Diet
In order for the kidneys to remain functional for a long time, they cannot be overloaded or forced to strain in emergency mode. To do this, first of all, you need to reconsider your usual diet and way of eating. The simplest prevention of kidney disease is that food should enter the body evenly, without overloading the digestive system and kidneys, and not contain a critical amount of irritating substances - salt, spices.
The optimal option is split meals in small portions every 2.5–3.0 hours. The amount of food should be small, the total caloric content of the diet should not be less than 3500 Kcal per day. The menu should be balanced in terms of basic nutritional elements, vitamins and minerals. Cooking principle:
Steaming
- boiling;
- stewing or steaming;
- roasting with a small amount of fat.
A healthy person can eat any food, but it is advisable to limit consumption:
- spicy foods and dishes with a high content of hot spices;
- salted, pickled, canned food;
- fried foods;
- fatty, smoked, salted meat and fish;
- strong broths;
- salt, hot store-bought sauces and mayonnaise;
- legume products;
- fresh milk;
- sweets;
- nuts
A balanced diet includes eating vegetables and fruits, especially seasonal ones. With today's wide choice, each person can create a menu that is not only healthy for their body, but also delicious, which is pleasant to stick to.
Vegetables and fruits
For kidney diseases, a specially designed diet is used, which takes into account the nature of the disease and the type of metabolic disorder in the patient’s body.
A balance between the main components of a person’s diet is important for preventing the occurrence of urolithiasis:
Recommended topic:
Kidney diseases in children
- Kidney formations are at risk from meat eaters who do not pay due attention to plant products;
- stones will form in vegetarians who prefer sour vegetables and fruits.
Nutritionists recommend including in the daily menu:
- 150 grams of meat or offal, 50 grams of fish products (you can - 350 grams of fish once a week);
- 400 grams of vegetables;
- 400 grams of fruit;
- 400 grams of cereals and various types of bread.
Various types of bread
It will not be burdensome even for a very busy person to have a vegetarian day at least once a week, during which it is advisable to eat up to 1500 kg of fresh, stewed or boiled vegetables or fruits with a minimum salt content. Such preventive unloading will allow the kidneys to work in a gentle manner and restore full activity. This will definitely affect the general condition of a person - performance will increase, sleep will improve, weight will normalize due to the removal of excess fluid from body tissues.
Of the vegetables most recommended by doctors, it should be noted: beets, pumpkin, non-acidic apples, watermelons, cucumbers, cabbage, leafy herbs. For preparing salads, it is good to use any sunflower oil, but do not use vinegar. If desired, you can add a little lemon juice.
To prevent kidney disease, it is absolutely necessary to exclude food waste from any person’s menu - chips, crackers, salted nuts, fast food, sweet carbonated water (such food contains prohibitive amounts of salt and preservatives). In consultation with your doctor, you need to take vitamins E and B that are important for the body, the lack of which negatively affects the condition of the mucous membranes, including the genitourinary tract.
Self-administration of vitamin-containing medicinal complexes for the purpose of prevention is not recommended - excess intake of these substances into the body can cause an effect similar to poisoning. Human consumption of foods with a high content of vitamins E and B (seeds, nuts, vegetable oil) does not cause such an effect.
Prevention of kidney diseases: types
The kidneys act as a filter that eliminates pathogenic compounds, harmful microorganisms, decay and metabolic products from the body in children and adults. Their acute illnesses manifest themselves as high temperature and blood pressure, back pain, changes in appearance (edema), nausea, weakness, and decreased performance. Chronic kidney pathologies, quietly destroying the body from the inside, often manifest themselves in forms that require urgent decisions to save a person’s life.
There are two types of kidney disease prevention:
- primary, which is aimed at keeping the kidneys healthy and preventing disturbances in their activity;
- secondary, aimed at timely diagnosis and correct treatment of diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary tract, eliminating the causes of relapse of the pathology.
