It is very important to follow a diet when there is sand in the kidneys. By following proper nutrition, it will be possible to prevent further development of the disease and the formation of real stones. And now it’s worth briefly talking about permitted and prohibited products, as well as highlighting other nuances related to this topic.
general information
Urolithiasis, or as it is also called “sand” in the kidneys, is the result of a violation of mineral metabolism in the body. As a result, they accumulate in the organ.
First of all, doctors associate this process with poor lifestyle and nutrition.
Most often, this disease occurs in people of working age. For many it occurs without visible symptoms, for others it causes severe pain and discomfort. Sand can be detected by undergoing an ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
The entire process of sand formation in the kidneys can be represented in this way: as a result of metabolic processes in the human body, soluble and insoluble salts of uric acid, calcium, cystine, etc. are formed.
They accumulate in the organ itself and the urinary tract. If diagnosis and treatment are not timely, sand turns into stones.
The therapeutic diet includes prohibiting foods that provoke uric acid deposits, as well as drinking enough fluid.
It is important to note that adjusting your diet is carried out in parallel with drug therapy; in itself, it always brings the desired effect.
Recommendations for nutrition and product selection
The main nutritional requirements for sand in the kidneys are:
- Drinking large amounts of liquid. It is very important that the patient produces up to 2.5 liters of urine per day, this will help prevent further formation of urate compounds.
- Reducing the amount of table salt in food. Dishes should be practically unsalted; alternatively, lemon juice or other natural ingredients can be used.
- Limit the consumption of sugary drinks (this applies to carbonated water and juices).
- Including vitamin A or foods containing it in your diet. It helps to launch tissue regeneration processes in the kidneys that are damaged by sand or stones.
It is imperative to correctly calculate the daily calorie content and amount of nutrients, eat in small portions, but often. The selection of a diet is carried out exclusively by a nutritionist; you should not make decisions about this on your own.
How to choose a diet?
Only after carrying out diagnostic measures, the most important of which is a urine test, does a specialist prescribe a diet on an individual basis, first of all, he sets restrictions on harmful components. This is important for the specific composition and type of stones. It is imperative to conduct an ultrasound examination, donate blood for analysis and, if necessary, nephroscintigraphy. More serious and precise measures are indicated if the presence of large stones is suspected. Urine analysis will determine the chemical composition of kidney sand, based on this, the diet is adjusted as follows:
- the presence of oxalates leads to the restriction of those products that contain oxalic acid;
- if phosphates are detected in the kidneys, limit foods that contain phosphoric acid, for example, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, sesame seeds;
- if urates have been diagnosed in the kidneys, then you should limit the consumption of fish or meat, because they contain a large amount of purines, and they are eventually converted into uric acid.
Types of kidney stones
In addition to the typical menu, you should follow a number of rules and recommendations regarding the diet created to combat sand and other solid deposits. To do this, you should adhere to the following aspects:
- reduce the amount of salt consumed;
- balance the drinking regime, which will inhibit the precipitation of salt;
- limit the amount of sweet foods in your diet, and you also need to completely give up soda;
- At least 2-3 grams per day should be consumed of vitamin A, since it accelerates the regeneration of kidney tissue that is damaged by stones and sand.
Herbal medicine with a set of products of plant origin has an additional effect.
If the patient immediately began to implement the recommendations of the attending physician, then an improvement in the condition should be expected in the near future. Herbal medicine has an additional effect; the fact is that the urinary system responds remarkably to products of plant origin. Every day you need to use medicinal herbs and their products; rose hips, lingonberry leaves, flax seeds, carrots, millet and many other ingredients have proven themselves best in this matter.
The abundance of products in the diet allows you to choose the very menu that will be most preferable for a woman, that is, she will not have to particularly limit herself. Of course, there will be no fatty, smoked, salty food there, but you can prepare equally nutritious, tasty and enjoyable dishes from healthy products.
Features and basic principle of the diet
When selecting nutrition, it is necessary to proceed from a urine test; it will show which salts exceed the norm.
There are products that are excluded in any case: canned food, spices, fried and fatty foods, smoked foods, fatty meat and fish, tea, coffee and alcoholic beverages.
The therapeutic diet is aimed at preventing the formation of mineral salts in the kidneys. It is not recommended to eat hard cheeses and spicy foods.
On average, the duration of the diet ranges from 30 to 180 days (depending on the amount and type of mineral deposits).
As a liquid, you can use not only ordinary water, but also fruit drinks or non-acidic juices. The diet is selected depending on the acidity of the urine and the salts that predominate in it. Let's look at this in more detail.
With uric acid salts
The main requirement is to exclude foods that contribute to the formation of uric acid salts. These include fatty meats, cheese, alcoholic drinks, chocolate and chocolate products, strong tea and coffee, pickled vegetables, some types of vegetables and fruits (tomatoes, gooseberries, legumes, plums and apples).
