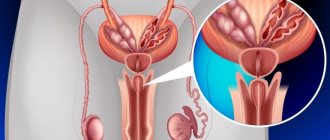
The problem of involuntary urination worries many people: women, men, and children face this problem. There are many reasons for this pathology; it is not a matter of any single explanation. Very often, such a delicate problem is caused by cystitis - inflammation of the bladder wall.
Sometimes, along with the cure of cystitis, the problem of urinary incontinence is solved, but sometimes it is triggered by a disease, and the pathology remains.
Menopausal patients most often complain to a urologist about urinary incontinence. Urgent urinary incontinence is a component of the traditional symptoms of cystitis. The disease manifests itself in the involuntary leakage of urine, which occurs during the urge to urinate.
It is difficult to say what is worse for the patient – pain and pain or urinary incontinence. And many patients are afraid: what if cystitis goes away, but enuresis does not go away? There really is such a possibility.
Cystitis
Cystitis is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. There are many reasons for the development of this disease:
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Fungi
- Injuries
- Oncological pathologies of the bladder
- Autoimmune processes in the body
- Surgical interventions.
Bacteria are considered a common cause of cystitis. The pathology most often affects women. The structure of a woman’s urinary system has features, the main one of which is the urethra.
In women it is much shorter than in men, and also has a funnel shape, which allows bacteria to quickly penetrate the bladder.
Risk group
In representatives of the stronger sex, this disease usually appears after 40 years. But most often women from 16 to 65 years old encounter it. The predisposition is due to the anatomical features of the body. The urethra, through which most of the infection enters, is much shorter than in men. In addition, the openings of the anus, vagina and urethra are quite close to each other, which also facilitates the easy penetration of pathogenic or opportunistic bacteria into the urinary system.
At risk are people who do not follow the rules of personal hygiene and who have frequent, promiscuous, unprotected sexual intercourse. The infection can be caused by girls who practice specific sex (anal alternating with vaginal) or those who wash themselves incorrectly (from the anus to the urethra).
Cystitis is a companion of pregnant women and women during menopause, which is associated with hormonal disorders in the body. Children do not get it so often, and it is almost impossible to find a baby or newborn child with a similar diagnosis. It appears mainly in girls 4–12 years old due to insufficient hygiene.
Why does cystitis occur?
Cystitis is a bacterial disease. It can be caused by several groups of bacteria, such as E. coli or chlamydia, but regardless of the nature of its origin, inflammation always occurs in the bladder and urethra.
The disease is manifested by frequent and painful urination in small quantities, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. Advanced disease can cause complications such as pyelonephritis.
This disease occurs more often in women than in men. This is due to the peculiarities of the constitution of the female body. A short urethra, as well as a small distance between the genitourinary organs and the anus, increase the risk of bacteria entering the urethra and causing disease. Urinary incontinence is also 10 times more common in women, for the same reason.
Treatment
In most cases, cystitis develops as a result of penetration of pathogenic flora into the organs of the genitourinary system. That is why complex therapy is being developed, and it contains antibacterial, antifungal, and painkillers. It is very important to include products that will reduce bladder activity, such as Driptan or Spazmex.
To restore damaged nerve fibers, neotropic medications are prescribed, among which Picamol is the best, and vitamin-mineral complexes. To improve the condition, it is recommended to take warm baths. You can strengthen the muscle fibers of the pelvic organs by performing a set of Kegel exercises.
From traditional medicine recipes, as a supplement, you can use a decoction of such a common herb as chamomile. it is a natural antiseptic, so it helps to quickly stop inflammation. It is taken both internally and through douching and sitz baths. The duration of the course is 1-2 months, but first you should make sure that you are not allergic to plants.
To quickly relieve acute symptoms, which almost always bother women with cystitis, as well as to eliminate problems such as urinary incontinence, doctors advise taking Canephron. This medication is often part of complex therapy for various infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
Its peculiarity lies in its natural composition. Due to the unique combination of active components, it is possible to quickly get rid of various painful and uncomfortable sensations in the bladder, as well as normalize the frequency of the urge to defecate. The medicine should be taken three times a day.
Symptoms of cystitis
Symptoms include urinary disorders and deterioration. Disorders of urination manifest themselves in the form of increased frequency, as well as the appearance of pain and burning along the urethra. In the first days of illness, body temperature rises to 39˚C. Subsequently, with adequate treatment, it decreases to normal.
If treatment is not carried out, it remains at the same numbers, or decreases to 38˚C. Patients complain of increased fatigue, sweating, and decreased appetite.
