Any illness in a child always causes fear and panic among parents and close relatives. Urinary tract infections are especially unpredictable, due to the fact that it is very difficult to diagnose the disease in time and often it is almost impossible to identify its root cause. The most common disease among children of preschool and primary school age is acute and chronic cystitis.
The main symptoms are incontinence, frequent urination at any time of the day, accompanied by acute pain. Children of any gender are affected by this disease, however, according to statistics, at older ages, girls suffer from cystitis several times more often than boys. This is due to the structural features of the genitourinary organs, the tendency to have gynecological abnormalities, and various disturbances in the normal functioning of the endocrine system.
It is extremely difficult to determine the localization of infection in an infant, because as a rule, such diseases are hidden, almost asymptomatic.
Many caring parents, trying to find out the cause of their baby’s illness as soon as possible, focus their attention on the recommendations of authoritative doctors, among whom the famous pediatrician, host of the famous TV show, Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky, has recently become popular.
Many of his works, publications, and videos reveal the causes, symptoms and methods of treating genitourinary system infections. Cystitis in children, Komarovsky calls for suspicion in case of any prolonged fever, lack of weight gain in infants.
Bacterial pathogens can enter the bladder in different ways:
- from natural reservoirs of infections (genitals, anus);
- from the upper genital tract, kidneys;
- from other pelvic organs;
- from other foci of the inflammatory process, through the wall of the bladder.
The physiological properties of the bladder contribute to natural protection from the negative effects of many bacteria, due to the presence of a pathogen-resistant mucous membrane. Some important conditions for preventing the development of microbial inflammatory process of the bladder should be taken into account:
- timely, complete emptying;
- integrity of the skin of the bladder and mucous membranes;
- high level of local immunoprotection.
Causes
Normally, the bladder has good protection against infections: there is a protective mucopolysaccharide layer of the bladder; there is local immunological, hydrodynamic, antibacterial protection; periurethral glands produce mucus with a bactericidal effect.
If the defense is weakened and risk factors are present (hypothermia, surgical interventions, poor genital hygiene, etc.), the infection attacks the bladder, bladder inflammation develops, children have a weaker immune system than adults and the ability to resist infections is lower.
The most common route of infection is ascending, when bacteria enter through the urethra.
In most cases, cystitis in boys and girls is caused by gram-negative flora, with Escherichia coli leading among them. In severe postoperative patients and children with immunodeficiency conditions, mycotic cystitis of the bladder may develop; in a child who has not reached the age of majority, this type of disease can acquire a chronic form.
Some medications, allergens, poisons, and toxic substances can also contribute to the development of cystitis in children.
Specific forms of the disease caused by ureaplasma, gonococci or trichomonas are usually characteristic of adults, but are sometimes registered in adolescence based on examination results. This is not a complete list of pathogens, but doctors are unanimous in how to treat cystitis in children caused by bacterial infections - antibacterial therapy is needed.
Parents should know about the causes of cystitis in children
Symptoms
Inflammation of the bladder can occur even in the youngest children (even a one-year-old child), but the signs vary depending on the gender and age of the child.
The manifestations of the disease are correlated at certain ages, and it is important to detect it in time. Also, as the child grows, the symptoms may become less obvious (a 5-year-old child will tolerate the pathology somewhat easier than a 3-year-old child).
Cystitis in children is a dangerous disease, as it can become chronic or lead to even more serious diseases, for example, pyelonephritis.
Signs of cystitis are not immediately apparent and can only be detected by urine analysis. A video with details about the tests can be viewed from Dr. Komarovsky. In them, the pediatrician explains all the nuances and explains how to interpret the meaning of urine tests.
But the occurrence of cystitis in boys is immediately expressed by acute symptoms. Ignoring the symptoms of the disease can lead to the development of a chronic disease.
A chronic disease cannot be completely cured, so children will be forced to undergo therapy courses throughout their lives.
The first sign is always an increase in body temperature, because the body begins to fight foreign bodies (bacteria) or infection.
Up to 1 year
In addition to general symptoms such as fever and tearfulness of the child, the color of his urine may change. Parents need to be careful and not attribute everything to children’s whims, since the child cannot yet say that something is wrong with him or what exactly hurts him.
If you notice these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor, because cystitis can become chronic.
From 1 year to 3 years
The temperature rises, there is a frequent urge to urinate, and the child may cry while urinating. At this age, cystitis is especially dangerous for a child’s body because pyelonephritis can also develop against its background.
If blood or blood streaks appear in the urine, it is necessary to examine not only the urethra, but also the kidneys.
From 3 years to 8 years
Pain in the lower abdomen, false urge to urinate or, conversely, incontinence, possible bladder spasms, which affect the deterioration of urine outflow.
All symptoms are pronounced, since children’s immunity is still difficult to cope with them.
From 8 years to 16 years
In older children and adolescents, the immune system is stronger and does not allow the symptoms of cystitis to manifest themselves as brightly as in younger ages. There is frequent urination. There is a danger of inflammation of the urethra and testicles in boys during exacerbation of the disease.
In addition to visual symptoms or the child's complaints of pain, a urine test is important. Dr. Komarovsky discussed this topic in detail.
