Salt diathesis of the kidneys is a fairly common phenomenon. In most cases, this condition is a harbinger of a much more serious pathology - urolithiasis.
Salt diathesis can hardly be called an exclusively nephrological disease.
Kidney organs
Basically, its cause is a complex of a number of different factors, ranging from systemic pathologies of the body to lifestyle and diet.
Therefore, for effective treatment of salt diathesis, it is necessary to eliminate everything that can have such a negative effect on the kidneys.
What it is?
Salt diathesis (or urolithiasis) is a kidney disease accompanied by the deposition of salts and minerals in the parenchyma of the organ, which provokes a decrease in kidney function and general intoxication.
The function of the excretory system is to remove harmful substances from the body, including salts and minerals. Thus, with salt (urine-salt) diathesis, such substances crystallize and are deposited in the renal calyces, pelvis and bladder.
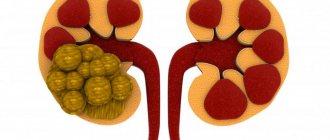
With further development of the disease without proper treatment, the amount of deposits increases and stones form . The main calcium and magnesium compounds prone to crystallization are:
- urates;
- phosphates;
- oxalates;
- carbonates.
Diathesis is secondary . It is most likely to develop during inflammatory processes in the kidneys, when their activity is reduced. Inflammation and the addition of infection deforms and damages the kidney structures and contributes to the occurrence of renal failure.
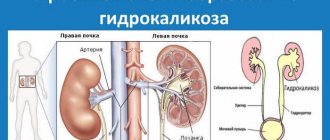
As a result, urine is retained in the pelvis and is excreted more slowly than in healthy organs. Its accumulation at high concentrations provokes the crystallization of inorganic substances contained in the urine and their deposition on the walls of the organ. When deposited, they resemble red sand .
Doctors say that without timely treatment, salt diathesis leads to urolithiasis. In addition, its exacerbation is possible with repeated inflammation of the organs that make up the excretory system.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, tenth edition (ICD-10), salt diathesis of the kidneys is a disorder of purine and pyrimidine metabolism and has code E79.
Find out the distinctive features of uric acid diathesis here.
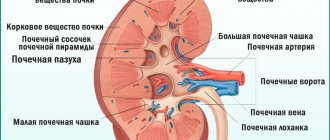
Structure of the urinary system
Nephron
Urine formation occurs in the kidneys. During this process, many functions are performed:
- filtering and cleansing the blood of nitrogenous wastes and end products of the breakdown of foreign compounds that have entered the body, for example, some poisons and medications are broken down in the kidneys;
- regulation of the concentration of electrolytes in the body, their excess is excreted in the urine;
- maintaining a constant volume of intercellular and intracellular fluid in all organs and tissues;
- maintaining a stable level of blood pressure by removing excess fluid and elements such as sodium, potassium, chlorides, etc.;
Urine formation occurs in the functional cell of the kidney - the nephron. They are located in the renal tissue - parenchyma, which is covered on the outside with a protective fibrous capsule.
The final urine accumulates in small calyces, which are combined into two large ones. They, in turn, merge into the pelvis.
From there, urine flows through the ureter into the bladder, and from it through the urethra it is excreted from the body.
Causes
Damage to kidney tissue of an inflammatory and infectious nature leads to the formation of urolithiasis in a patient. Thus, its development is often due to pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. In addition, this pathology is provoked by the following factors :
- An unbalanced diet, replete with fatty and salty foods, alcohol abuse. This leads to metabolic disorders, due to which a large amount of salts is formed.
- Lack of fluid. Water participates in metabolic processes, which, if disrupted, produce by-product minerals. Also, the reduced amount of fluid makes the urine more concentrated, which makes it easier for salts to crystallize.
- Vitamin deficiency. This phenomenon also destabilizes metabolism.
- A hereditary predisposition to kidney inflammation makes them vulnerable to various types of pathologies.
- The anatomical features of the structure of the renal structures lead to urine retention in the organs.
- Long-term drug treatment that increases the salinity of urine.
- Hormonal imbalance affecting metabolism and the performance of the excretory system.
- Excessive purification of water deprives the body of necessary chemical compounds.
- Severe intoxication also impairs metabolism and the ability of the kidneys to perform their functions.
The combination of these reasons leads to stagnation of urine in the pelvis , an increase in its concentration and the appearance of salts prone to crystallization.
Authorized Products
For oxalate salts:
- A dairy-vegetable diet is necessary. It is important to eat any dairy products every day.
- To reduce the absorption of oxalates, you need to consume vitamins B1 and B6 with foods: eggs, liver, fish, meat, poultry. They are chosen as low-fat varieties and prepared boiled or baked.
- Any bread and all types of cereals.
- Healthy vegetables include: carrots, cilantro, pumpkin, cucumbers, cauliflower and white cabbage, potatoes, and eggplants should be limited.
- The diet should include foods with magnesium: seafood, seaweed, porridge (oatmeal, pearl barley, buckwheat), wheat bran, peas, soybeans, wholemeal bread, dried apricots. This is due to the fact that magnesium binds oxalic acid to form magnesium oxalates - these salts are highly soluble. With a lack of magnesium, insoluble calcium oxalate salts are formed.
- Vegetable oil and butter should always be present in the diet.
- A variety of fruits: apricots, bananas, dogwoods, grapes, peaches, quinces, pears, plums, apples, watermelons, melon. The removal of this type of salts is helped by the consumption of apples, decoctions of fruit peels, pear leaves, currants and grapes.
- Alkalinization of urine is caused by dried fruits, which should always be in the diet.