Urine with cystitis changes color, impurities of pus or blood appear. Because of this, it becomes reddish or cloudy with a greenish tint.
Symptoms
Cystitis, which causes urinary incontinence, can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- inability to voluntarily control bladder emptying in unpredictable situations;
- feelings of incomplete urination when residual urine is present in the organ;
- painful sensations during deurination;
- frequent desire to go to the toilet at night, as well as uncontrollable leakage of urine throughout the night;
- the appearance of cloudy urine mixed with blood;
- pain of varying intensity in the lower abdomen.
In some cases, vomiting and nausea occur. If the temperature remains above 37.5 degrees, you must urgently go to the doctor so as not to get complications in the form of pyelonephritis and kidney disease. To begin with, the woman receives a referral to a gynecologist, who, after an initial examination, refers to a urologist.
Disease prevention measures
It is recommended to follow certain rules:
- Treatment of urinary incontinence in elderly women with folk remedies and medications
- Change your underwear daily and limit yourself to wearing tight clothes. During your menstrual cycle, you need to change tampons and pads frequently.
- You should drink from one and a half to two liters of water per day. You will have to limit your drinking, smoking, spicy and salty foods. Preference should be given to vegetables and fruits.
- Immunoprophylactic measures should be taken for the body to maintain the bladder’s immunity and avoid hypothermia.
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle (at the workplace), you should warm up your muscles once an hour, devoting ten to fifteen minutes to gymnastics.
- Do not allow the bladder to overflow.
Prevention
Prevention of urinary incontinence involves timely treatment of cystitis, pyelonephritis and other diseases of the excretory system.
Measures to prevent incontinence include getting rid of bad habits, maintaining an active lifestyle, and hardening the body.
To prevent cystitis, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- Maintain personal hygiene, change underwear daily. Limit wearing things that are too tight. During menstruation, change sanitary tampons and pads more often.
- Drink 1.5−2 liters of water every day. Do not abuse hot, salty, spicy foods and alcohol. Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Carry out immunoprophylaxis of the body, which, in turn, strengthens the local immunity of the bladder mucosa. Avoid hypothermia.
- When working sedentarily, you need to do a warm-up every hour for 10-15 minutes.
- Avoid overfilling your bladder.
- Stop smoking.
Herbal medicine is of great importance in the prevention of cystitis. Bearberry, horsetail, and thyme have a diuretic effect, thereby promoting the removal of harmful organisms through the urinary tract. Cranberries protect the walls of the bladder from E. coli, one of the main causative agents of cystitis. Many medicinal plants have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects: St. John's wort, lingonberry leaf, lavender and others.
Urinary incontinence with cystitis
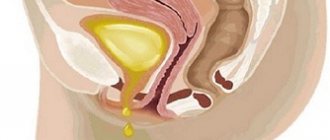
Sometimes patients experience urinary incontinence due to cystitis. This occurs in cases where the inflammatory process involves areas of the bladder that are close to the urethral sphincter.
Inflammation leads to impaired sphincter muscle tone and is unable to hold urine. Voluntary discharge occurs even when there is a small amount of urine in the bladder. Incontinence leads to unpleasant consequences:
- Irritation of the skin of the perineum and external genitalia. Urine is an aggressive medium and leads to damage to the surface layer of the skin. This risks the affected skin becoming an open gate for infection. This condition threatens the development of pustular processes.
- Sphincter dysfunction. Prolonged atony of the sphincter muscles leads to dysfunction. This condition is the cause of the development of deficiency. In such a situation, incontinence will continue even after recovery.
Mechanism of development of urinary incontinence
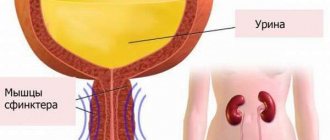
As the bladder fills, its walls stretch and mechanical receptors are irritated.
The excitation impulse travels along the nerve fibers to the spinal cord. The spinal control center is controlled by brain structures. In the cortex, there is an “assessment of the situation, a solution to the problem” with a “search for the toilet” and sending a “guide to action” back. After “getting permission,” the spinal cord relaxes the external urethral sphincter, and the body ejects urine. After urination, a few milliliters of urine always remain in the bladder.
Emptying occurs through the urethra. In the fair half of humanity, nature hid it in the pelvic cavity. For a strong woman, she brought it out and placed it inside the penis.
Doctors call incontinence the process of uncontrolled urination, when urine “comes out” against desire, “without permission” from the brain.
