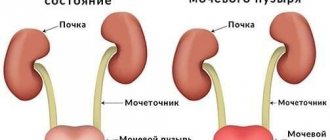
Cystitis is a common female disease that causes severe discomfort. Its manifestation does not depend on the age threshold. Girls and older women suffer equally from bladder inflammation. Over the years, only the causes of its occurrence and symptoms change. Cystitis in older women often manifests itself in a more hidden form or as a complication of other diseases.
Which doctor treats cystitis in women?
The main reason for the development of cystitis is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the bladder cavity.
The causative agent of the disease can be bacteria, viruses, fungi and even protozoa. Most often, cystitis of a bacterial nature is observed, when the causative agent is Escherichia coli. The most common types of cystitis in women are defloration and associated with sexual intercourse.
In addition to pathogenic bacteria, the following factors can cause cystitis:
- taking certain medications, such as Ifosfamide or Cyclophosphamide;
- ionizing radiation, which is used in the treatment of cancer;
- a foreign body, which can be a urethral catheter;
- exposure to chemicals that are part of personal care products;
- other diseases of the genitourinary system, for example, urolithiasis, prostatitis;
- damage to the spinal column, etc.
In some cases, it is not possible to determine the cause of the disease, so this cystitis is called interstitial.
There are also a number of factors that contribute to the development of the inflammatory process in the bladder, which include the following:
- local or general hypothermia of the body;
- stagnation of urine in the bladder;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- unbalanced and unhealthy diet (eating large amounts of hot and spicy foods);
- pregnancy;
- childbirth;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- wearing tight or synthetic underwear and clothing;
- sexual infections;
- surgical interventions and invasive research methods on the organs of the reproductive and urinary systems.
The first signs of cystitis in women may be as follows:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- feeling of bladder fullness;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain and burning along the urethra after urination;
- the appearance of pathological impurities in the urine (mucus, blood, pus).
In severe cases, the clinical picture of cystitis can be supplemented by symptoms of general intoxication of the body, namely: increased body temperature, general weakness, chills, excessive sweating, etc.
If you are concerned about the above symptoms, do not under any circumstances engage in self-diagnosis or self-medication, as this does not always bring the expected result.
A urologist diagnoses and treats cystitis. Only a specialist knows how to properly treat this disease in order to avoid chronicity of the inflammatory process and not cause harm to health.
Therefore, if you experience at least one of the above signs of cystitis, contact your nearest clinic for an appointment with a urologist. The doctor, after conducting a comprehensive examination of the body, will make an accurate diagnosis and select the most effective treatment regimen for you.
Treatment of cystitis is mainly carried out on an outpatient basis under the guidance of a urologist. Indications for hospitalization of patients may be severe intoxication syndrome, spread of the inflammatory process to the kidneys, or cystitis in pregnant women.
You can treat cystitis at home only after consulting a urologist, since all drugs have side effects, and folk remedies are not effective enough to cope with bacterial inflammation.
An experienced specialist can cure acute cystitis quickly, in about 2-3 days, but the fight against chronic inflammation of the bladder can take several weeks.
Before treating chronic cystitis, it is necessary to find out the cause, because only by eliminating it can a positive effect of therapy be achieved.
When treating cystitis, specialists are guided by the following principles:
- bed or semi-bed rest throughout the entire period of acute symptoms of the disease;
- therapeutic nutrition. The diet for cystitis should be dairy-vegetable, that is, fermented milk products, vegetables and fruits should predominate in the patient’s daily diet. Fried, hot, salty and spicy foods, as well as alcoholic drinks are strictly prohibited;
- antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics are prescribed first with a broad spectrum of action, and after obtaining the results of urine culture and antibiogram. An antimicrobial drug is used, to which the causative agent of cystitis is sensitive;
- analgesic therapy. For severe pain in the bladder, patients are prescribed painkillers and antispasmodics;
- installation of antiseptics in the bladder;
- phytotherapy. Diuretic herbs and herbs are used. Let's look at it in more detail below;
- physiotherapeutic treatment (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, inductothermy, UHF and others).
