Edema in kidney diseases is a fairly common occurrence and is characterized by varying degrees of persistence and severity.
Quite often detected in various types of renal failure. This symptom represents a certain diagnostic problem, since it also manifests itself in cardiovascular failure.
Nowadays there is a sharp increase in the incidence of various pathologies of the urinary system, so this problem is quite relevant for medicine.
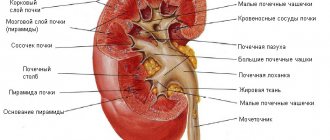
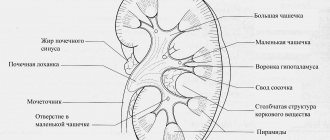
In the human body, the kidneys perform a number of important functions: regulating the constancy of blood composition, maintaining acid-base balance at the proper level, excreting metabolites of protein metabolism, maintaining ionic and osmotic balance in the blood.
Violation of this function causes “renal” edema.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Edema is excess fluid in the intercellular space of tissue. It can get there from vessels that have a semi-permeable wall.
It is worth noting that under normal conditions this does not happen due to the presence of such physical quantities as osmotic and oncotic pressure.
The necessary substances to maintain these values are chlorine ions, sodium, glucose, urea, and proteins.
Due to kidney disease, the content of these substances in the blood is significantly reduced, which leads to the leakage of plasma into the surrounding tissues, which immediately leads to edema.
Among the reasons that cause edema in kidney diseases, only two can be distinguished: the first is the pathophysiological mechanism of origin of this phenomenon and the second is kidney pathology, which causes a cascade of physiological reactions.
The mechanism of edema formation is due to:
- increased elimination of proteins through the renal filter - going into the primary urine, proteins draw a significant part of the water onto themselves, taking it from the vascular bed, which leads to a drop in oncotic pressure;
- initially low level of serum protein – protein starvation of the body, disruption of the protein-producing function of the liver;
- decreased filtering ability of the kidneys - when blood pressure decreases, vascular receptors send signals that increase the reabsorption of sodium ions in the renal tubules;
- large water load on the body - with kidney disease, the filtration rate is greatly limited, therefore, accumulating in the vascular bed, water causes edema.
The most significant pathologies for the formation of edema are those nosological units that affect the glomerulus.
These may be phenomena of nephrosclerosis, autoimmune aggression against the basement membrane, glomerulonephritis, renal amyloidosis, renal failure, pregnancy nephropathy, diabetic nephropathy.
Types of edema in kidney diseases, their localization and severity
Edema is a fundamental symptom that accompanies kidney disease, regardless of the cause and severity of the pathological process. They may appear gradually, over several weeks, with chronic glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis. Their increase over several days indicates a pronounced process in the organ with the development of acute renal failure.
Mechanism of edema development
Their development in kidney diseases contains several main mechanisms:
- violation of excretory function - this condition leads to an increase in the concentration of sodium chloride in the blood, which is a hypersomolar compound and retains water in the vascular bed; when a certain volume threshold increases, fluid leaves the vessels into the tissues, causing their swelling;
- decrease in oncotic pressure of blood plasma - oncotic pressure is provided by plasma proteins (albumin), which prevent excessive release of fluid from the vascular bed; in various diseases of the kidneys and impairment of their function, protein is excreted in large quantities in the urine, oncological pressure is reduced and fluid leaves the vessels in fabrics;
- increased permeability of the capillary wall - occurs in various inflammatory diseases of the kidneys; as a result of increased permeability, fluid easily escapes into the surrounding soft tissue from the capillaries;
- increased systemic blood pressure - the kidneys, in addition to the excretory function, regulate systemic blood pressure; disturbances in their work lead to an increase in fluid pressure in the vessels and its increased filtration into the tissue.
Important! The localization and severity of the development of edema in kidney diseases depend on which mechanism prevails.
Symptoms of edema
The rate of appearance, localization and severity of soft tissue edema in kidney diseases depend on the mechanism of their development and directly what kind of disease:
- Swelling of the soft tissues of the face - the area around the eyes and eyelids is primarily affected; the swelling is more pronounced in the morning after sleep, then decreases during the day, and disappears in the evening. This type is associated with a decrease in the oncotic pressure of the blood plasma due to the high excretion of proteins by the kidneys during glomerulonephritis. With a pronounced decrease in oncotic pressure, swelling covers the entire area of the face, changing it beyond recognition. In this case, it is necessary to differentiate them from facial swelling due to allergic reactions.
- Minor swelling of the tissues of the face, torso and limbs in the form of pasty skin is associated with increased permeability of the vascular wall in acute or chronic pyelonephritis. It is also worth remembering that pasty skin can be caused by genetic factors and be present in a person throughout his life.
- Severe edema of the lower extremities - their development is determined by the accumulation of sodium chloride in the blood, with its reduced excretion by the kidneys. They can appear with any disease accompanied by renal failure. They are present with equal intensity throughout the day.
Important! Edema of the lower extremities can accompany the development of chronic heart failure when the pumping function of the heart is reduced. The mechanism of their development is associated with stagnation of blood in the capillaries of the lower extremities. It is characteristic that, unlike renal edema, the appearance of these edemas is more pronounced in the evening. In the morning after a night's sleep, they may disappear, with a gradual increase in the evening.
Treatment of the disease
Edema is the result of a pathological process, so their treatment is associated with eliminating the cause of its appearance. This is usually conservative treatment, including antibiotic therapy for pyelonephritis, and the use of immunosuppressive drugs for glomerulonephritis.
Diuretics are also used, which enhance the removal of fluid from the body and from the tissues in which it has accumulated.
(No votes yet) Loading…
tvoelechenie.ru
Signs of edema during nephrosis
It must be remembered that edema is not an independent disease and it cannot have symptoms, but they have certain demarcation frameworks by which cardiac edema can be separated from renal edema.
Edema due to nephrosis is strictly localized on the upper part of the body, symmetrical, found in the eyes, face, tends to spread from top to bottom, the skin on the surface is dry.
This can be explained by the fact that these areas have looser fiber and therefore facilitate the accumulation of fluid due to stagnant processes during sleep.
Swelling of the eyelids is a signal of kidney problems
Chronologically, renal edema appears in the morning and gradually decreases in the evening.
When palpated, the swelling is mobile and, after squeezing, can move in any direction. Visually, the area is paler than the surrounding tissue, but warm to the touch; it can be described as soft and loose.