The list of foods whose intake is limited includes dairy and fermented milk products, eggs, strawberries, wild strawberries, mushrooms, onions and garlic.
It should be noted that the number of eggs eaten should not exceed 5 eggs per week. It is not recommended to eat sweet baked goods and cakes.
The main diet for this diet includes:
- lean meat and fish;
- oil;
- whole grain cereals and breads;
- vegetables (potatoes, carrots, cucumbers, greens);
- fruits and nuts;
- lemon juice.
To improve the effect, it is recommended to completely eliminate the intake of fish or meat dishes at least 3 times a week. It is also useful to do fasting days, but it is forbidden to completely starve.
Diet with phosphate acid salts
The purpose of this diet is to increase the acidity of urine. In this case, the following are completely excluded:
- milk and fermented milk products;
- liver and seafood, which contain large amounts of vitamin D;
- alcohol.
It is very important to quit smoking and engage in moderate physical activity. The list of acceptable foods includes: cereals, eggs, lean meats and fish, sour vegetables and fruits. The amount of fluid should be adjusted depending on the acidity level of the urine.
With oxalic acid salts
In this case, the patient’s urine pH level increases, so nutrition is directed towards reducing it. Prohibited smoked foods, fatty meats and fish, canned food, hard cheese, some types of vegetables and fruits, herbs, sour berries, citrus fruits, chocolate products.
Ready meals should be steamed, boiled or stewed. As a liquid, you can use ordinary still water, fruit drinks made from non-acidic fruits and berries.
Rare variants of formations
In addition to the three main mineral deposits, residues of carbonic acid salts and calcifications can form in the kidneys.
In this case, there are also certain nutritional requirements.
It is not recommended to eat cottage cheese or fermented milk products, eggs and milk in large quantities.
In this case, all dishes must be boiled, stewed or steamed; oatmeal is allowed from cereals.
Some patients experience a disease such as cystonuria. This is the deposition of a large amount of amino acids in the kidneys.
Very often diagnosed in men, it is usually caused by poor genetic inheritance. In this case, it is prohibited to eat cheese, eggs and any fish. The main diet includes potatoes and liver.
Products for oxalates
Deposits of this type of compound are caused not so much by poor nutrition as by other concomitant diseases. You can read more about oxalates by following the link.
However, when the level of oxalic acid salts increases, patients are advised to limit the consumption of foods containing them and increase the consumption of foods that are enriched with magnesium and vitamin B6.
Nutrition for urates
In this case, the acidity level of urine decreases. This is caused by a high content of purine compounds in food, excess weight, and alcoholism. A proper diet helps improve the effectiveness of treatment. The patient is prohibited from eating meat, fish, legumes, and alkaline foods.
Features of dietary nutrition
Diet for oxalates
Oxalates are formations that consist of salts of oxalic acid. More than half of diagnosed kidney stones are oxalate stones. Their formation is provoked by diseases of the digestive system, a lack of magnesium in the body, problems and malfunctions of the pancreas, and excess vitamin C. For oxalates, the doctor will recommend the following diet plan:
- Remove from your diet foods containing oxalic acid and
its salt. These are sorrel, legumes, parsley leaves and roots, asparagus, red grapes, spinach, gooseberries, blueberries and blackberries.
- Add foods to your menu that help eliminate kidney stones and prevent new ones from forming. These are white grape varieties, pear, dogwood, green apple varieties, plums, quince.
- Enrich your diet with foods that contain the element magnesium. These are various dried fruits, bran, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, millet.
- Foods with gelatin should be removed, as they provoke the production of oxalic acid.
- Increase the consumption of foods rich in vitamin B6 - buckwheat and oatmeal, bran bread, whole grain cereal bread.
Diet with phosphates
Phosphates are formed in the body due to an imbalance in the exchange of phosphorus and calcium in the body. Stones are formed due to the alkaline environment in the organs, and when consuming large amounts of salt and phosphorus-containing foods. The disease also manifests itself in bone pathologies, malfunctions of the thyroid gland, and metabolic and digestive disorders. In this case, you need to adhere to the following rules of diet therapy:
- Increase eggs, meat, fish and sour fruits in the menu. This helps acidify the urine, causing phosphates to begin to dissolve.
- Reduce foods that contribute to the formation of an alkaline environment - milk, sweet fruits, seeds, nuts.
- You need to give up vegetarianism.
- Avoid foods that contain vitamin D - liver, red caviar.
- Establish a drinking regime according to the patient’s health condition.
Diet for urates
If there are a lot of uric acid derivatives in the urine, it means that the pH level in the body is low and the body is acidic. The cause of the development of pathology is smoking, abuse of alcoholic beverages and beer, and excessive excess weight. If urates are formed due to bad habits, you need to gradually get rid of them, follow the doctor’s recommendations and lead a healthy lifestyle. Patients with urates are advised to follow the following dietary rules:
- Avoid dishes and foods that contain a lot of urea and purines. These are red meats, poultry, yeast products, fish, beans, mushroom dishes, and seafood.
