Sometimes a sediment of microscopic solid crystals or salts is found in the urine - this is a suspension. This is a pathological phenomenon that should not be present in a healthy person. The suspension indicates disorders that exist in the urinary system.
In the bladder, sediment may appear due to injuries, disturbances in the urination process, stagnation, and high salt concentrations. Prolonged presence of sediment in the urine can lead to the formation of sand and stones. If the results of the study show the presence of suspension, it is necessary not to delay eliminating the problem and begin treatment immediately.
Types of suspension in the bladder
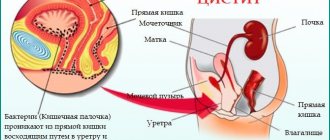
A distinction is made between primary and secondary suspension. Primary occurs directly in the bladder from urates, which are formed from an excess of uric acid in urine. This syndrome often occurs with cystitis. Secondary suspension is the result of pathologies associated with the kidneys (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis). It enters the bladder through the ureter.
At the early stages, a fine suspension is formed. These are microscopic crystals of salts no larger than 0.0005 mm in size. As diseases develop, the microscopic suspension becomes overgrown with epithelial and blood cells, forming coarsely dispersed formations.
There is also a hyperechoic suspension in urine. It is based on small particles of salts (urates, oxalates, phosphates) and concentrated urine. The highest content is cholesterol. The longer urine stagnates in the bladder, the higher the content of various salts and the higher the risk of suspension formation.
When is the research done?
If sediment begins to accumulate in the bladder, the symptoms of this pathology do not appear immediately. At the initial stages it does not manifest itself. This feature of the symptoms, its vague nature, makes diagnosis difficult.
What signs should alert a person and force him to undergo an examination?
- Painful sensations. They appear mainly when emptying the bladder. Sometimes accompanied by other diuretic problems.
- A burning sensation spreading in the lower abdomen.
- The urge to urinate may become strong and the process is almost always painful. Urination is suddenly disrupted, so it can be resumed by changing body position .
- White suspension and flakes are found in the urine. Changes in the color of urine and its smell are possible.
- Traces of blood appear in the urine. This phenomenon is called hematuria.
- The pain that bothers a person when he urges to urinate can shift and be localized in the urethra. This occurs because highly concentrated urine containing sediment moves through the urinary tract.
- The formation of suspension and sediment may be indicated by swelling of the legs .
- In men, the pathology may be accompanied by erectile dysfunction.
- Possible increase in pressure.
If suspensions form in the bladder, their appearance is signaled by pain. They are the first symptom indicating a dangerous pathology. Pain is felt every time the bladder is emptied and is localized in the groin.
Reasons for education
In both men and women, the formation of suspension in the bladder is of the same nature. The only exception is the state of pregnancy in women. The bladder descends due to the increase in size of the uterus, the outflow of urine is impaired. Stagnation occurs and the concentration of salts in urine increases. All this leads to the settling of small particles on the walls of the bladder.
The cause of suspensions is often inflammatory processes in the hollow organ - cystitis. With prolonged disruption of the outflow of urine, irritation of the mucous membrane occurs. The bladder undergoes certain changes - “working hypertrophy” occurs. The muscle walls thicken greatly, which shift the mucous membrane upward, forming thickenings up to 4 cm. Due to the thickening of some areas, others may become thinner. Such conditions are very dangerous and can cause the bladder to burst.
Learn about the causes of orange urine and methods for treating pathological conditions.
The causes of dysmetabolic nephropathy in children and the treatment of pathology are written on this page.
Pathological conditions that provoke the appearance of suspended matter:
- injury to bladder tissue (ruptures, bruises);
- parasitic infections of the genitourinary area;
- consequences of incorrectly performed operations;
- pyelonephritis;
- improper metabolism;
- hormonal imbalance;
- kidney inflammation;
- stones in the kidneys;
- unbalanced diet;
- dehydration.
Pathologies
Sediment in urine occurs against the background of inflammation affecting the bladder, penetration of foreign bodies into this organ, surgical interventions, injuries, and infection with parasites.
Reference! In children, the presence of suspended matter is not necessarily a sign of impairment. This is often a consequence of natural physiological processes. Parents need to ensure that the child does not complain of pain.
An echogenic suspension often forms in people who often suffer from cystitis. This is typical for women. Inflammatory processes occur more often in them due to their anatomical structure.
Clinical picture
The presence of suspension in the bladder is recognized when its concentration is high enough and the following symptoms clearly appear:
- pain and stinging when urinating;
- unexpected urge to go to the toilet;
- the stream of urine during urination is intermittent;
- hematuria;
- the hue, transparency, and smell of urine changes.
With a significant concentration of suspension, a pain syndrome appears, reminiscent of renal colic. These symptoms are not specific to the presence of suspension; they accompany various diseases of the urinary system.
Self-medication is prohibited! Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment after carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of suspended matter forming, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Maintain good hygiene. This will help avoid the development of genitourinary infections. Take a shower after each bowel movement and sexual intercourse, remove excess moisture after procedures and do not wear synthetic underwear.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. Bad habits contribute to the formation of sediment. Proper nutrition and exercise improve metabolism and urine flow.
- Drink enough water. Due to the lack of natural purification, the concentration of substances in urine increases. This is the main risk factor.
