The kidneys are the most important organ, responsible for a wide range of functions. They help eliminate toxic substances and waste from the body, normalize water-salt balance, are responsible for the production of certain hormones, and regulate blood pressure.
If at some point the kidneys stop functioning, the human body dies within 3 days. Unfortunately, kidney diseases are very insidious, since during their course, there are generally no pronounced symptoms.
The absence of symptoms leads to the fact that the pathology is diagnosed only at the stage of development of renal failure, when it is almost impossible to cure the disease, therefore, to save the patient’s life, one has to resort to hemodialysis or a kidney transplant from a donor. The worst thing is that kidney diseases affect the younger generation.
This term was coined by radiologists. It means the cessation of the functioning of one of the organs. In other words, when one of the kidneys is unable to perform its immediate duties. The most important thing is that the clinical symptoms of a “silent kidney” are completely absent.
For a long time, all the main work is performed by the second working kidney, but the patient does not even know about it. As a rule, the diagnosis of a “dead kidney” occurs accidentally, during a comprehensive examination.
Kidney stones on ultrasound
Therefore, the question of whether ultrasound shows kidney stones comes to one of the first places in the diagnostic plan.
Urolithiasis is detected by a variety of research methods. It is recorded in almost every hundredth patient, especially often among males. People at particular risk have up to a twenty percent chance of developing kidney stones, and in half of the cases the disease progresses very quickly, and the number of stones increases rapidly.
Most often, pathology is differentiated according to the cause that causes it.
The factors that inevitably lead to the occurrence of urolithiasis are most often:
- infections;
- excess salts in daily consumed water;
- abuse of calcium supplements;
- violation of fluid removal from the urinary system;
- lack of water in the body;
- constant physical inactivity;
- excessive passion for coffee;
- obesity.
The procedure for identifying urolithiasis is very simple and does not take much time.
The patient lies down on a special couch and exposes the body in the area to be examined. It is treated with a special airtight gel, and then the doctor places a sensor on it.
The ultrasound passes to the kidneys, detects the presence of tumors and sends an echo signal to the computer. His image appears on the monitor screen. The specialist analyzes it, takes the necessary photographs and, based on them, makes an accurate diagnosis.
After the procedure is completed, the patient receives a complete study protocol with a detailed transcript of the results and an expert opinion.
Therefore, ultrasound scanning of the kidneys becomes a very informative way to diagnose the disease. It helps to determine the presence of stones in any part of the urinary tract, analyze tissue changes and identify obstruction of the excretory system.
An ultrasound of the kidney shows even a stone that is not detected by X-ray contrast examination. In addition, it visualizes the lower parts of the ureters, which are usually difficult to distinguish with other examination methods.
Ultrasound scanning is also included in the differential diagnosis system to distinguish urolithiasis from other diseases with a similar clinical picture.
The method is used to monitor the ongoing treatment of urolithiasis. It causes less stress on the body than radiography, so it can be performed multiple times.
Causes of kidney necrosis
There are quite a few sources for the development of this pathological process. Any disease that develops in the genitourinary system can cause necrosis of one of the kidneys. In some patients, the kidney may not be functional from birth.
The most common causes of kidney necrosis include:
- Congenital underdevelopment of the kidney.
- Urolithiasis, during which stones form in the area of the urinary system. If a stone blocks the ureter, the kidney stops functioning. In this case, surgical intervention will help save the dysfunctional organ.
- Nephrosclerosis is a pathological condition in which renal tissue is replaced by connective tissue. As this disease progresses, there is an excessive decrease in the size of the kidney, which first leads to a disruption of its functionality, and then to a complete cessation of capacity.
- Glomerulonephritis is a disease during which the kidney glomeruli are damaged.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process that occurs as a result of damage to the genitourinary tract by various infections and bacteria. Acute pyelonephritis can cause deformation of the kidney tissue. If the disease continues for a long time, it can cause kidney failure.
- Hydronephrosis. This disease is characterized by dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces due to impaired outflow of biological fluid. With prolonged progression of this disease, the kidneys begin to atrophy and stop functioning completely.
- Diabetes. This disease is characterized by abnormal blood glucose levels. It occurs due to insufficient production of the hormone insulin, which is formed in the pancreas. During the course of this disease, there is strong pressure on the kidney organ, which, as a result, leads to the development of its failure.
- Hypertension, which is characterized by an increase in blood pressure. If measures aimed at stabilizing blood pressure are not taken for a long time, the performance of the kidneys will begin to decline significantly.
- Polycystic kidney disease is a congenital or acquired pathology. It is characterized by transformation of the renal parenchyma, which causes a progressive decline in kidney function.
- Urogenital tuberculosis. It occurs due to damage to the kidneys, as well as all organs of the urinary system, by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Kidney amyloidosis is a systemic disease during which the deposition of a specific substance (amyloid) occurs. When amyloid is deposited in the kidney tissue, the process of stopping the functioning of the kidneys begins.
- Cancer is the appearance of malignant tumors in the kidney area.
Classification of kidney stones by number and shape
Experts identify multiple
or
single
stones. In addition, two- or three-concrete conglomerates are sometimes found.
They differ in volume and weight. The patient encounters both sand and stones ranging in size from one millimeter to fifteen centimeters, as well as up to two kilograms and above. They affect one or both kidneys.
Stones come in a wide variety of shapes, smooth or crystalline. Sometimes their outlines correspond to the volume of the calyx or pelvis when it fills it entirely.
The location of the stones also differs very noticeably. They can be located in the bladder, ureters or kidneys.
There are different types of stones:
- coral-shaped
; - round
; - multifaceted;
- flat
; - with spikes.