With the improvement or restoration of the functioning of the renal filters, the edema quickly resolves. These patients do not have shortness of breath.
As edema progresses, other symptoms of kidney damage often appear: general weakness, aching and uniform lower back pain, impaired urine outflow.
All these symptoms most often appear some time after a streptococcal or viral infection.
A general urine test can detect a large amount of protein (massive proteinuria) and an increase in excreted electrolytes.
A biochemical blood test demonstrates an increase in creatinine, urea and other metabolites of protein metabolism.
As stated earlier, swelling can be of varying degrees of severity - from mild pastiness in remote areas of the body and limbs, to pronounced, when it seems as if a person is saturated with water like a sponge.
Difference between cardiac and renal edema
It is known that the human body contains more than half of water, which is distributed in cells and intercellular space. If there is a malfunction of some organs, it can manifest itself in the form of edema in any part of the body and is divided into: cardiac, kidney, liver and others.
It is worth considering separately renal and cardiac edema and their differences, which every person should know.
Renal edema
There are many reasons for the development of renal edema, the main ones worth noting are:
- drinking a large amount of liquid, which does not have time to leave the body naturally, and therefore begins to accumulate in the intercellular space;
- abuse of salty foods, including table salt;
- high vascular permeability and decreased protein in the blood;
- Various diseases of the genitourinary system can provoke swelling, since during the inflammatory process the filtration process is significantly reduced, which leads to a water-salt imbalance of the entire system.
Therefore, renal edema can be caused by the following diseases:
- Kidney failure.
- Development of infectious processes.
- Vascular disease, as well as changes in blood composition.
- Some medications, which can lead to negative consequences such as swelling.
As a rule, renal edema begins to form from the upper part of the body, develops quite quickly, and can have varying degrees of severity and be localized in any part. Usually, in areas of swelling, the skin becomes pale and dry. Typically, renal edema can go away on its own, without the use of any measures.
Renal edema is characterized by its symmetry; when pressure is applied to its area, it can move without causing pain. Initially, they appear on the eyelids, puffiness of the face appears, and gradually moves to the lower parts of the body.
As a rule, this process becomes noticeable after sleep, because at this time there is practically no urine output, and may be accompanied by pain in the lumbar region. When normal kidney function is restored, the swelling subsides.
Cardiac edema
This type of pathology is considered a fairly common occurrence when the cardiovascular system is disrupted, which quite often leads to death. They occur in both men and women, and the main cause is poor lifestyle and poor nutrition.
The development of cardiac edema is greatly influenced by the composition of the blood:
- Proteins that hold a significant part of the liquid in the vessels, preventing it from leaking into the interstitial space.
- Glucose, which attracts liquid.
- Sodium is an osmotically active substance that can retain fluid inside blood vessels.
- A significant component is hormones, which are responsible for reducing or increasing the permeability of vascular walls.
When the concentration of these substances in the blood is disrupted, fluid begins to accumulate in the space between the cells, starting in the lower extremities during wakefulness, and in the lumbar region and buttocks during rest or night rest.
The main causes of edema in this case can be considered heart failure, which in turn can be caused by such ailments as: congenital heart defects, cardiosclerosis, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia and other pathologies.
Unlike renal edema, cardiac edema is distinguished by its asymmetry, manifests itself in the evening after a long stay on the feet, and is long-lasting.
They rise from the feet, involve the lower part of the body, and can appear on the arms, but swelling on the face due to diseases of the cardiovascular system almost never occurs.
They are quite dense in consistency, touching them causes pain. The skin in the area of edema acquires a bluish tint, is cold to the touch, and gradually goes away by morning.
In addition, edema associated with cardiac dysfunction may be accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, such as:
- shortness of breath with rapid heartbeat;
- fast fatiguability;
- headaches and behind the sternum;
- blue lips;
- periodic or constant arrhythmia.
Therefore, regardless of the manifestation of swelling, it is imperative to undergo a full examination by a specialist: a cardiologist, urologist or nephrologist.
To find out the cause of this disease, a comprehensive diagnosis is required, including: a general and biochemical blood test, a urine test, kidney tests to confirm or exclude their disease, blood tests for the presence or absence of heart disease, as well as Dopplerography of blood vessels to determine their natural permeability.
Advanced forms of diseases in one case or another can lead to serious consequences, so a trip to the doctor should not be postponed to a later date.
Hidden swelling
In medicine there is such a thing as “hidden edema”. This means that human tissue can hold about 7 liters of water without visible changes. They can be diagnosed by taking daily weight measurements.
If the weight increases, then this may speak in favor of edema of renal origin. It is also necessary to keep a daily record of the water consumed and excreted, making allowances for that excreted during breathing and sweating.
If the amount of fluid accumulation in the intercellular space reaches 12 liters, then a transition to all other tissues of the body is possible, up to the formation of anasarca and its accumulation in body cavities.
The human body consists of 70% water, 2/3 of which is contained inside cells, 1/3 in the intercellular space. This is where the kidneys send water if there is some kind of malfunction in their work. As the fluid accumulates, it causes swelling of this organ, which, if left untreated, can result in irreversible consequences.
Renal edema: symptoms
A condition dangerous to the body can be determined by the puffiness of the face, bags under the eyes, swelling of the limbs - external signs that in some cases may not appear. An increase in body weight without visible pathologies also indicates the possible presence of kidney edema.
The main symptoms of renal edema:
- Painful sensations of varying degrees of intensity resulting from acute inflammatory processes caused by infection, blockage of the ureter, and movement of stones. The pain is localized under the lower ribs, in the lower back, can radiate to the groin area or leg, and is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Often after renal colic, swelling appears within 24 hours - a later symptom indicating a malfunction of this organ.
- Urinary dysfunction. The daily rate of urine volume for an adult is about 1.5 liters per day or 3/4 of the amount of fluid consumed. The decrease in this indicator is due to water retention in the body caused by inflammatory processes present in it.
- Neurological manifestations caused by the accumulation of toxins in the body. The latter, in the absence of filtration, must be excreted in the urine, and if they remain inside, they accumulate and irritate nerve tissue, causing sleep disturbances, drowsiness, headaches, muscle pain, and skin itching.
Renal edema in a latent form can be detected by consuming diuretics. If it is present, the weight loss per day due to the excreted fluid will be 1-2 kg.
