Simultaneous damage to several body systems is often a consequence of the development of uric acid diathesis in adults. Symptoms and treatment for the accumulation of uric acid in the blood are not new to medical science, but people put off visiting doctors for a long time, not even realizing that their ailment is a harbinger of serious health problems.
Uric acid diathesis (uraturia) is a pathology in which uric acid is not excreted in full with urea, but accumulates in the body. An excess of this substance leads to increased action of stress and aggression hormones, and negatively affects the functioning of the kidneys, gallbladder, musculoskeletal system and nervous system. Uraturia is detected in every third adult.
Uric acid diathesis is not an independent disease - it is a condition of the body that provokes many diseases.
General information
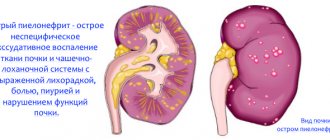
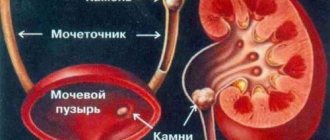
Uraturia is a pathological process during which large volumes of acid accumulate and are released during urination. Basically, the pathology is associated with a disrupted metabolic process in the creation and filtering of urine by the kidneys. At normal levels, different components are released in the urine, dissolved in it and excreted in the usual way. In case of failures, uric acid diathesis is formed, urine salts are transformed into sandy sediments and then crystallize. With this condition, the normal process of urination is disrupted. This pathology is a common problem in urology and is observed in both adults and children.
Prevention measures
Diet for uric acid diathesis remains the main method of preventing the progression of the pathological process in the body. But there are other important nuances:
- Daily physical activity should be moderate.
- It is important to promptly treat the organs responsible for urine excretion.
- Maintain drinking regime.
- Refusal of alcoholic drinks.
A competent approach to therapy and prevention for uric acid diathesis helps to quickly eliminate the problem and prevent the development of various pathologies in the body.
Causes and mechanisms of development
The main reason for the manifestation of this anomaly is a hereditary factor. When loved ones suffer from diabetes mellitus, gout and urolithiasis, the risk of developing uric acid diathesis increases. An unfavorable lifestyle provokes the development of an anomaly. Various inflammatory processes of the kidneys are the cause of uric acid diathesis. Feeling any discomfort is a reason to seek advice from a specialist. An anomaly detected in time is easier to correct, which will help avoid dangerous consequences.
The manifestation of uric acid diathesis is typical for people with pathologies in the urinary system. The level of uric acid salt in the blood increases, which is the impetus for the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, gall bladder and kidney organs. This disorder is determined by the deposited salt deposits in urine (urate). Their formation occurs due to insufficient chemical influences with the liquid (without dissolving in it) and they come out as microcrystals. Urates are present in the blood, thereby causing acidic reactions in the body, provoking an acidotic state.
Also, the reasons that caused the pathology include:
- unbalanced diet (high consumption of protein foods);
- chemotherapy;
- reduced immunity;
- alcohol abuse;
- long course of taking antibacterial drugs;
- chronic diseases of the liver and pancreas;
- frequent emotional stress and stressful situations;
- insufficient water consumption;
- prolonged refusal to eat;
- intoxication of internal organs.
Salt diathesis - a cause for concern or a problem-free condition
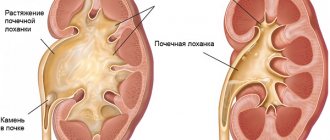
Urinary salt diathesis is the threshold for the formation of sand and kidney stones. Its cause may be congenital, caused by metabolic disorders, or anatomical defects of the urinary tract.
But there is still no unified theory of the pathogenesis of urolithiasis. The very definition of the word “diathesis” means “threshold changes” - this is not yet a disease, but there are already changes in the body that can lead to disease - with changes in immunity, injuries, hypothermia.
And then the formation of stones may begin. Often people who have urinary salt diathesis may not even be aware of this.
Interestingly, when urologists do a urine test for their family members, it often turns out that, for example, out of six people (grandparents, two children and parents), two people will definitely be diagnosed with this condition.
Women suffer most from salt diathesis due to frequent inflammatory diseases - mainly of an ascending nature. Due to the short and wide urethra, women often experience cystitis.
If you treat the disease yourself and incorrectly, the infection will eventually penetrate into the submucosal layer, from where it will penetrate the kidneys.
Where there is inflammation, under favorable conditions, a so-called “matrix” of stone formation is formed.
If there is persistent urolithiasis in the family, especially in the female line, if stones have formed (it is not necessary that they be operated on), and if the woman does not take adequate care of herself, there is a possibility of triggering a full cascade of biochemical changes.