Komarovsky also talks about determining the type of pathogen and that the presence of protein and red blood cells in the urine indicates the occurrence of cystitis. Komarovsky managed in his videos to easily talk about all the nuances of treating cystitis, depending on its location, shape and other factors.
Symptoms of the disease
In acute form of cystitis in children, the symptoms are:
- pain in the lower abdomen, which becomes more pronounced when the bladder is filled and palpated;
- painful and difficult urination, sometimes with blood;
- frequent urges, sometimes literally impossible to suppress;
- urination in small portions;
- urinary incontinence.
In the chronic form of a child, cystitis manifests itself as:
- bed-wetting;
- frequent urination;
- urine becomes cloudy, maybe with blood;
- other signs of cystitis in children, which are characteristic of the acute form of the disease.
Chronic childhood cystitis can manifest itself with “erased” symptoms, less often with relapses during exacerbation of underlying diseases, hypothermia and other provoking factors. With relapses, the symptoms of cystitis in children become more pronounced, and the urine may contain blood.
Only a doctor can diagnose cystitis in boys and girls, excluding other diseases. Do not decide how to treat cystitis in a child without consulting a doctor; it is necessary to conduct an examination before prescribing medications.
Symptoms
The manifestations of cystitis are quite characteristic and specific. For children of any age they are the same:
- severe cutting pain when urinating, especially after the end of the process;
- the frequency of urination increases, and the amount of urine decreases;
- the color of the urine is cloudy, sometimes you can see blood in it;
- sometimes there is an increase in body temperature;
- urinary incontinence;
- the appearance of cutting pain in the lower abdomen in the center.
Mothers of infants should be especially careful: the only symptom by which they can suspect cystitis in babies is increased crying immediately after urination.
Cystitis under 1 year of age
Diagnosis of cystitis in children under 1 year of age is complicated by the fact that the baby cannot describe the symptoms that bother him. Therefore, the disease in little girls or boys may go unnoticed for a long time, and medical care for the inflammatory process will not be provided in a timely manner.
According to statistics, among newborn children, boys are more often diagnosed with cystitis. Among older children, on the contrary, boys suffer less, cystitis is more often noted in girls (about 5–6 times more often), this is due to the structural features of their urinary tract.
The disease can be suspected in infants based on the following symptoms:
- Intermittent urination.
- Straining and redness of the face when urinating.
- Crying and restlessness before and during urination.
- Weak stream of urine.
- Urine with blood.
- Darkening of urine.
- Bloody discharge on diapers.
Long-term use of diapers and their untimely replacement contribute to the development of the disease: bacteria multiply and can easily enter the urethra.
Regularly changing diapers and not using them around the clock is one of the measures to prevent bladder inflammation. A pediatrician can tell you more about the symptoms and treatment of cystitis in infant girls or boys.
Komarovsky’s opinion on cystitis: why it appears, how to treat it
Pediatrician Komarovsky has his own professional opinion about cystitis and knows the treatment regimen.
Children's doctor Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky today enjoys authority and great popularity among new parents. Many people listen to his opinion, and even more people want to receive advice.
After all, this person is truly a professional in his field. He is a pediatrician, the host of his own television show, and the author of books on the topic of child health and development.
The appearance of the disease in children
According to pediatrician Komarovsky, cystitis in a child is a fairly common occurrence. This is a disease characterized by inflammation of the bladder mucosa. The causative agents are staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli and other types of protozoa.
Girls have a greater risk of falling under the influence of this disease than boys, namely, the former get sick 5-6 times more often. This dynamics is associated with the characteristics of the genitourinary system, and, in particular, the urinary canal.
So, in girls it is wider and shorter, unlike in boys, which makes it easier for germs and pathogenic organisms to enter.
Symptoms and signs of cystitis
According to Dr. Komarovsky, it is quite difficult to determine cystitis in children and prescribe treatment, even if there are some symptoms.
This can be explained by the fact that the child, due to his age and knowledge, cannot describe the sensations that he experiences and explain what exactly is bothering him. Therefore, very often parents do not even suspect the existence of a problem.
Dr. Komarovsky determines the presence of cystitis by a number of specific signs. Symptoms also differ according to age. For example, in babies of the first year of life, the initial manifestations of the disease are:
- change in urine color, cloudiness, possible admixtures of blood and sediment;
- elevated temperature, higher than 38;
- incessant crying, worse during urination.
Older children, as well as schoolchildren, are already able to report their feelings themselves, and the presence of inflammation can be diagnosed by the following signs:
- pain, cutting during urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, groin and suprapubic region;
- change in urine color, unpleasant smell of discharge;
- incontinence, especially at night;
- increase in body temperature.
Symptoms may vary depending on the individual case. It should also be remembered that only the attending physician or urologist can confirm the diagnosis, so you should definitely seek advice from a specialist. Dr. Komarovsky determines the presence of cystitis in a child by performing a urine test, a complete blood test, and an ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys.
This disease can occur in two forms - acute and chronic. If the acute form cannot be identified in time and appropriate measures taken, the inflammation develops into a chronic form, which becomes much more difficult to eliminate.
Why does cystitis appear in children?
