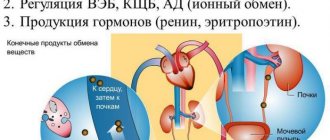
Excludes: trauma to the peritoneum and retroperitoneum (S36.8)
The following subcategories are provided for optional use in additional characterization of a condition where multiple coding is impossible or impractical:
0 - no open wound in the abdominal cavity
1 - with an open wound in the abdominal cavity
- Adrenal gland
- Prostate
- Seminal vesicles
- Vas deferens
Excludes: open wound of other and unspecified external genitalia (S31.5)
ICD-10 alphabetical indexes
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Medicines and chemicals - table of medicines and chemicals that have caused poisoning or other adverse reactions.
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997 No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Abbreviations and symbols in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
NOS
- without other instructions.
NEC
— not classified in other categories.
†
— code of the main disease. The main code in the dual coding system contains information about the underlying generalized disease.
*
- optional code. An additional code in the double coding system contains information about the manifestation of the main generalized disease in a separate organ or area of the body.
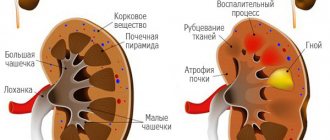
Internal organs are quite well protected from mechanical damage. However, injuries are possible here too. Kidney bruise is not the most common occurrence and is usually associated with damage to other pelvic organs.
Kidney bruise
The ribs and spine, back muscles, subcutaneous fat, perirenal tissue - all this creates a reliable barrier to mechanical factors. However, injuries are still possible.
According to its characteristics, a bruise belongs to the category of closed injuries along with crushing, rupture of the fibrous membrane, contusion, and so on.
There are 2 types of damage:
- isolated injury - there is a bruise of only the right or left kidney, the patient is admitted to the urology department;
- combined – several different organs are damaged. Victims often end up in the surgical department.
An organ bruise causes short-term positive pressure above 1000 atm, or low negative pressure of 50 atm.
Two factors can provide this effect:
- direct trauma – fall on a hard object, blow, bruise of the lower back, compression;
- indirect impact - falling from a height, jumping.
If the injury was preceded by kidney disease, then a bruise occurs with the most minor blows, even a fall. Moreover, even low-energy shock wave pulses are considered damaging factors.
According to statistics, the left kidney is more often damaged, since it is located somewhat lower and less protected by the ribs.
The ICD-10 codes are:
- S37. – trauma to the pelvic organs;
- S37.0 – kidney injury;
- S37.00 – organ injury without open damage to the peritoneum
- S37.01 – injury with an open wound of the peritoneum;
- S37.7 – injury to several pelvic organs.
Types of kidney injury
Open damage
Open wound injuries occur as a result of injuries caused by various instruments. Gunshot wounds are considered one of the most severe injuries. This is explained by the fact that the position and shape of the wound channel, when the wound is inflicted by a firearm, is quite complex, and the lesion is quite extensive. In addition, such wounds are most often accompanied by large blood loss. With such injuries, the kidney may be torn off, as well as crushing of the organ. In case of stab wounds, how the incisions are positioned relative to the blood vessels in the kidney is critical. If the main vessels or the renal pedicle are damaged, this significantly expands the affected area. In such cases, the risk of suppuration, urinary infiltration, and phlegmon increases, especially if the wound penetrates deep into the peritoneum.
The main sign that determines the presence of kidney damage is the leakage of urine from the wound.
As a rule, it does not appear immediately after injury, but there are laboratory methods for detecting even a small amount of urine in the blood from a wound. Such methods are used when it is impossible to visually assess the presence of urine, but there is a suspicion that the kidney is damaged.
Open damage - causes
Pathogenesis
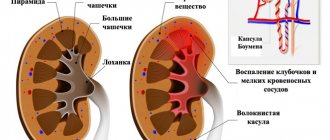
By organ bruise we mean an injury in which there is numerous hemorrhage into the kidney parenchyma without ruptures. The degree of changes varies - from minor hemorrhages to complete destruction of the kidney tissue. The damage may not impair the integrity of the organ at all, but the bruise has an even stronger effect on the functionality of the kidneys.
Hemorrhage naturally leads to the formation of a hematoma: small vessels rupture under pressure and blood ends up in the tissues. With more severe injuries, there is a risk of vascular blockage.
The bruise is classified according to severity as follows:
- 1 – subcapsular hematoma without tissue rupture. Damage leads to the loss of 1–15% of nephrons, which does not affect the functions of the organ;
- 2 – perirenal hematoma, possible damage to the superficial cortical layer. A bruise is not accompanied by hematuria, that is, blood in the urine;
- 3 – damage to the renal tissue to a depth of 1 cm is observed. Hematuria is present. Loss of up to 30% of renal parenchyma is possible;
- 4 – damage involves the pyelocaliceal system. Possible renal artery thrombus;
- 5 – multiple irreversible tissue changes, there is a high probability of thrombosis of the renal artery or vein. Irreversible dystrophic kidney damage can reach 65%.
Treatment
Most often, kidney injuries require hospitalization. Treatment will depend on the patient's diagnosis, what type of injury, and how severe the injury is. Therapy can be carried out using surgical methods, or can be carried out using a conservative method.
