Causes of urinary incontinence
There are certain risk factors that influence the development of urinary incontinence in women:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Diabetes mellitus, a disease in which vascular changes occur in all organs, including the genitourinary system;
- Neurological diseases (stroke, heart attack, etc.);
- Hormonal imbalances (excess of the hormone estrogen affects functional changes in the membranes of the organs of the genitourinary system and can provoke disease);
- Age category (women over 40 years old).
- Postpartum genital injuries.
Risk factors for the development of urinary incontinence in women
Here I will list several factors that increase the likelihood of urinary incontinence (we are talking mainly about the stress form):
- Multiple and/or traumatic births;
- Work involving heavy lifting;
- Excess body weight;
- Constipation;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Prevention of urinary incontinence will include regular physical activity, body weight control, and daily bowel movements.
Author: candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category, Rotov Anton Evgenievich
Diagnosis of the disease
In order to accurately diagnose urinary incontinence, you need to seek help from a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe the necessary tests.
Agnostics includes the following activities:
- Examination by a specialized specialist. Collection of medical history and complaints. The doctor prescribes keeping a special urination diary, which displays the volume and number of urinations per day.
- Gynecological examination (examination of the anatomical structures of the female reproductive system).
- Cough test. The study is carried out on a full bladder. The woman needs to cough or strain. If urination occurs after coughing, the test is considered positive.
- Uroflowmetry (a method for diagnosing urodynamics that involves measuring urinary flow). It is carried out strictly on a full bladder, using a special uroflowmeter device.
- Cystoscopy (examination of the surface of the bladder).
- Ultrasound (necessary for a more accurate visualization examination).
- A combined urodynamic study (CUDI) is necessary to determine the cause of urination.
Laboratory research
- Creatinine, urea - to assess the state of kidney function;
- General urine analysis;
- Blood test for the level of glycated hemoglobin;
- Flora smear;
- Cytological examination of the cervix.
At the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, you can undergo all the necessary diagnostics and laboratory tests in one day, which will significantly save your time. However, the list of studies can be changed depending on the indications and health status of the patient. The doctor will prescribe all the necessary procedures during a face-to-face consultation and, based on the results, will select the most optimal treatment method.
Urge incontinence
To whom does it happen ? It is equally common in women and men.
How it manifests itself. In this case, the need to urinate (including at night) arises immediately, so strong that the patient simply does not have time to run to the toilet. In this case, quite often, urge urinary incontinence is accompanied by frequent urination.
Why does it arise? Due to spasm of the bladder, which loses its ability to store and retain urine. In some cases, these uncontrollable bladder contractions can be caused by injuries, spinal cord and brain tumors, lower urinary tract infections and even multiple sclerosis, but in 50% of cases the cause of urge incontinence is a mystery.
How to treat it. The gold standard for the treatment of this type of urinary incontinence is medications that relieve bladder spasm: anticholinergics and beta-3-adrenergic receptor agonists of the bladder. Injections of botulinum toxin type A into the bladder wall have a good effect on overactive bladder. True, after 8–10 months its relaxing effect on the muscle structures of the bladder weakens. And the injections will have to be repeated again.
There is another option for treating urge urinary incontinence - electrical stimulation, which stimulates the fibers that innervate the bladder.
Don't lose a drop! Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles Read more
Treatment of urinary incontinence
Currently, non-drug, drug and surgical methods are used in the treatment of urinary incontinence.
Non-drug methods include behavioral therapy. This is a special bladder training in which you need to visit the toilet strictly according to a specific schedule. It is recommended to visit the toilet every hour or two throughout the day, and increase the periods between visits by 15-30 minutes each week. This method can lead to a gradual reduction in the manifestations of the disease. The patient begins to control the number of visits to the toilet, as a result of which the volume of the bladder gradually increases. The goal of this therapy is to try to avoid urinating for as long as possible. Any methods (lying down and sitting) that suppress calls to go to the toilet are used. The longer you delay going to the toilet, the more your bladder stretches. To strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, specially designed sets of exercises are used that restore the smooth muscles of the pelvic floor. This exercise gives positive results and promotes recovery. The introduction of drugs based on hyaluronic acid (filler) under the urethra has proven itself to be excellent.
