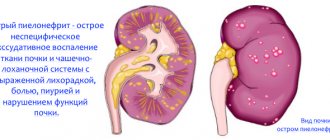
Pyelonephritis is a disease that occurs with inflammation of the kidney tubules and is characterized by damage to the calyces, pelvis and parenchyma. Most often caused by bacterial agents.
Pyelonephritis is a common complication during pregnancy. The main causative agent of urinary system diseases in women is uropathogenic Escherichia coli. According to studies, it is detected in 61% of cases of pyelonephritis in pregnant women.
Also, the kidneys can be affected by the following infectious agents:
- klebsiella pneumoniae;
- enterococcus spp.;
- proteus mirabilis;
- enterobacter spp.
Escherichia coli is the most common causative agent of kidney pathology, since it has additional virulence factors. These include the presence of pili and a flagellum, which allow better contact with kidney tissue.
The disease can develop at any week of pregnancy, but is more common in the second trimester. With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, complications can be prevented.
That is why it is so important, if you experience back pain or painful urination, to immediately seek help from a specialist. A prolonged course of the disease can lead to serious complications, including death.
Complexity of the disease
Forms
There are many variations of the disease. Pyelonephritis can be primary or secondary, depending on the route of entry of the infectious agent into the kidneys. The secondary form of the disease develops in cases where there is obstruction of the urinary tract. The primary form is characterized by the entry of an infectious agent through the blood.
In addition, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- acute and chronic;
- obstructive and non-obstructive;
- purulent and serous;
- one-sided and two-sided.
There is a classification according to the clinical course of the disease.
The following forms of pyelonephritis are distinguished:
- latent (characterized by an asymptomatic course, in some cases there may be a slight increase in body temperature and impaired urine output);
- anemic (accompanied by a decrease in hemoglobin levels);
- hypertensive (increased blood pressure comes first in the clinical picture).
Carefully! Pyelonephritis in pregnant women occurs in a latent form. The patient may not know about the presence of the disease until it is time to get tested.
Symptoms of gestational pyelonephritis disease, diagnosis of the disease
Acute gestational pyelonephritis begins with severe chills, which alternate with profuse sweating. Body temperature rises to 39 −40 degrees. General malaise and muscle weakness appear. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by signs of severe toxicity - nausea, vomiting, and the latter can last for several days.
Pyelonephritis can also be characterized by pain in the groin
Lost appetite. Pain appears in the waist area, radiating to the groin and leg. Frequent urination. To alleviate the condition, the woman lies on her healthy side and bends her legs at the knees. To avoid complications, a pregnant woman should definitely go to a consultation, where a gynecologist will issue a referral for tests.
The diagnosis is made by analyzing blood and urine, which must be collected according to the rules and diagnosed using several methods.
Preference is given to the “morning” portion. There are no daily fluctuations in indicators, which makes the analysis objective in terms of parameters. Urine is collected in a sterilized container, after washing with soap. The first portion is not used (there is a possibility of bacteria getting from the vagina and urethra), and the second portion is collected so that there is no contact of the dishes with the body. Portion - at least 70 g. Cover the dish tightly with a lid. It is recommended to donate urine on an empty stomach and not take any medications beforehand.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. Increased protein, increased leukocytes, red blood cells, casts. The normal number of leukocytes is 4 thousand, erythrocytes - 2 thousand.
- Zemnitsky's test. The patient collects urine every three hours. The specific gravity of urine is calculated, and it decreases with pathology. An important factor in confirming the disease is nighttime diuresis higher than daytime diuresis. Bacteriuria is also an important symptom of pyelonephritis.
- Biochemical analysis shows the total amount of protein.
Pathological changes in kidney function can be a consequence of chronic infections and illnesses suffered in childhood - tonsillitis, pneumonia. The disease has long passed, but the infection remained in the kidneys and, against the background of physiological changes, manifested itself as protenuria (a small amount of protein), leukocytouria.
Chronic pyelonephritis
The main feature of all forms of the disease is that in a person who has been ill once, changes occur in the renal collecting system. If pyelonephritis recurs in the future, it becomes chronic.
This stage is different in that at the moment when a person is healthy, it is in remission. But with respiratory infections, as well as sore throats, an exacerbation is observed. During pregnancy, against the background of weakening of the body, an exacerbation of pyelonephritis is often observed.
Women suffering from chronic pyelonephritis should be observed by their doctor. Particular attention should be paid to urine and blood tests. In some cases, maintenance therapy is indicated.
Chronic bilateral pyelonephritis can lead to serious complications - nephrosclerosis and pyonephrosis. That is why it is so important to carry out preventive measures to avoid exacerbation of the disease.
