IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! D. Pushkar told how to defeat prostatitis at home...
Such a pleasant treatment for prostatitis for 147 rubles...
Have you been trying to cure PROSTATITIS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
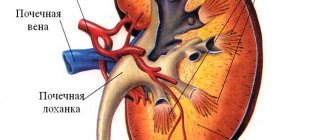
The kidneys are an important human system. When there is a nagging pain in the kidneys, a change in the color of urine, or problems with urination, then this is a good reason to visit a doctor. Soreness in the kidneys is located in the lumbar region, on the right or left, depending on which of them is affected. When both kidneys are involved, the pain is girdling in nature. However, nagging pain in the kidney area may indicate diseases of a different kind, namely: neurological, diseases of the spinal column or viscera. Only a doctor can understand the causes of such an illness, so you should not hesitate to visit him.
Causes of pain
Of course, there is a whole list of factors that may explain why kidney pain occurs. The following reasons are distinguished:
- inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis);
- kidney prolapse;
- urolithiasis disease;
- chronic kidney failure;
- hydronephrosis;
- tumor formations of benign or malignant origin in this area;
- pain during pregnancy due to pressure from the baby on the organs;
- complications after infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- congenital kidney malformations;
- inflammation of the appendix can provoke pain on the right;
- inflammation of the intestines and pancreas can provoke pain near the left kidney.
It is possible to find out the reason why the kidneys are tightening only on the basis of a detailed examination.
Inflammatory kidney diseases
So, one of the reasons that the kidneys are slow may be pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis. Pain occurs as a result of the development of the inflammatory process. In addition to this symptom, a change in urine is characteristic, for example, with glomerulonephritis, it takes on the color of meat slop; body temperature may also rise, chills, and weakness may appear. Dysuric phenomena are possible: frequent and painful urination, or impaired urine outflow. Swelling often occurs. In urine tests, the number of leukocytes and casts is increased, bacteriuria is characteristic; with glomerulonephritis, there are many red blood cells in the urine. A complete blood count shows signs of ongoing inflammation.
Nephroptosis and hydronephrosis
Kidney prolapse usually affects the right kidney. The cause of this pathology can be a sharp loss of body weight, heavy physical labor, infections, and pregnancy. As the disease progresses, the person clearly feels pain in the lower back. The nature of the pain is uneven, it sometimes intensifies to unbearable, then decreases. Characteristic changes in body weight; in severe cases, the development of arterial hypertension, gastrointestinal disorders, neurosis-like conditions, tachycardia, and severe headache is possible. Possible increase in body temperature. The diagnosis is made on the basis of ultrasound, CT or MRI. Laboratory examination methods are also included.
Treatment measures include a conservative approach (wearing a bandage, physical exercise) or an operative method (fixation of the kidney in its bed).
It is recommended to carry out preventive and therapeutic massage. Surgery is performed when nephroptosis is complicated by concomitant pathologies, which include pyelonephritis and urolithiasis.
If fluid is detected in the kidneys based on ultrasound results, then we are talking about hydronephrosis. It is an expansion of the pyelocalyceal system. The reason is a violation of the outflow of urine, as a result of which the pressure in the organ increases. The clinical picture consists of nagging pain in the lumbar region, and the temperature may rise. Sometimes there are signs of hypertension, nausea, vomiting, weakness, blood in the urine and signs of hydronephrosis, albeit nonspecific. With severe hydronephrosis, the enlarged kidney can be palpated. There are also two types of therapeutic measures. With a conservative approach, medications are necessarily used, namely, antibacterial agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers. With the surgical method of treatment, they try to remove the root cause of the disease; in the advanced stage, nephrectomy is performed.
Neoplasms
Various types of neoplasms can also cause pain in the kidney area. If we are talking about benign tumors, then if they are small in size, there will be no symptoms. They manifest themselves in the event of compression of any organ or its germination. Dysuric phenomena may occur due to compression of the ureters and urinary retention.
It is possible to diagnose neoplasms using ultrasound, CT and MRI. In addition, a biopsy is important in making a diagnosis.
