surgeons call TUR a minimally invasive procedure. The risk of developing complications when performing it is minimal, and rehabilitation after surgery occurs in a short time.
Recommendations for recovery
bladder catheterization
Prevention of complications of surgical treatment, as well as speeding up the rehabilitation of a man, is possible by following the following simple recommendations:
- All salty, spicy foods, smoked foods and alcoholic drinks should be excluded from the diet. Such products lead to increased irritation of the urethra. In the diet, increase the amount of lean meats (fish, rabbit meat), as well as vegetables and fruits containing large amounts of vitamins and microelements;
- Every man should ensure regular physical activity aimed at overall body tone and strengthening the pelvic floor muscles. For the latter purpose, Kegel exercises and other types of therapeutic exercises are used;
- If any unpleasant symptoms or discomfort appear in the perineal area, a person should immediately contact their doctor, who will conduct the necessary examination and determine the cause of these sensations.
Compliance with these recommendations does not require a major change in a man’s life, however, it can significantly reduce the risks of developing the consequences of removal of prostate adenoma.
The “gold standard” for eliminating BPH is surgical excision of the altered tissue of the gland or the entire organ. In case of any non-compliance with the indications and contraindications, a man may experience various pathological processes localized in the prostate area.
The patient's awareness of them, as well as the early detection of any pathological processes, allows timely prescribing the necessary treatment and preventing the development of severe conditions. A man’s compliance with recommendations for the rehabilitation period plays a great role in preventing the consequences of surgical interventions.
Prostatitis “burns out” within a day! Take a simple remedy...
An unconventional technique with a stunning effect!
>
Carrying out resection
The procedure is carried out using a special device – a resectoscope. It is inserted into the man's urethra.
A resectoscope is a device used for resection of the prostate
To perform direct removal, the doctor must carefully examine the affected area. Particular attention is paid to:
- bladder;
- urethra;
- areas surrounding the adenoma.
Only after this is resection performed using a special device in the form of a loop.
To perform transurethral resection, in order to avoid complications, it is necessary to maintain visibility of the treatment field. This is created by the influx and outflow of fluid through the resectoscope channels. At the time of tissue removal, visibility may be limited due to bleeding from the vessels. Therefore, it is important to stop it in time.
The procedure is performed only by a qualified specialist. Positive results and the absence of negative consequences can be observed when:
- the doctor’s knowledge of anatomical landmarks;
- the ability to distinguish pathological tissues from healthy ones;
- good visibility in the manipulation area.
After removing the adenoma, the tissues and bladder cavity are washed. Next, the surgeon examines the condition of the organ and the surgical site. If bleeding is observed, it is stopped immediately.
When the resectoscope is removed, a catheter with an inflated balloon at the end is passed through the urethra into the bladder area. It is called a Foley catheter. It is necessary to constantly irrigate the area and prevent the formation of blood clots. If the procedure is not carried out, the channels for the outflow of fluid may become clogged. The catheter also helps normalize the functioning of the bladder.
The result of washing can be assessed by the color of the flowing liquid. If no blood tint is noted, then after 2–4 days of rinsing, the catheter is removed.
Recovery after a TUR of prostate adenoma is observed after removal of the auxiliary instruments. Feedback from patients indicates that the process of urination returns to normal. But pain and urine of a pale pink hue often appear.
After a TUR of prostate adenoma, pain is often observed
When men cannot avoid complete prostate removal
Complete removal of the organ is carried out based on the results of a thorough examination, which includes various diagnostic methods. The operation is performed in patients with hematuria, bladder stones, actively developing prostate cancer and renal failure.
In addition, the indication for surgery is acute urine retention in the bladder, a complication of prostate adenoma or an infectious disease of the genitourinary system. In the presence of such problems, organ elimination cannot be avoided even if the tumor does not respond to other therapeutic methods.
How is resection performed?
TUR of prostatic adenoma of the prostate gland is always done under anesthesia. The choice of anesthesia is made by the patient together with the anesthesiologist. The procedure can be performed either under general anesthesia or in conjunction with epidural anesthesia.
In the first case, during the operation the patient falls into deep sleep. General anesthesia has a number of contraindications and is difficult to tolerate for elderly patients - much more difficult than the operation itself to remove the adenoma.
Epidural anesthesia involves blocking the receptors responsible for pain and mobility of the lower body. The anesthesiologist injects the drug into the epidural space of the spine. A catheter is installed in this place, through which the drug is administered. During epidural anesthesia, the patient remains conscious, but does not feel the manipulations being performed. Recovery from this method of pain relief occurs very quickly, the risk of complications is low, however, epidural anesthesia is contraindicated in some diseases of the spine.
Immediately before insertion of the resectoscope, the bladder is emptied and then filled with a special solution. An endoscopic tube is inserted into the urethra, passes through the bladder and reaches the prostate gland. The device for performing the operation consists of:
- cameras;
- lighting device;
- electric loop;
- fluid supply systems.
The camera allows you to display the image on the monitor. This ensures full control over the operation and reduces the likelihood of medical errors.
Benign hyperplasia tissue is removed layer by layer. This ensures there is no blood loss and the risk of damage to healthy prostate tissue. Depending on the size of the adenoma and additional manipulations (removal of stones, dissection of urethral stricture), the entire procedure takes from 40 minutes to an hour and a half.
After removing the instruments, a catheter is installed in the bladder, which will ensure urine drainage over the next few days. After epidural anesthesia, the patient regains sensitivity after 2-2.5 hours.
