What is pyelectasia?
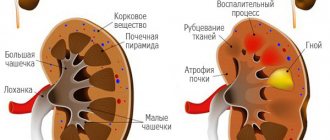
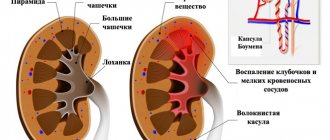
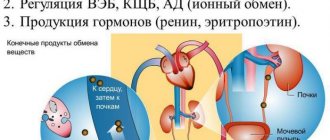
The renal pelvis performs a storage function - blood-filtered urine accumulates in a small cavity inside the organ, and is then evacuated through the ureter into the bladder . The size of the pelvis determines how much urine is stored inside the kidney. With increased cavity sizes, urine is retained in the organ, which threatens the development of inflammatory and infectious kidney pathologies.
Pyeelectasis is a congenital or acquired enlargement of the pelvic cavity. In newborns, the pathology usually develops in utero; the baby is born with an increased capacity of the pelvis. If the pelvis of only the left or right kidney is enlarged, pyeelectasis is called unilateral. The bilateral form is fixed during expansion in both kidneys.
Kidney examination using ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the kidneys requires virtually no special preparation. Parents of children prone to flatulence, on the eve of the study, should limit foods that cause gas formation in their diet. You can also take Smecta or Espumisan .
There is an examination option - with a water load, when the child must come for an ultrasound with a full bladder. To do this, 40-60 minutes before the procedure, the child should be given 300-600 ml of plain water to drink (the amount of liquid depends on age). The degree of bladder filling required by the doctor is calculated using a special formula: age in years is multiplied by 30, after which 30 must also be added to the resulting number.
Ultrasound of the kidneys with water loading is carried out in several stages:
- First, the bladder filled with urine is examined and its volume is calculated;
- then the doctor asks to turn the child on his stomach with his back up and measures the diameter of both pelvises;
- after this, the child should slowly urinate and return to the office again;
- after miction, the volume of the bladder and the diameter of both pelvises are measured again;
- When the bladder is empty, a thorough examination of the kidneys is performed.
Such a study allows us to identify the maximum degree of filling of the bladder, determine the volume of residual urine, suspect active vesicoureteral reflux and confirm the presence of a sinus cyst. In addition, ultrasound scanning of the kidneys in the water load mode is indicated if ureterohydronephrosis, megaureter (pathological dilatation of the ureter) or an inflammatory process is suspected.
Infants undergo a standard ultrasound (without water loading). When examining newborns and infants, it is also important to take into account the anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the kidneys at this age. They often exhibit fetal lobulation of the kidneys or the syndrome of “hyperechoic pyramids,” which is the norm in the first months of life.
Also, when conducting ultrasound screening during pregnancy, the doctor may discover that the fetus has an enlarged pelvis in the right or left kidney (sometimes on both sides). This can be either a congenital pathological condition or a false result due to the special situation of the unborn child.
What threatens
An enlarged pelvis provokes the accumulation of urine in the body of the kidney. The pathology can be asymptomatic in infants for a long time, which increases the risk of the disease if the condition of the organ is insufficiently monitored. A kidney with excess accumulated urine works under overload, which often leads to the development of hydronephrosis, degeneration of organ tissue and loss of function.
Stagnant urine is a convenient environment for the proliferation of pathogenic flora, which often leads to infection of the kidney and other parts of the genitourinary system. Due to damage to kidney tissue, nephrogenic hypertension can develop, and the pressure is practically impossible to correct. The development of these pathological processes may result in renal failure.
Important: when dilation of the pelvis is diagnosed in infants, regular examinations and constant monitoring of kidney function are important.
Stages and symptoms
As pyeloectasia progresses, it goes through several stages, each of which is accompanied by certain changes in the renal tissues and urinary system.
Initial, easy stage
At this stage, the renal pelvis of a newborn is slightly enlarged and does not interfere with the functioning of the organ. The child does not experience any unpleasant sensations, and the pathology itself can only be diagnosed using ultrasound during fetal development or immediately after birth.
Average
The second stage of the pathology is accompanied by a pronounced expansion of the pelvis, there is damage to the external tissue of the organ, its function is reduced by 40%. At this stage of the disease, severe symptoms may be present, which forces parents to consult a doctor. The child becomes restless, often cries when urinating, and there may be blood in the urine.
