Many patients with urolithiasis (UKD) have virtually no health problems. Until a stone migrating through the urinary tract clogs the lumen of the ureter and causes acute urinary retention. This condition develops quite often and in medicine is called renal colic. How a stone in the ureter manifests itself, and how such a condition is diagnosed and treated: let's figure it out.
Types of stones
Stones are dense formations found in the cavitary organs and excretory ducts of the glands, which are formed mainly due to an imbalance of salt and colloids in the urine, provoked by a number of reasons (malnutrition, excessive use of medications, the presence of various diseases, etc.) .
Before taking any measures to remove stones from the ureter, it is necessary to identify what type they are. Depending on their chemical composition they are divided into:
- Struvite – characterized by the ability to quickly increase in size.
- Oxalates are the most dangerous, since due to their spiked structure they often injure the mucous membranes of organs, including bleeding,
- Urates are the most easily soluble.
- Phosphates - despite the fact that they have a loose structure, are quite dangerous, as they grow to large sizes.
- Carbonates.
It should be noted that for each type of these formations it is necessary to apply individual treatment methods and methods of removal from the damaged organ.
Preventive measures
Any disease, including urolithiasis, is easier to prevent than to treat.
The most important preventive measures:
- drinking at least two liters of clean water per day. Plain water removes sand, microorganisms, mucus, etc. from the body, which contributes to the coordinated and stable operation of the entire excretory system;
- eating plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits. In winter, when there is little fresh food, it is worth drinking a decoction or infusion of rose hips, carrot, pomegranate or pumpkin juice, and infusions of dried fruits every day;
- if there are any inflammatory processes in the bladder or kidneys, they must be treated correctly and on time;
- It is important to lead an active lifestyle, walk a lot in the fresh air, and eat right. Quitting alcohol and smoking reduces the risk of disease several times;
- If you have already encountered problems with the kidneys, then it is periodically necessary to use special herbal preparations. As a rule, they include herbs that have a mild antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and diuretic effect, which is an excellent prevention of any diseases of the human urinary system.
Causes of stones and characteristic symptoms in men and women
There is a fairly extensive list of factors influencing the formation of stones in the ureter. These include:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Infectious and non-infectious inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
- Disturbances in the renal pyelocaliceal and endocrine systems, in the structure of the ureter.
- Insufficient fluid intake.
- Poor nutrition.
- Stagnation of urine.
- Calciferol deficiency.
- Bad habits.
- The occurrence of pain in different locations: - when a stone is located in the upper or middle part of the ureter, acute cramping pain appears in the lumbar region and lateral abdomen, which may not stop for up to 12 hours, intoxication, sedimentation of proteins, a large number of leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine, – when moving to the lower part of the organ, pain manifests itself intensely, radiating to the scrotum and groin, similar to inflammation of the epididymis.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Abnormal bowel movements, in which diarrhea alternates with constipation.
- Headache.
- Fever.
In men, stones can form under the influence of diseases such as prostatitis and pyelonephritis.
The presence of stones in the ureter does not manifest itself in any way until the outflow of urine through this organ is disrupted. Small stones can even be expelled along with biological fluid without any symptoms.
In case of blockage of the ureter with a stone, patients will experience various manifestations, and they are different for both sexes.
Symptoms of ureterolithiasis in men depend on the location of the formation and its mobility.
For example, fixed stones that partially block the ureteral ducts practically do not cause any negative manifestations. This is due to the fact that in this case a compensatory reaction occurs, reducing the pressure on the kidney.
Moving stones can completely block the duct of the organ, which will provoke a decrease in the outflow of urine, swelling of the kidney tissue and an increase in the size of the kidneys. The patient is “signaled” to these failures by symptoms such as:
In women, this disease is indicated by symptoms that they often do not notice, since they are similar to the “harbingers” of menstruation. Such manifestations are:
- Feelings of strong pressure in the lower abdomen.