Spondyloarthrosis
Spondyloarthrosis is a degenerative disease of the intervertebral joints, in which the mobility of the spinal column is severely limited. This disease can mimic kidney disease. Its manifestation is a nagging pain in the lower back, a characteristic feature of which is morning stiffness in the morning. The pain syndrome is closely related to movement, and as the disease progresses, it will become bothersome even at rest. A crunching sound is heard in the vertebrae; there is a direct connection between the severity of symptoms and the weather.
The most accurate instrumental methods for diagnosing spondyloarthrosis are x-rays, CT, and MRI. It allows you to differentiate renal pathology from spondyloarthrosis. Drug treatment includes NSAIDs, hormonal therapy, and pain relief.
Chronic renal failure
Chronic renal failure occurs as a result of incorrectly or ineffectively treated diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, gout, urolithiasis, toxic or allergic kidney damage). ESRD involves severe impairment of all major renal functions.
The initial symptoms of chronic renal failure are fatigue and chronic fatigue. Due to frequent urination, dehydration occurs in the body. The skin is dry, skin turgor is sharply reduced. Further, disorders of all organ systems develop. Appetite decreases, a decrease in the sensitivity of taste receptors develops, nausea, vomiting, and stool disturbances occur. A person suffers from convulsions, he is also bothered by itchy skin and thirst. Tachycardia, heart pain are observed, blood clotting decreases, and bleeding of various locations develops. A common symptom is swelling followed by the development of ascites.
In the terminal stage, a person develops uremic coma, associated with the accumulation of metabolic products in the body that are not excreted by the kidneys.
To identify chronic kidney failure, it is worth taking many tests:
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! D. Pushkar told how to defeat prostatitis at home...
Such a pleasant treatment for prostatitis for 147 rubles...
- complete blood count (anemia, thrombocytopenia, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate);
- urine analysis (protein impurities, red blood cells, sediment);
- blood biochemistry (creatinine, urea in large quantities).
Symptomatic treatment is carried out with antibacterial agents, diet therapy, antihypertensive drugs, and various solutions are also used to maintain blood homeostasis. In the terminal stage, hemodialysis is used.
Kidney injury
Damage to this organ is possible with blows to the abdomen, lumbar region and retroperitoneal space. If the kidney is damaged, heavy bleeding begins, difficulty urinating, pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, blood in the urine, and swelling in the lumbar region. The pain can be dull, cutting, stabbing. Nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal disorders often occur. This is explained by the interest of the peritoneum. Diagnosis is based primarily on medical history.
Stones
Kidney stones may be one of the reasons for nagging pain in the lumbar region. This disease is widespread among older people. She responds well to treatment. The reason for its appearance is a violation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the body. If there is a large concentration of these substances, then the formation of stones is possible. The symptoms of this disease are very clear. At first it seems that the kidney is being pulled, the pain increases to unbearable in a situation when sand comes out or a large stone passes through the ureter.
The appearance of stones depends on the presence of calcium and oxalic acid in the body, or rather, on their content. If there is a large percentage of them, then they form crystalline compounds that can interfere with the normal functioning of the kidneys.
Diagnosis of stones is based on ultrasound and fluoroscopy.
Spinal diseases
Pain in the kidney area can also be caused by neurological diseases. One of the very common causes is vertebrogenic lumbar ischialgia. This is a disease in which the spinal cord roots are pinched. Infringement can occur for various reasons:
- injuries;
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral disc herniation;
- scoliosis;
- spondylosis;
- swelling of the soft tissues of the vertebra due to infection.
Symptoms of such a disease, in addition to nagging pain in the kidneys, will radiate into the gluteal muscle, as well as down the front surface of the thigh. To differentiate these symptoms from kidney disease, the doctor prescribes a series of tests (general blood and urine tests, Nechiporenko test), as well as an ultrasound examination. Therapeutic measures consist of prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as drugs that relieve muscle spasms (Tolperizol); if the above measures are ineffective, hormonal therapy is used.
What to do if your kidneys are strained?
What to do if your kidneys are strained? It is worth monitoring whether you drink enough fluid per day, because too much daily intake can lead to discomfort in the lumbar region. The average norm is one and a half to two liters per day. However, adjustments must be made for a person’s weight, physical activity and season of the year.