There are also cases when chronic cystitis in women has to be treated using surgical methods. Surgery is necessary if the outflow of urine from the bladder is impaired by a stone, tumor or foreign body. Also, surgical intervention is indispensable when the walls of the bladder become wrinkled, when an antiseptic solution is injected into it under general anesthesia to straighten it.
Antibiotics occupy a central place in the treatment of acute and chronic cystitis. The selection of an antibacterial drug should be done exclusively by a specialist, since self-medication can lead to irreversible health consequences.
Let's look at the most effective antibiotics used for cystitis in women.
Nitroxoline
Nitroxoline is a derivative of eight-hydroxyquinoline and belongs to the oxyquinolones. The drug is active against most gram-positive and gram-negative microbes, as well as some fungi, in particular candida.
Nitroxoline is indicated for cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis.
Scheme and doses: 2 tablets (100 mg) 4 times a day with meals for 14-21 days.
Cost of the drug: 120-170 rubles.
nitroxoline
Monural
Monural is a broad-spectrum antibiotic with bactericidal properties, which is obtained by processing phosphonic acid.
Monural is prescribed for acute cystitis and urethritis of a bacterial nature. In addition, this drug can treat cystitis with blood, as well as asymptomatic bacteriuria in a pregnant woman, since the drug is harmless to the fetus.
Scheme and doses: for adults the drug is prescribed once (3 grams), but if necessary, the dose can be repeated every other day. Children are recommended to take only a single dose of 2 grams.
Monural is a powerful antiseptic, so there is no need to do a urine culture or antibiogram before using it.
Before taking the granules, dissolve 60 ml of warm water and drink the solution on an empty stomach or before bed.
Cost: 380-500 rubles.
Monural
Furadonin
Furadonin is a representative of a number of nitrofurans, the main purpose of which is the treatment of urinary tract infections. The drug is active against most gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, but resistance to this drug often develops.
Furadonin is prescribed for the treatment of cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, as well as for the prevention of urinary tract infections after invasive diagnostic methods (cystoscopy, urography, etc.).
Scheme and doses: adults are prescribed 100-150 mg 3 to 4 times a day after meals for 7-10 days. The drug should be taken with plenty of liquid.
Cost: 80-160 rubles.
Furadonin
Furamag
Furamag belongs to the antimicrobial drugs of the nitrofuran series, which have a wide spectrum of action. Resistance to this drug practically does not develop. In addition, Furamag not only destroys pathogenic bacteria, but also reduces the synthesis of their toxins, and also strengthens the body's defenses.
Furamag is used for cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis, as well as for some gynecological infections.
Scheme and doses: 1-2 (50-100 mg) tablets three times a day after meals. Children: 1-2 (25-50 mg) tablets 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician and usually takes from 7 to 10 days.
Cost: 480-700 rubles.
Furamag
Nevigramon
Nevigramon is an antibacterial drug that has a detrimental effect on almost all known pathogenic bacteria.
Nevigramon has an impressive list of indications, including urinary tract infections, in particular cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, pyelitis and others.
Scheme and doses: adults are prescribed 2 tablets (1000 mg) 4 times a day for a week. For children over two years of age, the daily dose is 60 mg/kg, divided into 3-4 doses.
Cost: 5400 rubles.
You can treat cystitis at home with traditional medicines. Only before starting such treatment should you consult with your doctor. It is also necessary to understand that traditional methods and remedies are not effective enough to cure cystitis completely, and therefore can be used exclusively as a complement to the main therapy.
We bring to your attention the simplest and most effective methods of treating cystitis with folk remedies.
Dill seeds
At home, women with cystitis have been using dill, or rather its seeds, for a long time. Both decoction and infusion are suitable for treatment.
To prepare the infusion, pour boiling water over one tablespoon of dill seeds, cover with a lid and leave for 2-3 hours.
The decoction is prepared as follows: one tablespoon of dill seeds is poured into a glass of water and put on fire; after the drug boils, the intensity of the fire decreases. You need to boil the broth for 4-5 minutes. After this, the finished medicine is removed from the heat and filtered through a fine sieve.