Salts do not necessarily turn into stones. If there is no constant chronic inflammatory process, there are no anatomical features of the development of the genitourinary system, if a person drinks enough water, then there are no favorable conditions for the laying of stones. For example, out of ten patients with salt diathesis, treatment is necessary for one or two.
However, when making a diagnosis, you do not need to wash out the salts with large amounts of water, as this can be harmful. If there are any warning signs of problems, then a diet excluding fried, smoked, and salty foods is recommended. Food should be boiled and steamed - not irritating. With the correct water regime, the kidneys are cleansed; watermelon and kidney teas have a good effect.
Inborn error of metabolism does not go away. But urinary salt diathesis in itself does not create a big problem for society. Once a year he always does an ultrasound. If he is alarmed by the appearance of salts, he can go on a diet, drink kidney herbs, go to a sanatorium for water.
It is believed that 60-80% of urinary stones are calcium compounds.
When salts begin to form into stones, it makes sense to find out what salts they are: oxalates, phosphates, urates, calcium compounds? For example, phosphates break down easily and are eliminated from the body more quickly, but at the same time they are more often combined with infection. Urates and oxalates have a spinous surface and are quite dense. Calcium ones are the densest, but are associated with fewer infections.
There is no need to worry too much about salt diathesis. The human body is a “universal computer”: it feels that it needs to get rid of unnecessary things. And under normal water conditions, the unnecessary is washed away.
But if a urine test reveals a high salt content, a person needs to think, at a minimum, about the nature of the diet and water regime, because salts will fall out with acidic or puddle urine.
The nature of nutrition is an important risk factor in the development of urolithiasis, and therefore diet therapy and adequate maintenance of water balance play an important role. With urates, it is necessary to exclude meat products, legumes, coffee, and chocolate.
With calcium oxalate salts, limit milk, cheese, green vegetables, strawberries, strong tea, and cocoa. With calcium phosphate salts, it is not recommended to often eat fish and dairy products.
See also:
- Is your stomach sad? You have gastritis! →
- Eat, eat, eat... →
- Summer dangers →
Source: https://aif.ua/health/life/solevoy_diatez_-_povod_dlya_bespokoystva_ili_besproblemnoe_sostoyanie
Signs in adults
There are no specific signs indicating the presence of this pathology. However, experts identify some symptoms that indicate this pathology in adults. These include:
- detection of elevated levels of acid in the blood or urine;
- visual detection of flakes in urine;
- the appearance of aching pain (due to the deposition of crystals);
- sudden manifestations of renal colic when changing body position (due to the formation of stones in the renal organs or ureters);
- temperature increase;
- nausea, vomiting;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- feeling of weakness;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- migraine;
- increased blood pressure.
Uric acid diathesis in adults manifests itself with extensive symptoms and involves all internal systems of the body, as a result of which it negatively affects human health. A person’s emotional state also changes. When the breakdown of uric acids is impaired, people experience an increased state of anxiety, groundless worries, aggressive and irritable behavior, and insomnia. With uric acid diathesis, the musculoskeletal system is affected. The patient experiences pain in the joints, this is especially pronounced at night. As a rule, all symptoms appear in the later stages of the pathology.
Symptoms in women
Symptoms of pathology in women:
- visual change in urine;
- burning sensation when urinating;
- violation of intestinal functions (constipation);
- high blood pressure;
- muscle weakness;
- arrhythmia;
- chronic course of pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- constant fatigue.
Uric acid diathesis in women during menopause can occur along with gout.
The detection of urate salts in pregnant women is a common occurrence; while expecting a baby, doctors often diagnose MCD. Symptoms during pregnancy depend on various reasons: hormone imbalance; infectious lesions of the urinary and reproductive systems; abuse of meat and smoked foods, chocolate; lack of fluid entering the body. If the detection of urate salts is the only deviation in the analysis, you should switch to dietary nutrition and repeat the analysis in a couple of weeks.
Concept of pathology
MKD - what is it, what is urolithiasis? The pathology is not considered a separate disease and is characterized by an excess of uric acid, which is prone to crystallization.
When urinating, a small amount of salt crystals leaves painlessly, without causing discomfort. Such crystals in the sediment are similar to small pink and reddish grains of sand.
Uric acid kidney diathesis occurs in women during menopause, in men - after 40 years, in children - in most cases it is congenital.
The pathology is diagnosed in every third person. Such statistics are provoked by the presence of congenital kidney diseases or acquired pathologies.
