Home / Types of cystitis
Back
Published: 12/03/2017
Reading time: 3 min
0
108
One of the common diseases is recurrent cystitis. We will talk about the causes, treatment methods and reviews below. Unlike acute and chronic pathology, its symptoms manifest themselves in periodic attacks that bother the woman at least 3-4 times a year.
Very often, doctors are contacted with just such a diagnosis, when the problem has been treated, but over time it returns with renewed vigor. What to do and what to do in this case, what treatment regimen to prefer in order to get rid of the annoying disease forever?
- Symptoms and epidemiology
- Prerequisites for the appearance of cystitis
- Reasons for relapse
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment regimen
- Preventive measures
- Reviews
Symptoms and epidemiology
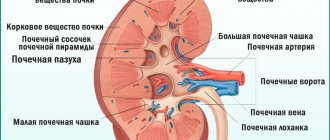
What is cystitis? This is an inflammation of the bladder mucosa, which can be infectious or non-infectious. In the first case, it appears due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the disease from nearby organs. In the second option, the pathology can be caused by other factors - viruses, allergies, trauma, etc.
It happens that the acute form is cured completely, but after three months or even earlier the inflammation recurs. In this case, doctors diagnose recurrent cystitis. Women most often suffer from it, since they have a natural predisposition to this - a special structure of the genital organs with a short and wide urethra. It is this factor that explains why cystitis in men is much less common.
And yet, not every woman is exposed to this disease. Only half of the fairer sex encounters unpleasant symptoms, and only a third of them, after treatment, turn to the doctor again for help within a short period. Such recurrent cystitis is most common in women 20-45 years old, but after 55 it is diagnosed in almost every second woman.
This disease is recognized by the following main symptoms:
- pain when urinating;
- increased urge even when the bladder is not full enough;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen throughout the day or night.
With exacerbation, relapses of cystitis can also cause general weakness, increased body temperature and other symptoms of an acute condition. What is typical for this form of the disease is repeated attacks after the completed course of therapy. And if the attending physician discovers such a problem, then he should refer the patient for a more detailed examination to a nephrologist or urologist.
Clinical manifestations
Permanent recurrent cystitis is in many ways similar to the typical form of the disease, including clinical manifestations. Medical specialists believe that a recurrent form of pathology is ordinary cystitis, recurring after a certain period of time. It may happen that the interval between the onset of the disease is several weeks.
The constant occurrence of the disease entails irreversible consequences. Frequent provoking causes come from a weakened body that is resistant to infections. The patient’s body weakens, the immune system cannot cope with its protective function, and the usual medications stop working. In order to promptly respond to the occurrence of pathology, it is necessary to know a number of characteristic clinical manifestations of recurrent cystitis:
Pain when urinating
- Frequent urination, even with a small amount of accumulated urine.
- Serious illness, possible short-term fever.
- Sharp pain when visiting the restroom.
- The presence of foreign elements in urine, often blood or purulent clots.
- Discomfort and pulling sensation in the groin.
- Sometimes there is an unpleasant tingling sensation in the kidney area.
The danger of this form of the disease lies in the fact that in the absence of proper treatment, the disease can provoke a deviation in the functioning of paired organs - the kidneys, which will lead to the development of pyelonephritis. It is recommended not to neglect your own health and well-being; at the first suspicious urge, contact a medical institution for diagnostic measures, drawing up a clinical picture and prescribing a full therapeutic course, based on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Reasons for relapse
But all this does not explain why in some women cystitis returns with constant frequency, while in others it appears 1-2 times in their lives. Doctors identify the following provoking factors that can affect this process:
- A constant source of infection inside the body (for example, kidney stones, the presence of a catheter, protrusion of the urethral wall, chronic inflammation in the urinary system).
- Congenital structural features of the pelvic organs in a particular woman are dystopia of the urethral opening, ectopia of the ureters or bladder, hypermobility of these organs, the presence of adhesions, etc.
- Prolapse of the pelvic muscles, which is more common during the postmenopausal period, provokes the accumulation of excess urine and its incomplete excretion, which leads to infection.
- Various neurological disorders associated with the functioning of the spinal cord, diabetes, etc.