A decoction or infusion of dill seeds is taken one glass three times a day until the symptoms of cystitis subside.
A decoction of millet will help quickly cure cystitis and urethritis in women. To prepare this medicine, you will need two tablespoons of millet, which you need to pour 500 ml of boiling water and boil over low heat for 4-5 minutes. After this, remove the broth from the heat, let it brew for 10 minutes and pour the liquid into a glass.
On the first day, during an acute attack of cystitis or urethritis, take 20 ml of millet decoction every hour throughout the day, on the second day - 60 ml every hour, and on the third - 100 ml every hour. The course of treatment is one week.
Pharmaceutical chamomile
10 grams of pharmaceutical chamomile should be poured into 250 ml of boiling water, cover with a lid and let steep for 15-20 minutes.
Prevention
To prevent the development of cystitis, an elderly woman is recommended to wear loose underwear and take medications that restore hormonal balance. It must be remembered that the disease occurs for many reasons.
Therefore, in order to avoid the development of bladder inflammation and exacerbation of chronic pathology, you should strengthen your immune system and stop eating harmful foods.
Sources:
https://noalone.ru/infocentr/zdorove/cistit-u-pozhilykh-zhenshhin-simptomy-i-lechenie/ https://uromir.ru/vospalenie-mochevogo-puzyrya/terapiya/cistit-simptomy-i-lechenie- u-pozhilyh-zhenshhin.html https://propochki.info/mochevoj-puzyr-i-mocheispuskanie/cistit-u-pozhilyh
Causes of cystitis in older people
When a woman is over 50, she may experience a burning sensation when urinating, discomfort in the perineum, a constant urge to go to the toilet, and the urine may be cloudy in color or have bloody streaks - all these are signs of developing cystitis.
Urologist about cystitis: Do not buy expensive drugs, not all of them treat cystitis, I did research and found the most effective and cheapest remedy!
There can be many causes of cystitis, and to accurately determine the original source of the disease, you need to consult a urologist.
There are several reasons for the development of cystitis in older women:
- decreased immunity;
- changes in hormonal levels (decrease in estrogen levels, learn more about cystitis during menopause here);
- gynecological diseases;
- slowdown of metabolic processes, deterioration of blood circulation.
All these reasons can be associated with age-related changes. During menopause in a woman, a decrease in hormones provokes pathological processes in the reproductive system: the vaginal microflora is disrupted; the mucous membrane becomes thinner, it is easily injured, which becomes a favorable environment for the development of bacterial infection.
Often, disturbed microflora gives impetus to the proliferation of yeast-like fungi Candida, and thrush develops (article about thrush and cystitis here).
Irina, 30 years old: “Only this remedy helped me in the treatment of cystitis:
This is especially true for antibiotics, which are essential for bacterial cystitis.
The inflammatory process in old age does not always manifest itself as acute symptoms. If there is any sign of cystitis, do not put off visiting a doctor. Only a qualified specialist will be able to select the necessary drugs for treatment, taking into account concomitant diseases.
The dosage form also plays an important role, for example, some drugs are available in the form of tablets, drops or suppositories.
For hormonal disorders associated with a decrease in estrogen, the following drugs are most often prescribed:
- "Ovestin". It is successfully used to treat urogenital symptoms associated with estrogen deficiency. Restores the vaginal mucosa and its normal microflora;
- "Elvagin." Used as hormone replacement therapy. Available in the form of cream and vaginal suppositories. Stimulates blood circulation, is effective against atrophic changes in the epithelium, increases resistance to infections and inflammation.
Additionally, analogues of estrogen drugs include: “Ovipol Clio”; "Estrocade".
Vitamin therapy in older people is an important part in the treatment regimen for inflammatory processes of the urinary tract. Vitamins and beneficial microelements can be found both in special combination preparations and in products that must be included in the daily diet.
Diet for cystitis is important at any age; you also need to monitor the amount of fluid you drink per day, this plays a big role in the treatment of bladder infections. Increasing the fluid will help “flush” the urinary tract.
