The bladder is part of the excretory system through which the human body is freed from toxins and waste. Often, foreign formations accumulate in it, penetrating from the kidneys, or forming here. The reasons for the appearance of salt deposits in the bladder are different in all patients. This question will be of interest to many, since women and men suffer equally from this pathology, regardless of age. Let's figure out how sand appears in the bladder and whether it is possible to get rid of it.
Causes
Sand forms in internal organs for several reasons. For example, due to negative environmental factors or as a result of a person’s negligent attitude towards health: unbalanced diet, chronic diseases (urinary tract, endocrine or intestinal).
In women, the cause of the development of the disease can be hormonal imbalances and pregnancy, when the fetus compresses the bladder and impairs its functioning.
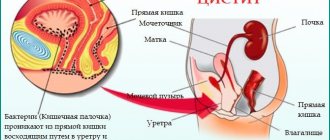
Sand can enter the bladder through a descending route from the kidneys or ureter.
Provoking factors
- Diseases of the genitourinary system such as pyelonephritis, urethritis or cystitis provoke the formation of sand.
- Poor nutrition. Eating salty foods in large quantities increases the risk of crystal formation. Metabolic disorders, deficiency or excess of vitamins and minerals are also provoking factors.
- Dehydration. Insufficient consumption of clean water leads to the formation of sand in the organs. Due to lack of fluid, all the particles do not come out of the bladder.
- Unhealthy lifestyle: alcohol and nicotine abuse.
- Sedentary work.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Signs
Small grains of sand usually come out unnoticed, without injuring the urethra. However, even in this case, part of the crystalline formations remains in the body. These grains of sand will serve as a nucleus for the growth of salts and the formation of large stones. To prevent the process, you should undergo appropriate treatment. You can understand that there is sand in the bladder by the following signs.
- Frequent trips to the toilet for no apparent reason. Feeling of bladder fullness.
- Concomitant hepatic dysfunction.
- The presence of chronic inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, especially in women.
- Leading an unhealthy lifestyle. Abuse of salt, fatty, smoked foods, alcohol.
- Insufficient fluid intake. Change in urine color to a darker or pinkish tint, appearance of blood, cloudy discharge.
- Use of medicinal mineral waters without a doctor’s prescription.
Specialist consultation
The key to successful treatment of any disease is timely detection of the disease and prescription of medications. By analyzing the presence of certain signs and symptoms of sand coming out of the bladder, you can notice deviations in time and seek medical help.
Symptoms
The presence of sand in an internal organ is recognized by the following signs:
- Pain in the lower abdomen or lower back. The sensation intensifies when urinating.
- A burning sensation in the urethra even at rest, this symptom is especially typical for men.
- Frequent urge to urinate, sometimes false.
- Feeling of an unemptied bladder;
- Swelling of the body, especially the lower extremities.
- The urine becomes cloudy, sometimes with bloody discharge.
- Difficulty urinating.
In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Renal colic, burning, pain, discomfort during urination are signs of sand leaving the body.
Sometimes they accompany other diseases that arise as a result of the formation of sand in the bladder.
Features of the course of the disease in men and women
Treatment and diagnosis are the same for both sexes, but the symptoms and development of the disease are different. Men are more susceptible to this disease due to the structural features of the genitourinary system. As the disease progresses, they experience a feeling of discomfort in the penis. Men suffering from prostate adenoma, which causes stagnation of urine, are especially susceptible to this ailment.
Men suffering from prostate adenoma, which causes stagnation of urine, are especially susceptible to the appearance of sand in the kidneys.
Women may develop other urological diseases due to sand in the organs. The deposits, when transformed, turn into coral-shaped spiked stones (that's the name of a type of stone).
How can it be dangerous?
Sand in the urine is a sure sign of the onset of urolithiasis. At the stage of its formation, large stones do not yet appear in the kidneys or bladder, and therefore small crystals easily pass through the urinary canals.
Symptoms during this period are not pronounced. There may be only slight comfort when urinating.
