Treatment with antibiotics often leads to consequences if you do not follow the doctor's exact instructions. Many patients face problems related to the body's excretory system, namely, severe pain in the kidneys after taking antibiotics. This is due to the fact that antibacterial drugs have a negative effect on healthy kidney cells and tissues, thereby causing disorders and even diseases.
Kidneys can hurt in different ways. The patient often complains of frequent and recurrent attacks. By nature they can be sharp, aching or pulling. Taking antibiotics is especially dangerous for patients with chronic pathologies: pyelonephritis or renal failure.
The attending physician must prescribe therapy with antibacterial agents , and uncontrolled use of medications will lead to disruption of vital human organs. After all, it is the kidneys that remove antibiotic breakdown products from the body.
How does kidney damage occur?
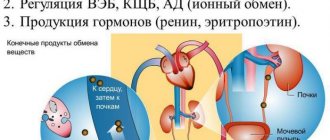
An increase in the level of urea in the blood during antibiotic therapy is the main signal of disturbances in the body. Therefore, changes in the functioning of the urinary system can also be manifested by a change in the amount of urine excreted (both an increase in the volume of diuresis and its decrease), severe thirst, and an increase in the level of urea in the blood plasma. These manifestations indicate a violation of the absorption and release of fluid.
In clinical practice, there are two mechanisms of renal tissue damage:
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the tubular epithelium.
- Poor circulation, changes in the hemodynamics of the liver parenchyma and its subsequent ischemia.
If the patient has not previously observed disorders in the renal organ, then the risk of developing side effects is minimal. But if there is a history of inflammatory diseases, then before taking antibiotics the patient should warn the attending physician about this.
general information
Antibacterial drugs help stop the inflammatory process; they block the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. But drugs of this class not only lead to the death of pathogenic microorganisms, they also have a harmful effect on beneficial bacteria.
There are several types of antibiotics and not all of them are toxic to the kidneys. There is a group of drugs called nephrotoxic. It includes not only antibacterial agents, but also medications of other types.
Antibiotics, in most cases, are used for bacterial infection; if we are talking about drugs that have a toxic effect on the kidneys, then taking them can cause:
- disruption of the glomerular filtration process;
- increased blood pressure in the kidneys.
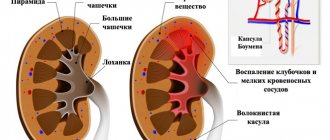
Disruption of the glomerular filtration process occurs due to damage to epithelial tissue and can lead to the development of renal failure. Against the background of such changes, the filtration function of organs decreases, fluid stagnation occurs in the body, and the likelihood of death arises.
An increase in the level of pressure in the kidneys is renal hypertension, a disease that leads to pathological processes. Against the background of an increase in blood pressure in the kidneys, damage to large arteries occurs, as a result of which inflammatory and infectious processes develop in the glomeruli.
Doctors are well aware that certain medications are nephrotoxic, for this reason they recommend:
- if there are contraindications, do not use antibiotics that are hazardous to health;
- do not combine several types of tablets without the knowledge of a specialist;
- do not violate the rules for using drugs (dosage, course of treatment, mechanism of administration);
- If you have chronic kidney disease, notify your doctor.
Not all antibacterial agents are toxic to the kidneys, but combining several medications or increasing the dosage can negatively affect the health of these organs.
What to do if pain occurs?
If you don’t know what to do if your kidneys hurt after antibiotics, then go to your doctor. To identify the cause of any violations, a general blood and urine test is performed. This helps make assumptions about the level of damage to the kidney tissue.
Self-prescription of medications for the development of nephropathy is unacceptable. If the patient's condition is not corrected in a timely manner, negative consequences may develop, which include glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, uremia, and hepatic-renal failure. Despite this, it is possible to suspend the course of previously prescribed medications after consulting a urologist, since abruptly stopping them can cause a deterioration in well-being due to aggravation of the underlying disease.
Kidney pain after antibiotic therapy
Treatment of a number of diseases requires the use of antibacterial drugs. They actively suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganism cells, consistently destroying their DNA, and have a detrimental effect, preventing the development of infectious processes. But often beneficial bacteria that normalize kidney function also come under their influence. The main function of the paired organ is filtration and excretion, so it is most often exposed to negative effects. The lack of beneficial microorganisms harms the kidneys, causing various disorders.
