Acute urinary retention (ICD-10 code, R33) is an emergency condition characterized by the inability to drain urine from a full bladder. This disorder is a companion to a variety of diseases. This condition was included in the international register a long time ago, but not everything is known about it to this day. Acute urinary retention is diagnosed when such a disorder develops suddenly and has not previously been observed in the patient. More often, men suffer from the disorder, which is due to the anatomical structure of the urinary canal. The development of this disorder requires immediate medical attention, as there is a high risk of bladder rupture, kidney damage and other equally dangerous complications.
Clinical picture of acute urinary retention
The disease has certain development factors. This condition can occur in males and females. Women very rarely encounter this problem. The female body reacts with acute urine retention to the process of tumor growth in the female reproductive system. This occurs due to mechanical compression, which leads to urinary retention.
Difficulty urinating in women occurs while carrying a child (pregnancy) and when the bladder is prolapsed.
Factors leading to urine retention in the male half have their own characteristics.
Among them, the most common ones are noted:
Stressful situations
- failure of the central nervous system;
- prostate adenoma (hyperplasia);
- urolithiasis;
- sclerotic condition of the cervical region of the bladder;
- the occurrence of neoplasms;
- blood clots;
- severe intoxication;
- depression, stress;
- acute prostatitis.
Ischuria (impaired urine outflow) can occur as a result of infection entering the genitourinary system. Sometimes this pathology can develop as a complication after surgery on the rectum and adjacent pelvic organs.
Boys or adolescents experience this pathology with acute urinary obstruction. For example, phimosis (narrowed condition of the flesh). At a young age, in girls, as in adolescence, blockage of the outflow of urine occurs in very rare cases. Most often, if this happens, it is due to systemic pathology within the body.
ICD 10 ischuria - according to international qualifications, does not attach importance to the causes of the occurrence of pathology in men and women.
Causes of the disease
The pathogenesis of various forms of ischuria is based on 3 main mechanisms and various additional factors, of which the most common are given below.
The mechanisms of development of ischuria are as follows:
- increased intraurethral resistance,
- impaired contractility or atony of the bladder,
- disturbance of the vesical innervation, both motor and sensory.
Neurogenic urinary retention occurs regardless of the gender and age of the patient and can be unfavorable. It is provoked by various pathologies of the nervous system, such as:
- stroke and its consequences,
- multiple sclerosis,
- myelitis, meningitis, encephalitis,
- oncological processes in the brain,
- spinal injuries,
- postoperative innervation disorders.
Other, most common causes of ischuria are functional and reflex in nature:
- prolonged stay in a forced position, for example, if it is necessary to comply with complete bed rest,
- shock, often spinal, reaction to injury and pain,
- emotional overexcitement,
- toxic effects of neurotropic drugs, tranquilizers, ganglion blockers, opiates, alcohol,
- provokes urinary retention by taking anticholinergic drugs,
- complications after anesthesia,
- osteochondrosis,
- Schmorl's hernia,
- spinal tuberculosis,
- frequent constipation,
- hysteria accompanied by spasms of the urethral sphincter.
Sometimes such conditions appear after active sex, with severe fright, prolonged stress, alcohol intoxication, hypothermia and other conditions unfavorable to the body.
What can cause dysuria in men?
The most common causes of male urinary difficulties are mechanical. Difficulty urinating in men most often occurs due to impaired fluid outflow due to compression of the urethra during:
- prostate adenoma,
- postoperative urethral adhesions,
- polyps and other neoplasms,
- swelling with paraphimosis and phimosis,
- obstruction of the urethra with blood clots due to trauma or massive hematuria,
- urolithiasis, especially with bladder stones,
- inflammations of various etiologies.
In addition, in men, the phenomenon of ischuria can be observed for a short period after ejaculation.
Causes of dysuria in women
As in men, the causes of urinary retention in women can arise from neoplasms, various inflammations, and urolithiasis. But difficulty urinating in women is sometimes observed during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, after a difficult long labor or in the presence of gynecological pathology, for example, with prolapse of the uterus. The development of many pathological processes accompanied by this problem can also be facilitated by severe menopause.
What causes ischuria in children?
In pediatric practice, conditions that may be accompanied by difficulty urinating also occur. In a newborn child, this can happen due to compression of the urethra or bladder by neighboring organs due to congenital anomalies or, for example, due to oncology or abscesses.
In younger boys, the inability to urinate sufficiently can be caused by a phenomenon called phimosis or paraphimosis. When the head is unskillfully exposed, inflammation occurs, due to which the lumen of the urethral canal narrows. Determining such a pathology is not difficult, but correction requires mandatory surgical intervention and removal of the foreskin.
In girls, the most likely cause is cysts of the lower urethra.
In addition, it is children who most often suffer perineal injuries as a result of careless and overly active games.
In adolescents, the causes of acute ischuria are the same as in adults.
Symptomatic manifestation
The pathological process of removing urine from the bladder is usually accompanied by painful symptoms, to which it is impossible not to react. The main manifestation of the disorder is acute, unbearable pain. Men often feel pain in the penis.
In addition to all the unpleasant sensations, there is incontinence, a frequent urge to go to the toilet, but it is not possible to have a full bowel movement, and sometimes it is not possible at all. Due to unsuccessful attempts, pain increases.
Characteristic signs of the development of acute urination include:
Urine does not pass
- growing anxiety;
- abdominal bloating;
- irritation in the abdominal area;
- decreased appetite;
- impaired bowel movement;
- gag reflex with nausea;
- increased weakness;
- restless sleep;
- dizziness;
- flatulence;
- elevated temperature.
Sometimes there are manifestations of pain symptoms in the lumbar region. This indicates the development of a pathological process in the kidneys, which is a sign of the impossibility of removing accumulated urine from the organs. In some cases, due to rapidly increasing symptoms, you even have to call an ambulance.
Classification
Based on the location of urine discharge, transurethral (true) and extraurethral (false) incontinence are distinguished. In the true form, urine is excreted through the intact urethra; if false - from abnormally located or damaged urinary tracts (from ectopically located ureters, extrophied bladder, urinary fistulas). In what follows, we will talk exclusively about cases of true incontinence. The following types of transurethral urinary incontinence occur in women: • stress.
Involuntary loss of urine associated with incompetence of the urethral sphincter or weakness of the pelvic floor muscles.
• imperative (urgent urinary incontinence, overactive bladder) – unbearable, uncontrollable urges caused by increased bladder reactivity; • mixed.
Combining signs of stress and imperative incontinence (a sudden, uncontrollable need to urinate occurs during physical stress, followed by uncontrolled urination;
• reflex.