The camera displays the image on the monitor
Types and methods of transurethral resection
TUR differs in the type of energy used, which affects the adenomatous node. In urological practice, there are three types of this manipulation.
Monopolar TOUR
During surgery, an electric current passes through electrodes throughout the body and affects not only the pathological focus, but also healthy tissue. Plain water is used to conduct current, which often leads to negative consequences.
Monopolar TUR is the oldest type of endoscopic method for treating prostate adenoma. It has more disadvantages than all other types. These include:
- inability to influence large adenomatous nodes (more than 80 cm3);
- dissipation of electric current through healthy tissues;
- the frequency of postoperative complications is much higher (especially TUR syndrome);
- a large number of contraindications.
Monopolar TUR is not used in patients with artificial pacemakers (pacemakers). This type of resection is also completely contraindicated in older patients with severe concomitant diseases, especially the cardiovascular system. In men with rhythm disturbances (various types of arrhythmias), monopolar TUR can lead to a worsening of the condition, because the electrical activity of the heart may change due to the effect of the current.
Bipolar TOUR
This type of TUR is the most common in urological practice. Saline solution is used as a current conductor. The advantages of the method include:
- lack of systemic influence of current on the body;
- minimal risk of postoperative complications;
- possibility of resection of large adenomatous nodes;
- practically does not damage healthy tissue around the adenoma;
- the list of contraindications is much narrower.
Bipolar TUR can be successfully used in patients with heart disease and other somatic diseases. The recovery period after this type of TUR is several times shorter than after a monopolar one, and the incidence of postoperative complications is no more than 3%.
Plasmakinetic TUR
The use of a plasmakinetic resectoscope is the most modern method of endoscopic resection of adenoma. It has a minimal traumatic effect on healthy prostate tissue, and there is no effect on the entire body. The device has a high ability to stop bleeding from damaged vessels due to its coagulating properties. The frequency of postoperative complications, incl. and urinary incontinence, is no more than 1%. The relative disadvantages of plasmakinetic TUR are that it is poorly studied (the method was developed recently) and the high cost of the equipment.
At the urology clinic of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov, it is possible to conduct any type of TOUR. The tactics of treating BPH and determining the optimal method of endoscopic intervention are discussed with each patient individually.
Features of home restoration
The first months after discharge from the hospital, a man needs to behave extremely carefully. It is strictly forbidden to lift weights exceeding 3 kg in weight, no matter how much his family asks him to do so. In addition, it is important not to make sudden movements, as this can lead to injury to the postoperative wound and complications.
Removal of an adenoma, even with such a low-traumatic method as TUR operation, requires adherence to a careful behavior regimen for at least 2 - 2.5 months after discharge from the hospital.
Men are recommended:
- Drink as much liquid as possible per day. Natural juices, mineral, non-carbonated waters are the healthiest. It’s better to temporarily give up strong tea or coffee.
- Try not to strain during bowel movements. A nutritionist can help with this by prescribing a special diet.
- You must refrain from riding a bicycle or driving a personal car. But you need to walk as much as possible, this helps restore all functions and speed up tissue regeneration.
- Under no circumstances should you allow hypothermia.
- Regularly undergo medical examination by a urologist to avoid relapse of the disease.
The ideal option would be sanatorium treatment for the entire recovery period. This will help avoid many difficult situations, including psychological conditions.
Do's and don'ts after prostate surgery
In addition to heavy lifting and exposure to hot temperatures, special attention is paid to nutrition after a tour. The caloric content of the daily diet is not limited, but all substances and products that increase the irritating properties of urine are excluded:
• marinades; • spices; • vinegar; • citrus fruits; • tomatoes; • spinach and sorrel; • smoked meats; • pickles; • chocolate; • onion and garlic; • soda, strong tea and coffee; • alcohol.
Gradually, after 2 months, if you feel well, a gradual expansion of the diet is allowed, taking into account individual characteristics and preferences. All unknown food additives, sweeteners, dyes, stabilizers, preservatives should be excluded.
In the first week after TUR of the prostate, it is necessary to increase the drinking regime to 2 - 2.5 liters, unsweetened compotes, jelly, decoctions of plant components (birch buds, dill seeds, bear ears), lingonberry and cranberry juice, compote of dried apricots, prunes, raisins and other dried fruits. You can drink regular non-carbonated artesian water.
It is better to refuse milk, especially if you previously had problems with phosphaturia. It is justified to take cystone 2 tablets. 3 rubles/day 1 month, this will prevent the process of salt formation.
On the first day after a TOUR of the prostate, nutrition is as gentle as possible: only liquid (non-rich broths, compotes, water). Then pureed steamed dishes are gradually introduced. Plant foods should make up the majority of the diet:
• zucchini; • potato; • pumpkin; • carrot; • beet.
Low-fat varieties of meat and fish are preferable. Fermented milk products (250 ml) and low-fat cottage cheese (no more than 150 g per day) are useful as they help restore intestinal microflora.
Fruits contain a large amount of vitamins and fiber, so you shouldn’t give them up.
It is healthier to eat eggs in the form of an omelet, but no more than 2-3 per week.
If there is no tendency to flatulence, 3-4 weeks after TUR of the prostate, you can prepare dishes from legumes.
Porridges that are useful are: buckwheat, oatmeal, rice (if there is no constipation), barley, etc.
Jam, honey, marshmallows, jelly, if blood sugar levels are normal, can be included in the diet.
Important! All food is prepared in a gentle way and taken 4-5 times a day, in small portions.