Treatment of chronic pyelonephritis is a complex process, one of the most important components of which, in addition to adequate antibacterial therapy, is ensuring normal urine outflow.
In this regard, the following interventions may be prescribed:
- treatment of urolithiasis;
- treatment of kidney prolapse;
- surgery for developmental anomalies.
Among the drugs, in addition to antibiotics, the use of sorbents, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics, as well as drugs that increase circulation in the kidneys are indicated. If during pregnancy there are several periods of exacerbations, it is possible to prescribe antibacterial agents during the period of remission.
Causes of the disease
The disease is classified as “Kidney infection during pregnancy” according to the ICD-10 catalog code No. 023.0. This pathology occurs no earlier than the thirteenth week of pregnancy, when there is an increase in corticosteroids, progesterone and estradiol in the blood.
As a result, the tone of the bladder muscles decreases and the condition of the kidneys is destabilized, and if we add here the pressure exerted on the internal organs by the uterus, which increases during fetal development, penetration of the pathogens of gestational pyelonephritis into the genitourinary tract becomes only a matter of time.
But this disease does not occur in everyone during pregnancy and its development is influenced by certain factors, including:
- weakened immunity;
- kidney anomalies of congenital origin;
- bacteriuria diagnosed before pregnancy;
- urolithiasis disease;
- dysfunction of the bladder and ureters;
- any chronic kidney disease.
Sometimes the disease does not occur against the background of pathologies, but due to such physiological characteristics of pregnant women as a narrow pelvis or polyhydramnios , as well as due to the development of twins or triplets in the uterus.
Acute pyelonephritis
Characterized by the appearance of a clinical picture. If the disease worsens, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Pyelonephritis begins after a sore throat or other cold.
If, after an illness, there is increased urination or pain in the lumbar region, it is necessary to undergo a general urine test to exclude a pathological process. Acute pyelonephritis begins with an increase in temperature and the appearance of pain. During pregnancy, an asymptomatic course of the disease may occur. The disease can only be suspected if there is a change in the color of the urine.
Observation Treatment of pyelonephritis in the acute phase must necessarily include the use of antibacterial drugs. It is necessary to normalize your diet and drink enough fluids.
Treatment
Treatment of pyelonephritis is carried out only with the use of antibiotics. Despite the harm of antibacterial drugs to the fetus, therapy is justified. The risk of premature birth and complications is reduced by 5-50%.
The choice of antibiotic depends on the stage of pregnancy. In the first trimester, penicillin drugs are used, for example, Amoxiclav or Amoxicillin. Starting from the 4th month, the use of cephalosporins is allowed. Claforan, Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone are suitable. In case of severe inflammation, Gentamicin can be taken from 20 weeks.
Macrolides, for example, Sumamed or Vilprafen, are safe during pregnancy, but have a narrow spectrum of action.
Pyelonephritis during pregnancy is under no circumstances treated with Levomycetin, Biseptol, tetracycline or fluoroquinolone drugs.
Treatment with antibiotics is carried out in courses. In the acute form, therapy lasts up to 10 days, in the chronic form – up to 5 days. During treatment, a pregnant woman must remain in bed.
In addition to antibiotics, antispasmodics (Pyatnok) and drugs that improve placental blood circulation (glucose solution, saline) are prescribed. Additionally, diuretics are used. Both medications (Phytolysin, Canephron or Eufillin) and folk remedies are suitable.
Has a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect:
- lingonberry or cranberry juice;
- nettle decoction;
- infusion of birch leaves;
- oat decoction;
- infusion of horsetail.
To reduce the symptoms of intoxication, saline solutions and Reopoliglucin are injected.
A pregnant woman needs to follow a drinking regime; the volume of liquid she drinks increases to 2-3 liters. It is necessary to give up strong tea and coffee, give preference to clean water, jelly, fruit drinks and compotes.
Fried, fatty and spicy foods, smoked foods, fast food, chocolate, carbonated drinks and alcohol should be excluded from the diet. Food can be consumed boiled, baked or stewed.
Why does it occur
Most often, the infection enters the kidneys from the bladder. Therefore, pyelonephritis may be preceded by cystitis. In this case, the disease is secondary. The pathogen can enter the organ through lymph or blood. Primary pyelonephritis is diagnosed only when it is not possible to establish where exactly the primary focus of the disease was located.
There are no clear causes of pyelonephritis, but there are risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing this disease.
These include:
- promiscuity;
- disruption of the outflow of urine due to obstruction of the ducts by stones or compression of the ureters by tumors;
- vesicoureteral reflux;
- reduced immunity;
- history of urinary system surgeries.