It is also necessary to mention what kind of chemical structure kidney stones are usually seen by a urologist on an ultrasound. Concretions are a combination of various mineral and organic structures. Experts distinguish carbonates, oxalates, struvites, urates, phosphate-ammonium-magnesium formations or phosphates. There are also conglomerates of protein, xanthine, cholesterol, and cystine types.
Diagnostics
It is advisable to determine the type of stones at the examination stage. It is unrealistic to do this at home, but with the help of modern laboratory and instrumental research methods it is quite possible.
Using a general urine test, a doctor can tell a lot about the functioning of the urinary system. The alkaline or acidic reaction of the fluid removed from the body is of great importance (with acidification there is a risk of oxalate and urate stones, with alkalization - calcifications, phosphate and struvite stones).
It is important to assess the urinary tract excretion of protein, leukocytes, red blood cells and bacteria. The determination of these elements indicates inflammatory changes that usually accompany kidney stones. It is imperative to evaluate the chemical composition of urinary sediment. Minerals and their salts will clearly indicate the possible structure of the stone.
With an x-ray examination, the doctor can presumably determine the composition of the stone. All stones containing calcium salts (calcifications, oxalates, phosphates, struvites) give a clearly visible shadow on an x-ray. X-ray negative stones (protein, urate, xanthine, cystine) are not visible on the images. To identify them, special radiopaque techniques are used.
Using ultrasound scanning, you can quickly and safely detect stones invisible to x-rays and estimate the size of the renal formation. However, ultrasound will not help determine the composition of the stones.
Assuming the chemical composition, structure and size of the stones, the doctor will prescribe effective methods of conservative therapy or suggest surgical treatment. Subsequently, correction of metabolic disorders and adherence to diet will prevent the recurrence of kidney stones.
Ultrasound diagnosis of urolithiasis
The image taken during the procedure can tell the doctor a lot.
Nowadays, ultrasound scanning is the method of choice for diagnosing urolithiasis. It is much more preferable than X-ray contrast examination, which until recently became the main way to detect the presence of kidney stones.
Ultrasound is a more reliable and efficient method. Moreover, it allows you to visualize some organic formations that are not captured by alternative methods.
Ultrasound scanning is an inexpensive and convenient examination for diagnosing urolithiasis. The photo taken during the procedure allows you to record:
In addition, the echogram makes it possible to see the smallest formations and even sand. Such data is very important, since urolithiasis not diagnosed in time can lead to the most severe consequences. Sometimes an infectious agent joins with the development of various dangerous diseases, the migration of stones along the excretory tract with the formation of their obstruction, and the occurrence of colic. Sometimes kidney failure or swelling of the organ develops.
Therefore, timely detection of urolithiasis can save the patient’s life.
Ultrasound examination can already detect microlithiasis, which represents the first stage of the pathology. The formations are still very small and sometimes do not cause clear symptoms. But their traces are already detected in the laboratory in the secreted liquid. Subsequently, sand is formed, from which larger stones are subsequently formed. All this has a pronounced echogenicity and is quickly detected by ultrasound equipment.
Microliths on a sonogram are defined as formations with an increased echo structure and have an elongated shape. Sometimes they have an acoustic hypoechoic shadow.
From time to time, symptoms of prominent pyramids and changes in the renal sinus are also detected. In addition, the study allows the specialist to detect diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the organ in the form of hyper- or hypoechoic areas.
Therefore, the question of whether kidney stones are visible on ultrasound can definitely give a positive answer. In those rare cases when they are not detected by sensors, the diagnosis is made by the blocked lumen of the urinary ducts.
Due to the absence of any harm to the body, ultrasound of the kidneys has no contraindications. To pass it, you need to follow a certain diet, as well as take enough fluid.
It is difficult, and therefore the patient suffers not only from pain, but also from uncertainty. You can read the results of the study yourself only if you have a good understanding of medical terms and standards.
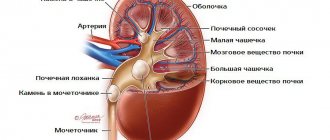
Kidneys perform an important job in the human body. Blood passing through this organ is cleansed, and harmful substances are eliminated from the body along with urine. Blood and plasma pass through the Shumlyansky-Bowman capsule and are separated into blood and primary urine. With the further passage of fluid through the body of the kidney, some of the nutrients are again mixed with the blood and distributed throughout the body, and all filtered substances, such as creatine and uric acid, enter the ureters and are excreted from the human body. In just one day, all the blood in the body passes through the kidneys up to 100 times, and up to 150 liters of primary urine and only about one and a half liters of secondary urine are formed from it.
There are usually two kidneys in the body.
They are located symmetrically near the posterior abdominal wall, closer to the lumbar region, with the right kidney usually 1-2 cm lower than the left.
The upper edge of the right kidney is adjacent to the liver, and the apex of the left kidney is at the level of the 11th rib.
In rare cases, the location of organs in the body may be changed, the kidney may wander, and even more rarely, there may be more or less than two organs. Patients with such pathologies are regularly observed by a doctor. The normal size of the organ is up to 12 cm in length and up to 6 in width, and the standard weight does not exceed 200 grams. But in the presence of pathologies or congenital features of a person’s physique, the size of the organs may change. Whether the size is a pathology or a variant of the norm - only a doctor can say after examining the whole body.
Nephrologists treat kidney diseases. A physician (or pediatrician) can refer a patient to them if the patient complains of discomfort when urinating, lower back pain, or if surgical intervention in the body is necessary, for example, a kidney transplant.
