Cystitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder; this disease is extremely common. Various factors can influence the occurrence of the inflammatory process; many people, especially women, often discover cystitis after intimate intimacy; the reasons for its occurrence are worth considering in more detail.
Related articles:
We treat cystitis at home in women Symptoms of chronic cystitis in women and its treatment Nitroxoline - use for cystitis Furadonin or Furagin - which drug is better to choose for cystitis Lingonberries for cystitis - uses and contraindications
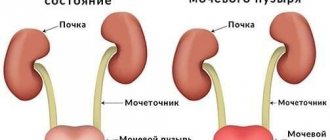
Often cystitis occurs together with urethritis, inflammation of the urethra. The infection seems to rise upward, capturing these organs of the genitourinary system. Without proper treatment, cystitis and urethritis can lead to serious problems, and there is a possibility of further spread of infection to the kidneys, which can lead to kidney failure.
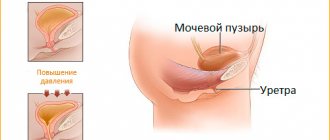
Cystitis occurs much more often in women due to the structural features of the genitourinary system. The urethra in women is much shorter and wider than in men, so any infection spreads much faster and easier.
There are two main forms of the disease: primary and secondary cystitis. Primary occurs due to infection from the outside, while secondary is a consequence of other diseases of the bladder or organs closest to it. Non-infectious cystitis also occurs, which occurs due to various injuries, stagnation of urine and for a number of other reasons.
Cystitis often occurs after sexual intercourse, especially if it is the first with a new partner. It is worth knowing why this disease can develop after intercourse, what preventive methods exist to help protect against infection, what are the main treatments for cystitis.
Reasons for the development of cystitis after intimacy
In urology, the following reasons for the development of cystitis after intimacy are identified:
- Failure to maintain personal hygiene for each partner. Smegma and secretions from the female genital organs, in the absence of proper hygiene, create favorable conditions for the proliferation of bacteria. It is during intimate intimacy that pathogenic microflora moves into the genital canals of a healthy partner and the subsequent development of inflammation.
- Damage to the bladder can be caused by episodes of sexual overstimulation and excessive sexual activity of partners.
- The anatomical features of the bladder in women can provoke inflammation. In particular, if the organ is located very close to the vagina, and friction causes it to be compressed, vibrate, or shift.
If you do not complete the full course of anti-inflammatory therapy, the likelihood of the disease becoming protracted increases. Even slight hypothermia will exacerbate the disease. The process can also spread to the kidneys, which aggravates the clinical situation. In men, chronic cystitis causes prostatitis and negatively affects the quality of potency.
Methods of protection
How to protect yourself from cystitis after sexual intercourse. Follow these simple rules and you will certainly avoid problems:
- follow the rules of intimate hygiene;
- do not ignore lubricants;
- do not leave infectious diseases running;
- the appearance of cystitis is possible during rough, unprotected sex;
- if you are predisposed to cystitis, take anti-inflammatory drugs after sexual intercourse;
- do not alternate vaginal sex with anal sex;
- some positions, especially the missionary position, are most favorable for the appearance of cystitis, if you have a predisposition, take this into account;
- avoid unprotected sex with an unfamiliar partner;
- an empty bladder before and immediately after sex will reduce the risk of cystitis;
- Reduced immunity can provoke the appearance of cystitis.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of inflammation of the bladder after intimacy is characterized by the following signs:
- An increase in body temperature to high levels accompanied by chills and slight aches in the body.
- Pain in the lumbosacral back.
- The appearance of blood in the urine. Indicates an increase in the inflammatory process and a high risk of kidney involvement. Blood appears due to the destruction of blood vessels.
- Pain during urination. It begins with minor irritation in the urethra. Then he notices an increased urge to urinate, but urine is released drop by drop. The process causes a feeling of remaining urine, causing discomfort and burning. The pain persists for several minutes after visiting the toilet.
The listed symptoms are aggravated by neurological disorders, since taking antispasmodics without treating the underlying pathology provides a short-term effect. After the pain syndrome is relieved, chills, dysuria and body aches return, which negatively affects general well-being. In rare cases, cystitis causes menstrual irregularities.
Interesting: Can cystitis go away without pain and burning when urinating?
Traditional treatment
The most common alternative treatment for cystitis is heating with a red brick. To do this, it must be warmed well over a fire, and then placed in an enamel bucket. The treatment consists of the patient sitting on a bucket, completely wrapped in a warm blanket. You need to sit in this position for about 20 minutes. After this time, you should wipe the wet areas on your body dry, hide in a warm place and go to bed.
You can also use medicinal decoctions and infusions that have an anti-inflammatory effect. The most effective medicinal plant in this case is St. John's wort.
Diagnostics
To confirm the presence of bladder inflammation, the following tests are performed:
- Laboratory analysis of blood and urine. An increase in the level of leukocytes and an increase in ESR are detected. If hematuria occurs—blood in the urine—a decrease in hemoglobin concentration is observed.
- Bacteriological examination of urine. Aimed at identifying the pathogen.
- Ultrasound of the bladder, kidneys. A safe, fast and effective method for visualizing conditions. Allows you to assess the extent of inflammation and exclude the fact that the kidneys are involved in the infectious process.
In addition to the diagnostic results, the doctor focuses on the nature of the patient’s complaints and draws a conclusion based on the information received about the patient’s medical history and lifestyle. Women will additionally have to visit a gynecologist to rule out the presence of relevant pathologies.