Problems begin as the disease progresses, if measures are not taken at the initial stage:
- Pain syndrome appears in the lumbar area when sand leaves the kidneys, grains of sand in the urine become visible to the naked eye, and the color of the urine changes.
- Gradually, urination causes difficulties (frequent urge, urinary retention), swelling under the eyes, low-grade body temperature, and general weakness.
- Over time, acute pain syndrome develops in the area of the ureter, and renal colic is felt.
- Increased pain, urinary retention and blood impurities indicate the development of nephrolithiasis.
- Unremoved grains of sand from the buds become the center of crystallization, on which new sand layers are superimposed. This is how stones of significant size are formed (most often, microcalcifications with clear boundaries).
- Gradually, the stones fall lower, reaching the ureter and bladder, which leads to the spread of pain to new areas.
- Another danger awaits a person even at the stage of sand removal. Moving along the urinary canals, it damages their walls. This creates favorable conditions for the life of various pathogenic microorganisms and provokes an inflammatory reaction. This is how pyelonephritis arises.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. To do this, you will need to take a urine test and undergo an ultrasound with a contrast agent. The screen shows the appearance of a suspension in the internal organ. Sometimes this procedure is also performed to examine other internal organs in order to exclude diseases with similar symptoms.
Often, diagnostics involve x-raying the kidneys and collecting a blood test. The results allow us to identify the causes and source of sand formation.
After viewing the test results, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Possible complications
Sand in the urine, like any disease, is very dangerous. Even if the initial symptoms disappear over time, this does not mean that the disease is cured. This means that salt deposits settle on the walls of the bladder and begin to harden, forming stones. Passing stones from the urinary tract is a much more painful process. Constantly ignoring inflammatory processes leads to their development into a chronic form. Cystitis and urethritis develop frequently and are difficult to treat.
If sand and stones are constantly in the bladder, they constantly provoke the appearance of cystitis or urethritis.
Diagnosis of salt formations in any organ of the urinary system signals urolithiasis. Sand and stones can equally form in all organs of the urinary system. Timely cleansing of the kidneys from such deposits allows you to avoid further complications. The longer you delay the treatment of stones, the more painful further therapy for their crushing and removal will be.
Treatment
To treat urolithiasis, medication is most often used. Following the doctor's recommendation, you can use traditional medicine methods. Diet becomes an obligatory factor in treatment, because most often poor nutrition provokes the disease. In severe cases, the urologist will refer the patient for an ultrasound procedure or surgery.
To treat urolithiasis, medication is most often used.
If you try to get rid of deposits in the bladder on your own, this will not help in the treatment of urolithiasis and will lead to complications.
Medicines
Medicines are prescribed by a doctor depending on the characteristics of the disease, causes and degree of neglect. The following medications are considered effective:
- Nevigramon, Furazolidone, Ampicillin, Cephalexin are drugs aimed at reducing pain and fighting infections. For pain relief, Drotaverine or No-Shpu is sometimes recommended.
- Uroflux, Uralit, Cyston, Petnoxifilline. Helps remove deposits. The preparations contain herbal components, so these products can also be used as a preventive measure. They have few contraindications and are recommended for long-term use.
- Sometimes doctors prescribe a mineral-vitamin complex to boost immunity.
Folk remedies
As an additional remedy for drug treatment, you can use traditional methods. The basis of this method is the use of diuretics. They include herbs that you can buy at the pharmacy or collect yourself. It is necessary to follow the doctor's instructions, since not all plants have a positive effect on the patient's health.
As an additional remedy for drug treatment, you can use traditional methods.
The following will help in the fight against sand formation:
- horsetail
- Linden;
- coltsfoot
- raspberries;
- cowberry;
- bearberry;
- juniper;
- licorice.
A common decoction is rose hips. It is prepared in a 1:2 ratio and infused for 2-3 hours. Take half a cup every hour for two months. The infusion will strengthen the immune system and help remove deposits painlessly.
To remove sand from the genitourinary system, parsley is used in the form of an infusion. Leaves, roots and seeds can be used dried or fresh. It can be added to soups, salads and other dishes.
