Home / Various symptoms of the disease
Back
Published: March 23, 2017
Reading time: 2 min
0
208
Diseases of the genitourinary system may not manifest themselves, but can cause a lot of inconvenience. Even more unpleasant is the combination of several diseases at the same time. Ureaplasma and cystitis can be combined. Their relationship is common. The methods of treating these diseases converge in modern medicine to one thing. But first you need to learn in more detail about their occurrence and manifestation.
- Ureaplasma
- HPV
- Cystitis
- Features of ureaplasma cystitis
- Detection of bacteria
- Treatment
Features of the manifestation of ureaplasma
Quite often there are situations when, during a preventive examination, a woman is diagnosed with ureaplasmosis.
It is worth noting that not in all cases the disease needs to be treated. This is due to the fact that ureaplasma belongs to the opportunistic flora, which indicates the presence of bacteria in the body. Such microorganisms do not cause problems and are not provocateurs, so there is no need for treatment. The pathogenic qualities of bacteria appear under certain conditions. At such moments, microorganisms begin to multiply, which can cause inflammatory processes.
As a result, women begin to develop infectious pathologies in the genitourinary system. The main causative agent of the disease is the bacterium ureaplasma, which is present in the normal microflora not only in women, but also in men. According to statistics, approximately 70% of women are carriers of ureaplasma, but not in all situations the bacterium is capable of causing disorders.
Basically, if there is a disease in the body, the symptoms are not pronounced. That is why the appointment of therapeutic therapy is not required. But in situations where tests in the body reveal an increase in the norm, conservative treatment methods are used. This is due to the fact that the inflammatory process develops, and at the same time the symptoms become pronounced.
Ureaplasma has a unique ability to penetrate into the inside of cells, where further proliferation of microorganisms continues. This process prevents the immune system from fighting the bacteria, and even taking special medications does not give positive results.
A woman may not have symptoms of the disease for quite a long period. The inflammatory process can only manifest itself when the immune function is reduced, or when concomitant diseases occur in the body. Ureaplasma is capable of exhibiting pathological activity at any appropriate moment.
Frequent cystitis
- performing an abortion;
- introduction of a spiral;
- the appearance of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
The activation of microorganisms can be caused by childbirth. Ureaplasmosis quite rarely develops as an independent disease. Most often, the disease is detected during examination and diagnosed along with other types.
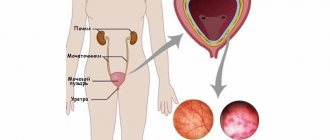
Cystitis is one of the most common diseases. The inflammatory process is localized in the bladder area. Disorders also affect the urinary tract. The main provocateurs of the disease include microbes that enter the genitourinary system.
By multiplying in the internal environment, they cause an inflammatory process. According to statistics, in 80% of cases cystitis occurs in women. This is due to the size of the urethra, since it is wider, as a result of which various bacteria get inside.
The main cause of cystitis is infection. Bacteria are able to enter the body during hypothermia or decreased immune function. Another cause of the disease is taking medications.
Medicines cause various side effects, one of which is cystitis. These drugs include cytostatics, which are used in the fight against malignant tumors.
If we compare this pathology with the previous disease, cystitis has severe symptoms. A woman suffers from itching and burning during urination, which already indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. This is due to the fact that microbes begin to actively secrete toxins that end up in the urine.
Another characteristic manifestation is pain in the lower abdomen. Often discomfort also occurs in the perineal area. The intensity of pain can be completely different. Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is another characteristic symptom of the pathology. This manifestation indicates a viral infection.
Cystitis and ureaplasmosis are a negative combination, since this inflammation has some negative features. Urologists say that even sufficient and competent treatment of such cystitis is still fraught with relapses, and frequent ones at that.
Another negative point is that the disease often develops asymptomatically. If you know what the signs of cystitis are, then you will expect increased urination, pain in the lower abdomen, and pain when urinating. But this may not be the case: or these symptoms are only slightly expressed.
The danger is that if treatment is not started on time, the infection can cause pyelonephritis. Also, such complicated cystitis can lead to the formation of stones in the bladder.
Ureaplasmosis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by ureaplasma. These bacteria are membrane parasites that live on the mucous membranes of the human genital organs and urinary tract, and provoke inflammation if the immune system is weakened.
Many women are infected with ureaplasma and don’t even know about it, since the bacteria does not manifest itself in any way. In small quantities, ureaplasma cannot begin to actively reproduce; it is suppressed by the beneficial microflora of the vagina. In simple words, the immune system keeps bacteria at bay.
If the body is weakened, there is dysbacteriosis in the vagina, then ureaplasma provokes colpitis, that is, inflammation of the vagina. Under the influence of certain factors or in the absence of proper treatment, bacteria can spread to internal organs: the uterus, appendages, as well as to the urinary system, causing urethritis, cystitis and even pyelonephritis.