Third degree
The most severe stage of the disease, which is characterized by severe symptoms. The child has an enlarged pelvis and the kidney itself, significantly reduced urine production, increased body temperature, pain when urinating and other symptoms that require a medical examination. The kidney tissue is significantly damaged, and when the pelvis is greatly expanded, it puts pressure on other tissues.
Possible reasons
One of the most significant reasons for the development of pyeelectasis in the fetus is considered to be heredity. In many cases, the expansion of the pelvis in an infant is recorded if the mother has renal pathologies - chronic or developed during pregnancy.
During the period of embryonic development, teratogenic factors are also imposed, that is, negative influences on the fetus from the external environment. This effect is especially dangerous at a time when the formation and function of the kidneys occurs. Let us highlight the most dangerous types of external influences during intrauterine development, often leading to pyelectasis in newborns.
Maternal infection
In case of infectious diseases in a woman, pathogenic flora and its metabolic products pass through the placenta and enter the blood of the fetus. The formation of kidney structures may be disrupted due to exposure to toxins.
Smoking
When a pregnant woman smokes, the fetus does not receive enough oxygen, and poisoning occurs with toxic substances from tobacco smoke. Smoking often provokes congenital pathologies in newborns.
Drug addiction
Even more dangerous is the effect of narcotic substances on the embryo. When using drugs, organogenesis is disrupted, which can lead to the development of pyelectasis.
Taking medications
Uncontrolled treatment during pregnancy is dangerous for the development of congenital pathologies in the fetus. Most medications are not indicated for use by pregnant women.
X-ray exposure
Even small doses of radiation during X-ray examinations of the mother pose a danger to the fetus.
Ecology
In women living in environmentally polluted areas or working in hazardous industries, the risk of dilated pelvis in the baby increases.
Treatment of dilated renal pelvis in children
If a child is diagnosed with congenital pyelectasia, which does not significantly affect the functionality of the urinary system, treatment is not required. Dynamic observation until he reaches the age of three years is sufficient. If the pathology progresses or it is an acquired disease, then complex therapy is suggested, including:
- taking certain medications;
- diet;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical intervention (in difficult cases).
Table: drug therapy for pyelectasis
| Group of drugs | Operating principle | Examples of drugs |
| Antibiotics | Eliminate infectious and inflammatory processes in the urinary system, suppressing pathogenic microorganisms |
|
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Eliminate pain and inflammation |
|
| Antispasmodics | Relieves smooth muscle spasms |
|
| Diuretics |
|
|
Photo gallery: medications used for pyeelectasis
Amoxicillin is prescribed for pyeloectasia caused by a bacterial infection.
Nise relieves pain and relieves inflammation
No-spa eliminates smooth muscle spasms
Furosemide has diuretic properties
Diet
The basis of nutrition for pyeelectasis is easily digestible protein foods:
- bird;
- lean meat;
- fish;
- vegetables and fruits.
If a child takes diuretics, then care should be taken to ensure sufficient potassium intake into his body. You can get it with dried fruits and milk.
If the renal pelvis is enlarged, you should avoid excess amounts of salt, which retains fluid, creating excess pressure in the urinary system. Meals should be regular and balanced; it is best to organize meals 5 times a day in small portions.
It is also important to maintain a drinking regime. The volume of fluid consumed should not exceed the previous daily diuresis (amount of urine excreted) by more than 0.5 liters.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Magnetic therapy is widely used for pyeelectasis in children. Its essence lies in the effect of magnetic fields on the body. This method is applicable in the presence of inflammatory processes.
Also, for secondary pyeloectasia, electrophoresis with antibacterial drugs is used, which allows for a targeted effect on foci of infection.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is justified in severe cases of the disease and the presence of complications. Its essence comes down to restoring renal passage (outflow of urine from the kidneys) and normalizing the function of the ureter. As a rule, the operation is performed using endoscopic equipment. Instruments equipped with a miniature video camera are inserted through small incisions, and morphological changes in the renal pelvis are eliminated.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for kidney diseases are used exclusively for the purpose of supportive, additional therapy. When using any prescriptions, you should consult your doctor first. The following remedies can be suggested:
- Recipe 1. Take equal parts (1 tablespoon each) of birch, dandelion and juniper leaves. The raw materials should be poured into 1 liter of boiling water and left in a thermos for 4 hours. Drink the resulting infusion 3 times a day, one teaspoon at a time, for 2 weeks.
