If problems with the bladder and bowel dysfunction occur at the same time, then it is not easy to cope with them. Diarrhea and cystitis develop under the influence of various factors, so eliminating one disease can provoke another. If pathology appears, you need to consult a doctor who will determine the disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment necessary to prevent possible complications.
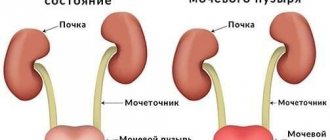
Stool disorder due to cystitis is a common unpleasant phenomenon that develops against the background of inflammation in the bladder.
Cystitis with diarrhea
Cystitis with diarrhea develops relatively rarely. With an altered microflora, diarrhea begins, and then inflammation of the organ joins the existing pathology. This occurs due to the penetration of E. coli into the bladder, which are considered pathogenic for it. One of the symptoms is severe cutting pain. The presence of the disease is confirmed based on test results or hardware examination. Sowing urine on a culture medium reveals the type of microbes and helps determine the antibacterial medication. Self-medication is fraught with complications in the kidneys.
Cystitis with diarrhea develops due to the penetration of E. coli into the bladder, which are considered pathogenic for it.
Reasons for the simultaneous appearance of diarrhea and cystitis
The pelvic and abdominal organs are located in close proximity to each other. This is the reason why inflammation spreads from one organ to another within a short period of time.
Diarrhea due to cystitis
The appearance of diarrhea due to cystitis is a common occurrence.
The reason for the appearance is:
- Dysbacteriosis during antibiotic therapy. Taking antibiotics leads to disturbances in the intestinal microflora, which manifests itself in the form of diarrhea.
- Transition of inflammation to areas of the intestine. In cases where inflammation affects not only the mucous membrane, but the thickness of the bladder wall, the inflammatory process spreads to adjacent areas of the intestine. Such processes cause diarrhea.
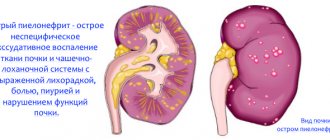
- Generalization of the infectious process. Cystitis complicated by pyelonephritis causes bacteria to enter the bloodstream. The circulation of bacteria in the blood is a dangerous condition; they are carried through the bloodstream into tissues, including the intestines.
The cause of diarrhea with cystitis is the use of antibacterial agents. This occurs in cases where the use of antibiotics is not accompanied by the use of drugs to protect the microflora.
This process is based on the fact that antibiotics destroy not only pathogens, but also those that are necessary for the human body.
In such situations, in addition to diarrhea, thrush appears, as well as fungal infections of the skin.
Cystitis with diarrhea
Cystitis can develop against the background of diarrhea.
The reasons that allow the disease to develop are identified:
- Poor personal hygiene due to diarrhea. During diarrhea, pathogenic bacteria are eliminated from the body. In the absence of hygienic measures, they remain on the skin of the perineum, and from there they penetrate through the urethra into the bladder. Cystitis caused by intestinal flora progresses rapidly and causes severe symptoms.
- Spread of inflammation from the intestinal loops to the wall of the bladder. Prolonged diarrhea causes inflammation of the small or large intestine. If those parts of the intestine that are adjacent to the bladder are inflamed, then the process is complicated by cystitis.
- Severe forms of intestinal infections. Some types of intestinal infections lead to severe intoxication and bacteremia. As a result of this complication, infectious foci arise in the organs.
Cystitis with diarrhea is caused relatively rarely. The cause of the appearance is considered to be poor hygiene. Escherichia coli and enterobacteria are considered pathogenic for the bladder. Therefore, contact with the mucous membrane of urea leads to cystitis.
Provoking factors
The development of cystitis and diarrhea against each other requires the presence of concomitant factors that will increase the likelihood of occurrence.
These include:
- Immunodeficiency states. Insufficient immune defense of the body makes it vulnerable not only to infectious lesions, but also allows bacteria to quickly spread throughout the body, causing complications and secondary processes. It is worth noting that immunodeficiency increases the risk of superinfection. This condition is characterized by the combination of several types of bacteria at the same time.
- The presence of chronic diseases of the urinary system and gastrointestinal tract. Chronic pathologies of these systems make them vulnerable to bacteria, even in a minimal amount that will not cause illness in a healthy person.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages. Alcoholic drinks have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the intestines and bladder. Irritated areas become susceptible to infectious agents.
- Sexual intercourse during illness.