Pregnancy is a risk factor for the development of pyelonephritis. It has been proven that urinary tract infections occur in 10 percent of pregnant women. In a third of cases, pyelonephritis may form.
The presence of one or more risk factors during pregnancy significantly increases the likelihood of getting sick. Therefore, it is so important to prevent diseases of the genitourinary system.
There are clear signs
Provoking factors
This type of pyelonephritis occurs only in pregnant women. The disease occurs due to infection. The growing uterus puts pressure on neighboring organs, increasing the risk of infection directly in the kidney. An infectious agent can enter an organ in this way:
- hematogenous - with blood flow;
- lymphogenous - with lymph flow;
- ascending - through the organs of the urinary system.
The causative agent of pyelonephritis in pregnant women can be staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, tuberculosis or Escherichia coli, viral infections, Candida fungi.
Provoking factors:
- increased renal blood flow;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- hypothermia;
- overheating;
- physical exercise;
- suffered from acute respiratory viral infection;
- acute cystitis or pyelonephritis, which was before pregnancy;
- bacteruria, bacterial vaginosis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- inflammation of the reproductive system;
- diabetes;
- failure to comply with the rules of genital hygiene.
Before pregnancy, you need to cure all infectious and inflammatory diseases, check your kidneys, since they have a huge load.
Symptoms
If a pregnant woman gets sick with pyelonephritis, the following signs will be noted.
- Temperature increase. In the first days of the disease, the temperature can reach 39 degrees. Then it begins to gradually decrease and remains at low-grade levels.
- Pain syndrome. In the lumbar region there is severe pain of a girdling nature. Pain syndrome can be of varying intensity. The severity of pain usually depends on the strength of the inflammatory process.
- Change in urination. Frequent urges are noted. Urination is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. The color of your urine may also change. It becomes cloudy.
It happens that pyelonephritis does not manifest itself during pregnancy. With a latent course, they learn about the disease by chance, after taking tests.
How dangerous is pyelonephritis for a pregnant woman?
A disease such as gestational pyelonephritis, the symptoms of which we discussed above, automatically puts a pregnant woman at risk. Why? The inflammatory process in the body increases the load on the cardiovascular system and kidneys. 30% of women with this diagnosis develop gestosis (late toxicosis).
In this condition, blood circulation in the kidneys, brain, and placenta noticeably deteriorates. The blood becomes thick and the amount of oxygen in it decreases. All this affects the nutrition of the fetus and the condition of the woman herself.
Experts include the following among the main negative consequences of this disease:
- The threat of miscarriage is the most common complication of gestational pyelonephritis.
- Premature birth.
- Multiple bleedings.
- Placental abruption.
- Anemia.
The appearance of a particular complication depends mainly on the severity of the inflammatory process and the timeliness of seeking medical attention.
Diagnostics
When the disease worsens, making an accurate diagnosis is not difficult. An examination supported by a general urine test is usually sufficient.
In addition to routine methods, the doctor may also require the following examinations:
- excretory urography;
- scintigraphy;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- CT;
- MRI.
Expert opinion Olga Borovikova These examinations may be needed if the doctor doubts the correctness of the diagnosis or suspects the development of complications. The most important examination in diagnosing pyelonephritis is a general urine test.
Analysis of urine
The main thing a woman should know is how to properly prepare for the test.
The following rules must be observed.
- Do not drink alcohol or smoke the day before the examination.
- It is not recommended to eat 12 hours before the test. You can only drink water.
- When taking diuretics, you must stop them at least one day before the examination.
In addition to a general urine test, which will indicate significant leukocyturia, as well as bacteriuria. A urine culture may be prescribed. This is necessary to determine the pathogen that caused the disease, as well as to find out which antibiotic is suitable to combat it.
The following indicators may be noted in a urine test:
- leukocytosis (more than 5 leukocytes in the field of view, in some cases their number reaches 20);
- proteinuria (appearance of protein in the urine);
- hematuria (in severe cases, blood appears in the urine).
A general urine test is often sufficient to diagnose pyelonephritis in a pregnant woman. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional examination methods.
What tests to take
GESTATIONAL PYELONEPHRITIS: ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT.
Styazhkina Svetlana Nikolaevna
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Department of Faculty Surgery
Vorobyova Anna Vladimirovna
student at Izhevsk State Medical Academy;
Makshakova
Natalia Petrovna
student of the Izhevsk State Medical Academy
Sukhikh Natalya Vladimirovna
student at Izhe State Medical Academy
Simanova
Alexandra Aleksandrovna
student of the Izhevsk State Medical Academy
Annotation.