What are the indications for ultrasound diagnostics of the kidneys:
- Renal failure, acute and chronic;
- Suspicion of the presence of stones or sand in the kidneys;
- Injuries and bruises of the organ;
- Tumors, cysts and swelling of the kidneys;
- Presence of gas in the kidneys;
- Pathological changes in the ureters and urinary tract, bladder;
- Successfully performed transplantation or preparation for it.
In addition, if the patient’s urine has an increased content of creatine, red blood cells, uric acid or other substances, then the doctor has reason to suspect a hidden inflammatory process, pyelonephritis, and undetected diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract. They often occur secretly in the patient’s body, and are considered grounds for additional diagnostic procedures that will help identify the disease.
Treatment
Any patient who has been diagnosed with this should understand that it is impossible to “make” this organ work. However, there are always exceptions. A “dead kidney” can only be cured if it has lost its functions fairly recently.
Surgical treatment can be a panacea for a failing kidney. For example, an operation can bring a positive result if a “silent kidney” was caused by a blockage of the ureter with a stone or an injury that led to a violation of the integrity of the organ.
When the kidney does not work for a long time, all treatment methods will be simply useless. In this case, the doctor either decides to remove it, or takes a wait-and-see approach, during which he checks how the non-functioning organ “behaves”.
Kidney removal is done in several ways:
- through an incision made in the anterior abdominal wall or in the lumbar region;
- through laparoscopy, which allows you to eliminate the damaged organ through several punctures made on the anterior abdominal wall.
When a patient is diagnosed with two silent organs, the only chance for him to survive is to use hemodialysis or undergo surgery for a kidney transplant.
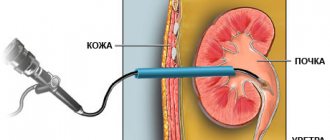
How is a kidney ultrasound performed?
Ultrasound of the kidneys can often be difficult due to the position of this organ.
Since ultrasound passes freely through soft tissues, but is scattered in the air and does not penetrate bones, it is possible to examine the kidneys in detail only from one side.
Therefore, during diagnosis, the doctor asks the patient to turn alternately on his stomach, back, and sides.
This allows you to show organs from all sides in more detail, and identify even subtle pathological changes. In order for the study to be accurate, it must be carefully prepared. First of all, before an ultrasound scan of the kidneys, you should not eat foods that cause gas formation, since ultrasound will not penetrate through the gas-filled intestines and the diagnosis will be uninformative.
Before an ultrasound, you should not eat cabbage, legumes, brown bread, drink beer or carbonated drinks. It is recommended to follow the diet for three days. If the patient suffers from constipation, he is recommended to cleanse the intestines, take a laxative or do an enema before the study.
In addition, before examining the bladder, it is necessary to drink about half a liter of liquid 1.5-2 hours in order to keep the bladder full.
You should not take medications or tonics or vasoconstrictors before examining the renal vessels. During the diagnosis, the patient lies on the couch, on his back. The laboratory technician applies the gel to the skin to better glide the sensor and remove air. A transducer that receives reflected ultrasound moves across the skin of the abdomen, creating an accurate black-and-white image of the kidney on a screen in front of the doctor. It is forbidden to perform an ultrasound while standing, as incorrect positioning of the patient may affect the accuracy of the diagnosis and not show the results. The only option in which an ultrasound can be performed standing is if the patient is not feeling well and cannot lie down.
Diagnosis is carried out in a similar way when the patient turns on his back, on his right and left side.
Only a comprehensive examination allows one to identify disease or pathological changes in the structure of the kidneys and genitourinary system, and name the cause of these changes.
What does a kidney ultrasound show?
Ultrasound diagnostics is considered one of the most accurate research methods that currently exist, and therefore if pathological changes are detected on ultrasound, then with a high degree of probability it can be said that the diagnosis is correct. But only a doctor can identify pathological changes in the system and explain their nature.
What does an ultrasound show:
Kidney sizes. This is one of the first parameters that the doctor and laboratory technician pay attention to. Standard sizes are as follows:
- 100-200 mm length;
- 50-60 mm width;
- 30-50 mm thickness;
- The thickness of the external tissue, parenchyma – up to 25 mm;
- Capsule size – up to 1.5 mm;
- The total weight of one organ is up to 200 grams.
If the size of the kidneys is outside the normal range, the doctor can diagnose a tumor, tissue hypoplasia, or identify other pathology. Most often, the kidneys enlarge in the presence of inflammatory processes, and the decrease in tissue is associated with the patient’s age, and the parenchymal layer usually decreases.
Tumors and cysts most often occur in the parenchyma. Due to its structure, this tissue is looser, softer, and subject to changes, including pathological ones. The opposite effect may also occur: if one kidney was removed, the parenchymal tissue of the other will develop twice as strong.
Diagnostic methods
To make sure that severe discomfort is caused by the movement of a stone along the ureter, the doctor will conduct an initial examination. It involves palpation.
Then the patient will be prescribed more accurate studies:
urine analysis, determining protein, salts, pus, blood cells; culture; urine analysis to study its acidity; x-ray examination; blood test; urography; ultrasound of the urinary system; CT scan of the kidneys; radioisotope diagnostics.
A complex of such examinations makes it possible to determine the location of the stone, identify the sources of the disease and select adequate therapy.
What is the structure of kidney tissue?
In the normal state, the parenchyma is heterogeneous, and lighter and darker areas are visible on ultrasound. This is due to the structure of the parenchymal tissue itself, which acts as a filter for impurities contained in the blood. The parenchyma consists of pyramids, the inner parts of the tissue adjacent to the renal calyces, and the outer layer, which on ultrasound appears as less dense, light-colored tissue.