Incontinence (neurogenic bladder) - spontaneous release of urine caused by impaired innervation of the bladder;
• iatrogenic.
Caused taking certain medications;
• other (situational) forms.
Enuresis, urinary incontinence from bladder overflow (paradoxical ischuria), during sexual intercourse. The first three types of urinary incontinence in women occur in most cases, all others account for no more than 5-10 %.
Diagnosis of pathology and therapeutic therapy for acute urine retention
Solving problems with severe urine outflow on your own is prohibited. Independent attempts to empty the bladder can have a detrimental effect on your health and worsen the course of the disease.
For example, if you put too much pressure on the peritoneum, the wall of the urinary organ may rupture. Taking measures to eliminate an overfilled bladder should be done by healthcare workers.
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and provide primary care.
Transportation to a medical facility can be dangerous due to a very overfilled bladder (risk of rupture), so first aid is provided to the patient at home
This occurs by installing a catheter through which urine is removed. To do this, a silicone tube with a very small diameter is installed (urination channel).
Using a catheter, the patient is relieved of muscle spasms by spreading the walls of the canal. This is done to easily remove accumulated urine. In some cases, home care is contraindicated for the patient, then the patient is taken to surgery, where surgery is performed through a tube that is inserted into the bladder through the peritoneum. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia; the procedure is called minimally invasive surgery.
The tube is left in place until the cause of the acute delay is found and eliminated. Sometimes the catheter is installed for a long period. To prevent infection, periodic rinsing of the bladder with antiseptics is carried out. The specialist may also prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy.
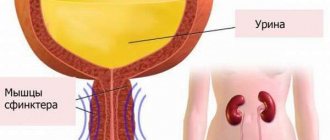
Urinary retention
(ischuria; acute complete urinary retention) - accumulation of urine in the bladder due to insufficiency or inability to urinate independently.
ICD-10
R33 Urinary retention N31 Neuromuscular dysfunction of the bladder, not elsewhere classified N31.1 Reflex bladder, not elsewhere classified N31.2 Neurogenic bladder weakness, not elsewhere classified N31.8 Other neuromuscular dysfunctions of the bladder bladder N31.9 Neuromuscular dysfunction of the bladder, unspecified N32.0 Obstruction of the neck of the bladder N32.9 Damage to the bladder, unspecified N33 Lesions of the bladder in diseases classified elsewhere N39.9 Disorder of the urinary system, unspecified.
CAUSES
Since women's urethra is much shorter than men's, urinary retention is extremely rare. The cause most often is a mechanical obstruction to the passage of urine: ■ adenoma and prostate cancer; ■ acute prostatitis; ■ sclerosis of the bladder neck; ■ foreign body of the urethra; ■ urethral stone; ■ urethral rupture; ■ neoplasms of the bladder and urethra. Urinary retention may be associated with pathology of the central nervous system or be of a reflex nature: ■ tumors and injuries of the brain and spinal cord; ■ urinary retention in the postoperative period; ■ urinary retention during treatment for acute myocardial infarction; ■ neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
DIAGNOSIS
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
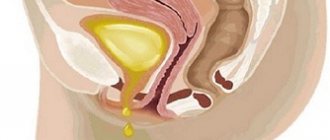
Partial and complete urinary retention are distinguished. With partial retention, urination occurs, but urine flows out in a thin stream or drops, and the bladder does not empty completely. Urinary incontinence with a full bladder is called paradoxical ischuria. ■ The patient is restless, as the clinic is determined by the sudden impossibility of emptying the bladder, accompanied by a painful, sharp and fruitless urge to urinate, and severe bursting pain in the lower abdomen. The pain can spread throughout the abdomen. ■ Since reflex intestinal paresis occurs, abdominal bloating appears, and symptoms of peritoneal irritation may occur. ■ Upon examination, a bulge is detected in the suprapubic region, which is especially visible to the eye in thin subjects. On percussion - dullness (a distinctive sign from intestinal bloating). An enlarged bladder is usually easily determined by palpation. Palpation is painful and increases the urge to urinate.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSTICS
■ First of all, the situation must be differentiated from anuria. Anamnesis matters. With anuria, the following are observed: ✧ water and electrolyte disturbances; ✧ smell of urine in exhaled air; ✧ lack of urge to urinate; ✧ bladder is empty. ■ Intestinal obstruction is manifested by repeated vomiting, bloating, and increasing dehydration. At a later stage, intestinal paresis and a picture of an acute abdomen develop. ■ Acute surgical pathology in the abdominal cavity is characterized by abdominal pain of a different nature. There is no urge to urinate. An objective examination reveals severe pain in some area of the abdomen or throughout the entire abdomen, symptoms of peritoneal irritation. An enlarged bladder in the suprapubic region is not palpable. ■ The result of catheterization of the bladder has differential diagnostic significance: the evacuation of a large amount of urine and the rapid improvement in the patient’s condition indicate precisely acute urinary retention.
TREATMENT
MEASURES
Acute urinary retention is considered an emergency urological condition requiring emergency intervention. Emergency bladder emptying is indicated. The intervention is carried out already at the prehospital stage. To do this, catheterization is performed with an elastic catheter (a metal catheter cannot be used) or suprapubic puncture of the bladder. ■ When catheterizing the bladder, asepsis must be observed. It is performed using sterile equipment. Catheterization in men requires some skill. It is carried out as follows: The patient is in a supine position. ✧ The penis is grabbed with the fingers of one hand using a sterile bandage; holding it slightly stretched upward, expose the head, wipe it with a disinfectant solution on a sterile swab. ✧ It is advisable to introduce 10 ml of 1% lidocaine gel into the urethra; in the absence of a gel, use sterile petroleum jelly, which is applied to the catheter. ✧ The catheter is inserted with gentle pushes until it penetrates the bladder, as evidenced by the appearance of urine at the outlet (if an obstacle occurs at the last stage, before the catheter penetrates the bladder, you need to wait 1-2 minutes, pressing lightly on the catheter - the catheter itself will easily will go further). ✧ Urine is collected for possible research in a sterile container. ■ Because women's urethras are shorter than men's, it is easier to catheterize their bladder. The manipulation is performed in compliance with the same aseptic rules. The mouth of the urethra is found by spreading the labia minora as far apart as possible. ■ Contraindications for catheterization are inflammatory processes in the area of the mouth of the urethra, urethritis, acute prostatitis, trauma to the urethra (history of trauma, bleeding from the urethra). If catheterization is unsuccessful, a suprapubic puncture of the bladder can be performed, however, at the prehospital stage, attempting to puncture the bladder should only be done as a last resort, when delivery of the patient to the hospital will take a long time. Contraindications are acute cystitis, paracystitis, suspicion of a bladder tumor or a decrease in its capacity (tuberculosis, interstitial cystitis, etc.). Method of suprapubic puncture of the bladder: ■ the patient is in a supine position; ■ make sure that the formation palpated above the pubis is caused precisely by an overfilled bladder; ■ observe asepsis as much as possible (as when performing an operation: sterile mask, gloves, gown, cap); ■ infiltrate the skin 2–3 cm above the upper edge of the pubic symphysis along the midline with a 1% lidocaine solution, having previously treated it with an antiseptic (the hair directly in the place where the puncture will be performed can be cut off with scissors); ■ puncture is performed with a thick long needle (with a lumen of 1 mm; length 15–20 cm) with a syringe connected to it; ■ insert the needle strictly vertically, constantly tightening the syringe piston. During puncture, the needle encounters two dense layers - the skin and the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscles, after which it easily penetrates through the muscle layers of the anterior abdominal wall and the wall of the bladder. Penetration of the needle into the bladder causes urine to appear in the syringe. To drain urine, a sterile tube is placed on the needle; ■ remove the needle at the end of the manipulation. After the intervention, the patient is usually hospitalized in the urology department for the purpose of additional examination and further treatment.