Treatment of closed kidney injuries
For minor injuries, doctors can generally limit themselves to observing the patient without using any methods of therapy. In almost 85% of kidney injuries without external damage, doctors use conservative treatment. This occurs when hemodynamics are stable and the injury is not life-threatening. In the absence of internal bleeding and obvious urinary infiltration, the patient is prescribed bed rest and complete rest, taking antiseptic and painkillers. In some cases, usually with moderate injuries, antibiotics and uroseptics may be prescribed. Medical personnel monitor hemodynamics and hemocrit, treatment is carried out until signs of blood in the urine disappear.
In cases where the wall of the pelvis is damaged, an internal hematoma grows, there is a lot of blood in the urine and the patient’s condition worsens, then surgical treatment of the damaged kidney is indicated.
Treatment of open kidney injuries
Conservative treatment for open injuries, as a rule, is not carried out. It is indicated only if the tissue damage is minor, the injury is isolated, and the patient is in satisfactory condition.
At the moment, science has methods to preserve organs and minimally invade the patient’s body. Using the endoscopic method under ultrasound control, it is possible to remove a growing hematoma, eliminate the consequences of urinary infiltration, and perform kidney embolization using a catheter.
Indications for surgical intervention are lack of hemodynamic stability, ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, growth of internal hematoma, extravasation of a significant volume of urine, combined damage to the kidneys and abdominal organs. If a relatively large area of the kidney is found that does not show signs of life, resection of part or all of the kidney is indicated.
Symptoms
Bruised kidneys, even if not severe due to the formation of a hematoma, immediately make themselves felt. Signs may vary, especially if you already have kidney disease.
For closed injuries, the following 3 signs are considered characteristic:
- pain in the lumbar region – a sign appears in 95%. The pain varies: dull, sharp, stabbing, radiating to the groin or thigh;
- swelling in the lower back - occurs in 10%, usually in more severe cases, since for this to happen, blood or urine with blood must penetrate the perinephric tissue;
- hematuria – the appearance of blood in the urine. This is the most indicative sign of a kidney injury. However, it may not appear immediately, but after a few days - secondary hematuria.
In addition, due to pressure on the peritoneum and blood loss, other symptoms appear: bloating, vomiting, pale skin and mucous membranes, hyper- and hypotension, and so on.
The brightness and number of symptoms depends on the severity:
- At the mild stage, there is no perinephric hematoma, hematuria is small, and there are no signs of peritoneal irritation.
- In the middle stages, blood pressure drops, hematuria increases, blood clots accumulate in the bladder, which makes urination difficult and can lead to acute retention. The stage of moderate severity is very conditional, and in most cases leads to a transition from a relatively satisfactory to a state of moderate severity.
Severe stages are characterized by severe pain, gross hematuria, and urohematoma in the lumbar region. Against this background, signs of internal bleeding appear and develop. As a rule, such a serious condition is a consequence of complex trauma.
Treatment of damage
If a person has all the symptoms and treatment should be carried out very urgently, then therapy is selected depending on the following factors:
- The severity of the injury.
- Problems with the kidneys.
- Complications appear.
- The presence of parallel pathologies of other internal organs.
If the degree of injury is not so serious, it can be treated in an outpatient clinic. When the injuries are severe or with complications, then the patient is admitted to the hospital.
How to treat at home
Despite the fact that this organ is protected by bones and muscles, it is still seriously damaged by falls and blows. If, when receiving various injuries, you immediately seek help from a specialist or call an ambulance, bruised kidneys will not cause a person any serious complications. If this is not done, then nephritis or other renal pathology may occur.
Until the ambulance gets to you, then your kidney injury can be localized by organizing treatment yourself. But the main thing you need to understand is that such damage cannot be cured using traditional medicine recipes.
First, you should apply ice, that is, a cold compress, after which you will feel a little better. If there is anyone else in the house, you can make a decoction of the medicinal herb arnica and immediately grind it after cold.
In addition, the signs of kidney injury that appear can be slightly alleviated with the help of a cabbage compress. Simply chop the cabbage and apply it to the bruised area.
Diagnostics
The reason to consult a doctor in such cases is lower back pain. Hematuria may be so slight that it is invisible to the eye.
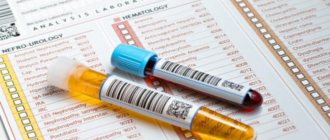
Based on the patient’s complaints, a laboratory test is prescribed:
- General urinalysis - allows you to detect hematuria. The latter indicates kidney damage;
- general blood test - a low level of hemoglobin and hematocrit in the blood is indicative, which indicates anemia or hidden bleeding;
- carry out separate urine tests to exclude other possible diseases.
Instrumental methods are used to clarify the diagnosis, detect other injuries, determine hematomas, and so on:
- The most informative are x-ray methods. They allow you to assess damage, accurately determine the location of hematomas, and, most importantly, determine associated injuries.
- Ultrasound is the safest method of examination and is quite informative: with the help of ultrasound, the diagnosis is made in 80% of cases. Allows you to determine the degree of change in the renal parenchyma and the location of hematomas.
- In case of disturbances in the blood supply, radiocontrast methods are also prescribed. Angiography and MRI, since these methods allow one to evaluate the condition of blood vessels and hemodynamics to a much greater extent.
Kidney bruise on ultrasound
Description
Closed damage to a paired renal organ due to trauma leads to hemorrhage and in extremely rare cases ends in kidney rupture.
Kidney contusion as an independent disease is noted in ICD-10 codes, which include the following conditions:
- S37 – damage to organs located in the pelvic area.