Kidney edema on the face, legs and arms: causes, symptoms, difference from heart edema, treatment - About the Kidneys
Swelling of the face, limbs, and sometimes the entire body in most cases is not a sign of fatigue or poor sleep. Increased swelling indicates kidney problems. Renal edema most often occurs as a result of impaired urine outflow due to inflammation and other pathologies of the urinary system.
Pathological mechanisms of renal edema
Renal edema on the face, limbs and other parts of the body occurs due to kidney dysfunction, namely impaired filtration. As a result, a metabolic failure occurs, which leads to the accumulation of harmful compounds in the body.
The main causes of edema are kidney diseases, in which there is a violation of the passage of urine and its release into the intercellular space.
Such pathological mechanisms include increased filtration of protein in the kidneys, resulting in an increase in its amount in the urine - proteinuria. Protein has the ability to interfere with the normal removal of fluid from the body.
With proteinuria, swelling of the face and limbs increases. Excessive intake of protein from food aggravates the patient's condition.
The next pathological condition is a violation of the process of sodium absorption, which also leads to fluid retention in the body.
This process is observed when renal filtration is impaired, resulting in the reabsorption of sodium into the intercellular space of organs.
Most often this happens with hypertension and other diseases of the cardiovascular system. Another reason for the accumulation of sodium in the kidneys and blood plasma is salt abuse.
Edema also appears when the walls of blood vessels become thinner, which leads to their increased permeability. As a result, fluid and some blood components enter the intercellular space, where they are retained, causing swelling of the body. Thinning of the vascular walls is often a consequence of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and other organs and systems.
Renal edema also develops in patients with chronic kidney disease who drink a lot of water. The accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space occurs due to a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate against the background of pathological processes with excess fluid intake.
Causes of pathological changes in the kidneys
Metabolic disorders and fluid retention in the body occur against the background of glomerulonephritis, amyloidosis, malignant diseases, as well as with systemic pathologies, poisoning and renal failure.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory disease in which the renal glomeruli are damaged when the immune complex penetrates the kidneys. These complexes are formed in the human gemma against the background of infectious and autoimmune pathologies and spread throughout the body through the bloodstream.
Glomerulonephritis during pregnancy
In the absence of proper treatment against the background of glomerulonephritis, a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate and fluid retention in the urinary organs occurs, and swelling of the body appears. Over time, the infection leads to the proliferation of fibrous tissue, which gradually grows over the glomeruli. As a result, the filtration function is completely disrupted.
Amyloidosis
Kidney amyloidosis is a disease in which there is an excessive accumulation of amyloid (protein) in the kidneys as a result of a lack of proper filtration. When retained, the protein accumulates in the kidneys and clogs the filtration membranes, disrupting renal circulation. Toxic compounds, breakdown products and fluid accumulate in the body.
Poisoning
Poisoning with heavy metals and some toxic compounds can cause edema of renal origin. When harmful compounds penetrate cell membranes, they die and healthy cells are gradually replaced by fibrous tissue. The result is kidney failure.
Kidney failure
This disease develops as a result of a complete impairment of kidney function against the background of other renal pathologies.
All tissues of the organ are destroyed and the cellular structure is replaced by connective tissue. This leads to disruption of the filtration function and water-electrolyte balance.
There is fluid retention in the body and the accumulation of toxic compounds that poison the patient’s body.
Tumors
Kidney dysfunction can occur against the background of both benign and malignant tumor formations. Hemangioma and kidney cysts can lead to impaired urine flow and its retention in the intercellular membrane. In oncology, swelling and the degree of organ damage will depend on the size, location and growth rate of the malignant neoplasm.
Symptoms
As a rule, edema does not appear on its own, but is a sign of other pathological processes that are associated with the kidneys. Therefore, during the examination, the doctor tries to determine the cause of the swelling, as well as to differentiate cardiac edema from renal edema.
With cardiac pathologies, fixed swelling of the legs is common, less often of the lumbar region. The swollen area becomes cold and bluish. There are symptoms of tachycardia, hypertension, hypotension.
A characteristic feature of renal edema is swelling of the upper body and eyelids. When pressed, swelling may migrate slightly from its location. The temperature of the swollen area does not differ from body temperature.
Also, swelling associated with impaired filtration and excretory functions of the kidneys appears simultaneously with impaired urination. The process of emptying the bladder is accompanied by pain, cutting in the lower back, perineum and lower abdomen. With significant kidney damage, pain symptoms do not subside even when changing position and after a long rest.
Against the background of prolonged stagnation of urine, symptoms of intoxication develop: body temperature rises, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted - constant nausea and vomiting appear.
The volume of urine excreted also decreases until it disappears completely. Normally, the daily volume of urine excreted is equal to 2/3 of the daily volume of liquid consumed. If this ratio changes, one can assume problems with the passage of urine against the background of the development of pathological processes in the kidneys.
Symptoms and treatment of urolithiasis during pregnancy
Changes in the results of clinical urine analysis are also observed: the level of protein, leukocytes, electrolytes, and red blood cells increases. With proteinuria and leukocyturia, the urine becomes cloudy or a white sediment appears in it. With an increased number of red blood cells, urine becomes red or brick-colored, and blood clots or streaks appear.
Often, edema due to renal pathologies is accompanied by neurological symptoms. The patient becomes restless, sleep is disturbed, and itchy dermatitis develops. Headaches, muscle and joint pains are also common.
As a rule, with kidney dysfunction, the entire body is poisoned by harmful compounds, therefore the performance of other organs is impaired. For example, the cardiovascular system may respond with the appearance of tachycardia, hypertension, arrhythmia, and fainting.
Diagnostics
If all the symptoms of renal edema are present, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe tests to determine their cause. For this purpose, a laboratory blood test is prescribed. A biochemical diagnostic method for kidney dysfunction will show an increase in creatinine, urea, uric acid, and lipids.
A mandatory diagnostic method is urine testing. Pathological processes in the kidneys will be indicated by an increase in protein, leukocytes, erythrocytes, while a decrease in the amount of creatinine and urea occurs.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to determine the condition of the kidneys, the degree of their damage, and the presence of tumors. Using Doppler, the state of the vascular system of the kidneys is examined to assess their patency, the presence of tumors, sclerosis and other pathologies.
To determine the condition of the kidneys and deviations in filtration function, a study of urine density and creatinine clearance is carried out, and dilution samples are also taken.
Treatment
Treatment of body edema, which has formed as a result of kidney dysfunction, is carried out in 5 areas. This includes taking diuretics, treating the root cause, strengthening blood vessels, normalizing water and electrolyte balance and following a diet.