FORECAST
The prognosis for urinary retention depends solely on the disease that caused it. On the one hand, in some patients, a single urinary retention associated with stress or another psychological factor may never happen again. On the other hand, in the presence of organic pathology of the genitourinary organs or the central nervous system (in the case of functional urinary retention), the condition recurs.
According to accepted standards, acute urinary retention according to ICD 20 has code R33. An emergency pathological condition belongs to the class of signs and symptoms and is located under the heading of the genitourinary system.
This syndrome is characterized by a lack of urination due to blockage of the urinary tract or atony of the bladder. Since urine is not excreted from the body, dangerous breakdown products return back into the blood. Azotemia occurs, which is characterized by a negative effect on the central nervous system. When diagnosing acute urinary retention, emergency qualified medical care is indicated.
Diagnostics
Research methods • Urethrometry - shortening of the urethra • Urethroscopy, cystoscopy • Cystometry • TAM (true bacteriuria and leukocyturia with the addition of a secondary infection). Differential diagnosis • Urogenital fistulas • Neurogenic bladder.
TREATMENT OF EXERCISES • Exercises for the pelvic muscles • Exercises for the bladder. Drug therapy • For stress incontinence - sympathomimetics (ephedrine 0.025 g 3 times a day) or - adrenomimetics for 1.5 months • For forced incontinence - imipramine 50 mg 4 times a day or oxybutynin 5 mg 3 times a day . Surgical treatment • Narrowing of the anterior part of the vagina • Abdominal retropubic urethropexy •• According to Marshall-Marghetti-Krantz •• According to Burch •• Paravaginal plastic surgery • Transvaginal suturing •• According to Pereira •• According to Stamay •• According to Gittes • Pubic-vaginal loop • Artificial urinary sphincter • Collagen urethral implant. Complications • Urinary tract infection • Depressive and anxiety states.
Course and prognosis • With surgical treatment, cure occurs in 84% of cases, improvement - in 4% • With exercise therapy - 12% and 75%, respectively • With drug treatment - 14% and 60%, respectively. Synonym. Anishuriya
ICD-10 • N39.3 Involuntary urination • N39.4 Other specified types of urinary incontinence • N39.9 Unspecified urinary system disorder • R32 Unspecified urinary incontinence
Causes of the condition
Main diseases and risk factors that can lead to this complication:
- development of a benign prostate tumor;
- chronic prostatitis;
- urethral strictures;
- compression of organs during pregnancy;
- damage to the nerve endings of the bladder;
- the presence of stones in the urinary tract;
- oncological processes in the genitourinary system.
The listed pathologies do not always lead to acute urinary retention
, but increase the risk of this urgent condition. Doctors should be aware of the possibility of developing such a process and warn patients about it. Timely and correct elimination of risk factors minimizes the likelihood of symptoms of urinary retention, and most importantly, damage to the nervous system.
Causes
Etiology
. Primary enuresis. In healthy children, by the age of 1.5-2 years, a conditioned reflex connection is formed: the urge to urinate leads to awakening. If the formation of this connection is delayed, we speak of primary enuresis.. Enuresis is usually not associated with mental, neurological and anatomical disorders.. One of the causes of enuresis is considered to be an insufficient level of physiological maturity.. Insufficient bladder capacity (usually functional).. Psychological factors.. It is assumed that enuresis is associated with a violation of the ADH secretion cycle; in children suffering from enuresis, morning vasopressin levels are reduced. One of the possible causes is sleep disorder. Secondary enuresis. Secondary enuresis is caused by a violation of an already formed conditioned reflex.. Somatic diseases: diabetes, urinary tract infections.. Stressful situation.. Organic and functional diseases of the urinary system: obstructive or neurogenic bladder dysfunction, pseudoenuresis - paradoxical ischuria during sleep.
Genetic aspects
. Enuresis runs in families and is often combined with mental disorders. Nocturnal enuresis, type 1 (*600631, 13q13-q14.3, ENUR1 gene, Â), nocturnal enuresis, type 2 (*600808, 12q13-q21, ENUR2 gene, Â).
Risk factors
. Heredity.. If one of the parents suffered from enuresis, the incidence of the disease in the child is 44%. If both parents suffered from enuresis, the incidence is 77%. Children suffer more often from their first birth.
Treatment according to ICD 10 protocols
In the international classification of diseases, urinary retention is located in the category of additional clinical symptoms, that is, it is a complication. The general principles of treatment for this condition are as follows:
- Catheterization of the bladder, if possible, and emptying it (simultaneous or continuous).
- Emergency surgical intervention aimed at restoring the patency of the urinary tract.
- Conservative treatment of the underlying disease, if possible (with simultaneous catheterization to remove urine).
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, also offers methods for preventing this complication, which are much easier and safer for the patient.
Urinary retention is a painful phenomenon in which a person is unable to voluntarily empty a full bladder. Another name for this condition is ischuria
. There are a large number of reasons that can cause a violation of the outflow from the organ. The doctor must conduct a full examination of the patient to find out the nature of the pathology and, based on this, prescribe the correct treatment.