Diet
The doctor sets a diet for the patient during treatment: proper nutrition and drinking regimen. It is prescribed individually to each patient, based on pathology, human metabolism and individual food intolerance. But there are a number of rules that everyone must follow when prescribing a diet:
- Salty foods, marinades, and consumption of alcoholic beverages and mineral water are prohibited.
- Eliminate cocoa and chocolate from your diet.
- Give preference to stewed, boiled, steamed food.
- Reduce salt intake to 1 tsp. in a day.
- Eat in small portions, chewing food thoroughly.
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of clean warm water. Sometimes it is recommended to add lemon juice. Increasing acidity helps dissolve deposits.
- The diet must include meat, cereals, and eggs.
The doctor sets a diet for the patient during treatment: proper nutrition and drinking regimen.
If it turns out that the cause of the disease is an excess of calcium, then you should not eat vegetables, fruits and dairy products.
Nutrition should be balanced. It is important that the body receives a sufficient amount of vitamins.
Healing procedures
Ultrasound can detect sand formed in the ureter. To clarify the diagnosis, X-ray examination, tomography, and urinalysis are used. Since the formation of sand is only a consequence, and before treating the disease, it is necessary to accurately determine its cause. If the essence of the problem lies in kidney pathology, you need to focus on its treatment.
Diabetes mellitus is corrected with a low-carbohydrate diet, insulin or glucose-lowering drugs. For bacterial infections, appropriate therapy is prescribed.
The choice of agent depends on the result of the microflora sensitivity test, but preference is given to broad-spectrum antibiotics, such as:
- "Furazolidone";
- "Ampicillin";
- "Cephalexin";
- "Pentoxycycline";
- "Nevigramon";
- "Norfloxacin".
To improve urodynamics and speed up the removal of sand, herbal preparations such as “Cyston” or “Uroflux” are used. They have a diuretic and antispasmodic effect.
Formations of small diameter (up to 5 mm) are removed without the use of medications. The patient is prescribed dietary nutrition. Products that provoke the formation of the corresponding salts are excluded from the therapeutic diet. If the composition of the stones is oxalates, the patient is recommended to eat a diet with a predominance of meat, eggs and cereals. It is recommended to exclude products containing calcium: milk, cottage cheese, some vegetables and fruits. If there is an excess of phosphorus salts, doctors give similar advice. In addition, it is recommended to drink sour juices: lemon or cranberry.
If the problem is caused by uric acid salts, the diet, on the contrary, excludes the consumption of meat, especially fatty meat, rich broths, jellied meat, and offal. With all types of stones, fried, salted, smoked, cocoa is prohibited. Boiled or steamed dishes are preferable. You need to eat little, but often. Salt is used to a minimum, no more than 4 grams per day.
Drinking plenty of fluids helps remove sand. Preferably clean water, low in salts, and some types of juices. It is better to drink coffee and tea, including green tea, little by little. But there is no need to give them up at all; they have a slight diuretic effect, which is very useful in the presence of sand. Decoctions of medicinal plants are used for therapeutic purposes, combining them with drugs, or independently.
Disease prevention
Preventative measures mainly consist of proper nutrition and drinking plenty of fluids. It is necessary to control the consumption of salt, mineral water, and alcohol.
A sedentary lifestyle also provokes the appearance of sand in the bladder; physical activity should not be avoided. It is necessary to monitor your weight and exercise to strengthen your immune system.
You cannot tolerate the urge to urinate; you need to visit the toilet as needed. Holding urine can lead to infection and sand formation.
Treatment options
Sand in the urine is the stage of urolithiasis when conservative treatment can still be done.
It should be sent:
- to normalize salt metabolism,
- restoration of acid balance,
- improving the removal of sand from the kidneys (relaxation of smooth muscles, expansion of the lumen of the urinary canals, elimination of stagnant zones).
Treatment is long-term and follows a complex scheme. An important role is given to a specific diet, drug therapy, and preventive measures. Efficiency increases the use of folk remedies.
The treatment regimen and course duration are determined by the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
Special diet
An unbalanced diet is considered one of the important causes of stone formation, and therefore a special diet is a prerequisite for treatment.