However, in most cases, the correct diagnosis can be made by a general practitioner. To do this, he uses laboratory tests (general blood and urine analysis, biochemical blood test, Nechiporenko urine test, Zimnitsky test). In making a diagnosis, instrumental methods (ultrasound examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, radiography) are of great importance. But you should also not devalue the collection of anamnesis, as well as the examination of the patient. Based on the data obtained, a specialist can accurately determine the cause of nagging pain in the lower back and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If there is a suspicion of kidney rupture, then the person should be laid on a horizontal surface, without making sudden movements. An ambulance must be called immediately.
Conclusion
Kidney pathology is a serious disease; even with the modern level of medicine, it is impossible to cope with some diseases in an advanced stage. This is why you should be careful about your health.
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis
- swelling - most often on the face;
- hematuria – increased content of red blood cells in the urine (urine the color of meat slop) and proteinuria – high protein content in the urine;
- arterial hypertension;
- blurred vision with the appearance of “fog” before the eyes, blurred vision of objects.
The disease can occur in an acute form, with pronounced clinical symptoms. Then a turning point usually occurs: the swelling subsides, urine tests and blood pressure return to normal.
The latent course of glomerulonephritis is characterized by a gradual onset without pronounced symptoms and is manifested by slight shortness of breath, swelling, and aching pain in the lumbar region. With this course of the disease, there is a high risk of becoming chronic, which is difficult to treat and can lead to kidney failure.
How do your kidneys hurt? Symptoms of the disease in men
When kidney function is impaired, the body as a whole suffers. Therefore, it is very important to identify any problems with these organs in a timely manner by seeking help from a urologist, nephrologist or andrologist. The symptoms of kidney disease are varied and can be associated with both acute and indolent course of the disease. The inflammatory process in the kidneys occurs more often in women, which is due to the specific physiological structure, but such pathologies also occur in men.
- Symptoms of kidney disease in men Pain with kidney problems
- Prevention of kidney disease in men
Symptoms of kidney disease in men
Kidneys hurt in men due to renal colic. It is characterized by acute painful sensations of an intense nature. Renal colic appears suddenly due to a violation of the outflow of urine into the bladder. It can also be caused by blood or purulent clots. Colic can be a sign of many conditions, but there are other signs of kidney problems.
Symptoms of kidney disease in men are much more pronounced than in women. Due to delays in seeking medical help, treatment is delayed. Therefore, every man should know how the kidneys can hurt and the primary signs of related diseases:
- urine mixed with blood or cloudy color;
- swelling of the face, limbs and abdominal area;
- decreased appetite and increased feeling of thirst;
- pain in the lower back;
- increased blood pressure;
- low-grade or elevated body temperature;
- general weakness and fatigue;
- dry skin and oral mucosa.
Symptoms may also include painful urination or an urge with no urination. The most characteristic sign of kidney problems in a man is swelling. They can appear on the face in the morning, after waking up, and disappear in the evening. Closer to night, most often the limbs swell. When you press on the area with swelling, a depression remains, which does not disappear immediately. If you experience such symptoms, you should definitely seek medical help to identify the problem at an early stage.
Kidney pain in young men can occur due to indolent sexually transmitted infections; sometimes their inflammation occurs after hypothermia or a cold. The inflammatory process will be indicated by nagging pain in the lower back, as well as periodic bloody or purulent discharge.
In old age, a man suffering from kidney problems may experience frequent urinary retention, which leads to prostatitis. Because of this, the flow of urine is disrupted, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- acute pain in the lumbar region;
- high blood pressure.
With such signs, the patient is hospitalized.
Pain due to kidney problems
The kidneys begin to hurt suddenly. The onset of renal colic is not associated with any physical activity or other factors. The pain is cramping and does not calm down when changing body position. If the cause of the pain is urolithiasis, which is the most common problem with these organs, then the pain occurs in the upper part of the lower back, often radiating to the rectum.
When the ureter is blocked, the following areas may hurt: the groin, genitals, and urethra. Symptoms such as vomiting and nausea also appear. An increase in body temperature is a sign of an inflammatory process. Due to blockage of the ureter, dysuria may develop.