Photo 1. Urinary retention is a serious disease with serious consequences. Source: Flickr (leslie)
Diagnosis of enuresis
Diagnosis of enuresis includes two stages. At the first stage, complaints and medical history are studied in detail, a physical examination is performed, urine sediment is examined and the functional capacity of the bladder is assessed based on a urination diary. During the interview, attention is paid to obstetric history (birth trauma, hypoxia during childbirth, etc.), the presence of enuresis in parents and relatives is clarified, and conditions in the family are clarified. It is important to determine the presence of a “dry” period and its duration, the number of cases of enuresis (per week, month), pay attention to the nature of sleep (deep, anxious, etc.). The physical examination should include a thorough examination of the sacral region and genitalia. With anomalies of the development of the nervous system (meningocele), subcutaneous lipomas, areas of increased hair growth, skin retraction and age spots are often found in the sacral region. Neurological examination includes determination of skin sensitivity, examination of lower limb reflexes and bulbocavernosus reflex, as well as assessment of anal sphincter tone.
Based on the urination diary, the number of urinations and episodes of urinary incontinence during the day and night is determined, and bladder capacity is assessed. In cases where bedwetting is the only symptom, treatment is prescribed.
In case of unsatisfactory results of treatment, as well as identification of other dysfunctions of the lower urinary tract (urinary incontinence during the day, frequent urination, etc.), neurological disorders, urinary tract infections and in cases of suspected urological diseases, a detailed examination is indicated. The purpose of such an examination is to identify diseases, one of the symptoms of which is bedwetting. Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder with determination of residual urine, descending cystourethrography, complex ultrasonography and CT or MRI of the spine are performed. A consultation with a neurologist is indicated.
, , , , [
Signal therapy is considered the best treatment for patients with difficulty awakening and a slight increase in nocturnal urine output. Regular awakenings are prescribed or special alarm devices are used. The latter are designed in such a way that urine, which is released during involuntary urination, closes an electrical circuit and a signal sounds. This leads to awakening and the patient finishes urinating in the toilet. This treatment forms the urination reflex. Successful results are observed in 80% of patients with enuresis.
For patients with enuresis who pass large amounts of urine at night, treatment of enuresis with desmopressin is indicated. Desmopressin has a pronounced antidiuretic effect. The drug is available in the form of a nasal spray and tablets. It is recommended to start treatment with a minimum dose of 10 mcg per day, followed by an increase to 40 mcg per day. Positive results are noted in 70% of patients. Side effects of desmopressin are rare and usually disappear quickly after discontinuation of the drug. In case of overdose, hyponatremia occurs, therefore it is recommended to periodically monitor the sodium content in the blood serum.
The patient is prescribed a special drinking regimen. It is recommended not to take any liquid within two hours of bedtime. It is necessary to ensure that the child receives a sufficient amount of fluid during the day. Primary enuresis is often caused by a disturbance in the rhythm of vasopressin secretion, so patients with bedwetting are prescribed a synthetic analogue of this hormone, desmopressin. The dose of the drug is selected individually. Self-administration of desmopressin is unacceptable, since enuresis may be caused by another pathology (for example, developmental pathology or infection of the urinary organs). Patients with increased bladder tone are prescribed oxybutin. The drug acts on the smooth muscles of the bladder, increasing its volume and reducing spasms. In some cases, driptan therapy is combined with desmopressin. Patients with reduced bladder tone are advised to urinate every 2-3 hours and are prescribed drugs that increase smooth muscle tone (neostigmine). Psychological correction is indicated for patients suffering from neurotic enuresis. For neuroses and neurosis-like conditions, courses of vitamin therapy and drugs that improve metabolic processes in the brain (herbal medicines, picamilon, piracetam) are recommended. Comprehensive treatment of enuresis includes physiotherapeutic procedures (thermal procedures, ultrasound, current treatment), therapeutic exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and restorative massage. To develop a conditioned reflex, it is recommended to use special devices. When the first drops of urine appear, the device gives a sound signal, which wakes the patient up and trains him to wake up when he has the urge to urinate. The use of devices gives a good effect if parents manage to develop the correct tactics of behavior and come to an agreement with the child. Conflict situations that arise from repeated awakenings at night can lead to the child’s refusal to use the device. It should be remembered that treatment of enuresis of almost any etiology is a long process. Parents need to be patient and not wait for immediate results from therapy. Pressure on the child and increased expectations can lead to neuroticism in the child and complicate the treatment process. Enuresis changes the child’s psyche and leads to an exacerbation of feelings of inferiority. Patients are embarrassed by their peers, withdraw into themselves, and strive for privacy. A chronic psychotraumatic situation can cause low self-esteem, timidity, isolation, and indecisiveness. Sometimes children become aggressive. Character changes may go unnoticed by parents and become apparent only in adolescence. In order to minimize the negative impact of enuresis on the psyche, the child should be supported in every possible way. Any manifestations of condemnation or disgust are unacceptable.
Enuresis is involuntary urination during sleep. In medical practice, the term “enuresis” usually means involuntary urination during sleep more than once a month in girls over 5 years old and in boys over 6 years old. Frequency
- 40% of children aged 3 years, 10% at the age of 6 years, 3% at the age of 12 years and 1% at the age of 18 years.
Code according to the international classification of diseases ICD-10:
Types and forms of urinary retention
There are acute and chronic forms of the disease.
The first option is considered an emergency in urology. This is due to the fact that in the absence of outflow from the bladder, kidney function is impaired. Within a few hours, complete suppression of their activity may occur with the development of intoxication.
If a patient has had difficulty urinating for a long period of time, he is diagnosed with chronic retention. This condition is less dangerous for the health and life of the patient, but can significantly reduce the quality of life. If measures are not taken to get rid of the cause of this phenomenon, it can become acute.
The chronic form is divided into complete and incomplete.
Complete is characterized by the absolute impossibility of independent urination. In this case, the patient is given a catheter through which accumulated urine is removed.
Incomplete chronic ischuria is characterized by the presence after each act of urination. This pathology can progress and gradually become complete.
Separately, there is paradoxical ischuria, when a patient with a full bladder cannot spontaneously urinate, but a small amount of urine is released from the urethra. This is due to overstretching of smooth muscle fibers and disruption of nervous regulation.
Additional facts
Urinary incontinence in women is an involuntary and uncontrolled release of urine from the urethra, caused by violations of various mechanisms of regulation of micturition. According to available data, every fifth woman experiences involuntary urine leakage in reproductive age, every third woman in perimenopausal and early menopausal age, and every second woman in old age (after 70 years). The problem of urinary incontinence is most relevant for women who have given birth, especially those who have a history of natural childbirth. Urinary incontinence has not only a hygienic, but also a medical and social aspect, since it has a pronounced negative impact on a woman’s quality of life, accompanied by a forced decrease in physical activity, neuroses, depression, and sexual dysfunction. The medical aspects of this disorder are considered by gynecology, urology, and psychotherapy.