Diuretics
Since edema is the result of excess fluid in the body, treatment should include diuretics. They will help remove excess fluid from the body and get rid of swelling.
For this purpose, one or more medications are prescribed. Today, the most effective are Lasix, Oxodolin, Uregiit, Mannitol.
Traditional medicine (decoctions of lingonberry, currant leaves and other herbal infusions) are also suitable.
Kidney stones - a symptom or a disease?
Treatment of the underlying disease
Treatment of the underlying disease depends on the diagnosis. In case of infectious-inflammatory kidney damage, the doctor prescribes a course of antibacterial drugs. For autoimmune pathologies, hormonal anti-inflammatory medications are used.
In the absence of effect from medications and further development of edema syndrome, radical methods are used - hemodialysis and organ transplantation.
Hemodialysis is a method of extrarenal purification of gemma from toxic compounds and breakdown products that have accumulated as a result of metabolic disorders with decreased kidney function.
An organ transplant is necessary when there is a complete loss of the ability to perform the filtration function, when all tissues of the organ are replaced by fibrous tissue.
Strengthening blood vessels
This direction of therapy is used only for those patients in whom the cause of fluid retention in the body is increased permeability of the walls of blood vessels. The main treatment is supplemented with Ascorutin, which strengthens the vascular walls and restores their patency.
Restoration of water and electrolyte balance
To restore water-salt metabolism, the patient is given intravenous injections or droppers, with the help of which various salts missing in the body are introduced.
This method is also used when restoration of water-electrolyte metabolism is impossible due to diet, in case of digestive disorders and disturbances in the process of food absorption in the intestines.
Such treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Diet
At the first manifestation of renal swelling, the doctor makes adjustments to the patient’s diet. This will reduce the load on the diseased organ and restore its normal functioning. With the help of diet, you can prevent the development of processes associated with an increase in the amount of protein and sodium in the body.
The diet is prescribed depending on the underlying cause of the disease.
If the patient has signs of infectious and inflammatory pathologies, the doctor recommends diet No. 7, which involves the complete exclusion of salt from the diet.
It is necessary to eat food rich in proteins, vitamins C, P, PP and group B. In case of renal failure, diet No. 7A is prescribed, which limits the daily amount of salt, protein foods and liquid.
Signs of swollen skin can often include infectious and inflammatory processes, kidney cancer, and poisoning of the body with harmful substances. To eliminate the edematous symptom, therapy for the underlying cause of the disease is prescribed, a course of diuretics, drugs that strengthen blood vessels, injections to restore water-salt balance and diet.
Source:
Edema due to kidney disease
Edema in kidney disease is considered one of the most common symptoms of a dangerous pathology of this kind. Moreover, they make themselves felt equally often both during the chronic course of the disease and at the stage of acute development.
Once the kidneys fail, the body has to deal with the consequences of unhealthy levels of various substances in the blood. The imbalance becomes the reason for the development of puffiness, which affects not only the upper or lower limbs, but also transforms the oval of the face.
To avoid such an outcome, experts recommend that when the first warning signs are detected, immediately seek qualified help. Self-medication, as well as ignoring the problem, can harm overall well-being by triggering irreversible processes in the body.
The main causes of swelling
Schematically, all conditions that indicate destabilization of renal activity against the background of swelling can be divided into two camps. The first covers the direct pathological mechanism that provokes fluid to pour into the intercellular space. The second option covers the diseases themselves, which are considered to be the culprits of the anomaly.
Among the most common causes of immediate swelling due to kidney problems is increased filtration of blood proteins. Cleaning is carried out through the membranes of special glomeruli. Once proteins enter the primary urine, they take with them a small amount of water, which is a direct result of osmotic pressure.
Signs of kidney swelling
Renal edema, the symptoms and treatment of which depend on the causes that caused it, can develop in one day. The main feature of this condition is “mobility”, in which, depending on changes in body position, the swelling gradually goes down: first the face swells, then the torso and arms, then there is an increase in the size of the thighs, calves, and feet. Another distinctive feature of kidney edema is the rapid increase in its size. The renal nature of the edema is confirmed by its symmetry.
You should be able to distinguish renal edema from cardiac edema. The latter appear first on the legs, and swelling of the kidneys begins to move from the facial area.
Renal edema of the legs is observed in severe renal failure and nephritic syndrome and is characterized by equal severity in both limbs.
Kidney functions
It's no secret that the kidneys are one of the most important organs; a person's health directly depends on their work. In addition to a number of other functions, the kidneys are primarily designed to filter blood; on average, the kidneys filter more than one liter of blood per minute of vital activity.
Another important function worth mentioning is homeostatic. In simple terms, without going into medical terms, this means that the kidneys regulate two important processes:
- Water-salt homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant optimal water and salt balance in intracellular and extracellular spaces.
- The acid-base state is the main indicator of homeostasis, that is, maintaining normal values of the internal environment of the human body.
Renal edema, or rather its manifestation, directly depends on how healthy your kidneys are and how they work, whether they are able to fully carry out their homeostatic function. Of course, there are many more reasons, but as for the origin of edema, it is homeostasis that lies at the origins of its formation and treatment should begin with the diagnosis of renal failure.
Causes of kidney swelling
The causes of renal edema are:
- decreased presence of protein in the blood, due to a violation of its formation or resulting from loss during urination;
- increased amount of sodium ions in the blood; may be caused by increased intake (for example, in the form of table salt) into the body and gradual accumulation;
- excessive amount of fluid in the body; a person drinks a large amount of water, which, without having time to be released naturally, accumulates in the tissues, thereby forming edema;
- increased vascular permeability, facilitating the release of blood and fluid particles into the intercellular space.
The most common diseases leading to swelling
It is believed that ailments that cause puffiness throughout the body due to kidney problems are limited only by kidney failure. But in fact the list is much wider, covering:
- glomerulonephritis;
- amyloidosis;
- tumors;
- intoxication.
It is glomerulonephritis that is the main culprit of damage to the glomerular apparatus. The catalyst for pathology is damage to the filtration system due to a disorder in the immune system. But not all people far from medicine understand what reasons can cause the immune system to work against its own body. The main ones include:
- infections, including streptococci, causing tonsillitis, which can subsequently cause such a complication;
- autoimmune diseases.