- Frequent urge to urinate and nagging pain in the lower abdomen with it, there is no feeling of emptying the bladder.
In addition, severe pain appears in the lumbar region, which radiates to the perineum and labia, sweating, chills, dry mouth, the appearance of blood and particles of renal epithelium in the urine.
The essence of the problem
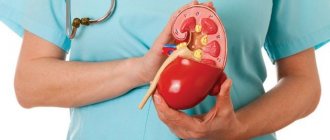
Urolithiasis is a common pathology of the organs of the excretory system, which develops against the background of metabolic disorders. ICD 10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision) assigned it the coding N20-N23. The main manifestation of the disease is the formation of calculi - crystallized salts of organic acids, the size of which ranges from 1 - 5 mm to several centimeters.
The most common site for stone formation is the kidney. It is there that the deposition of salts of uric, oxalic or phosphoric acid occurs, their combination and the formation of a dense calculus. Among the causes and risk factors for such pathological changes are:
- unhealthy diet (eating fatty, fried, pickled foods, large amounts of meat, refined sugar, leafy vegetables - sorrel, rhubarb);
- poor composition of water, the presence of many impurities and salts in it;
- vitamin deficiency, insufficient intake of vitamins with food;
- gout and other metabolic diseases;
- osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, disruption of the processes of mineralization and demineralization of bones;
- chronic gastritis, enteritis, pancreatitis, pathologies of the processes of absorption and assimilation of food;
- dehydration, which can occur due to insufficient fluid intake in the body, an infectious disease, or overheating;
- chronic diseases of the kidneys and organs of the urinary tract - pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis.
For some time, the formed calculus remains in the kidney cavity. Then, under the influence of various factors (for example, drinking a large amount of liquid, physical activity), it leaves the CLS and continues its movement.
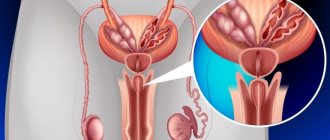
Normally, the diameter of the ureters does not exceed 4-5 millimeters. In addition, throughout this hollow muscular tube there are physiological constrictions. Therefore, if a small stone, the transverse size of which is 2-3 mm, freely leaves the body naturally, then a formation with a diameter of more than 6 mm often gets stuck and leads to the development of symptoms of renal colic. In this case, the patient’s condition will be alleviated only if the stone comes out on its own or is removed surgically.
Stones in the ureter in men and women are most often found in areas of greatest narrowing. Formations with a diameter of 7 mm or more are often localized:
- not far from the renal orifice, at the point where the ureter exits the pelvis - most often large stones with a diameter of up to 10 mm block the lumen here;
- at the intersection of the ureter with nearby blood vessels;
- in the distal part of the ureter, at the point where it flows into the bladder - a stop in the lower third of the ureter is typical for stones with a diameter of up to 6 mm (less often 8 mm).
Note! A large stone at the mouth of the ureter quickly leads to the development of hydronephrosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
After the appearance of symptoms of ureterolithiasis, the patient needs an urgent visit to a urologist , who will diagnose the pathology and give further instructions regarding its treatment.
The initial action of a specialist in diagnosing the location of stones is palpation, after which the doctor can prescribe studies in the form of:
- General urine analysis to determine the number of leukocytes, red blood cells, salts and pH level.
- Biochemical blood test.
- Bacteriological culture of urine.
- Identification of the type of pathogens.
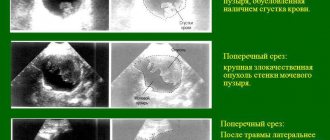
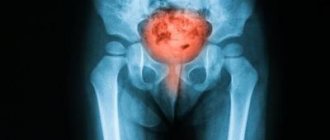
- X-ray radiation of the ureter to determine the location of cameos and their sizes.
- Endoscopic examination, computed tomography and ultrasound of the kidneys.
Taking into account the results of these studies, the urologist prescribes individual therapy to help remove the stones.