If pathological changes are present in the organ system, the parenchymal tissue will be changed, enlarged, or heterogeneous in whole or in part. The structure of the tissue is also related to the fact that cysts and tumors most often arise in this area of the organ, and during ultrasound diagnostics, the first changes, signs and symptoms of the disease can be identified by the condition of the parenchyma.
The outlines of the kidneys themselves should be smooth and clear. A blurred boundary, which is detected on ultrasound, signals the development of inflammation in the tissues and requires additional diagnostics.
Internal structure of the kidneys
The pyelocaliceal apparatus, which is responsible for the accumulation and removal of harmful substances from the human body. It is here that secondary urine accumulates, which will soon be removed from the body through the ureters and bladder.
The calyces are responsible for storing urine. There can be up to 10 of them inside one organ, 4-6 small and 3-4 large. Large calyxes are adjacent to the pelvis, cavities where urine accumulates. When the pelvis is partially filled, the muscle fibers surrounding the kidney contract and the accumulated urine is discharged into the bladder through the ureter.
When performing ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor examines the internal cavities especially carefully. The most common types of diagnosis include:
- Urolithiasis, that is, improper functioning of the body, due to which salts are deposited in the kidneys, forming stones and sand. This pathology is dangerous because the stone blocks the flow of urine to the ureter, and excess fluid compresses the parenchymal tissue, which atrophies from prolonged compression. In addition, urolithiasis gives the patient a lot of anxiety and discomfort;
- The development of tumors and cysts, which can also compress tissues and blood vessels and disrupt the functioning of individual parts of the kidney or the organ as a whole;
- Narrowing or curvature of the ureter, which leads to delayed urine flow and improper functioning of the entire system. This pathology leads to stagnation of fluid in the pelvis and accumulation of harmful substances in the body.
The ureter itself is examined no less carefully. It may look on the monitor screen like a tube less than 1 cm in diameter and up to 30 cm long. It is hollow inside, which means that on an ultrasound this organ will appear as a tube with light walls and a dark middle. If the ureter is clogged, for example, due to urolithiasis, when a stone comes out, then during ultrasound diagnostics a light spot will be noticeable.
One of the most common diseases of the kidneys and urinary system is pyelonephritis. This disease is characterized by constant pain in the lower back, high body temperature of the patient, painful urination, and an increase in white blood cells in blood and urine tests. There are other similar signs by which a doctor can make a diagnosis, but ultrasound will be one of the main methods for diagnosing this disease.
The term “pyelonephritis” most often refers to any inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and bladder. But, strictly speaking, pyelonephritis is an inflammation caused by bacteria and affecting the pelvis, calyces or parenchyma. During an ultrasound, an increase or change in the echogenicity of these organs can be detected, and based on the results of ultrasound diagnostics and blood tests, the doctor can prescribe treatment.
When the ultrasound diagnosis is completed, the patient receives his medical card with the results of the examination and tests. Based on the test data, the nephrologist will be able to make the most accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment that is most suitable for the patient. Blood and urine tests should be performed before a kidney ultrasound to obtain more accurate results.
It is equally important to perform an ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy, if the woman previously had problems with them. Since while a woman is carrying a child, her body weight and blood volume increases, and the load on the body increases, the kidneys suffer from this first of all. In addition, during the third trimester, all organs are compressed, which reduces the volume of the kidneys.
If there are complaints, the doctor usually refers the woman to an appointment with a nephrologist and an ultrasound scan, prescribes a diet, which allows her to notice the disease in time or simply reduce the load on the kidneys.
Regular examination of the kidneys and urinary system allows early detection of pathological changes, showing the onset of the disease and explaining its cause. With regular examination and monitoring of your health, even a serious disease can be identified and treated at an early stage.
Urolithiasis is the formation of sand and stones in the kidneys, a consequence of an impaired water-salt balance. According to statistics, more than 15% of the world's population suffers from kidney disease. But according to the same statistics, urolithiasis can be successfully treated. Modern medicine is developing rapidly and today there are several methods for diagnosing the disease.
An x-ray of kidney stones will provide the necessary information about a person’s health status. This is one of the least expensive, but quite effective methods to identify disorders of the body even at the initial stages of the disease. The vast majority of public medical institutions use two methods for detecting stones: using a plain X-ray and an X-ray with contrast.
What is kidney duplication and why does such an anomaly occur?
Double kidney is the most common defect of the urinary system, which develops during the intrauterine formation of the child’s internal organs.
According to statistics, this anomaly is much more common in girls than in boys.
What happens during pathology
Bud doubling is the formation of an additional bud, but it is not located separately, but is connected to the main one. Moreover, each part has an autonomous blood circulation, and sometimes a separate ureter.
In 85% of cases, this pathology affects only one organ, but there are also cases of bilateral anomalies.
Depending on the structure of the affected organ, a distinction is made between complete and incomplete doubling of the kidney.
Complete bifurcation implies the presence of two pyelocaliceal systems with two ureters that form two orifices in the bladder, or open as diverticula into the vagina or urethra.
Incomplete duplication of the kidney is much more common.
In this case, only one pyelocaliceal system can be formed, the second may also be present, but it will be underdeveloped.
If such an organ has two pelvises, then at the exit from the kidney there are also two ureters, but they merge into one, which connects to the bladder.
With this anomaly, the kidney is significantly increased in size. The double structure of the kidney is asymmetrical, the upper part is much less developed.
Sometimes the upper half is either symmetrical or larger than the lower half, but such cases are extremely rare.
Causes
Factors that contribute to the formation of such a congenital pathology are:
- genetic predisposition, that is, cases of a similar disease on the maternal or paternal side;
- lifestyle of a pregnant woman, drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- radiation exposure to the fetus;
- taking teratogenic (that is, negatively affecting the child) medications;
- avitaminosis;
- living in an ecologically unfavorable area.