- Poor nutrition. Getting the necessary substances from food is the key to a speedy recovery, as well as the prevention of complications. Malnutrition leads to cystitis and diarrhea.
Treatment
If diarrhea and cystitis appear at the same time, then therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating both pathologies.
For this purpose, the following treatment measures are carried out:
- Antibiotic therapy using drugs to normalize and protect microflora. For recovery, antibiotics are used in parenteral (intramuscular, intravenous) forms of administration. Thus, a therapeutic concentration of antibiotics in the organs is achieved. It is worth using antibacterial drugs that have a wide spectrum of action. They affect the intestinal flora and bacteria that cause cystitis.
- Diuretics. To avoid the accumulation of pus in the bladder, drugs or teas are used that increase urine production. A detoxification effect will be achieved.
- Anti-inflammatory. Non-steroidal drugs are used to eliminate inflammation. Since the upper and central sections of the gastrointestinal tract are involved in the pathological process, it should be used in the form of rectal suppositories.
- Diet. For diarrhea, follow a diet. The purpose of this diet is to reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract, as well as replenish fluid loss. They consume fermented milk products, they help restore normal flora due to the presence of lacto and bifidobacteria.
- Natural live yoghurts. These drugs are also prescribed to restore microflora.
For treatment, the patient should remain in bed. This is necessary in order to reduce the intensity of intestinal peristalsis and reduce pain caused by inflammation of the urinary tract.
Prevention
In order to avoid diarrhea and cystitis at the same time, adhere to a number of rules and recommendations:
- Regular toileting of the external genitalia and perineum. To prevent the spread of infection from the anus to the bladder, regular toileting is performed. It is better if hypoallergenic soap is used, since regular soap causes irritation when used frequently, which will create conditions for the growth of bacteria.
- Timely start of treatment. If you start treating the disease on time, the risk of complications is reduced to zero. This applies to the treatment of cystitis and diarrhea. Contact a doctor when the first symptoms appear; over time, the inflammation covers a larger area of the organ and takes more time to eliminate.
- The use of drugs to protect intestinal microflora during antibiotic treatment. These drugs are used immediately after starting antibiotic therapy. You should not neglect these drugs, because a violation of the microflora leads not only to diarrhea, but also to the appearance of severe chronic diseases. It has been scientifically proven that people who often suffer from dysbiosis have an increased risk of developing gastrointestinal cancer. More often, such patients develop malignant tumors of the large intestine.
Cystitis with diarrhea leads to a serious condition, because fluid is excreted through the digestive tract, which leads to a decrease in the amount of urine.
This process makes it possible for pus or blood to stagnate in the bladder. This stagnation creates comfortable conditions for the further spread of the infectious process through the urinary system.
Causes
The development of cystitis and diarrhea against each other requires the presence of concomitant factors that increase the likelihood of their occurrence.
In adults
There are several reasons that contribute to the development of pathology in women:
- immunodeficiency states;
- the presence of chronic diseases of the urinary system and gastrointestinal tract;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- sexual intercourse during illness;
- poor nutrition;
- Poor personal hygiene due to diarrhea.
Diarrhea with cystitis can be provoked by a diet that contains a large volume of fluid. The disease affects women more often than men.
Diarrhea with cystitis can be provoked by a diet that contains a large volume of fluid.
In children
Cystitis in children is most often caused by E. coli entering the bladder through the urethra.
Streptococci and staphylococci can provoke the disease. Pathology is also caused by worms, but this happens rarely. Healthy infants experience diarrhea at almost every feeding. This is fine. But frequent and loose stools mixed with blood clots and vomiting are a dangerous signal.
The disease progresses quickly in children under 2 years of age. It is easily tolerated, but only with timely treatment. Girls are susceptible to the disease from 2 years of age, and boys - up to 1 year.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman’s body experiences additional stress and diarrhea appears, causing cystitis. During gestation, hormonal levels change, the vaginal microflora changes, and immunity decreases. This leads to the development of cystitis, which is dangerous for both the mother and the unborn child. The woman may have kidney disease or premature birth.
Can cystitis be a consequence of constipation?
Conditions such as diarrhea or constipation, in combination with cystitis, are considered “synergists” of each other. In both cases, the leading causative factor is infection. And given the anatomical features (short urethra) and the proximity of the opening of the urethra and the rectum in women, this is precisely what determines the high incidence of both constipation or diarrhea and cystitis in females.