Surgical treatment is recommended for patients when conservative methods are ineffective.
Currently, a common method of surgical intervention is the TVT loop (special vaginal sling). This type of surgery is the “gold standard” for the treatment of urinary incontinence. A special sling is used as a support under the neck of the bladder and urethra and is used to prevent urine leakage.
TVT - the technique is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor makes a small incision in the skin of the front wall of the vagina. The TVT sling is placed under the mid-urethra and needles are removed through incisions in the abdomen. Once the “device” is in place, the needles are removed. The loop is independently fixed to the paraurethral tissues. Surgical sutures are then placed over the incisions. The operation is performed within 30 minutes.
Treatment tactics depend on the causes of the disease and are selected individually by the attending physician in each case. Urinary incontinence is a serious problem that requires immediate treatment. It is very important to consult a doctor in time to prevent negative consequences and start treatment in a timely manner.
If you have urinary incontinence, where to start?
If you or your loved ones are faced with this problem for the first time, then the algorithm of actions given below will help you quickly come to the correct solution to the problem.
- Note the factors that provoke incontinence (under what circumstances does it occur). This may include coughing, laughing, changing body position (for example, standing up), lifting heavy objects, eating spicy foods, alcohol, or caffeinated drinks.
- Keep a diary of urination, that is, write down the time and volume of urine. Note all episodes of incontinence, as well as times when you have difficulty holding in urine. For reliability, keep the recording for 2-3 days (including night hours).
- With this information, make an appointment with a urinary incontinence specialist. For example, contact me by calling 8-903-964-03-01 or filling out the electronic form via the link
The sooner you start acting, the sooner you will return to your usual comfortable “dry” life.
Herbal treatment
Among the traditional methods aimed at treating urinary incontinence, the use of herbs is recommended:
- infusion of dill seeds;
- infusion of sage herb;
- infusion of yarrow herb;
- infusion of St. John's wort herb;
- blueberry decoction.
Urinary incontinence can be temporary and can be cured with folk remedies, but such treatment requires careful adherence to recommendations for preparing infusions and decoctions. However, only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment; it is very important not to start a process that could cause a serious illness.
Folk remedy for incontinence
In alternative medicine, there is an alternative medicine that helps make the lives of older women more comfortable by relieving them of the signs of urinary incontinence. To prepare it yourself, it is recommended to follow the following recipe:
- take 1 tablespoon each of dried St. John's wort, yarrow and sage;
- pour medicinal plants into a metal container (this can be a small saucepan or ladle);
- pour 1 liter of boiling water over the healing herbs;
- close the container with a lid and wrap it with a thick cloth or towel;
- Leave the future medicine for 1 hour to infuse and cool.
Take 200 grams of herbal infusion 3 times a day 30 minutes before eating. It is strictly forbidden to add sugar to drinks. Treatment time is 20-30 days. The recipe for this folk remedy for urinary incontinence in elderly women was created by people who know the medicinal properties of field and wild plants, as well as their effect on the human body. The main thing is that the pathology is not advanced, and the nature of its origin is not related to tumor processes, a severe form of infectious lesions of the genitourinary organs, or urolithiasis.
Preventive measures
You can prevent urine leakage by:
- timely emptying of the bladder;
- normalization of body weight;
- regularly performing Kegel exercises;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- regular visits to doctors for preventive purposes;
- properly organized nutrition;
- giving up bad habits;
- alternating work and rest.
Reducing physical activity, abdominal training, and strengthening the pelvic floor muscles help prevent stress urinary incontinence. The risk of developing this pathology increases in women who have given birth more than 2 times or who have had severe ruptures of the perineal muscles during labor.
