Pyelocalicectasis of the right kidney - what is it?
There is a rare but dangerous disease called pyelocalicoectasia - only a specialist can tell you what it is and how it manifests itself.
This pathology can be congenital or acquired and is accompanied by an expansion of the renal collecting system.
It is often complicated by other diseases of the urinary system, so it is important to diagnose the problem in a timely manner to prevent complications.
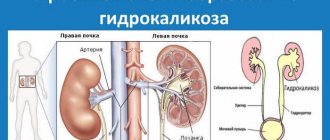
Pyelocalicoectasia of the kidney
Peculiarities
Pyelocalicectasia is not an independent disease. It occurs as the next stage in the development of pyeloectasia, characterized by an increase in only the renal pelvis.
Most often, the disease affects both kidneys at the same time, and the pathological process is complicated by dilation of the ureter. Much less often, pathology is determined only on one side.
It is possible to develop physiological pyelocalicoectasia, when a short-term increase in the lumen of the renal pelvis is observed.
This happens with frequent attempts to hold back urination, when a person takes diuretics, and also when drinking a large volume of liquid.
This condition is regarded as a compensatory reaction of the body to the action of unfavorable factors. In this case, the person does not need drug therapy, the condition gradually normalizes on its own.
Causes
In medicine, there is an opinion about the pathology of both or one kidney, that this is a congenital condition that occurs when the fetus is not formed correctly. But in adults, pathology is also possible against the background of certain diseases of the genitourinary system, which provokes an expansion of the cavities of the collecting apparatus.
Other reasons:
- Urolithiasis disease. Due to the formation of stones in the kidneys and their gradual growth, a violation of the outflow of urine develops. It accumulates in the internal structures of the kidneys, causing their expansion. A urethral stricture can also provoke a similar problem.
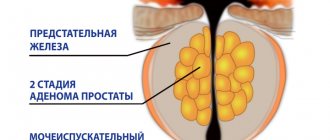
- Prostate hyperplasia. Due to the proliferation of prostate tissue, a narrowing of the urethra occurs. Urine does not completely exit the bladder, but accumulates. Over time, vesicoureteral reflux may develop, causing urine to back up into the kidney.
- Ureteral obstruction. It happens with injury or a prolonged infectious process, accompanied by the development of complications.
- Pyelocalicectasis of the left or right kidney is common during pregnancy. This is due to increased pressure from the uterus on nearby tissues and organs. As a result, problems arise with the normal functioning of the urinary system.
- Neurogenic bladder failure. Leads to constant overfilling of the bladder.
These reasons determine the acquired form of the disease. Congenital develops during the formation of the urinary system.
Causes of pyelocalicoectasia of the kidney
Symptoms
At the initial stages of the disease, there are no specific symptoms. This is due to the powerful compensatory capabilities of the human body. Especially if only the right or left kidney is enlarged. After all, another organ takes over all functions for a while.
With the progression of pyelocalicoectasia, the likelihood of developing complications sharply increases. This is the addition of a bacterial infection as a result of urine reflux, the development of pyelonephritis. Stagnation of urine occurs, its excretion is impaired, up to acute retention. Local pressure increases, which adversely affects the functioning of the urinary system.
The main symptoms of pyelocalicoectasia:
- difficulty urinating;
- pain during and after bowel movements;
- discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the area of the left or right kidney (on the affected side);
- the appearance of pathological impurities, changes in odor and other indicators of urine.
Symptoms of pyelocalicoectasia of the kidney
Diagnostics
Most often, ureteropyelocalicoectasia is diagnosed accidentally, during an examination of the abdominal organs in connection with other diseases.
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound examination of the kidneys. With its help, you can determine the degree of expansion of the renal pelvis apparatus, changes in the parenchyma of the organ, and determine the causes of the pathology.
To clarify the diagnosis, additional diagnostic methods may be necessary:
- Excretory urography. A special contrast agent is administered intravenously to the patient. Allows you to determine the features of the functioning of the renal apparatus.
- Renal angiography. Necessary for determining pathologies in the blood vessels that supply nutrition to the kidney.
Laboratory research methods include a general urinalysis and a biochemical blood test.
Using modern diagnostic methods, it is possible to establish congenital pathology even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. When conducting routine ultrasound examinations, the presence of defects and their severity are determined.