If a woman notices symptoms such as frequent urination and diarrhea, then in this case it is necessary to clarify what began to bother you first - intestinal upset or dysuria. If the intestinal disorder appeared some time after the symptoms of cystitis appeared, then the cause could be:
- Penetration of the infectious agent from the urinary system into the large intestine, due to the close location of the urethra and anus;
- Treatment of the patient with drugs from the group of antibiotics, which suppress the activity of normal intestinal microflora and can cause dysbiosis, which is precisely manifested by intestinal disorder such as diarrhea;
- Untimely measures taken to treat cystitis contribute to the spread of the inflammatory process to areas of the intestine adjacent to the bladder;
- Penetration of the infection into the bloodstream and its spread, and due to the abundant network of vessels that supply the intestinal walls with blood, the infection quickly penetrates precisely into this section of the digestive tract;
- The chronic course of cystitis, which with each exacerbation reduces the immune defense of the body as a whole, and as a result the activation of conditionally pathogenic flora in the intestines.
If we are talking about the development of cystitis against the background of existing diarrhea, then the main reason for this condition is non-compliance with personal hygiene measures, as well as hygienic care techniques for the genitourinary organs.
In this case, it is necessary to carry out hygienic treatment in the anus and genitourinary area after each act of defecation. If you do not follow such recommendations, then pathogenic bacteria can easily penetrate not only the urethra, but also the vagina in women, which will lead to gynecological problems.
In addition, the cause of cystitis in patients with diarrhea may be the transition of an advanced inflammatory process from the intestinal walls to the bladder wall, and as a result, its inflammation.
Factors that can contribute to the simultaneous course of cystitis and diarrhea:
- Immunodeficiency conditions, as a result of which a woman’s body is unable to resist infectious agents;
- Chronic process in the intestines (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease) and genitourinary organs (urethritis, colpitis and vaginitis);
- Frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages, which have a negative effect on the mucous membranes of the intestines and urinary tract;
- Experiments in the sexual life of partners: anal and vaginal sex, which is not accompanied by hygienic care of the organs;
- Eating disorders and abuse of fatty and spicy foods.
The development of constipation with existing cystitis may be due to:
- Limiting the patient’s physical activity during the period of acute cystitis;
- Nervous stress or worry about a real illness;
- Long-term treatment with medications, including antibiotics;
- Exacerbations of existing chronic intestinal diseases.
Also, questions often arise about whether constipation can provoke the development of cystitis. Constipation itself, which is an isolated nosological form or a separate symptom of a disease, cannot cause cystitis, but can become a provoking factor for its onset, namely:
- The pressure of solid feces on the walls of the bladder disrupts the blood circulation process, and ultimately leads to inflammation of its walls;
- Stagnation in the intestines leads to the fact that toxins begin to be absorbed from the feces back into the bloodstream, and as a result, general intoxication of the body and a decrease in protective forces occurs;
- Disruption of microcirculation processes in the bladder as a result of the action of toxins;
- Chronic constipation leads to disruption of metabolic processes in the intestines and a decrease in the body's defenses.
Pregnant women are most often susceptible to the simultaneous development of cystitis and constipation, and this is due to global changes in their body. In a pregnant woman, the T-cell component of immunity is suppressed so that the fetus is not perceived as foreign in the womb.
And such a change leads to the fact that the pregnant woman’s body becomes susceptible to infection. Also, as the fetus grows, it puts significant pressure on the pelvic organs and primarily on the bladder and intestines, and if a woman has previously had episodes of cystitis or suffers from chronic constipation, then the probability is quite high.
The presence of simultaneous symptoms such as constipation and frequent urination in women requires a thorough examination and determination of the reasons: whether the constipation resulted from cystitis, or from constipation cystitis.
Treatment of cystitis that occurs with intestinal disorders such as constipation or diarrhea is carried out only by specialists who select individual treatment regimens.
Etiotropic treatment with drugs from the group of antibiotics must be carried out under the guise of probiotics to maintain and establish normal intestinal microflora.
If cystitis is accompanied by constipation, then laxatives are prescribed - gutalax, duphalac and others. If accompanied by diarrhea, then enterosorbents are prescribed - smecta, activated carbon, polysorb.
It is also important to review your diet and consult a nutritionist or gastroenterologist about your diet. Timely and qualified treatment will allow you to forget about this problem forever.
source
Diarrhea and cystitis can occur simultaneously. The organs of the pelvis and abdominal cavity are located close to each other, so the inflammatory process, which is localized in the wall of the bladder, can spread to neighboring tissues. There are other reasons that can provoke the development of pathology.