- If for some reason there is a narrowing of the walls of the urethra, especially when this pathology is combined with stones in the urinary tract.
- Gynecological prerequisites (frequent change of sexual partners, unprotected contacts, sexually transmitted diseases, inflammation of the female genital organs).
- Some habits and incorrect actions (poor quality of personal hygiene, use of spermicidal methods of contraception, prolonged holding of a full bladder, especially during sexual intercourse).
- Hereditary factors.
- A decrease in estrogen levels during menopause leads to dry mucous membranes, thinning of tissues and blood vessels, decreased muscle elasticity, which significantly impairs the protective functions of the bladder and other organs.
- Fungal infections of the vaginal microflora.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostic measures are carried out in a comprehensive manner and involve the use of laboratory resources and instrumental examinations to identify the disease. If the patient has frequent attacks, he will only need to undergo a urine test to confirm the diagnosis. Appropriate records of the course of the disease must be present in the patient's medical record. Otherwise, diagnostic measures are carried out as follows:
- A urine test according to Nechiporenko is mandatory.
- Samples are taken to study the microflora of the body.
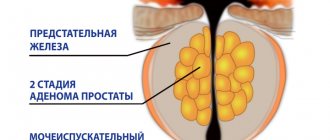
- You need to take a genital smear. Men require additional examination in the form of tests for the condition of the prostate. Recurrent cystitis in 50% of cases provokes an adenoma, which, in turn, leads to potency.
- An ultrasound scan of the hip area and urethra is performed.
- If necessary, the attending specialist prescribes fluoroscopy or cystoscopy. A man needs an X-ray of his prostate.
Urinalysis according to NechiporenkoRecommended topic:
Diet for cystitis
Recommended topic:
Antibiotics for cystitis
After a complete comprehensive diagnosis, you can select the appropriate course of therapy based on the data obtained.
Important: during the examination, the attending physician must warn the patient about possible side effects when taking prescribed medications. Otherwise, an allergic reaction resulting from uncontrolled medication use can harm the patient and aggravate recurrent cystitis.
Treatment regimen
There are various reviews on the topic of which pills help with cystitis, whether you need to take antibiotics, and people share folk methods of eliminating an unpleasant illness. But it should be understood that only a doctor can determine the treatment methods that are suitable in each case. Self-administration of medications will only lead to a deterioration of the general condition and serious complications.
Traditional treatment for recurrent cystitis usually goes like this:
- If there are abnormalities in the structure of the bladder and pelvic organs, which often lead to cystitis and other diseases, a surgical method to correct them is recommended.
- In the same way, prolapse of the pelvic floor muscles and other similar problems that cannot be affected by medication are eliminated.
- If estrogen levels decrease and cystitis occurs during menopause, hormonal medications are prescribed.
- In combination with gynecological problems, inflammation or infection, the gynecologist will prescribe the appropriate comprehensive treatment that eliminates the underlying cause of the pathology.
- To prevent cystitis, which recurs after each sexual intercourse, it is recommended to take broad-spectrum antibiotics once for two hours after the incident and adhere to the preventive rules, which we will discuss below.
- Antibiotics should be used to treat recurring symptoms of cystitis only as prescribed by a doctor and strictly after testing for bacterial sensitivity. Its results will show which microorganisms caused the disease and will help you choose an effective drug in each case. This may be Tsiprinol, Ciprofloxacin, Nitrofurantoin, Norfloxacin, Fosfomycin, etc. But since these drugs cause disruption of the intestinal and vaginal microflora, it is recommended to use lactobacilli and probiotics while taking them.
- To disinfect the bladder, direct lavage with antiseptic and antibacterial drugs can be used through the insertion of a catheter. But this is done only in stationary conditions.
- Cranberry juice is considered an excellent remedy for relieving the symptoms of cystitis inflammation. Doctors often advise using this drink simultaneously with a course of pharmaceutical drugs to speed up treatment. But you need to understand that juice alone will not help eliminate pathogenic bacteria from the bladder.
- The complex also includes other medications with symptomatic action - anti-inflammatory, immunomodulators, antispasmodics, painkillers.