Personal hygiene of women against cystitis
A few recommendations to help you protect yourself from cystitis:
- Wash yourself twice a day. It is advisable to do this with your hand and not with a washcloth.
- Change your underwear regularly.
- Don't wear thongs, they don't promote feminine hygiene.
- Give preference to cotton underwear.
- It is recommended to wash your genitals before and immediately after sexual intercourse.
These simple rules will reduce the risk of getting cystitis to a minimum. Don't ignore warning signs. Listen to the recommendations of doctors, do not darken your life with an unpleasant disease that can be easily cured.
Treatment of cystitis that occurs after intimacy
Honeymoon cystitis is scientifically called postcoital cystitis. The goal of treatment for postcoital inflammation of the bladder is to reduce pain and completely eliminate pathogenic microflora.
For this purpose, antibacterial therapy, the use of painkillers and antispasmodics are prescribed. To improve the body's immune abilities, vitamins and immunomodulators are administered.
A specific antibiotic is prescribed only after receiving a response from a bacteriological urine test. The causative agent of the infectious-inflammatory process is identified in the laboratory, and only then the drug to which the identified microorganism is sensitive is prescribed.
Antibiotics for the treatment of cystitis - Ceftriaxone, Ceftazidime. The listed antibacterial agents are administered intramuscularly or intravenously, 1 g twice a day, with an interval of 12 hours. Reviews of these drugs confirm their ability to quickly eliminate the inflammatory process.
Additionally, uroseptics are prescribed - Furazolidone, Furagin, Furadonin. Medicines of this pharmaceutical group have the property of relieving infectious processes of the urinary tract. The drugs color the urine a bright orange hue, which should not cause alarm. The average dosage for the treatment of postcoital cystitis is 2 tablets. every 4 hours. Duration of use – at least 10 days.
To prevent antibacterial agents from disturbing the natural intestinal microflora, the doctor prescribes the use of probiotics (agents that normalize the function and condition of the gastrointestinal tract). These include Linex, Bifiform, Hilak-Forte.
We must not forget that all oral medications have a certain likelihood of developing side effects. Among them are itching and skin irritation, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
A gentle antispasmodic that can be used by men and women is No-shpa. Contains drotaverine, is excreted from the body within 72 hours. The daily dosage should not exceed 240 mg. The drug is characterized by the property of slightly reducing blood pressure. Therefore, hypotensive patients need to take this medicine with caution. If it is impossible to see a urologist for certain reasons, you can take No-Shpu on your own at home before being examined by a doctor for no more than 3 days.
When cystitis periodically appears, herbal preparations are prescribed - Canephron, Phytolysin, Cyston. The listed medications destroy pathogenic microflora and normalize the functional ability of the bladder.
Why cystitis often develops in newlyweds
Frequent cystitis among newlyweds can also be explained by the fact that after the destruction of the hymen, the vaginal mucosa is more susceptible to infection by various infections. Since the urethra does not completely close after the first sexual intercourse, the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases, as well as “carrying” the infection into the bladder, increases significantly. Cystitis can begin almost asymptomatically.
In addition, possible neglect of the rules of personal hygiene can lead to worsening honeymoon cystitis.
In particular, refusal to use contraception and taking a shower after each sexual intercourse leads to the spread of infections in the body, especially in the genitourinary system.
Nutrition for the treatment of cystitis
Treatment of postcoital cystitis involves following a diet. It is necessary to exclude from the diet all foods that negatively affect the walls of the bladder - irritate them, cause spasms and associated pain. It is contraindicated to use:
- Salty, sour, hot, spicy, hot or overly chilled foods.
- Alcohol, coffee, strong tea, kefir, cocoa.
- Products containing high amounts of stabilizers, dyes, thickeners.
If cystitis occurs after sex, you need to abstain from intimacy for the period of treatment to restore the bladder. It is important to avoid hypothermia, take care of personal hygiene, get proper rest, and not overload yourself physically. In 90% of cases, both sexual partners will have to undergo treatment at the same time.
Prevention
A rational approach to preventing the development of cystitis is its prevention. To do this, just follow simple recommendations.
Measures to prevent postcoital cystitis include:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene during sexual intercourse;
- treatment of inflammatory diseases of the urogenital area;
- use of barrier contraception;
- permanent partner or infrequent change of partner;
- beware of hypothermia, stress, lack of sleep;
- strengthening the immune system;
- avoidance of tight underwear, especially those made from artificial materials;
- moderate use of panty liners, tampons, intimate hygiene gels;
- preventive examinations by a urologist and gynecologist, smear for flora once a year;
- timely consultation with a doctor when the first symptoms occur;
- sufficient fluid intake and timely emptying of the bladder;
- rational diet - balanced, frequent and moderate consumption of food.
Is cystitis dangerous for both partners?
Is cystitis transmitted from woman to man? Theoretically, this form of the disease occurs in men if:
- regular sexual intercourse without a condom with a woman;
- complicated urological history;
- developmental abnormalities of the genitourinary system;
- severe immunodeficiency.
Is cystitis transmitted to a male partner? Sexual transmission of cystitis to a man is practically impossible.
Is cystitis contagious and can you get infected with cystitis? Cystitis cannot be contracted like a sexually transmitted disease, but sex with a partner who has inflammation can contribute to the development of the inflammatory process.