- Vitamin C. You can find the required dosage in magnesium ascorbate or calcium ascorbate.
- Vitamin A and beta carotene. Useful for maintaining healthy cells.
- Zinc. Important for maintaining the body's defenses.
A popular remedy for treating cystitis is cranberry. It has anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating and diuretic effects. Since ancient times it has been used for urinary tract infections.
Cranberry juice recipe:
- 250 g cranberries
- 1 tbsp. l. honey
- 1 liter of water
- Sort the cranberries and rinse. Mash well in a plate, then squeeze the berries thoroughly through cheesecloth.
- Place the squeezed berries in a saucepan and add boiled water (temperature approximately 60 degrees). Leave for 30 minutes. Then strain.
- Add cranberry juice and honey, mix well.
Herbal medicines for the treatment of infections in the bladder will help relieve swelling in the organ and reduce pain. Some medicinal plants have antimicrobial effects.
A popular remedy is Canephron N drops. The drug contains a large number of herbs that have the necessary properties to reduce the inflammatory process in the bladder. "Canephron N" is used not only for the treatment of cystitis, but also as a prevention of urolithiasis.
For urinary incontinence in older people:
- "Driptane." Helps control the urge to urinate and increases bladder capacity. In old age, it is prescribed in a dosage of 5 mg 2 times a day;
- "Urotol". Indicated for overactive bladder. Use caution in case of liver and kidney diseases. Prescribed 2 mg 1-2 times a day.
Preventing cystitis in older people is not so easy. Pathological changes in the bladder are most often associated with age-related changes, but still, women must follow some rules at any age:
- do not forget about personal hygiene;
- avoid a “sedentary” lifestyle. Minor physical activity will help with poor circulation;
- eat only healthy foods and maintain a drinking regime;
- Do not neglect visiting a gynecologist; during menopause, consult about the advisability of using hormonal drugs.
Cystitis in older people develops due to diseases and disorders associated with age-related changes in the body. The main reason for the appearance of pathology after 50 in women is a decrease in estrogen levels, which is caused by the onset of menopause. Due to changes in hormonal balance, the mucous membrane becomes thinner. In addition, the acidity of the secretion secreted by the genitals increases.
Both factors provoke the proliferation of bacterial microflora and the activation of microorganisms that are constantly present on the mucous membrane. The addition of infections during menopause is also facilitated by a weakening of the general immune system, which together causes inflammation in the bladder.
Researchers have identified other risk factors for the development of cystitis:
- damage to the mucous membrane of the genitourinary organs (during sexual intercourse, during catheterization and other medical procedures);
- hypothermia of the pelvic organs;
- urolithiasis disease;
- stagnation of urine caused by dysfunction of the pelvic organs (constipation and other diseases);
- a sedentary lifestyle, wearing tight underwear, which impairs blood microcirculation;
- overweight;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- endocrine disorders not caused by hormonal changes during menopause.
The causes of cystitis in older women also lie in metabolic disorders. Decay products accumulate in the urinary system, creating favorable conditions for the development of microorganisms.
Diseases that provoke cystitis in older women include infectious pathologies, regardless of the localization zone. The possibility of inflammation of the urinary system due to non-compliance with intimate hygiene rules cannot be ruled out.
Preventive measures
Both during the treatment of cystitis and as a preventative measure, older women are advised to minimize physical activity. Overstraining the abdominal muscles is unacceptable. Excessive pushing will increase the pain and cause incontinence.
The main condition for prevention is regular intimate hygiene. It is important to take a shower every day (you need running water) using antibacterial or antiseptic cleaning products. The diet must be balanced; the development of constipation is unacceptable. Special attention should be paid to selecting comfortable shoes and clothing appropriate for the season.
As women age, it is recommended that they visit a urologist twice a year.