An incompletely treated disease can serve as an impetus for the gradual replacement of kidney tissue with connective tissue, which cannot perform the initial tasks assigned to the body’s natural filter. Over time, the patient’s well-being may deteriorate so much that only emergency hospitalization in a hospital will help him.
Amyloidosis is characterized by the accumulation of the protein of the same name, amyloid, in the walls of kidney vessels. When it does not pass the cleansing barrier, it begins to be deposited in the glomeruli, clogging both them and the nearest capillaries. When the membrane becomes clogged, it simply stops functioning, which leads to the formation of a mechanical obstacle to normal blood flow.
The swelling here is due to the fact that remnants of toxins accumulate in the blood, and excess fluid cannot find a way out, filling the free space wherever it finds a place.
Poisoning plays an important role in a number of diseases leading to edema of varying severity. We are talking about poisoning with heavy metal salts, which can occur when:
- labor activity in hazardous working conditions;
- long-term living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
Some salts of heavy metals are localized specifically in the kidney membranes. With prolonged accumulation of toxic substances, the mechanism of converting normal tissue into connective tissue is triggered without the ability to cope with the task of filtering urine. The clinical picture ends with classic chronic renal failure.
The traditional symptoms of this pathology cause acute or chronic disturbances in the normal functionality of organs. And not only the glomeruli are affected, but also the tubules, which completely disables the kidneys very quickly.
Another disease from the list of the most common is an oncological tumor of a malignant or benign nature. Determining exactly what type of neoplasm is found in a particular patient will only be possible through a carefully conducted instrumental diagnosis.
Here, the extent of swelling of the limbs, neck, and face will be directly related to what stage of development the disease is at, as well as what size the tumor is, and whether there are metastases. The speed of spread of the disease is also taken into account.
The more pronounced the pathological changes, the brighter the external signs of pathology will be. This relationship is explained by compression of blood vessels, tubules and the glomeruli themselves, which, as the disease progresses, quickly lose their cleansing abilities.
What causes kidney swelling
Of the diseases that can activate the above-mentioned mechanisms that cause the occurrence of renal edema, pathologies that negatively affect the glomeruli in the kidneys are of key importance. Due to the ongoing inflammatory process and growing connective tissue, the filtration process, manifested by fluid retention and water-electrolyte imbalance, is inhibited or completely stopped. In some painful conditions, the exact opposite occurs: filtration increases, and substances that should be in the blood enter the intercellular space.
Renal edema can be caused by:
- glomerulonephritis;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- kidney amyloidosis;
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- tumor processes;
- renal and heart failure;
- changes in blood composition;
- vascular diseases;
- infectious processes;
- diseases of the lymphatic and urinary system;
- side effects of medications.
Depending on the underlying pathology, renal edema, photos of which can show varying degrees of severity, localization, persistence, are characterized by pallor of the skin in the swollen areas, as well as dry skin. In nephritis, a disease of an inflammatory nature, the swelling is pronounced and can disappear on its own, without treatment.
Edema causes and treatment
The accumulation of fluid in the subcutaneous tissue is one of the most common reasons for patients seeking medical help. Swelling often indicates the need to provide emergency care to the patient. What are their reasons? How to relieve swelling at home? Let's figure it out.
Edema is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the human body, subcutaneous tissue. They can be general and local. General edema according to localization is divided into peripheral and cavitary (hydrothorax, hydropericardium, ascites. The cause of fluid accumulation of this type is
- heart disease
- kidney
- liver
- hypoproteinemia
Edema may occur in cases of liver cirrhosis, starvation, or as a pathology of pregnancy. Complications can also be of non-inflammatory (transudate) and inflammatory (exudate) origin. Local edema is also caused by disturbances in the outflow of blood or lymph.
Cardiological factors of edema
In heart disease, swelling is a consequence of impaired myocardial contractility and one of the manifestations of heart failure, mainly right ventricular. The cause of cardiac edema is mainly the overflow of the veins of the systemic circulation with blood with an increase in hydrostatic capillary pressure, retention of sodium and water in the tissues.
Such swelling is usually located symmetrically in the lower parts of the body - on the legs, anterior abdominal wall, lower back, and in bedridden patients - most often on the sacrum, back; the distribution of edema is due to the displacement of fluid under the influence of gravity.
Typically, swelling is combined with cyanosis, but appears later and indicates more severe decompensation. When examining the heart, gross pathology is revealed in the form of a defect, cardiosclerosis, cor pulmonale. Peripheral edema in heart disease is always combined with liver enlargement.
The prevalence of pathology can serve as one of the indicators of the degree of decompensation. Extensive swelling indicates severe circulatory failure. Significant swelling due to heart problems is often combined with edema of the cavities - accumulation of fluid in the abdominal (ascites) and pleural (hydrothorax) cavities.
Renal causes of swelling
Edema in acute inflammatory kidney diseases - glomerulonephritis, affecting the glomeruli and nephron tubular apparatus, often begins from the face, affecting the torso and limbs. The distribution of swelling due to kidney problems is determined not by gravity, but by the looseness of the subcutaneous tissue. Edema due to kidney problems can develop acutely. In contrast to cyanotic cardiac edema, renal edema has pale skin. Renal edema can be dense (with nephritis) or loose, doughy (with nephrotic syndrome). The origin of renal edema is associated with an increase in capillary permeability and a decrease in the protein content, especially its albumin fractions, in the blood plasma. Renal edema is often combined with acute arterial hypertension and patient complaints of painful headaches, oliguria, and hematuria, as a result of which the urine may look like meat slop.
A characteristic of swelling due to kidney problems is their localization in areas where there is a lot of loose subcutaneous fat (for example, on the veins). The period of increasing edema of renal origin is accompanied by oliguria.
Hepatic sources of edema
| Hepatic sources of edema. Source: patologii.net |
Hepatic edema develops due to disturbances in the portal vein system or cirrhosis of the liver. Causes of this type of swelling include: alcoholism, hepatitis or jaundice. On examination, isolated ascites or ascites in combination with peripheral edema, splenomegaly, “spider veins”, liver palms, gynecomastia, developed venous collaterals on the anterior abdominal wall (“head of the medusa”) are revealed.
Edema due to liver problems usually accompanies cachexia of various origins - cancerous exhaustion, nutritional dystrophy from malnutrition.
The reason for the development of edema is a significant decrease in the level of protein in the blood plasma (hypoproteinemia). Hypoproteinemic edema has a soft, doughy consistency; the skin over them is thinned and transparent.