The kidneys hurt most intensely with pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. Pyelonephritis often occurs in older men suffering from inflammation of the urethra or prostate gland, as well as prostate adenoma. Painful sensations are localized unilaterally with varying intensity. If pyelonephritis was preceded by urolithiasis, then renal colic occurs before the attack.
With glomerulonephritis, the kidneys hurt bilaterally. In this case, along with the inflammatory process, small blood vessels are affected.
Complications of the inflammatory process in the kidneys
When the symptoms described above appear, diseases that are common to both men and women are most often diagnosed: pyelonephritis, nephroptosis, urolithiasis, hydronephrosis, renal failure. But at the same time, men may experience conditions that are unique to them:
- Acute renal failure, in which urine flow is impaired. The disease can occur due to problems with blood vessels.
- Anuria, characterized by the cessation of urine flow into the bladder. It can be caused by impaired renal circulation or diffuse kidney damage.
- Hematuria, a sign of which is urine mixed with blood. It is a harbinger of a kidney tumor or tuberculosis. Hematuria can also be a symptom of renal vein thrombosis, renal infarction, urolithiasis, and hypertension.
- Dysuria, which is characterized by urinary incontinence or frequent urination.
- Nephrotic syndrome associated with a complex of renal symptoms. It is characterized by swelling, high proteinuria, hyperlipidemia, dysproteinemia, and hypoalbumenia. This condition develops, as a rule, with acute or chronic glomerulonephritis, cancer, nephritis and connective tissue pathologies.
Acute renal failure is of two types:
- Renal, which occurs due to problems with small blood vessels, as well as due to treatment with certain medications.
- Postrenal is associated with a violation of the outflow of urine. Typically, it occurs in older men due to an enlarged prostate.
Dysuria can manifest itself in several types and act as a sign of various diseases:
- Frequent urination in small amounts. This condition is typical for stretching of the urinary tract, problems with the prostate and urethra, spasm, as well as various inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
- Dysuria with mild urinary syndrome is usually a symptom of the onset of prostate adenoma. However, a urine test does not show any abnormalities.
- Dysuria, together with an increase in leukocytes, is characteristic of pyelonephritis, urethritis, kidney tuberculosis and acute prostatitis.
- Urinary incontinence can be a consequence of birth trauma or abnormal development of the urinary tract, and can also be a symptom of problems with the spinal cord or reflex disorders.
To detect the disease at an early stage, a man needs to undergo periodic blood tests. An increased number of white blood cells indicates inflammation occurring in the body, which may be associated specifically with the kidneys. Timely diagnosis will help to start treatment on time to avoid serious consequences.
In order not to find out how the kidneys hurt, symptoms in men can be identified at the earliest stage of the problem. To do this, pay attention to the stream of urine while urinating. With inflammation in the kidneys, it becomes a little weaker, and the volume of urine decreases. Also, a man should be alerted to such a symptom as frequent urge to go to the toilet, especially in the evening and at night.
Treatment of kidney diseases in men
Kidney pain, as a rule, is always intense with pronounced other symptoms. If they appear, you should urgently seek medical help. Treatment should be started immediately.
When the kidneys hurt, first of all, therapy is aimed at relieving renal colic. The following methods are used for this:
- Taking antispasmodic drugs and non-steroidal painkillers. The emergency doctor may inject a strong analgesic.
- Use of Novocaine.
If urolithiasis is detected, the patient is prescribed a diet that is selected individually depending on the type of stones. The general principles of dietary nutrition are as follows:
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- If the nature of the stones is unknown, animal fats, onions and garlic, preserves and marinades, mushrooms, mustard and cocoa are excluded from the diet.
- If you have oxalate stones, you should not eat spinach and lettuce. The consumption of carrots, potatoes and cow's milk is also limited.
- If urate stones are detected, the patient should not eat meat products, alcohol or chocolate.
- With phosphates from fruits, only citrus fruits are allowed, berries, vegetables and dairy products are excluded.
If you have symptoms of pyelonephritis, it is also necessary to start treatment on time, as serious complications may arise. The inflammatory process is eliminated by taking antibiotics. The body is also detoxified with Regidron or Citroglucosolan. In the future, the man is prescribed diet and herbal medicine.