Urinary incontinence in women
Causes of pathology in men
Difficulty urinating in men, up to complete delay, can occur in the presence of mechanical obstacles and functional disorders
which are associated with impaired tone of the muscle tissue of the urinary tract.
The first group of reasons include:
- urolithiasis
, when a calculus enters the bladder and closes its outlet; - phimosis
, or narrowing of the foreskin, which compresses the head of the penis; - pelvic hematomas and vascular lesions
; - inflammatory diseases of the genital organs
- acute and chronic prostatitis plays an important role here; - hyperplasia
() of the prostate gland - with an increase in its size, compression of the urethra occurs, which leads to impaired outflow; - genital injuries
.
Functional disorders that can cause urinary retention:
- diseases of the central nervous system
,
tumors of the spinal cord and brain, myelitis, neurosyphilis
; - impairment of the reflex associated with urination
after surgery on the pelvic organs, mental illness, poisoning, etc.
Note! The most common cause of chronic and acute urinary retention in men is prostate adenoma. This disease occurs in most patients over 60 years of age. Therefore, urinary retention can be called a pathology of old age.
Causes of enuresis
It is important to understand that enuresis is a symptom, not a disease. Unfortunately, to date, the cause of enuresis has not been precisely established, and the pathogenesis has not been fully studied. It is believed that enuresis can be caused by various reasons. In particular, the following reasons are identified: impaired formation of central nervous system control over the function of the lower urinary tract, sleep disorders, impaired secretion of antidiuretic hormone during sleep. genetic factors.
Enuresis is often observed in children with developmental delays. Such children begin to talk and walk late. There is a strict correlation between the general development of the child and the timing of the formation of central nervous system control over the function of the lower urinary tract.
Symptoms and signs
Manifestations of pathology include:
- inability to urinate independently;
- the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen
; - with significant filling of the bladder - an increase in the size of the abdomen, the appearance of swelling above the pubis
. When pressing on it, the pain may increase; - constant strong desire to urinate
.
At the same time, the patient may exhibit signs of another pathology that has caused a disturbance in the outflow of urine. For example, there may be increased body temperature, the presence of blood clots in the urethra
, symptoms characteristic of pelvic and abdominal trauma.
Note! If any of the above symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Untimely medical assistance can lead to serious complications.
Leading symptoms
The patient's complaints and signs of impaired bladder emptying are very characteristic. The first thing a patient with acute retention will point out is the physical inability to urinate, despite the desire. Often there is severe pain radiating to the perineum above the pubis. An overfilled and very enlarged bladder is defined as a protrusion in the lower abdomen.
A characteristic and dangerous symptom is the appearance of blood - urethrorrhagia, which requires urgent care and possible surgery. Bleeding can be minor, in the form of small discharge, or massive, threatening the patient's life.
Depending on the cause of ischuria, other symptoms may appear, for example, painful or traumatic shock.
Sometimes, before the onset of acute urination problems, “precursors” may be observed: frequent trips to the toilet, especially at night, burning in the urethra, weakness, anxiety, sleep disturbances, fever, nausea and even vomiting.
Methods for treating urinary retention
Since urinary retention is not an independent disease, first of all it is necessary to determine the cause that caused the outflow disturbance. Only after this can treatment begin; it may be necessary to involve not only urologists, but also doctors of other specialties.
A catheter is inserted into the patient's
to remove accumulated urine through it.
This will relieve the acute condition and move on to drug therapy. In some cases, for example, when the urethra is significantly damaged, it is impossible to insert a catheter into it. Then a cystostomy operation
, in which a hole is created in the wall of the bladder to drain its contents.
Drug therapy
For urinary retention, patients are prescribed antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs
.
Among antibiotics,
preference is given to representatives of the sulfonamide group. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician based on the severity of the disease and the cause.
Note! Medicines and folk remedies cannot lead to a complete cure of the patient, since they do not affect the cause. In many cases, it is necessary to perform an operation aimed at eliminating a mechanical obstruction to the outflow of urine.
Folk remedies
Such medications should be taken as an addition to primary therapy. They make it possible to reduce the severity of the manifestations of the disease, relieve pain and inflammation.
.
To do this, you can use an alcohol tincture of the fruits of tea rose, rose hips, and ground walnut shells.
.
A decoction of juniper bark
will also be useful .
To prepare a tea rose infusion, take the fruits of this plant and pour alcohol or vodka over them. Leave for several days until the mixture turns straw-yellow. You should take 10 drops dissolved in water, 2 times a day.
An infusion of rose hips is prepared in a similar way.
Leave to infuse for a week, shaking regularly. The readiness of the product can be determined by its light brown color. You should take 10 drops dissolved in water no more than three times a day. Photo 2. Traditional medicine in this case does not deny the merits of traditional medicine.
Treatment
Treatment of nocturnal enuresis in a child requires only an integrated approach, namely:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- taking medications;
- psychotherapy.
Drug treatment is prescribed based on the form of the disease and the age of the child. In general, your doctor may prescribe the following medications for enuresis in children:
- anticholinergic;
- tricyclic antidepressants;
- antidiuretic hormone substitutes;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
As for physiotherapeutic procedures, this should include:
Treatment of enuresis in children with folk remedies is possible, but only after consultation with your doctor. In this case, the following decoctions can be used:
- cherry-blueberry;
- from dill;
- from St. John's wort and centaury.
You can also give your child tea made from lingonberries, blueberries and corn silk. At the pharmacy you can buy a special wine tincture made from agrimony.
Tablets for urinary incontinence, folk remedies and other methods of treatment are strictly prescribed by the attending physician, so you cannot give your child any medications on your own.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe a diet for the child; in case of enuresis, it is selected purely individually. In general, a child’s diet should be light, but high in calories. As a rule, enuresis in a child is treated at home.
Provided that treatment is started in a timely manner, complications can be avoided, and complete recovery in some forms of the disease is 98% of general cases.
Treatment of childhood enuresis with non-drug methods
Bedwetting in 80% of children goes away over time. This is due to the maturation of the central nervous system, improvement of the reactions of the nerve endings of the urinary system and the brain.
The main starting point in the treatment of enuresis in children, according to many pediatricians and the authoritative doctor in our country, Dr. Komarovsky, should be motivation for “dry nights.”
Since incontinence therapy begins at a conscious age - over 7 years old, you need to create a strong desire to get out of bed dry in the morning. The effectiveness of the method is reinforced with praise and encouragement. Unintentional mistakes should not be scolded or punished. This will worsen the course of the disease. The child should feel confident and know that everything will work out for him.