- Increase your consumption of foods that alkalize the body. These are milk and dairy products, fruits and non-acidic vegetables, alkaline mineral water.
- Limit the consumption of animal fats and empty carbohydrates in your diet. This includes sour cream and cream, sweets with cream fillings, white flour bread, baked goods, and confectionery.
- Remove acidic plant foods from the menu.
- Drink tea and coffee in moderation, as they stimulate the secretion of urea.
Prevention and prognosis
It is very important to prevent the formation of sand in the kidneys. To do this, it is recommended to monitor your diet, reduce fatty, fried and spicy foods.
Limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products. Exercise regularly and take a urine test to detect salt deposits in a timely manner.
With a properly selected diet, the prognosis for patients is positive. It is very important that the selection of nutrition is carried out exclusively by a doctor; self-medication can cause serious complications.
Sand in the kidneys is an alarming symptom. Very often it occurs without visible signs and develops into stones over time. As a treatment, doctors prescribe a special diet.
It is important to know the nature of the mineral salts that are formed in the kidneys. It is also necessary to adjust the amount of fluid you drink per day in order to increase the excretion of sediments in the urine.
Urolithiasis is one of the most common diseases of the human urinary system. This pathology does not form immediately - the precursor to kidney stones is sand. It is at this stage that the disease should be identified and treated, since if a large number of stones accumulate, there is a high risk of developing renal failure and other severe and life-threatening conditions. According to statistics, this pathology occurs three times more often in men than in women, so representatives of the stronger sex should pay special attention to its first signs.
Description of sand in the kidneys in men
There is a misconception that sand and kidney stones are essentially the same thing. In practice, urologists note that stones (calculi) should be understood as visually visible structures consisting of various types of salts and having a diameter of more than 1 mm. Sand is a suspension of salts, mainly urates, oxalates and phosphates, which cannot be visualized using instrumental diagnostic methods due to their small size. The diameter of one “grain of sand” can be tenths and hundredths of a millimeter.
In this regard, it may seem that the presence of such impurities in the urine does not adversely affect the functioning of the kidneys, but this is not entirely true. The total amount of sand can be quite significant and sufficient to disrupt the proper functioning of the urinary system. In addition, in the absence of proper treatment, sand will eventually form into denser structures - stones, therefore the presence of such impurities in the urine is considered to be an early stage in the development of urolithiasis.
The precursors of kidney stones are suspensions of salts with small element sizes (less than 1 mm)
Sample menu
To quickly eliminate sand and kidney stones, the diet must be followed correctly. It is better to eat 4 times a day. Small meals are not encouraged, but overeating is strictly prohibited. Here's what a sample menu might look like:
Before going to bed, you are allowed to drink apple compote and snack on grain bread. Food can be baked, fried, boiled, or steamed. But cooking fat cannot be used.
Causes and development factors
Men are more susceptible to the appearance of sand in the kidneys. It is worth noting that the disease can manifest itself at any age, but the risk of developing urolithiasis increases with age. The main reasons for the formation of sand in the kidneys are:
- irrational, unbalanced nutrition with a predominance of fatty and heavy foods in the diet;
- low level of physical activity;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- lack of drinking regime or regular consumption of liquids with a high content of mineral salts;
- hormonal instability, caused primarily by disorders of the thyroid gland.
Risk factors for the formation of sand in the kidneys include:
- work in hazardous industries;
- obesity;
Obesity is one of the risk factors for the development of urolithiasis
Symptoms of sand in the kidneys in men
The presence of sand in the kidneys may not manifest itself in any way for a long time. The only symptom is weakness, which many men, especially older ones, usually do not pay attention to. As the disease progresses and the amount of salts increases, the patient begins to experience the following unpleasant sensations:
- difficult and painful urination;
- slight pain in the lower back;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headaches, shortness of breath, tachycardia (increased number of heartbeats), which indicates increased blood pressure;
- swelling of the lower extremities.
In addition, the patient may notice changes in the color of urine, which becomes darker, as well as an increase in its density, which is a consequence of the high content of salts of various origins.
The presence of sand in urine can be manifested by cloudiness or the formation of sediment at the bottom of the sample collection container
The disease is characterized by the periodic release of sand in the urine. During this period, the man begins to experience quite significant pain in the groin area, as well as discomfort and pain in the penis when urinating. After the sand comes out, the patient usually experiences relief - his general health improves, and the above symptoms disappear. However, this improvement is imaginary, since if the cause of the disease is not eliminated, sand will again accumulate in the kidneys.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
Instrumental diagnostic methods, widely used for suspected urolithiasis, are completely useless for identifying sand in the kidneys. Neither ultrasound nor x-ray can visualize small fractions, which is sand. In this regard, the leading role in this case is played by laboratory diagnostic methods, in particular, an ordinary general urine test (UCA).
