Nephrologist
Lavrova
Olga Nikolaevna
21 years of experience
Nephrologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Make an appointment
In the group of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the excretory system, kidney pyelonephritis occurs equally often in adults and children. The bacterial infection affects all structural parts: pelvis, calyx, peranchyma. The pathology occurs in acute or chronic form. Pyelonephritis is insidious in its secrecy and ability to masquerade as a cold, cystitis, gastritis, radiculitis. At a young age, women are more often affected, but with age the ratio shifts towards men due to the manifestation of age-related problems with the prostate gland. According to statistics, kidney pyelonephritis is diagnosed in 20% of the population.
Symptoms and signs of pyelonephritis
The disease is characterized by an acute onset with severe malaise. For this reason, the patient's general condition resembles a cold. Further pyelonephritis symptoms can vary, depending on the form of the disease. The list includes:
- high temperature up to 38-40°C;
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the lumbar area;
- increased sweating;
- feeling of thirst;
- nausea and vomiting;
- trembling and chills.
One of the characteristic signs is urine with pyelonephritis with a strong odor due to the development of infection. The patient's condition may also be worsened by belching, muscle weakness and swelling. The skin is pale due to intoxication of the body.
Diagnostics
The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Laboratory tests (carried out if the test material is available): blood and urine tests. They allow you to quickly establish the cause of inflammation and begin effective treatment.
- Instrumental, x-ray and radionuclide research methods.
During a general blood test, the following are measured: acceleration of ESR, leukocytosis, iron level, etc. A biochemical study allows us to determine an increase in creatinine, urea, transaminase.
A medical urine test for pyelonephritis may not indicate leukocyturia for the first four days. This happens when inflammation is in the cortical layer of the kidney parenchyma. Bacteriological studies are used to determine the pathogen and its resistance to antibacterial therapy.
Urine Gram stain allows you to quickly obtain information about the nature of the pathogen. This method was first proposed by the physician Hans Christian Gram in 1884. In almost all cases, it is recommended to conduct a urine culture test, which takes little time and gives an accurate result.
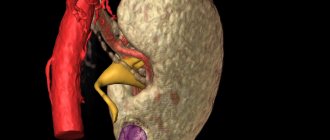
Instrumental research methods include ultrasound of the kidneys, which makes it possible to detect enlargement of the organ and the presence of pathological changes in it. Diagnosis takes a minimum of time and allows you to start treatment as quickly as possible.
X-ray methods include excretory and survey urography, abdominal aortography, retrograde pyeloureterography.
Causes of the occurrence and development of the disease
Pyelonephritis has bacterial causes. The infection can enter through the urethra even if hygiene rules are not followed. In this aspect, pyelonephritis in women occurs 6 times more often than in men. This is due to the anatomical features - a short and wide urethra. Rarely does a single bacterium become the causative agent. Most often, tests reveal a number of pathogens (staphylococci, E. coli, Proteus, Enterococcus, Klebsiella). The following pathological conditions can also cause the development of the disease:
- history of urolithiasis;
- tumors in the genitourinary system;
- intestinal diseases;
- irregular flow of urine;
- weakened immune system;
- diabetes;
- prostate adenoma.
Ways of infection by bacteria
Pyelonephritis occurs in women in some cases due to insufficient hygiene of the genital organs. The condition of urinary retention, which creates a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microflora, is also dangerous. Impaired blood flow in the kidney has a similarly detrimental effect. The most common route of infection is the ascending route of infection - from the urethra, bladder and higher towards the kidneys.
Pyelonephritis: women suffer more often
Let's start with the fact that pyelonephritis - inflammation of the tissue and pelvis of the kidney - is a very common disease. Thus, according to statistics, about a million new cases of this disease are registered in Russia every year.
Let us emphasize that pyelonephritis affects the fair sex 6 times more often . This is due to anatomical features: the urethra in women is shorter and wider than in men, as a result of which pathogenic microbes easily penetrate into it urogenously, for example, from the bladder quickly get to the kidney. Infectious agents include Escherichia coli, staphylococcus and some other microorganisms. By the way, they can enter the kidney not only urogenously, but also through the bloodstream from an existing source of inflammation in the body, as well as from the outside. Let's add to this that pyelonephritis can be unilateral or bilateral .