The second, no less important, point in the treatment of childhood enuresis is careful adherence to the daily routine and drinking schedule. All active noisy games are postponed to the first half of the day so that the child’s nervous system calms down before bed. After 17:00, liquid can be consumed only if you are very thirsty.
Before going to bed, ventilate the bedroom well and humidify the air. You should not wrap your child too much - this will cause increased sweating and a desire to drink.
One of the most effective means in the treatment of nocturnal enuresis, both in boys and girls, is the so-called urinary alarm clock. The essence of the method is to develop a reflex to the sound or vibration signal of an alarm device, which is triggered when drops of liquid hit the sensor. The awakened child goes to the toilet and finishes urinating.
After 8-12 weeks the reflex becomes stable. Alarm therapy eliminates bedwetting in up to 80% of patients.
An alternative option is to wake up with a regular alarm clock during the night. The technique involves gradually increasing the interval and moving urination to the morning hours.
Overactive Bladder
Urinary tract dysfunction is characterized by urinary incontinence and frequent urge. With age, symptoms increase, which is due to morphological changes in the walls of the organ and chronic diseases. Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) occurs in more than 40% of the adult population. Despite the fact that the pathology is more characteristic of women, recently there has been a tendency towards its constant increase in men over 60 years of age. Let's understand what OAB is, determine the factors for the development of the disease, methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Reasons for development
The main cause of urinary incontinence is the involuntary contraction of the detrusor muscle as the bladder fills, which in turn is caused by many factors. There are two forms of bladder overactivity: neurogenic and idiopathic. In the first case, in approximately 25% of patients, UI is a consequence of neurological diseases (Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, strokes).
Overactive bladder of the idiopathic form is considered as independent until the true diagnosis is determined. Identification of the cause of pathology is verified only after a comprehensive examination, but the theory of pathogenesis assumes generally accepted factors that determine the occurrence of dysfunction. These include:
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic inflammation and ischemic organ damage;
- kidney diseases;
- endocrine pathologies;
- tumors;
- urolithiasis disease;
- depression;
- increased body mass index;
- constipation;
- limited mobility;
- heart failure.
Elderly patients are at risk, which is explained by a decrease in the density of nerve fibers in the detrusor walls and the development of increased sensitivity of muscarinic receptors that transmit signals to muscle structures.
Bladder dysfunction often accompanies the postmenopausal period in women. The physiological condition is characterized by a decrease in estrogen production and hormonal imbalance, which disrupts metabolic processes in the muscular layer of the organ, leading to its hypoxia and uncontrolled contractions.
When verifying the diagnosis, the effect of medications taken for concomitant pathologies is also taken into account. For example, antihypertensive and diuretics contribute to the rapid filling of the natural reservoir and increased urine excretion. Such symptoms mimic the phenomena inherent in OAB, which can complicate diagnosis.
Characteristic symptoms
An overactive bladder in women and men significantly reduces the quality of life, leads to insomnia and stress. It is important to recognize alarming symptoms in time and seek qualified medical help, which includes modern diagnostic methods and specific therapy. Clinical manifestations include:
- frequent urination in small portions (more than 8 times);
- irresistible (urgent) urge to empty the organ;
- involuntary leakage of urine;
- nocturnal polyuria (more than twice).
Treatment of overactive bladder is based on medical history and differentiation of factors leading to the pathological condition. A few days before visiting a specialist, the patient should start keeping a diary, which records the amount of liquid drunk and urine excreted, and the frequency of visits to the toilet. The records are informative and allow you to assess the daily pattern of urination and the form of the disease.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out by primary care doctors - a gynecologist, urologist and, if necessary, a neurologist and endocrinologist. Particular attention is paid to the study of the whole organism, since at this stage an important task is to exclude other diseases with similar symptoms. The diagnosis of overactive bladder can only be verified if there is a proven absence of urinary system infections or diseases such as genital prolapse, tumors of various etiologies, bladder stones, cystitis or prostatitis in men. The basic minimum is represented by the following medical procedures:
- taking anamnesis;
- examination by a gynecologist;
- rectal examination of the prostate in men;
- assessment of neurological status;
- Ultrasound of the bladder with measurement of the volume of residual urine;
- Clinical blood and urine tests;
- cystoscopy;
- electromyography.
If pathological processes of a different etiology are suspected, the patient is sent for consultation to specialized specialists, for example, an endocrinologist, oncologist or nephrologist, after which additional clinical studies may be prescribed.
Principles of therapy
Treatment of overactive bladder is effective only when combined with drug therapy, changes in behavioral habits and regular exercise aimed at strengthening the pelvic floor muscles.
When selecting a treatment regimen, direct relationships between concomitant pathologies and nervous system disorders are taken into account. Specific medications are selected, and the “gold standard” is considered to be a regimen consisting of the following combination:
- Adrenergic blockers, for example, Segetis (improves urodynamics, inhibits contractions of prostate smooth muscles and has a positive effect on metabolism, preventing tissue hyperplasia).
- Hololytics (Vesicare, Solifenacin) to reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the urinary tract.
- Drugs for the treatment of concomitant pathologies; for example, for infections, Metronidazole (Trichopol) tablets are prescribed in combination with suppositories of the same name, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial and sedative drugs.
All medications are easy to use, have no side effects and have a prolonged effect.
In the treatment of overactive bladder, non-pharmacological approaches have a great influence, which increase the effectiveness of drug therapy and calm the agitated bladder walls. The main components of rehabilitation measures are:
- control over the amount and frequency of fluid intake;
- Kegel exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles;
- correction of the daily diet and exclusion of caffeine-containing drinks and alcohol;
- routine visits to the toilet and double urination;
- avoiding drinking liquids before bedtime;
- keeping a diary for timely correction of drug therapy.
Features of the development of pathology in children
Overactive bladder in children occurs in 15% of young patients. It has been scientifically established that organ dysfunction at an early age is caused by increased sensitivity of the detrusor to acetylcholine, a mediator of the parasympathetic nervous system (brain and spinal cord). As the child grows and the body develops, sensitivity quickly decreases, and bladder function is restored.
Symptoms of the pathology are manifested by sudden urge and urinary incontinence, especially at night. With insufficient examination, the disorder is mistakenly identified as enuresis. Inadequate diagnosis and therapy lead to psychological trauma and the formation of an inferiority complex.
In childhood, the disease is reversible and in most cases the child “outgrows” the problem. After examinations and verification of the diagnosis, antimuscarinics are prescribed, for example, Oxybutynin, which is considered the “gold standard” for the treatment of pediatric patients. Physiotherapeutic methods of influence and behavioral correction are successfully used as part of complex treatment:
- regular exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles;
- categorical exclusion of sweet sodas, chocolate and tea from the diet;
- teaching the baby to visit the toilet at certain intervals;
- training in proper bowel movements;
- creating a friendly atmosphere and eliminating stressful situations.