The presence of sand in the kidneys according to the results of OAM is indicated by the following indicators:
- increased density of urine, changes in its consistency and color;
- the presence of urates, phosphates or oxalates in the urine;
- excess leukocyte content, which indicates the development of inflammatory processes;
- the presence of red blood cells in urine, which is a consequence of minor mechanical damage to the ureters and urethra by fine sand fractions.
When making a diagnosis, sand in the kidneys should be clearly separated from the presence of large concretions or stones. With urolithiasis, the severity of symptoms is very high (severe pain, signs of intoxication of the body), and stones are easily visualized using ultrasound and x-rays.
Treatment
Despite the fact that the disease at an early stage, as a rule, does not manifest itself clinically, treatment must be started as soon as possible, since its absence leads to the progression of the disease and the formation of hard stones. The basis of therapy for sand in the kidneys is taking certain medications and diet.
Table: drug therapy for the presence of sand in the kidneys
| Group of drugs | Operating principle | Examples of medicines |
| Diuretics | Promote the timely release of sand, preventing the development of urolithiasis |
|
| Anti-inflammatory and antispasmodics |
|
|
| Litokinetic (stone expelling) agents | Promotes sand removal |
|
Photo gallery: drugs for sand in the kidneys in men
Diet
For sand in the kidneys, a certain diet is prescribed, which, in principle, is the basis of treatment, since the formation of foreign fractions in the urinary system is associated with errors in nutrition in most cases. The diet should include:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- dairy products;
- boiled and stewed lean meat;
- porridge;
- dried fruits;
- honey.
It is strongly recommended to exclude:
- semi-finished products;
- fat meat;
- confectionery;
- legumes;
- sea fish;
- pickles;
Cheese and sausage contain a lot of salt, so their consumption should be sharply limited
In addition, if you have sand in your kidneys, it is important to drink at least 2.5 liters of clean drinking water per day, as well as be physically active.
Video: what to eat and not to eat if you have stones and sand in your kidneys
Features of the course of urolithiasis in women
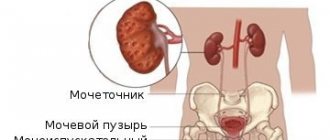
Urolithiasis is a pathology of the urinary system, accompanied by the formation of stones in the kidneys, excretory ducts or bladder. Urolithiasis is diagnosed in patients of any age, but most often this disease affects people 25–50 years old. The stones are capable of moving, in which case they may descend from the kidneys into the ureter and below - then the stone can cause obstruction (blockage) of the ducts and an inflammatory process. Stones are most often localized on the right side. Urolithiasis in women is 3 times less common than in the stronger sex, which is due to anatomical features.
Causes of pathology
Stones appear when water-salt metabolism is disrupted; salt crystals settle in the kidneys in the form of sand, which is gradually overgrown with new deposits and turns into stones.
Causes of urolithiasis in women:
- genetic predisposition;
- drinking poor-quality tap water;
- prolonged dehydration due to infectious diseases, poisoning;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- long-term use of sulfonamides, ascorbic acid, antacids, tetracyclines;
- deficiency of vitamins A, D;
- osteoporosis, osteomyelitis;
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary system, gastrointestinal tract;
- unbalanced diet;
- congenital pathologies of the structure of the urinary system;
- treatment with glucocorticoids;
- prolonged stay in a supine position;
- inactive lifestyle.
Symptoms of urolithiasis in women are more acute; the pathology occurs with the formation of coral-shaped stones, which can reach large sizes.
The risk of developing urolithiasis increases if several provoking factors are present. Violation of the outflow of urine from the kidneys makes it difficult to remove metabolic products, they crystallize and precipitate as a salt, and general intoxication of the body occurs. The cause of urodynamic failures can be stenosis of the pelvic system, stricture (narrowing) of the ureter, cystic reflux, bacterial infections of the genitourinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis).
Multiple bladder stones in women are diagnosed by drinking hard water with a high content of calcium and magnesium ions. Dehydration of the body when living in a dry, hot climate stimulates the formation of stones. Against the backdrop of heat, a person drinks a lot of liquid, and sodium is washed out along with urine, and the acidity of urine increases.
Clinical picture
In case of urolithiasis in women, the symptoms of malaise depend on the location of the stone, its size, type, the presence of a bacterial infection, and disruption of the outflow of urine from the bladder. In the initial stages, the disease can be completely asymptomatic, but as the size of the stone increases, discomfort begins to appear:
- acute pain in the groin, lumbar region - colic;
- blood in the urine;
- unilateral or bilateral tension of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall;
- discharge of small stones;
- anuria (no urine).
If an infectious process is associated with urolithiasis, women complain of hyperthermia (increased body temperature), cutting pain during urination, frequent urge to go to the toilet, surges in blood pressure, nausea, and vomiting. During walking and physical activity, discomfort appears in the lumbar region.