Doctor Komarovsky sees the following as the causes of cystitis in young girls and boys:
- hypothermia;
- low temperatures unfavorable for the child’s body;
- effects on the body of parasites;
- weakened immune system;
- lack of vitamins and minerals for a growing body;
- various chronic diseases;
- improper or insufficient personal intimate hygiene;
- serious kidney problems;
- infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- consequences of taking medications;
- operating and postoperative surgical interventions (installation of catheters, drainages).
Dr. Komarovsky still explains the occurrence of cystitis in most cases by infections of various kinds, and the above-mentioned causes are indirect. Infections and pathogens have several ways of entering the body:
- by the urethra;
- through the kidneys;
- through the upper urinary tract.
Thus, in medical practice the problem is, in particular, infectious in nature. But there are also cases of non-infectious cystitis. Unfortunately, doctors have not yet fully studied this phenomenon, and it is difficult to talk about its nature. Possible sources of its occurrence include problems with metabolism, traumatic injuries to the genital organs, and exposure to toxins.
Nowadays, treatment of cystitis according to Komarovsky has become popular. Specialist Evgeny Komarovsky, thanks to his many years of practice and experience, gives simple, but important and practical advice to young parents.
He also gives recommendations to nursing mothers on how and how to treat cystitis during breastfeeding.
Thanks to his program “Dr. Komarovsky’s School,” you will learn how cystitis is treated in children, and on his personal channel you can watch various videos on this and other topics.
We also suggest visiting our forum about cystitis
, reviews can help you a lot or leave your comments. Remember that by sharing your experience you can provide all possible help to someone. Only for Russia!
We recommend paying attention to a unique drug that is not sold in pharmacies.
.
Natural herbal complex helps against pain, inflammation and urge. To learn more
.
Adblock detector
Source: https://tsistit-lechenie.ru/doktor-komarovskij-o-tsistite/
Drug treatment
As mentioned above, when cystitis is detected in children, treatment is based on antibacterial therapy aimed at destroying pathogens. Antispasmodic drugs are also used, and in chronic forms - local therapy (instillation of drugs into the bladder).
Recommended:
- drink plenty of fluids, have a balanced diet;
- limitation of physical activity, bed rest;
- frequent change of underwear;
- washing with soap at least once a day;
- as prescribed by a doctor - vitamins, immunotherapy.
Only a specialist who knows exactly how cystitis manifests itself in children and how to cure cystitis in a child can prescribe specific medications. Contact your doctor to confirm your child's diagnosis and receive clinical treatment recommendations.
Treatment
It is necessary to treat cystitis, says Evgeniy Komarovsky. Trying to wait until everything passes is a bad tactic. It’s even worse to start treating bladder inflammation using folk remedies. Self-medication in this case is inappropriate.
At the first signs of cystitis, Komarovsky advises contacting a doctor, who will ask you to take a urine test.
Bacterial culture will allow you to understand which microbe or fungus caused the damage to the bladder. After this, the doctor will prescribe the necessary antibiotics that are effective against this particular pathogen.
Diuretics will probably also be prescribed, since the more often the child defecates, the more pathogens will leave his body along with the urine. In connection with the prescription of diuretics, it is wise to give the child warm drinks as much as possible: compotes, fruit drinks, parsley decoction, and tea are good options. The liquid should not be cold or hot: only when its temperature approaches body temperature does the liquid begin to be absorbed and absorbed much faster.
During treatment, you should avoid spicy, salty, pickled foods, spices, sour berries and fruits, and carbonated drinks.
At home, mothers can perform local procedures on their child - sit him in a warm bath to relieve pain. The water temperature should not exceed 36-37 degrees. If you overheat an inflamed bladder, the pathological process will only worsen.
In case of acute cystitis, which occurs with an increase in temperature, it is advisable to provide the child with bed rest.
Phytotherapy
Herbs are used as an auxiliary treatment - infusions for sitz baths, decoctions for oral use. For cystitis, warm baths with infusions of oak bark, chamomile, sage, and birch leaf are useful. For drinking, infusions of chamomile, lovage root, St. John's wort, centaury, blackberry leaves, linden, black currant, clover, motherwort, string, calamus, lemon balm, seeds and dill herb are prepared.
Many medicinal herbs are available at any pharmacy
Remember that medicinal plants provide benefits only when used rationally! You need to be careful with the choice of herbs and dosage, otherwise the plant may cause harm. To eliminate mistakes when preparing herbal infusions, you can use ready-made preparations based on herbal ingredients, in which the dosages of active substances are strictly observed.
They are often sold over the counter, but we recommend consulting with your doctor before giving these products to your children.
One can debate for a long time how effective ready-made preparations based on herbal components are and whether they are effective in treating childhood cystitis. Therefore, we present data from a study that assessed the effectiveness of the combined herbal drug Canephron.
Baseline: 60 girls (age 3–12 years) diagnosed with acute cystitis. All were prescribed basic antibiotic therapy for three days. Patients were divided into specific groups:
- First group: 30 children. During antibiotic therapy and 3 months after, they received Canephron in age-appropriate dosages. By the end of the second day of treatment, only 2 girls suffered from dysuria. On the third day, bacteriuria was eliminated in 93.3% of children; after 3 months of preventive therapy with Canephron, this figure increased to 96.7%. There was only one relapse within 3 months in the group.