Thus, we can say with confidence that ureaplasma causes cystitis if it somehow gets into the bladder. But it is impossible to say for sure that cystitis arose precisely because of ureaplasma, even if it was found in the vagina. Other microorganisms could also provoke inflammation of the bladder, so a comprehensive examination is required.
Doctors identify a number of factors that can provoke active proliferation of ureaplasma and the occurrence of cystitis:
- Promiscuous sex life without a condom.
- Installing a catheter in the bladder in the presence of ureaplasma in the vagina, even in a sleeping state.
- Chronic colpitis, lack of treatment for ureaplasmosis.
- Hypothermia of the body, even wearing wet panties on the beach can cause the infection to intensify.
- Frequent colds, weak immunity.
- Long-term use of antibiotics, which disrupts the microflora of the vagina and intestines.
- Poor hygiene, wearing tight underwear and rarely changing it, rarely changing pads, both daily and during menstruation.
- Very poor nutrition, constant mono-diets, hunger strikes.
- Childbirth, abortion, surgical interventions on the pelvic organs.
All these factors significantly increase the risk of developing ureaplasmosis in a woman and the entry of pathogens into the bladder.
Ureaplasma provokes inflammatory processes in the human body. Men will experience urethritis or prostatitis. In women, complications include pyelonephritis.
When ureaplasma causes cystitis, the course of the inflammatory process is characterized by the following features:
- There are no symptomatic manifestations, which makes diagnosis difficult and makes it possible for the pathology to progress.
- Late treatment due to delayed diagnosis allows cystitis to become chronic.
- According to medical observations, ureaplasma in the body is adjacent to chlamydia and gonococci, which can cause complications when the immune system is weakened.
Timely contact with a specialist prevents the possible spread of bacteria to nearby organs. To get rid of cystitis and ureaplasma, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy is required. They will prevent possible complications and allow you to get rid of pathology.
Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy is used to treat the disease.
When treating cystitis caused by ureaplasma, therapy is based on broad-spectrum antibiotics in order to simultaneously destroy secondary infections. Anti-inflammatory drugs are required to reduce the severity of symptoms characteristic of inflammatory processes of the mucous membranes. Taking this category of drugs makes it easier to urinate.
Diuretics are used as auxiliary agents - they are required for mechanical cleansing of the pathogen from the urinary canals due to frequent and more intense urination. An anesthetic category of medications is required to relieve pain. Medicines of this group are used only in cases of pronounced pain.
The exact dosages of the drugs and the schedule for taking them are determined by the doctor. It is necessary to observe accompanying measures, the main thing is to follow a therapeutic diet.
Diets for cystitis are as follows:
- It is necessary to remove spicy, hot, sour and smoked foods from the diet. The specified list of dishes must be removed due to the fact that they are characterized by the ability to change the acidic parameters of urine, which negatively affects the mucous membranes of the bladder, which are already inflamed.
- Increase fluid volumes to increase urination frequency. This circumstance is necessary in the case of using diuretic drugs. If you do not consume volumes of fluid while taking diuretics, the body will become dehydrated.
- Reduce the amount of salt you consume. This circumstance facilitates the excretion of urine by the kidneys.
This treatment is used in the acute phase of the disease. As the patient recovers, immune function needs to be strengthened. To ensure this, you need to take immunostimulants and mineral complexes recommended by your treating specialist. During the recovery stage, it is necessary to include foods rich in vitamins in the diet:
- rose hip;
- cranberry;
- watermelon;
- citrus;
- tomatoes.
Ureaplasma may not manifest itself; systematic examinations by a physician are necessary as a preventive measure.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of ureaplasmosis, you need:
- Avoid promiscuous intimate relationships.
- Use barrier methods of contraception.
- Every six months, be examined by a gynecologist, especially if ureaplasma is already present in the body.
- Maintain immunity: maintain a work and rest schedule, eat healthy foods, spend more time in the fresh air, take multivitamins in winter and spring.
Cystitis can become chronic and also cause complications such as pyelonephritis.
To avoid it, it is enough to follow simple rules of prevention:
- Don’t wait until the last minute, go to the toilet on time and empty your bladder completely.
- Wear loose cotton underwear.
- Take a shower instead of a bath.
- Maintain perineal hygiene.
- Wipe from front to back.
- Urinate as soon as possible after sex to flush out bacteria from the urethra that may have entered there during intimacy.
Ureaplasma and cystitis in women require mandatory treatment, otherwise the reproductive system may be significantly damaged.
In itself, a single protozoan, the population of which does not exceed the norm, does not pose any threat. Many people live full lives with ureaplasma, often without even suspecting its presence in their bodies.