Symptoms of renal colic are observed in 85% of women with urolithiasis. Exacerbation occurs when the urinary canal is blocked by a stone and the outflow of urine is obstructed or with complete anuria. The pain occurs suddenly, is characterized by pronounced intensity, begins in the lumbar region and spreads to the groin area, genitals, and inner thighs. Attacks may alternate with periods of relief. It is difficult for the patient to find a comfortable body position; he tries to take an unnatural position.
Colic goes away when the stone moves further or is passed out.
Signs of dysuria appear when the stone is localized in the ureter; if it is located in the intramural section, the patient suffers from a frequent urge to urinate. When sand and small stones come off on their own, the symptoms of colic may bother you, or this process does not cause discomfort. Pain also occurs if the stones have a spiky surface, and with inflammation of the urinary system.
Types of stones
The acid-base balance of urine plays an important role in the formation of stones in urolithiasis in women. About 70% of all stones are formed by calcium compounds. Other types include:
- urates;
- phosphates;
- oxalates.
Urates are formed in an acidic environment and consist of uric acid salts. They have a dense structure, a brownish tint, and a smooth or rough surface. Phosphates precipitate when an alkaline environment is created. Such stones are white or light gray, have a fragile structure, and are often accompanied by cystitis and pyelonephritis.
Oxalates are formed in an alkaline or acidic environment. They are formed by crystals of oxalic acid salts. The stones are dense, very dark in color, their surface is covered with sharp thorns. When oxalates move, bleeding occurs due to damage to the walls of the ureter by the cutting edges.
In most cases, stones have a mixed composition; protein, cholesterol, xanthine or cystine crystals are quite rare. Uric acid stones occur predominantly in elderly patients.
Diagnostic methods
To detect a stone in the bladder, kidney or ureter, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination, computed tomography, or contrast-enhanced radiography. These diagnostic methods make it possible to assess the condition of the urinary system and differentiate urolithiasis from other diseases of the pelvic organs.
The urologist palpates the abdomen and lumbar region. The diagnosis can be confirmed with a positive Pasternatsky reaction. Percussion (tapping) of the bladder is also required to identify signs of cystolithiasis, a delay in the outflow of urine that occurs due to obstruction of the excretory canal.
If colic symptoms are bothering you, the doctor examines the patient, finds out how long the attack lasts, whether there is a hereditary predisposition to urolithiasis, recurrent pathologies of the digestive system, or congenital diseases.
If a stone has formed in the bladder in women, laboratory tests are prescribed. In case of urolithiasis, accompanied by an infectious process, a large number of leukocytes and an increased blood ESR are found in the urine. In addition, the acidity of urine, its specific gravity, the presence of salt sediment, hematuria, protein, and single cylinders are determined. For infectious diseases of the urinary system, bacteriological urine culture is indicated to determine the causative agent of the disease and select an effective antibiotic.
After a biochemical analysis, women with urolithiasis are found to have increased concentrations of creatinine, uric acid, phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium in the blood. To assess the functioning of the kidneys, daily diuresis is determined; if the ureter is obstructed by a stone, its volume is significantly reduced.
Methods of therapy
Treatment of urolithiasis in women is carried out taking into account the location of the stone, its size, the presence of inflammation, and concomitant diseases. Therapy is aimed at normalizing the flow of urine, eliminating infection, and removing or dissolving stones. To relieve the symptoms of colic during an exacerbation, antispasmodics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Treatment of urolithiasis can be medicinal or surgical. The conservative method is indicated for patients with stones less than 0.5 cm; for this purpose, drugs are prescribed that promote natural passage, dissolution of stones and change the acidity of urine to the alkaline side. Only stones of mixed genesis and urates are subject to softening. Medicines (Urolit, Blemaren) contain citrate substances, which increase the concentration of sodium and potassium ions in the urine. Therapy lasts 1–6 months. To remove stones localized in the lower part of the ureter, adrenergic blockers are prescribed.
If a small stone appears in the bladder, treatment with herbal remedies may be prescribed: Canephron, Cyston, Phytolysin. The active components of these drugs relieve inflammation, have a diuretic, antioxidant and nephroprotective effect, and increase the effectiveness of antibiotics.
Antibacterial therapy is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process. For urolithiasis, drugs from the group of fluoroquinols, cephalosporins, and aminoglycosides (Ceftriaxone, Amikacin) are used. Thiazide diuretics, magnesium, vitamin B6, bisphosphonates are prescribed to correct the biochemical composition of blood and urine.
Diet therapy
Following a diet for urolithiasis allows you to normalize the pH of urine, metabolic processes, and reduce the risk of progression of the disease. Changing the diet depends on the chemical composition of the stones.
When urates are formed, meat, sausages, legumes, coffee, alcoholic beverages and chocolate are excluded from the daily menu. Patients need to consume at least 2–3 liters of fluid per day, eat more fresh vegetables, fruits, berries, and whole grain cereals.