Symptoms of cystitis
The danger of the disease lies in the fact that the symptoms of cystitis often begin to bother people during a period when the inflammation has become chronic. Pathology especially often manifests itself in this way in older people. Acute cystitis in women provokes the following symptoms:
- increased frequency of urination (more than 10 times a day);
- the need to urinate at night (up to 2-3 times);
- the appearance of blood clots in the urine;
- the amount of urine excreted at a time decreases, a feeling of urinary retention appears;
- itching and burning in the intimate area.
The main signs of the disease appear with varying degrees of intensity. There are often cases when the development of the inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system is accompanied by an increase in body temperature (usually up to 38 degrees) and nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Women also experience discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Cystitis has uncharacteristic symptoms. Similar phenomena are of concern in other diseases of the genital and urinary organs. Therefore, if problems arise related to the work of the latter, it is recommended to seek advice from a urologist or gynecologist (depending on the location of the pathological process).
Features of cystitis in elderly women In the case of cystitis in elderly women, symptoms and treatment are determined depending on the stage of development of the disease. More often, in patients over 60 years of age, the pathology is detected when the inflammatory process has become chronic. During this period, pain in the lower abdomen is rarely a concern.
- urolithiasis disease;
- polyps on the walls of the bladder;
- neoplasms on the mucous membrane.
This condition is difficult to correct with medication. The prescribed drugs help improve the patient’s condition, but do not suppress the inflammatory process and do not eliminate complications.
In advanced cases, treatment with antibiotics (even those prescribed by a doctor) does not help, and frequent bleeding along with urine provokes the development of iron deficiency anemia due to a decrease in hemoglobin levels.
In this regard, older women need to begin treatment for cystitis when the first signs of the disease appear. Otherwise, it will take several months or years for the body to fully recover.
Features of the course of pathology in elderly women
In old age, cystitis, regardless of its form and characteristics, is severe and often recurs even after proper therapy. This is explained not only by a decrease in the body’s defenses, but also by a deterioration in the tone of the urethral walls. The infection can penetrate through it into the bladder over and over again, causing inflammation. For this reason, taking antibiotics in the treatment of cystitis may not be enough, and antimicrobial therapy must be combined with local procedures.
Difficulties in treating inflammation may also arise due to the fact that older women are often diagnosed with urolithiasis, neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the excretory organs, as well as diverticula in the walls of the bladder. If these provoking factors are not addressed, therapy will not give the desired result, no matter how aggressive it is. An important point is the timely initiation of therapy, which can prevent the transition of an acute condition to a chronic one. Otherwise, complete recovery will take months or even years.
Diagnostics
Methods and specifics for diagnosing bladder inflammation are determined by the nature of the disease and the presence of concomitant disorders. If inflammation in the bladder is suspected, the following are indicated:
- blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound;
- urography.
If necessary, catheterization is performed. Regardless of the woman’s condition, the diagnosis of cystitis is complemented by an examination by a gynecologist. To exclude neoplasms, CT and MRI of the pelvic organs are used. If tumors are detected, a biopsy is prescribed.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of cystitis in elderly women is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused inflammation in the bladder, restoring hormonal levels and strengthening general and local immunity.
Antibacterial therapy shows effectiveness in the case of the bacterial nature of the inflammatory process in the bladder. Antibiotics based on fosfomycin are considered the safest in old age. These include Monural, Phosphoral, Uronormin F, etc.
For complicated forms of cystitis, injections of Cefuroxime, Gentamicin, Fosmitsin are indicated. The choice of injection depends on the type of pathogen and is determined by the attending physician.
With the non-infectious nature of the disease, treatment with antibiotics does not show positive results.
What tests are performed for cystitis?
To confirm cystitis, the specialist must prescribe the following tests to the patient:
- general urine analysis;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- bacteriological examination of urine;
- cystoscopy;
- ultrasound examination of the bladder and abdominal organs, including the kidneys.
In urine with cystitis, you can find a large number of white blood cells, bladder epithelium, as well as bacteria that caused this disease.
Urine culture allows you to determine which microbe caused cystitis and which antibacterial drug it is sensitive to and which it is resistant to, which greatly facilitates the selection of an effective treatment regimen.