Ureaplasma infection affects about 15% of the population, of which 80% are women. Approximately half of those infected are carriers and have no obvious symptoms of the disease.
Can ureaplasma cause cystitis? Doctors answer this question positively. Ureaplasma and cystitis caused by it are a fairly common combination.
Both men and women suffer from cystitis, but in the latter, bladder inflammation occurs tens of times more often.
The essence of ureaplasma
Situations arise when, as a result of a medical examination, ureaplasmosis is diagnosed. The disease does not always require treatment; ureaplasma is included in the category of opportunistic flora, which indicates the presence of bacteria.
Microorganisms do not provoke disorders - pathogenic ones appear under certain conditions. Pathogens begin to multiply and can provoke the onset of an inflammatory process.
A woman begins to develop pathology of the urinary system of an infectious nature. The main causative agent of pathologies is ureaplasma, which is found in the microflora of women and men. About 70% of women are carriers of ureaplasma, but it does not always lead to disorders.
Symptoms may be absent for a long time, but may appear when the body’s defense mechanisms are reduced. It often manifests itself in situations:
- performing an abortion;
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- introduction of the spiral.
The birth process can help increase the activity of microorganisms. Ureaplasmosis only occasionally acts as an independent disease and is usually detected during examination along with other types of pathologies.
Cystitis is a disease that is caused by inflammation of the bladder. It can also spread to the urinary tract. The main provocateurs are pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the urinary system.
According to medical statistics, about 80% of cases of cystitis occur in females. The circumstance is determined by the size of the urinary canal - it is wider and the likelihood of various bacteria entering is higher.
Another cause of cystitis is the use of drugs, mainly cytostatics, which are used in the treatment of malignant neoplasms.
With ureaplasma, cystitis is characterized by vivid symptoms, which are caused by inflammatory processes and toxins secreted by microorganisms.
What kind of diseases?
It cannot be said that diagnostics are 100% informative. Unfortunately, even modern equipment and instruments do not always reveal the true cause of the infection.
It turns out like this: by taking a test, other pathogens are found in a woman, therapy is prescribed, but it does not produce results. The patient is undergoing a new examination, ureaplasma is detected, and a new therapeutic regimen is being thought out. But time has already passed, and sometimes this interferes with treatment.
The most accurate tests will be urine culture and the PCR method. A doctor should not and cannot make a diagnosis based solely on the patient’s words. That is why it is so important to come to the urologist on time, take the necessary and informative tests on time, develop a treatment regimen, and follow it to the end.
Ureaplasma is an infectious disease caused by the activation of opportunistic bacteria on the mucous membrane of the urinary tract and reproductive organs. A characteristic feature of such microorganisms is the breakdown of urea. And the pathological process that develops in the bladder and is caused by the activity of pathogenic microorganisms causes inflammation of the entire organ - the disease cystitis.
If any signs of ureaplasma or cystitis appear, you must visit a urologist or gynecologist and undergo diagnostics. It includes:
- lab tests;
- PCR;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- vaginal smear;
- analysis of prostate secretions in men.
Symptoms
Since ureaplasma is most often in a latent state, an inflammatory process does not occur in the vagina. When bacteria enters the bladder, a woman complains of symptoms characteristic of cystitis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- burning sensation when urinating;
- the urine becomes cloudy, sometimes blood appears due to damage to the mucous membrane.
In this case, it is possible to establish that cystitis was caused by ureaplasma only through laboratory testing of urine, in which pathogenic microorganisms will be detected.
If ureaplasma nevertheless provokes inflammation in the vagina, then signs of colpitis are added to the symptoms of cystitis. Among them are a burning sensation in the vagina, especially when urine gets on the mucous membrane, a change in discharge, and an unpleasant odor from the vagina.
Ureaplasmosis is a rather insidious disease. Although it itself may not appear for a long time, ureaplasma disrupts the microflora, as if preparing the ground for other pathogens. Therefore, inflammation will eventually occur, it is only a matter of time. If the immune system is very strong, then ureaplasma can live on the mucous membrane for years.
How to treat cystitis caused by ureaplasma
Of course, there should be no doubt that treatment is, first of all, antibacterial therapy. You cannot do without antibiotics, whether you like it or not.
The following are considered effective means:
- Tetracyclines - for example, Doxycycline;
- Fluoroquinols – Cifran, Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin;
- Macrolides – Josamycin, Azithromycin.
You should not look for an alternative in the form of various folk remedies. Even the most powerful urological preparations can only partially help. And if you use them as aids, they can be useful. But if you replace antibacterial therapy with such recipes, the infection will remain in the body, and the consequences can be serious.