It is prescribed after identifying the composition of the nodules and takes into account the following basic recommendations:
- If oxalates are detected, it is necessary to limit as much as possible in the diet the consumption of foods with a high content of calcium, ascorbic acid, oxalate compounds - dairy products (including cheeses), chocolate, greens (especially spinach and sorrel), cocoa, black tea, strawberries, black currant. The drinking regime should be at least 2.2 l/day.
- If you have urates, you should exclude foods based on purine compounds - meat dishes (including broth, offal, sausages), legumes, chocolate, coffee and cocoa. The volume of beverage consumption is 2.7-3.2 l/day. Recommended products – vegetables (carrots, potatoes, lettuce, cauliflower) and fruits, nuts, milk
- In the case of phosphates, it is necessary to eliminate the entry of phosphorus into the body. You should limit foods such as fish and dairy products. You need to drink at least 2.4 l/day. It is recommended to increase the consumption of eggs, raisins, and prunes.
The diet during the course of therapy should be agreed with a nutritionist.
Poor nutrition can significantly aggravate the problem.
The basis of drug treatment is the following medications:
- Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms and stop the inflammatory response. The following medications are prescribed: Ampicillin, Furazolidone, Cephalexin.
- To normalize blood circulation - Petnoxifilline.
- To speed up the excretion of urine and eliminate its stagnation - Uroflux, Cyston, Uralit.
- Antispasmodics – No-shpa.
All medications are taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor. If kidney or other pathologies are detected, he prescribes drugs to treat this particular organ.
Folk recipes
To increase the effectiveness of treatment at home, you can use the following proven folk remedies:
- Rosehip infusion. Recipe - 100 g of berries are poured with boiling water (1 l) and infused in a thermos for at least 2.5 hours. Take 140-160 ml every 1.5-2 hours. The course of treatment is 50-60 days.
- Diuretic mixture: parsley root, cornflower flowers, birch buds, bearberry (all in equal quantities). The mixture is poured with water (at the rate of 1 tablespoon per 200 ml) and simmered over low heat for 12-16 minutes. The product is taken 2-3 times a day, 50 ml. Course – 15 days.
- An infusion of a mixture of bearberry with juniper fruits and licorice root. The ratio of ingredients is 3:3:1. The raw material is poured with boiling water (1 tablespoon per 200 ml) and infused for at least 2 hours. It is consumed daily, before breakfast. Course – 15-20 days.
How to cure a neurogenic bladder
If a person experiences a malfunction of the nervous system, he begins to suffer from functional disorders. One of them is called neurogenic bladder. Already from the age of 2, a child can control the process of urination, that is, endure the need at the moment when the bladder is filled with liquid.
But if an adult or a child over 3 years old is unable to control the urge, this will indicate neurogenic dysfunction. The disease occurs approximately equally in men and women, with a slight bias towards the weaker sex due to the structural features of the genitourinary system.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
The concept of neurogenic dysfunction?
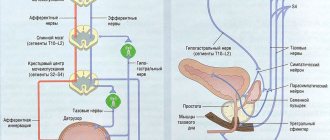
When a patient begins to suffer from problems with bowel movements, it is called neurogenic bladder dysfunction. The most common manifestation of this pathology, both in older people and in children, is urinary incontinence. The inside of the bladder consists of a special stratified mucous epithelium. Below it are the detrusor fibers, that is, smooth muscles, which are controlled by the cerebral cortex.
During the day, the organ begins to fill with fluid, stretching the mucous epithelium. As a result, signals are sent to the head through the nerve channels, after which the person feels an urge. If this process is disrupted and urination occurs involuntarily, it is necessary to begin investigating the problem with an ultrasound scan; these are clear signs of a neurogenic bladder.
Reasons for deviation
The manifestation of pathology is always associated with disruptions in the passage of nerve impulses to the organ. The progression of neurogenic bladder dysfunction in adults or children can occur against the background of other ailments or be a congenital defect. If a deviation was diagnosed in a child, this could be due to the following reasons:
- Often the deviation is congenital or develops over time due to constant stress.