Uraturia in children
Uric acid diathesis in children is associated with metabolic disorders of proteins in the child’s body. The underlying cause of the disorder is the child's excessive consumption of meat products. With the help of the fiber purine bases of the muscles of meat products, the disease is triggered in childhood.
The main symptomatology of uric acid diathesis in children is manifested in the detection of elevated levels of uric acid salts in the blood. At the beginning of the disease, all symptoms converge to the appearance of flake components or sandy sediment of red shades when urinating. Symptoms of uric acid diathesis in children:
- acetone odor from the mouth;
- irritability and capricious behavior for no reason;
- problems with appetite;
- sudden weight loss;
- vomiting and nausea;
- headaches and joint pain;
- discomfort in the renal area;
- allergic reactions.
Manifestation in the form of neuro-arthritic diathesis in a child, overstrain of the central nervous system is observed: regular hysterics and sleep disturbances; intolerance to strong aromas, fears at night. Children with this pathology may have a lag in mental development compared to their peers.
Why does MCD occur?
Among the main causes of the violation, scientists identify:
All cells of living organisms (humans, animals, plants) contain special substances purines. In this case, the natural process of destruction of cellular structures leads to the breakdown of purines.
As a result of their breakdown, uric acid is formed, which in normal concentrations is a natural antioxidant, has the ability to cleanse the body of excess nitrogen, protects blood vessels from damage, and stimulates brain function.
It is eliminated from the body naturally. The normal level of uric acid in one hundred milliliters of blood in men is considered to be 3.4-7.0 milligrams, and in women – 2.4-5.7.
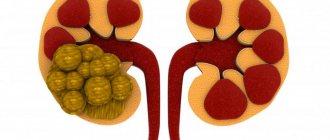
However, in the presence of certain metabolic disorders, in particular water-salt metabolism, when the acid is retained in the body, its level increases, and urate salts, called urates, usually kept dissolved, crystallize and precipitate.
These crystals can be deposited under the skin, in joints, tendons, kidneys, and other organs. In urine, such sediment looks like red grains of sand.
Moreover, the presence of such salts in the urine is the main sign of uric acid diathesis.
Thus, a distinctive feature of hyperuricuria is the excess content of uric acid in the bloodstream due to a violation of its excretion.
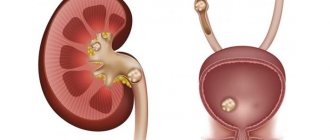
In the absence of treatment, complications may develop in the form of gouty arthritis, urolithiasis, when urate stones are formed from grains of sand in the kidneys and bladder, kidney failure, acute nephropathy, dysfunction of the digestive system and other diseases, including those leading to changes in the psychological state of the patient , since acid has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, enhancing the effect of stress hormones (adrenaline) and aggression (norepinephrine).
Uric acid diathesis (hyperuricuria or hyperuricosuria, uraturia) is characterized by a very abundant precipitation of uric acid and uric acid salts (urates) from the urine, which are normally kept in a dissolved state.
In this case, urine has persistent and significantly increased acidity, which is crucial in the process of stone formation. The concentration of uric acid in the urine plays a minor role in the process of stone formation.
The precipitate of uric acid salts looks like red sand.
Diagnosis of uric acid diathesis
To diagnose uric acid diathesis, you should contact urologists or nephrologists. The doctor prescribes a thorough examination, which includes:
- biochemical blood test including determination of acid levels;
- general urine test;
- urine analysis per day to determine the content of hydrogen indicators and other minerals;
- blood test for hydrogen indicator;
- Ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system to detect sand deposits.
An examination of the lungs and liver is carried out if disturbances in the acid-base balance (acidosis) are diagnosed. In such circumstances, the examination includes:
- blood test from an artery for the total amount of all blood anions;
- analysis of blood from an artery for total carbon dioxide tension;
- blood test for corticosteroids.
Changing your diet
Treatment of uric acid diathesis is impossible to imagine without diet therapy. It is based on a sharp restriction of proteins and salt in the diet, but an increase in the content of “slow” carbohydrates. You will have to give up fatty and fried foods, meat, sweets and canned food. The diet must include fresh vegetables and fruits, a variety of cereals, vegetable oil and nuts.
Dairy products and eggs are allowed to be consumed no more than twice a week, as they negatively affect the functioning of the kidneys. The total calorie content of the daily diet should be 2-3 thousand kcal. If there is a need to normalize weight, this indicator can be changed up or down.
Moderate physical activity is recommended to maintain a balance between calories expended and calories consumed. For example, walking, running or cycling. Morning exercises are especially useful. However, you should not be too zealous and strain the body. Otherwise, physical activity may have the opposite effect and increase the urate content in the urine.