Therapy for depression
Treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women begins with the prescription of sedatives. These include antidepressants and nootropics. The first ones normalize sleep, creating conditions so that a person can recognize the desire to urinate in a dream. The second group improves metabolic processes in the tissues of the nervous system and has a slight calming effect.
The main objectives of urinary incontinence tablets for women suffering from stress enuresis are to relieve anxiety and gently calm the nervous system. Due to this, the patient gains greater control over urinary retention during exercise.
Antidepressants
For stress urinary incontinence in women, antidepressants are the most successful treatment.
- Imipramine and drugs containing it (Tofranil, Melipramine) have a calming effect, help cope with involuntary urination during sleep, and relax the walls of the excretory system. Take 1 – 3 tablets per day shortly before bedtime. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. Prescribed to patients at least 6 years of age.
- Duloxetine acts centrally, relaxing the muscles of the urinary reservoir and reducing the likelihood of spontaneous leakage of urine. The standard dosage is from 2 to 4 capsules 1 time per day. Prescribed to patients over 18 years of age.
Antidepressants have a number of side effects, including dry mouth, dizziness, and visual disturbances. They cannot be used for glaucoma, hypertension, liver disease, pregnancy (the substance penetrates the placental barrier to the fetus).
Important! Medicines in this group affect vascular tone and can cause an attack of a sharp increase in blood pressure. The patient taking them should regularly check blood pressure readings in both arms.
Antidepressant medications should not be stopped at once. This provokes interruptions in the functioning of the heart, dizziness and nausea. The withdrawal or replacement of the medication should be done gradually.
Nootropics
They act more gently than antidepressants and have fewer contraindications.
- Phenibut reduces vascular tone, reduces anxiety, and improves sleep quality. The drug reduces excessive emotionality, which provokes neurotic reactions and stress incontinence. The dose and duration of administration depend on the patient’s age and the severity of the disorder.
- Pantogam stimulates metabolic processes in the cells and tissues of the nervous system, has a slight tonic effect without causing excitement. Prescribed 1 - 2 tablets 2 times a day after meals. The course of treatment is 2 – 3 months.
- Glycine helps get rid of insomnia and provides restful “watchdog” sleep (during which a person is able to wake up to go to the toilet). The tablets are dissolved in the mouth (under the tongue), 1 tablet three times a day.
Nootropic medications can enhance the effect of sleeping pills, painkillers, and anticonvulsants and reduce their side effects. Drug treatment is initially carried out with half the selected dose, gradually increasing it to the whole dose by the middle of the course, then the dosage is reduced back until the end of therapy.
Important! Most medications for urinary incontinence in women have contraindications and serious side effects. Under no circumstances should you take them on your own, without a doctor’s prescription. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to check the compatibility of the drugs with other tablets taken continuously.
What to do and how to treat?
Urinary incontinence is a problem that worsens not only hygiene, but also quality of life, causes emotional discomfort, and complicates social relationships. Often a woman is forced to completely change her lifestyle, avoid communicating with people, visiting public places, and quit her job.
Many ladies do not go to the doctor when they discover this problem and try to deal with it on their own. This is especially true for elderly patients who believe that incontinence is a variant of the norm for their age. As a result, the condition only gets worse, after which treatment becomes really difficult.
You should contact a urologist or gynecologist with this problem, who will tell you how to treat urinary incontinence in women. Medicine has developed many ways to combat incontinence. However, it is necessary to treat the condition taking into account the underlying disease that caused it.
Treatment of urinary incontinence in women includes medications, surgery, psychotherapeutic methods, physical exercise, physiotherapy (microcurrents, heating, electromagnetic effects).
Conservative methods are indicated in the initial stages of the disease, with high risks associated with surgery.
Diagnostics
But before prescribing a course of treatment, the doctor diagnoses the disease. Initially, a gynecological examination and interview of the patient is carried out in order to collect an anemnesis. In this case, the doctor seeks to obtain the following information:
- cause of pathology
- details of the development of pathology,
- duration of the disease,
- severity of incontinence symptoms,
- how often urine is released at night and during the day,
- whether the patient is taking any medications,
- whether the patient has any gynecological or urological diseases.