The article is devoted to the prevalence of gestational pyelonephritis among pregnant women. Modern ideas about the issues of etiology, diagnosis and treatment of gestational pyelonephritis in pregnant women and their prevention in healthy individuals are described.
Keywords:
gestational pyelonephritis, ureteropyeloectasia, pyeloectasia.
Relevance of the problem.
Kidney diseases occupy a leading place among the pathologies of pregnant women. Despite advances in the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections in recent years, they continue to remain one of the most important areas of modern medicine.
Gestational pyelonephritis is a nonspecific infectious and inflammatory process that occurs during pregnancy, with initial and predominant damage to the interstitial tissue, pyelocaliceal system and renal tubules; subsequently, the glomeruli and renal vessels are involved in the process. [3]
There are acute and chronic pyelonephritis. Acute pyelonephritis occurs in 2–10% of pregnant women, more often during the first pregnancy (80%) than during the second pregnancy (20%). In primigravida women, the disease manifests itself at 4–5 months of pregnancy, in multipregnant women – at 6–8 months. [4]
Etiology of gestational pyelonephritis
. During the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman's hormonal background changes, the level of estradiol and progesterone increases. These changes directly affect the renal collecting system and the tone of the bladder muscles. An enlarged uterus puts pressure on the urinary tract, which leads to stagnation, which in turn increases the risk of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms and their reproduction, provoking the development of inflammation in the kidneys. There are community-acquired and hospital-acquired pyelonephritis, in the first case the causative agent of the infection is Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli), which accounts for 85-90% of cases, in the second case - more often gram-negative (Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Serratia), and gram-positive bacteria (Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Staphylococcus aureus). [3]
But the main factor in the development of gestational pyelonephritis is a violation of the urodynamics of the upper urinary tract or the presence of infection in the woman’s body.
During the most pronounced hormonal changes in the placental system, a critical period for the development of pyelonephritis is identified - 23-28 weeks. [2]
Pathogenesis of the development of gestational pyelonephritis
.
Ways of spread of infection.
1. Hematogenous from the source of infection. 2. Urinogenic (ascending) pathway with vesicoureteral reflux.
Risk factors for the development of gestational pyelonephritis are:
previous history of urinary tract infection, especially before 20 weeks of pregnancy; malformations of the kidneys and urinary tract, kidney and ureteral stones; inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs; diabetes; urodynamic disorders caused by pregnancy (dilatation and hypokinesia of the intracavitary system of the kidneys, ureters against the background of metabolic changes), low socio-economic status. Acute pyelonephritis in pregnant women develops in 20-40% of women with untreated asymptomatic bacteriuria, which allows us to consider the latter also as a risk factor for the development of gestational pyelonephritis. Extragenital diseases are also a premorbid background for the development of pyelonephritis during pregnancy. Among extragenital diseases, the main place belongs to chronic tonsillitis and diabetes mellitus.[4]
Ureteropyeloectasia occurs during pregnancy due to an enlarged uterus pressing on the ureters, reducing their tone and causing disturbances in the blood supply and urodynamics of the kidneys, as a result of which urine stagnates in the upper urinary tract. After 6 weeks, hyperkinesia of the ureters occurs, and at 8 weeks, hypotension and hypokinesia of the calyces and renal pelvis occurs.
A decrease in tone directly underlies neurohumoral factors, for example, a weakening of the sympathetic nervous system leads to changes in the urinary tract, therefore we can trace the relationship between the autonomic nervous system and the function of the smooth muscles of the ureters and renal pelvis. [5]
During the second and third trimester, a decrease in calcium ions occurs in the body of a pregnant woman, which leads to a decrease in the sympathetic nervous system and, consequently, to a decrease in the tone of the smooth muscles of the ureters. [4]
Symptoms of the disease
. The most common and common symptoms include:
— Increase in temperature from low-grade (38°C) and higher, accompanied by chills.
— Pain in the lumbar region on the affected side (or both sides).
- Pain when urinating
- Increased amount of urine
- Change in urine color
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Headache
In addition, as a rule, the clinical picture of gestational pyelonephritis during various periods of pregnancy is characterized by a number of features. In the first trimester, severe pain may occur in the lumbar region, radiating to the lower abdomen and external genitalia (the pain resembles renal colic). In the second and third trimester, the pain is usually less intense, sometimes dysuria predominates, and patients take a forced position with their legs pressed to their stomach. [3]
Diagnosis of the disease
.