- Birth injury.
- Accompanying illnesses.
Note! The formation of the urea and its nerve cells stops at 2-3 years of age, so it will not be possible to diagnose the problem earlier. It is during this period that parents need to pay attention to the baby’s urination pattern.
If neurogenic bladder is found in men or adult women, the causes may be:
- damage to the functions of the nervous system. These may include problems with the brain of the back, tumors or infections;
- constant stress at work and significant emotional distress;
- if we are talking about a neurogenic bladder in men, treatment should begin with eliminating problems with prostate adenoma, if any;
- spina bifida;
- constant physical activity in the form of weight lifting;
- polyneuropathy in various manifestations;
- neurogenic bladder in women can develop as a result of prolonged labor, urinary incontinence after childbirth;
- degenerative changes in the bladder due to frequent surgical interventions in the pelvic organs;
- long-term course of a chronic infectious disease that affects any of the organs of the urinary system;
- the patient's ongoing use of psychopharmacological medications;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- congenital malformations of the spinal column (sacral dysgenesis and agenesis).
Types of pathology
Disorders related to urinary regulation can manifest themselves through overactive or weakened muscle tone. Before treating a neurogenic bladder, doctors determine its type, it can be as follows:
- Hyper-reflexive. This means that the pathology occurs due to disorders of the brain. In this case, the smooth muscles are constantly under tension, preventing the person from relieving himself when it occurs on time. As a result, incontinence develops, since fluid is unable to remain inside the organ. This can also lead to complications in the form of cystitis, reduction of the bladder and degradation of its cells.
- Neurogenic bladder dysfunction of the hyporeflex type always develops against the background of problems with the sacral part of the spinal cord. Here the muscle tissue, on the contrary, does not show activity and is constantly in a relaxed state. This provokes stretching of the fibers and enlargement of the organ as it fills with fluid. Then problems arise with the functioning of the sphincters and, due to strong pressure, the patient shows signs of incontinence. If the bladder is filled to capacity, it can also cause urine to flow back.
Symptoms accompanying the disease
Here the situation may be different, depending on the type of neurogenic bladder.
In women, symptoms appear almost the same as in men, the only difference is the nature of the disease. If the patient suffers from an overactive neurogenic bladder, the symptoms will be as follows:
- Difficulty trying to defecate.
- Incontinence.
- At night there is a strong urge.
- Constant changes in blood pressure readings.
- Insufficient volume or absence of the required amount of liquid in the bladder.
- Increased sweating.
If the patient has a particularly complicated form of the disease, it may not show any activity. In this case, you need to pay attention to pain in the lower abdomen and urinary retention. Another type of deviation is a hypoactive form of neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Treatment will be aimed at eliminating the following symptoms:
- lack of activity in the form of urea contractions;
- constant feeling that there is a large amount of fluid in the organ;
- inability to empty your bowel movements completely, even if the urge is strong;
- no signs of intravesical pressure;
- straining during micturition.
What complications can there be?
In some cases, the cause of kidney stones will be a neurogenic bladder. In this case, ultrasound is performed as a preventive measure in order to promptly diagnose the presence of stones. This will also provoke other inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system, since stagnant urine will return back through the ureters.
Important! The disease can be especially dangerous for young children. If not treated in a timely manner, a neurogenic bladder causes serious problems in the functioning of the kidneys and the entire genitourinary system. Over time, some diseases can become chronic.
It is very important to pay sufficient attention to the psychological factor. If a child develops a disorder, there is a high probability that the disorder will not leave him in adulthood.
Methods for diagnosing the problem
To fully solve the problem, it is necessary to correctly diagnose the neurogenic bladder in women. Treatment is applied only after completing the entire complex of studies, which looks like this:
- Biochemistry and general blood check.
- Submission of urine to determine the type of infection.
- Analyzes according to Nechiporenko.
- General examination of urine.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include the following:
- X-ray;
- MRI and ultrasound;
- uroflowmetry;
- cystoscopy;
- profilometry.