Incontinence may be caused by the following factors:
- Failure in the functioning of any link in the neuro-reflex regulation of the urination act.
- Changes in the anatomy of the urinary system and surrounding organs, both congenital and acquired.
One of the causes of the condition may be cystitis - inflammation of the walls of the bladder.
Causes and classification
It is worth noting that urinary incontinence in women is a symptom of an advanced disease. Frequent urge to urinate with cystitis can no longer be under the control of the patient, and urine is released randomly. There are many diseases that can cause a woman to experience incontinence:
- Difficult natural childbirth. If the fact of a narrow pelvis in a woman in labor is established, the urethra is injured when the baby’s head, which is large in comparison with the opening, passes through the birth canal.
- Climax. During this period, vaginal tone decreases due to a decrease in estrogen levels. Thus, bladder support is weakened.
- Old age, when the bladder muscles weaken and cannot hold urine.
- Injuries to the pelvic organs, including previous operations, with damage to the nerves of the pelvic floor muscles or bladder. Uterus removal.
- Congenital pathologies of the bladder.
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
- Diabetes. Obesity. Chronic cough.
- Inflammatory processes, tumors or spinal cord injuries.
- Strong physical activity (sports or work).
- Cystitis.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane and increased pressure on the bladder create the problem of urinary incontinence for women. Even with a small accumulation of urine, the nerve endings give a signal about the need to empty the bladder; the signal can be so sharp that there is not enough strength to hold back urine and the patient may spontaneously urinate.
Damage to the bladder requires urgent surgery. After the site of the rupture has been identified, the detected defect in the bladder wall is sutured.
Incontinence is classified according to symptoms:
- Extraurethral. Fistulas between the bladder and vagina, ectopia of the ureter.
- Enuresis is bedwetting in women. Inability to control urine output during sleep.
- Fullness of the bladder, due to difficulty in the outflow of urine (tumor, inflammation, stones).
- Reflex incontinence is a dysfunction of the bladder due to pathologies of the spinal cord.
- Imperative - the occurrence of urges when exposed to external factors (water noise, sudden change in ambient temperature).
- Stressful – characterized by increased pressure on the bladder (during coughing, sneezing, laughing, heavy physical activity).
Incontinence can also occur permanently. It is not uncommon for such symptoms to appear during sexual intercourse or orgasm.
Causes of pathology
Women are susceptible to cystitis more often than men due to the nuances of the anatomical structure. The small distance from the urethra to the anus and vagina and the short length of the urethra lead to inflammation of the bladder when the slightest infection occurs.
More on the topic: How to prepare for an ultrasound of the genitourinary system?
Irritation from the inflamed organ is transmitted to the mucous membrane, damages its surface and reduces the body's immunity. Because of this, the nerve endings transmit incorrect signals, which are deciphered by the brain as a desire for deurination. Such a constant desire is a symptom of cystitis.
The causes of cystitis may be prolonged hypothermia of the body, insufficient hygiene during sexual intercourse and non-compliance with the rules for treating the external genitalia, spicy salty foods in large quantities, long periods of sedentary work, prolonged constipation, and infectious diseases.
If the problem of urinary incontinence is not associated with the development and occurrence of another pathology, then treatment is quick and effective. Pathologies that complicate the situation are surgical injuries, stress urinary incontinence, muscle atrophy, diabetes mellitus and neurological diseases. Against this background, women may have various hormonal or gynecological diseases.
Men also have their own factors that provoke the disease - problems with the genitourinary system, urethra, prostate gland or epididymis. In pregnant women, cystitis develops against the background of changes in hormonal levels and decreased immunity.
What to do if urinary incontinence occurs
If incontinence occurs, treatment requires compliance with additional restrictions and the use of special means.
To restore normal tone of the urethral sphincter, attend physiotherapy sessions.
Electrophoresis shows positive results. Electrical impulses have a tonic effect on smooth muscles, which leads to normalization of sphincter tone.
- Causes, diagnosis and treatment of urinary incontinence in women before and after 50 years of age
Physiotherapeutic measures are the basis for eliminating this unpleasant manifestation. To reduce the irritating effect of urine, liners are used.
Made from fabric or absorbent diapers. An option is precisely absorbent diapers - they absorb moisture and do not release it back, unlike fabric.
If incontinence is severe, then diapers can be used.
Care measures for such patients are aimed at reducing the negative effects of urine on the skin of the perineum and genital organs.