Pyelonephritis often develops against the background of urolithiasis , as well as prostate adenoma in men, accompanied by disturbances in the outflow of urine. Other factors contributing to the onset of the disease include weakened immunity, stress, and lack of vitamins . Pyelonephritis can be acute or chronic . The main signs of the first include pain in the lumbar region, difficulty urinating, fever, chills. As intoxication increases, the patient may experience nausea, vomiting, and headache. If you have the above symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor , otherwise the disease may become chronic.
Among all urinary tract infections, chronic pyelonephritis in our country, according to statistics, is registered in 53 % of cases. It can be asymptomatic , which sometimes makes it difficult to diagnose. In such cases, the disease manifests itself only during periods of exacerbation. In this case, the patient complains of dull pain in the lumbar region and general weakness, his temperature rises, and frequent urination appears. Another characteristic symptom of chronic pyelonephritis is increased blood pressure , especially if both kidneys are affected. It is important to know that in the absence of timely and competent treatment, chronic pyelonephritis is fraught with dangerous complications that can lead to the development of renal failure.
Speaking about the treatment of acute and chronic forms of the disease, it should be noted that antibacterial therapy . It is aimed at fighting infection, and is prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. Along with traditional drugs, traditional medicine , in particular, vitamin-rich cranberry juice . Infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants are also widely used. For example, an infusion of blue cornflower , which has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory and restorative effect. It is prepared as follows: pour a teaspoon of dry raw material with a glass of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, strain. Drink 1/2 glass 2-3 times a day.
In the fight against pyelonephritis, it is difficult to overestimate the importance of therapeutic nutrition . So, in the acute form of the disease, the patient is advised to follow a sugar-fruit diet in the first two days, including sweet fruits and vegetables, such as prunes and zucchini. Sweet juices, compotes, jelly, rosehip decoction, tea are useful. By the way, a patient with pyelonephritis should drink at least two liters of fluid per day. But protein foods should be excluded at the beginning of the disease, as they create additional stress on the kidneys. As you recover, the diet expands to include boiled meat, fish, and cereals. However, spicy, fatty, fried foods for a long time are contraindicated as they can cause aggravation. A gentle diet is also necessary for chronic pyelonephritis: for example, vegetable soups, boiled meat or fish, dried white bread, dairy and fermented milk products are recommended.
Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of pyelonephritis? How to resist a possible exacerbation of an existing disease? Since the disease usually develops against the background of a weakening of the body’s defenses, one should first strengthen the immune system . To this end, it is necessary first of all to complete the treatment of existing foci of chronic infection, for example, cystitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder) or tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils). Strengthening the immune system is facilitated by a healthy lifestyle , which includes a balanced diet, adherence to a work and rest schedule, physical education and sports.
To prevent pathogenic microbes from entering the kidney, it is necessary to maintain hygiene of the genitourinary organs. In addition, the cause of pyelonephritis is often hypothermia , so try to avoid it.
Risk factors
The risk that acute pyelonephritis will turn into chronic is quite high. This can happen if the diagnosis is incorrect and the treatment is incorrect. Children under 7 years of age, women of any age, as well as elderly men over 55 years of age are always at risk for the disease. For the development of the disease, several factors must coincide. One of them is the presence of systemic diseases. Any infectious foci in the body also increase the risk of becoming a patient diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis. Often the preceding factor is cystitis. In some cases, pyelonephritis may develop during pregnancy, as the kidneys experience increased stress. This is a dangerous condition that affects 1 in every 10 women. Risk factors may also include:
- congenital anomalies of organs (urethra, kidneys, bladder);
- surgeries in the urinary system;
- installation of a catheter in the bladder;
- spinal cord injury;
- uterine prolapse;
- AIDS.
Differential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis is made with genitourinary tuberculosis, congenital reduced kidney and chronic glomerulonephritis.