Symptoms and treatment depend on the course of the disease. The sooner you start complex treatment, the greater the chance of preventing complications.
Diagnosis of renal pyelocalicoectasia
Prevention
To prevent kidney disease, you need to regularly undergo a medical examination, visit a doctor, and undergo laboratory and instrumental tests in a timely manner.
If a person has problems (pyelocalicoectasia on the right or left, etc.), measures must be taken to stabilize the condition and prevent complications from occurring.
First of all, you need to monitor your diet.
For diseases of the excretory system, you should avoid spicy, fried, salty and other foods that have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the ureters and bladder.
You should minimize the amount of salt when preparing food. It is necessary to monitor the drinking regime - if there are problems with the outflow of urine, it is necessary to limit fluid intake.
Avoid hypothermia and do not sit on cold surfaces. If a person’s work is sedentary and involves staying in the same position for a long time, it is necessary to regularly do a short warm-up to prevent stagnation of urine.
Prevention of kidney pyelocalicoectasia
You cannot take medications on your own. Taking any medications should be agreed with a urologist or nephrologist.
Pyeelectasia in pregnant women: developmental features
Pyeloectasia of the kidney occurs in 1% of pregnant women, of which 20-30% of cases are caused by diseases of the genitourinary system. In 50%, the pathology also manifests itself in the form of hydronephrosis. Patients are at increased risk of pyelonephritis, renal failure, hypertension, and all-cause mortality. Ultrasound has made it easier to identify urological abnormalities. The degree of dilation of the pyelocaliceal system depends on the stage of pregnancy and the underlying etiology.
Antenatal hydronephrosis has received considerable attention, and ultrasonography has become a major screening tool. Much of the controversy surrounding the use of ultrasound stems from the difficulty in determining which lesions are obstructive and potentially harmful to fetal and maternal development. In general, patients with obstructive uropathy who pose a significant risk of neonatal death due to pulmonary hypoplasia may be considered candidates for prenatal treatment and evaluation.
Possible reasons
Pyeelectasis is quite common and affects pregnant women mainly in the third trimester. Hormonal changes and increased progesterone concentrations weaken the ureters. Dilatation allows urine to flow from the bladder back to the kidneys. However, not all people have hormones that expand the pelvicalyceal system.
If the renal pelvis is enlarged in a pregnant woman, this may indicate the following diseases:
- kidney infections;
- kidney cancer;
- obstruction of the urinary tract by a foreign body;
- congenital malformations of the pyelocaliceal system;
- cystitis;
- cystic kidney disease;
- stones in the kidneys.
The baby in the womb grows steadily and takes up more and more available space. Fetal movements can disrupt the flow of urine. As a result, it can flow back into the bladder and then into the renal pelvis. Patients who suffered from bladder infections before pregnancy have a higher chance of developing pyelectasis. Fatigue, fever, and cold-like symptoms occur with pyelonephritis, an inflammation of the renal parenchyma and pelvis.
Other causes of pyeloectasia on the right side during pregnancy are various diseases and complications - stones, benign neoplasms of the bladder, urinary tract, colon or cervical cancer.
Development mechanism
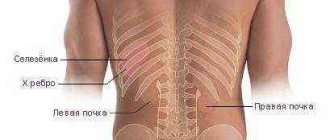
The kidneys are located to the left and right of the spine: in the back of the upper abdomen. They are protected by ribs and a thick fat capsule from external influences. The right kidney is approximately 2-3 cm lower than the left. If pain appears on the left or right, pathological changes occur in only one of the two kidneys. Sometimes back pain originating from nerve roots can be misinterpreted as kidney pain.
During pregnancy, the rapidly growing baby and the uterus require more space, so the two ureters are more or less subject to pressure, which can cause pyelectasis. Significantly enlarged renal calyx, pelvis and urinary tract occur in 3% of pregnant mothers.
The excretory organ must release pollutants and toxins and control electrolyte and fluid balance. However, with pyeloectasia of the right kidney, urinary function is impaired during pregnancy.
Toxic substances and pathogens damage mucous membranes. Patients complain only of nagging pain in the sides and back. If an infection has formed, it goes hand in hand with a fever. Symptoms of pyelectasis usually appear in the late trimester of pregnancy. To prevent this from happening, a woman should control her urination and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Pyeelectasis can affect both kidneys. The left urinary tract is protected from damage by part of the intestine, but the right one is at significant risk of injury.