Even painkillers and antispasmodics are usually not prescribed for such cystitis. The fact is that there are no special inflammatory symptoms, the woman practically does not complain about anything, which means that symptomatic therapy is not needed. But diuretics (diuretic drugs) can be taken. They increase urination, which is very important for bacterial cystitis.
Let us once again clarify an important point: ureaplasma is present in the vaginal microflora of 70% of women. But under normal conditions, the bacterium “sleeps” and is not dangerous. A huge percentage of the vaginal microflora consists of lactobacilli, which are not pathogenic bacteria. A small part are pathogenic organisms, but a woman’s healthy immunity prevents them from multiplying.
If ureaplasma is found in a woman’s body in a non-dangerous ratio, then they say that she is simply a carrier of the infection. But increasing the permissible values is a reason to urgently undergo treatment.
As already mentioned, a pregnant woman’s immunity is under serious stress. It is not surprising that ureaplasma is activated at this time. It is not harmless: previously this infection was considered a reason to terminate pregnancy, but today, fortunately, such drastic decisions have been abandoned.
But detected ureaplasmosis requires treatment. Both the expectant mother and her partner should take safe therapy. The doctor will select antibiotics that do not affect the health of the fetus.
If left untreated, a healthy pregnancy will be at risk. Against the background of ureaplasma, other infections can develop. The bacteria also contributes to loosening of the uterine cervix, which threatens premature birth. Finally, there is a high probability of developing cystitis, which is difficult to treat during pregnancy.
Cystitis and ureaplasma are mandatory treatment under medical supervision, with accurate diagnosis and a well-thought-out effective regimen. Don't spread the disease, take care of yourself!
Video - How dangerous is ureaplasma.
Diagnostics
It is quite difficult to confirm that cystitis is caused by ureaplasma. Since this infection is opportunistic, any analysis will detect it in the body.
But it is impossible to determine that the microbe caused the inflammation. The following diagnostic methods are used to detect ureaplasma:
- detection of the microbe in urine and scrapings of the genital tract mucosa;
- identification of the genetic material of a microbe in any biological fluid;
- detection of antibodies to ureaplasma in blood serum.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of these data for long-term genitourinary infections.
Supporting the body with cystitis against the background of ureaplasma
You may also need to take immune support products. But do not prescribe such medications yourself - a doctor should do this. Naturally, immunity needs to be supported, including vitamin therapy.
Pay attention to your own menu - it should not help the infection. This applies to sweets: remember that sweets and starchy foods are undesirable in any inflammatory process. You should not eat anything that can irritate the walls of the bladder. Eliminate all spicy and salty foods, as well as fatty, fried, smoked foods. You must adhere to the principles of dietary nutrition and, of course, exclude any alcohol, even weak alcohol, for a long time.
Diagnosis of ureaplasma cystitis
It is difficult to identify ureaplasma; the establishment of a final diagnosis is hampered by infections that develop in conjunction with ureaplasmosis. Secondary infections, in addition to complicating diagnostic measures, affect the speed of the recovery process.
They are able to interact with ureaplasma and complicate the progression of the pathological process - due to the presence of a number of infections in the body, it is more difficult for the doctor to solve the problem.
An examination for suspected ureaplasma cystitis involves the patient undergoing the following series of laboratory tests and hardware tests:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood biochemistry;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction);
- bacteriological examination of urine;
- Ultrasound of the bladder, pelvic organs;
- smear on vaginal flora - in women;
- analysis of prostate secretions - in men.
The patient must be examined in a timely manner
Examine the patient in a timely manner. As a specialist receives the examination results, he will have the opportunity to establish a diagnosis and select the optimal treatment tactics for a clinical case.
Possible complications of diseases
Due to the fact that the manifestations of ureaplasma and the cystitis caused by it in women and men are non-specific, insignificantly expressed, treatment is delayed. This contributes to the development of complications:
- pyelonephritis - chronic inflammatory kidney disease;
- urethritis - inflammation of the urethra;
- urolithiasis - the formation of stones in the organs of the urinary system;
- prostatitis - inflammation of the prostate gland.
Active ureaplasma provokes not only cystitis, but also other pathologies. These include secondary infertility, miscarriage, and fetal development abnormalities. Ureaplasmosis is more dangerous for women.
Preventive measures
The basis for preventing cystitis caused by ureaplasma is following protective measures during the selection of a sexual partner. It is also recommended to use barrier contraception - the most effective protection against sexually transmitted infections. When a patient is already infected with ureaplasma, it is necessary to take measures aimed at strengthening immune function. This will prevent the occurrence of cystitis.
Undiagnosed ureaplasmosis that has not been treated can lead to pathologies, not only cystitis. For this reason, if you have any suspicions, you need to seek help.