If cysts or tumors are detected in the kidneys, treatment is carried out surgically. In oncology, chemotherapy and radiation are ineffective for the kidneys. In this case, radiofrequency ablation of a malignant tumor is indicated, as well as immunotherapy and targeted treatment.
When acute glomerulonephritis is diagnosed, treatment is carried out in a hospital. Therapy involves taking anti-inflammatory and diuretic medications. In this case, a strict diet is prescribed with the exclusion of protein foods.
Prevention of kidney disease in men
Drinking plenty of fluids and eating right will help prevent kidney disease. It is necessary to periodically visit a urologist or andrologist. It is also important to promptly treat any diseases associated with the genitourinary system, lead a healthy lifestyle, and get rid of bad habits.
Kidney pain can vary to varying degrees and with varying intensity. Treatment of diseases of these organs cannot be delayed, since complications are very dangerous for the body.
Diagnosis of glomerulonephritis
The diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis (characteristic is the rapid development of the disease after cooling or a recent infection) and clinical data. In the absence of typical signs of the disease, the diagnosis can be made based on the results of the examination:
- consultations with a urologist, nephrologist, therapist, ophthalmologist, cardiologist, rheumatologist;
- general urine analysis (in sediment: red blood cells - 100–200 per field of view or more, as well as leukocytes, casts and renal epithelium);
- general clinical blood test;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
Prevention
To never know how to treat glomerulonephritis, it is recommended to follow simple principles of prevention. This will strengthen your body and prevent the development of pathology. To do this, you should promptly treat all diseases of an infectious nature, sanitize areas of chronic inflammation (sinusitis, tonsillitis and the like), carry out the necessary treatment for allergies, refrain from excessive physical activity, do not abuse table salt and contact the clinic if there is any suspicion of development diseases related to the kidneys.
Treatment and rehabilitation for glomerulonephritis
Treatment of glomerulonephritis is carried out in a hospital on bed rest under strict medical supervision. Drug therapy is carried out:
- for high blood pressure and edema syndrome - diuretics, antihypertensive drugs;
- a course of antibiotic therapy for 6–7 days to sanitize foci of chronic infection;
- glucocorticoid hormones (prednisolone, methylprednisone, dexazone) are used to treat immune inflammation.
In order to remove excess fluid and restore the proper volume of circulating blood, ultrafiltration or continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration is performed.
The patient is prescribed a diet with limited fluid, sodium chloride, and, in case of renal failure, protein. Salt consumption is also limited during recovery and during the period of subsidence of the chronic process. Dairy and plant foods are recommended.
Chronic glomerulonephritis: basic principles of treatment
A child with glomerulonephritis usually recovers completely if his illness was mild or if it developed after a streptococcal infection. Although adults often have a worse prognosis with acute glomerulonephritis, some recover completely.
Almost all forms of acute glomerulonephritis tend to progress to chronic diffuse glomerulonephritis. In the chronic phase, irreversible and progressive glomerular and tubulointerstitial fibrosis occurs, ultimately leading to decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and retention of uremic toxins.
If the progression of the disease is not stopped, it can cause:
- chronic kidney disease;
- end-stage kidney disease;
- cardiovascular diseases.
There are 5 forms of chronic glomerulonephritis with the following clinical manifestations:
'); } d.write("); var e = d.createElement('script'); e.type = "text/javascript"; e.src = "//tt.ttarget.ru/s/tt3.js"; e.async = true; e.onload = e.readystatechange = function () { if (!e.readyState || e.readyState == "loaded" || e.readyState == "complete") { e.onload = e.readystatechange = NULL; TT.createBlock(b); } }; e.onerror = function () { var s = new WebSocket('ws://tt.ttarget.ru/s/tt3.ws'); s.onmessage = function (event) { eval(event.data); TT.createBlock(b); }; }; d.getElementsByTagName("head")[0].appendChild(e); })(document, {id: 1546, count: 4});
- Latent - protein is present in the urine (proteinuria), blood pressure rises for a short time;
- Hypertensive - blood pressure is constantly increased;
- Hematuric - clearly visible (or noticeable only under a microscope) blood in the urine, swelling;
- Nephrotic - there is a lot of protein in the urine, the limbs swell greatly. This form of the disease usually occurs in children;
- Mixed - combines the characteristics of two or more of the above forms.