- S37.0 – kidney damage.
- S37.00 – kidney bruise accompanied by a closed injury to the abdominal cavity.
- S37.01 – open violation of the integrity of the abdominal region.
- S37.7 - multiple injuries affecting several organs.
Among the reasons leading to the listed pathological conditions are:
- falling onto a hard surface;
- consequences of blows;
- sharp compression of the kidney.
Often the main factor is domestic trauma.
Kidney damage. Violation of the integrity of the kidney due to traumatic exposure. Closed kidney damage occurs with direct (bruise, compression, falling on the back) and indirect (fall from a height) injuries, open - with stab, cut and gunshot wounds.
Manifested by hematuria and lower back pain. With open injuries, urine leaks from the wound. To confirm the diagnosis, data from laboratory tests, ultrasound, CT, radiography and angiography are used. Treatment of closed kidney injuries in most cases is conservative, while open ones are treated surgically.
What to do and how to treat
A kidney bruise, if not complicated by the development of any diseases or concomitant severe injury, does not require surgical intervention. However, even with a mild illness, bed rest must be observed. The greatest danger with such an injury is a subcapsular hematoma: when moving, it puts pressure on the kidney tissue, which contributes to further damage to the blood vessels, and, therefore, the spread of the injury.
With a mild degree of the disease, a kidney bruise can be treated at home, and with good hemodynamics and the relatively healthy condition of the patient himself, it does not include drug therapy. The main condition for recovery is complete rest for 2 weeks.
ICD 10 classification, manifestations and treatment of lumbar spine contusion
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Women are most susceptible to the disease, although there are also many men who have had to deal with cystitis.
In this class, the section designated S is used to code various types of injuries related to a specific area of the body, and the section designated T is used to code multiple injuries and injuries to individual unspecified body parts, as well as poisoning and some other consequences of exposure external reasons. According to statistics, chronic cystitis or acute cystitis is a manifestation that affects up to 35% of the entire world population.
Causes
All injuries develop as a result of various mechanical influences, impacts, road accidents, etc. A kidney bruise is an injury in which soft tissues are not injured. This organ is most susceptible to such injury due to its anatomical location.
Despite the muscular frame, this organ can suffer from a strong blow to the lumbar region. A kidney bruise is often observed due to a fall. Children are more often susceptible to this injury. Since the child’s muscle tissue is not sufficiently developed and a fall on the lower back is fraught with such consequences as a kidney bruise.
People with kidney pathologies are at risk. Even weak mechanical impacts on the kidney area can lead to kidney injury.
Due to the anatomical structure, the right kidney is lower than the left, it is most susceptible to injury.
The damage is accompanied by pain in the lumbar region, bruising, and deterioration in health. The nature of the injury depends on the strength of the mechanical impact, muscle tissue, etc.
Signs that the kidney is injured
With kidney injuries, the patient experiences sharp sensations in the lumbar region. Some time after the injury, hematuria, internal bleeding (pallor of the skin, hypotension, increased pulsation), and urine leaking from the open wound are observed. The urethra may become blocked by blood clots, making it impossible for the patient to empty the bladder.
Hematoma on the side due to rupture
Symptoms
When a kidney is bruised, symptoms appear immediately after injury. The main ones are: severe pain, blood in the urine, swelling that occurs in the lower back and hips, bruising, a change in general condition for the worse, nausea and vomiting may occur.
Symptoms of a kidney injury depend on the nature of the injury. There are:
- Mild degree, which is the result of minor damage. The victim feels general weakness and gets tired quickly. The pain is not severe and is localized in the area of injury. The presence of blood or blood clots in the urine is irregular and weak.
- Medium - accompanied by severe pain that radiates to the abdominal cavity, groin, legs. The development of hematuria (blood in the urine) is observed, urination is impaired, and the amount of daily urine decreases. Bruises appear in the lumbar region, hypotension and tachycardia.
- A severe degree is characterized by clear signs of kidney injury. Severe pain in the lower back. The patient's condition is regressing. Hyperthermia, rapid heartbeat, and changes in blood pressure appear. A symptom of “acute abdomen” may appear. The injury is accompanied by pain in the abdominal area. Urine changes color - severe hematuria. Anuria may develop due to blockage of the ureteral canal by a blood clot.
Note! Hematuria may occur several days after a kidney injury.
If the main symptoms are supplemented by pale skin, cold sweat, loss of consciousness, there are signs of post-traumatic shock. The victim should be hospitalized immediately.
If a kidney injury is moderate or severe, internal bleeding (kidney tissue is affected) and large bruises may occur.
Use of medications
If the symptoms of the disease are combined with a rib fracture, urgent treatment of the disease is necessary. The danger of the pathology should not be underestimated, as it can lead to collapse of the lungs (atelectasis).
The following subcategories (fifth character) are provided for optional use in additional characterization of a condition where multiple coding is impossible or impractical to identify a fracture or open wound; If a fracture is not classified as open or closed, it should be classified as closed:
Excluded:
- dislocation, sprain and strain of the hip joint and ligaments (S73.-)
- obstetric trauma of joints and ligaments of the pelvis (O71.6)
- ruptures or displacement (non-traumatic) of the intervertebral disc in the lumbar region (M51.-)
In some cases, the likelihood of suffering such kidney damage increases. Children who are very active by nature and people with diseases of the urinary system (prolapsed kidney, urolithiasis) can get severe bruises.