Treatment in adults and children
Before starting therapy, it is important to search for the root cause that contributed to the occurrence of uric acid diathesis. If the cause is excessive protein consumption, then the basis of treatment is proper dietary nutrition. When kidney stones are detected, drug treatment is resorted to. Medicines are prescribed that break down urates. Diuretics (diuretics) are used to increase urine flow. For greater treatment effect, the doctor prescribes complex therapy with medications and physical therapy methods. If necessary, treatment is used to eliminate symptoms, vitamin or mineral treatment.
Consequences and prognosis of the disease
The natural history of uretheria can cause the formation of urate stones, which is a serious burden on the kidneys. Doctors call kidney failure with complete organ failure as a serious complication of hyperuricuria.
Complex hyperuricosuria can cause acute nephropathy: urate deposits in the kidneys and urinary tract and causes partial or complete obstruction of the genitourinary organs.
With a healthy and balanced diet, attention to your well-being and health, the prognosis for recovery is positive. The main thing is to strictly follow the course of treatment prescribed by your doctor.
Diet for uric acid diathesis
Diet plays a major role in the treatment of uric acid diathesis. The diet involves limiting the consumption of foods rich in purines. However, this should not affect the calorie content of a serving; on the contrary, the latter increases to 2800 kcal per day. The following products are excluded:
- alcoholic drinks;
- canned food;
- chocolate ingredients;
- smoked, legumes and dishes made from them;
- taking mineral waters with a high calcium level;
- fatty meat and fish varieties;
- mushrooms;
- spicy foods and spices;
- rich first courses;
- strongly brewed teas, coffee, cocoa;
- products with yeast components;
- spinach, radish, sorrel.
The dietary menu includes foods with vitamin and alkaline indicators, namely:
- plant food;
- dairy products;
- butter and vegetable oils;
- seaweed;
- cereals in the form of porridges and soups from wheat, buckwheat, rice and oats;
- mineral water with alkalis;
- sprouted cereal seeds;
- bran;
- nuts;
- eggs;
- fruit drinks;
- vegetable soups;
- dried fruits.
How to treat?
Treatment therapy should begin with the organization of a diet. Without it, even taking pills will be ineffective, because metabolism will not return to normal. Alkalinizing foods should be included in the diet:
- vegetables fruits;
- dairy products;
- vegetable oils;
- butter;
- seaweed;
- whole grain porridge;
- mineral water;
- fruit drinks, compotes;
- nuts;
- vegetarian soups.
Foods containing purines should be severely limited or completely eliminated. This includes smoked meats, canned food, pork and beef, mushrooms, legumes, tea, coffee, and alcohol. Among the vegetables that are harmful are sorrel, spinach, radishes, and cauliflower. You should add water to your diet - up to 2 liters/day. The amount of salt, on the contrary, is sharply reduced (according to doctor’s prescriptions).
Treatment of the pathology involves taking medications to lower uric acid levels. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed medications that alkalize the urine. Most often, the doctor prescribes the following medications:
- Blémarin;
- Soluran;
- Urocyte;
- Kalinor.
For gout, the drug Allopurinol is introduced into the course of therapy; the same medicine will be useful for uric acid diathesis. It inhibits the production of uric acid and normalizes metabolism. Also, to improve overall metabolism, the patient may be prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes, which the doctor selects individually (depending on the results of a biochemical blood test).
Herbal treatment will also benefit the patient. To remove excess salts, kidney herbs with a diuretic effect are used - bearberry, wheatgrass, knotweed, lingonberry leaf, rose hips. Infuse them in a thermos (a spoonful of raw materials per glass of water), drink 100 ml three times a day in courses of 3-4 weeks. Physiotherapy is also indicated for many, especially for chronic inflammatory processes in the kidneys (microcurrents, magnetic therapy, ultraviolet radiation).
Treatment with traditional medicine
In the treatment of urate diathesis with folk remedies, diuretic herbs are used that are capable of breaking down urate salts. Among such plants are: knotweed grass; birch leaves and birch sap; parsley roots, celery, corn silk, asparagus; elderberry fruits and others. If a chronic infection in the urinary tract is detected during the treatment of uric acid diathesis, they resort to herbs with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic properties. Therapy with folk remedies lasts about 2 months. Recipes:
- Take 5-6 grape leaves, rinse and peel thoroughly. Place the leaves on the bottom of a glass jar and pour in 175 ml of boiling water. Keep in a water bath for 5-7 minutes. After cooling, strain the tincture. Take half a glass 3 times a day after meals.