If cachectic edema develops in an elderly person with cardiosclerosis and pulmonary emphysema, then heart failure is of some importance in its origin, however, vigorous cardiac and diuretic treatment of edema in these cases has little effect, and examination usually reveals a malignant neoplasm.
Venous edema and its nature
If cardiac, renal and cachectic edema are usually symmetrical, then edema due to impaired blood outflow during vein thrombosis, compression by inflammatory or tumor infiltrates, is local and, depending on the location of the process, affects the right or left leg or arm. Such unilateral swelling, leading to a significant increase in the volume of the limb, is often combined with pain and other signs of inflammation - fever, redness of the skin.
Inflammation as a cause of swelling
Inflammatory processes are often accompanied by swelling. The principle of the occurrence of edema during inflammation is as follows: inflammation promotes the formation of gaps between endothelial cells, in which protein fractions and fluid (water and lymphatic fluid) collect. An example of swelling due to inflammation is swelling of the cervical spine due to the inflammatory process in the cervical lymph nodes.
In the mechanism of edema due to inflammation, an important role is played by the increased permeability of the walls of capillary vessels under the influence of histamine and other active biological substances. In the mechanism of edema, a large role is played by the difficult outflow of blood and lymphatic fluid from the area of inflammation through the blood and lymphatic vessels. Stagnation leads to the penetration of lymph and blood into tissues and muscles, which contributes to the formation of swelling.
Swelling due to inflammation has some protective function. Proteins included in the edematous fluid are able to bind to toxic substances and breakdown products that form in inflamed tissues and neutralize them. Thus, the inflammatory focus is localized and does not spread to the entire body as a whole.
Inflammation as a cause of cervical edema
Let's consider swelling during the inflammatory process in the cervical lymph nodes. First of all, it is necessary to find out the cause of the swelling, because the lymph nodes are of great importance in our body. Causes of neck swelling may include:
- an infectious disease such as mumps
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity or respiratory organs
- frequent viral infections
- lymphogranulomatosis is a disease of the lymphatic system that is oncological in nature
When the lymph nodes are inflamed, swelling may be very noticeable, or may not appear externally. To determine the true causes of swelling during inflammation, it is necessary to conduct some laboratory and instrumental studies.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is accompanied not only by swelling. It is quite painful, and there is also a headache, fever and general malaise and weakness. In no case should inflammation of the lymph nodes be ignored and you should immediately consult a doctor for help. Self-medication in cases of edema due to inflammation is a crime against oneself.
Features of the treatment of edema
Treatment of cardiac edema
| Treatment of cardiac edema. Source: otekhelp.ru |
The combination of huge edema with hydrocele, cyanosis, shortness of breath, and a forced sitting position creates the characteristic appearance of a seriously ill patient with cardiac decompensation, often in need of emergency care and emergency hospitalization. In the treatment of the disease, the use of cardiac glycosides, diuretics, vasodilators, and a diet with limited salt in most cases gives an immediate effect.
Treatment of renal edema
Edema of renal origin is treated with the use of various diuretics (Furosemide, Hypothiazide, Veroshpiron, etc.). To assess the dynamics of the disease, it is necessary to regularly weigh patients. A common symptom of kidney disease is arterial hypertension, which is usually quite persistent (especially diastolic pressure) and, over a long period of time, leads to:
- left ventricular overload
- development of heart failure
- damage to the blood vessels of the retina and visual impairment
- cerebrovascular disorders
When treating edema of this type, patients with renal hypertension are systematically monitored, limit the consumption of table salt, and prescribe regular use of antihypertensive drugs in combination with diuretics. This way you can eliminate the causes of renal edema and avoid this unpleasant phenomenon.
If patients have edema, daily treatment takes into account daily diuresis and the amount of fluid drunk; the sodium chloride content in the diet of patients is limited to 1–3 g per day. It is permissible to reduce fluid intake only in the absence of signs of renal failure.
Treatment of venous edema
The absence of hepatomegaly helps exclude heart failure as a cause of edematous syndrome. Patients with these symptoms should be examined by a surgeon. Sometimes it is necessary to urgently hospitalize them in the surgical department.
How to relieve swelling at home?
To treat edema, the underlying disease that causes it should be treated.
Folk remedies that will help relieve swelling
If you suffer from swelling of the legs, you should take fresh, not very old birch leaves and chop them finely to make a glass. After this, add 1 liter of boiling water and a tablespoon of salt. Leave for half an hour. Then, with this infusion for swelling, you need to make compresses on your legs 5-6 times daily. After these procedures, swelling quickly subsides, and the legs return to normal.
In addition, an infusion prepared from birch leaves will help relieve swelling. It is effective for renal and cardiac edema. Young leaves should be used in spring, since summer leaves are no longer so useful and may contain toxic substances.
One hundred grams of leaves must be crushed, then add two glasses of warm boiled water. To preserve beneficial substances, you do not need to pour boiling water over the leaves. After this, they should be left to infuse for 5–6 hours, strain and squeeze. The resulting infusion for the treatment of edema should be allowed to settle until sediment appears. It will not be needed, so after settling, you should pour the infusion to get rid of the sediment. This infusion for swelling should be taken half a glass three times a day before meals.
To relieve swelling, you should take equal quantities of hawthorn fruits, calendula flowers, linden flowers, rose hips, blueberry leaves, birch leaves, plantain leaves, and viburnum fruits. Pour two tablespoons of pre-chopped collection into 0.5 liters of boiling water in a thermos and leave to steep overnight. Take a third to a quarter glass three to four times a day to treat edema. The course for edema is two to three months. This collection for edema can be taken during pregnancy, having first consulted a doctor.
Folk remedies for the treatment of edema are highly effective, so you can choose the most suitable one for yourself. However, it should be remembered that first of all it is necessary to treat the underlying disease, which is the cause of the swelling.
mymylife.ru
If you want to read all the most interesting things about beauty and health, subscribe to the newsletter!
Did you like the material? We will be grateful for reposts
Tell your friends about the article or feed it to the printer
doctor.kz
Diagnosis of renal edema
If you suspect renal edema, it is recommended to consult a physician and undergo the following tests:
- laboratory testing of blood and urine;
- X-ray examination of the urinary tract and kidneys,
- magnetic resonance diagnostics and computed tomography of the kidneys;
- Doppler ultrasound aimed at identifying impaired blood flow in the kidneys;
- nephroscintigraphy, which analyzes the functional abilities of the organ being studied and probable thrombosis.