Features and mechanism of action of antibiotics on the kidneys
Experts identify two main principles of the pathological effect of antibiotics on the paired organ, the reaction of which begins to manifest itself after the first contact with the medication. Kidney damage can develop as a toxic or allergic type. Quite often they are combined, and then pathological changes begin to occur in the organ.
Toxic
Due to impaired blood filtration, the toxic components present in it are not eliminated, but circulate through the vessels, causing harm, first of all, to the kidneys. As a result, the following conditions arise:
- the glomerular apparatus is affected, leading to the development of glomerulonephritis;
- the inflammatory process characteristic of pyelonephritis begins to develop;
- Blood pressure increases and diabetic nephropathy may develop.
Allergic
Kidney damage develops as a result of a toxic reaction after the initial interaction with drug allergens and the formation of immune complexes. With the further influence of antibiotics, antibodies and antigens are formed, which, due to their large molecular structure, are unable to penetrate the renal tubules.
Should I stop taking antibiotics?
The only correct tactic when pain in the kidneys appears after antibiotics is to follow all recommendations for taking the drug, which are described in the instructions. There is no need to reduce the dosage of tablets or the frequency of their use. If painful side effects occur, you should immediately inform the doctor who drew up the treatment plan. Some patients may need an ultrasound and urinalysis to evaluate kidney function. A large amount of water will help remove toxic antibiotic metabolites.
Mechanism of damage
When the blood filtration process is disrupted, toxins are retained in the body, they cause damage specifically to the kidneys, having the following effects on them:
- destroy glomerular cells, leading to signs of glomerulonephritis;
- cause inflammation, as in pyelonephritis;
- increase the level of blood pressure in the kidneys (as in renal hypertension and diabetic nephropathy).
Antibiotics cause damage to the kidneys, glomeruli, and increase blood pressure in the organs. All this causes pathological, structural changes that lead to the development of renal failure.
How to normalize kidney function?
Side effects from antibiotics can be significantly reduced or even prevented if you follow the basic recommendations for the use of this group of drugs :
- Use only those medications recommended by your doctor.
- Observe the duration of the therapeutic course, do not adjust the dosage yourself.
- Do not interrupt the course if side effects of the drugs occur.
- Follow the instructions for the drug or follow the doctor’s recommendations (how to use the drug correctly, what to take it with, etc.).
- For a faster recovery, stick to the prescribed diet, follow a rest regime, monitor your health over time by visiting a doctor again and taking tests.
There are several effective methods aimed at normalizing the functioning of the urinary system. These include:
- drinking enough liquid;
- compliance with bed rest;
- replacement of the drug.
At this stage, you should stop using diuretics, since in combination with the therapy used, they can only enhance the toxic effect of antibiotics. It is better to drink natural decoctions of rosehip or hawthorn and minimize the use of other medications.
During the recovery period, it is also recommended to completely eliminate foods containing caffeine, various carbonated drinks, alcohol from the diet and reduce the consumption of table salt. It is also worth reducing physical activity (refusing to go to the gym, heavy physical activity) and avoid hypothermia. Taking sorbents, probiotics and vitamins, which are prescribed only after consulting a doctor, will help improve your well-being.
Correction of drug therapy in the event of pain in the kidneys depends on: the nature of the toxic effect, its severity, contraindications to other drugs. The main thing is the level of dysfunction of the renal parenchyma. Since some patients with such complications are indicated for a course of hemodialysis, diet and lifestyle adjustments to restore normal functioning of the body.
What are the symptoms of the lesion?
There are a number of specific signs indicating that antibacterial therapy has had a toxic effect on the condition of the urinary system.
These symptoms include:
- pain in the lumbar spine;
- decreased or increased urine outflow;
- constant thirst, general weakness of the body;
- the appearance of blood in the urine (hematuria);
- increase in blood creatinine level.
Other specific signs of the underlying disease (if any) may also occur.
What leads to this condition
The condition develops against the background of kidney disease. Toxins only aggravate the patient’s general condition, since, due to impaired filtration functions, the kidneys are no longer able to fully perform their filtration function.
Prevention of complications during antibiotic therapy
If you experience side effects from antibiotics, you should first consult a doctor. As a rule, treatment correction consists of changing the drug and its dosage.
To prevent complications it is recommended:
- Drink enough fluids daily.
- During antibiotic therapy, adhere to proper nutrition.
- Do not change the dosage of the drug, frequency and duration of its use.
- Stop using toxic substances, which include ethanol.
- Do not use antibacterial drugs for prevention.