Symptoms
Kidney duplication is often not accompanied by pronounced clinical manifestations. Moreover, a person can live almost to old age without even knowing about his pathology.
The main symptoms are provided by diseases that appear against the background of this congenital anomaly.
Only if the ureter is connected to the vagina or urethra can uncontrolled urination be observed, regardless of the urge to empty the bladder.
A double kidney is more susceptible to bacterial infections, urolithiasis, and very often suffers from impaired urodynamics - in this case, hydronephrosis often develops.
Bacterial inflammation can be expressed in the form of pyelonephritis (almost every fifth case of doubling) or tuberculosis (develops in 34% of patients with the pulmonary form of this disease).
Pyelonephritis is manifested by an increase in temperature to fairly high numbers (38 - 38.5º), aching pain in the lower back, which intensifies when tapping in this area with the edge of the palm. The urine may become cloudy and sediment may appear in the form of flakes.
Tuberculosis is much more dangerous. Symptoms of this disease appear when atrophy of kidney tissue and cells occurs.
Therefore, people with double kidneys and lungs affected by Koch's bacillus should pay special attention to the organs of the urinary system.
Urolithiasis may be asymptomatic until the stone begins to move through the ureter.
Then the doubling of the kidney is accompanied by the classic symptoms of renal colic: sharp unbearable pain, which is paroxysmal in nature. The pain syndrome is accompanied by fever, nausea or vomiting, and increased sweating.
If the size of the stones is small, then their movement along the urinary tract is accompanied by an increased urge to urinate, pain and burning during urination.
Hydronephrosis is an increase in the size of the renal collecting system. It develops in approximately 10–15% of cases of kidney duplication. It can occur for a long time without pronounced clinical manifestations.
Sometimes there may be a dull aching pain in the lumbar region. This disease is dangerous due to atrophy and irreversible death of kidney cells. As a result, there is a high risk of developing chronic renal failure.
Diagnostics
Previously, kidney duplication could only be detected by chance during examination of other nearby organs or during a preventive examination.
Currently, general screenings are required for a child in the first year of life, which includes an ultrasound examination of the kidneys. Therefore, such pathology is detected during this examination.
In addition, it is possible to distinguish such a pathology on ultrasound in the second half of pregnancy. Particular attention is paid to the intrauterine examination of the child if, for the above reasons, there is a risk of kidney doubling.
Once a diagnosis has been made, the following is prescribed for additional examination:
- Doppler ultrasound, which evaluates renal blood flow;
- excretory urography. This test is performed using a contrast agent that is excreted in the urine. Its movement through the kidneys and urinary tract is monitored on a series of x-rays;
- cystoscopy. This is an endoscopic examination of the inner surface of the bladder. This is how the number of ureteric orifices is determined;
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, due to their high accuracy and the ability to obtain images in several planes, are considered the most effective.
Treatment
As such, there is no treatment for kidney duplication. Symptomatic treatment of emerging complications is carried out. For bacterial infections, antibacterial and immunostrengthening drugs are prescribed.
Facilitation of the passage of stones through the urinary tract is ensured by taking antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Diuretics are used to remove small crystals and sand.
In case of complications of the condition, danger of developing kidney failure, or constantly recurring bacterial inflammation, surgery is performed.
During surgery, the affected organ is resected while preserving its normal structure as much as possible.
Survey X-ray
This is an x-ray of the abdominal cavity, which allows you to detect the presence of stones without the use of a special contrast agent. The method is successfully used to identify radiopaque stones. Kidney stones are a pathological condition that develops due to disturbances in the properties of urine. Sometimes they are not visible even on a plain X-ray.
Superposition of the shadow of the stone on the shadow of the vertebrae prevents diagnosis. Also, the formation of gases in the intestinal cavity can obstruct vision, which will not allow the medical professional to see the presence of pathology. There are a number of urological phenomena that mimic the presence of a calculus. These include calcified lymph nodes or the presence of gallstones. Among the positive aspects of this diagnostic method are:
- the ability to establish the presence of stones consisting of calcium in the patient’s body;
- low cost of research;
- accessibility, x-rays can be taken at any medical institution.
Characteristics of the pathology
Urolithiasis is a fairly common disease. Its appearance is provoked by many different factors. Most often, pathology occurs against the background of poor nutrition and unsatisfactory quality of drinking water. Initially, stones form in the kidneys.
Most patients do not even suspect the presence of stones for a long period of time. After all, signs of the disease do not appear immediately. Meanwhile, the stones “grow” in the kidneys. And as a result of certain factors, stones may appear in the ureter.
What are the symptoms in women? This is, first of all, severe pain. It indicates renal colic (indicates the sinking of a stone into the ureter). In such situations, you should immediately consult a doctor.
X-ray of the kidneys with contrast
Kidney X-ray with contrast is the most popular diagnostic method today. The medical worker has the opportunity to obtain not only information about the content of the calculus in the organ. A nephrologist can determine the size of the stone and its exact location (this can be seen in the photo), and obtain information about the condition of the urinary system.
It is not difficult to identify kidney stones on an X-ray with contrast; you need to properly prepare for the examination. An iodine-containing substance is injected into the human body through a vein. After the contrast agent enters the urinary system, the medical professional takes several photographs of the damaged organ. The advantages of this method are obvious:
- high sensitivity of X-ray with contrast;
- will make it possible to determine the exact dimensions of the calculus;
- Kidney stones are different from other radiopaque particles.