- Second group: 30 children. They were treated only with a 3-day course of antibiotics; there was no prophylactic therapy. By the end of the second day, 9 girls were still suffering from dysuria. On the third day, bacteriuria was eliminated in 76.7% of children; after 3 months this figure decreased to 73.3%. Infantile cystitis in girls in the group returned within 3 months in 7 patients.
Composition of the combined herbal preparation Canephron
Taking into account these studies, it can be argued that taking herbal preparations makes the treatment of cystitis in children more effective and reduces the likelihood of relapses. They can be recommended for inclusion in complex therapy.
Symptoms and treatment of cystitis in children
Most of the world's population has experienced cystitis at least once, and children are no exception. This unpleasant disease can occur at any age and is diagnosed even in newborns. We will tell you where inflammation comes from and how to treat cystitis in children in this article.
Causes
Normally, the bladder has good protection against infections: there is a protective mucopolysaccharide layer of the bladder; there is local immunological, hydrodynamic, antibacterial protection; periurethral glands produce mucus with a bactericidal effect.
If the defense is weakened and risk factors are present (hypothermia, surgical interventions, poor genital hygiene, etc.), the infection attacks the bladder, bladder inflammation develops, children have a weaker immune system than adults and the ability to resist infections is lower.
The most common route of infection is ascending, when bacteria enter through the urethra.
In most cases, cystitis in boys and girls is caused by gram-negative flora, with Escherichia coli leading among them. In severe postoperative patients and children with immunodeficiency conditions, mycotic cystitis of the bladder may develop; in a child who has not reached the age of majority, this type of disease can acquire a chronic form.
Some medications, allergens, poisons, and toxic substances can also contribute to the development of cystitis in children.
Specific forms of the disease caused by ureaplasma, gonococci or trichomonas are usually characteristic of adults, but are sometimes registered in adolescence based on examination results. This is not a complete list of pathogens, but doctors are unanimous in how to treat cystitis in children caused by bacterial infections - antibacterial therapy is needed.
Parents should know about the causes of cystitis in children
Symptoms of the disease
In acute form of cystitis in children, the symptoms are:
- pain in the lower abdomen, which becomes more pronounced when the bladder is filled and palpated;
- painful and difficult urination, sometimes with blood;
- frequent urges, sometimes literally impossible to suppress;
- urination in small portions;
- urinary incontinence.
In the chronic form of a child, cystitis manifests itself as:
- bed-wetting;
- frequent urination;
- urine becomes cloudy, maybe with blood;
- other signs of cystitis in children, which are characteristic of the acute form of the disease.
Chronic childhood cystitis can manifest itself with “erased” symptoms, less often with relapses during exacerbation of underlying diseases, hypothermia and other provoking factors. With relapses, the symptoms of cystitis in children become more pronounced, and the urine may contain blood.
Only a doctor can diagnose cystitis in boys and girls, excluding other diseases. Do not decide how to treat cystitis in a child without consulting a doctor; it is necessary to conduct an examination before prescribing medications.
Cystitis under 1 year of age
Diagnosis of cystitis in children under 1 year of age is complicated by the fact that the baby cannot describe the symptoms that bother him. Therefore, the disease in little girls or boys may go unnoticed for a long time, and medical care for the inflammatory process will not be provided in a timely manner.
According to statistics, among newborn children, boys are more often diagnosed with cystitis. Among older children, on the contrary, boys suffer less, cystitis is more often noted in girls (about 5–6 times more often), this is due to the structural features of their urinary tract.
The disease can be suspected in infants based on the following symptoms:
- Intermittent urination.
- Straining and redness of the face when urinating.
- Crying and restlessness before and during urination.
- Weak stream of urine.
- Urine with blood.
- Darkening of urine.
- Bloody discharge on diapers.
Long-term use of diapers and their untimely replacement contribute to the development of the disease: bacteria multiply and can easily enter the urethra.
Regularly changing diapers and not using them around the clock is one of the measures to prevent bladder inflammation. A pediatrician can tell you more about the symptoms and treatment of cystitis in infant girls or boys.
Phytotherapy
Herbs are used as an auxiliary treatment - infusions for sitz baths, decoctions for oral use.
For cystitis, warm baths with infusions of oak bark, chamomile, sage, and birch leaf are useful.
For drinking, infusions of chamomile, lovage root, St. John's wort, centaury, blackberry leaves, linden, black currant, clover, motherwort, string, calamus, lemon balm, seeds and dill herb are prepared.
Many medicinal herbs are available at any pharmacy
Remember that medicinal plants provide benefits only when used rationally! You need to be careful with the choice of herbs and dosage, otherwise the plant may cause harm. To eliminate mistakes when preparing herbal infusions, you can use ready-made preparations based on herbal ingredients, in which the dosages of active substances are strictly observed.
They are often sold over the counter, but we recommend consulting with your doctor before giving these products to your children.
One can debate for a long time how effective ready-made preparations based on herbal components are and whether they are effective in treating childhood cystitis. Therefore, we present data from a study that assessed the effectiveness of the combined herbal drug Canephron.