The tuberculosis process in the kidneys is characterized by the predominance of leukocytes in the urine over microhematuria. The patient is subject to examination by a urologist at an anti-tuberculosis dispensary, where he will undergo a urine test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and excretory urography. In the differential diagnosis of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis, a clarifying answer can be obtained by carefully taking anamnesis and examining urine.
Below are the main signs - the differences between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
A hypoplastic (reduced in size) kidney has clear contours, no deformation of the internal cavities, and characteristic tissue density.
Pay attention to the absence of urological diseases in the anamnesis; if there was no urological pathology, then there is more evidence for hypoplasia.
When to see a doctor
Pyelonephritis exhibits symptoms similar to other pathological conditions, which complicates its diagnosis. Pain in the kidney area is one of the symptoms that should alert you and be a reason to consult a doctor. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a urologist at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in the center of Moscow. It is necessary to be examined both in acute conditions and in protracted cases of the disease. Chronic pyelonephritis is well disguised as a long-term cold or gynecological diseases. It is also necessary to consult a doctor if you have problems with the outflow of urine. The unknown reason for this fact is a constant source of bacterial infection. Its onset may be indicated by a sharp and unpleasant odor of urine. Pyelonephritis symptoms may present aggressively and treatment in such cases should begin immediately. This will help avoid structural changes in the kidneys. The appearance of blood inclusions, increased protein levels in a urine test, and renal colic are also reasons for a visit to the urologist.
Causes
There are two causes of pyelonephritis:
- Reduced natural defense mechanisms of the body.
- The presence of pathogenic microflora.
The inflammatory process begins after E. coli, enterococcus or staphylococcus enters the body. Other parasitic bacteria can also lead to infection of the urinary tract. In the presence of cystitis or urethritis, they pass through the ureters from the bladder to the kidneys. Inflammatory processes can occur in other organs when microbes enter the circulatory system and spread throughout the body.
There are factors that contribute to the occurrence of pyelonephritis:
- Injuries in the lumbar region.
- Malfunctions in the functioning of the system regulating the activity of internal organs.
- Hypothermia.
- Anomalies of kidney development.
- Pregnancy.
- Impaired urine flow.
- Microtraumas that appear during sexual intercourse.
- Operations or instrumental diagnostics on the urinary tract.
- Taking intrauterine contraceptives.
- Reusable catheter.
- External lithotripsy.
If the first signs of the disease appear, you should consult a urologist who follows clinical recommendations for pyelonephritis.
Nosocomial strains that are resistant to antibiotics are the most aggressive in terms of infection. Patients often experience multidrug-resistant and combined forms of the disease. The first appear as a result of unsystematic and incorrect antibacterial treatment.
Routes of infection:
- Hematogenous - through the blood.
- Ascending - through the intestines or urogenital organs.
In the first case, the source of infection can be inflammation located in any organ. Pathogenic bacteria spread throughout the body, entering the circulatory system.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis
At the appointment, the doctor collects data on the patient’s condition and conducts a general examination. Tests for pyelonephritis help confirm the diagnosis. The doctor makes the appointment. Urine and blood tests (general clinical) are first on the list. Additional instrumental studies are required to clarify the current state of the patient’s excretory system and internal organs: computed tomography, radiography. They make it possible to detect chronic pyelonephritis even several years after the disease. At JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) on Mayakovskaya metro station you can undergo a full examination. All types of studies are available to patients: laboratory tests, CT, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray, scintigraphy, angiography.
Stages of chronic pyelonephritis
There are four stages of chronic pyelonephritis:
At the first stage of development of the disease, the glomeruli of the kidneys are intact, that is, they are not involved in the pathological process, and the atrophy of the collecting ducts is uniform.
At the second stage of development of the disease, some glomeruli become hyalinized and empty, the vessels undergo obliteration and significantly narrow. Scar-sclerotic changes in the tubules and interstitial tissue increase.
At the third stage of the disease, the death of most glomeruli occurs, the tubules become severely atrophied, and the interstitial and connective tissue continues to grow.