List of symptoms
Kidney pain is the first sign of complicated pyelectasis. The doctor detects problems with kidney function during routine blood and urine tests. Even back pain often indicates dilation of the renal pelvis during pregnancy.
Pain occurs on both the left and right side, depending on whether one or both kidneys are affected. During pregnancy, pain occurs when there is very high pressure on the urinary tract. Sometimes megacystis is observed - an increase in the size of the bladder. Normally, with minor pyelectasis, pain rarely occurs. Some patients experience pain and burning when urinating, high body temperature, chills, headache, fatigue or nausea.
Types of pyelectasis
According to the prevalence, pyelectasis is bilateral and unilateral. Both one and two kidneys can hurt at the same time. Women are more likely to suffer from kidney problems than men.
Based on etiology, primary and secondary forms of the disease are distinguished. The exact cause of the pathology cannot be established in all cases.
Risks for mother and fetus
Complications depend on the causative disease that caused pyelectasis. If the mother is diagnosed with urolithiasis, there is a possibility of renal colic and migration of bacteria into the systemic circulation. Sepsis threatens the life of both the pregnant woman and the fetus.
Pyelocalicectasia of the right kidney - what is it, clinical picture and complications
Pyeloectasia of the kidneys, what is it - many people have to face this question. This pathology can hardly be called a disease. This is just one sign of health problems. That is, this is not an independent diagnosis - its appearance is preceded by other disorders.
What is pyelectasia?
Behind the frightening name lies a pathology in which the renal pelvis dilates.
What exactly is renal pyeloectasia? Doctors consider it an indirect sign indicating that there are certain disturbances in the process of urine outflow from the pelvis.
This can be caused by various factors - from an anomaly to an infectious lesion. According to statistics, men are more likely to find out what pyeelectasis of the kidneys is, what it is, than the fair sex.
Types of pathology
This disease can affect one kidney - right or left, but most often bilateral renal pyelocalicectasia is observed, when both pelvis and bowls are dilated, and the ureter is enlarged.
The disorder has several stages of development and can be mild, moderate or severe.
It is important to begin treatment of the disease in its early stage, otherwise serious consequences in the form of dilation of the ureter, which can cause ureteropyeloectasia or ureterohydronephrosis, cannot be excluded. Therefore, under no circumstances should you delay contacting a good doctor.
Pyeloectasia of the kidneys - causes
In different organisms, the same pathology is caused by different factors. In most cases, problems are associated with poor outflow of urine from the pelvis or its reflux back into the kidneys.
Finding out what causes kidney pyeloectasia is very important at the beginning of treatment - this will help you choose the most appropriate therapeutic methods and quickly cope with the problem.
A specialist must be involved in finding out the reasons.
Congenital renal pyelectasis
There are two main forms of the disease. One of them is congenital - one in which the expansion of the renal pelvis occurs due to congenital pathologies. The latter are organic and dynamic. Congenital organic pyelectasis of the kidneys, what is it? This is the problem that occurs in the background:
- pathological processes that caused pressure on the ureter;
- changes caused by blood vessels;
- pathologies of the upper urinary tract;
- incorrect structure of the ureter.
Dynamic reasons include:
- narrowing of the lumen of the urethra;
- phimosis;
- neurological diseases that cause disturbances in the process of urination;
- valves in the urethra.
Acquired pyelectasia
Another form of the disease is acquired. In this case, pyeloectasia of the kidneys develops already during life. It can also be caused by dynamic and organic factors. Among the latter, the most common are the following:
- inflammation of the ureter and neighboring organs;
- narrowing of the ureter caused by mechanical damage;
- urolithiasis disease;
- kidney displacement;
- neoplasms (of various types) in the urinary system;
- Ormond's disease.
Acquired dynamic renal pyelectasis, what is it? It is provoked by the following factors:
- infections (especially those that poison the body);
- diabetes;
- diseases due to which the volume of urine increases;
- hormonal imbalances;
- benign formations in the prostate or urethra;
- kidney inflammation.
Methods of therapy
Diagnostics helps to identify the causes of pyelocalicectasia. Congenital forms in children often disappear during growth. However, often only surgery can help overcome the disease. They are necessary in 25-40% of cases.