What measures can you take at home?
For colic, which is caused by stones in the ureter, you can take an antispasmodic (for example, no-spa) and an anesthetic drug. If the pills help relieve the pain, try removing the stone.
To do this you need to do the following:
1. Prepare an infusion that has a diuretic effect:
- from dill seeds;
- from bearberry or half-burnt;
- from horsetail.
The infusion needs to be cooled, strained and poured into a convenient decanter. (The detailed process of preparing herbal tinctures is described in the article: herbs for kidney stones)
If you don’t have time to prepare, simply pour a liter of boiled water generously acidified with lemon juice.
2. Take a warm bath for 20-30 minutes and at the same time drink the prepared drink.
3. Jump vigorously for about 10 minutes. You can run up the stairs or jump rope.
If after all this, during urination (all these recommendations apply to both men and women), the stone does not come out, repeat the procedure from the beginning. You can do them every day until you get results.
Warning: if you have a fever or blood in your urine, you should not take a bath. In this case, do not delay visiting a doctor.
Methods for removing stones
To remove stones, 2 areas of treatment are used, depending on the complexity of the situation and the size of the formations, namely:
The first direction is used in the presence of stones with a diameter of 2-3 mm that do not block the ducts. Such stones can come out on their own, so medications such as:
- "Nifedipine" or "Tamsulosin" to speed up the passage of stones.
- “No-shpa”, “Drotaverine” to relieve spasms.
- Ibuprofen to relieve pain and inflammation.
You can use traditional medicine and drink diuretic decoctions, which include herbs such as horsetail, dill and corn silk.
This therapy involves attending physiotherapy and exercise therapy, as well as following a special diet that limits the consumption of foods with oxalic acid (cabbage, spinach, nuts, currants and legumes).
In the presence of large stones, active therapy is used, using a method such as lithotripsy (removal of stones by crushing). It comes in the following types: remote, contact, pneumatic, laser, ultrasound and percutaneous.
In the most severe cases, surgical intervention is necessary.
How to expel a stone from the ureter at home?
Any methods of influence, even if they seem simple and harmless to you, can be practiced after consultation with a urologist. Any traditional methods should only be a means of additional therapy to the treatment prescribed by a doctor. Unfortunately, there are many tragic cases where people tried to get rid of the stone on their own, thereby causing irreparable harm to their own health.
If stones have formed in the ureter, treatment at home can be carried out with the approval of the attending physician:
Pine twigs and cones, rose hips, horsetail, oat straw are the best products on which you can prepare warm baths. You need to take two handfuls of the product, or a mixture of them, pour three liters of boiling water, simmer on fire for ten minutes, leave for three hours. The strained infusion is poured into a warm or hot bath, in which the person should spend a quarter of an hour. It is not recommended to take the procedure longer;
medicinal baths.- juice therapy. Black radish infused with honey helps a lot, the norm is: a tablespoon of the liquid formed in the cavity of the vegetable three times a day. It is permissible to drink parsley or carrot juice with lemon in equal proportions, the norm is a glass a day. The juices of the following plants and fruits are suitable: watermelons, lemons, beets + carrots, birch, pomegranates. They need to be diluted with water and taken 200 ml three times a day. It is advisable to start with small doses, gradually increasing to the norm of two hundred milliliters;
. Option 1: chop six tablespoons of rose hips, simmer on fire for seven minutes, after pouring three glasses of boiling water. Infuse, take a glass an hour after meals. Option 2: pour a tablespoon of knotweed herb into a glass of boiling water, leave, divide into three doses, and drink throughout the day. Option 3: mix 250 ml of boiling water and a tablespoon of dry crushed leaves of the oregano. Leave for 8 hours, drink a third of a glass three times a day.
special herbal teas
Why is it so important to consult a doctor before taking any folk remedies? Often the stones are located in the kidneys, and pushing them to move can cause renal colic and acute inflammation.