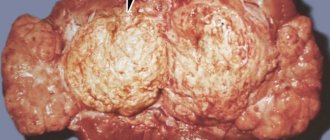
At the fourth stage of development of chronic pyelonephritis, most of the glomeruli die, the kidney becomes smaller in size, and its tissue is replaced by scar tissue. The organ looks like a small wrinkled substrate with a bumpy surface.
Treatment of kidney disease
Pyelonephritis treatment requires complex treatment. Therapy is used with medication and physiotherapy. Treatment tactics are selected individually by the urologist. Antibiotics are prescribed for pyelonephritis in the acute stage to suppress the bacterial infection. In the first place is the need to restore the outflow of urine and find the cause of urodynamic disturbances. Diet for pyelonephritis and bed rest are also indicated. 3-5 days after the start of complex therapy, the degree of manifestation of symptoms decreases.
The chronic stage of the disease cannot be completely cured due to structural changes in the kidneys. Remission is periodically replaced by exacerbations, which are treated according to the principle of acute pyelonephritis. During remission, you must follow a diet and do not forget about maintenance therapy.
Symptoms of chronic pyelonephritis
The course of the disease and symptoms of chronic pyelonephritis largely depend on the localization of inflammation, the degree of involvement of one or two kidneys in the pathological process, the presence of urinary tract obstruction, and the presence of concomitant infections.
Over the course of many years, the disease can be sluggish, with the interstitial tissue of the kidney involved in inflammation. Symptoms are most pronounced during an exacerbation of the disease and can be almost invisible to a person during remission of pyelonephritis.
Primary pyelonephritis gives a more pronounced clinical picture than secondary. The following symptoms may indicate an exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis:
Increase in body temperature to high values, sometimes up to 39 degrees.
The appearance of pain in the lumbar region on both one and both sides.
The occurrence of dysuric phenomena.
Deterioration of the patient's general well-being.
Lack of appetite.
The occurrence of headaches.
Abdominal pain, vomiting and nausea occur more often in childhood than in adult patients.
The patient's appearance changes somewhat. He can notice these changes on his own, or the doctor will pay attention to them during the examination. The face becomes somewhat puffy, swelling of the eyelids may be observed (
Home remedies
Traditional medicine does not stand aside, offering various herbal collections and decoctions from them. There is an opinion that birch sap is an excellent remedy. It is recommended to drink 200 ml daily in the morning on an empty stomach. The juice should be natural, and not from a store-bought can. Caution: this method is contraindicated for people with urolithiasis. During the watermelon season, you can save yourself from illness with these sweet large berries. They perfectly remove excess fluid from the body and improve kidney function. On the watermelon day of the diet, liquids other than water should not be consumed. Unloading in this way can be carried out after the end of the exacerbation period.
A bud collection of sage, chamomile and calendula, birch and lingonberry leaves has bactericidal properties, allowing you to suppress the development of infection and inflammation. A decoction of bearberry has a good effect. It is enough to pour 1 tbsp of boiling water. herbs, infuse and take 3 times a day before meals, 2 tbsp. An alcohol tincture is also made with bearberry. To prepare it you need to take 2 tbsp. herbs per 100 ml of vodka. Mix and leave for 2 weeks. Take 15 drops after meals. The course of treatment is 2 months. Please note that any recipes and advice from traditional medicine must be agreed with your doctor.
Instrumental diagnosis of chronic inflammation in the kidneys
Chronic pyelonephritis is diagnosed by the following methods:
• X-ray examination of the kidneys: intravenous and infusion urography. Pyelonephritis is characterized by an increase in the renal-cortical index (> 4), as well as a decrease in the thickness of the renal parenchyma at the poles (Hodson's symptom). • radioisotope methods (renography, dynamic computer scintigraphy), • ultrasound methods.
The main X-ray signs of chronic pyelonephritis:
• Changes in the size and contours of the kidneys. • Slow down contrast release. • Changes in the architecture of the kidneys. • Expansion of the pelvis. • Hodson's symptom (if the calyces of a healthy kidney are located along a symmetrical line, then with chronicity the distance between the calyces and the contour of the kidney is different and the line connecting them is incorrect).