Traditional methods and preparations
When choosing treatment methods for pyelocalicoectasia, the causes of occurrence are taken into account and measures are developed to eliminate them. Here are the main ones:
- if the outflow of urine is obstructed by stones, crush the stones and remove them, take the drugs Fitolysin, Canephron;
- taking antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazmalgon);
- painkillers (Dexalgin, Nalbuphine);
- drugs to improve microcirculation (Pentoxylin);
- uroseptics (Azithromycin, Palin).
Treatment at different stages
The initial stage, which is not characterized by a fatal impairment of kidney function, requires the elimination of inflammatory processes in the urinary and adjacent organs. This will keep the process of expanding the ChLS under control.
Prescribed drugs help control the outflow of urine, prevent its return and reduce pressure in the organ.
It should be remembered that the pathological expansion of the cups and pelvis can only be completely eliminated through surgery.
Surgical intervention
Surgical measures can be carried out endoscopically or using abdominal surgery.
Treatment
Having established an accurate diagnosis, doctors develop a plan for providing medical care so that subsequent measures do not negatively affect the condition of the fetus.
First of all, therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the cause that provokes poor urine flow. It is very important to restore the urinary process, since such a failure can cause extremely dangerous complications.
Cessation of the urination process causes the death of the right or left kidney, and is a provocateur of renal failure.
If the blockage of the urinary ducts is caused by the presence of stones, doctors provide treatment aimed at preventing complications of the urinary tract.
Medications that act to dissolve kidney stones can be dangerous to the fetus during pregnancy.
Only a doctor will be able, taking into account the individual characteristics of the woman and the fetus, to determine which medications should be trusted.
If, during pregnancy, pyelocalicoectasia of the right kidney was caused by a kink in the ureter, doctors determine what caused such an anomaly.
In the presence of nephroptosis or a wandering kidney, doctors direct the woman to wear a special bandage that prevents the kidney from leaving the natural space.
Accordingly, the occurrence of congestion is prevented, and along with them, pyelocalicectasis of the right kidney is prevented.
If the cause of such a pathology during pregnancy is infectious or inflammatory processes, doctors carry out conservative treatment using mild medications.
Medications are selected with extreme caution so as not to harm the fetus. Herbal preparations may be recommended.
Causes of kidney pyelocalicoectasia: types of disease, symptoms and methods of treatment
Pathological enlargement of the pyelocaliceal part of the kidneys is called pyelocalicoectasis.
Formally, this condition is not a disease, but the excessive size of the cavity in the organ can cause many pathologies, both of the kidneys themselves and of the entire urinary system.
Dilatation of the pyelocaliceal system (PSS) can be observed in one kidney or both.
Causes of pathology
The body of the kidney has cavities (calyces) in which urine accumulates. From there it passes into a large cavity called the pelvis.
The reason for the increase in the volume of the renal cups and pelvis is often intrauterine pathology of the fetus.
During the formation of the urinary system, sometimes a malfunction occurs, which leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the ureter, the formation of a horseshoe kidney or pyelocalicectasia. Often these genetic pathologies develop together.
An increase in the size of the pyelocaliceal region can also be acquired. It is caused by the following factors:
- Poor urine flow . The resulting urine does not leave the kidneys in a timely manner, increasing pressure on the walls of the cups and pelvis. As a result, the cavities stretch. Urine is formed constantly, and regardless of the impaired outflow. Poor urine output is caused by stones (calculi) in the cavity and tumors.
- The backflow of urine from the ureter is reflux. Urine released from the kidneys due to defects in the structure of the urinary tract or their disease is returned back from the bladder. Most often this occurs due to pathological changes in the ureter.
Both of these reasons lead to increased pressure in the cups and pelvis and stretching of their walls. The pressure is transmitted to all parts of the kidney. In the future, this leads to disruption of the nephrons and can lead to the development of renal failure.
The acquired form of pyelocalicoectasis can be caused by:
- urolithiasis - stones block the path for the free outflow of urine;
- injuries with damage to the genitourinary tract, this may include the consequences of unsuccessful surgical operations;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- hormonal disorders, including diabetes;
- prolapse of the kidney with deformation of the ureter;
- inflammatory processes of the urinary organs.
Inflammation of neighboring organs and tissues, damage to large vessels and the lymphatic system can cause expansion of the collecting system.