The most revealing test for diagnosing pyelonephritis is a general urine test. With this disease, leukocyturia (10–15 per field of view or more), proteinuria, and bacteriuria are observed. In the analysis according to Nechiporenko, the number of leukocytes is more than 2000 per 1 ml. A general blood test reveals signs of inflammation: leukocytosis and increased ESR. Ultrasound examination of the kidneys reveals dilation of the calyces and pelvis (pyelectasia) and an increase in the size of the kidney. It is also necessary to monitor the condition of the fetus through ultrasound, CTG and Dopplerometry. [4] Results obtained:
The study included medical records of patients for 2016—29 cases.
Analysis of medical records showed that age ranged from 16 to 36 years, 16-20 years - 11.4%, 21-25 years - 38.6%, 26-30 years - 50%. [1]
Pregnancy rates among patients with GP: first - 30%, second - 45%, third - 15%, fourth - 10%.
Acute pyelonephritis in the first trimester was diagnosed by us in 1 (7.2%) patients at a period of 8-13 weeks; in the second trimester in 23 pregnant women (72.8%) with a gestation period of 14-26 weeks; in the third trimester in 5 women (20%) at 27-40 weeks of pregnancy. In 35.7%, the disease is an exacerbation of a chronic one. [1]
The most common symptom of patients with acute pyelonephritis in the pregnant women we studied is aching pain in the lumbar region (100%). Urological symptoms, also observed in pregnant women with acute infectious and inflammatory process in the kidneys, include frequent and painful urination. During our examination, 5 women (37.5%) were found to have frequent urination; in 14.3% - frequent and painful (cramping). The symptom of concussion was expressed in 11 (78.6%) of the examined. An increase in temperature was observed in 21.4%.
All pregnant women were examined clinically, bacteriologically and by ultrasound, which made it possible to confirm the suspected diagnosis. All examined pregnant women (100%) were found to have an increased number of leukocytes in the blood (leukocytosis).
In 64.3% of those examined by ultrasound of the kidneys, the conclusion was “ureteropyelocalicoectasia”. Unilateral damage is observed in 58.1%, bilateral - in 41.9% of cases. The ratio of the side affected by gestational pyelonephritis in the group of patients we studied is as follows: right-sided pyelonephritis - 35.7%, left-sided pyelonephritis - 21.4%. Acute pyelonephritis was diagnosed in 64.3% of those examined, and in 35.7% - exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis.
Basic principles of therapy. Therapy depends on the form and stage of the disease, the type of pathogen, and the duration of pregnancy. The basis of treatment is antibiotics against the background of restoring the passage of urine from the diseased kidney using catheterization of the ureters after preliminary chromocystography. Evacuation of inflammatory detritus from the kidney tissue prevents the development of bacterial shock, which may be associated with the release of large amounts of endotoxins from microorganisms killed under the influence of antibiotics when the excretory function of the urinary tract is impaired. In the first trimester, semi-synthetic penicillins are used that do not have embryotoxic effects - ampicillin, oxacillin, methicillin. In the second trimester, the range of antibiotics expands due to the inclusion of the protective function of the placenta. It is strictly forbidden to administer tetracycline drugs, streptomycin and chloramphenicol. Use aminoglycosides (kanamycin, gentamicin) with caution due to their oto- and nephrotoxic effects. Surgical treatment is used for complicated cases.
As a preventative measure,
pregnant women are recommended to:
§ Drink cranberry juice. It promotes acidification of urine and prevents the proliferation of bacteria;
§ drink more fluids. If there is no swelling of the legs, the pregnant woman is not subject to high blood pressure, she should drink at least 2 liters. liquids per day, including borscht, soups, jelly, juicy fruits.
§ maintain personal hygiene;
§ move more, stay in the fresh air;
§ can’t stand it when you want to go to the toilet;
§ eat healthy and balanced;
§ do special gymnastics to reduce pressure on the pelvic organs and kidneys;
§ visit an obstetrician-gynecologist in a timely manner, regularly take all tests prescribed by him;
§ at the first signs of illness, immediately contact your doctor.[2]
Conclusions: Thus, gestational pyelonephritis was more common in women aged 26-30 years (50% of cases). Most often, GP occurs in the third trimester - 35.7%, in the second pregnancy (45%) and in most cases has bilateral localization - 42.9% of all cases.
Literature:
1. Archive of medical histories of the Republican Clinical Hospital No. 1 of the city of Izhevsk.
2. Dovlatyan A.A. Acute pyelonephritis in pregnant women / A.A. Dovlatyan. - M.: Medicine, 2004. - 215 p.
3. V.L. Pecherina, E.V. Brain. Prevention of late gestosis. Russian medical journal No. 3 2000 - 140 p.
4. Styazhkina S. N. Epidemiological features of the disease with chronic pyelonephritis in women during gestation / S. N.