- In some cases, physiotherapeutic procedures have an excellent additional therapeutic effect.
To completely eliminate the problem, doctors insist on abstaining from sexual intercourse for the period of treatment, and also suggest following a certain diet. It is advisable to give up smoking and alcohol, salty, spicy, fried and smoked foods. You also need to increase your fluid intake per day to two liters in order to efficiently and actively flush out pathogenic bacteria from the affected organ.
Recurrent cystitis and its treatment
Cystitis is a disease caused by infections, bacteria, and E. coli in the bladder. Leads to the onset of the development of the inflammatory process and unpleasant symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- increase in temperature;
- cloudy urine, discharge with blood and an unpleasant odor.
Cystitis is often diagnosed in women, and it manifests itself in episodes, attacks throughout life and has a chronic recurrent nature. It is observed in women 25-55 years old, is prone to relapses and requires treatment, sometimes surgical intervention for:
- severe disturbance of urodynamics;
- pathological changes in the bladder;
- hyperplastic changes in the tissues of the cervix;
- obstruction of the urethra.
When pseudopolyps appear in the neck of the bladder or in the proximal section, medications are prescribed.
If there is no improvement after completing the treatment course, it is possible to prescribe transurethral electrovalorization of the urethra or bladder neck to eliminate the causes of the disease.
If dystopia of the urethra is diagnosed diagnostically, then surgical correction, transposition of the urethra by cutting adhesions when they form, is indicated.
Why does cystitis occur?
There are quite a few reasons for the appearance of cystitis. These can be either acquired or congenital provoking factors. Congenital develops in the absence of the anterior wall of the bladder, in the case of dystopia of the canal, or when the external opening is quite close to the anterior wall of the vagina, when doctors diagnose postcoital cystitis.
The reasons for the development of acute cystitis may be due to:
- entry of a virus, bacteria, infection;
- development of urolithiasis, pyelonephritis;
- hypothermia;
- hormonal imbalances;
- severe decrease in immunity.
The occurrence of cystitis may be associated with:
How to cure chronic cystitis?
- the presence of roots in the urethra;
- excessive narrowing of the urethra;
- women engaging in promiscuous sexual relations;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- using certain vaginal suppositories to prevent pregnancy;
- heredity, when there are all the prerequisites for the development of this disease.
If you do not take timely measures to eliminate the acute form of primary cystitis, then within a year patients will experience repeated recurrent chronic cystitis, and the symptoms will appear constantly from time to time, similarly occurring in the form of painful urination, cloudy urine with the discharge of an unpleasant odor, discomfort and burning sensation in the urethra area, pain in the lower abdomen.
Reasons for relapse
So, relapse of cystitis occurs for two reasons:
- re-infection;
- restoration of the concentration of pathogenic bacteria.
That is, based on this, inflammation occurs again either due to neglect of the recommendations of the attending physician, or due to inadequate treatment when the disease was previously detected.
Why does relapse occur only in women? This is explained by the structure of their genitourinary system, in which there is simply no protected urethral canal, like in men (it is hidden in the penis, while in women it is between the labia).
And often reinfection occurs against the background of an active reaction of the body to a certain infection. Moreover, infection can occur even from a regular sexual partner (husband). It’s just that his body does not react in any way to the same staphylococcus, while in his wife it causes acute inflammation of the bladder. Such cases are very common in medical practice.
It is noteworthy that cystitis returns mainly as a concomitant disease. That is, the patient either has a cold before this, or is being treated for a sore throat, inflammation of the appendages, and the like.
Reinfection occurs when the body is weakened and the immune system cannot cope with suppressing the activity of pathogenic bacteria. For this reason, doctors recommend that those diagnosed with recurrent cystitis consult an immunologist.
It is possible that the patient will be diagnosed with lupus or similar diseases in which antibody proteins attack the body itself instead of infection.
We recommend reading:
Since this form of cystitis is more often diagnosed in women, doctors also recommend undergoing a comprehensive gynecological examination.
It is quite possible that the culprit of the relapse is an infection of the genital organs (affecting the mucous membrane).