The following subcategories (fifth character) are provided for optional use in additional characterization of a condition where multiple coding is impossible or impractical to identify a fracture or open wound; If a fracture is not classified as open or closed, it should be classified as closed:
Excluded:
- dislocation, sprain and strain of the hip joint and ligaments (S73.-)
- obstetric trauma of joints and ligaments of the pelvis (O71.6)
- ruptures or displacement (non-traumatic) of the intervertebral disc in the lumbar region (M51.-)
The degree of kidney injury depends on the strength and direction of the blow to the lumbar region. In addition to the physical condition of the kidney itself (the presence of pathologies), the development of the muscular frame (how strong it is), abdominal pressure, and the amount of fat in the lumbar region are important.
Among the reasons leading to the listed pathological conditions are:
- falling onto a hard surface;
- consequences of blows;
- sharp compression of the kidney.
The ambulance crew that arrived at the scene takes the person to the hospital. To do this, the victim is placed on a soft stretcher face down or on a hard stretcher face up.
Unpleasant sensations may vary depending on intensity and location. Often, along with pain, disturbances in motor activity and sensitivity are observed.
Injuries localized in this area of the spine are assigned code T2 according to ICD 10. At the same time, they are further divided into several groups. It all depends on the injuries identified, the severity of the victim’s condition, and complications that arise. Therefore, almost every type of injury has its own original code, which doctors determine at the time of making the final diagnosis.
Kidney damage. Violation of the integrity of the kidney due to traumatic exposure. Closed kidney damage occurs with direct (bruise, compression, falling on the back) and indirect (fall from a height) injuries, open - with stab, cut and gunshot wounds.
All bruises are different in the nature of the damage, the direction of the blow and its strength. The difference will also depend on the location of the organ in the body, as well as on its condition at the time of injury, the amount of adipose tissue, muscle mass and many other indicators.
A kidney injury is accompanied by pain in 95% if it is an isolated injury, and in 100% if it is a combined injury. The pain syndrome is caused by a growing hematoma - it puts pressure on the peritoneal area and stretches the fibrous capsule. In this case, ischemia of the renal parenchyma begins, and the urinary canals become clogged with blood clots.
How do injuries of varying severity affect kidney function? What complications are possible after an injury? What signs indicate serious problems after a fall or a strong blow to the lumbar region? How to treat a kidney injury? The answers are in the article.
Often, kidney injury in accidents is combined with other dangerous injuries: rib fractures, injury to the liver and lungs, the development of acute inflammation in the abdominal cavity, active internal bleeding.
If signs of compression or bruising of the kidney appear, you should immediately contact a urologist. If the condition worsens rapidly, specialist assistance will be needed to provide emergency care. In critical situations, only urgent hospitalization with diagnosis and treatment can save the bean-shaped organs and the patient’s life.
In addition, clinical signs such as:
- weakness;
- pale skin;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- temperature increase;
- abdominal bloating;
- bad feeling;
- decrease or increase in blood pressure.
There are situations when impacts are not accompanied by rib fractures, but swelling of the lung tissue and impaired blood supply lead to hematomas (local limited accumulation of blood). If these injuries are not treated in a timely manner, serious consequences occur with restriction of breathing and blood supply.
Their advantage is that they are very effective against E. coli and enterococci. But at the same time, they have a significant drawback - they are powerless against the causative agents of pyelonephritis.
First aid
In case of any damage, it is necessary to call a team of paramedics, then measures are taken to provide first aid to the victim. If an injury such as a kidney bruise is suspected, the victim is laid down (sudden movements and walking should be avoided).
Cold compresses are applied to the lumbar region for about 20 minutes. This procedure reduces pain, swelling and blood loss to some extent. The use of analgesics is prohibited as they may worsen the patient's condition.
What to do if you have a kidney injury
In case of a kidney injury, self-medication is not recommended, even with a mild degree of damage. What to do if the pain syndrome is pronounced? Taking painkillers is prohibited. Consult a doctor promptly to diagnose the injury and receive subsequent qualified therapy.
A delayed visit to the doctor leads to complications, including necrosis of the kidney tissue.
Consequences, prognosis for kidney injury
Kidney damage can be fatal in cases of large blood loss or painful shock. Severe injuries can cause dangerous complications, sepsis and suppuration around the damaged organ, and can also lead to the need for kidney resection and subsequent disability. Also, the consequences of kidney injury include the development of chronic pyelonephritis, expansion of the renal collecting system, and pathologies of the arterial-venous blood supply to the kidneys. In some cases, stones and sand may form in the kidneys.
Establishing a correct diagnosis plays a decisive role in the treatment of kidney damage. In most cases, this gives a favorable prognosis even with severe injuries.
Patients with kidney injuries require long-term observation, since there is a high risk of complications even after a long time after treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment
To obtain a complete picture of the nature and extent of damage, a comprehensive examination is carried out. Based on the general condition and complaints of the patient, an x-ray is taken. After which the presence or absence of other injuries and the location of the injury are determined. Additionally, excretory urography, retrograde ureteropyelography, angiography and ultrasound, a general blood test and a general urinalysis are performed.
Based on the results of a general examination and research, the nephrologist can determine the degree of kidney injury, the presence of hematomas, and the condition of the kidney parenchyma. And, based on the diagnostic data, make a decision on how to treat the kidney injury.