If the data are insufficient to accurately identify a neurogenic bladder, treatment is not given until further examination of the brain of the back and head has been performed.
What treatment is used
The methodology and program of treatment is always determined by several doctors, a psychologist, a neurologist and a urologist. Attention is also drawn to the individuality of the patient’s body and the causes of the deviation.
Typically therapy is carried out in the following ways:
- Operational.
- No medications.
- Medication.
The latter will mean that the patient is prescribed medications with such a spectrum of action as:
- antidepressants (tricyclics);
- oxybutynin;
- Kalimin for neurogenic bladder is used to improve neuromuscular transmission;
- calcium antagonists;
- alpha blockers.
If a patient is diagnosed with a hypoactive form of the disease, treatment will be much more difficult. Here additional inflammatory processes in the kidneys and ureters may be observed.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
Conclusion
As preventive measures, a person needs to adhere to proper nutrition, avoid excessive drinking and smoking. The development of pathology is also influenced by wet feet in rainy weather and untreated chronic diseases.
Causes of urolithiasis
Kidney stones appear both after inflammation and without it. The reasons leading to the formation of stones include:
- Genetic predisposition. Metabolic disorders lead to impaired absorption of certain amino acids by the small intestine, so they remain in the urine and crystallize.
- Wrong diet. When consuming meat and dairy products, pickles and smoked meats, smoking and drinking alcohol with a lack of vegetables and fruits leads to oxidation of the body and increased urine acidity. Vegetarianism, lack of protein foods, and passion for fruit diets lead to alkalization of the body and a decrease in acidity. All this leads to the formation of stones.
- Lack of vitamins and sunlight. Vitamin D levels also affect the formation of stones, both a deficiency and an excess of the vitamin.
- Urogenital infections. Very often, after removing stones, bacteria are found inside them, which have become a capsule around which a calculus has formed.
- Hot climate. People living in countries with tropical climates are much more likely to suffer from urolithiasis.
- Thyroid diseases. Hypothyroidism, or insufficient production of the hormones T3 and T4, impairs the kidney's blood flow and reduces its ability to filter.
Contrary to popular belief, water quality has less of an impact on stone deposition. In order for stones to be deposited due to poor drinking water, it must be a truly undrinkable, poorly purified liquid that a person takes due to the development of an infection.
Proven traditional medicine recipes
- Rose hip decoction. 100-200 g of berries are crushed and placed in a thermos. Fill with boiling water. They insist for an hour. Drink a glass 5-7 times a day.
- Tincture of bearberry, juniper and licorice root . A spoonful of the mixture is filled with 200 ml of boiling water. Drink half a glass three times a day.
- A decoction of a multicomponent diuretic collection (linden, coltsfoot, raspberries, lingonberry leaves, anise fruits). Equal proportions of the above ingredients are poured into 200 ml of boiling water. Take before meals 2 times a day.
Kidney stones in pregnant women
There is a high risk of developing urolithiasis in pregnant women. This is due to changes in hormonal levels, in particular, an increase in progesterone levels. It prevents embryo rejection, but at the same time relaxes smooth muscles, causing urinary stagnation.
Also, during pregnancy, the immune system weakens, which causes microflora to change. Often a woman expecting a baby is tormented by thrush. Pathogenic microflora easily reaches the bladder through the short urinary tract, and from there to the kidneys. Stagnant urine is an excellent environment for the development of pathogens. All this contributes to the formation of stones or sand.
Also, the expectant mother needs to carefully monitor her diet. You should reduce your consumption of meat, but not give it up altogether. On the one hand, protein is a building material for the growing fetus, on the other hand, it helps to increase the acidity of urine.
Pregnant women also move less and limit themselves to fluids. Hormonal levels change taste preferences, and women, who have been limiting themselves to sweets and starchy foods throughout their lives, relax during pregnancy and indulge in sweets, pizza, carbonated drinks, and smoked sausages. In a word, a pregnant woman automatically falls into the risk group.