During a gynecological examination, inflammatory processes of the genital organs, prolapse or prolapse of the uterus and vagina may be detected. Palpation of the lower abdomen helps to identify tumors and determine the location of pain.
Also for diagnostic purposes:
- An ultrasound scan of the bladder and pelvic organs is performed,
- X-ray, urodynamic and endoscopic examinations of the bladder are carried out,
- A general urine test is taken to help identify inflammation and infections of the urinary system.
Instrumental methods for examining the bladder:
- retrograde cystometry (assessment of bladder reservoir function),
- cystography (radiography of the bladder with a contrast agent),
- pad test (determining the volume of urine flowing from the bladder),
- uroflowmetry (assessment of urine flow rate),
- urethrocystoscopy (endometric method of visual examination of the bladder and urethra),
- electromyography (study of electrical activity of the bladder muscles).
Urodynamic tests
Urodynamic tests include:
- stress test,
- Bonnie test,
- gasket test (daily or hourly).
The stress test is intended to assess the condition of a patient with a stress form of urinary incontinence. The patient with a full bladder is asked to cough or strain. If urine leaks during this test, this indicates the presence of a stress form of the syndrome. The Bonnie test differs from the stress test in that the bladder neck is elevated using a special device.
The pad test uses disposable pads to measure how often and how much urine leaks from the bladder. After the end of a certain period, the gaskets are weighed and, based on this value, the volume of leaked liquid is calculated.
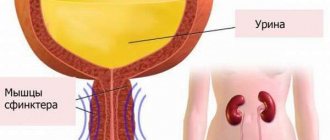
About urine leakage
Urine leakage is an uncomfortable condition that has an unpleasant effect on a person’s life. This problem falls within the competence of several medical specialists - neurologists, urologists and gynecologists. Urine leakage is usually caused by certain pathological processes .
Treatment of the disease is determined individually in each case. Urine leakage can be divided into several types:
Stress leakage of urine occurs during the following symptoms: coughing, fast walking and other actions that provoke an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. With stress leakage of urine, the patient has no desire to urinate.
Urgent urine leakage is characterized by a strong desire to urinate and the patient does not have time to carry it out in time. In quite rare cases, a person may not experience the urge; urine leakage occurs suddenly .
Mixed urine leakage is characterized by several types of urine leakage, mainly in one patient. In most cases, this is a combination of stress and urgency incontinence and is most often observed in women of advanced age. In this case, patients' complaints are addressed to urine leakage with uncontrollable initial urges.
Overflow incontinence is a form of urine leakage that is common in men who are predominantly older and have prostate disease. Due to impaired urinary outflow, the bladder overflows and stretches, which causes this type of urine leakage.
Diagnosis of causes
To identify the causes and form of the disorder, an examination by a gynecologist and urologist is required. When collecting anamnesis, the doctor pays attention to the timing of the onset of signs of pathology, the connection with the load, and the nature of the urge.
Examination in a chair is necessary to identify prolapse of the pelvic organs, cysto-, urethro- or rectocele, and genitourinary fistulas. Laboratory methods used:
- general urine test;
- bacterial culture of urine;
- survey microscopy of a smear.
Instrumental examination methods help determine the conditions that cause urine leakage. Prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- cystometry, uroflowmetry;
- cystoscopy;
- urethrocystography;
- urethroscopy.
Ask the patient to cough to detect stress urinary incontinence. Due to impaired distensibility and contractility of the sphincters, their ability to influence the process of urine excretion is lost. This indicates a neurological disorder.
Problems with urination as a result of previous bladder infections
Basically, these are previous cystitis that were not treated or were not cured on time. Acute cystitis is most often caused by a bacterial infection, namely E. coli, which easily penetrates the bladder, especially if the body is weakened. Girls sometimes experienced a burning sensation when urinating, a feeling of pain, and a frequent urge to urinate. However, only in 0.5% of cases do they see a doctor, and even less undergo treatment. The infection affects the sphincter and weakens it with age, leading to urinary incontinence later in life.