American doctors were the first to talk about the fact that the prevention and prevention of kidney diseases is a dire necessity, having studied the incidence statistics in the United States. It turned out that the number of people suffering from various kidney pathologies exceeds the number of patients from cardiovascular diseases, and only 20% of them get an appointment with a urologist. The remaining 80% find out about their kidney ailments after they are admitted to the clinic with a diagnosis of myocardial infarction. Unfortunately, many simply do not survive until the true cause of their body’s condition is discovered.
The factors causing some kidney pathologies in humans have not been fully studied, but doctors know what specifically can affect the condition of this organ. The following will help maintain the health of the kidneys and genitourinary tract:
Proper nutrition
- proper nutrition;
- optimal drinking regime;
- healthy lifestyle.
Causes of kidney disease are:
- a sharp change in a person’s weight - both an increase and immediate weight loss disrupt the normal placement of the kidneys in the body;
- systemic diseases (diabetes);
- acute viral pathologies;
- a person’s lifestyle (inactivity, bad habits);
- hypothermia of the body, both one-time and permanent.
In order to prevent the occurrence of pathology, it is necessary to eliminate external and internal causes that cause the body and kidneys to be overly stressed.
Prevention of kidney disease during pregnancy
The period of bearing a child is dangerous for women who have a predisposition to the development of kidney diseases. Kidney overload results in back pain, metabolic disorders, swelling and increased blood pressure.
When planning a pregnancy, a woman needs to undergo a preventive examination by a urologist (nephrologist) and receive appropriate treatment. During the period of bearing a child, you need to adhere to a low-salt diet and control urination to prevent kidney failure. Neglecting the doctor’s recommendations can lead to a difficult pregnancy and premature termination.
Traditional methods for kidney prevention
Herbal decoctions
Folk remedies take into account the need for increased kidney function during illness or pregnancy. To normalize the condition of organs, as a means of prevention, mild medications are offered - decoctions of bearberry, horsetail, corn silk, cranberry juice. They will prevent the formation of sand and stones in the body, cleanse the urinary tract, and strengthen the bladder.
Symptoms
There are a number of signs that parents cannot miss. Below we list the main symptoms of kidney problems in children:
- unpleasant sensations in the lumbar region, of varying intensity - from nagging to acute;
- changes in the appearance of urine;
- rise in temperature without signs of respiratory infection;
- swelling of the face in the morning;
- noticeable swelling under the eyes;
- weakness and fatigue;
- dry mouth and constant thirst.
It also happens that the pathology does not show itself as symptoms.
For kids who still cannot explain their feelings, there are signs. In addition to changes in urine, the following changes will become noticeable:
- the belly will increase;
- the stream of urine may become weaker (we are talking about boys, although with phimosis this is normal).
Slightly older children may point to their stomach, urinate frequently, or vice versa - very rarely. The baby may also refuse to go to the toilet. If previously the child produced a normal amount of urine, during illness it decreases significantly.
As we have already said, any ailment can lead to a serious problem - kidney failure.
Diagnostics
clinical analysis of blood, urine;
blood chemistry;
microscopic examination of urine sediment;
urine culture for sterility;
determination of the level of prostate-specific blood antigen.
In addition to laboratory tests, diagnosis of hematuria
Ultrasound of each part of the urinary system;
Computer tomography of the pelvic and abdominal organs
cavities;
MRI;
X-ray studies;
Cystoscopy;
Excretory urography.
cavities;
MRI;
Cystoscopy;
cavities;
MRI;
Cystoscopy;
cavities;
MRI;
Cystoscopy;
Strengthening the immune system
Modern man lives in a particularly aggressive environment, which affects the body through polluted air, undrinkable water, and high levels of carcinogenic substances in food. Under the influence of these factors, the human immune system is suppressed and ceases to perform its functions - to protect the body from the influence of invading infectious agents.
Strengthening the immune system
The enemies of the immune system are alcohol and tobacco. Even a small glass of alcohol sharply reduces its level for 24 hours, which makes the human body, and especially the kidneys, defenseless against infectious attacks.