Who is at risk
There is a group of people who are most susceptible to bladder weakness. Women of childbearing age are most often affected. The threat arises due to certain predisposing conditions:
- Anatomical features. After defecation, it is easier for pathogenic microorganisms to penetrate from the rectum into the female urethra than into the male urethra.
- Pregnancy, during which, against the background of decreased immunity and hormonal changes, an enlarged uterus puts pressure on the bladder and impairs microcirculation processes in its walls.
- Childbirth. Irritation of the walls occurs when the catheter is inserted, and possible reflex urinary retention.
- Sexual intercourse contributes to the penetration of the partner’s microflora from the vagina into the urethra.
Consequences of incontinence
Cystitis, as well as urinary incontinence, not only worsen the patient’s physical well-being, but also bring psycho-emotional disorders into the patient’s life. The unpredictability of the next urge to empty the bladder forces such people not to go far from the toilet, stay away from crowded places, and generally deprive themselves of the joys of life.
Inflammation of the urinary tract occurs with the release of an impressive amount of bacteria into the urine, which also brings its own unpleasant aspects: urine has a foul odor, and with constant urination, this “amber” penetrates into clothes and interior items. Therefore, a person is constantly haunted by unpleasant odors, and he thinks that others smell them.
Frequent trips to the toilet at night make the patient's sleep sensitive and easily disturbed. Insufficient night rest deprives a person of vitality, and he constantly looks tired.
Even if such a patient goes out somewhere, he still needs to stay as close to the toilets as possible in order to be on alert at any time.
Treatment of advanced cystitis begins primarily with taking medications that suppress the further development of the inflammatory process. However, it is better to take care of your health in advance than to suffer later.
- Enuresis tablets - a list of drugs for the treatment of urinary incontinence in adults and children
We recommend reading:
Every day, many patients come to see a urologist with the problem of involuntary urination. This pathology predominates in women, especially of retirement age. Urgent urinary incontinence is a symptom of cystitis. It is manifested by involuntary leakage of urine that occurs during a sudden urge to urinate. With cystitis, not only pain occurs, but also discomfort that interferes with a person’s daily life.
What could be the consequences of the pathology?
Pain due to cystitis significantly affects your well-being. The difficulty with urinary incontinence that arises at the same time only worsens the situation:
- The patient is completely at the mercy of his illness and is afraid to go to crowded places. An uncontrollable desire forces me to always keep in mind the layout of public toilets.
- A depressive state develops from dissatisfaction with one’s hygiene.
- The foundations of life are being destroyed. There is a need to give up many familiar things, and problems arise in intimate relationships.
- There is chronic fatigue in the body. The desire to urinate at night makes sleep more sensitive.
- Patients suffering from mental sensitivity begin to feel their own inferiority.
The main consequences associated with uncontrolled urination are manifested in human psychology.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of cystitis, anamnesis is sufficient. To prescribe correct and complete treatment, a number of diagnostic measures are carried out that will help determine the severity and root cause.
The basis of diagnosis is bacteriological examination of urine and ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Bacteriological culture of the flora is needed to determine the type of bacteria that led to the onset of the disease.
This examination helps determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to groups of antibacterial agents. Ultrasound of the bladder and other pelvic organs determines the area of the lesion, as well as the involvement of other organs.
This examination plays a role in predicting complications, and also helps to identify erosive and ulcerative forms of the disease.
These examinations include a general blood and urine test, which are mandatory for all diseases. To detect incontinence, stress tests are performed.
They are carried out through physical activity, which is accompanied by contraction of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. If no urine is released during exercise, this is considered a positive sign.
Diagnosis of the disease
Once a problem with involuntary urination appears, you should not hope that the body will overcome it on its own. In this case, the patient has every chance of getting a chronic form of cystitis, which will regularly worsen and periodically remind itself of itself with urine incontinence. For this reason, in such a situation, you should definitely visit a specialist.
If there is a suspicion of a connection between involuntary urination and cystitis, the doctor will prescribe an examination, which will include laboratory and instrumental studies and the necessary tests. Having identified the cause of uncontrolled urination and made the correct diagnosis, the doctor will determine an adequate therapeutic course.
Diagnosis and treatment
Self-treatment of cystitis does not always have positive results and may lead to a chronic form of the disease in the future. With such an intimate problem, you need to consult a doctor - a urologist or gynecologist (for women). The doctor must conduct a preliminary survey of the patient and special examinations:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- examinations for the presence of infections (Trichomonas; ureaplasma, mycoplasma, Candida fungi);
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (bladder);
- cystoscopy (visual examination of the bladder);
- electromyography (method for studying the neuromuscular system).