Baseline: 60 girls (age 3–12 years) diagnosed with acute cystitis. All were prescribed basic antibiotic therapy for three days. Patients were divided into specific groups:
- First group: 30 children. During antibiotic therapy and 3 months after, they received Canephron in age-appropriate dosages. By the end of the second day of treatment, only 2 girls suffered from dysuria. On the third day, bacteriuria was eliminated in 93.3% of children; after 3 months of preventive therapy with Canephron, this figure increased to 96.7%. There was only one relapse within 3 months in the group.
- Second group: 30 children. They were treated only with a 3-day course of antibiotics; there was no prophylactic therapy. By the end of the second day, 9 girls were still suffering from dysuria. On the third day, bacteriuria was eliminated in 76.7% of children; after 3 months this figure decreased to 73.3%. Infantile cystitis in girls in the group returned within 3 months in 7 patients.
Composition of the combined herbal preparation Canephron
Taking into account these studies, it can be argued that taking herbal preparations makes the treatment of cystitis in children more effective and reduces the likelihood of relapses. They can be recommended for inclusion in complex therapy.
Are antibiotics always needed to treat childhood cystitis?
The goal of therapy is to eliminate pain, normalize the process of urination and eliminate the inflammatory process. If you can get rid of pain with the help of antispasmodics, then you will not be able to get rid of inflammation without antibacterial therapy.
As long as microorganisms are in the bladder or can spread from other sources of infection, they will attack again and again, which is why successful treatment of cystitis in boys or girls without antibacterial drugs is unlikely.
Is there treatment without antibiotics? You can do without them only if the cystitis in a boy or girl was not caused by bacteria (the causes of cystitis in children are different, for example, taking certain medications). Then uroseptics (furadonin, furagin, etc.) are prescribed to prevent purulent complications.
Uroseptics are indispensable assistants in the fight against cystitis
Local treatment
The treatment regimen for common chronic cystitis in children may include intravesical therapy with certain medications, namely the administration of drugs with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects directly into the bladder.
To evaluate the effectiveness of intravesical therapy, a study was conducted with the participation of 68 girls. The age of the patients is from 5 to 16 years. All girls were divided into three groups:
- The first group: 37 patients, girls, received instillations of 1% dioxidine solution and Enterosgel paste in equal doses, a total of 40 ml per 1 procedure.
- The second group: 26 girls, received instillations of only 1% dioxidine solution, 40 ml per 1 procedure.
- Third group: 5 girls with granular chronic cystitis received instillations of a 0.05% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine and Enterosgel paste in equal parts, a total of 40 ml per 1 procedure.
Before the start of treatment, the tests of most patients showed massive leukocyturia; according to the results of bacterial studies, Escherichia coli was most often cultured.
Research results:
- First group: the number of leukocytes in the urine returned to normal within 7–8 days. After a course of instillations, in 97% of cases, urine cultures were sterile.
- Second group: the decrease in the number of leukocytes to normal occurred within 14–18 days. After a course of therapy, urine cultures were sterile in 60% of cases.
- Third group: the leukocyte count decreased to normal levels in 6–8 days.
As can be seen from the study data, intravesical antibacterial therapy is effective and can be recommended as part of a comprehensive treatment.
The drug Enterosgel is used in the complex treatment of urinary tract infections
Possible complications of childhood cystitis
If the disease in its acute form has not been treated or the treatment course has not been completed (sources of infection remain), it is likely to become chronic, and relapses will make themselves felt in the future. Therefore, at the first symptoms, take your baby to the doctor and strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations. The following complications are common:
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Urethritis.
What should parents do if a child has cystitis? It is necessary to immediately show the baby to the doctor. Any medications can be given only with the consent of a doctor.
Prevention
- You should explain to your child that you need to urinate regularly, emptying your bladder completely. It is harmful to endure for a long time, since stagnation of urine is an excellent environment for the growth of bacteria. With regular emptying, the bladder is cleansed, the stream literally washes away harmful microorganisms.
- A balanced diet without spicy, salty, fatty, smoked foods and carbonated drinks is recommended. Children need to drink enough liquid (cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks, still water, green tea) and maintain a normal water balance.
- Hypothermia should not be allowed; babies need to be dressed warmly.
If you have a cold, no self-medication! Contact your doctor immediately. - Pay special attention to children's hygiene. Explain exactly how to wash yourself, taking into account the anatomical features of boys and girls. Tell us about the symptoms you need to pay attention to - bloody urine, pain and frequent urges.
- After swimming in open water, children must be changed into dry clothes.
E. O. Komarovsky about childhood cystitis
Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky is a pediatrician, highest category, presenter of the program “ShDK” (School of Doctor Komarovsky). Evgeniy Olegovich is known for his modern approach to the treatment and prevention of childhood diseases.
In the presented video materials, Dr. Komarovsky talks about what cystitis is in children, what its symptoms are and how to properly treat the disease.
Conclusion
Cystitis can occur in children of any age; they develop even in the first months of life. The most common cause of the disease is a bacterial infection, to combat which complex therapy is used (antibacterial drugs, antispasmodics, local treatment).