If a stone in the bladder or kidney is formed by oxalates, limit the amount of dairy and fermented milk products, black currants, strong coffee, tea, sweets, strawberries and herbs. The daily drinking regimen is 2 liters of clean water.
If you have phosphate stones, you should not eat large quantities of dairy products, fatty meats, fish, hard cheeses, and confectionery products. Daily fluid intake is calculated from the volume of daily diuresis (on average 2–2.5 l).
You can drink clean, still water, green or herbal tea made from chamomile, half a stick, and bear ears. It is recommended to steam or bake the dishes in the oven. If you cannot eat meat, then the ban also applies to meat broths and soups. They can be replaced with vegetables, excluding tomatoes, sorrel in case of increased acidity of urine.
Surgical treatment options
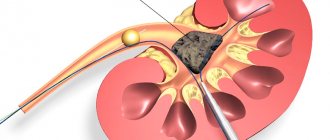
The indication for surgical intervention for urolithiasis is a violation of the outflow of urine caused by obstruction of the excretory canals by stones. Stones are removed using traditional or minimally invasive methods.
With the classical technique, an external incision is made, and after the intervention a long recovery period is required, complications often arise. Nowadays, operations are most often performed using minimally invasive or endoscopic methods. The first type is performed using laparoscopic instruments that are inserted through small punctures in the abdominal wall. If the stone is large, lithotripsy (laser crushing) is first performed, and then small parts are removed.
Endoscopic surgery does not require any incisions or punctures; instruments are inserted through the natural openings (urethra) and the stone is removed. In case of prolonged obstruction of the ureter and a high risk of dystrophic changes, a stent is inserted into the canal, expanding the lumen and improving the outflow of urine.
External lithotripsy is the crushing of stones with a laser beam into smaller fragments, which are later released naturally. This method of treatment is prescribed if the doctor is confident that the stones will be able to completely leave the body without causing complications.
Prevention of ICD
The development of urolithiasis in women can be prevented with a balanced diet. The diet must contain all the necessary vitamins, amino acids and microelements. If tap water is of low quality, it must be purified and purchased bottled.
To prevent urolithiasis, it is important to promptly treat inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, concomitant ailments of other internal organs, strengthen the immune system, lead an active lifestyle, and visit sanatoriums.
If symptoms of illness appear, you should consult a doctor and treat urolithiasis at an early stage.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
Provided that adequate treatment of the disease is started in a timely manner and lifestyle correction (in particular, by observing the drinking regime and diet), the prognosis of the disease is favorable. If left untreated, sand in the kidneys quite quickly forms into solid fractions and is complicated by the occurrence of urolithiasis, which, in turn, can cause the development of chronic renal failure, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the kidneys (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis). These conditions are extremely difficult to treat and lead to disability of the patient.
Diet for sand in the bladder
Timely cleansing and getting rid of toxins, urination is part of our daily life, just like breathing, drinking, eating.
Sometimes it is difficult for the body to cope with accumulated toxins, especially if they enter the body in large quantities. Therefore, if you want to have good health, your body needs to be periodically helped to remove waste substances through safe or natural means.
This way you will not only improve your health, but also prolong your youth. Failure to take measures to eliminate sand from the urinary system leads to serious complications. Over time, the particles will increase in size, transform into stones, and interfere with the normal functioning of organs and the timely release of urine.
The kidneys are a paired organ that performs the function of purifying the blood and normalizing the water-salt balance. When these processes are disrupted, it increases the risk of salt and mineral crystals forming. If they are small in size, they come out on their own and without pain. However, when they accumulate, urolithiasis develops, which requires specific therapy with proper nutrition.
The result is infections that develop in tissues, inflammation, including cystitis, pathologies and kidney dysfunction. In addition, the treatment itself will be longer and more intense, and grinding the stones and then removing the fragments can be painful. The sooner salt deposits in the genitourinary system are detected, the greater the chance of getting rid of them quickly and with minimal discomfort. Timely measures taken will help to avoid more serious pathological situations and maintain normal kidney and bladder function.
If it is quite easy to get rid of sand in the bladder using medications and diuretics, then it is more difficult to prevent the formation of new salt formations.
That is why, if similar problems have already been diagnosed, there is a predisposition, then the following measures must be observed: It is impossible to completely eliminate the formation of particulate matter in the bladder and kidneys, but preventive measures will help reduce this likelihood.
Preventing the appearance of sand in the kidneys
Prevention of the formation of sand in the kidneys is the elimination of risk factors for the development of the disease, such as:
- proper, balanced nutrition;
- moderate physical activity;
- eliminating bad habits;
- compliance with the drinking regime.
Video: how to prevent urolithiasis
Sand in the kidneys is a common disease in men, which may not manifest itself for a long time. But being the first stage in the development of urolithiasis, this condition requires immediate treatment, the basis of which is lifestyle correction and supportive drug therapy if necessary.