To treat cystitis, patients are prescribed antibiotics. They help destroy bacterial flora, but not only in the place where the inflammatory process is localized, but also in other organs. This leads to disruption of the intestinal microflora, which causes diarrhea.
If treatment was not started in a timely manner, and the inflammatory process spreads to areas of the intestine adjacent to the bladder, then such a complication can lead to the appearance of loose stools.
When cystitis is complicated by pyelonephritis (an inflammatory disease of the kidneys of bacterial etiology, characterized by damage to the renal pelvis (pyelitis), calyces and kidney parenchyma), the infection can enter the bloodstream.
When they reach the intestines, indigestion develops, which is accompanied by diarrhea.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YySQElwPO44
Cystitis that occurs against the background of diarrhea is common. Its main reason for its appearance is non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. During bowel movements, pathogenic bacteria leave the body. If hygiene measures are not taken after visiting the toilet, microorganisms remaining on the skin of the perineum can penetrate the urethral canal and cause inflammation of the bladder.
With prolonged diarrhea, inflammatory processes often occur in the small or large intestine. If the pathological area comes into contact with the wall of the bladder, then there is a risk of complications in the form of cystitis.
Intoxication, which occurs as a result of a severe intestinal infection, poisons the entire body.
Foci of inflammation can be diagnosed in any organs, including the bladder.
To find out the cause of the disease, you need to see a doctor and undergo the appropriate tests. Laboratory results can help identify the source that is causing the health problem. This will allow you to choose the right treatment.
Cystitis is diagnosed more often in women than in men. This is explained by the anatomical feature of the body. In the fairer sex, the urethral canal is short and wide, which allows the infection to quickly reach the bladder.
The causes of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system and the appearance of diarrhea include:
- Weak immunity. If the body's natural defenses are weakened, a person cannot fully resist pathogenic microorganisms. Immunodeficiency can cause several types of infections to occur at once.
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system.
- Alcohol. Alcohol-containing drinks have an irritating effect on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and bladder. Tissues damaged by alcohol are vulnerable to infectious agents.
- Sexual intercourse. The source of infection can be a sexual partner.
- Poor nutrition and poor processing of foods before consumption. Health problems can arise during travel when a person tries exotic (unfamiliar to the body) food or drinks untreated water.
Diarrhea and cystitis in children can occur for the same reasons as in adults.
While carrying a child, the female body becomes vulnerable to any infections. Most often, the cause of unpleasant symptoms during pregnancy is an exacerbation of a chronic urogenital disease, which occurs against the background of a weakened immune system.
Treatment of cystitis or diarrhea should begin when the first signs of pathology appear. Problems with urination are one of the symptoms of inflammation of the bladder mucosa.
The patient is prescribed treatment that is aimed at suppressing the source of inflammation and eliminating unpleasant symptoms.
All medications and their dosage must be prescribed by a doctor.
- Antibiotics. Broad-spectrum drugs are prescribed, for example Monural or Furagin. In severe cases of the pathological process, medications can be administered by injection.
- Diuretic. Drugs that increase urine production are necessary to remove pathogenic bacteria from the body. They also help prevent the accumulation of pus.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs suppress inflammatory processes.
- Proper nutrition. Products should be easily digestible.
- Dietary supplements that contain microcultures (probiotics).
How to eliminate an unpleasant manifestation
If cystitis and diarrhea appear at the same time, then they are treated together.
Medicines
The main principle of treatment is medication. Only a urologist can select medications, among them:
- Levomycetin. A highly effective broad-spectrum antibacterial drug. It is prescribed for the development of both diarrhea and cystitis. Affects bacteria of the intestinal flora and bladder.
- Monurel. This is an antibiotic that helps destroy bacterial flora and has a therapeutic effect with a single use. Effectively sanitizes the urinary tract. Recommended for use during pregnancy, as well as for prevention during travel.
- Canephron. Has a diuretic and antispasmodic effect. It contains plant materials:
- lovage;
- rosemary;
- rose hip;
- centaury.
4. Ibuprofen. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Most often prescribed in the form of rectal suppositories. The goal of treatment is to relieve the main signs of the inflammatory process:
- swelling and dysfunction of the inflamed organ;
- pain and reflex muscle spasm.
During the treatment period, it is recommended to drink teas prepared according to traditional recipes.