Protein in the urine during cystitis, regardless of its quantity, should in no case go unnoticed, since its appearance may be a sign of impaired kidney function.
Cystoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the bladder, which is performed using a special device - a cystoscope. A cystoscope is a metal tube equipped with a video camera and a set of instruments, which is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. Using this study, you can carefully examine the bladder mucosa, take material for histological analysis, and, if necessary, perform a minor operation, for example, remove a polyp.
An ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys is carried out to assess the condition of the organ itself and surrounding tissues.
Diagnostic procedures
The examination will help make an accurate diagnosis and determine the causes of the disease, determining the choice of treatment methods.
The following are required:
- Carrying out general and biochemical blood tests.
- General clinical, biological and cytological analysis of urine. It is microbiological culture of urine for flora that will help select antibiotics to which the causative agents of cystitis are sensitive in a particular case.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and kidneys, with the help of which the localization of the inflammatory process is determined, and it is also possible to identify tumor neoplasms.
- Excretory urography allows you to evaluate the position, shape, size and contours of the kidneys, as well as their functional state, the contours of the ureters and bladder.
- Catheterization (urine drainage by puncture and insertion of a special catheter).
- Carrying out a biopsy.
- Spiral computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. These procedures are recommended for all elderly patients with suspected cystitis.
An important point in diagnosis is determining the tumor etiology of the disease. Age-related changes favor a slowdown in the process of cell division and promote the development of various neoplasms. In this regard, additional examinations may be prescribed.
Treatment
Atrophic cystitis in older people is treated comprehensively. The disease requires taking several medications and lifestyle adjustments. Features of the treatment of cystitis are that when choosing medications, it is necessary to take into account the presence of concomitant pathologies and the elderly age of the patient.
In the treatment of cystitis in the elderly, the following are used:
- antibiotics;
- herbal medicines;
- antispasmodics;
- diuretics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- restorative medications;
- probiotics;
- antiseptics.
If necessary, other drugs that relieve associated symptoms are included in the drug treatment of cystitis in elderly women.
Antibiotic treatment is selected based on the type of microorganisms that have affected the mucous membranes. If necessary, drug therapy includes antiviral (mainly against herpes) or antifungal drugs. Given that older women have a weakened immune system, non-aggressive medications are used as part of antibacterial treatment.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs during cystitis suppress the pathological process in tissues and accelerate the recovery of the latter.
Elderly women are recommended to use topical herbal medicines, available in the form of suppositories, ointments or drops.
Diuretics for cystitis in elderly women are used with extreme caution. This is especially true when treating patients over 80 years of age. This caution is explained by the fact that as a person ages, the functioning of the cardiovascular system changes and metabolic disorders are possible.
Long-term use of certain types of diuretics provokes the leaching of calcium from the body, which negatively affects the general condition of a person. Therefore, treatment with diuretics is carried out with the direct participation of a doctor.
Antispasmodics for inflammation of the bladder are prescribed to eliminate painful sensations. Medicines in this group help restore normal urine flow and relieve other symptoms characteristic of the disease.
If treatment is carried out with antibiotics, therapy is supplemented with probiotics. Medicines in this group normalize intestinal function.
If there is no effect from treatment with antibacterial agents, the administration of antiseptic solutions directly into the bladder is prescribed. Medicines suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. To carry out this procedure, the patient is admitted to the hospital.
The success of cystitis treatment depends on the general condition of the body. Therefore, in addition to these medications, patients are prescribed immunostimulants and vitamin complexes, the action of which is aimed at strengthening the immune system.
In advanced cases, treatment is supplemented with catheterization. The procedure is performed to restore the flow of urine and eliminate associated symptoms.
Diet food
Dietary nutrition for cystitis includes:
- refusal of sugar, fatty foods;
- limiting salt intake;
- reducing the amount of fried foods, canned food, baked goods and sweets consumed;
- daily consumption of about two liters of fluid;
- avoidance of pickles and spices
- exclusion of strong tea and coffee from the menu;
- filling the diet with fresh vegetables and fruits, easily digestible foods.