Urolithiasis (UCD) is accompanied by metabolic disorders in the body. This gradually leads to the formation of sand and stones (calculi) in the urinary tract area. They can have different sizes, shapes and compositions. At the very beginning of salt metabolism disorders (nephrolithiasis), stones do not yet appear. In this case, sand can already be found in the urine, which from a medical point of view is called uric acid diathesis. A diet for sand in the kidneys helps stop the development of the disease and eliminate dysfunctions occurring in the body.
When is nutritional adjustment needed?
With a problem such as sand in the kidneys, diet and proper nutrition are very important. The sooner measures are taken, the greater the chances of a positive outcome and the absence of complications. KSD is accompanied by dysfunction of the kidneys, ureter and bladder. In this case, the outflow of fluid becomes difficult. In advanced cases, life-threatening conditions may develop that occur when the lumen is blocked - peritonitis, urosepsis and rupture of internal organs.
There are no symptoms of sand in the kidneys until the formations reach 3 mm in size. If the stones exceed this size, then an acute condition may develop - renal colic, which is characterized by urination problems and severe pain.
Over time, small salt particles damage the mucous membranes of the urethra and ureter. Most often this is observed when sand comes out of the kidneys. This process is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Burning in the perineal area.
- Pain when urinating.
- The appearance of blood in the urine.
- Discomfort in the area of the ureters (4-7 cm from the navel on both sides).
Improvements occur when small stones leave the urinary tract, the listed symptoms of urolithiasis disappear and the person begins to feel absolutely healthy. But this does not mean that healing has occurred. After some time (2-3 months - 1-3 years) a relapse will occur.
Delicious and healthy recipes
Talking about the diet and nutrition indicated for sand in the kidneys, it is worth considering several interesting recipes. An excellent and versatile option would be vegetable stew. Here's how to prepare it:
A diet with sand in the kidneys (especially for women) can be difficult without sweets. But you don’t need to limit yourself completely. Here is a good recipe for casserole with rice and cottage cheese for tea:
When does diet cure?
Food affects the chemical composition of urine. What we eat increases the volume of stones or dissolves the formations and removes the remains naturally. The effectiveness of dietary nutrition is aimed at changing the pH level of urine - a pH value that indicates the number of hydrogen ions.
The diet for kidney urolithiasis eliminates sand and stones, fighting not only the symptoms of the disease, but also the causes of development.
- Corrects lack of fluid in the body.
- Restoring impaired blood supply processes in the kidney area.
- Normalizes the acidity of urine and improves the removal of stones.
With the help of properly selected products, you can cure the initial stages of the development of infectious diseases of the urinary tract.
Please note that it is important to consider the type of salt deposits. Each of them has its own corrective measures.
When is a diet necessary?
It should be noted that a diet for kidney stones and sand helps to cope with various causes of the development of urolithiasis, be it urates, phosphate salts or oxalates. The main thing is to start taking measures in time, which allows you to cope with the pathological process in the body at the initial stage of its development. If you do not adjust your diet, there is a high risk of developing serious complications that can cause dysfunction of internal organs and, in severe cases, cause emergency conditions.
In any case, with ICD you cannot do without a diet. Proper nutrition can be the main corrective measure or an auxiliary one. Dietary nutrition is often recommended in conjunction with drug therapy. After surgical correction, there is also a need to consume gentle foods that help prevent the formation of moles in the kidneys and promote their elimination.
About the effectiveness of the diet
Of course, a well-designed diet will definitely lead to recovery. There is no need to doubt the need for a diet. On the contrary, if a person continues to consume foods that lead to the formation of a problem, nothing good will come of it.
But before starting the diet, you need to undergo a urological examination. The doctor will help determine what kind of sand is in the patient’s kidneys, what it consists of, and how much of it there is.
The doctor will also select the optimal dosage of the drugs needed for treatment and determine the frequency of administration. Drug therapy is as important as maintaining proper nutrition.
If a person does everything correctly, the stones will begin to dissolve within 2 weeks from the start of the diet and treatment. It is very important not to interrupt the course you have started and not to allow yourself “weaknesses” in your diet.
Oxalates
Acidic salts or salts of oxalic acid are corrected by eliminating salt and acidic foods from the diet. With a large amount of oxalates, there are risks of developing oxaluria. The causes of body dysfunction are disturbances in the metabolism of glyoxylic acid and glycine.
| Nuts (hazelnuts, peanuts, walnuts) | ||
| Strictly prohibited | Limit quantity | Basic diet |
| Offal (brains, tongue, kidneys and liver) | Whole milk | Meat, fish, sausage, frankfurters |
| Cheeses (hard and salty) | Vegetables (potatoes) | Fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese) |
| Fruits (pears) | Mushrooms | Oils (vegetable, butter) |
| Vegetables (beets) | Sweets (honey, jam, sugar) | Cereals (oatmeal, millet, pearl barley, buckwheat) |
| Spinach, sorrel, mushrooms, rhubarb | Drinks (tea) | Vegetables (turnips, eggplants, cabbage, pumpkin) |
| Berries (strawberries) | Fruits (bananas, apricots) | |
| Broths (meat, fish, mushroom) | Drinks (mousse, compote, jelly) | |
| Smoked products | ||
| Salty and spicy snacks (caviar, canned food, horseradish, mustard) | ||
| Sweets (sweets, chocolate) | ||
| Drinks (coffee) |
Physical activity is of great importance. Special gymnastic exercises help remove sand from the kidneys faster.