That is, a so-called differential diagnosis is prescribed, the basis of which is to search for diseases directly or indirectly related to the functioning of the genitourinary system.
Effective therapy
No doctor can immediately say how recurrent cystitis is treated, since each such case is inherently unique.
And most of the time is spent not on treatment, but on diagnosing the body and searching for the “culprit” of bladder inflammation.
At the same time, complex therapy is prescribed, aimed at eliminating painful symptoms and inflammation of the bladder.
The simplest option is to take broad-spectrum antibiotics that suppress the spread of infection and attack the protein structure of microbes.
But we should not forget that in women, recurrent cystitis is not of a bacterial nature. As a rule, in this case, either sand is found in the kidneys, or a tumor in the bladder itself, the urethra (renal cords). In this situation, treatment with antibiotics will not bring any results. It may even cause harm!
If cystitis is diagnosed in a pregnant girl, then she is recommended to use only the following medications:
- Amoxicillin;
- Cefuroxime;
- Ceftibuten.
These are those medications that are guaranteed not to have any negative effects on the unborn child and do not penetrate the placenta, as is the case with conventional broad- and narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
But it should immediately be noted that the treatment will be quite long and will take at least 3 weeks. The antibiotic can be used for no more than 7 days, after which maintenance therapy is used aimed at restoring the functionality of the immune system.
And we are talking exclusively about those cases when recurrent cystitis of a bacterial nature is diagnosed.
If inflammation of the bladder is caused by sand or stones, then treatment primarily involves taking diuretics, which accelerate the process of natural passage of stones. Drinking pills that speed up the process of breaking down stones is strictly prohibited. In women, because of this, the toxins contained in the sand enter the bloodstream, and from there into the placenta.
Conservative methods
What is meant by conservative treatment of recurrent cystitis? Complete refusal of antibiotics, taking long-acting drugs and immunocorrectors.
But this option is allowed only when treatment for sexually transmitted infections is not needed. It is not possible to get rid of them solely by stimulating the immune system.
In this situation, you can only earn the transition of the disease to the chronic stage, nothing more.
Naturally, treating recurrent cystitis without antibiotics is allowed only after medical consultation. The rehabilitation process takes a fairly long period.
On average, full recovery will take at least 3 months. During this period, the body will be able to produce a sufficient number of antibodies and acquire at least temporary immunity against the causative agent of cystitis.
This option can also be used in pregnant women.
If in pregnant women, in addition to cystitis, other infectious diseases are found that accompany inflammation of the bladder (this may be paraproctitis, inflammation of the rectum, infection of the kidneys), antibiotics are necessarily used for treatment.
Unfortunately, no other methods of combating infection have yet been provided. And conservative treatment is not used for the simple reason that there remains a high probability of the disease progressing to the chronic stage.
And if the source of infection is located precisely in the kidneys, then all this in total will lead to the formation of pus inclusions in the cavity. Such problems are already solved mainly surgically. And for pregnant women this is generally contraindicated.
It turns out that the only way for them to protect themselves and the child is to artificially cleanse the blood of toxins (hemodialysis).
General characteristics of the disease
According to statistics, attacks of acute cystitis are observed in every third woman under the age of forty. Regular inflammatory processes cause recurrence of the disease.
In most cases, exacerbation of pathology is caused by repeated infection. This condition is regarded as a newly acquired disease. If the infection persists, the disease returns after a few weeks.
Source: https://manexpert.club/muzhskoe-zdorove/retsidiviruyushhij-tsistit-i-ego-lechenie.html
Preventive measures
In order to prevent recurrence of exacerbations, you need to follow simple rules:
- Maintain daily genital hygiene, wash yourself properly, use high-quality detergents, change your underwear to clean ones on time, etc.
- It is advisable to have sexual intercourse with only one regular partner, and after intercourse, immediately empty the bladder.
- Choose underwear from natural fabrics with a classic cut. It is also important that it does not put pressure on the pelvic organs.
- If contraceptives are unsuitable, talk to your doctor about choosing ones that are safer for the body.
- Maintain a regular drinking regime - drink at least two liters of clean water per day.
- Avoid hypothermia and treat any diseases in a timely manner.