- Don't hold back. Suppressing the urge leads to bladder overflow, inflammation and stagnation of urine.
- Do not self-medicate. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics, diuretics, antispasmodics and other drugs can aggravate the situation or cause other symptoms.
If any alarming signs appear, you should consult a doctor. After 40 years, the risk of asymptomatic development of diseases increases, so it is necessary to visit a urologist every six months.
Diagnostics
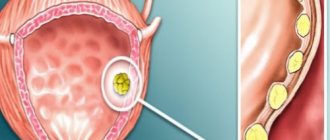
The best way to detect the presence of sediment is an ultrasound of the bladder. The study helps determine the amount of suspension, as well as detect concomitant pathologies of the bladder that affect the general condition of the patient.
In order to determine the composition of the sediment, laboratory tests of urine and blood are carried out. Additionally, the following may be assigned:
- ;
- MRI;
- pyelography.
How is it detected?
Ultrasound examination is most often performed:
- transabdominal;
- transrectal;
- transurethral route.
Usually the first method is used, and the last of them is the most important in diagnostic terms, but is used only in the most critical cases, since it is quite difficult to perform.
During an ultrasound scan, the sonologist detects a flocculent deposit on the monitor screen, which is especially noticeable when the patient’s body position changes. Most often it is located at the posterior wall of the mucous membrane of the bladder. The suspension is hyperechogenic and is perfectly visualized by an ultrasound device. Often different substances combine into conglomerates.
The more intensively the pathology develops, the more mucous strands or formed elements are present in the sediment.
Sometimes the sediment turns white and then becomes difficult to see in photographs. If it can be liquefied, the resulting lumps may have signs of anechoicity. Then they are displayed on the monitor screen as unevenly outlined structures.
Most often, ultrasound allows you to detect the following features of the patient’s condition and the presence of echo suspension:
- number of formations;
- their localization;
- sediment volume;
- particle size;
- contours of emerging structures;
- pathologies of the kidneys and bladder;
- presence of stones;
- diseases of the urinary system;
- condition of neighboring anatomical formations.
In diagnostic terms, ultrasound is truly indispensable for identifying various diseases of the human excretory system, as it very quickly and informatively allows you to find not only stones, but also suggest the presence of the main prerequisites or reasons for their formation.
Effective treatments
Main principles of treatment:
- relieving inflammation;
- cleansing the bladder;
- strengthening the immune system.
The scheme of therapeutic measures will depend on the reasons for the formation of suspension, particle size, their composition, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
If an echogenic fine suspension is detected, which appears as a result of the release of sand from the kidneys or after crushing stones, as a rule, radical treatment methods are not required. Plenty of fluids and a special diet are recommended to facilitate the passage of particles through the urinary tract.
Drug therapy
For pain, it is recommended to take antispasmodics and analgesics:
- Drotaverine;
- No-shpa;
- Spasmalgon;
- Baralgin.
If the cause of the suspension is inflammation of the bladder, the basis of therapy should be antibacterial drugs (Monural, Palin, Nitroxoline and others.).
Additionally, plant-based uroseptics are prescribed:
- Canephron;
- Urolesan;
- Uronephron;
- Phytolysin;
- Cyston.
Among the folk remedies, decoctions of the following plants have anti-inflammatory properties:
- chamomile;
- bearberry;
- birch leaves.
To strengthen the body's defenses, courses of vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed.
Diet and nutrition rules
From the diet you need to remove foods that can act as irritants to the bladder mucosa, as well as those that contribute to the accumulation of salts:
- pickles;
- smoked;
- spices;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- soda;
- alcohol.
What do diffuse kidney changes mean and how to get rid of the pathology? We have the answer!
Learn about what kidney parenchyma tissue consists of and what it is from this article.
Go to the address and read about how and from what to prepare a good diuretic at home.
What treatment is prescribed?
If a stone has formed in the bladder, it is dissolved with the help of drug therapy. If there is no result, they resort to surgical intervention. Main objectives of treatment:
- elimination of symptoms;
- removal of salts and stones from the body;
- strengthening the immune system;
- prevention of relapse.
Sometimes a sediment of microscopic solid crystals or salts is found in the urine - this is a suspension. This is a pathological phenomenon that should not be present in a healthy person. The suspension indicates disorders that exist in the urinary system.
In the bladder, sediment may appear due to injuries, disturbances in the urination process, stagnation, and high salt concentrations. Prolonged presence of sediment in the urine can lead to the formation of sand and stones. If the results of the study show the presence of suspension, it is necessary not to delay eliminating the problem and begin treatment immediately.
Useful tips
To reduce the risk of sediment appearing in the bladder, it is necessary to eliminate as much as possible the influence of provoking factors:
- conduct a medical examination 2 times a year;
- drink enough clean water without impurities;
- eat right, eat less irritating foods;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- move more;
- do not overcool;
- monitor genital hygiene;
- stop inflammation of the urinary organs in a timely manner.
Suspension in the bladder is the first signal of problems in the functioning of the urinary system. If deposits are detected, you need to find out the reasons as soon as possible and take all necessary therapeutic measures. Delaying treatment can result in serious complications for the patient, which will be very difficult to cope with.