When treating urinary incontinence caused by cystitis, a conservative method is used, which in 100% of cases gives a positive result. In the treatment of cystitis, antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, and painkillers can be used. The treatment regimen for urinary incontinence caused by cystitis should be supplemented with drugs to reduce bladder activity (Driptam, Spazmex), neotropic drugs (Picamilon), and vitamin preparations to improve the condition of nerve fibers. Drug treatment is complemented by diet and the use of warm baths to reduce pain. Surgical intervention is used extremely rarely. For women, therapeutic exercises (Kegel exercises) to strengthen intimate muscles will be effective.
Return to contents
ethnoscience
The herb St. John's wort is a reliable remedy for urinary incontinence.
Traditional medicine offers its own methods of overcoming cystitis. Among them, chamomile, bearberry, celery seeds, lovage root, plantain and many others are considered effective. Herbal decoctions are taken orally in courses of 1-2 months. The herb St. John's wort is considered a reliable remedy for urinary incontinence. It is brewed like tea and drunk 1 teaspoon per dose.
Return to contents
"Canephron N"
"Canephron N" is a drug that helps eliminate acute and infectious diseases of the bladder and kidneys. This remedy has an anti-inflammatory effect thanks to extracts of lovage, rosemary and centaury. "Canephron N" eliminates urinary incontinence by relieving inflammation and spasms from the bladder. Take it 3 times a day with water. The presence of herbal ingredients does not cause side effects.
Return to contents
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of urinary incontinence begins with the use of medications that can affect the foci of infection in cystitis that provoked the inflammatory process of the bladder.
Drug treatment
Taking into account the source of the disease, the following can be applied:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antiviral agents;
- antifungal drugs.
The treatment course of cystitis, which is complicated by urea hyperactivity, can be supplemented. In such cases, the doctor prescribes:
- anticholinergic drugs that reduce high bladder activity;
- drugs of the neotropic group, which improve the conductivity of neural signals that control the functioning of the bladder;
- metabolic medications, vitamin complexes that improve the condition of fibers in nerves and muscles.
It is recommended to take sedatives during treatment to help bring balance to the functioning of the nervous system, weakened by the negative manifestations associated with urinary incontinence.
Surgery and minimally invasive techniques are rarely used to treat frequent urination. Experts advise performing special therapeutic exercises that can help restore muscle tone in the pelvic area. Women are recommended to move according to the Kegel technique.
You should not reduce the amount of liquid you drink per day. This will not help solve the problem, and highly concentrated urine can irritate the urinary mucosa.
Do not neglect the opportunity to get rid of uncontrolled urination and cystitis at the initial stage of the problem. Only a competent therapeutic course helps to avoid chronic diseases.
ethnoscience
An excellent remedy for the treatment of urinary incontinence is the herb St. John's wort. It should be brewed instead of tea and taken one teaspoon at each time.
In addition, field chamomile, bearberry, celery seed, lovage roots, plantain and other herbs are popular among people. Prepared herbal infusions should be taken in courses that last from one to two months.
Diagnostics
When incontinence develops with cystitis in women, it is important to establish the true cause of this problem. If the diagnosis is made incorrectly, there is a risk of incorrect treatment, which will lead to blurring of symptoms. This can be prevented by timely contacting a urologist and gynecologist.
The principle of performing ultrasound screening of the pelvic organs. Source: uziwiki.ru
The process of making a diagnosis and developing treatment tactics is as follows:
- Examination of the patient;
- Taking anamnesis;
- Identification of concomitant pathologies;
- Testing (blood, urine, bacteriological culture)
- Ultrasound screening of the pelvic organs;
- Examination of the bladder using cystoscopy;
- Carrying out electromyography.
If urinary incontinence due to cystitis is confirmed, treatment must be carried out using a conservative method. In this case, you can count on a full recovery if you follow all medical recommendations. It is very important not to self-medicate and also to follow a diet.
Treatment methods for cystitis and urinary incontinence in women
Very often, women turn to a urologist with problems of urinary incontinence and involuntary leakage.
This pathology usually appears in females in old age. Urgent incontinence in this case is a sign of damage to the genitourinary system by cystitis. This manifests itself in the leakage of urine, which is not controlled by volitional efforts, and is accompanied not only by pain syndromes, but also by a certain discomfort that reduces a woman’s quality of life.
Many people consider enuresis a “dirty” disease and do not contact specialists at the clinic on time, preferring to look for information in the public domain. Indeed, by searching for “cystitis and urinary incontinence treatment in women,” you can find a lot of information, but this concerns your own health, so you should not treat yourself on your own, with the risk of complications. You need to report the problem to your doctor to receive proper and effective treatment.