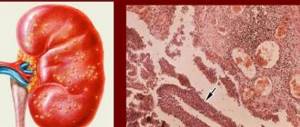
With the standard picture of pyelonephritis, a decrease in the size of one of the kidneys, an increase in the density of the shadow and the vertical axis at the site of the affected kidney are visualized.
Excretory urography is a method for diagnosing chronic inflammation in the upper urinary tract. X-ray signs of pathology are diverse, and the asymmetry of changes depends on the ratio of areas of inflammation and areas of sclerosis.
Retrograde pyelography is used less frequently, as there is a possibility of kidney infection from a hospital infection.
Chronic pyelonephritis is characterized by gradual atrophy of the renal parenchyma, which is more accurately determined using the renal-cortical index.
To clarify the condition of the kidneys, radioisotope renography is used; the method makes it possible to clarify the function of each kidney separately and evaluate changes during therapy over time.
Dynamic scintigraphy determines the quantity and quality of functional renal parenchyma in chronic inflammation.
The method is more accurate compared to excretory urography, since sometimes there is no renal dysfunction on urograms, and dynamic scintigraphy gives a clear picture of the presence of changes.
Signs of chronic pyelonephritis on ultrasound
Signs of hydronephrotic transformation
Ultrasound of the kidneys is a non-invasive, painless method of examination; when performing the study, the expansion of the kidney cavities and the diffusely heterogeneous structure of the parenchyma are visible. Ultrasound helps to distinguish a hypoplastic kidney from a sclerotically wrinkled one and diagnose many other urological pathologies.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of pyelonephritis
The biggest misconception is that any kidney disease must be accompanied by severe pain. This is one of the possible symptoms, but it may not always be pronounced. The latent course of the disease (chronic and asymptomatic) can be detected accidentally on an ultrasound or CT scan during examination for some other reason. Pressure surges, fever, malaise, and general weakness are rarely taken seriously enough to make an appointment with a urologist.
If pyelonephritis occurs in men, then it is impossible to clean the kidneys with beer, although many are sure of the opposite. This is another big misconception. Beer has no benefits for the kidneys. But you can’t get too cold – that’s true. This leads to ascending inflammatory processes.
Prevention of chronic pyelonephritis
Prevention of patients with pyelonephritis comes down to timely and thorough treatment of patients at the stage of acute pyelonephritis. Such patients should be registered at the dispensary.
There are recommendations for the employment of patients with chronic pyelonephritis: patients are not recommended to be employed in enterprises that require heavy physical labor, which contribute to being in constant nervous tension. It is important to avoid hypothermia in and outside the workplace, avoid working on your feet and at night, and avoid working in hot workshops.
You should follow a diet with limited salt as recommended by doctors.
The success of preventive measures for secondary pyelonephritis depends on the complete elimination of the cause that led to the development of the disease. It is important to remove any obstructions to the normal flow of urine.
It is important to identify and treat hidden foci of infection and intercurrent diseases.
After discharge from the hospital, patients must be registered with a dispensary for a period of at least one year. If after this time bacteriuria, leukocyturia and proteinuria are not detected, then the patient is removed from the register. If signs of the disease persist, the observation period for such patients should be extended to three years.
If primary pyelonephritis is detected in patients, then the treatment is long-term, with periodic placement in a hospital.
Correcting the immune system and maintaining it normal is no less important. This requires maintaining a healthy lifestyle, prolonged exposure to fresh air, and dosed physical activity as prescribed by a doctor.
Staying in specialized sanatorium-resort institutions can reduce the number of exacerbations of the disease.
Prevention of the disease in pregnant women and children, as well as in patients with weakened immune systems, deserves special attention.
With a latent course of the disease, patients do not lose their ability to work for a long time. Other forms of pyelonephritis can have a significant impact on a person’s performance, since there is a threat of rapid complications.
Author of the article: Vafaeva Yulia Valerievna, nephrologist, especially for the site ayzdorov.ru
Interpretation of online tests - urine, blood, general and biochemical. What do bacteria and inclusions mean in a urine test? How to understand the tests of a child? Features of MRI analysis Special tests, ECG and ultrasound Norms during pregnancy and the meaning of deviations.. Explanation of tests
What it is?