A timely visit to a doctor and following the rules described above will help the child overcome the problem and adapt among his peers.
Involuntary urine discharge may indicate serious illnesses: mental and endocrine disorders, inflammation of the kidneys and bladder, and in girls, gynecological problems.
Features in men
According to statistics, bladder overactivity in representatives of the stronger sex occupies one of the leading places among pathologies that affect a decrease in quality of life and self-esteem, especially after 60 years. An overactive bladder in men in most cases manifests itself against the background of prostate diseases: chronic prostatitis and hyperplasia.
An important role in the development of pathology is played by genitourinary infections, trauma to the urethral canal, and the body’s tendency to form stones. In this case, treatment is impossible without surgery.
To increase social activity, older men are recommended to use special devices (catheters, hand clamps, urinals), absorbent pads and panties. This helps calm the nervous system and overcome psychological problems.
In the absence of a pronounced effect, new technological approaches are used to treat overactive bladder in women and men: the introduction of botulinum toxin for local paralysis of muscle fibers and electrical sacral neuromodulation. The technique is based on the effect of weak electronic impulses on the spinal nerves that regulate the functioning of the pelvic organs. If using the above methods the pathology cannot be stopped, then the possibility of cytoplasty is considered. The radical method is aimed at increasing the volume of the bladder and strengthening muscle fibers.
Notes
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, van Kerrebroeck P, Victor A, Wein A. The Standardization of Terminology of Lower Urinary Tract Function Neurourol. Urodyn 21:167–178. 2002
- Raz S. Female Urology / WB Sauders Company, 2nd ed., 1996. - P.134 - 213. Hunskaar S. et al. Presented at ICS Annual Meeting; Aug 26-30, Heidelberg, Germany
- Abrams P, Blaivas JG, Stanton S, Andersen JT. The Standardization of Terminology of Lower Urinary Tract Function Neurourol.Urodyn 7:403-26. 1988
- Pushkar D. Yu., Diagnosis and treatment of complex and combined forms of urinary incontinence in women. Author's abstract. dis. doc. med.n.auk. M., 1996
- Enhörling G. Simultaneous recording of intravesical and intraurethral pressure: a study on urethral closure in normal and stress incontinent women. Acta Chir Scand. 1953;32:285-307.
- McGuire EJ. Stress urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 1976;47:255-264.
- Green TH. Classification of stress urinary incontinence in the female: an appraisal of its current status. Obstet Gynecol Survey 1968;23:632-634
- DeLancey J.O. Stress urinary incontinence: where are we now, where should we go? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996;175:311-319
- Petros PE, Ulmsten UI. An integral theory of female urinary incontinence: experimental and clinical considerations. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl. 1990;153:731.
- Ulmsten U. Herniksson L. Johnson P. Varhos G. An ambulatory surgical procedure under local anesthesia for the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 1996; 7:81-5
- Delorme, E.: Transobturator urethral suspension: mini-invasive procedure in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women. Prog Urol, 11: 1306, 2001
- De Leval J., Novel surgical technique for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: transobturator vaginal tape inside-out. Eur Urol. 2003 Dec;44(6):724-30.
Prevention
Prevention of urinary incontinence in women consists of giving up bad habits and addictions, controlling weight, strengthening the abs and pelvic floor muscles, and controlling bowel movements. An important aspect is careful management of childbirth, adequate treatment of urogenital and neurological diseases. Women faced with such an intimate problem as urinary incontinence need to overcome false modesty and seek specialized help as early as possible, when conservative measures can be effective.
Stress urinary incontinence
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
Involuntary loss of urine (incontinence) is not only a medical problem, but also a social one. Pathological urination dramatically worsens the quality of life. The consequence of an unresolved problem is psycho-emotional disorders, everyday, family and social maladjustment.
About 20% of the world's population suffers from various types of incontinence. About 40% of people are in no hurry to treat the pathology, preferring to hide the intimate problem even from the doctor.
Involuntary urination occurs:
- stressful;
- urgent;
- mixed;
- night;
- senile.
If a few drops of urine appear from time to time, the development of incontinence can be assumed. Typically, the disorder begins with intermittent minor symptoms and then progresses to more serious pathology.
Which groups of people are susceptible to the disease?
The bulk of those suffering from this delicate problem are women of different ages. This is due to certain characteristics of the body. Most often, symptoms of the disease are observed in women aged 40–50 years.
40% of women experience episodic or regular urinary disorders, but only every tenth seek professional help. The constant feeling of discomfort that occurs with stress urinary incontinence in women interferes with living a full life, so the disease requires prompt treatment. Symptoms of incontinence are familiar not only to ladies, but also to representatives of the stronger half of humanity.
Among men under 40 years of age, the disease is rarely diagnosed, however, with age, the number of cases increases
The number of men experiencing urinary problems is increasing due to age-related changes in the prostate. Stress urinary incontinence occurs not only in adults, but also in very young patients. If the disease is diagnosed in 15–40% of mature men and women, then the number of affected children can reach up to 70%.
Causes
Urinary incontinence is a consequence of dysfunction of the bladder sphincters. There is an opinion that the pathological condition develops due to a decrease in the length of the urethra (urethra). Proponents of the theory believe that the critical length of the urethra, allowing a woman to retain urine, is at least 3 cm.
An important role is played by the size of the posterior urethro-vesical angle. For the normal mechanism of emptying the bladder, it is very important to maintain its correct degree (130 – 160 at rest, 145 – 180 during stress).
Most often, stress urinary incontinence in women occurs for the following reasons:
- Traumatic childbirth, during which not only the bladder suffers, but also the muscles that support the pelvic floor.
- Hard physical labor.
- Prolonged overexertion and stress.
- Entering menopause.
- Prolonged or rapid labor.
- Endourethral interventions.
- Constant constipation.
- Gynecological surgeries, such as hysterectomy.
The causes of stress urinary incontinence in children are varied. Having noticed that a child is suffering from enuresis, the worst thing you can do is scold and shame the child. By focusing on the problem, you can develop insecurity, isolation and low self-esteem in a little person. Parents should seek help from a doctor so that a specialist can identify the root cause of the pathology.
Childhood urinary incontinence can occur:
- Against the background of diseases of the central nervous system or urological pathologies.
- After emotional trauma or severe psychological shock.
Young children often cannot say out loud what exactly is bothering them.