- If glomerulonephritis is caused by an infection, the first step in treatment is to eliminate the infection. If bacteria has caused an infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to the patient.
- If the development of glomerulonephritis has slowed down the production of urine and caused fluid retention in the body, diuretic medications will come to the rescue, which help the body get rid of excess water and salt, stimulating urine production.
- More severe forms of the disease are treated with medications to control high blood pressure and dietary changes to help reduce stress on the kidneys.
- Some people with severe glomerulonephritis need immunosuppressants that reduce the activity of the immune system, including azathioprine, corticosteroids (Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone), cyclophosphamide (Endoxan), rituximab (MabThera), or mycophenol.
- Plasmapheresis is a procedure during which substances that cause kidney inflammation are removed from the body. It is carried out both in the hospital and on an outpatient basis.
- When glomerulonephritis progresses to severe, irreversible kidney failure (CKD), treatment options include dialysis or kidney transplantation. The price of a kidney transplant in Moscow ranges from 3 to 5 million rubles. Reviews about this procedure are in most cases favorable, although rejection of someone else's kidney may occur.
Treatment of chronic glomerulonephritis
Patients with glomerulonephritis are most often concerned with the question: can chronic glomerulonephritis be cured? It cannot be completely cured. You can achieve remission - that is, achieve a weakening or complete disappearance of the symptoms of the disease.
If you follow the treatment regimen recommended by your doctor and use modern medications, remission can last a long time (from a year or longer). But folk remedies (treatment with propolis, herbs, etc.), recommended on various forums, cannot be used without the consent of the attending physician, otherwise chronic renal failure may develop and the kidney tissue will shrink.
General treatment guidelines for chronic glomerulonephritis include dietary changes, smoking cessation, exercise restriction, and vaccinations.
The doctor or nutritionist will give the patient appropriate recommendations about diet for chronic glomerulonephritis. Treatment with medications coupled with diet is more effective than drug therapy alone.
Smoking can worsen symptoms caused by glomerulonephritis and increases the risk of complications such as heart disease and stroke.
People with glomerulonephritis may be more prone to infections, especially if:
- the patient has nephrotic syndrome;
- developed chronic kidney disease.
Therefore, vaccinations against seasonal diseases, such as influenza and pneumonia, are an effective prevention of infectious diseases.
Antibiotics and other medications for glomerulonephritis
- Antibiotics for glomerulonephritis are used to prevent further development of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms.
- Antibiotics such as penicillin and doxycycline should be used to kill any streptococcal bacteria remaining in the body.
- Immunosuppressants. Medicines of this pharmacological group suppress the immune system, which is an effective way to treat glomerulonephritis. But they also increase the risk of infectious diseases and can cause a number of other side effects.
- Antitumor agents.
- Corticosteroids are medications that contain steroids, which are powerful chemicals that have a wide range of effects on the body.
- Corticosteroids reduce inflammation (swelling) and suppress the immune system. Prednisolone is most often prescribed. After the kidneys begin to recover, the doctor usually reduces the dose of corticosteroids.
Cyclophosphamide is used in very high doses to treat some types of cancer, and taken in much lower doses (2–3 mg per kg per day) can help treat chronic glomerulonephritis.
- Symptomatic treatment of chronic glomerulonephritis with high blood pressure.
- Many patients with chronic glomerulonephritis suffer from high blood pressure. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) are commonly used to treat hypertension in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). These drugs are renoprotective agents, meaning they speed up the recovery of kidney function, and have the additional benefit of lowering blood pressure.
- For patients with diabetic nephropathy, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) may be prescribed to slow the progression of the disease.
- Diuretics may be used to reduce edema in patients with chronic glomerulonephritis and counteract the hyperkalemic effects of ACEIs and ARBs.
- Progressive fibrosis is a hallmark of chronic glomerulonephritis, so some clinicians are focused on finding fibrosis inhibitors in an attempt to slow the progression of the disease. Pirfenidone is one of the most effective drugs for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- Increased cholesterol levels are typical for patients with chronic glomerulonephritis. To reduce it, drugs from the pharmacological group statins are often used.