Styazhkina, L.N. Yunusova, G.I. Saetova, M.L. Chernenkova // Modern problems of science and education. – 2020. – No. 3. – P.89-94.
5. Obstetrics. National leadership. Ed. E.K. Ailamazyan, V.I. Kulakova, V.E. Radzinsky, G.M. Savelyeva 2009 From 214-234.
Information about authors:
1- Styazhkina Svetlana Nikolaevna - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Department of Faculty Surgery;
2- Vorobyova Anna Vladimirovna - student of the Izhevsk State Medical Academy; e-mail
3- Makshakova Natalia Petrovna - student of the Izhevsk State Medical Academy;
4- Sukhikh Natalya Vladimirovna - student of the Izhe State Medical Academy:
5- Simanova Alexandra Aleksandrovna - student of the Izhevsk State Medical Academy;
GESTATIONAL PYELONEPHRITIS: ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT.
SN Styashkina, AV Vorobeva, AA Simanova, NP Makshakova, NV Syhyh.
Summary:
The article focuses on the prevalence of gestational pyelonephritis among pregnant women. Described modern ideas about the etiology, diagnosis and treatment of gestational pyelonephritis of pregnant women and the prevention in healthy persons.
Key words:
gestational pyelonephritis, ureteropyeloscopy, pyelectasis.
References:.
1. Archive histories of the Republican clinical hospital No. 1 of the city of Izhevsk. 2. Dovlatyan AA Acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women / AA Dovlatyan. - M.: Medicine, 2004. - 215 p
3. VL Pecherina, EV Brain. Prevention of late gestosis. Russian medical journal, No. 3, 2000- 140 rub.
4. Styazhkin SN Epidemiological features of chronic pyelonephritis in women during the period of gestation / CN
5. Styazhkina, LN Yunusova, GI Kuznetsov, ML Chernenkov // Modern problems of science and education. – 2020. – No. 3. – S. 89-94.
6. Midwifery. National leadership. Under the editorship of EK aylamazyan, VI Kulakov, VE Radzinsky, GM Savelyeva 2009. With 214-234.
How to treat
There is no difference in the period at which pyelonephritis was diagnosed. If a woman falls ill in the first, second or third trimester, treatment must necessarily include antibacterial therapy. Many women are afraid that antibiotics can harm the fetus, but drugs have long been available that are absolutely harmless to a pregnant woman.
In addition to antibacterial therapy, it is also recommended to follow a diet, and after recovery, take maintenance medications necessary to reduce the risk of recurrence of pyelonephritis.
Listen to your doctor
What medications can you take?
Antibiotics that can be taken during pregnancy are now available in large quantities.
For pyelonephritis in pregnant women, it is recommended to use the following antibacterial drugs:
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides.
The drug of choice is cephalosporins. In particular, Cefazolin. Like the other drugs mentioned above, cephalosporins are completely safe for the fetus, so they can be safely taken during pregnancy. Of the macrolides, the drug of choice is Vilprafen.
The following drugs can be prescribed for therapeutic purposes:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diuretics;
- detoxifying agents;
- drugs that improve kidney microcirculation.
Expert review Olga Borovikova After completing a course of antibacterial drugs, maintenance therapy is necessary. The herbal preparation Canephron has proven itself very well. According to studies, taking it after treatment of pyelonephritis reduces the risk of relapse several times. Despite the fact that pregnancy is not a contraindication for taking Canephron, it should be taken strictly as prescribed by your doctor.
Treatment with folk remedies
Pyelonephritis is a serious disease, so doctors do not recommend resorting to traditional medicine during its exacerbation. It is best to use traditional methods.
During the period of remission, the following traditional methods can be used to reduce the risk of relapse.
- Birch juice. It is recommended to drink one glass of natural birch sap per day. This must be done on an empty stomach. A two-week course of treatment with this remedy allows you to normalize the mineral balance in the body, as well as reduce the likelihood of developing infectious diseases.
- Cranberry juice. A glass of fruit drink made from cranberry pulp should be drunk once a day for a month.
- Herbal infusions. The most popular is the bud collection, which includes chamomile, birch leaves, calendula, lingonberries, and corn silk.
Before using any traditional methods, you should consult your doctor.
Clinical guidelines
The main part of treatment is antibacterial therapy. The use of antibiotics from the Streptomycin and Tetracycline groups is prohibited. They have a pronounced teratogenic effect and can disrupt the normal development of the fetus.