Drugs for the treatment of urge incontinence
Therapeutic measures to eliminate enuresis, the root causes of which are infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract, almost always involve the use of drugs in association. In almost all cases, this complex includes anticholinergic drugs ( Ditropan, Ditrol, Oskitrol).
These medications are characterized by a long-lasting effect and almost immediate elimination of the manifestations of the disease. The big disadvantages of taking these medications are: dry mouth, decreased vision, constipation, urinary retention.
Urgent urinary incontinence is stopped with the help of antispasmodics:
Driptan is the most effective method, since it has a positive effect on the smooth muscles of the bladder and blocks the movement of impulses that cause spontaneous urination.
Vesicare (Solifenacin)
The drug is produced only in tablets, containing 5 or 10 mg of the active ingredient - solifenacin succinate.
This is a specific inhibitor of membrane cells through which nerve signals are sent.
Refers to very effective medications for incontinence in women.
For unnaturally frequent urge to urinate and hyperactivity of the urinary organs, this drug is very effective.
In order to get rid of enuresis, take 5 mg tablets once a day; in other complicated cases, the dosage is increased to 10 mg. A medicine based on solifenacin succinate has an anticholinergic and antispasmodic effect.
Spazmex (trospium chloride)
A medication based on the active substance trospium chloride helps weaken the smooth muscles of the bladder.
It has antispasmodic and ganglion blocking properties.
All specialists prescribe the drug to patients over 14 years of age.
The exact dose and course to be taken is determined by the doctor, based on individual symptoms and indicators. Optimal consumption before meals with plenty of drinking water.
The drug Spazmex is produced in different dosages. Taking tablets is associated with the proportion of the active component present in it, for example, a 5 mg unit is taken up to 3 times a day, the time interval between each use is at least 8 hours.
When using tablets of 15 mg of active substance, it is recommended to drink 3 tablets per day, and take half a tablet containing 30 mg of active substance in the morning and evening.
In case of insufficient kidney or liver function, the dosage per day is no more than 15 mg. The general course of therapy is up to 3 months.
Toviaz
Fesoterodine is a competitive, specific antagonist of muscarinic nerve endings that reduces the number of urinations and spontaneous enuresis.
Does not transform or interrupt the QT interval on the ECG.
The drug is very quickly dissolved through nonspecific serum esterases to the 5-hydroxymethyl component, the main clinically active metabolite that determines the effectiveness of fesoterodine.
Mirobegron
Mirabegron is the newest word in pharmaceuticals, the principle of action is due to the formation of adrenergic receptors from the tissue of the bladder lining.
For this reason, the volume of the urinary organ increases.
According to medical annual statistics on taking this medication, adverse episodes are quite rare. If they did occur, they stopped immediately when the dosage was reduced.
Basically, this phenomenon was detected as a violation of heart rhythms, infections in the urethral excretory system. When prescribing a medication, combination with other medications must be taken into account.
Surgical treatment
In young patients, the problem can be solved with conservative treatment; in women about 60 years old, urinary incontinence, especially the stress form, can only be corrected by surgical intervention. There are more than 200 types of such operations, which are aimed at reconstructing the anatomically correct location of the urinary neck and urethra.
- Sling procedures. For adjustments, special support loops are used.
- Burch's operation. Suspension of the urethra using the vaginal walls.
- Artificial sphincter. Replacement of the sphincter is resorted to in case of complete or partial loss of functionality.
- Injections. The injection of collagen provides volume to support the urethra.
- Stimulation of the sacral nerves.
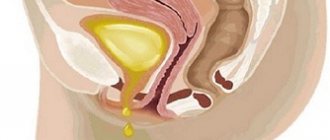
Stress urinary incontinence, or stress incontinence
This type is associated with the failure of the anatomical structures of the pelvic organs. In this case, urine leakage occurs in situations associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure.