Folk remedies
During the treatment period, you need to saturate the body with vitamins and drink teas prepared according to folk recipes. The following recipes are required:
- Rose hips, sea buckthorn, black currants and strawberry leaves take 2 tbsp. l. and add 300 ml of hot water. After 7 hours, the infusion must be filtered and taken before meals at least 2 times during the day, half a glass. The duration of treatment should be at least 2 months.
- Dry strawberry and sea buckthorn leaves, mix and pour 1 tbsp. l. mixture 200 ml boiling water. Leave until completely cooled, strain and take 100 ml of the product for a month before meals.
Diet
Diarrhea requires dietary nutrition to reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract and replenish fluid loss. Doctors recommend fermented milk products, live yoghurts, vegetable soups, and boiled fish. You need to refrain from consuming spices, herbs, and alcohol.
The diet for cystitis should be aimed at flushing the urinary tract, this will remove pathogens, so you need to drink more fluid.
During the treatment period, bed rest is indicated, this reduces pain caused by problems with urination.
Problem during pregnancy
Against the backdrop of the additional burden on the body in the form of carrying a baby, the expectant mother may be much more likely to experience ailments such as cystitis and diarrhea. The first problem is already more common among women.
And although it is quite easy to recognize this disease, you should not start treatment at home. Visit your doctor to prescribe a course of therapy that is right for you. Diarrhea and cystitis at the same time can cause the development of a considerable number of pathologies.
What is associated with pain during illness?
With cystitis, pain in the lower abdomen is a characteristic sign and one of the main symptoms of the pathology. The bladder is closely interconnected not only with other organs of the genitourinary, but also the digestive system. Its inflammation, accordingly, causes disruption of the functioning of neighboring internal organs.
Abdominal pain caused by cystitis can be of a different nature, which depends on the degree of development of the disease, its severity, and the presence or absence of concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system. The pain can be cramping, dull, aching.
The intensity of symptoms can also vary. At the beginning of the disease, pain in the lower abdomen is moderate, similar to the sensations that arise before menstruation. The reason for the development of a painful symptom is that when the bladder becomes inflamed, its walls swell, which leads to pathological protrusion. The walls begin to put pressure on the roots of the nerve endings, irritating them.
Considering the reasons for the development of the symptom, the only way to get rid of pain is to stop the inflammatory process. When cystitis develops, if a woman ignores the symptoms and does not seek medical help in a timely manner, the disease progresses. The inflammatory process intensifies, infection of neighboring healthy soft tissues and internal organs occurs, causing abdominal pain to intensify.
Often the appearance of the symptom is due to the fact that cystitis, without timely treatment, provokes a number of complications, affecting the genitourinary organs, leading to their dysfunction. The most common complications that develop are:
- oophoritis;
- cervicitis;
- urethritis;
- endometritis.
Such diseases cause severe painful symptoms in the abdomen, as a result of which a woman cannot always correctly assess her condition, not knowing that the symptom is caused not only by cystitis, but by a serious complication. If your stomach hurts due to cystitis, you should immediately consult a doctor; perhaps the symptom is caused not only by inflammation of the bladder, but also by complications.
Therapeutic measures
Painful discomfort in the abdomen during cystitis often leads to the fact that a person is forced to remain in bed, his level of performance decreases, and his general health rapidly deteriorates. To relieve a painful symptom, it is necessary to cure the disease - the root cause. Therapy for pathology with pain radiating to the lower abdomen includes:
- taking antibacterial medications;
- prescribing medications that have an anti-inflammatory effect;
- use of painkillers.
To reduce pain, medications with an analgesic effect, produced in tablet form, are first prescribed. If the pain is very intense and the prescribed medications do not give positive dynamics, painkillers are administered intramuscularly.
It is strictly forbidden to take any medications on your own without a doctor’s prescription. Cystitis can be caused by bacterial, viral pathogenic microflora and fungi. Depending on the causes of cystitis, the doctor prescribes the necessary medications.
If illness and abdominal pain are caused by pathogenic bacteria entering the body, antibiotics are prescribed. The doctor decides which medications will be needed based on the results of tests to determine the type of pathogenic microflora. The viral nature of cystitis is treated with antiviral drugs.
Risk factors
- Sexual activity: Cystitis is sometimes called “honeymoon cystitis.” During sex, bacteria can spread from the perineum to the urethral opening. In addition, friction of the penis with insufficient lubrication of the vagina causes the appearance of small abrasions, which contribute to the growth of bacteria and their settlement in the urethra.