- During the course of treatment, stop using tablets that may reduce the effectiveness of antibiotics (after consulting with your doctor).
Drugs with toxic effects on renal tissue can be replaced by others with similar pharmacodynamics. As a rule, toxic medications are not used in clinical practice due to the high risk of side effects.
There are pharmaceutical drugs that, when used, cause 4 out of 5 patients to develop complications associated with kidney damage. Their prescription is possible only in the absence of an alternative solution and the rapid deterioration of the condition due to the progression of the underlying disease. They are used with extreme caution and monitoring the patient’s well-being over time.
Treatment for inflammatory diseases includes antibiotic therapy to kill germs. This is the only way to guarantee a quick and complete recovery of the patient. However, this group of drugs has side effects, so if pain in the kidneys develops after antibiotics, you should consult a doctor.
- Category: Articles
Should I stop taking my medications?
Therapy with antibacterial drugs is aimed at eliminating inflammatory reactions, suppressing the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and destroying colonies of pathogenic bacteria. During treatment of the underlying disease, patients often complain that their kidneys hurt when taking an antibiotic, so the idea arises of stopping the drug in order to get rid of unpleasant symptoms. Under no circumstances should you make such a decision on your own; this will disrupt the entire treatment cycle, increase the risk of the pathological process becoming chronic, and may cause complications. The first thing to do is to report all side effects, including those related to pain, to your doctor:
Antibacterial therapy
- To effectively destroy pathogenic bacteria, targeted action is required over a certain period of time; the course of treatment usually takes from five days to two weeks, depending on the extent of the damage. If you stop taking antibiotics because of pain earlier than expected, there is a chance that bacteria will become more resistant to specific effects, so in the future you will have to choose a drug from a different group, which may be even more toxic. If pain is associated with side effects of a certain group of antibiotics, the doctor prescribes an additional urine test to determine sensitivity to other types of antibacterial agents and selects a less toxic drug for treatment. Another option to reduce side effects is to reduce the dosage of the initial antibacterial drug, which makes treatment more comfortable, but requires increasing the duration of use.
- Pain may be associated not only with the effect of the antibiotic on kidney function. During their life, pathogenic bacteria produce specific toxins that are eliminated from the body, including through the urinary organs. Increased stress on the kidneys can cause pain. In this case, it is recommended to increase the amount of fluid you drink in order to reduce the concentration of residual waste products, reduce the load on the kidneys and speed up the removal of toxins from the body.
- Pain in the kidney area may be a symptom of an underlying disease, so refusing antibiotics will slow down the treatment process and will not provide relief. Before prescribing any medications, the doctor finds out the main cause of the pathological process and selects medications to influence the source of the problems. In the case of inflammatory processes, the cause of pain can only be eliminated by suppressing the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
Kidney ultrasound
During treatment with antibiotics, a prerequisite for successful treatment is periodic monitoring of the condition of the kidneys using ultrasound, urine tests to determine the microflora, and strict adherence to the recommended dosage of the drug.
Recommended topic:
Pregnancy and kidney disease
Any medications have side effects, but this is not a reason to refuse antibiotics and other medications on your own. Any questions regarding drug therapy should be discussed with your doctor, since compliance with the treatment regimen determines how successful the recovery from the pathological process will be.
At the examination stage and when receiving recommendations on the use of drugs, you should ask your doctor about possible side effects, whether your kidneys can hurt and what measures can be taken to reduce the risks. During a course of taking antibacterial agents, you need to monitor your diet, drinking regimen, follow the recommended dosages, and be sure to undergo intermediate examinations of the body’s condition.
Treatment
If pain or any symptoms occur, the patient should immediately consult a doctor. It should be noted that immediate withdrawal of the antibacterial drug is not sufficient treatment. The process of kidney damage has already started, so a number of specific measures will be required as therapy. Initially, you will need to undergo a certain set of tests, and then a consultation with a urologist will be scheduled.
At your appointment, you should tell the doctor your complaints and list all the medications, vitamins or dietary supplements you are taking. Regardless of whether they were prescribed by a doctor or taken on their own initiative. It is best to bring the original packaging with you.
During treatment, your doctor may recommend:
- follow a special diet;
- use probiotics;
- completely abandon physical activity;
- do not overexert yourself psychologically;
- take proper rest;
- take vitamins;
- strengthen the immune system.
In cases where it is impossible to stop taking antibacterial drugs, the doctor prescribes medications that will keep the kidneys in working condition and prevent the development of complications.