Recommended topic:
Kidneys hurt with cystitis
Nicotine sharply worsens the functioning of the genitourinary system due to the release of a large amount of toxic substances into the human blood, which disrupts the filtration of fluid and the removal of decay products from the body. Clinical data show that smokers are 20 times more likely to develop chronic glomerulonephritis than their non-smoking peers. All inflammatory diseases in patients dependent on nicotine are difficult to treat, causing frequent complications. A person's refusal to drink alcohol and cigarettes is important for the prevention of kidney disease.
Biology lesson in 8th grade
Chapter 7. Urinary system.
Lesson No. 33 Date________________
Topic: Structure and functions of the kidneys.
Author, developer:
Teacher Talitskikh M.V.
Item:
Biology
(the work program is compiled on the basis of the Federal State Educational Standard, the author’s program in biology by I.N. Ponomareva and is focused on the use of the textbook edited by A.G. Dragomilov “Biology. Grade 8”)
Class:
8th grade
- Lesson objectives: Educational:
• Show the final stage of metabolism and the organs through which decomposition products are removed. - Introduce the general plan of the structure and functions of the organs of the urinary system;
- Find out the role of urination, explain the functions of the kidneys and urinary organs.
- Establish the role of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis of the blood and the internal environment as a whole. Developmental:
• develop concepts about the diversity of living organisms;
• continue the development of basic biological concepts, elements of creative activity through immersion in solving problematic issues and involving schoolchildren in independent work of a partial search and research nature. Educational:
• Foster a love of nature; • develop the ability to listen and hear others, respect for the opinions of comrades;
- contribute to the ethical education of students.
Health-saving technologies:
- monitor students’ posture; carry out exercises to relieve eye strain; ventilation of the room.
Patriotic education:
- developing a sense of patriotism through stories about Russian scientists.
Formation of UUD - see in the Appendix:
- P 1:
Know the general plan of the structure and functions of the organs of the human urinary system;
- P 2:
Have an idea of the role of urination, kidney function and urinary organs; - P 3:
analysis and synthesis of information;
- For the main didactic purpose:
a lesson in learning new material; - By way of organizing activities:
individual-group; - According to the leading teaching method:
problem-search.
- Methods - see Appendix
- Student activities - see Appendix
- Means of education:
- Textbook by Dragomilov A.G. Biology. 8th grade. M.: Venta-Graf, 2015;
- Additional text material;
- Interactive pictures “Structure of the urinary system”, “Macrostructure of the kidney”, “Microstructure of the kidney”. Animation “Formation of primary and secondary urine.” Photo “Left Kidney”.
- Equipment:
projector, computer. - Progress of the lesson
(see technological map).
Technological lesson map
| Lesson stage | DU | Methods | UUD | |
| I. _ Self-reliance on activities. Org. moment | The bell rings and students prepare for class. Teacher's greeting. (Students' response) | DU 1 | D 1 | L4 R1 |
| II . Updating students' existing knowledge | Let's repeat what we studied in the last lesson:
4 . | DN 2 DN 7 | D 5 | L4 R1 K1 |
| III . Setting up the lesson tasks, fore-ka topic of the lesson and goals. | – So we covered the topic “Metabolism and Energy.” What do you think we will talk about in class today? - What do you know about the human excretory system? - What goal will we set for ourselves? (Goal of the lesson) That's right, at the end of this lesson we should know the structure and functions of the human kidneys, as well as what a NEPHRON is and how it “works.” We write the number in p/t above the topic of the lesson. | DN 1 DN 4 DN 5 DN 6 | D 5 | P2 P3 K2 |
| IV . Explanation of new material | The teacher organizes an explanation of new material and asks questions.1.Structure of the urinary system -interactive in show all mode.