It is important for pregnant women to maintain a drinking regime and engage in therapeutic exercises. Especially during the period of remission. Diet therapy also gives positive results. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, pyelonephritis occurs without consequences for both the fetus and the mother.
The influence will be
Treatment tactics for pyelonephritis during pregnancy
1. Determination of the type of infectious agent and its sensitivity to antibiotics of various groups, by submitting urine for analysis for bacterial culture.
According to the results obtained, the pregnant woman is prescribed antibiotics that do not provoke the development of severe birth defects in the baby. Therapeutic course - up to 14 days.
A woman carrying a child needs to remember the following: whether she wants it or not, the inflammation must be treated! Let expectant mothers not be scared by the word “antibiotic”, because infection causes much more significant harm to the baby than this drug.
Antispasmodics are also prescribed to relieve pain, combined anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents, for example, the drug Canephron N.
It is recommended to take Phytolysin. It helps remove bacteria from the source of their reproduction, relieves inflammation, and improves the excretion of urine from the body. The drug is made on a natural basis and is approved for use during pregnancy.
As a complex therapy, pregnant women are often prescribed Cyston tablets. They have antispasmodic, bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effects, and also provide a mild diuretic effect.
Until the culture results are obtained, the pregnant woman may be prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics (for example, Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Ceftriaxone, Erythromycin, Spiramycin).
If taking antibiotics does not give the desired result, then alternative treatment is carried out using bacteriophages. Bacteriophages are “good” viruses that destroy a certain type of pathogenic bacteria. Depending on the type of pathogen, streptococcal, staphylococcal, coli, Proteus, Klebsiella bacteriophages, etc. are distinguished.
Bacteriophages are taken orally (swallowed) or introduced through a catheter or drain into the kidney.
2. Observance of strict bed rest.
In case of unilateral damage, sleep should be exclusively on the “healthy” side!
3. Drink plenty of non-carbonated water of low mineralization (it is advisable to drink a glass of water on an empty stomach), cranberry juice. Taking diuretics, for example, kidney tea or Brusniver collection.
In summer, it is recommended to eat ripe watermelons and melons. Black currants (if you are not allergic to vitamin C), peach, grapes, and pear are also useful. And a fresh cucumber should be the main ingredient in a salad for lunch.
4. Adhere to a therapeutic diet. During an exacerbation of the disease, you should eat food without salt, and hot, spicy, pickled and fried foods should be completely excluded from the menu.
Drinking coffee is not recommended! Chicory is a useful alternative.
5. Adopting the knee-elbow position for 15-20 minutes 3-5 times a day. This position helps improve the outflow of urine when urinating is difficult.
Throughout treatment, the child’s condition should be carefully monitored for early detection of possible hypoxia and delay in its development.
In case of repeated pyelonephritis, a catheter is inserted into the ureter through the urethra to drain urine, and antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
Surgical intervention is necessary only if taking medications does not produce the expected results or the inflammation is aggravated by a purulent process in combination with the destruction of kidney cells. In severe cases, due to the lack of proper treatment, the disease can cause kidney failure, the development of a kidney abscess, and threaten the woman with death.
Qualified medical care will help you avoid negative consequences. If hospitalization is offered, you should not refuse!
After treatment, it is necessary to submit urine for general analysis once every 2 weeks until the end of gestation, and monthly for bacterial culture. The probability of re-exacerbation of the disease before childbirth is about 20%.
Diet
The treatment menu for pyelonephritis is included in the Pevzner diet complex. “Table No. 7” allows you to increase the effectiveness of drug treatment in pregnant women, as well as reduce the risk of early relapses.
For proper dietary therapy, the following recommendations must be followed:
- the basis of nutrition should be “slow” carbohydrates;
- per day, no more than 90 g of protein and 100 g of fat should enter the body;
- Every day you need to consume at least 3 liters of fluid;
- limit or stop salt consumption altogether;
- do not eat pickles, fast food, pickled foods, or semi-finished products containing salt;
- eat small meals, at least 5 times a day;
- do not cook food by smoking or frying;
- exclude alcoholic drinks.
Pregnant women with pelonephritis have a list of prohibited foods. What should you not eat or drink if you have this disease?
Doctors do not recommend adding the following to your diet:
- chocolate;
- fish and meat of fatty varieties;
- sausage;
- legumes;
- mushrooms;
- sour cream with high fat content;
- coffee.
To obtain sufficient effect, experts recommend sticking to the diet for at least 5 months after the disease has passed the acute phase. If you follow all the recommendations and exclude prohibited foods, the effect of the diet can be noticed in the first months.