The task of parents is to know how to identify alarming symptoms and, when they appear, immediately take the child to the doctor. There is no need to try to treat inflammation on your own so that the disease does not cause complications.
Source: https://MyCistit.ru/lechenie/u-rebenka
Are antibiotics always needed to treat childhood cystitis?
The goal of therapy is to eliminate pain, normalize the process of urination and eliminate the inflammatory process. If you can get rid of pain with the help of antispasmodics, then you will not be able to get rid of inflammation without antibacterial therapy.
As long as microorganisms are in the bladder or can spread from other sources of infection, they will attack again and again, which is why successful treatment of cystitis in boys or girls without antibacterial drugs is unlikely.
Is there treatment without antibiotics? You can do without them only if the cystitis in a boy or girl was not caused by bacteria (the causes of cystitis in children are different, for example, taking certain medications). Then uroseptics (furadonin, furagin, etc.) are prescribed to prevent purulent complications.
Uroseptics are indispensable assistants in the fight against cystitis
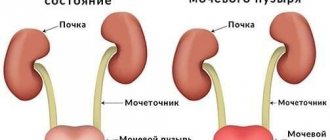
What is a disease
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder. In this case, its urothelium - the mucous (epithelial) membrane - and the submucosal layer located underneath it suffer. Inflammation is most often caused by pathogenic microbes.
Babies under one year old suffer from cystitis much less often than older children, and the cause of the inflammatory process in infants, as a rule, is either congenital anomalies of the urinary tract or gross neglect of the rules of hygienic care.
The peak incidence of bladder inflammation occurs at 4–10 years of age, with girls getting sick 5–6 times more often than boys. This is due to the anatomical features of the female body - a wide and short urethra and its very close location to potential reservoirs of bacterial infection - the vagina and rectum. Girls of preschool, and especially primary school age, are susceptible to various gynecological pathologies, which can easily provoke the penetration of infection into the bladder and the development of an inflammatory process in it.
Cystitis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the bladder
In a child of any age, cystitis can occur in isolation or be combined with infection of neighboring organs - the urethra or kidneys.
Cystitis is classified by pediatric urologists according to the following criteria:
- Clinical course. It can be acute or chronic. The acute process is accompanied by catarrhal or hemorrhagic changes in the bladder wall. In the chronic course, inflammation affects the deeper, muscular layer of the organ wall, and the nature of the changes can be: phlegmonous;
- granular;
- bullous;
- encrusting;
- gangrenous;
- polyposis;
- bullous-fibrinous;
- interstitial;
- necrotic.
- primary - occurs without structural abnormalities and functional disorders of the organ;
- VUR (vesicoureteral reflux - reverse reflux of urine);
Simple catarrhal cystitis is characterized by hyperemia (redness) and swelling of the mucous membrane of the organ. Blood vessels are dilated and permeable. With the development of a severe form of cystitis, inflammation spreads to the submucosal and muscular layers, their swelling occurs, the walls of the bladder thicken, and inflammatory and then purulent infiltrates form.
The mucous membrane of the bladder in acute cystitis is edematous, hyperemic, the blood vessels of the urothelium are dilated
The chronic form of the disease develops as a consequence of untreated or incompletely treated acute inflammation. Children of primary school age are more susceptible to chronic cystitis. Like an acute process, chronic inflammation can be diffuse (widespread) or limited (local). Usually all layers of the bladder wall are affected, the elasticity, contractile function and physiological capacity of the bladder decrease, and over time its walls shrink. The course of the chronic form of the disease can be asymptomatic or recurrent.
Local treatment
The treatment regimen for common chronic cystitis in children may include intravesical therapy with certain medications, namely the administration of drugs with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects directly into the bladder.
To evaluate the effectiveness of intravesical therapy, a study was conducted with the participation of 68 girls. The age of the patients is from 5 to 16 years. All girls were divided into three groups:
- The first group: 37 patients, girls, received instillations of 1% dioxidine solution and Enterosgel paste in equal doses, a total of 40 ml per 1 procedure.
- The second group: 26 girls, received instillations of only 1% dioxidine solution, 40 ml per 1 procedure.
- Third group: 5 girls with granular chronic cystitis received instillations of a 0.05% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine and Enterosgel paste in equal parts, a total of 40 ml per 1 procedure.
Before the start of treatment, the tests of most patients showed massive leukocyturia; according to the results of bacterial studies, Escherichia coli was most often cultured.
Research results:
- First group: the number of leukocytes in the urine returned to normal within 7–8 days. After a course of instillations, in 97% of cases, urine cultures were sterile.
- Second group: the decrease in the number of leukocytes to normal occurred within 14–18 days. After a course of therapy, urine cultures were sterile in 60% of cases.
- Third group: the leukocyte count decreased to normal levels in 6–8 days.
As can be seen from the study data, intravesical antibacterial therapy is effective and can be recommended as part of a comprehensive treatment.