Attention! The main disadvantage of kidney x-rays with contrast is the occurrence of an allergic reaction to the iodine-containing composition. It is recommended to first apply a little iodine to the skin on the elbow. If there is no itching or irritation, you can safely use contrast.
Laboratory research
The primary stage of research after examining the patient will be laboratory tests. Their results provide the doctor with information about the functional functioning of the kidneys and determine the presence of a pathological process. Laboratory methods are safe and highly accurate. The result can be obtained in a fairly short period of time.
Return to contents
One of the first things patients suspect of renal pathology is a urine test. It does not require preliminary preparation or financial investment. Based on its results, you can immediately find out about a problem in the functioning of the kidneys. The patient must submit:
- morning urine analysis;
- 24-hour urine analysis.
The main indicator is red blood cells in the urine. An increased content of red blood cells accompanies not only urolithiasis. But the doctor, having studied the history of the disease, comparing it with the results of the analysis, can easily make a presumptive diagnosis. In addition to red blood cells, salt crystals, proteins, and bacteria are detected in the urine. If you have kidney stones, their number will be overestimated. Studying the chemical composition of salts will tell you about the type of stone.
Return to contents
More often, a general blood test in patients shows normal results, but it must be taken. During an exacerbation, an increase in leukocytes is observed. Their percentage shifts to the left and this indicates the development of the inflammatory process. In addition, pay attention to changes in ESR and the manifestation of anemia. Based on these indicators, we can conclude that renal function is impaired.
Return to contents
What stones are visible on x-ray?
Doctors note that not all kidney stones are visible on x-rays. Calcium-containing compounds are amenable to diagnosis. Among them are oxalates and phosphates. Oxalates have a fairly dense structure, the color varies from dark gray to black. Stones are almost impossible to dissolve and the use of magnesium preparations is more of a preventive measure than a therapeutic measure. They are formed due to an excess of ascorbic acid, vitamin B6 deficiency and diseases of the small intestine.
Phosphates have a homogeneous structure, smooth and white or slightly gray in color, consisting of calcium salts of phosphoric acid. They are easy to spot in a photo; they are impressive in size and grow quite quickly. Phosphates appear in human kidneys due to a sedentary lifestyle, deficiency of vitamins A, E and D, and metabolic disorders.
Unfortunately, not all types of stones can be detected using x-rays. Uric acid or cystine stones are not visible on imaging. In such cases, the nephrologist will prescribe another diagnostic method. This may include ultrasound, computed tomography, renal angiography, retrograde pyelography, or magnetic resonance imaging.
Dr. Litza is a board-certified family physician in Wisconsin. She is a practicing physician and has been teaching for 13 years. She graduated from the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health in 1998.
Number of sources used in this article: . You will find a list of them at the bottom of the page.
The diagnosis of renal colic (kidney stones) will depend on the symptoms and signs present, as well as the results of diagnostic tests. If you are diagnosed with obstruction due to kidney stones, you will need outpatient treatment.
Drug treatment
How to remove a stone from the ureter?
Conservative expectant therapy includes:
Prescription of urolitic drugs. Medicines "Nifedipine" or "Tamsulosin" speed up the passage of stones. The use of painkillers and antispasmodics. The patient is often recommended NSAIDs, such as Ibuprofen, Naproxen. The woman is prescribed physiotherapy and special physical therapy.
In addition, the doctor recommends that the patient reconsider her diet.
Steps
Part 1
Symptoms and signs
- Notice the pain.
One of the defining signs of kidney stones is the presence of severe pain when they get stuck and form a blockage. The pain usually occurs in the side (between the ribs and pelvis). It can also occur in the lower abdomen and eventually move closer to the groin.
- Pain due to kidney stones comes in “waves”: at first you feel better, and then severe pain occurs and everything happens again.
- As a rule, people find it painful to sit and lie down, but walking can relieve some of the pain.
- Beware of blood in your urine.
Blood in the urine is another telltale sign of kidney stones. However, it is worth mentioning that blood may or may not be visible.
- If it is visible, your urine will be pinkish or reddish in color.
If you don't see any changes in the color of your urine but are experiencing pain and other symptoms of kidney stones, your doctor may test your urine and look for microscopic traces of blood in it that might not be visible to the naked eye.
In addition to blood in the urine, many people with kidney stones have other urinary tract symptoms. These include:
- Urgent need to relieve yourself
Pain when urinating
The likelihood of having kidney stones increases according to risk factors such as:
- The patient has a history of kidney stones
Presence of kidney stones in the patient's relatives in the past
Part 2
Further examination
- Take a general urine test.
If your doctor suspects you have kidney stones, he will ask you to take a urine test, which will evaluate various components of your urine. If the results indicate the presence of kidney stones, the doctor will move on to specific imaging tests to look for the kidney stones that are causing the blockage and pain.
Get a CT scan.
A specialized CT scan (spiral CT without contrast agent) is a visual diagnostic method that is used to diagnose kidney stones. If you do have kidney stones and they are causing a blockage in your urinary tract, it can help you get the best picture of them. It also allows the doctor to confirm the diagnosis of renal colic,
- A CT scan is carried out in the radiology department, within a few hours of your arrival (if your case is considered "urgent", a CT scan can be done immediately without having to wait in line).
During the scan, you will lie in a large, round machine for several minutes while it takes pictures.
- There is enough space in a CT scanner (unlike an MRI), so cases of claustrophobia are quite rare.
- While the device is taking pictures, you will not feel anything. The images are obtained using radiation, so the entire procedure is completely painless.
- Ask your doctor about ultrasound.