- Use of contraceptives - diaphragms and condoms. Diaphragms can cause incomplete emptying of the bladder, and condoms can lead to irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Chemical contraceptives kill good bacteria in the vagina, promote the growth of bad bacteria, and can also lead to allergic reactions.
- Menopause is accompanied by a drop in estrogen levels, which leads to a decrease in vaginal elasticity, a decrease in lubrication secretion and a change in vaginal pH. This set of age-related changes increases the risk of bacterial infection. With low estrogen levels, the tone of the pelvic floor muscles and the tone of the bladder muscles decrease, resulting in incomplete emptying of the bladder, concentrated urine, irritation of the mucous membrane, proliferation of bacteria and infection of the mucous membrane. Concentration of urine also causes limited fluid intake.
- blockage of the urinary tract by stones, birth defects, cysts;
- fetal weight during pregnancy; during pregnancy, it is very important to treat cystitis in a timely manner to prevent kidney inflammation;
- pelvic organ prolapse.
There is a high risk of cystitis in women with diabetes, spinal cord injury and multiple sclerosis.
- Vaginal infections, such as thrush or trichomoniasis, dramatically increase a woman's risk of cystitis.
- Genetic predisposition to recurrent infections.
- Personal hygiene (wiping from back to front when visiting the toilet).
Preventive measures
Cystitis is a preventable disease. Prevention measures are very simple and should be followed by all women who do not want to face a very unpleasant and quite painful manifestation of the inflammatory process in the bladder.
The main preventive measure is careful adherence to intimate hygiene. It is imperative to carry out intimate hygiene before and after intimacy. Pathogenic microflora that provokes the development of cystitis can penetrate during intimacy, so it is imperative to use a condom with untested partners.
It is not recommended to constantly wear tight underwear or thongs made of artificial fabrics, which cause friction, irritation and create a good environment for the development of pathogenic microflora. Passing a medical examination at least once a year is a prerequisite for preventing the disease.
Many inflammatory processes and pathologies that are transmitted during unprotected sex contribute to the occurrence of cystitis, but do not have a pronounced and specific symptomatic picture in the initial stages of development. If pain, discomfort, pain in the genitourinary organs and frequency of the urge to urinate appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How can cystitis and diarrhea be related?
Problems with urination can provoke the development of intestinal diseases, which in most cases is caused by the spread of the infectious process to the lower part of the small intestine.
Diarrhea and cystitis occur simultaneously in patients with weakened immune systems and those who neglect the doctor’s recommendations regarding taking drugs based on lactobacilli when treating inflammation in the bladder with antibiotics.
Problems with urination can provoke the development of intestinal diseases, which in most cases is caused by the spread of the infectious process to the lower part of the small intestine.
Traditional methods for pain relief
Cystitis is a disease that, having occurred once, can worsen from time to time under the influence of provoking factors. In the case of a chronic course of the disease, the intensity of the symptomatic picture is much lower than in the acute form of the pathological process, but constant, aching pain in the lower abdomen causes a lot of inconvenience.
The main mistake of most patients is that, having once had cystitis and undergoing treatment, they believe that in case of exacerbation of the disease there is no need to visit the hospital again, because they know perfectly well what drugs the doctor prescribed for them. This behavior is absolutely wrong.
If the first time cystitis occurs due to pathogenic bacteria, there is no guarantee that the second time the disease will be of the same nature. Antibiotics will be absolutely useless if the disease is caused by a virus, and, conversely, antiviral drugs will not give positive dynamics if bladder inflammation is caused by pathogenic bacteria.
The use of traditional medicine is useful as an adjuvant for the treatment of cystitis. Various decoctions of medicinal herbs help relieve inflammation and reduce the manifestation of a painful and unpleasant symptomatic picture.
The following herbs are used to prepare medicinal decoctions: cornflower, chamomile, elderberry. The ingredients can be brewed separately or prepared as herbal infusions. The raw materials are poured with boiling water and left for 1 hour to brew. Decoctions can be used for internal use. If the drink turns out sour, you cannot add sugar to it; a teaspoon of honey is allowed.
Healing decoctions are often used to take sitz baths. In such cases, a liter of the resulting decoction must be diluted in 5 liters of water. Bath water should not be hot. The optimal temperature is 38 degrees. For baths, it is recommended to prepare a decoction based on horsetail and chamomile. This combination will help reduce the inflammatory process, relieve the symptomatic picture, and soothe the aching pain in the abdomen.