Percutaneous percutaneous lithotripsy
This method is more applicable for removing stones located in the kidneys. However, sometimes it is also used to remove stones from the upper third of the ureter, if there are contraindications or technical difficulties for DLT, as well as after several ineffective attempts at non-contact lithotripsy.
The essence of the method is that the renal pelvis is punctured through the skin in the lumbar region under X-ray control, a pyeloscope is inserted into it, which is passed further into the ureter. Using micro-instruments, stone extraction or contact lithotripsy is performed, followed by extraction.
The operation is performed under epidural anesthesia.
Consequences and possible complications
Stones entering the ureter obstruct urinary outflow, which can lead to the development of the following complications:
- pyelonephritis;
- sepsis;
- hydronephrosis;
- renal failure;
- pathological strictures of the ureter.
Prevention of urolithiasis
To prevent stones from forming, you must follow a diet and drink as much fluid as possible. It is recommended to filter water before drinking. If mineral metabolism is disrupted, consultation with an endocrinologist is required. A disease such as gout is a reason to give up alcoholic beverages.
The genitourinary system of men is more susceptible to stone formation than women. It is difficult to say where such discrimination against men based on urolithiasis comes from. Most likely, this is due to men’s addiction to spicy and salty foods, which leads to excess acid and salts in urine and disruption of acid metabolism. However, let’s talk about the reasons for stone formation in more detail. The ureter itself does not produce stones. They enter it from the kidneys.
Traditional medicine methods
To remove the stone, methods of conservative and surgical medicine are used. What type of treatment the doctor will insist on depends on the size and composition of the stone, as well as the patient’s health condition.
Conservative treatment
This type of therapy is prescribed by a doctor if the examination shows that the size of the stone is small - up to 3 mm. This type of treatment is called “expectant” because it is aimed at creating conditions for the stones to pass independently.
Tactics include:
- taking special medications (urolytics, antispasmodics, antibiotics);
- water load (the daily volume of water drunk during this period should exceed 2 liters);
- special diet;
- physical therapy and physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, inductothermy, amplipulse, etc.).
Diet therapy
This method is based on the exclusion from the diet of foods that initiate stone formation, and on the increased consumption of those that contribute to the dissolution and removal of uroliths from the urinary tract. Sediment and solids form from highly concentrated urine, so diet should prevent this.
The diet is selected depending on the sediment that formed the stones: phosphates, oxalates, proteins or urates.
The diet should contain many vitamins, the emphasis is on foods high in vitamin A: pumpkin, carrots, broccoli.
Hot and overly spicy foods should not be consumed, and the water regime should include at least 2 liters of water and drinks per day.
Foods that should not be eaten contain a lot of oxalic acid:
- sorrel;
- White cabbage;
- parsley;
- spinach;
- nuts;
- beans;
- sour currant;
- figs, etc.
Weekly fasting days on watermelon, melon or cucumbers are recommended.
A detailed diet and the timing of its use are selected for the patient by the doctor, taking into account the dynamics of the reduction of the stone or its movement towards the exit.
Self-administration of this diet for a longer period is not advisable, as it can lead to a deficiency of certain vitamins and minerals in the body.
Instrumental methods
If conservative methods are ineffective, instrumental methods are used to eliminate uroliths.
There are several types of surgical operations that can urgently relieve a patient of a calculus in the ureter ranging in size from 3 to 20 mm. The operation is quite complex and can only be performed by a highly qualified urologist surgeon. It is prescribed when the kidney is in danger of death from increased hydraulic pressure and stagnation of urine.
The initial stage of such an abdominal operation is the installation of a catheter through the bladder to establish the outflow of urine. Then, using special tools, stones or sand are removed from the lumen.
The specific type of operation chosen depends on where the mechanical obstruction is stuck in the ureter and its size:
- Ureterolithoextraction - removal of stones larger than 6 mm using a trap loop. Such a loop is inserted into the lumen using a urethroscope and the stone is removed.