Chronic pyelonephritis is the most common form of kidney disease and occurs in all age categories of the population. It is characterized by inflammatory processes in the tissue membranes of the kidneys (parenchyma) and in the pyelocaliceal system, which is responsible for the functions of accumulation and excretion of urine.
The disease is often discovered unexpectedly in patients, due to a general deterioration of their condition or based on the results of a urine test. Since the chronic form of pyelonephritis quite often develops without acute symptoms, and patients do not even suspect its presence.
Prevention is the best defense
Treatment of pyelonephritis in women is often associated with gynecological diseases that can occur due to hypothermia. Compliance with physical activity and diet will have a beneficial effect on men. If the disease is chronic, it is necessary to prevent exacerbation of pyelonephritis. Common preventive measures for all will be supplemented by the following points:
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- control of secondary infectious foci (caries, tonsillitis);
- undergoing preventive examinations;
- regular consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits;
- Periodically you need to take a urine test.
About pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is a common dysfunction of one or both kidneys caused by pathogenic microbes entering the kidney tissue.
During the inflammatory process, the tubular system of the organ, its parenchyma, calyx and pelvis are affected. The disease often has a bacterial etiology. In most cases, symptoms of pyelonephritis occur in women, especially during pregnancy, when the fetus puts pressure on the bladder. With the help of excisional and puncture biopsy, it is possible to determine the stage of the disease: acute, chronic or chronic with exacerbations.
Pyelonephritis in children often develops after pneumonia and influenza. In infants, the disease is expressed by the following symptoms: vomiting, refusal to eat, convulsions, high body temperature, cyanosis and pale skin. The danger of the situation is that the baby cannot tell what exactly hurts him. Therefore, if symptoms of pyelonephritis appear in children, you should immediately seek help from a pediatrician.
In childhood, the disease is registered in 3% of girls and 1% of boys.
Pregnant women suffer from kidney inflammation for two of the most common reasons:
- Due to a violation of the outflow of urine as a result of compression of the bladder by the uterus.
- Due to severe hormonal imbalance and immunological changes.
Pyelonephritis during pregnancy is recorded quite often. According to BME data, the acute form occurs in 2-10% of women, often in primigravidas.
The disease can develop in the first few weeks after birth with complications. But mostly it is recorded at the end of the second and beginning of the third trimester, when the hormonal ratio changes and the uterus increases in size.
How to make an appointment with a urologist
Pyelonephritis in adults and children must be promptly diagnosed and treated. This is the responsibility of a urologist, with whom you can make an appointment by telephone at a convenient time. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located in the Central Administrative District at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10.
An appointment booking function is available on the clinic’s website. In a special form you need to indicate your contact information and the doctor’s specialization. After sending, the administrator will call you back and clarify the details of the appointment.
To diagnose pyelonephritis, treatment is mandatory, regardless of the stage of the disease. The most important thing is to take care of yourself and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Features of the treatment of chronic inflammation in the kidneys
Treatment of chronic pyelonephritis in remission does not require the use of antibiotics. To be sure that there is no inflammation, undergo an ultrasound, give your urine for a general analysis and a Nechiporenko test. If urine culture for flora doesn’t show growth, it’s definitely in remission. In this case, seasonal preventive therapy with uroseptics (spring - autumn), 10 days each, and taking herbal medicines are sufficient.
When pyelonephritis has a continuously relapsing course and is complicated by any concomitant pathology that suppresses the immune system, antibiotics are needed. In this case, with each repeated exacerbation of the disease, urine culture is performed to verify the pathogen(s) and sensitivity to the antibiotic.
If possible, you should definitely check the state of your immune system and, based on the results, choose the right immunotherapy drugs.
Periodic intake of herbal diuretics helps remove pathogenic microorganisms from the urinary system and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Don't forget about proper nutrition.
During the period of remission, treatment with mineral waters is indicated: Zheleznovodsk, Truskavets.