The drug Enterosgel is used in the complex treatment of urinary tract infections
Traditional methods of treatment
- Pour one teaspoon of dry St. John's wort herb into a glass of hot water and let it brew in a water bath for about half an hour. Cool and strain the product, drink a quarter glass 4 times a day half an hour before meals for 10 days;
- Pour three tablespoons of ground dry bergenia rhizomes into one glass of hot water, put on medium heat and evaporate ½ of the liquid. Remove from heat, cool, strain. Take 10 drops 3 times a day before meals for 1 week;
- Take 1 cup of birch leaf, chamomile, oregano, and oak bark in equal proportions, pour a liter of boiling water over them and let it brew for 15 minutes. Strain and pour the liquid into a warm bath, stirring thoroughly. Help your child do a relaxing session in a sitting position for 15 minutes. The recommended thermal water temperature is 37–38 degrees.
Possible complications of childhood cystitis
If the disease in its acute form has not been treated or the treatment course has not been completed (sources of infection remain), it is likely to become chronic, and relapses will make themselves felt in the future. Therefore, at the first symptoms, take your baby to the doctor and strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations. The following complications are common:
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Urethritis.
What should parents do if a child has cystitis? It is necessary to immediately show the baby to the doctor. Any medications can be given only with the consent of a doctor.
Prevention
- You should explain to your child that you need to urinate regularly, emptying your bladder completely. It is harmful to endure for a long time, since stagnation of urine is an excellent environment for the growth of bacteria. With regular emptying, the bladder is cleansed, the stream literally washes away harmful microorganisms.
- A balanced diet without spicy, salty, fatty, smoked foods and carbonated drinks is recommended. Children need to drink enough liquid (cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks, still water, green tea) and maintain a normal water balance.
- Hypothermia should not be allowed; babies need to be dressed warmly. If you have a cold, no self-medication! Contact your doctor immediately.
- Pay special attention to children's hygiene. Explain exactly how to wash yourself, taking into account the anatomical features of boys and girls. Tell us about the symptoms you need to pay attention to - bloody urine, pain and frequent urges.
- After swimming in open water, children must be changed into dry clothes.
General recommendations
Dr. Komarovsky urges parents who suspect that their child has cystitis to immediately consult a doctor.
According to a popular pediatrician, self-medication of inflammatory diseases affecting the children's urinary system is simply unacceptable.
If parents start giving their child the wrong medications, the baby’s condition may worsen significantly, and the disease will become chronic, which will be even more difficult to get rid of.
It is necessary to select an effective treatment regimen only based on the results of tests and examinations. A blood and urine test, as well as an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, will help identify the cause of cystitis and understand exactly what medications will be needed to eliminate the symptoms of the disease. To get the most reliable clinical picture and find out which bacteria provoked the inflammation, it is necessary to do a urine culture.
If a doctor has prescribed antibacterial drugs to a child to treat cystitis, parents should give such medications to the baby strictly according to the instructions; an overdose of antibiotics can cause irreparable harm to the child’s body.
Diagnosis of pathology
Most often, concerned parents turn to a pediatrician, but a full range of diagnostic measures and treatment prescriptions are carried out by a pediatric urologist.
To make a correct diagnosis, you need to undergo the following tests:
- General urine analysis. Usually, the urine of a sick child contains leukocytes, hematuria of varying degrees - individual red blood cells or blood clots, a lot of mucus and transitional epithelial cells.
- Urine culture for microflora. Material for research should be collected after a thorough toilet of the genitals. The analysis determines the type of bacteria that caused the inflammation.
- Two-glass sample. In this case, urine is collected in two doses - 30–50 ml in one container and the rest of the portion in another container. Then a microscopic examination of the material is carried out: if leukocytes are detected only in the first portion, this indicates inflammation in the urethra, if in both, then this indicates cystitis.
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests. In the general analysis, an increased number of leukocytes, acceleration of ESR (signs of inflammation) are determined; biochemical analysis serves to assess the functional abilities of the urinary system.
Instrumental studies for bladder inflammation:
- Two-stage echography (ultrasound) of the bladder - before and after urination. In this case, thickening of the mucous membrane of the organ and many echo-negative elements in its lumen are detected.
- Cystoscopy and cystography. They are carried out in children with chronic cystitis during remission. These methods are aimed at assessing the nature and extent of pathological changes in the inner lining of the bladder. Cystoscopy is the most reliable method for diagnosing the disease. In young children and boys, the examination is carried out under general anesthesia. Before the procedure, electrocardiography and examination of the child by an anesthesiologist are required.
If cystitis is suspected, an ultrasound of the bladder must be performed.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following pathologies:
- acute pyelonephritis;
- neoplasms of the bladder;
- gynecological pathologies in girls;
- acute urethritis;
- paraproctitis (inflammation of the rectal tissue);
- acute appendicitis.
To exclude these pathologies, the child may be referred for consultation to specialists: a pediatric surgeon and a gynecologist.
Useful tips
When carrying out treatment, parents must follow all the instructions of the attending physician. If the treatment for an inflammatory disease follows all the rules, the baby will quickly recover.