In some cases, when the patient’s condition regresses due to a severe injury to the kidney, emergency surgical treatment is performed.
Inpatient therapy includes:
- Bed rest,
- Minimum fluid intake (to reduce the load on the kidneys) and diet,
- Painkillers and hemostatic medications,
- Medicines that prevent infections (antibiotics)
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
The dynamics of organ recovery are monitored by performing ultrasound and urine tests. How many days treatment will last depends on the degree of kidney damage. Treatment is considered complete when traces of blood in the urine disappear.
After receiving a kidney injury, it is forbidden to take a steam bath or go to the bathhouse. Since this can provoke a relapse of the disease.
In uncomplicated cases, treatment lasts about 2 weeks.
How to treat a kidney bruise
Treatment of a patient with a kidney injury is prescribed by a doctor after interviewing the patient and making the necessary diagnosis. For mild kidney damage, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis. How to treat a kidney bruise at home? All types of therapy are based on the doctor's recommendations. During the treatment period, the patient needs rest. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications are prescribed.
Pain and swelling due to a kidney injury on the first day can be relieved with cold compresses. A few days after the injury, treatment is continued with warm compresses and heating the injury site.
At home, you can use traditional methods of treatment (tinctures of medicinal plants in rubbing alcohol, etc.), you must follow bed rest and diet to reduce the load on the kidneys. In the first weeks after a kidney injury, you should limit physical activity and walking.
Consequences and possible complications of kidney injuries
Lack of proper treatment can lead to unpleasant consequences :
- Sepsis;
- Fistula;
- Internal bleeding, which can lead to anemia;
- Suppuration near the kidney;
- Non-healing wounds around the organ;
- Scarring of damaged tissue;
- Chronic pyelonephritis;
- Other chronic diseases and inflammatory processes of the urinary system.
In addition, a bruise can be accompanied by various complications. One of the most common is peritonitis, which can be fatal if left untreated.
With severe damage, kidney rupture : with a strong and direct blow, the organ is compressed by the lumbar vertebrae and ribs, the pressure of blood and urine increases, which leads to rupture. In such a situation, it is almost impossible to save the kidney.
Click to view (do not watch for the impressionable)
Kidney injuries, as already mentioned, are usually accompanied by damage to other organs. So, the victim may be diagnosed with rib fractures, back bruises, intestinal or lung injuries. Often there is a separation of the pedicle of the vessel, ureter or pelvis.
To prevent such developments, it is important to contact a specialist immediately after receiving an injury.
Consequences of injury
Due to the lack of a unified system, kidney injuries are classified according to several criteria.
Most often, injuries are divided according to their type; classification is also accepted according to which side of the body the injury is located. Depending on which side the injury is inflicted or received, we can talk about left-sided, right-sided or bilateral damage. Injuries can also be open or closed. With open kidney injuries, skin damage occurs and internal organs come into direct contact with air. With closed injuries, the integrity of the skin is not compromised.
Based on the severity of kidney injuries, they are divided into the following types:
- lungs, these are, as a rule, bruises, as a result of which the integrity of the organ is not compromised;
- injuries in which there is destruction of the pelvis or pyelocaliceal system;
- a wound without damage to the system in which urine is collected;
- multiple ruptures with crushing of the organ;
- injury to the vascular pedicle or main blood vessels of the organ.
Kidney injuries can occur in the absence of disturbances in the functioning of neighboring organs, or they can be part of a complex of injuries to the pelvic organs or peritoneum.
Types of kidney ruptures
Timely consultation with a doctor and competent therapy reduce the risk of complications, but cannot completely eliminate them. Common consequences of kidney injury are:
- anemia;
- inflammation of the renal pelvis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- infectious process;
- blood poisoning.
After treatment, you need to regularly examine your kidneys for several years and go to the clinic if you have any symptoms of illness. This will help to identify pathological processes caused by injury in a timely manner.
Kidney bruise from a fall: symptoms and signs of bruise, home treatment and diagnosis
Injuries to internal organs do not happen as rarely as we would like; it is enough to fall unluckily on the street or while going down the stairs.
A kidney bruise can easily be caused by an unfortunate fall or while playing sports. Injury to this paired organ is very painful and dangerous to health, so it is important to provide timely assistance by starting therapy.
So, what are the consequences of injury, and how to treat damaged kidneys?
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader got rid of her kidney problems using an effective method. She tested it on herself - the result was 100% - complete relief from pain and problems with urination. This is a natural herbal remedy. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast. EFFECTIVE METHOD.
Kidney injuries
The most common causes of kidney bruises include:
- fights;
- sports activities;
- accidents;
- falls.
The kidneys are protected from physical stress by the ribs and muscles, but one of the kidneys (the left one) is usually located lower than the right one. It is she who is most often injured because she is less protected. But for a child, the risks of injury are much higher, since the kidneys are more mobile due to the not yet developed muscular framework.
Often a relatively small external impact is enough to injure the kidney. People with kidney diseases or pathologies in the development of this organ are also at risk.
Kidney injury is aggravated by the fact that during an impact the organ hits hard ribs or the spine, this creates additional damage. Depending on the force of the blow, numerous hemorrhages open inside the kidney tissue.
In addition, if the impact was too strong, this leads to damage to the cups or numerous hemorrhages. Depending on which part and at what angle the blow came, different areas may be injured:
- upper or lower part of the kidney;
- organ body;
- vascular pedicle.