Birch leaves have diuretic and bactericidal properties, therefore they are used in many kidney teas
- Recipe 2. Add 1 tbsp to 1 liter of mineral water. a spoonful of olive oil and 30 ml of lemon juice. Drink a glass on an empty stomach for a month.
Reasons for the development of acquired forms
Pyeelectasis can develop after the baby is born for the following reasons:
- infectious diseases;
- kidney development abnormalities;
- blocking of the ureter with purulent masses, tumors;
- compression by neighboring organs;
- kidney displacement.
In premature babies, the muscular structures of the urinary tract are often underdeveloped, which provokes stagnation of urine in the kidney.
Reference: pyeloectasia is, to a greater extent, a disease of boys - dilation of the pelvis occurs in them 3-4 times more often than in girls.
How does it manifest in a child?
Symptoms of dilated pelvis are absent in most cases. The disease manifests itself when inflammation and infection caused by pyeelectasis occur. The disease can develop in 3 forms.
Initial
This form is typical for most infants - the expansion of the pelvis does not manifest itself in any way. In the initial period, constant monitoring of the condition of the kidneys is important so as not to miss the addition of pathological processes. Usually, with the growth and development of the genitourinary system in infants, the size of the pelvis comes to physiological norms.
Average
The average form is characterized by minor symptoms - aching pain in the lower back, urination problems. In infants, this is expressed in anxiety, crying for no obvious reason, rare, difficult urination with screaming. Drug therapy is prescribed in courses.
Heavy
Severe forms require intensive care, often surgical treatment. If treatment measures are not timely, the parenchyma degrades and chronic renal failure may develop.
Consequences of complications
Complications of dilated pelvis in children include various pathologies of the genitourinary system:
- inflammation caused by stagnation of urine;
- infection;
- hydronephrosis;
- nephropathy;
- narrowing of the ureter;
- violation of the outflow of urine - problems with urination;
- ectopia with the edge of the ureter flowing into the urethra in boys, and into the vagina in girls;
- ureterocele;
- degeneration of parenchyma into connective tissue;
- formation of stones.
Complications develop when the transition of the disease to a severe stage is not detected in a timely manner and there is no adequate treatment.
Types of pyelectasis
Kidney abnormality may be:
- right-sided;
- left-handed;
- two-sided.
Provoking factors for dilation of the renal pelvis:
- Anomalies of intrauterine development occur during the formation of the urinary system in the fetus.
- Congenital occurs due to disturbances in urine excretion (more often appears in newborn babies).
- Organic (acquired type) appears due to the disease nephroptosis, as well as with tumors on nearby organs and with trauma to the ureters, leading to a narrowing of the lumen of the ureter.
- Dynamic (acquired type) occurs due to urolithiasis, various neoplasms in the urethra or prostate gland.
How to identify
Congenital pyelectasis is usually detected by ultrasound during pregnancy. After birth, the baby is regularly examined, tests are monitored, and control ultrasound examinations are performed.
Laboratory research
The following tests are performed on infants:
- urine analysis - usually shows no changes, an increase in leukocytes, fixation of protein and bacteria occurs during inflammatory processes;
- blood test for creatinine and urea - check for kidney dysfunction.
When pathogenic flora is detected, a bacterial culture is performed to determine the pathogen.
Instrumental diagnostics
It is recommended that infants undergo control ultrasound examinations for dilated pelvises every 3 months. If changes appear in the kidney, the following is additionally carried out:
- CT, MRI of the kidneys;
- urography;
- angiography;
- X-ray;
- radiological examination (nephroscintigraphy).
Using these methods, the condition of the kidneys and other parts of the urinary system is determined.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
In differential diagnosis, the causes of pyeloectasia are identified, that is, what provoked the expansion of the pelvis. Pathologies of the structure of the genitourinary organs and diseases that can cause an enlargement of the kidney cavity and lead to renal failure are determined. In case of a physiological form associated with underdevelopment of the baby’s organs, observation is continued and control studies are prescribed at intervals of 2-3 months.
Diagnostics
Pyeelectasia is a disease that requires constant monitoring, its severity is assessed as it progresses. Monitoring is carried out by regular ultrasound, but a final diagnosis cannot be made only on the basis of this procedure and during pregnancy up to 32 weeks.