A sitz bath with herbal infusions is best taken before bed, so that you can then lie down and rest. Rest and good sleep are very useful for a patient with cystitis who experiences pain in the lower abdomen.
Forecast
Acute cystitis can sometimes go away on its own, without the need to see a doctor. For this, a woman is recommended
- drink more liquid (exclude tomato juice, citrus fruits and their juice), drink a solution of baking soda - a teaspoon per glass of water - to alkalize urine;
- Place a bottle of hot water wrapped in a towel between your legs - relieves pain when urinating.
If a woman is pregnant and symptoms of cystitis persist for more than a day or she has fever, chills, back pain, nausea and vomiting (symptoms of a kidney infection), she should consult a doctor immediately. Cystitis during pregnancy can lead to high blood pressure and the birth of a low birth weight baby.
The doctor will definitely prescribe a urine test. For analysis, it is necessary to take a urine sample from the “middle” of the stream in order to exclude contamination by bacteria from the vagina and perineum: in the toilet, flush the first portions into the toilet, then pee into the container, and flush the remainder from the bladder into the toilet.
How to treat?
First of all, you need to find out how these 2 problems are connected. Here, either preliminary observations of the patient or a doctor who can accurately determine the root of the disease can help. If a person has diarrhea and cystitis at the same time, treatment measures should be selected carefully so as not to aggravate one of the problems. But in all cases the following actions will be prescribed:
- Diet. Eliminate fatty, spicy, hot, fried and other foods that are difficult for the body from your diet. Increase the amount of liquid you drink to 2.5 liters per day. This is important not only for restoring water balance, but also for flushing the bladder. If you have cystitis and diarrhea, taking fermented milk products and natural yogurts would be a good addition;
- The following medications will be prescribed: Antibiotics. Elimination of infections, bacteria, viruses, fungi Furadonin, Monural, Palin, Rulid;
- Probiotics. Restoring the balance of microflora. Hilak forte, Linex, Bifiform, Enterozermina and others;
- Anti-inflammatory (non-steroidal) Diclofenac, Paracetamol, Nimesil. If the patient has diarrhea, then such medications are not used in the form of suppositories for obvious reasons;
- Diuretics. They do not allow pus to accumulate in the urine and have a kind of detoxification effect Furosemide, Amiloride;
Cystitis in pregnant women: treatment with folk remedies
During pregnancy, the load on a woman’s body increases, in particular, the fetus puts pressure on the bladder, which can cause cystitis. It is better to treat this disease during pregnancy with folk remedies, since medications can harm the unborn child. What symptoms should alert a pregnant woman and force her to seek treatment?
Symptoms of cystitis
During pregnancy, cystitis has more pronounced symptoms. These include:
- pain when urinating;
- frequent urination;
- lack of relief after bowel movement;
- lower abdominal pain;
- possible increase in body temperature.
Usually, with proper treatment, bladder inflammation goes away in 7-10 days, but if the disease gets worse, pus or blood may appear in the urine.
Often, if a woman had chronic cystitis before pregnancy, it will worsen during pregnancy. Indeed, during this period, hormonal levels change and immunity decreases, which are the main conditions for exacerbation of the disease.
Cystitis is very undesirable in the first trimester of pregnancy. This disease can threaten the normal development of the fetus. To protect yourself from this, you need to take preventive measures.
Disease prevention
Pregnant women who, even before their interesting situation, had chronic cystitis need to think about preventing this disease. After all, during pregnancy it can appear again. Any infection, both intestinal and genitourinary, can trigger the appearance of acute cystitis.
The following is recommended for pregnant women:
- It is imperative to undergo a gynecological examination, because any genitourinary infection or gynecological diseases (especially of an inflammatory nature) can provoke the appearance of acute cystitis.
- Visit a urologist.
- Do not wear tight clothing, especially if it compresses the pelvic area, impairing blood circulation.
- Wear only cotton underwear, no synthetics.
- Adjust your diet to prevent constipation. Eat more dairy products, fruits and vegetables. Prunes and kefir will be especially useful.
- Limit the consumption of salty and spicy foods, smoked foods.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Rest more, sleep at least 9 hours a day. Daytime naps are also beneficial for pregnant women.
- Before and after sexual intercourse, you need to urinate, this helps reduce the number of bacteria in the urine.
- For genital hygiene, it is better to use neutral products, fragrance-free soap. You need to wash yourself every day from front to back.