Risk factors include diseases accompanied by coughing, sneezing, and constipation. In addition, urine leakage accompanies physical activity, laughter or other emotional states.
The mechanism of incontinence in this case is simple. Increased intra-abdominal pressure is transmitted to the full bladder. Accordingly, in order for urine to be retained in it, the structures responsible for this must withstand this increased pressure.
And if in young women this happens without difficulty, then with age, when the muscles and ligaments, as they say, are no longer the same, urine at the moment of tension can be released against the will of the owner.
Treatment
The first thing to do is pay attention to your diet. You should remove from your diet those foods that irritate the bladder. These include tomatoes, caffeine, citrus fruits, dairy products, sour berries, vinegar.
You can try to increase the size of the organ. To do this, you should endure the urge and allow the bladder (UB) to fill. Regular training will increase the time between visits to the toilet. You can create a schedule for going to the restroom at a certain interval and stick to it.
Kegel exercises will be beneficial for both women and men.
Doctors sometimes prescribe anticholinergic drugs, which help control urge incontinence in men and women by relaxing the bladder. These include:
- Solifenacin;
- Tolterodine;
- Oxybutynin;
- Darifenacin.
These drugs affect the contractility of the organ. The drug Flavoxate is used to relieve muscle spasms. Tricyclic antidepressants can also help. With their help, you can reduce the activity of the muscle that expels urine from the body.
Physiotherapeutic methods are also used. Thus, treatment for urge urinary incontinence in women involves the following: stimulating the nerves that are connected to the bladder. We are talking about the effect of electricity on the tibial and sacral nerves.
For women, pessaries are suitable, which are fixed in the vagina. Using this device, you can keep the urethra closed and create additional pressure. Pessaries are convenient for active activities.
If all of the above methods are ineffective, then doctors may suggest surgery.
Operations for women
Any intervention is aimed at returning organs to their usual places. As a result, you can completely overcome the urgent urge to urinate. What it is? There are special loops - slings. Their installation is low-impact, and there are many advantages. The effect is already noticeable after a few hours, rehabilitation does not take much time . The operation is performed under local anesthesia. To install the loops, the surgeon inserts a mesh into the incisions under the organs, which acts as a hammock.
After the operation, you cannot be sexually active for a month and a half. Antibiotics will be appropriate to prevent inflammation.
Colpopexy. A method in which the genitals are fixed in the correct position and do not interfere with the functioning of the bladder.
Neuromodulation. Urgent urinary incontinence is corrected quite successfully thanks to an implant - an electrode implanted into the spinal cord. And then the function of regulating the muscles of the urethra and small pelvis is transferred to it.
Injections. Botox injections into the tissue will have a temporary effect. The impact on the nerves and muscles will help eliminate incontinence from six months to a year. Then the procedure is repeated.
Operations for men
Urgent urinary incontinence in men is often overcome with the help of loops, as well as with the installation of an artificial sphincter. The latter is a silicone prosthesis consisting of an inflatable cuff and a pressure-regulating reservoir. Part of the structure is a pump that controls its operation. The sphincter is installed where the urethra passes into the bladder.
The pump is located in the scrotum. The cuff is filled with fluid. She squeezes the urethra. When it's time to go to the toilet, the man presses the pump and the sphincter opens as water flows into the reservoir. When the bladder is emptied, the sphincter fills with fluid again, constricting the urethra. The design is 90% efficient. It allows you to solve the problem of urge urinary incontinence in men, both complete and partial.
Slings. Loops are considered less effective than an artificial sphincter, but the operation is simpler and cheaper.
A sling is a mesh made of inert synthetics. It is implanted into the perineal area, fixing it to the pubic bones. The urethra is pinched, pressure is created and urine does not leak. For mild incontinence, surgery may help. If the sphincter is completely out of order, then this method will not bring the expected effect.