It is necessary to highlight separate factors for the development of pathology in men and women. In men, prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma) can lead to pyelocalicoectasia.
In women, the pathology often develops during pregnancy. The uterus growing along with the fetus puts pressure on the ureter and bladder, preventing the free movement of urine and deforming the ureter. Poor urine outflow provokes an increase in pressure in the esophagus and the development of the disease.
Classification of the disease
Although the kidneys are a paired organ, usually one of them is affected. Statistics show that pyelocalicoectasia of the right kidney usually develops.
Calicopyelectasia of the left kidney is less common. There are two types of pathology:
- If one kidney is damaged , the second one performs most of the functions of excreting urine. Therefore, the course of unilateral pyelocalicectasis is often long and asymptomatic. The disease begins to manifest itself when inflammation occurs.
- Bilateral ureterocalicopyelectasia is a pathological enlargement of the cups and pelvis of both kidneys, which is also accompanied by dilation of the ureter. This is the most dangerous form of damage. With a bilateral increase in heart rate, renal failure quickly develops.
Symptoms of pathology
It is impossible to detect the presence of pyelocalicoectasia based on symptoms. The manifestations of the pathology are similar to other lesions of the urinary system. With an increase in the pyelocaliceal system, the following are observed:
- urination problems, they become painful, urine portions are small;
- Emptying the bladder requires effort;
- urine has a pungent odor and is opaque;
- bloody impurities in the urine;
- increased blood pressure;
- general weakness, nausea and vomiting, chills with a sharp rise in body temperature.
First there is a feeling of heaviness in the back. Painful sensations are localized on the side of the affected kidney, subsequently affecting the entire lumbar region and radiating into the peritoneum.
Palpation is painful; tapping intensifies the pain. Patients develop nephrotic edema.
Stages of flow
The disease has three stages - mild, moderate and severe:
- in the mild stage, the expansion of the maxillary joint does not have a significant effect on the functioning of the organ, the increase in pressure in the maxillary joint is insignificant;
- medium - the outflow of urine worsens, problems with urination begin, and inflammation occurs. Patients experience swelling;
- severe stage - the kidney is significantly enlarged, hydronephrosis.
Most often the disease is diagnosed between the ages of 25 and 40 years.
Diagnostic measures
The clinical picture of the disease is typical for most lesions of the urinary organs. Ultrasound of the kidneys helps diagnose pyelocalicoectasia.
It will show an increase in the volume of the ventricular region, a change in the size of the kidney itself, thinning of the parenchyma, and stones.
Prescribed studies: It should be noted that congenital fetal pyelocalicoectasia is well diagnosed during pregnancy using ultrasound at 19-24 weeks. In most cases, by birth the expansion of the cervical joint decreases.
Infants with pathology undergo ultrasound at the age of 1-2 months. If abnormalities in urine output are observed, surgery is performed. Infants with pathology undergo an ultrasound scan at the age of 1-2 months. If disturbances in urine output are observed, surgery is performed.
The pathology is treated by nephrologists and urologists. Congenital pathology has a code according to ICD 10 - Q62, acquired - N39.
Traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies can be considered an auxiliary method for eliminating the inflammatory process and improving the outflow of urine. Use:
- Madder roots. Widely used to remove stones and reduce organ tone. The rhizomes are ground to a powder. 1 teaspoon is poured into 1.5 cups of boiling water and boiled for 10 minutes. Strain. Drink 3 times a day after meals, 0.5 cups. The pharmaceutical drug is available in the form of tincture, tablets and extract.
- Rhubarb root , immortelle flowers, and yarrow are mixed in equal proportions. For 1 tbsp. Take a spoonful of the mixture, take a glass of boiling water, cover and leave until it cools. Drink 0.5 glasses 2 times a day.
Before using any herbal preparations, a doctor's advice is required. In addition, you need to be confident in the quality of the raw materials.
Disease Prevention
There are no special methods of prevention. Doctors advise to be attentive to problems of the genitourinary system.
Pain in the lower back or lower abdomen and problems with urination do not need to be treated with home remedies.
A visit to the doctor will allow you to diagnose the disease. General recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia;
- empty the bladder in a timely manner; stagnant urine is a breeding ground for microorganisms;
- dosed physical activity;
- do not consume large amounts of liquid if you have problems with urine output;
- promptly treat acute kidney and genital infections.