If you want to limit your exposure to radiation (for example, if you are a child or pregnant), your doctor may recommend an ultrasound instead of a CT scan. Although ultrasound is not as reliable as helical CT without contrast for detecting and diagnosing kidney stones, it can detect them in most cases and is usually sufficient to make the diagnosis.
- If the diagnosis is still inaccurate, after you undergo an ultrasound, your doctor will advise you to undergo a CT scan.
Part 3
Treatment of kidney stones
- Determine if you can be treated at home.
If you have severe pain and/or nausea, you will be treated in a hospital. You should also be treated as an outpatient if you have a fever due to an infection that can enter the bloodstream (and be fatal if not treated quickly). If all this does not apply to you, treatment can take place at home under the careful guidance of a doctor:
- Oral pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) are often prescribed to relieve pain if needed.
Doctors also often prescribe tamsulosin to increase the rate at which kidney stones pass.
- The doctor may ask you to strain your urine and fish out the stones so you can collect them and bring them to him for examination.
- Your doctor will figure out what the stones are made of (oxalate, uric acid, calcium, etc.) and can come up with preventive measures for you that will reduce your risk of developing kidney stones in the future.
- Take painkillers.
If your pain is severe, your doctor will likely give you a narcotic like codeine or morphine to relieve your symptoms. The pain from kidney stones can be very debilitating, so take pain medication to ease your pain.
Ask your doctor to prescribe anti-nausea medications for you.
If you have severe nausea and/or vomiting, you may be prescribed anti-nausea medications (antiemetics), such as ondansetron (Zofran) and dimenhydrinate (Gravol).
The Internet is replete with a huge variety of recipes: they say you can dissolve the stone with fir oil, mineral water, sour juices, and even just plain water. Which of this is true and which is not, says Evgeny Shpot, urologist, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the department of urology of the medical faculty of the First Moscow State Medical University. I. M. Sechenova
Litholytic therapy - that is, the ureter with the help of medications - is most effective in patients with urate stones. The basis of such stones is uric acid salts.
How much does a kidney transplant cost in Russia?
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
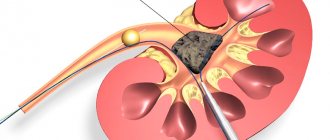
Until recently, a person with kidney failure simply slowly faded away. Now an organ transplant gives the patient years of a full life. Kidney transplantation in Russia and its cost are important issues that concern the patient. This is a complex operation that must be performed by experienced specialists, but often for Russian citizens the problem is not in finding transplant specialists, but in the difficulty of finding a donor kidney.
Kidney transplantation in the Russian Federation
Kidney transplant is the most common operation in transplantology. Such procedures account for 50% of all organ transplants. Every year, 30 thousand such operations are performed worldwide, and five-year patient survival is achieved in 4/5 cases. But the number of patients who need a kidney transplant is significantly greater than the number of transplantations performed. This is mainly due to the shortage of donor organs.
According to Russian law, donation is free of charge, and the sale of organs is illegal. A kidney for transplantation is selected subject to several conditions:
- it must be compatible with the patient’s body;
- the donor is related to the recipient by family relationship;
- there is a person’s consent to the use of his organs after death.
Any citizen of Russia can count on free provision of a donor organ and payment of all medical expenses. There is no queue for organs in the Russian Federation, but there is a waiting list. After adding a patient to this list, he must be ready to rush to the hospital at any time.
The wait for a suitable organ can range from a couple of days to several years.
In fact, most patients die without waiting for surgery, so wealthier patients prefer to go to private medical centers.
Factors influencing the cost of surgery
In private medical centers, the cost of transplantation may fluctuate. This will depend on the following factors:
- type of medical facility;
- who is the donor;
- urgency of the operation and the patient's condition.
How much a transplant costs also depends on the experience of the specialist performing the operation. When we are talking about a transplantologist with many years of experience, the cost of the operation increases by 30%, or even by half. Therefore, there is no clear answer to the question of how much a kidney transplant costs in Russia.
Often the cost varies from 30 to 100 thousand dollars.
It has already been mentioned that the trade in organs is officially prohibited in the Russian Federation. But if the sale of a kidney were allowed (as in Iran), then one could get from 10 to 200 thousand dollars for it, that is, from 600 thousand to 15 million rubles. In fact, organs are sold on the black market, where the cost of such a “good” is much lower. The following factors influence pricing:
- state of the organ;
- blood type (its rarity);
- lifestyle and bad habits of the donor;
- predisposition to allergies and intolerance to certain drugs.
And although there is no official data on how much this organ costs in the Russian Federation, according to some sources, it will cost the buyer 10-100 thousand dollars, but the donor himself often receives 2-20 thousand dollars. The price is significantly influenced by the specific location. So, in the provinces you can buy a kidney for just 30-40 thousand rubles.
Indications for transplantation
As a rule, a transplant is necessary at the end stage of renal failure, when both organs (or a single kidney) can no longer cleanse the blood. Nitrogenous waste accumulates in the body, poisoning the body. Without urgent correction, this phenomenon leads to death. But no drugs can slow down the development of kidney failure.
Pathology is provoked by the following diseases:
- chronic pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis;
- congenital kidney pathologies;
- tumor formations;
- urolithiasis disease;
- nephropathy in diabetes;
- injuries.
For these indications, kidney transplantation is performed first on children, since hemodialysis is very difficult for them.
Contraindications for organ transplantation
When a depressing diagnosis is announced and a kidney transplant is planned, the patient is given a list of examinations to be added to the waiting list. During diagnosis, contraindications for organ transplantation are excluded:
- AIDS;
- drug addiction;
- active hepatitis;
- psychical deviations;
- active form of tuberculosis;
- malignant formations;
- diseases with a lifespan of up to 2 years;
- severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- respiratory failure due to chronic lung diseases.