Traditional medicine recipes
Not all “grandmother’s” methods will alleviate the condition. A hot heating pad, for example, can increase inflammation and urinary incontinence.
Herbal medicine refers to the methods of traditional medicine. Medicinal plants are used as additional, auxiliary agents and have the same effects as tablets from the pharmacy: antimicrobial, analgesic, immunostimulating, anti-inflammatory.
On the Internet you can read favorable reviews about the use of cranberry juice, alcoholic tincture of bearberry, infusion of celandine in milk, baths with chamomile decoction, infusions of St. John's wort, licorice, juniper, calendula, as well as recipes for preparing various herbal mixtures and preparations. The beekeeping products of Tentorium enterprises have a positive impact.
Alternative medicine methods can cause unpredictable reactions if used inappropriately. You should not experiment on your own body; you should discuss with your doctor the risks and benefits of using traditional methods of treatment.
Development mechanisms
Control of the nervous system over the contractility of the detrusor (muscle tissue of the bladder) does not allow the manifestation of involuntary movements. Inflammatory reactions in the cavity of the bladder lead to failure of the process, regardless of the genesis of the development of cystitis. Against the background of prolonged inflammation in the bladder tissues, the integrity of the mucous membrane of the reservoir cavity is disrupted and the immune defense mechanism is reduced, which causes the development of bladder hyperactivity.
Inflammatory reactions cause irritation of nerve receptors, which give false signals to frequent urination.
Even a slight accumulation of urine in an inflamed bladder can deform the walls of the bladder and become a catalyst for irritation of receptors. Receiving distorted information about the need to urinate, the brain issues a command to muscle contraction of the detrusor muscle. The urge is sometimes so intense that it is simply impossible to control the process of reservoir emptying.
Cystitis and urinary incontinence (UI) can provoke:
- pregnancy, against the background of which the circulatory functions in the bladder walls are disrupted due to compression by the enlarged uterus;
- violation of reflex functions in the process of trauma to the bladder during childbirth;
- thinning of the bladder walls caused by an age-related decrease in estrogen secretion (during menopause);
- pelvic floor incompetence and vaginal prolapse.
Treatment and diagnosis
Treatment of cystitis at home without consulting a doctor often remains ineffective and only worsens the situation when cystitis becomes chronic. The doctor can find out the patient’s medical history and prescribe a number of examinations of the body, including:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, as well as the bladder;
- clinical studies on the presence of candida fungi and infections that could be acquired through sexual contact;
- general analysis of the patient’s biomaterials, blood and urine, for laboratory tests;
- examination using cystoscopy and electromyography;
- diagnostics of nerve endings of organs.
If urinary incontinence occurs due to cystitis, then a conservative method with a medication regimen will be successful in 100% of cases. For this, doctors use antiviral, painkillers, antibacterial and antifungal drugs. The regimen is supplemented with drugs that reduce bladder activity, these are Spazmex and Driptan, as well as neotropin drugs, Picamilon.
More on the topic: Where to get an ultrasound of the bladder?
Experts recommend taking vitamins to maintain nerve fibers in the organ. Treatment with medications is best combined with Kegel exercises for women, which strengthens the intimate muscles. Maintaining proper nutrition during treatment and warm baths to relieve pain symptoms have also proven to be excellent.
Causes of enuresis
If it is precisely established that involuntary urination is a consequence of cystitis, then the causes of its occurrence include:
- some features of the anatomy of the female body (short urethra, etc.);
- improper adherence to personal hygiene rules, including insufficient hygiene procedures after sexual intercourse;
- frequent hypothermia;
- leading a sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive consumption of spicy foods and foods;
- various injuries to the genital organs;
- constipation that continues for a long period;
- infectious lesions;
- birth injuries and postpartum complications;
- weakening of the perineal muscles.
Urinary enuresis is often accompanied by pathologies that significantly complicate treatment, delaying the time of complete recovery. These include:
- urinary incontinence due to the patient’s complex stressful condition;
- injuries received during operations on the pelvic organs;
- diabetes;
- neurological diseases;
- gynecological diseases;
- hormonal disorders and diseases.
Causes of the pathological process
The bladder has the appearance of a hollow muscular organ that is capable of changing its volume and location under the influence of the fluid accumulated in it. In the absence of pathologies, a person feels the fullness of the urinary bladder when it is half full. When ¾ full, the brain receives signals about the need to empty the bladder.