3. The structure of the nephron -
interactive in display mode - the formation of primary and secondary urine 4.
| DN 4 DN 7 DN 6 DN 7 DN 6 DN 4 DN 7 DN 6 DN 7 | ABOUT | R4 R5 K3 K4 K5 K6 L5 |
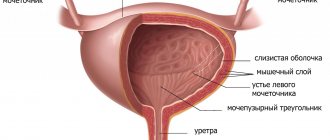
| V. _ Reinforcing the material learned | Let's summarize our lesson, check our understanding of the material - Appendix 1 Vocabulary: volume, two, shape, kidneys, ureters, lower back, unpaired, spine, width, mass. TEXT: In humans? kidneys They are located at level ?, on both sides ?. The right kidney is “pressed” by such a “giant” as the liver, so it is 1–1.5 cm lower than the left one. By ? the bud resembles a bean. Magnitude? - the size of a man's fist. ? – 150-200 g, length – 10-12 cm, ? – 5-6 cm. Approximately every 7 cm, another portion of urine comes out of the kidneys, which enters the ureters.? – tubes 30 cm long, 4-7 mm in diameter. With smooth movements, the ureters move urine to the bladder. Bladder - ? organ, ? 500-700 ml. It's not too big and not too small - why accumulate extra weight that has no useful qualities? interactive in test mode | DU11 DU13 DU14 | P6 P3 | |
| VI . Reflection | -How do you evaluate your work in the lesson? (The teacher’s opinion about the work of each of the respondents.) -Will knowledge of biology be useful to you in life? Complete the sentence by expressing your opinion about the lesson Today in the lesson .... I learned I learned It was difficult It was easy I liked it I didn’t like it I was surprised | DU15 | ||
| VII . D/z | §39 pp 157-159, R/t pp _________ Thanks for the lesson!!! | DU16 | D 6 | L5 P7 |
Annex 1
Dictionary:
volume, two, shape, kidneys, ureters, lower back, unpaired, spine, width, mass.
TEXT:
A person has ______ kidneys. They are located at the level of __________, on both sides __________________. The right kidney is “pressed” by such a “giant” as the liver, so it is 1–1.5 cm lower than the left one.
In terms of ______________, a bud resembles a bean. The size of ___________ is about the size of a man’s fist. ____________– 150-200 g, length – 10-12 cm, ______________– 5-6 cm.
Approximately every 7 weeks, another portion of urine comes out of the kidneys and enters the ureters.
_______________ - tubes 30 cm long, 4-7 mm in diameter. With smooth movements, the ureters move urine to the bladder.
Bladder —_______________
organ, __________________ 500-700 ml. It's not too big and not too small - why accumulate extra weight that has no useful qualities?
Annex 1
Dictionary:
volume, two, shape, kidneys, ureters, lower back, unpaired, spine, width, mass.
TEXT:
A person has ______ kidneys. They are located at the level of __________, on both sides __________________. The right kidney is “pressed” by such a “giant” as the liver, so it is 1–1.5 cm lower than the left one.
In terms of ______________, a bud resembles a bean. The size of ___________ is about the size of a man’s fist. ____________– 150-200 g, length – 10-12 cm, ______________– 5-6 cm.
Approximately every 7 weeks, another portion of urine comes out of the kidneys and enters the ureters.
_______________ - tubes 30 cm long, 4-7 mm in diameter. With smooth movements, the ureters move urine to the bladder.
Bladder —_______________
organ, __________________ 500-700 ml. It's not too big and not too small - why accumulate extra weight that has no useful qualities?
Annex 1
Dictionary:
volume, two, shape, kidneys, ureters, lower back, unpaired, spine, width, mass.
TEXT:
A person has ______ kidneys. They are located at the level of __________, on both sides __________________. The right kidney is “pressed” by such a “giant” as the liver, so it is 1–1.5 cm lower than the left one.
In terms of ______________, a bud resembles a bean. The size of ___________ is about the size of a man’s fist. ____________– 150-200 g, length – 10-12 cm, ______________– 5-6 cm.
Approximately every 7 weeks, another portion of urine comes out of the kidneys and enters the ureters.
_______________ - tubes 30 cm long, 4-7 mm in diameter. With smooth movements, the ureters move urine to the bladder.
Bladder —_______________
organ, __________________ 500-700 ml. It's not too big and not too small - why accumulate extra weight that has no useful qualities?
Source: https://multiurok.ru/files/urok-po-biologhii-v-8-klassie-stroieniie-i-funktsi.html