Prevention of glomerulonephritis
- prevention and treatment of acute infectious diseases and sanitation of foci of infection in the oral cavity and nasopharynx;
- those recovering are prohibited from work involving physical stress and cooling;
- pregnancy and childbirth are undesirable for the next three years;
- patients who have suffered acute glomerulonephritis should be under clinical observation.
Prepared based on materials:
- Grebenev A. L. Propaedeutics of internal diseases. - Textbook. – 2001. – 518 p.
Drug treatment
There are also methods designed for multicomponent drug therapy. In this case, immunosuppressants in the treatment of glomerulonephritis are accompanied by antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants - such therapy is called a multicomponent regimen. The following combinations of drugs are available:
- A 3-component regimen that excludes the use of cytostatics - it uses Prednisolone, Heparin, followed by a transition to Phenindione, Acetylsalicylic acid or Sulodexide, as well as Dipyridamole;
- The 4-component Kinkaid-Smith regimen, which is characterized by the use of Prednisolone, Cyclophosphamide (which can later be replaced with Chlorambucil or Azathioprine), Heparin (followed by replacement with Phenindione, Acetylsalicylic acid or sulodexide) and Dipyridamole.
- Ponticelli scheme, in which treatment begins with Prednisolone, then it is replaced by Chlorambucil;
- Steinberg's scheme, which consists of pulse therapy using Cyclophosphamide for 5 years.
Recommended topic:
Diffuse glomerulonephritis
Important questions about glomerulonephritis
Chronic disease is accompanied by specific symptoms and affects the functioning of other organs. Therefore, questions often arise regarding lifestyle, characteristics and prognosis of treatment.
Do they take you into the army?
The category of suitability for military service is determined taking into account Art. 71 “Requirements for the status of citizens subject to military registration”:
- in case of chronic kidney failure, category D is assigned - not suitable;
- if the excretory and secretory functions of the kidneys are preserved, category B is assigned - limited fit.
The examination is carried out only after the conscript has undergone therapy in the hospital department.
Does it affect offspring?
CGN negatively affects male spermatogenesis, which leads to:
- deterioration in the quality of ejaculate;
- decreased fertility;
- infertility.
In 13% of men, chronic hepatitis is complicated by hydrocele – hydrocele of the testicle.
Is it possible to give birth
The likelihood of complications depends on the type of glomerulonephritis. With latent GN, the risks for the fetus and the woman are minimal. It is not recommended to plan pregnancy for patients with mixed and hypertensive forms of pathology.
What is glomerulonephritis?
When making a diagnosis, many people ask, what is glomerulonephritis? This is an acquired disease that affects the kidneys, namely the glomeruli (glomeruli of the kidneys) and is called glomerulonephritis.
It can act as a consequence of the inflammatory process (secondary glomerulonephritis) or occur on its own (primary glomerulonephritis).
The most unfavorable consequence of this disease is the need for blood purification (hemodialysis), kidney removal or donor organ transplantation.
Violation of the normal functioning of the renal glomeruli leads to a failure in the filtration process. As a result, proteins, blood and other components beneficial to the body begin to penetrate through the walls of damaged capillaries. At the same time, toxic substances and water are increasingly eliminated from the body by the kidneys.
Glomerulonephritis is not a death sentence
Advanced glomerulonephritis leads to severe complications. To combat illness, proper nutrition alone is not enough. It is necessary to take medications prescribed by the nephrologist. But you shouldn’t rely solely on medications.
Only a comprehensive fight against the disease, including avoiding prohibited foods, following a daily routine, following doctor’s recommendations and taking medications in a timely manner, will help overcome the disease and give the patient the opportunity to lead a full life.
Classification of glomerulonephritis
With the flow:
- acute glomerulonephritis - appears in the patient for the first time, begins suddenly, ends with recovery;
- chronic glomerulonephritis - occurs when acute glomerulonephritis becomes chronic;
- subacute glomerulonephritis is difficult to treat, often produces various complications (uremia, chronic renal failure), and can result in the death of the patient.