The process is thought out by nature down to the smallest detail. Control by the nervous system and the contractility of the muscular tissues of the urinary organs prevent involuntary urination.
Cystitis, regardless of origin, is manifested by inflammation of the walls of the bladder. Prolonged and periodically repeated irritation during the inflammatory process leads to disruption of the integrity of the mucosa and reduces local immune mechanisms. These factors cause hyperactivity of the urinary organ.
Nerve receptors, under the influence of irritating factors, send unauthorized signals, which forces women to visit the toilet more and more often. A sharp urge to urinate during cystitis occurs when there is a slight accumulation of urine. Brain cells, receiving false information about the need to urinate, transmit the appropriate command to contract the muscle tissue of the bladder. Often the urge is so strong that emergency evacuation occurs without the ability to control the process.
When pressure is applied to the walls of the bladder, involuntary urination occurs
Remember! Incontinence can also be a sign of such serious pathologies as pyelonephritis and the presence of stones in the urethra. Treatment of such pathologies is strictly contraindicated without examinations and medical recommendations.
Causes and methods of treating cystitis in children 3-5 years old
Cystitis in a 3-year-old child is a common occurrence. This is due to the fact that immunity is still developing during the first years of life, so exposure to any infections can lead to the development of diseases that, under some conditions, become chronic. To eliminate the possibility of symptoms of the inflammatory process in the future, you need to learn more about what factors provoke it.
Forms of the disease
Cystitis affects the bladder. This is an inflammatory process that affects the surface of the mucous layer. It is accompanied by dysfunction of the organ: urine passes slowly, there is a frequent urge to urinate. The complexity of this pathology lies in the fact that the child cannot yet accurately describe his condition and indicate the cause of the pain.
There are 2 forms of cystitis in children 3 years old:
- spicy;
- chronic.
In the first case, rapid development of the pathological process is noted. Symptoms of acute cystitis are obvious. There is severe pain. In this case, inflammation develops on the mucous membrane, without penetrating into the deeper layers of the walls of the bladder, and treatment gives results faster.
Chronic cystitis develops smoothly. The signs of this pathological condition are less pronounced. In this case, the deep layers of the bladder walls are affected, which complicates treatment.
The chronic form of the disease is dangerous because often only obvious symptoms are eliminated and then therapy is stopped.
As a result, after some time the pathological process is activated again and signs of inflammation appear.
Causes of cystitis in children 3-5 years old
The development of the disease is provoked by infections caused by various pathogens:
- coli;
- ureaplasma;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- chlamydia.
The routes of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms differ. This may be the entry of feces or urine into the vagina when the child is not properly washed after urination or defecation. A descending route of transmission of infection is also noted - through the kidneys. Infectious agents spread through the lymph flow. Another factor contributing to the development of infection is the septic process. Girls are sometimes diagnosed with vulvovaginitis; pathogens also spread to the bladder.
The causes of cystitis can be various factors:
- Hypothermia. Low temperatures promote the development of infections.
- Congenital or acquired pathological conditions, for example, bending of the bladder. In this case, cystitis develops due to improper urination.
- Drug therapy aimed at treating other diseases.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Preparation for surgery, recovery period after surgery. A common cause is the insertion of a catheter.
For girls
Cystitis often develops due to improper washing. The reason for this is the physiology of girls. The urethra is located closer to the vagina and anus, and microbes overcome the barrier much faster, penetrating the urinary organ.
In boys
The main cause of cystitis in boys is streptococcal/staphylococcal infection. Boys are less susceptible to developing inflammation in the bladder. If this happens, you need to look for the cause in the microflora.
Symptoms of cystitis in children
In a 3-year-old child, cystitis manifests itself with a number of signs:
- Painful sensations. Their intensity can be different: moderate, acute, mild. It all depends on the form of the disease.
- Frequent urge to urinate (common symptom for children 2-5 years and older). Children at an early age (2-4 years) may experience urinary incontinence.
- Cloudiness, change in urine color (it becomes dark yellow, sometimes brown), sedimentation.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, groin and lumbar region.
With cystitis, the temperature may rise. However, this symptom is not specific and often indicates other pathologies. The inflammatory process is accompanied by an increase in temperature to +38°C. Not all 3-year-old children are able to explain to adults the cause of pain. If the child still speaks poorly, you can suspect a pathology by his behavior: the baby behaves restlessly and often cries.