For cystitis, it is recommended to eat small portions 4-5 times a day, avoiding overeating. Such a diet will strengthen the body and protect against the development of complications.
In addition to correcting nutrition, it is recommended to devote time to physical exercise (Kegel complex, “bicycle”) for cystitis. Exercise therapy improves blood microcirculation in the pelvis, thereby reducing the intensity of the inflammatory process.
Traditional treatment
Treatment of cystitis with medicinal herbs can only complement and not replace drug therapy. Traditional medicines are effective in cases where intolerance to certain drugs has been identified, as well as in general strengthening of the body.
Medicinal herbs are used in the form of teas or infusions for douching. This treatment speeds up the patient’s recovery. However, traditional medicine is not able to cope with severe pain and inflammation.
When choosing herbal infusions, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Risk factors
The mature age of the patient determines risk factors that contribute to the development of cystitis. It is age-related changes that are the source of all other factors that increase the risk of pathology:
- changes in hormonal balance due to natural processes due to age
- the presence of chronic inflammatory processes. Pathologies of other organs and tissues that can spread to the bladder area.
- decreased elasticity of tissues of the urinary and reproductive system
- pathological processes associated with impaired filtration of urine and its excretion, congestion in the bladder
- changes in blood circulation: a decrease in the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels leads to disruption of microcirculation, providing protective functions with the help of leukocytes. This creates conditions for the development of various pathological processes
- change in metabolic rate: disruption of the exchange of nutritional products and the excretion of metabolic products in organs and tissues creates a breeding ground for the development of pathogenic microorganisms
- the presence of a tumor in the pelvic area. The most common neoplasms of the appendages tend to spread to surrounding organs and tissues through metastasis.
All factors are mainly associated with age-related changes in any organism, which are completely beyond the control of a person to prevent. But it is possible to correct and maintain them for the purpose of prevention.
A woman herself can contribute to the development of cystitis by failing to comply with the rules of intimate hygiene, frequent hypothermia, and an inadequate diet.
Herbal preparations for cystitis
Cystitis and urethritis in women can also be treated with herbal remedies, which are not inferior in effectiveness to synthetic analogues. Let's look at them.
Canephron N
Canephron is available in the form of tablets or drops, which consist of rosemary leaves, lovage and yarrow roots.
Canephron effectively eliminates pain in the urethra and reduces the severity of the inflammatory process in the bladder. It can also be used to prevent exacerbations of cystitis.
Scheme and doses: adult women are prescribed two tablets or 50 drops three times a day before meals.
Cost: 410-480 rubles.
Monurel
Monurel is an extract of cranberry fruits combined with ascorbic acid. The drug has antimicrobial, diuretic, and immunostimulating properties.
Monurel is used both for the treatment and prevention of exacerbations of cystitis.
Scheme and doses: 1 tablet before bedtime for 30 days.
Cost: 470 rubles.
Cyston
Cyston is a medicine that consists of more than ten plant components. The drug has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antimicrobial and diuretic properties. Cyston also dissolves stones in the urinary tract and prevents their formation.
Regimen and doses: two tablets twice a day for 2-3 weeks.
Cost: 380 rubles.
Traditional medicine
It should be remembered that all traditional methods of treating any disease are only auxiliary. This is an addition to the main treatment, and it is possible to cure the disease on your own.
Various infusions, teas, decoctions and mixtures are used. Chamomile, bearberry, blueberry, horsetail, and coltsfoot have good properties in the treatment of cystitis.
Complex herbal medicines can be prescribed: “Canephron N”, “Cyston”, “Fitolysin”.
It is common among people to treat cystitis with cranberry juice. To prepare it you need 200-250 g of berries, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of honey and a liter of water.
The berries are washed and dried well, then squeezed through cheesecloth. The cake is poured with boiled water at 60 degrees and left for 30 minutes. Strain, add the originally obtained cranberry juice and honey. Mix everything thoroughly.
Use half a glass up to 5 times a day, preferably not on an empty stomach. The duration of drinking fruit drink is not limited.