- Try not to hold urine, but go straight to the toilet if desired.
Azithromycin for cystitis
It is known that most often inflammation of the bladder tissue occurs due to infection entering the organ. In such a situation, doctors use antibacterial drugs to treat cystitis in their patients. In case of non-infectious disease, antibiotics are not needed. However, we are not able to diagnose cystitis on our own, so if the doctor prescribed you Azithromycin, it means that your body is unable to independently cope with bladder inflammation caused by microbes. In such situations, antibacterial therapy is one of the most effective ways to solve the problem of cystitis.
Today we want to talk about the features of the treatment of this disease with the use of Azithromycin. Is this drug effective in treating cystitis? How to use it correctly? Does this antibiotic have any contraindications? You can find comprehensive answers to all these questions in our article.
Pharmacological properties of the drug
Azithromycin belongs to the group of macrolide antibiotics with a wide spectrum of antibacterial action. The active substance of the drug is azithromycin dihydrate. The medicine is produced in the form of tablets of 250 and 500 mg.
The pharmacological action of Azithromycin is based on blocking the production of vital protein in bacteria. This drug destroys infections caused by streptococci, staphylococci, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella, Bordetella, Neisseria, Helicobacter pylori bacteria and other pathogens.
This medication has found its use in the treatment of infections of the genitourinary system: prostatitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, vaginitis, endometritis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis and other pathologies. It is also used in the treatment of infectious diseases of the respiratory system and ENT organs, skin, and peptic ulcers. Consequently, Azithromycin has a wide spectrum of action against pathogens of various infections, so it can be called one of the most effective antibacterial agents used to treat internal inflammatory processes.
Instructions for use
In the treatment of acute and chronic bacterial cystitis, the dosage of the drug is selected by the doctor. As a rule, children under 12 years of age are prescribed Azithromycin 1 tablet (250 mg) once a day. The course of treatment takes three days. In complicated forms of cystitis that have led to the development of pyelonephritis, the dosage of the drug can be doubled (500 mg per day). The capsule should be taken on an empty stomach with plenty of water.
Contraindications and side effects
Azithromycin is not prescribed for the treatment of cystitis and other infectious diseases for people with liver and kidney failure, allergies to the components of the drug, and women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Side effects of Azithromycin are quite extensive, but are rare. During treatment with this drug, there is sometimes a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood, causing a tendency to bleed. Increased nervousness, anxiety, and insomnia may also occur. Side effects of the drug include ringing and noise in the ears, headache and dizziness, arrhythmia, bloating, vomiting and nausea. It is extremely rare that during treatment with Azithromycin, pain in the joints appears, inflammatory changes in the kidneys, and fungal infections of the intestines and vagina are observed.
In case of an overdose of Azithromycin, the following clinical picture occurs: temporary hearing loss, diarrhea, vomiting, nausea. In such a situation, it is necessary to stop the medicine and rinse the stomach.
Analogues of Azithromycin are drugs such as Azitsin, Sumamed, Zomax, Azitral, Azitrox, Zitrox, Sumametsin, Azax.
Conclusion
So, we found out that the antibiotic in question has a wide spectrum of action, so it is prescribed for the treatment of bacteriological cystitis. However, you cannot take this drug without permission, since it has a number of contraindications and side effects. Based on this, we can conclude that treatment of cystitis with antibiotics should be trusted to experienced urologists.
Be healthy!
Reviews
“I am always prescribed antibiotics and they help quickly. But every six months the disease returns. Perhaps there is a reason for this in the structure of the organs, but the doctor never spoke about such an examination” - Larisa.
“It seems to me that if the body has a predisposition to cystitis, then it returns with any hypothermia. I even stopped going to the urologist, since the treatment they prescribe is always the same. I just go to the pharmacy with the same list of medications” - Christina.
“I have exactly the case when such symptoms occur after every sexual intercourse. Moreover, the partner is always the same. But with the help of a gynecologist, I was able to find better contraceptives, which so far have also saved me from cystitis” - Lilya.