- Take a tablespoon of dried black currants and pour them into a thermos, pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours. Strain the tincture. Drink 2-3 times a day, regardless of meals.
urolithiasis - The most interesting things in blogs
With certain disorders of kidney function, excess water accumulates in the tissues, which manifests itself on the body in the form of edema, and this increases your weight, or, on the contrary, this water may not be enough, which can lead to premature aging of the skin and its dryness. Therefore, it is necessary to take timely care of the treatment of this important filter, even for aesthetic purposes.
The easiest way to determine kidney function. After eating beets, your urine should not turn red or pink.
Prevention and treatment of urolithiasis and urolithiasis is impossible without a properly selected diet (diet therapy) and periodic monitoring of the acid-base state of urine.
A rational diet helps restore normal metabolism and maintain homeostasis.
The reaction of urine determines the possibility of stone formation:
urate - in an acidic environment, oxalate - in a neutral-acidic environment, phosphate - in a more alkaline environment.
Using pH test strips (litmus paper) or an inexpensive handheld electronic pH meter, you can easily, quickly and accurately monitor your urine's response to a selected diet. Positive pH dynamics can serve as a criterion for the correctness of the chosen diet or treatment.
A urine pH value below 5.0 indicates that it is strongly acidified, and above 7.5 indicates that it is strongly alkaline. If the pH level fluctuates between 6.0-6.4 in the morning and 6.4-7.0 in the evening, then your body is functioning normally.
The most optimal level is slightly sour, in the range of 6.4-6.5.
For example, uric acid stones virtually never occur when the urine pH is greater than 5.5, and phosphate stones never form unless the urine is alkaline. The best time to determine your pH level is 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. Check the pH level 2 times a week 2-3 times a day when treating urolithiasis.
KIDNEY STONE DISEASES AND DIET THERAPY
Treatment methods
The main treatment for uric acid diathesis is a diet that limits protein and salt intake. It is accompanied by a significant increase in daily fluid intake.
A sodium-restricted diet helps:
- reducing its excretion from the body;
- reducing the amount of mononarium urate formation;
- decreased calcium excretion in urine.
Medicines used for treatment are aimed at:
- alkalinization of urine and reduction of uric acid content (Kalinor, Urotsit, Potassium citrate, Policitra - K, Soluran, Blemaren);
- xanthine oxidase inhibition, which prevents the formation of uric acid (Allopurinol);
- stimulation of metabolic processes (vitamin and mineral complexes with microelements);
- stimulation of the diuretic process with folk remedies (infusion and decoction of knotweed, bearberry, rosehip, lingonberry leaf, elecampane).
Uric acid diathesis is treated with homeopathic remedies (Lycopodium, Causticum).
To alleviate the condition, physiotherapeutic methods such as
- darsonvalization;
- ultrasound therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- magnetic-laser and laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- singlet oxygen therapy.
The best results occur when different treatment methods are combined.
Complications
If you neglect treatment of uric acid diathesis, there is a risk of developing serious complications, such as:
- formation of stones and sand due to increased concentration of urate salts;
- renal failure;
- problems with the functioning of the digestive system;
- uric acid infarction.
If the moment is missed and the disease progresses, the following may appear:
- urate nephropathy;
- gout;
- joint diseases.
Further development of the disease leads to disruption of the functions of all body systems and at the same time affects the mental state of the patient.
Consequences of urolithiasis
If a person has kidney MCD, and what it is, how the condition manifests itself, he does not know, the disease may not be detected in time. This will lead to the development of complications: acute nephropathy, urolithiasis, problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract system, as well as the risk of developing uric acid infarction.
With advanced renal pathology, all organ systems suffer, especially the central nervous system, which is responsible for a person’s psychological health. The positive thing is that all consequences are eliminated without surgical treatment.
Signs of uric acid accumulation
Signs of urolithiasis are clearly expressed. The main one is severe pain in the lumbar back. When the stone moves, the pain spreads to the entire abdomen. Therefore, the pathology can be confused with an exacerbation of appendicitis or ulcers.
Symptoms accompanying the phenomenon:
- painful bowel movements;
- the presence of blood and urates in urine;
- lack of desire to eat and sudden weight loss;
- poor sleep;
- weakening of the body, nausea, constipation;
- colic in the kidney area, tachycardia;
- fever, severe headache.
With urolithiasis, a person does not control his emotions and is often irritated. If you do not see a doctor promptly, seizures may occur. Signs may not appear all the time, but only when the condition worsens.