Kidney stones are dangerous for pregnancy because in the initial stages, a stone passing through the ureter causes a spasm of smooth muscles, which can provoke rejection of the fertilized egg from the uterine wall. At later stages, stagnation of urine and the infection developing in it can spread to the placenta.
A pregnant woman should definitely see a doctor. A high-precision ultrasound machine will show the position of the stone, and if there is a threat of its movement, measures will be taken to reduce the risk for the mother and the unborn baby.
Treatment of salt deposits
Ultrasound crushing of stones is the main method of treatment.
If there is a small amount of sand in the kidneys and bladder, and ultrasound does not show the presence of large formations, treatment consists of prescribing plenty of soft, non-mineralized water to drink. It is best to consume it in the first half of the day and at the same time follow a diet. Treatment options fall into three groups:
- medication treatment;
- ultrasonic crushing;
- surgical intervention.
The choice of treatment methodology depends on the degree of advanced disease.
Treatment with medications is prescribed when the cause of sand accumulation in the urinary tract is provoked by the deposition of salts on the walls of the ureters. Special medications are prescribed to increase the acidity level of urine. They do not have a harmful effect on the walls of organs, but dissolve stones and promote their removal from the body.
Stones and sand in the bladder are treated by crushing using high-frequency sound. The method is similar to ultrasound, but it uses high-frequency sound waves. This option for removing stones is very common and effective. The only possible side effect may be a slight inflammation, but it goes away on its own a few days after the procedure. In a situation where deposits and stones are more than 5 cm, an operation is prescribed to remove them.
Sand in the bladder occurs in women and men of completely different ages. Fine particles, the diameter of which rarely exceeds 4-5 mm, are usually detected during ultrasound examination. The appearance of sediment in the bladder is a common case of urolithiasis, which requires immediate treatment.
Sand in the bladder appears for various reasons. In most cases, stones are painlessly eliminated by the body in urine. But if the urinary system malfunctions, then microscopic particles accumulate in the kidneys, ureters and bladder. And this leads to serious consequences in the form of various diseases: pyelonephritis, urethritis, kidney stones, etc.
The main reasons for the appearance of grains of sand in the bladder include:
- Infectious diseases of the reproductive and urinary systems.
- Lack of vitamin D.
- Poorly performed stone crushing procedures.
- Toxicosis of a pregnant woman in the first trimester.
- Unbalanced diet, abuse of smoked, spicy and salty foods, carbonated drinks.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Metabolic disease.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, parathyroid gland, etc.
Symptoms and treatment of sand in the bladder in women: is it possible to get rid of it?
Sand in the bladder is common in women. This is due to disordered eating and advanced diseases of the genitourinary system.
It causes a number of painful symptoms and requires immediate treatment. This is a serious pathology that signals possible diseases of the internal organs or an unhealthy lifestyle.
Reasons for education
The kidneys purify more than 1000 liters of blood plasma and produce about 1.5-2 liters of urine every day. It is in urine that all harmful or unnecessary substances dissolve. The urine then enters the bladder, where it is stored until urination.
If disturbances occur in the functioning of the urinary system, then, as a consequence, pathologies develop, including the formation of sand.
The appearance of sand in the bladder is facilitated by a violation of the water-salt balance, which is regulated by the kidneys. When there is an excess of mineral compounds entering the body along with food and liquid, they accumulate in the bladder, because harmful products do not have time to dissolve and be eliminated in a timely manner.
This is facilitated by external and internal factors. External:
- low quality of drinking water;
- alcohol and tobacco abuse;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- kidney injuries;
- frequent dehydration;
- radiation exposure;
- taking pills for a long period of time;
- hypothermia of the body;
- abuse of mineral water.
Internal:
- pathologies of the structure of the organs of the urinary system;
- hormonal disorders;
- infectious kidney diseases;
- benign and malignant tumors in the kidneys;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- diabetes;
- prolonged exposure to stress.
To summarize, sand is formed when the kidneys are overloaded. This may be due to an excess of toxic substances coming from the outside, or to disruption of the kidneys due to any diseases that reduce the performance of the organ.
Read our article on how to cleanse your kidneys of sand and toxins.