- You shouldn’t wait if you want to go to the toilet, and you shouldn’t urinate too often. The optimal option for urination is 6 times a day.
It is best to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and urologist before planning a pregnancy, because in this case there is a 100% chance of avoiding unpleasant consequences.
A pregnant woman in the first trimester needs to pay special attention to her health, because during this period it is undesirable to use any medications. And when acute cystitis appears, it is difficult to get rid of the disease without antibiotics.
Some folk remedies, such as cranberry juice, are also useful for the prevention of cystitis.
If it was not possible to avoid inflammation of the bladder, you need to start treatment immediately, because the infection can quickly penetrate the kidneys and cause their inflammation, which is much more dangerous for the normal course of pregnancy.
Treatment with folk remedies
Despite the fact that medicinal herbs are much safer than some medications for cystitis, you should still consult a doctor before starting treatment.
There are a huge number of traditional medicine recipes for cystitis during pregnancy, here are some of them:
- A decoction of rosehip roots. Boil 4 tablespoons of rose hips in a liter of water and drink 100 ml 4 times a day.
- Chamomile herbal tea can help reduce inflammation.
- Cranberry juice, lingonberry compote or birch sap are suitable as antibacterial agents. Lingonberry compote helps well with cystitis; to prepare it, you need to take two teaspoons of berries and pour 200 ml of boiling water, boil for 15 minutes. You can drink compote little by little throughout the day.
- A decoction of hernia flowers and leaves has a diuretic and antispasmodic effect. Pour a tablespoon of this herb into 200 ml of boiling water and cook for 5 minutes. Drink a tablespoon 4 times a day after meals.
- A decoction of bearberry is suitable as a strong antiseptic.
- For chronic cystitis, a decoction of hop cones helps. To prepare, you need to take two tablespoons of hops and pour 500 ml of boiling water, leave for 2 hours and drink half a glass three times a day before meals.
- For cystitis, a decoction of yarrow is also suitable. The decoction is prepared similarly to the decoction of hop cones.
- A mixture of honey and black radish juice. To prepare, take the ingredients in equal proportions, drink the mixture three times a day, a tablespoon half an hour after meals.
It is worth noting that cranberry is especially useful during pregnancy, because it not only prevents infections in the bladder, but is also rich in vitamin C.
The effect of herbal medicine is visible only a few weeks after regular use of herbal decoctions.
Important! Before taking medicinal herbs, be sure to familiarize yourself with the contraindications.
Cranberry juice is still the safest during pregnancy with cystitis, but besides it it is useful to drink the following decoctions instead of tea:
- decoction of dill seeds;
- decoction of red rowan berries;
- decoction of lingonberries with honey;
- infusion of birch leaves;
- decoction of black currant leaves;
- black radish juice with honey.
Cystitis can be treated not only with decoctions, but also with certain procedures. It is very popular to treat cystitis using hot bricks.
To do this, you need to take two bricks and heat them on a fire, then put them in a bucket and sit on it without underwear. The lower part of the body needs to be wrapped in something warm so that the whole body is well warmed up by the warmth of the brick.
After the procedure, you need to quickly lie down under the blanket. Only 3 such procedures are enough for recovery.
Important! If there is a threat of miscarriage or uterine tone, treatment with hot bricks is contraindicated.
Among the procedures for the treatment of cystitis in pregnant women, there is treatment with paraffin.
There are several ways to use paraffin as a compress for gallbladder inflammation:
- Take melted paraffin and apply a thin layer to the lower back a few centimeters thick, cover with gauze on top and wrap in a blanket.
- Apply melted paraffin (temperature 60 °C) to gauze, fold it in ten layers, and place it on the lower back.
This procedure should be done every other day for half an hour. A course of treatment using this method may include from 10 to 15 procedures.
Important! Hot paraffin must be applied to the skin very carefully to prevent burns. It is also necessary to consult a doctor to avoid bleeding.
During pregnancy, you can use chamomile decoction not only internally, but also externally. To do this, you need to take three tablespoons of chamomile in a bucket of boiling water. The decoction is suitable for sitz baths, but not more than 20 minutes.
For severe cuts and pain when urinating, you can douche with a decoction of mumiyo. To do this, you need to take 2 g of mumiyo per glass of warm boiled water.
At the first symptoms of cystitis, a pregnant woman should consult a doctor. It is better not to self-medicate, because some herbs are contraindicated during pregnancy. You should especially not get carried away with treatment using thermal procedures, which can cause miscarriage or premature birth.