Nutrition with oxalate sand
The formation of oxalates in the kidneys occurs due to excessive production of oxalic acid in the body. Therefore, the diet should include those foods that can dissolve oxalate stones. You need to exclude dishes that contain oxalates from the menu.
Allowed products: alkaline mineral water, boiled fish and meat, sausages and sausages, dairy products and cereals (barley, buckwheat, millet and oatmeal), pasta and fresh vegetables, bananas and apricots, fruit juice and kvass, weak coffee and tea.
Prohibited products: salted fish, offal (kidneys, liver, etc.), gelatin-based dishes, cheese and mushrooms, rhubarb and spinach, sorrel and strawberries, pears, beans, pickles, meat and fish broths, smoked meats, horseradish and mustard, as well as chocolate, cocoa and strong coffee.
Phosphate salts
The main task of the diet is acidification of urine. In this case, it is necessary to limit the intake of calcium into the body.
| Prohibited Products | Limit quantity | Basic diet |
| Canned and smoked products | Sour cream (no more than 50 g per day) | Poultry and fish (low-fat varieties) |
| Hard cheeses and cottage cheese | Chicken egg (3 pieces per week) | Broth (meat, mushroom, fish) |
| Fresh chicken egg | Vegetables (pumpkin, cabbage) | Flour products |
| Dairy | Legumes (peas) | Herring, caviar |
| Vegetable soups | Fruits (sour apples) | Cutlets (meat, fish) |
| Citrus fruits (grapefruit, orange, tangerine) | Berries (lingonberries, strawberries, red currants) | Butter (butter, vegetable) |
| Spicy snacks (mustard, garlic, red and black pepper) | Nuts – no more than 40 g per day | Porridge and pasta, weak tea and fruit drinks (cranberries, lingonberries) |
| Rose hips and alcoholic drinks | Sweets, watermelons |
Lemons can be eaten no more than 1 piece. in Week. Dairy products should be completely excluded from the diet. Fruit drinks should be drunk in large quantities. You should drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day.
Dietary recommendations for children
A diet for sand in the kidneys for children involves avoiding salty foods. You are allowed to consume no more than 5 g of salt per day. It is important to give your kidneys a rest. For this, doctors most often recommend a potato-cabbage diet, after which they prescribe diuretics for 2 weeks of treatment. Most often they make do with infusions and decoctions prepared from medicinal herbs: knotweed, plantain.
From the beginning of the 3rd week, it is recommended to drink 1-1.5 liters of mineral water for 7 days. This helps restore the mineral balance of the body and eliminates the likelihood of relapses.
For a month, it is unacceptable to eat foods rich in proteins (meat, fish, dairy and fermented milk, chicken eggs, spinach, nuts and legumes). It is also not recommended to eat food that contains mineral salts (mushrooms, caviar, smoked meats, saturated broths, millet, buckwheat). Sour foods are not recommended, such as pickles, rhubarb, sorrel, sour berries, sauerkraut, rose hips.
Children should be given potatoes, cereals (rice, semolina, oatmeal), cabbage, squash and cucumbers, as well as sweet pears and apples. It is recommended to exclude sweets.
Recommendations for creating a diet
After identifying a disease such as sand in the kidneys, a person must regularly visit a doctor and follow all his instructions. In addition to drug treatment, a prerequisite for getting rid of this pathology is a well-chosen diet.
The main component of the diet is clean water. You need to drink as much of it as possible, this will help reduce the concentration of sand. Under no circumstances should you replace water with liquids such as juices, soda, etc. Instead, you can use, for example, rosehip decoction.
Another important rule of the diet for sand in the kidneys is compliance with the energy value. Under no circumstances should you force the body to starve; food should be balanced. It is best to eat small meals 5-6 times a day.
When choosing a diet for the treatment of urolithiasis, it is very important to take into account the characteristics of the body. If you choose the wrong diet, digestive system disorders can worsen. This will provoke a deterioration in the absorption of vitamins and microelements, which can lead to the formation of stones.
Depending on the characteristics of the body and the nature of the disease, sand in the kidneys can be urate, oxalate and phosphate. This division into species is associated with its basic composition. A mixed type is quite common.
The diet for sand in the kidneys is different for each type of disease. For example, a suitable diet for removing sand from phosphate will be completely unacceptable for the urate type. On the contrary, it can provoke the formation of stones.