Additionally, the injury may affect only one side or both. The consequences of the blow largely depend on the degree of impact, location, as well as the development of the muscles of the victim himself, and the thickness of the fat layer.
Mild degree
With a mild injury, there are practically no significant changes in well-being. There is no swelling or hemorrhage; if hematuria occurs, it is short-term or insignificant. The pain is moderate, treatment at home is possible, surgery on the diseased organ is not required.
Average degree
Moderate trauma is characterized by:
- traces of blood in urine;
- low blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- difficulty urinating;
- visible hematoma in the area of the damaged kidney;
- pain radiating to the pelvis and genitals;
- blockage of the urinary tract.
In the middle stage of a bruise, pain may be almost not felt; such an injury requires observation and treatment in a hospital setting.
Severe degree
Severe kidney injury is extremely dangerous; if measures are not taken in time, it can even lead to death. Such an injury requires urgent hospitalization and surgical intervention, only this will help avoid serious consequences for the patient’s life. This condition is characterized by:
- strong pain;
- state of shock;
- prolonged macrohematuria;
- nausea, vomiting;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- sticky sweat;
- blockage of the ureter;
- hemorrhage in the kidney tissue or in the abdomen;
- "acute abdomen" syndrome.
Most often, the most severe kidney injuries occur as a result of a fall from a great height or a car accident.
Possible complications
In most cases, severe bruises of the kidneys occur together with damage to neighboring internal organs. The most common complications are:
- lung and intestinal injuries;
- liver damage;
- separation of the vascular pedicle;
- separation of the pelvis or ureter;
- peritonitis.
Peritonitis is a dangerous complication that, in the absence of qualified assistance, leads to the death of the victim. To save a person’s life, it is important to urgently call an ambulance; you cannot hesitate. Renal rupture is no less dangerous.
The cause of such a serious injury is a direct blow to an organ, compression or severe bruising. The rupture occurs due to the fact that the kidney is squeezed between the ribs and the spine.
As a result, there is an increase in pressure inside the organ and, as a result, rupture.
There is no prophylaxis that could 100% prevent possible kidney injuries. To minimize risks, you need to carefully monitor your activity and be careful.
You should avoid back bruises, try not to fall, and observe safety precautions when playing sports. If an injury does occur, it is worth undergoing diagnostics to determine the extent of the damage.
It is important to carefully monitor children; they are mobile and active, they love to run, climb and jump everywhere, so the risk of injury increases.
Kidney injuries often lead to serious complications, so in case of bruises you should not hope that everything will go away on its own. It is important not to self-medicate and be sure to consult a doctor. During the examinations, the extent of organ damage will be revealed and appropriate treatment will be prescribed. How long it lasts depends on the injury.
Source: https://MpsDoc.com/bolezni/boli/ushib-pochki/
general information
The kidneys are a paired organ that looks like a bean seed. This is a kind of filter through which toxins and breakdown products entering the human urinary system are removed.
The kidneys are located on the sides of the lumbar region and are reliably protected by muscle tissue and ribs. Despite this, a strong blow can cause damage and hemorrhage inside the organ.
Each degree has characteristic distinctive features.
- First. There is a slight aching pain in the back. A person feels a loss of strength and lack of appetite. Blood in the urine is observed in isolated cases. During the examination, small hematomas are revealed that do not violate the integrity of the tissues.
- Second. Painful symptoms are pronounced. Acute pain pierces the lower back, radiates into the stomach and legs. The temperature is rising. The renal pelvis may be damaged. Urine excretion is difficult. It often comes out mixed with blood.
- Third. Excruciating pain, chills, dizziness, nausea and other signs of intoxication are alarming. For some people, blood pressure drops critically or jumps up. Urine is dark brown in color. Anuria develops - a condition when urine stops flowing into the bladder. Ultrasound reveals a large-scale hematoma and dystrophic changes that violate the integrity of the organ.
For the convenience of doctors, an international classification of diseases, tenth revision, has been created. Injuries to the urinary organs are grouped under numbers S30 - S39. ICD 10 code for kidney contusion is S37. This includes injuries that provoke minor, major hemorrhages and complete rupture of the organ.
Kidney injury
The kidneys are paired organs that are located in the retroperitoneal space. They are protected from negative external influences by the ribs, massive spinal muscles and perinephric tissue. Despite such protection, doctors encounter kidney bruises quite often.
This type of injury is accompanied by multiple hemorrhages into the kidney parenchyma, without causing rupture of the organ itself.
Kidney contusion is classified according to ICD 10 code S37.0
Causes of kidney injury
Among the causes of bruises of the kidney, as well as other organs, we can distinguish all kinds of injuries:
- falling onto hard surfaces/objects;
- domestic injuries;
- prolonged compression;
- blows delivered to the lumbar region;
- injuries caused by road accidents, etc.
Depending on how the kidney injury was sustained, the severity of the harm to health is determined by the doctor, who prescribes immediate therapy to minimize risks and consequences.
Kidney bruise: diagnosis
To diagnose a kidney injury, you must have the following information:
- History of the disease.
- Complaints indicated by the patient.
- Data from laboratory and instrumental studies.
Laboratory research means:
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis;
- separate urine samples.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- cystoscopy and chromocystoscopy;
- excretory urography;
- plain radiography;
- retrograde ureteropyelography;
- isotope renography;
- Ultrasound scanning;
- angiography.