Symptoms of sand
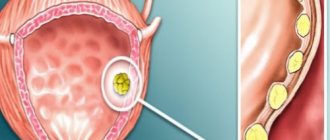
The inner surface of the bladder is covered with small crystals of mineral compounds. Over time, the crystals increase in size due to new undissolved molecules. They accumulate and form large fractions. As a result, it becomes more difficult to dissolve them. This is how sand appears in the bladder.
Every person has sand in the bladder, but in different concentrations. Normally, it should constantly dissolve and be excreted along with urine. It does not cause concern and is not felt in any way. Problems arise when the grains of sand become large in size or their number increases.
This manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- pain in the lower abdomen when pressed;
- burning when urinating;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- feeling of incompleteness of the urination process;
- sudden sharp pain in the abdomen when changing body position;
- change in urine color;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- inability to completely empty the bladder;
- weak stream pressure when urinating.
The symptoms of sand in the bladder are similar to various diseases of the female genitourinary system. Sand covers the walls of the bladder and irritates it in the same way as infectious diseases, such as cystitis.
Further, when sand enters the urethra, it can damage its walls with the sharp edges of the grains of sand. As a result, pain and burning appear, as with urethritis.
How to treat?
During urination, grains of sand can come out along with urine.
Small particles pass through the urethra asymptomatically. However, larger ones can completely block the urethra. This will manifest itself in the form of a weak stream pressure and a persistent desire to urinate. When released, the sharp edges of the grains of sand cause damage to the walls of the urethra and provoke bleeding. Acute attacks of pain in the lower abdomen and burning sensation when urinating occur. The pain may come on suddenly and disappear again or not go away for several days. It all depends on the degree of damage to the walls of the urethra and bladder.
In addition, damaged areas can become inflamed due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, so sand in the bladder is often accompanied by infectious inflammatory processes.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, you should contact a nephrologist. First, the patient will be interviewed and palpated in the lower abdomen. Next, hardware and laboratory tests are prescribed:
- A general urine test will show elevated protein levels.
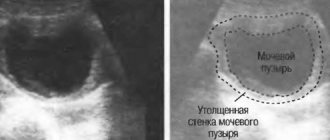
- Ultrasound of the bladder - the localization of large grains of sand and their sizes will be visible.
- X-ray is rarely used. Only shows stones larger than 3mm.
- Urography (excretory) - helps to detect sand in both the bladder and urethra using a contrast agent.
- CT scan allows you to detect grains of sand of any size in the bladder and urethra.
After conducting all the studies, the doctor should have no doubt about the diagnosis.
How to remove sand?
To get rid of sand in the bladder, therapy must be comprehensive. It includes taking medications, diet and using folk remedies.
Medicines
The following medications are used to treat pathology:
- diuretics – have a diuretic effect and dissolve sand (Avisan, Cyston, Fitolit, Marelit);
- antibiotics - used to treat concomitant infectious diseases (Ciprofloxacin, Amoxicillin, Norfloxacin, Furazolidone);
- anti-inflammatory drugs - eliminate inflammation and reduce the level of pain (Urolesan, Fitolysin, Canephron);
- antispasmodics – relieve spasms and pain (No-Shpa, Drotaverine).
Treatment should be aimed not only at dissolving and removing sand, it is also necessary to eliminate the cause of its formation.
Diet
Monitoring drinking and eating is an important component of the treatment of sand in the bladder. First you need to drink more fluids (2.5-3 per day). Regular drinking water without a large amount of minerals is best suited for this.
Then you should give up salt and salty foods, chocolate, coffee, mineral water, alcohol, smoked foods, spicy and spicy foods. It is also necessary to limit the consumption of dairy products (primarily cottage cheese) and fatty fish.
In turn, it is recommended to diversify your diet with the following products:
- cereals (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal);
- White bread;
- lean meats (rabbit, turkey);
- low-fat fish (pollock, pike perch, pike, trout, hake);
- boiled vegetables;
- fruits, berries, greens;
- eggs.
It is advisable to boil or steam all dishes, but not fry them.