Catering
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
| Product groups:
In case of chronic renal failure, protein intake is limited. |
The purpose of the drinking regime is to “flush” the kidneys. You can drink almost everything, because... the disease does not lead to fluid and salt retention:
| If gestosis occurs against the background of pyelonephritis (late toxicosis with edema and increased pressure), the drinking regime is organized according to the recommendations of the attending physician. |
Effect on pregnancy and fetus
Pyelonephritis with a prolonged course affects not only the pregnant woman, but also the fetus. Thus, impaired renal function can lead to deterioration of feto-placental function. Impaired placental function, in turn, threatens serious hypoxic damage.
The following complications are possible:
- intrauterine infections;
- anemia of pregnant women;
- gestosis;
- premature delivery.
All children born from a pregnancy that occurred against the background of pyelonephritis should be placed at risk for perinatal pathology.
In the early stages
It is dangerous for the fetus because if left untreated, the risk of miscarriage and the development of intrauterine infection increases significantly. If pyelonephritis develops in the early stages, it is extremely important to start treatment measures in a timely manner to avoid serious complications.
In the later stages
Poses a danger to mother and fetus. Against the background of pyelonephritis, gestosis develops, and this already increases the risk of giving birth to a child with hypoxia and intrauterine infection. This is why it is dangerous to develop pyelonephritis during pregnancy. With timely initiation of treatment measures, the risk to the fetus is minimal.
Consequences for the child
Complicated course of pyelonephritis can lead to the following consequences for the fetus:
- prematurity;
- asphyxia;
- development of intrauterine infections;
- malnutrition;
- hypoxic brain damage;
- intrauterine growth retardation.
The percentage of such complications is relatively low. Prematurity is the most common condition. The most common is intrauterine infection. Given the severity of these conditions, it is recommended to extremely carefully monitor the development of a child born from a pregnancy that occurred against the background of pyelonephritis.
Complications can be avoided
Complications
The consequences of pyelonephritis are severe:
- late gestosis;
- threat of miscarriage in the early stages;
- placental insufficiency;
- weak labor activity;
- anemia;
- bleeding during or after childbirth;
- infection or blood poisoning;
- toxic shock;
- acute renal failure;
- purulent-septic diseases after childbirth.
You can avoid dangerous consequences if you do not neglect treatment.
Prevention
Preventive measures play a very important role in preventing the disease. Moreover, they should begin at the planning stage.
To reduce the risk of developing the disease, a pregnant woman must follow the following recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases;
- drink enough fluids;
- do not walk with a full bladder;
- get enough vitamins.
To reduce the likelihood of complications, it is necessary to undergo timely examinations by a gynecologist and take all necessary tests. This will make it possible to detect the disease in the early stages of formation.
Exercises
Therapeutic physical training for pyelonephritis should not be carried out during an exacerbation of the disease. This can worsen the general condition of a pregnant woman. During the period of remission, you can carry out a set of exercises that have a positive effect on kidney function.
A properly selected set of exercises allows you to achieve the following goals:
- restoration of normal renal circulation;
- normalization of the body's metabolic processes;
- improvement of urination;
- restoration of normal blood pressure values.
You should not engage in professional sports if you have pyelonephritis. There is also no need to go to the gym and lift heavy weights.
The following are examples of exercises to improve kidney function.
- Lying on your back, bend your right leg at the knee, take a deep breath, raising your left arm. Take the starting position, exhale deeply and then repeat the exercise with opposite limbs. It is recommended to do 8-10 repetitions.
- Lying on your right side, take a deep breath, bring your left knee to your chest and raise your left arm up. Then exhale. Repeat the exercise 8-10 times.
- Lie on your back with one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach. Take deep breaths and exhales. Perform the exercise for 2-3 minutes.
Such simple exercises help to recover faster after an exacerbation. However, before engaging in physical therapy, it is imperative to consult with your doctor.
Preventive actions
To prevent the development of gestational pyelonephritis, it is extremely important for expectant mothers to include several points in their daily routine:
- Moderate physical activity. Doctors recommend taking short walks (about 1 hour) every day.
- Special gymnastics for pregnant women. Today, many sports centers conduct classes for women in position, thanks to which the back muscles are strengthened and the tone of all internal organ systems is improved.
- If you have a history of diseases of the urinary system, you must follow a special diet that promotes the outflow of urine.
- It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids per day.
- You should empty your bladder at least every three to four hours.
Paying attention to your own health and preventing gestational pyelonephritis is the key to giving birth to a strong baby. Such an insidious disease should not be neglected. If primary symptoms appear, it is better to consult a doctor and take all necessary measures to eliminate the pathology. Be healthy!