It is necessary to follow a diet. Diet helps reduce the load on the urinary system. You also need to reduce your salt intake to 5 g per day and avoid smoked and spicy foods.
For cooking, boiling, stewing and steaming are used. You should drink the prescribed amount of liquid in the form of fruit drinks, decoctions and still mineral water.
Paying attention to your health will help you avoid severe forms of the disease.
We recommend other articles on the topic
Symptoms of pathologies accompanied by calicoectasia
The danger of excessive expansion of the calyces or the entire CL lies in the compression of the parenchymal tissue of the kidneys, which can affect the weakening of the functions of the excretory organs. If the degree of compression of the parenchyma is significant, subjective, objective and laboratory symptoms of renal failure may appear.
Subjectively, this is manifested by poor health, fatigue, dry mucous membranes, and headaches. Objective signs will be, first of all, swelling, the massiveness of which directly depends on the degree of kidney failure.
The main laboratory sign of incomplete functional capacity of the excretory organs is a sharp increase in the blood levels of creatinine and other unresolved nitrogen-containing toxic substances, which is detected during biochemical analysis.
What is ureteropyelocalicoectasia?
Many people are interested in why ureteropyelocalicoectasia occurs and what it is. A shorter name for this disease is pyelocalicoectasia. It is one of the most common diseases of the urinary system. The disease must be detected as early as possible in order to begin treatment, since the absence of therapy can lead to serious deterioration of the kidneys.
With pyelocalicectasia of the kidneys, an unnatural enlargement (congenital or acquired) of the pyelocaliceal system occurs. Depending on the location, a distinction is made between unilateral (one kidney is affected) and bilateral (both kidneys are affected) type of disease. The disease can occur in mild, moderate and severe degrees.
It should be remembered that this disease causes increased inflammation in the kidneys and, as it progresses, can lead to serious complications.
Signs and methods of diagnosis
Most often, a violation of urine output associated with damage to the left or right kidney; no pronounced signs are observed. In moderate cases, while maintaining normal urine output, minor symptoms may be present.
The appearance of signs indicates an increase in renal pressure, stagnation of urine, recurrence of infection, and difficulty urinating.
When the process affects not only the two kidneys, but also their calyces and pelvis, the progression of the disease occurs much faster.
Typically this pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- feeling of heaviness, discomfort in the lower back on the left and right sides;
- disturbance of the urination process;
- change in physical signs of urine (color, appearance of sediment);
- pain during urination;
- Acquiring an unpleasant odor in urine.
If you notice one or more symptoms, you should seek help from a doctor. As a rule, diagnosis and treatment are carried out under the supervision of a urologist.
In order to determine the necessary therapeutic methods, it is imperative to identify what caused the disease and what is the stage of its development. Only under this condition is it possible to carry out effective therapy and completely get rid of the disease.
Diagnosing the disease does not require complex manipulations. The diagnosis can be established by examining the organs of the urinary system with ultrasound or using radiopaque methods (excretory uropyelography, MSCT).
With the help of ultrasound examination, all foci of expansion, even the most insignificant ones, are well identified, why they arose and what the residual level of urine is.
In many cases, pyelocalicoectasia is detected by a routine routine examination during pregnancy.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of pyelocalicoectasia is not difficult and can be done by examining the kidneys and other parts of the urinary system. For this purpose, ultrasound or contrast X-ray examination (excretory uropyelography, MSCT, etc.) is prescribed.
During examination using an ultrasound machine, even the smallest dilations are clearly visualized, as well as the reason for its appearance and the amount of residual urine. Quite often, pathology is diagnosed during pregnancy during a banal routine examination.
Prevention
Preventive measures for pyelocalicoectasia are quite simple. Doctors recommend:
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- maintain a daily routine;
- exercise;
- do not abuse medications;
- Healthy food;
- avoid stressful situations;
- undergo regular medical examinations;
- abstain from drinking;
- strengthen the immune system;
- control water consumption;
- follow the recommendations of specialists;
- communicate with a medical facility in a timely manner, without waiting for the condition to worsen.
Taking care of yourself is necessary. The main thing is to understand that kidney diseases lead to complications, and prevention is much more effective than treatment. Quitting harmful addictions, dressing appropriately for the weather, and a balanced diet can relieve many serious pathologies.
mpsdoc.com