Diagnostics
First you need to contact your pediatrician, he will refer you to a pediatric urologist. To confirm cystitis, an external examination is not enough. To make a diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct a number of studies:
- A general blood test will help confirm the development of the inflammatory process;
- urine analysis, which evaluates deviations of key indicators of biomaterial from the norm: color, transparency, composition;
- biochemical analysis of urine - based on the results of the study, the quantitative component of salts and protein in the biomaterial is determined;
- Bacteriological culture of urine helps determine the type of microorganisms that provoked cystitis.
To exclude other diseases, an ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system is prescribed.
Treatment of cystitis in children
Therapy must be comprehensive. To cure cystitis in a child 2-4 years old, it is recommended to take the product in the form of syrups. Children over 4 years old are allowed to give drugs in tablets. Stages of treatment:
- Drug therapy. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents are prescribed.
- Traditional methods of treatment. Herbal baths are effective.
- Diet. Cystitis will go away faster if you change your diet. The diet is aimed at reducing irritation of the mucous membrane.
For cystitis, bed rest is indicated. Inflammation can be cured faster at 5 years than at 3 years old, since the child is already able to talk about his feelings. Therapy begins at the first signs of pathology.
Drug therapy
At temperatures above +38°C, you can take antipyretic drugs. Antibiotics are prescribed by a doctor. Medicines are aimed at reducing the intensity of inflammation by getting rid of pathogenic microflora.
Children are prescribed penicillin antibiotics. The course lasts from 3 to 7 days.
When determining the dosage, the age and weight of the child are taken into account. The following drugs are prescribed: Sumamed, Azithromycin, Augmentin, Amoxiclav.
Herbal remedies are also used, for example, Canephron. They act gently and do not contain chemical components. Alcohol-based drugs should be used with caution and in minimal doses.
Folk remedies
Cystitis in a child should also be treated locally using baths. The principle of their use is the same for girls and boys: the child is seated in a container filled with a medicinal decoction. You can use herbs with anti-inflammatory properties: calendula, chamomile or sage. Recipe:
- Prepare raw materials: 2 tbsp. l. herbs, 1 glass of boiled water.
- Leave for 30-60 minutes.
- Dilute the decoction with warm water (6-8 l)
Diet
Diet can remove toxins from the body. Its principles are:
- drinking plenty of water;
- reducing the amount of salt;
- ban on eating spicy and fatty foods;
- refusal of sugar, use of its substitutes;
- consumption of fermented milk products;
- The basis of the diet should be plant foods.
Prevention
To prevent cystitis from developing again in the future, it is recommended to adhere to a number of rules:
- Timely treatment of infectious diseases, including dental caries, is necessary. Any bacteria has a tendency to spread throughout the body.
- It is important to monitor the child’s hygiene: wash it in a timely manner, change linen daily. Girls are washed in the direction from the vagina to the anus.
- Sharing a towel is prohibited.
- If a child has a tendency to develop cystitis, it is necessary to periodically submit biomaterial for testing.
It is important to maintain immunity. To do this, you need to periodically take vitamin complexes and pay attention to the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Main symptoms of the disease
The resulting incontinence significantly worsens a person’s life. For women, who are much more often at risk of developing such a problem, the process is accompanied by serious complications. A typical day begins with the constant thought of a possible desire to visit the toilet at the most inopportune moment. The ongoing disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- there is a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- the frequency of urination increases;
- there is no ability to control the moment of going to the toilet in various situations;
- increased frequency of night awakenings associated with visiting the toilet;
- uncontrollable urination during sleep;
- changes in the shade of urine, its smell and degree of transparency;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
Bacteria in the urine causes changes in odor, and uncontrolled leakage causes the perineum to always be wet. Not very pleasant odors permeate your underwear and become noticeable to your surroundings. This fact worsens a woman’s psycho-emotional mood. She begins to avoid crowded places, withdraws into herself, and becomes irritable. Problems arise at work and in your personal life.
How does pathology manifest itself?
In acute cystitis, negative changes develop in the bladder wall. They lead to increased activity of the hollow organ. This happens due to certain reasons:
- infectious and inflammatory changes in smooth muscles;
- damage to nerve receptors;
- disorders of neuro-reflex regulation.
The need to urinate occurs suddenly when the bladder is not completely filled. The patient cannot resist the desire and does not have time to run to the toilet. A person suffers from frequent painful urination at any time of the day. Worrying about enuresis - leakage of urine at night, during sleep.
Doctors call this type of incontinence urgent, emergency, imperative.
The disease worsens the quality of life, creates psychological discomfort, and causes a feeling of self-doubt.