Renal edema: treatment
To treat renal edema, the doctor prescribes diuretics that stimulate the removal of fluid from the body: Spironolactone, Hydrochlorothiazide, Oxodolin, Triamterene, Mannitol, Furosemide. You should know that:
- treatment should be carried out against the background of constant monitoring of the amount of urine, blood pressure, and electrolyte levels;
- in case of urgent need, drugs can be administered intravenously;
- self-medication is strictly prohibited due to the high likelihood of complications.
Edema in pregnant women
Most often, renal edema occurs during pregnancy. This condition was previously called nephropathy (that is, kidney damage), now it is called preeclampsia and is included in the category of gestosis (toxicosis) in the second half of pregnancy. Preeclampsia is characterized by only one, two or three symptoms:
- swelling;
- excretion of protein in the urine;
- increased blood pressure,
and suggests that the mother’s body perceives the fetus as a foreign organism.
To diagnose edema in pregnant women, routine checks have been developed when visiting a antenatal clinic. This is a test with putting on a ring (the same ring should fit each time), weighing (weight gain of more than 300 g/week indicates edema). To identify kidney damage, a pregnant woman must very often give urine, in which they look for protein.
If minimal abnormalities are detected in the urine or the other two samples, the pregnant woman is prescribed a herbal preparation that improves kidney function (“Canephron”, “Fitolysin”). After this, she is asked to retest her urine in a week, and if changes are observed, she is offered to be hospitalized in an obstetric hospital. This is due to the threat of developing seizures (eclampsia), which is life-threatening for both mother and child.
During pregnancy
Renal edema during pregnancy is very dangerous. They are quite difficult to identify, since during the period of bearing a child, swelling of the arms, legs, and face is quite common. The body's need for fluid increases, and a woman in an interesting position, as she approaches childbirth, becomes increasingly thirsty. At the same time, sodium, which retains water, accumulates in the body.
Most often, during pregnancy, the legs swell: it becomes extremely difficult to put on shoes, and a mark from the elastic of the socks appears on the ankle. If by the morning this alarming state remains, and at the same time there is renal swelling on the face with bags under the eyes and swelling of the hands, you should definitely visit your doctor. Excessive weight gain (more than 0.3 kg per week) should also be a serious cause for concern.
Traditional methods of treatment
In some cases, renal edema can be treated with traditional methods, namely medicinal herbs that help remove excess fluid from the body.
It is effective to use a collection of lingonberry leaves, crushed juniper fruits, birch buds, bearberry leaves, taken in the same proportion. Pour boiling water over a tablespoon of the prepared mixture and simmer over low heat for 10-15 minutes. Filter. Drink 2 tbsp. spoons 4-5 times a day.
Tea made from dandelion leaves, which has a diuretic effect and restores potassium reserves in the body, will help relieve kidney edema. Drink 1 glass 3 times a day.
Traditional medicine recipes in the treatment of renal edema are recommended to be used only with the permission of the attending physician in the absence of special contraindications and the cause of this condition is not too serious.
Renal edema is one of the types of swelling that manifests itself in case of kidney problems and is the main, characteristic symptom in acute or chronic renal failure.
In most cases, swelling can occur under the eyes due to kidney disease, as well as in the arms and legs. All of them require immediate attention from a doctor, since they can cause many irreversible pathological processes.
Folk recipes
The simplest is to take kidney teas or decoctions, which are sold in pharmacies. The main component of such herbs is orthosiphon staminate. It is brewed according to the instructions on the package.
It is also recommended to drink green tea. You can drink no more than 2 cups a day, and make sure that no more than a liter of liquid is consumed (unless the doctor says otherwise).
Corn silk. 25-30 g of stigmas are poured with a glass of boiling water, wrapped in a towel and left for 2-3 hours. You need to take 50 ml three times a day, 30 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 5 days.
Source: zdravotvet.ru
We are in social networks:
More information:
- how to distinguish between renal and cardiac edema lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- swelling in kidney diseases lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- swelling in the kidneys lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- swelling due to kidney pathology lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- how to distinguish renal edema lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- kidneys and facial swelling lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- renal edema and cardiac edema lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- drugs for renal edema lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- swelling due to kidney disease lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
- how to relieve renal edema lNDq9RCid8X3B9CEA3R6MBpbO4vHfIdsmJJetenx4duA4Z5zZOuCiKGWI8uQBA1ObJTvP2UOeffb5dCXUXq8zZR2R […]
How does the process of swelling of a body part occur?
If we talk about the mechanism of this process, it is provoked by a number of factors and root causes:
- Intracapillary pressure increases and, accordingly, fluid filtration in the tissues themselves increases and its reabsorption decreases.
- The level of protein in the plasma decreases significantly - this leads to a disruption in the removal of excess fluid from the tissues.
- The permeability of blood vessels and capillaries increases significantly, and the functioning of the excretory system of the kidneys is disrupted.
- The water-salt balance is disrupted - the production of the hormone aldosterone increases, which in turn leads to water retention in the body and sodium ions.
Causes of renal edema
Renal edema on the face and legs, arms can be a consequence of the development of the following pathologies and diseases:
- Renal failure is a disease that is marked by a failure in the basic functions of the kidneys, filtration and maintaining a normal level of water and electrolyte balance in the body.
- Amyloidosis is a disease in which there is an excessive accumulation of protein in the kidneys and provokes blockage of its membranes. As a result, there is a disruption in the blood flow and the accumulation of toxins in the body, subsequent poisoning with decay products and swelling.
- Tumors - when the kidneys are affected by a benign or malignant neoplasm, the latter cannot cope with the volume of filtration, and this provokes a pathological condition.
- Glomerulonephritis is an immunological lesion of the patient’s glomerular renal apparatus. Most often, the cause is infectious and autoimmune diseases, which, affecting the functioning of the kidneys, provoke a stoppage of filtration and swelling.
- Poisoning and intoxication – poisons and heavy metals, dangerous substances. All of them do not have the best effect on the functioning of the kidneys and their ability to remove them along with fluid from the body.
Causes
Renal edema occurs for various reasons, which are conventionally divided into two classes. The first class of causes are pathological mechanisms that cause the release and accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space. The second class is caused by renal pathologies, in which the above mechanisms operate.
Among the renal pathologies that contribute to edema, the most significant are those that affect the glomerular structures, causing disturbances in filtration activity.