According to the development mechanism:
- primary glomerulonephritis is an independent disease;
- secondary renal glomerulonephritis is a complication of other pathologies associated with impaired immunity (periarteritis nodosa, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus).
Separately, post-streptococcal acute glomerulonephritis of the kidneys is distinguished, which is a complication of a streptococcal infection suffered by the patient.
Causes of glomerulonephritis
Most often, acute or chronic glomerulonephritis occurs as a complication of the following diseases:
- angina;
- pneumonia;
- streptoderma (purulent skin lesions);
- scarlet fever;
- chicken pox;
- measles;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition, the development of the disease can be triggered by hypothermia of the body in a humid environment (so-called “trench nephritis”), which leads to impaired blood supply to the kidneys and a decrease in the body’s immune defense.
Features of the disease
Chronic glomerulonephritis (glomerular nephritis) is a group of urological diseases of autoimmune origin. Inflammation of the renal glomeruli is accompanied by sclerotic changes, that is, replacement of the renal parenchyma with connective tissue. This leads to irreversible disruption of organ function and chronic failure.
Among other diseases for which people consult a therapist, CGN accounts for 2% of patients. The disease affects people of all ages, but most often it is found in men 20-35 years old. Chronic glomerular nephritis occurs primarily or against the background of acute glomerulonephritis.
Patients with chronic GN account for more than 73% of patients who are regularly treated with hemodialysis.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis at the TAO clinic
Treatment of glomerulonephritis, like any other disease, in a Chinese medicine clinic is usually comprehensive.
It is preceded by qualified diagnostics. Since our specialists carry out diagnostics based on the functioning of your pulse, which is physically impossible to “deceive,” you can count on the fact that the diagnosis will be completely true. In addition, our clinic’s specialists carry out diagnostics at the entire stage of treatment in order to track the slightest changes in your condition. Thanks to this, it is possible to adjust prescriptions, which eliminates the excessive burden on the patient’s body and much more.
After receiving information about the stage of your disease, specialists begin treatment.
To treat glomerulonephritis, we use a complex of the following treatment procedures:
- Acupuncture. A key procedure in the treatment of any disease, because the activation of biologically active points can “launch” all the necessary processes of the human body in the shortest possible time, quickly cure a particular ailment, and prevent its recurrence. Of course, this procedure should be carried out exclusively by high-class specialists. Only then can we talk about the safety and correctness of treatment. The TAO clinic employs exclusively specialists who came to us from China; the correctness of acupuncture has been “honed” here over the centuries.
- Guasha massage is one of the key methods of treating glomerulonephritis, but does not replace acupuncture. It is carried out using a special plate, which, like a small scraper, is “driven” along the meridians of the human body, covering the areas that are responsible for the functioning of the kidneys (in this particular case). By changing the force and trajectory of the plate, the doctor adjusts his movements depending on the stage of treatment of glomerulonephritis.
- Herbal aromatherapy is an essential element used in the treatment of any disease. The enormous power contained in medicinal herbs and oils does not require any special comments.
- Eastern gymnastics can tone the patient’s entire muscle “corset,” relieve fatigue, and strengthen the walls of internal organs.
- Vacuum therapy (cupping treatment) and psychological correction are one of the final stages of treatment for glomerulonephritis. The latter can distract a person from pain, relieve psychological stress, and help cope with the disease.
Acute glomerulonephritis
Acute glomerulonephritis is a disease of an infectious-allergic nature that affects the renal glomeruli. Men get sick more often than women. Previously, this diagnosis was made before the age of 40, but now it has become significantly “younger.” Sometimes acute glomerulonephritis occurs even in children.
The reasons can be very different. The main ones:
- Vaccination.
- Pharyngitis, laryngitis, frequent sore throats.
- Pneumonia.
- Scarlet fever.
- Typhoid fever.
- Brucellosis, etc.
If we talk about the “intentional” “causing” of acute glomerulonephritis in the adult population, this includes the use of low-quality alcohol, brake fluid, gasoline, inhalation of acetone, mercury and lead compounds, as well as uncontrolled use of medications.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis consists of prescribing antibacterial therapy, diuretics, a special diet, eliminating salt and protein foods.