- Ureterolithotripsy is performed in cases where renal colic cannot be relieved, so it is not planned. It is used for stone sizes over 10 mm. In addition to open, laparoscopic ureterolithotripsy is used, after which the rehabilitation period is much shorter.
- Pyelolithotomy is an operation without large incisions; 3-4 small holes in the skin are enough for it.
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy - used for coral formations with a large number of processes above 2 cm, located in the upper part of the ureter. A nephroscope is inserted through an incision in the lower back, which is used to control the grinding of solid elements lodged in the lumen. After grinding, these particles are evacuated using surgical forceps.
In addition to the indications, the choice of type of operation is also determined by the capabilities of the clinic, its instrumental and hardware base, as well as the qualifications of the surgeon.
In case of dense jamming and large size of the stone, a minimally invasive method of remote lithotripsy is recommended - preliminary crushing, as a result of which smaller parts are formed. These parts can be removed from the body independently or with the help of medical instruments.
There are two types of lithotripsy:
- Ultrasonic is used for stones of low density. Using ultrasound, it is possible to achieve a particle size of up to 1 mm, which allows them to pass freely along with urine without pain.
- Laser lithotripsy is performed when the density of the stone structure is high. After crushing with a laser, the fastest rehabilitation period is observed. Within a day after crushing, the patient can be discharged from the hospital. Almost immediately after discharge, the person returns to the normal rhythm of life.
At the moment, they are increasingly resorting to closed operations without significant damage. This is facilitated by a short recovery time, no need for long-term anesthesia and a quick return to work.
External shock wave lithotripsy (ESWLT, ESWL)
The essence of the method is in its name. Remote means carried out at a distance, without contact with the stone itself. Shock wave means that the destruction of a stone occurs when exposed to microwaves of such energy that can break a solid conglomerate into small fragments. High and low pressure waves are generated at high frequencies, which destroy the crystal lattice of the stone.
There are special lithotripters for DLT. This device is a table for the patient with a focusing system built into it (this is a lens system that very specifically focuses energy on an object) and a generator of the wave energy itself. Modern lithotripters use electrohydraulic, electromagnetic, piezoelectric or laser energy.
The main patient population for extracorporeal lithotripsy are patients with X-ray positive stones up to 2 cm in size located in the kidneys, as well as the upper and middle third of the ureter. There are also contraindications for this method.
Absolute contraindications:
- Pregnancy.
- Presence of an artificial pacemaker.
- Reduced blood clotting.
- The presence of anomalies of the skeletal system that do not allow adequate positioning and focusing.
- Kidney tumor.
Relative contraindications:
- Obesity of the 4th degree.
- Height is above 2 m.
- Stones larger than 2 cm.
- Urate stones (X-ray negative).
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
- Inflammatory process in the urinary tract.
- Kidney failure.
- Menstruation.
- Cystine stones (very high density).
How does the remote stone crushing procedure work?
External lithotripsy is very convenient for both doctors and patients. It does not require long-term hospitalization and can even be performed on an outpatient basis.
Although DLT is a non-invasive method, anesthesia is still required, since the patient may experience quite severe pain during crushing. In addition, the duration of the procedure is about 40-60 minutes. Intravenous anesthesia is usually used. But spinal anesthesia is also possible, or sedation with tranquilizers is sufficient.
The patient is placed on the table on his stomach or back. A prerequisite for successful stone crushing is the accuracy of the installation under X-ray television or ultrasound control. Between the device and the patient's body there is a bag filled with water.
In an aquatic environment, waves conduct well, and when they encounter an obstacle in the form of a dense stone, they disintegrate it. The stone breaks up into small fragments, which are then removed on their own over a certain period of time (sometimes up to a month).