In cases where, after this stage of pregnancy, suspicions of pathology remain, it is possible that after the birth of the baby he will be given a definitive diagnosis.
Additional diagnostic procedures can help determine pathology:
- uro- and cystography;
- MRI;
- CT;
- fluoroscopy.
X-ray of the kidneys with pyeloectasia.
Based on the results of the diagnosis, the localization and extent of the lesion are established, on the basis of which the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. Most often, it is impossible to do without surgery, especially in severe cases.
Treatment methods
In most cases, the baby does not need special treatment for pyeloectasia. Doctors monitor the dynamics of changes in the size of the pelvis by conducting regular ultrasound examinations.
Surgery
Surgeries are indicated for renal dysfunction. The intervention is carried out using endoscopy, laparoscopy or open methods, depending on the type of operation. Types of surgical interventions:
- plastic surgery – suturing of the dilated pelvis;
- restoration of urine outflow - removal of stones, expansion of the ureter, excision of tumors.
Kidney removal is practically not performed in children, since even with 10% healthy tissue, the functions of the organ can be restored and return to normal due to the high regeneration properties at a young age.
Conservative therapy
Drug treatment begins with the development of infectious and inflammatory processes (pyelonephritis, cystitis, others). It is aimed at eliminating pathogens and restoring kidney function. Drugs used:
- antibiotics;
- uroseptics;
- herbal remedies that improve urine flow;
- regulators of immunity.
Children are also prescribed multivitamins for general strengthening of the body and a diet that reduces the load on the kidneys.
Determining the disease
Only an experienced doctor can determine pathological enlargement of the kidneys in the fetus by conducting an ultrasound examination of the pregnant woman and prescribing appropriate laboratory tests.
If pathology is suspected, constant monitoring and observation is required. After the birth of the baby, additional diagnostic measures are carried out, and if a significant change in the size of the kidneys is detected, appropriate treatment is prescribed. In the case of stage 2 or 3, surgical intervention is necessary; conservative treatment methods are used only for mild forms of the disease.
Clinical manifestations
One of the main activities to determine the presence of the disease is monitoring the baby’s condition. However, hydronephrosis in newborns may not always manifest itself; often the disease is hidden, or parents equate all existing signs with the baby’s usual anxiety.
This is how stage 1 of pathology usually manifests itself, which can only be determined by carrying out a series of diagnostic measures. Sick children, as a rule, are restless; a state of weakness and irritability may predominate in them.
But a more accurate clinical picture will be given by the following symptoms:
- presence of blood or pus in the urine;
- strong smell of urine;
- vomit;
- lethargy;
- lack of appetite;
- lethargy when sucking the breast;
- increased body temperature;
- when urinating, the child begins to cry, moan or scream, this indicates pain during urination;
- the baby's nervousness may indicate that he feels a feeling of itching;
- bloating.
Irritability and anxiety in a baby can be caused by various reasons.
The disease can be determined by palpation of the abdomen. When pressing on it, a strong tension is felt in the area of the anterior abdominal wall.
And during a palpation examination, the doctor determines that the kidney is enlarged. These symptoms indicate progression of the disease, in which case immediate treatment is required.
Diagnostics
Numerous diagnostic methods allow a more accurate diagnosis of the disease. At the 15th week of pregnancy, an ultrasound can already see all the internal organs of the fetus and compare their sizes with the norm. If there are abnormalities, the pregnant woman is prescribed an ultrasound scan every month of the prenatal period.
After the baby is born, another ultrasound is performed, which allows you to determine the degree of dysfunction of the paired organ.
Additional diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- excretory urography (allows you to compare the excretory capacity of the right and left kidneys);
- CT;
- voiding cystography (excludes suspicion of reflux of urine from the bladder);
- general and biochemical urine analysis;
- general blood analysis.
Fact. Congenital renal hydronephrosis is not uncommon in infants. According to statistical indicators, per 100 pregnant women there is 1 case of hydronephrosis developing in the fetus while still in the womb.
Special urinals will make it easier to collect urine from newborns for testing.
If, nevertheless, the doctors’ doubts after the birth of the baby were confirmed and he was diagnosed with hydronephrosis, then depending on the severity, the doctor prescribes treatment. In some situations, you can do without surgical intervention, but it is important to know the rule: for children suffering from a disappointing diagnosis, regular ultrasound examinations are recommended (at least once every 3 months).