Preparation for transplantation
In order to identify contraindications in a timely manner, a set of examinations is carried out:
- fibrogastroscopy;
- coronary angiography;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- laboratory tests of urine and blood;
- HLA histocompatibility typing;
- X-ray of the lungs and study of their functionality.
While waiting for a transplant, the person undergoes hemodialysis regularly. He has to do tests for hidden infections, as well as vaccinations. Since an invitation to surgery can arrive at any time, you should always be prepared for it. After the notification, you need to refrain from eating and quickly get to the medical center.
Pros of an organ from a living donor
Waiting for a donor organ is a long process. Often, kidneys come from people who have been declared brain dead, mostly those who died in car accidents. But the practice of organ transplantation from a living donor is becoming more widespread. This is explained by the following factors:
- planned intervention;
- fewer complications;
- greater likelihood of survival;
- thorough examination of the donor;
- decreasing the duration of cold ischemia;
- no long wait;
- the likelihood of transplantation before the start of hemodialysis;
- increased life expectancy after surgery.
A donor can be any person aged 18-65 years who has given consent to remove a kidney. He should not have somatic or mental pathologies and arterial hypertension. The doctor must ensure normal kidney function, since the donor will have to live with one organ in the future.
Types of transplantation
Kidney transplantation in Russia and abroad uses 2 main methods:
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
- orthotopic;
- heterotopic.
During an orthotopic transplant, a kidney is implanted in its typical location, replacing a non-functional one. During the operation, the renal arteries and veins are sutured to the patient’s vessels. But such interventions are rarely performed due to many side effects.
In a situation with heterotopic surgery, the kidney is sutured in an uncharacteristic place (iliac zone). During such an operation, the vessels of the organ are connected to the iliac vessels, and only after the blood supply to the kidney is restored, the ureter is sutured into the urinary reservoir.
The latter option is much easier, because the iliac vessels are larger than the renal vessels and access to them is not difficult. The transplant lasts 3-4 hours. Time is of the essence when performing a cadaveric organ transplant. If an organ is being transplanted from a living donor, two teams of transplant surgeons work simultaneously in the operating room.
How to tell the difference?
When diagnosing, urate stones are clearly visible on ultrasound, but, unlike other types of stones, they are not visible on X-ray, which is due to their low density. You can accurately determine the composition of the stone by examining a stone that has previously passed or was removed during surgery. An analysis that confirms the presence of urate stones is pH testing, in which the acidity of the urine is below normal. Sometimes, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a computed tomogram - with the help of this study, you can find out the exact density of the stone. But this study is not necessary: if there is a stone on an ultrasound, but not on an x-ray, and a shift in urine pH toward acidic is repeatedly detected, then you can try to dissolve it.
| There is no sand in the kidneys | |
| We diagnose nephrolithiasis (urolithiasis) only if the detected stone has a dense structure, is more than 0.5 cm in diameter and has an acoustic track (that is, ultrasound does not pass through it). If the “something” in the kidney does not fit this description, it is not stones. And there is no diagnosis of “sand in the kidneys”. Small “grains of sand” detected on ultrasound may turn out to be simply vessels, compacted fiber or encrusted renal papillae. If you were told about “sand” at the clinic, do not rush to take diuretics. Monitor the condition of your kidneys - do an ultrasound every six months. In this way, you can determine over time whether the stone is growing, or whether your kidney just always looks like that on an ultrasound. | |
Often, urate stones occur in patients with impaired purine metabolism, for example, with gout, so all patients with suspected urate nephrolithiasis must determine the level of uric acid in the blood.
Causes of the disease
Ureteral calculi are formed from various substances:
uric acid; cystine; calcium phosphate; struvite.
Most often, the process of stone formation is influenced by the following factors:
Genetic predisposition. Doctors say that the disease is more often diagnosed in patients who have a family history of urolithiasis. Impaired outflow, stagnation of urine. The development of the disease may be based on congenital pathologies. Most often, the disease is provoked by narrowed ureters in women, their underdevelopment, kinks or abnormalities of the bladder. Diseases of the urinary tract in a chronic form. Infectious diseases can lead to the development of pathology. For example, pyelonephritis. Impaired metabolism. Acquired or congenital ailments may be accompanied by the penetration of lithogenic substances into the urine - calcium (if hyperparathyroidism is diagnosed), urates (in the case of gout). Diseases of the digestive system. If the absorption function is impaired, stones may form. Use of medications. Some medications can lead to the development of the disease. For example, such consequences are provoked by uroseptics from the nitrofuran category.
Doctors say that uroliths often form in women living in hot and dry climates. High-calorie foods rich in animal proteins can trigger the development of the disease.
Dreams of balance
To dissolve urate stone, you need to lower the level of uric acid - that is, you need to increase the acid-base balance (pH): so that the urine changes from acidic to slightly acidic or alkaline. For this purpose, citrate preparations are prescribed - alkaline drinking. It takes at least 2 months to dissolve urate stones, and depending on the size of the stone, treatment can take up to six months. Therefore, for large urate stones (2 cm or more), it is preferable to first perform a session of remote or contact endoscopic crushing, followed by dissolution of the remaining small fragments. It is important to combine such treatment with a properly selected diet and plenty of fluids.
Unfortunately, we most often come to people whose stone has “gone”, that is, it has traveled from the kidney through the ureter. In this case, there is no longer time for dissolution. After all, the movement of a stone can be accompanied by renal colic and complicated by obstructive pyelonephritis. It is necessary to take emergency measures - to remove the stone in one way or another, and, if possible, dissolve the remaining ones.