Therefore, renal edema is most typical for the following pathologies:
- Amyloidosis. With pathology, a protein called amyloid accumulates in the kidneys, which gradually clogs the membranes, preventing normal blood flow. All this reduces the filtration capacity of the kidneys, leading to the accumulation of toxins in the blood and fluid in the tissues.
- Glomerulonephritis. This is an immune lesion of the glomerular renal apparatus. Immune complexes that provoke pathology are usually formed in the blood against the background of autoimmune and infectious pathologies such as streptococcal tonsillitis, etc. The glomerular apparatus becomes inflamed under the influence of immune complexes, and filtration is impaired.
- Renal failure is a violation of all renal functions, including water-electrolyte balance and filtration, which is the cause of edema.
- Tumor lesions. With some tumor formations, renal activity is impaired, which negatively affects filtration capacity.
- Poisoning. Some heavy metals and toxic substances can accumulate in the body. Against the background of their toxic effects, normal cells die, being replaced by connective tissue structures. As a result, kidney failure occurs, accompanied by edema.
In addition, the causes of swelling may be due to nephropathy due to diabetes or pregnancy, systemic connective tissue pathologies, etc.
Symptoms of edema in kidney disease
Swelling of the kidney shows its symptoms most often in the morning and in the area of the arms and legs, which lose mobility, swell, the skin in these places is pale and marked by excessive dryness. This should include the following:
- Pain in the lumbar back. Most often, such attacks of pain bother the patient until pathological swelling appears - the latter can be very intense and provoke attacks of nausea and vomiting. They can radiate to the leg or groin area.
- The patient is also concerned about problems with going to the toilet and urinating - if water is retained in the body, the amount of urine decreases and the lower this indicator, the worse the patient’s condition will be. Among other things, the color of the urine itself changes, becoming dark or light, and when urinating, the patient feels pain in the lumbar region.
- Neurological malfunctions and disorders also show themselves - toxins, poisoning the body, have a negative effect on the central nervous system, provoking the development of paralysis and coma, encephalopathy. At the very beginning, intoxication will show itself as rashes all over the body and itching, migraine attacks and pain, muscle stiffness.
What is the difference between renal edema and cardiac edema? Doctors identify a number of characteristic symptoms and signs. In particular, doctors identify the following signs of swelling caused by heart problems:
- First of all, the lower extremities will swell - excess fluid is localized in the lower legs and feet, and when taking a horizontal position - in the lumbar region.
- If you have heart problems, the skin in the area of swelling will be cold and acquire a bluish tint.
- By pressing on the site of swelling, the patient experiences pain, and the swelling itself remains motionless.
- I am worried about attacks of pain in the sternum and cardiac shortness of breath, but the composition of the urine itself does not change color.
Diagnostics
If swelling appears in the eyelids, face, or discomfort in the lumbar area, you should visit a urologist or nephrologist; if there is pronounced swelling of the legs, pain in the sternum, consult a cardiologist. The data from the table will help you figure out which doctor to come to for an appointment. If in doubt, you need to visit a therapist, then the doctor will refer you to a specialist.
To determine the cause of swelling, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out:
- biochemical and general blood test;
- kidney tests to clarify the nature of the damage to the bean-shaped organs;
- urine analysis (general and bacterial culture);
- blood test for rheumatic factor;
- Dopplerography of vessels of natural filters.
Renal edema is differentiated from manifestations of other diseases:
- vascular thrombosis. The main symptom is the unilateral nature of the swelling in the area of venous blockage;
- obesity. When you press on the swollen area, you can hear that the subcutaneous fat layer is loose, there is no pain. Excess adipose tissue slowly accumulates; fighting the signs of obesity is more difficult than eliminating renal edema;
- heart diseases. The main differences from swelling due to damage to the renal tissue are indicated in the table;
- lymphedema. The problem occurs when lymph stagnates; in advanced cases, elephantiasis develops with active tissue proliferation. The swollen areas are dense, swelling increases if the patient sits for a long time;
- swelling in the area of inflammation. Characteristic features: the tissues are hot, dense, the skin is tightly stretched, palpation provokes sharp pain. Negative symptoms are observed around purulent wounds and inside tissues after the penetration of infectious agents.
Learn how to prepare for a kidney CT scan with contrast and how the procedure is performed.
The first signs and symptoms of nonspecific urethritis in women are written on this page.
Recommendations for relieving swelling
Treatment of renal edema involves, first of all, the prescription of drugs and the development of a course that relieves swelling.
- Prescribing diuretics is the main component of the course of treatment when diagnosing renal edema. The drugs remove excess fluid retained in the tissues and should only be prescribed by a doctor. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Oxodolin, Triamterene, and Mannitol.
- After eliminating the pathological swelling, they proceed to treatment of the underlying disease. In this case, doctors may prescribe a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory, as well as hormonal drugs. To cleanse the body of intoxication products, the patient can undergo a course of hemodialysis.
- It is also mandatory to prescribe medications to strengthen the vascular walls - they are not a prerequisite for treatment and are prescribed by specialists as needed.
- Drugs are also prescribed that help maintain the water-salt balance in the body - most often this is a course of intravenous drips of saline solution. But such a procedure is carried out exclusively within the walls of a medical institution and under the supervision of medical workers.
Treatment
How to treat can only be said after determining the etiology of the swelling. The primary task is to eliminate the provoking factor. In general, treatment involves the use of the following techniques:
- Treatment of the underlying pathology. Necessary to eliminate the root cause of edema.
- Diuretic drugs. They stimulate the excretion of excess fluid (Furosemide, Oxodolin, Uregit, Dichlorothiazide, Triamterene, Veroshpiron, etc.
- Diet therapy. Aimed at being as gentle as possible for the kidneys. In severe cases, bed rest is indicated; at rest, it is easier for the kidneys to perform filtration, which helps eliminate swelling. The diet depends on the specific case. Patients are prescribed salt-free diet No. 7 or diet No. 7A, which limits fluid and salt intake.
- Means for strengthening blood vessels (Ascorutin, etc.). They are not prescribed to all patients, but only to those whose vessels are characterized by increased permeability.
- Means for normalizing water and electrolyte balance. Intravenous infusions or droppers with solutions of certain salts are used.
Long-term use of diuretics can provoke adverse reactions, so patients are often prescribed Asparkam or Panangin in combination with them.
These drugs are extremely important for maintaining normal heart function and preventing potassium leaching. The nephrologist controls the treatment process of renal edema and its root causes. A competent specialist in this case is extremely necessary to exclude various kinds of complications.