Radiological diagnostic methods can be called fundamental.
Using plain radiography, you can determine the location of the injury, as well as the presence/absence of a retroperitoneal hematoma, various fractures and damage to other organs, often observed with a kidney injury.
General information obtained from data using radiocontrast methods, angiography and radioisotope studies will allow for an assessment of renal dysfunction and changes in the process of their blood supply.
Kidney ultrasound is one of the simplest, most accessible and safe diagnostic methods. This type of study allows you to get a picture of the changes that have occurred in the structure of the renal parenchyma, the presence/absence of hematomas and their location.
If it is impossible to determine the nature and extent of a kidney injury, which is accompanied by a significant deterioration in the victim’s condition, emergency surgery is prescribed.
It is important to note that if you suspect a kidney injury, you should not make unnecessary movements, otherwise if a subcapsular hematoma occurs, you can rupture the renal capsule, thereby leading to the development of severe complications. In this situation, it is necessary to seek urgent help from medical personnel.
Basic principles of kidney injury treatment
- providing the patient with rest in the form of bed rest and limited fluid intake;
- cooling of the injury zone (at the initial stage);
- analgesic drug therapy (novocaine blockade for kidney injury and analgesics);
- physiotherapy.
To reduce hemorrhage and hematuria, a heating pad with ice is applied to the area of the damaged organ in the first days of treatment. After a few days, they resort to thermal procedures, UHF therapy, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy and other methods that help accelerate the resorption of the hematoma.
If the patient experiences severe pain, it is eliminated with the help of intramuscular or intravenous administration of painkillers.
The recovery of the damaged organ is monitored through periodic blood and urine tests, as well as ultrasound and radiographic examinations.
In conclusion, I would like to remind you that if, after receiving an injury, you find blood in your urine and feel pain in the lumbar area, do not try to make a diagnosis yourself, much less begin treatment, but consult a doctor immediately.
Even if there are no symptoms, it is better to consult a specialist, since kidney damage may only appear after some time, thereby leading to serious complications, including kidney removal, and even death.
How to treat at home
Despite the protection of the kidneys by the ribs and muscles, they are most often damaged by blows and falls on the back. There will be nothing wrong if you immediately consult a doctor or call emergency help. Otherwise, there is a risk of developing nephritis and other forms of this pathology.
While the specialists are on their way, you can take several measures to normalize your well-being; this is not a recipe for how to treat a kidney bruise at home. Remember, this cannot be treated with folk remedies.
Apply a cold compress to the injury site. This will improve things a little. If you have a “helper,” then let him make a decoction of arnica herb, which would be good to grind after the cold.
Shredded cabbage leaves can also be used as a compress for the kidneys.
Diagnosis of severe kidney injury
The administration of the portal categorically does not recommend self-medication and advises consulting a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease.
Our portal presents the best medical specialists with whom you can make an appointment online or by phone. You can choose the right doctor yourself or we will select one for you absolutely free
.
Also, only when you make an appointment through us, the price for a consultation will be lower than in the clinic itself.
This is our little gift for our visitors.
Source: https://medportal.net/ushib-pochki/
Kidney bruise: symptoms and treatment after a fall or blow
Kidney bruise is a special type of injury that can be classified as mechanical.
It occurs as a result of a traumatic effect on the lumbar region, but, as a rule, the integrity of the organ itself is not compromised, since the kidney is protected by the back muscles.
A damaged kidney needs qualified examination and treatment. Self-medication or lack of treatment often leads to irreversible negative health consequences.
Causes of damage
As already mentioned, the cause of a kidney bruise is a mechanical impact on the lumbar region and occurs as a result of:
- blow;
- falling onto a hard surface or object;
- domestic injuries;
- road accident;
- prolonged compression.
In some cases, the likelihood of suffering such kidney damage increases. Children who are very active by nature and people with diseases of the urinary system (prolapsed kidney, urolithiasis) can get severe bruises.
Severity of injury
The degree of kidney injury depends on the strength and direction of the blow to the lumbar region. In addition to the physical condition of the kidney itself (the presence of pathologies), the development of the muscular frame (how strong it is), abdominal pressure, and the amount of fat in the lumbar region are important. There are 3 degrees of injury:
- The first degree of kidney injury slightly worsens a person’s condition: he feels tired, increased fatigue. After the injury, the pain is mild. There is no blood in the urine or in a very small amount, which is often determined only after analysis. The kidney hematoma is minor.
- The second (medium) degree is characterized by significant pain. The pain becomes wave-like, manifests itself in attacks, radiates to the legs, abdominal cavity, and groin. Urine excretion is impaired up to temporary anuria, blood in the urine is clearly visible.
- The third (severe) degree is manifested by severe, acute pain. General health deteriorates greatly: nausea with vomiting, fever, pressure surges and rapid heartbeat. The color of urine changes due to the large amount of blood. There is a lack of urine (anuria). The subcapsular hematoma of the kidney is significant and can cause parenchymal rupture. Often the integrity of the kidney is compromised. This condition is life-threatening and requires emergency medical attention.
Symptoms of a kidney injury
It is easy to determine a bruised kidney injury after traumatic exposure. There are three specific symptoms of such an injury: hematuria (blood in the urine), severe pain, and swelling of the lower back. Let's look at them in more detail.