According to Dr. Komarovsky, treatment of cystitis in children will give excellent results if you perform the following actions and procedures:
- sitz baths with herbal decoctions (you can brew chamomile, St. John's wort, sage or other pharmaceutical preparations with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects in boiling water; the finished decoction should be cooled to 37 degrees, poured into a basin and the baby should be placed there for 10-15 minutes);
- warm compresses on the bladder area (heat will help overcome the inflammatory process, but too high temperatures can, on the contrary, harm the child’s body, so parents need to be careful and not overdo it during this procedure);
- bed rest (a young patient experiencing pain in the bladder area should move as little as possible, this is especially true for those children who have a high fever due to cystitis);
- diet (during treatment of cystitis, the baby should eat a lot of fruits, vegetables, fresh herbs, fermented milk products; the children's diet should not contain spicy, fatty, fried, salty foods);
- drinking plenty of fluids (a sick child should drink a lot of clean water, berry fruit drinks or compotes; the liquid entering the body will help mechanically remove the infection from the bladder);
- regular hygiene procedures (the external genitalia should always be clean; it is advisable to wash children suffering from cystitis after each trip to the toilet).
Cystitis in children: treatment using the Komarovsky method, advice from a famous pediatrician
Quite often, parents have to deal with one of the most unpleasant childhood ailments, namely cystitis. A painful process in the bladder mucosa very often occurs in school-age children, bringing a lot of anxiety and fear.
The only correct solution in this situation will be to contact a pediatrician as soon as possible. Today, the famous children's doctor Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky enjoys special authority among young parents.
So, if you suspect cystitis in your children, Komarovsky will suggest treatment.
What is cystitis?
Cystitis is an inflammatory disease of the bladder mucosa caused by pathogens: E. coli, staphylococcus, chlamydia and others. The special structure of the genitourinary system makes girls most susceptible to cystitis.
This disease occurs in two forms - acute and transitioning from it - chronic.
The second form in children occurs only in cases where timely medical care was not provided. Especially in infants, when it can be extremely difficult for young parents to determine the main cause of the baby’s anxiety.
Symptoms
In children of the first year of life, it can be extremely difficult to determine the symptoms of cystitis. If your baby is showing excessive anxiety, here are some signs to look out for:
- The urine becomes cloudy and may contain blood.
- Increased body temperature above 38 degrees.
- Crying, worse during urination.
An older and school-age child is already able to independently talk about his symptoms.
The following complaints may indicate the presence of cystitis:
- presence of pain when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- unusual color of urine mixed with blood;
- temperature increase;
- incontinence.
Naturally, in order to confirm the diagnosis, the child needs to undergo a general analysis of urine, blood, and an ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of the disease is the penetration of infection into the bladder. However, it is possible to identify indirect reasons that classify a child at risk.
These include:
- weak immunity;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- frequent hypothermia;
- infection of the body by parasites;
- infrequent hygiene procedures;
- kidney disease;
- taking certain medications.
Treatment and advice from Komarovsky
As soon as you suspect your child has cystitis, immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. The famous children's doctor Evgeny Olegovich Komarovsky gives parents very simple, but at the same time valuable advice.
- Forget about self-medication. Your wrong actions can contribute to the transition of an acute form of cystitis to a chronic form, which is much more difficult to treat.
- Boost your child's immunity. Do some hardening and review his diet.
- Teach your child proper hygiene procedures. This point is extremely important not only for the health of girls, but also of boys.
Since Komarovsky warns to engage in independent treatment in order to avoid life-threatening complications for the child, first of all, it is worth understanding that cystitis is a lesion of the genitourinary system, which means that a clinical urine test will help give a more accurate conclusion.
In addition to treatment with special drugs, Dr. Komarovsky recommends carrying out special procedures aimed exclusively at the source of the disease.
This includes sitz baths with various infusions of medicinal herbs: chamomile, sage and others. It is worth noting that the water temperature should be 37 degrees, but not higher.
Additionally, you can apply a dry warming compress to the bladder area. However, do not forget about precautions, since excessively high temperatures can only aggravate the course of the disease.
Since the child experiences pain symptoms, and the disease is often accompanied by fever, bed rest must be observed.
Evgeniy Olegovich recommends paying special attention to the child’s nutrition. The basis for a speedy recovery is a diet consisting of fruits and dairy products. Any spices and spicy foods should be excluded.
In addition to all of the above, Komarovsky recommends giving your child plenty of fluids. The daily dose of liquid must be approximately doubled.
This measure will help flush out pathogenic microflora, which means it will speed up recovery. Allowed drinks include water, weak fruit drinks and compotes.
After the first symptoms of cystitis appear, there is no need to wait until the next day or the moment when your child gets worse.
Call your pediatrician and ask him for a referral for a urine test. Only after receiving the test results will it be possible to confidently judge the correctness of the diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Always remember that preventing a disease is much easier than treating it later. This especially applies to young children.
on the topic
3 Comments
Source: https://mkb2.ru/tsistit-i-mochevoy-puzyir/u-detej/cistit-lechenie-komarovsky.html
Prevention measures
To avoid the appearance of cystitis or prevent relapses of the disease, Komarovsky recommends resorting to preventive measures. Parents should:
- strengthen the baby’s immunity with the help of hardening;
- feed the baby with nutritious, balanced food (for babies, breast milk remains the ideal food option);
- wash children correctly (girls are washed under running water in the direction from the vagina to the anus, boys are washed with clean water, without retracting the foreskin on the head);
- change baby diapers regularly;
- instill a culture of hygiene from childhood;
- choose comfortable underwear made from natural fabrics for your baby.