Understanding the bladder and genital area
Most urinary tract infections (UTIs) are caused by germs (bacteria) that usually travel from your own intestines to the urethra (urethra) and then to the bladder. They cause no harm in the intestines, but can cause infection if they travel to other parts of your body. Some bacteria begin to multiply rapidly while in the urine, which becomes the cause of infection.
Some bacteria are found in the anal area after using the toilet. These bacteria can sometimes spread to the urethra and bladder. Some bacteria multiply rapidly in the urine, which naturally causes cystitis.
Cystitis occurs much more often in women than in men, since their urethra (urethra) is much shorter and located close to the anus.
Why does acute cystitis recur?
Acute cystitis (ICD code 10 - 30.0) can recur for two reasons. This is re-infection of organs or regeneration of pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, the inflammatory process resumes due to insufficiently effective treatment of the acute form or as a result of failure to comply with the doctor’s instructions by the patient himself.
The disease tends to recur in females due to the peculiarities of their anatomical structure (the genitourinary system lacks a protective urethral canal).
Relapses of acute cystitis occur as a result of the body’s constant reaction to certain types of infection. Regular infections also occur during sexual contact. For example, men can be resistant to staphylococcus, while in their partners it can provoke an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system.
Recurrence of cystitis also manifests itself in the form of a concomitant illness. Especially if the person previously suffered from a cold or is undergoing treatment for a sore throat or other similar disease. Re-infection has every chance of spreading again, since the immune system can be greatly weakened and the level of resistance to pathogenic bacteria decreases. Therefore, before diagnosing an exacerbation or relapse of cystitis, you should consult an immunologist.
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that the gynecological medical history plays an important role in making a diagnosis. These are sexually transmitted infections, hormonal imbalance of the postmenstrual period. Therefore, a full examination by an appropriate specialist is recommended.
Features of the course of the disease in children
In most cases, cystitis in a child manifests itself in an acute form, but in advanced cases the disease becomes chronic. Clinical signs in infancy are mild, so the pathology is rarely diagnosed. As you get older, the disease can manifest itself in the form of problems with holding urine, which leads to involuntary urination. Most often in girls, acute cystitis is complicated by urethritis in a short time.
The main symptoms are painful sensations in the abdomen, increased urge to urinate, temperature fluctuations, and a feverish state. In some cases, patients experience purulent discharge from the urethra. Urine tests show a lack of protein and an elevated level of white blood cells.
Treatment of a child may be difficult due to the need to take antibiotics. Before starting therapy, the causative agent of the pathology should be identified. So, for example, if cystitis was caused by candidiasis, then taking antibacterial drugs only aggravates the patient’s condition, and the disease takes a more acute course. At the same time, the bacterial type prohibits the use of antifungal therapy.
Prevention and its power in solving the problem of recurrent cystitis
If cystitis constantly returns to you, it means that you yourself are doing something wrong. You don’t visit a urologist, don’t undergo systemic treatment, and, quite likely, don’t pay enough attention to preventing relapses of cystitis. And this is a huge, important part of general therapy. And it is multifactorial.
Diet and drinking regime:
- You need to drink a lot. There is no strict norm. Just keep plain clean water and herbal tea on hand and drink whenever you want. You won't drink more than you can. Because everyone has their own norm. But usually it does not fall below the mark of one and a half liters. Drinking plenty of fluids also stimulates increased urination, and this is a positive thing: urinary stagnation will not occur.
- Don’t “tease” the disease with food. If you have cystitis, then all the wild feasts and weekend get-togethers with beer, salted fish and fast food are taboo for you. Such food, and even in combination with alcohol, becomes a serious irritant to the walls of the bladder. And such irritation can “awaken” pathogens, which will again cause an exacerbation.
- If you do not suffer from gastrointestinal diseases, you can introduce acidic drinks into your diet: cranberry and lingonberry juice, currant compote make the urine reaction sour, which bacteria “don’t like.” But drinking fruit juice every day is pure madness; your stomach and intestines will definitely not thank you for such treatment.
A separate issue is the organization of sexual life. In women, persistence is not so rarely associated with sexual activity: it is at this time that pathogenic agents enter the bladder through the urethra. But even in such a situation, you can reduce the risks.
Always empty your bladder before sex and take a hygienic shower. Your partner should do the same.