Hematuria
Hematuria is the appearance of blood in the urine, the main sign of kidney injury. By the amount of blood and the duration of blood discharge along with urine, one can judge the degree of kidney injury. If the duration of hematuria is significant, the victim may experience anemia.
The concept of “secondary hematuria” refers to the late appearance of blood in the urine: not immediately after injury, but several days or weeks later. It is also possible that there is no blood in the urine if the injury is severe. A similar situation arises when there is a separation of the ureter or pelvis.
Blood is released into the tissue near the kidney, and blood clots clog the ureter.
Painful sensations
Pain in the lower back appears immediately after a bruise in the area of the kidney, and as it intensifies, it can radiate to the stomach, groin, and legs. The victim describes it as sharp and stabbing. It is localized around the affected area, on the side where the injured kidney is located. The pain increases in intensity and begins to decrease only on the 10th day.
The occurrence of edema
The appearance of swelling in the lumbar region is another specific sign of a kidney injury. Swelling on the side of the bruised area is pronounced. Sometimes the swelling rises to the hypochondrium area. The appearance of swelling is caused by the accumulation of blood or blood with urine in the perinephric or retroperitoneal tissue.
Urine ingress is a consequence of severe trauma when the kidney ruptures.
Other signs of bruise
Other, nonspecific symptoms of kidney injury appear gradually and depend on the degree of damage. These include: weakness, pale skin, deterioration of health up to a state of shock. The victim may have a fever, blood pressure changes up or down, nausea and vomiting.
“Acute abdomen” syndrome occurs when urine and blood enter the abdominal cavity itself and is characterized by sharp and severe pain in the abdomen and pathological tension in the abdominal wall.
If the injury is caused by a fall or traffic accident, then damage to the lungs, abdominal organs and rib fractures are likely.
Diagnosis of injury
Diagnostics includes studies to establish a diagnosis and determine the extent of damage. A conversation is held with the victim and an anamnesis is taken. Laboratory and instrumental methods are used:
- urinalysis to detect hematuria;
- complete blood count and blood test for anemia;
- cystoscopy and chromocystoscopy;
- survey and isotope radiography;
- excretory urography;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- MRI;
- Angiography.
Ultrasound of the kidneys shows the location and extent of the kidney hematoma. This is the simplest instrumental method listed.
In emergency cases, when a full diagnosis is impossible, due to the patient’s life-threatening condition, an operation is performed.
Treatment of kidney bruise
Although mild and moderate degrees do not require a specialized course of treatment, it is not advisable to treat yourself at home. Consultation with a doctor is necessary to exclude complications and choose the right treatment. With the permission of your doctor, you can make warm compresses at home.
The patient is prescribed rest, bed rest, and cold compresses on the lumbar region (the first few days). For the first 2 weeks, physical activity is completely excluded.
Food during treatment should be salt-free and low-calorie, drinking is limited. After the first acute period (approximately 3 days), it is advisable to undergo a course of physiotherapy.
Electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, UHF, laser therapy are well suited.
The drug course of treatment includes pain relief with tablets or intravenous injections (drugs based on ibuprofen and paracetamol, Novocaine and Lidocaine), when the pain syndrome is pronounced.
Antibiotic therapy is prescribed to prevent possible infections. Most often these are drugs of the penicillin group.
If hematuria is severe or urine is no longer excreted, the patient undergoes catheterization while the kidneys’ excretory function is restored.
The recovery period directly depends on the degree of kidney damage. A mild kidney injury completely resolves in about 14 days. For moderate injuries, treatment lasts about a month. Severe injuries are treated over several months. The urine status is regularly monitored throughout the treatment period.
Providing first aid
The most important thing to do in case of a kidney injury is to transport the victim to the hospital as quickly as possible. Especially if there is severe hematuria, severe pain, or shock. Such symptoms carry a mortal danger, because...
There is a suspicion of kidney rupture. The victim must be laid on a horizontal surface, for example, a shield, a board, a cushion placed under his knees and taken to the hospital in this form. In the absence of a state of shock and severe hematuria, the victim can be transported while sitting.
A cold compress is applied to the lower back.
When the pain is not severe and there is no blood in the urine, you don’t have to call an ambulance, but go to see a doctor at the clinic. In any case, you need to see a specialist and carry out all the necessary examinations.
Possible consequences of a bruise
Kidney bruise is often accompanied by damage to other organs: lung, intestines. In case of serious injuries, the pelvis and ureter may be torn off, which leads to the filling of the abdominal cavity with blood and urine.
If ruptures are not diagnosed in time and measures are not taken, inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis) is possible, which is a deadly condition. Without competent and timely measures taken, a person may die.
Other complications of a kidney injury may occur:
- sepsis;
- pyelonephritis (and other inflammatory kidney diseases);
- anemia, due to blood loss;
- stones in the kidneys;
- kidney atrophy;
- nephrectomy;
- nephrogenic arterial hypertension;
- pseudoaneurysm;
- renal artery stenosis.
There are many consequences of a bruise. Therefore, medical supervision is necessary under any treatment conditions: at home or in a hospital.
There is no special prevention for kidney injury. The main rule is to be careful and avoid back injuries. In addition, treat diseases of the urinary system, strengthen weak back muscles and lead a healthy lifestyle.
How to help your kidneys recover faster
Source: https://TravmoVed.com/ushiby/ushib-pochki/