In many cases, lithotripsy is performed after preliminary stenting of the ureter. That is, during cystoureteroscopy, a stent is placed in the ureter, which should bypass the stone. This prevents complete obstruction of the ureter and disruption of the outflow of urine after crushing the stone. Installation of a stent for ureteral stones increases the effectiveness of ureterolithotripsy by 20%.
The stent is left in the ureter until the bulk of the stone fragments have completely passed.
Main complications of SWLT
- Acute obstruction of the urinary tract as a result of the early sudden passage of a large number of fragments.
- A “stone walk” is a chain of many fragments in the ureter that leads to renal colic.
- Injury to the renal parenchyma and ureter by shock waves.
- Micro- and macrohematuria (blood in the urine, a normal phenomenon if it goes away after a few days).
- Acute pyelonephritis.
- Damage by shock waves to other internal organs, intestines.
Sometimes one session of DLT is not enough to adequately crush the stone. In such cases, it can be repeated after 5-7 days. The number of repeated sessions of DLT should not exceed 3-5, depending on the type of lithotripter. If ineffective, alternative methods are used.
After a lithotripsy session, moderate pain, frequent urination are possible, there is almost always an admixture of blood in the urine, low-grade body temperature is possible, and the release of sand and small stones when urinating.
Symptoms subside within a few weeks. After surgery, plenty of fluids, antispasmodics and antibacterial drugs are usually prescribed.
Patient reviews of remote non-contact lithotripsy are mostly positive. Patients are attracted by the non-invasiveness of the method and the possibility of performing it on an outpatient basis. The effectiveness of the method reaches 90%. Complications occur quite rarely.
The cost of crushing ureteral stones with ultrasound ranges from 15 to 45 thousand rubles. Laser lithotripsy is somewhat more expensive - from 30 to 50 thousand rubles.
Remote lithotripsy is also possible under the compulsory medical insurance policy free of charge.
Video: lithotripsy in the treatment of urolithiasis
Preparing for surgery to remove stones
In addition to the above examinations, in preparation for surgery it is necessary to carry out:
- Blood test for clotting.
- Electrocardiography.
- Examination by a therapist and cardiologist.
- Gynecologist examination for women.
- Fluorography.
- Testing for antibodies to HIV, hepatitis and syphilis.
If bacteriuria is detected before surgery, treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs to which the isolated microbes are sensitive.
Each method has its own indications and contraindications.
Traditional methods of treatment
Since the phenomenon of a stone getting stuck in the ureter has been known to people for a long time, traditional medicine has in its arsenal quite effective methods of combating this phenomenon. The only caveat with this approach is that these methods can only be used for chronic conditions and cannot help in any way with acute manifestations.
Traditional medicine involves correcting nutrition and taking herbal medications for a long period, which precludes their use in cases of obstruction and urinary retention in the kidneys. But sometimes they help avoid surgery.
The main measures of self-treatment are aimed at:
- changing the chemical parameters of urine to reduce or dissolve uroliths;
- exclusion of urinary tract infection;
- reduction of ureteral spasms.
To remove stones, daily use of infusions of the following herbs and plants is recommended:
- horsetail;
- half-burnt;
- bearberry;
- dill seeds;
- knotweed;
- juniper cones;
- lingonberries.
If it is not possible to prepare such infusions, their function will be performed by a drink of water and lemon juice, which must be consumed throughout the day.
Good results are obtained by drinking natural birch sap without sugar. You need to drink one glass in the morning, afternoon and evening. This recipe is very effective, but only if taken for a long time - at least 1 month.
A necessary condition for successful removal of stones is a sufficient supply of water to the body, so during treatment it is important to drink a lot of drinks every day, as well as eat watermelons and melons, if the season allows.
Taking warm baths every day followed by active physical movements for 10 minutes has worked well: jumping in place, going up and down stairs, jumping rope. This contributes to the initial displacement of the urolith from the place where it stopped.
It is imperative to reduce the amount of salty, sweet and fatty foods, and completely eliminate smoked foods.