What to do
Methods for diagnosing and treating relapses of chronic cystitis do not differ from those for the acute form of the disease. During an exacerbation, you need to drink as much fluid as possible, follow hygiene rules, and take all medications prescribed by your doctor. If the disease returns frequently, the use of the same antibacterial agents ceases to produce results. In this case, it is recommended to replace the usual means with more powerful ones. Antibacterial treatment is supplemented with the use of immunostimulants (Neovir), which increase the body's resistance.
Elimination of causes
Pathogenetic therapy is aimed at:
- Detection and elimination of chronic foci of infection. For this purpose, antibiotics, drainage and surgical interventions are used.
- Elimination of anomalies in the structure of the organs of the excretory system. There are a number of effective operations to help get rid of urethral dystopia and bladder ectopia.
- Normalization of the condition of the pelvic muscles. It is carried out using surgical and minimally invasive methods.
- Restoring hormonal levels in patients who have entered menopause.
- Elimination of sexually transmitted infections. Macrolides, fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines are used for this.
- Correction of vaginal microflora.
Pathogenetic therapy is aimed at normalizing the condition of the pelvic muscles.
Emergency help
To alleviate the patient’s condition during exacerbation of cystitis:
- Taking antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazmalgona). The drugs eliminate muscle spasms, relieving painful frequent urges.
- Warming procedures. Sand heated in a dry frying pan is poured into a canvas bag. The resulting heating pad is applied to the lower abdomen for 30 minutes.
- Drinking large amounts of liquid. Every hour you need to drink 1 glass of clean boiled water.
Use of antibiotics
When cystitis recurs, the following antibacterial agents are used:
- Palin. In medium doses it suppresses the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, in large doses it destroys them. The drug is available in the form of tablets, suppositories and capsules. In severe cases of the disease, tablets are used in combination with suppositories. The course of treatment is 6-10 days.
- Nitroxoline is an antibiotic that is effective against most bacteria and fungi, often found in the body during chronic cystitis.
- Nolitsin. Broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug. Most microorganisms are highly sensitive to the active substance, which explains the effectiveness of the product.
- Levomycetin. A powerful antibiotic used to treat advanced forms of cystitis. Used in the form of injection solutions.
Diagnostics
With the primary development of the inflammatory process in the bladder, doctors usually prescribe their patients a course of antibiotics (if the symptoms are mild and there is no elevated body temperature, their use can be avoided). If cystitis recurs, an examination is required, which will make it possible to determine the cause of the recurrence of the pathology and treat the disease. Comprehensive diagnostics includes:
- bacterial culture of microflora;
- laboratory tests of smears from the urethra and vagina;
- conducting an ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system;
- cystoscopy;
- passing urine tests according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko.
Using optical coherence tomography, it is possible to distinguish chronic cystitis from neoplastic changes. This type of diagnosis also allows us to track the type of modifications occurring in the submucosal structure and mucosa of the bladder.
Using these methods, doctors determine the form of the pathological process (viral, fungal, infectious). It is necessary to identify the presence and type of concomitant diseases, the level of bacterial resistance to medications. The last factor is very important, since it makes it possible to prescribe effective therapy by choosing the right combination of drugs.
Symptoms
The following signs are characteristic of exacerbation of cystitis:
- Pain and feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. The intensity of the discomfort increases as the bladder fills.
- Frequent, sharp urges. A healthy person visits the toilet no more than 6 times a day; with cystitis, the number of urges increases 3-4 times. Urine is released in small quantities, after which there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Burning and cutting in the urethra. The release of urine is accompanied by acute pain in the groin area, which disappears after the process is completed.
- Presence of bloody particles in the urine. In mild cases, the fluid becomes light pink; in severe cases, it becomes red. Sometimes large blood clots are found in it.
- Signs of body intoxication. With inflammation, body temperature rises, appetite decreases, and chills occur.
- Unpleasant smell of urine. Urine with cystitis becomes cloudy and acquires a putrid odor. This is due to the accumulation of pus in the bladder cavity.
- Nagging pain in the lower back. Caused by the spread of infection to the kidney tissue.