Sometimes the birth of a second child or daily quarrels between parents result in stress urinary incontinence for the baby, which is often accompanied by stuttering and nervous tics
In this case, not only medical, but also psychological help is required. Parents should be especially wary if the problem plagues a fairly mature child (about 5 years old). In men, excessive pressure in the bladder and, as a result, stress urinary incontinence also occurs due to defects in the sphincter mechanism.
Among the causes that cause urinary disorders are:
- Dysfunction of the genitourinary tract.
- Pathologies of the nervous system that lead to changes in the functioning of the pelvic organs.
- Neurogenic disorders, e.g. multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, brain tumors.
At any age, timely consultation with a doctor can eliminate the problem and get rid of psycho-emotional stress. Modern treatment methods offer both surgical intervention and conservative therapy. The first type of help is usually indicated in case of advanced pathology.
Conservative therapy
Due to shyness or poor awareness of modern methods of eliminating the problem, many people neglect professional help. Treatment of stress urinary incontinence requires a serious approach, most often a comprehensive one. Pills alone will not provide long-term results. Urinary incontinence is not an independent pathology, so the treatment course should be determined taking into account the underlying disease.
Restoring urinary function with a laser is the newest technology for eliminating the disease. This procedure is painless and does not require surgery or anesthesia. There is no rehabilitation period after laser treatment, so the woman can immediately go home. The correction is highly effective, there is no bleeding or scarring after its application.
In Russia, laser correction is carried out mainly in large cities. Some patients prefer treatment abroad, for example, in the Swiss city of Zurich, where urological problems are successfully solved.
Regular bladder training can help prevent urine leakage. The technique is based on the fact that for 6 weeks the patient is required to control urinary function. You need to visit the toilet every 30 to 60 minutes, regardless of how full your bladder is.
The desire to defecate that arises at an unplanned time must be suppressed, for example, by switching attention to a hobby or work. After 7 days, the interval between visits to the restroom should be increased by 30 minutes, and after a week, another half hour should be added to this time. Self-control will help to avoid frequent urges and involuntary urine discharge.
Pills
Drug treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women helps relieve the main symptoms of the disease. The drugs are prescribed for any form of urinary disorder, however, the greatest positive effect is noted by patients with urgent (imperative) incontinence.
Among the medications suitable for eliminating incontinence, there are several groups:
- Hormonal drugs that restore estrogen levels.
- Antibiotics that suppress the infectious environment.
- Medicines that relax the bladder or stimulate its contractions.
Sometimes significant relief comes from stopping previously prescribed medications, for example, those prescribed for the treatment of hypertension.
A folk method of cleansing the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
You should not select or discontinue medication treatment on your own. Only a doctor can choose the correct therapeutic course after reviewing the medical history.
Gymnastics
To prevent the development of pathology, it is necessary to regularly do certain exercises. Daily gymnastics is not difficult, but it effectively helps strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Training is recommended for all women who have given birth, as this is a natural way to strengthen the perineal ligaments and restore muscle strength.
Leading urologists and gynecologists recommend Kegel exercises, which are popular all over the world. The special gymnastics developed by an American doctor became known in the middle of the last century. Since then, a huge number of women have been using the treatment complex to eliminate urinary incontinence, as well as for preventive purposes. Kegel exercises are suitable for women who have given birth.
If the young mother’s well-being allows her to perform exercises, already in the maternity hospital you can begin to train the ligaments and sphincters, not forgetting to gradually increase the load
To achieve positive results, you need to feel and learn to tense exactly those muscles that are responsible for stopping urine. While straining them, imagine that you are stopping urination. The abdomen, thighs and buttocks should be relaxed during exercise. The exercise is repeated 20 times, alternately tensing (in this state you need to stay for 10 seconds) and relaxing the muscles.
Traditional medicine recipes
Quite often, herbal remedies are used to treat urological problems. They have good healing properties and help achieve a lasting healing effect. Suitable medicinal herbs include: sage, yarrow, lingonberry, blackberry, St. John's wort.
The following recipe will help you get rid of stress urinary incontinence:
- boil 300 ml of water;
- Mix hop cones, valerian, knotweed and St. John's wort in equal parts;
- 2 tbsp. l. pour boiling water over the collection and let it brew for 30 minutes.
The infusion is taken daily, drinking 1/3 glass 2 times a day.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods also help restore normal bladder function:
- electromagnetic influence used to guide the drug into the tissue;
- galvanic currents;
- constant pulse electric current.
It is advisable to continue conservative treatment for no more than 12 months. If the symptoms of the pathology do not disappear, and the dynamics of recovery are poorly expressed, it is necessary to undergo surgery.
Surgery
Today, the TVT loop operation, developed in Sweden, is considered the main and most effective (up to 97% of cases). This is a low-traumatic intervention performed using synthetic materials, such as polypropylene. The operation lasts about 30 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia.
Stress urinary incontinence is the main indication for the procedure. Despite its effectiveness, the operation has a number of contraindications (acute inflammatory diseases of the bladder and urethra, the presence of sexually transmitted infections, etc.). The intervention leaves very few cosmetic defects and allows you to quickly return to your normal rhythm of life.
Surgery to eliminate urinary problems in men involves the implantation of an artificial sphincter (spiral system) of the bladder.
This procedure is indicated if insufficiency of the urethral obturator mechanism, for example, after treatment of the prostate gland, has become the cause of severe urinary incontinence. The technique is suitable for eliminating delicate problems in patients with spinal cord injuries, bone injuries, and neurological diseases.
Prevention
To avoid the need for surgical intervention or long-term drug therapy, it is necessary to take preventive measures in time:
- eliminate infectious foci in the body;
- regularly perform pelvic floor strengthening exercises;
- empty your bladder on time;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- get rid of excess weight;
- drink enough fluids;
- Introduce fiber-rich foods into your diet to prevent constipation;
- overcome bad habits, such as smoking;
- do not exclude scheduled examinations by a urologist;
- remove sugar and sweeteners from your diet.
Carbonated and alcoholic drinks negatively affect the functioning of the genitourinary system. In addition, spicy foods and spices irritate the bladder.
Summary
Having noticed the first symptoms of pathology, there is no need to withdraw into yourself and neglect a full life. Having overcome the embarrassment, you need to go to a medical center, where a specialist will select the right treatment.
Reviews
A big mistake is made by those who hide the problem for years, not daring to discuss the delicate situation even with a doctor. Reviews from people left on thematic forums will help you make a choice in favor of competent treatment.
Features in older men
The causes of incontinence in older men are similar to those in the entire male population. Most often, problems with the prostate gland . It is also quite common to experience urinary incontinence during activities such as coughing, laughing or sneezing.
To correct the pathological condition, predominantly conservative treatment methods are used. In particular, taking various medications.