For urate salts it is recommended:
- Vegetables (except legumes and those containing oxalic acid). Vegetables are best consumed raw. Preference should be given to vegetables containing vitamin A (seaweed, broccoli) and vitamin B (bell pepper, corn, rose hips, white cabbage).
- Fruits containing vitamin C: strawberries, wild strawberries, sea buckthorn, grapes, rose hips, currants, kiwi, lemon and other citrus fruits.
- Milk, cheese, eggs, cottage cheese, butter.
- Various cereals.
- Bread (rye, bran and wheat). Preference is given to baking without yeast.
- Lean meat and fish are consumed 3 times a week. Due to the fact that turkey meat contains less purines, it should be preferred. Chicken breast contains less purine bases than chicken legs. When preparing meat or fish dishes, the products are first boiled with water replaced to reduce purines. Broths are not used.
- Vegetable and cereal soups with water or vegetable broth.
- Protein omelettes.
- Marmalade, caramel, jam, sugar, honey, marshmallows, pastille. You can't eat chocolate.
- During the day, drink bran decoction, water with citrus fruits, juices, herbal teas.
For phosphate salts, a diet dominated by meat and baked goods is recommended:
- Meat, chicken, turkey in any form.
- Fish, soaked herring, fish snacks and, occasionally, canned fish in small quantities.
- Different types of bread, pasta and other flour products, dough dishes, a variety of water porridges.
- Confectionery, jam and honey.
- Cereal soups, pasta, with egg mixture.
- Vegetable fats and sour cream for adding to dishes are allowed in small quantities.
- It is necessary to increase the intake of vitamin A, which is found in the liver of animals and fish, fish caviar, butter, as well as vitamin D from fatty fish and fish caviar.
- One egg a day.
- It is recommended to exclude almost all vegetables and vegetable juices. Eating pumpkin, green peas, mushrooms, and Brussels sprouts is allowed.
- You can include in your diet rosehip decoction, weak tea and coffee, kvass, cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks, sour apples, cranberry jelly, lingonberry, and red currant compotes.
Symptoms and signs of pathology
In the initial stages, salt diathesis is accompanied by the accumulation of salts in the kidneys, which does not cause discomfort in the patient, and therefore complicates diagnosis at this stage.
With pronounced development of pathology, the following signs are observed:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- burning and pain when urinating;
- feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- periodic pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- decreased amount of urine;
- blood in the urine;
- red sediment in urine;
- increased temperature due to inflammation;
- swelling;
- intoxication;
- increased blood pressure due to vasospasm;
- the smell of acetone in severe intoxication.
The first signs characteristic of salt diathesis are pain and difficulty urinating . If there is an inflammatory process in the body, the patient suffers from intoxication, fever and weakness.
If you notice these symptoms, it is recommended to seek medical help.
This can be explained by the fact that this disease requires immediate treatment, as it leads to the development of complications.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for salt diathesis of the kidneys caused by oxalate salts excludes:
- Products with oxalic acid and gelatin-containing dishes.
- Fatty meats and fish, and low-fat ones are allowed limited - no more than 150 g every other day.
- Do not eat soups with strong broths or bean soups.
- Sprouted grains.
- Salty cheeses, any canned food and smoked meats.
- Cocoa, kvass, coffee, chocolate.
- Sweet dough.
- You should limit your diet to dishes made from beets and potatoes, tomatoes, onions, carrots, eggplants, Brussels sprouts, zucchini, legumes, celery, parsley, and rhubarb.
- The consumption of dairy products, as well as vitamin C (oranges, lemon, currants, rose hips, tangerines, grapefruit, rowan, gooseberries, strawberries, sour apples, cranberries, dill, bell peppers, wild garlic) is significantly limited.
- You should also limit salt (3-4 g).
When using urates, avoid the use of:
- Offal and any broths. Only occasionally can you cook with secondary broth.
- Meat products and canned food. The diet limits animal protein and completely excludes meat from young animals. All meat and fish dishes are prepared by boiling.
- Beef and pork fat.
- Bean and sorrel soups.
- Dishes of halibut, sardines, carp, sea bass, tuna, mussels, as well as canned fish.
- Vegetables with a high content of oxalic acid are sorrel, radishes, pickled vegetables, spinach, asparagus, cauliflower, cranberries, raspberries and purines - legumes and mushrooms.
- Refined rice, oatmeal and dried fruits.
- Confectionery, beer, brewer's yeast.
- Cheeses, chocolate, tea and coffee, red wine, cocoa, which are rich in purines.
For phosphate microliths the following are not recommended:
- Milk, cottage cheese, sesame seeds, cheese and other calcium-containing products.
- Nuts, cocoa, sweet baked goods made with yeast.
- Greens and vegetables. The list of allowed vegetables includes only Brussels sprouts, peas, pumpkin, green peas, and mushrooms.
- Smoked meats, sauces, hot seasonings.
- Alcohol in any form.
Is it dangerous?
Without timely treatment, developing urolithiasis affects not only the kidney tissue, but also affects the entire body. Thus, the accumulation and disruption of the excretion of salts leads to the fact that they are deposited in the parenchyma of the organ and joints. The most common consequences of this disease are expressed in the following pathologies:
- urolithiasis of the kidneys;
- gout;
- arthrosis;
- arthritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- spondylosis;
- interstitial nephritis;
- urate nephropathy;
- severe renal failure.
These complications can be avoided by timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diet price
The diet of almost all diets is dominated by dairy products, fruits, vegetables and cereals. Based on this, food is not expensive, and its cost can be 1400-1500 rubles per week.
Work experience: Work as head of the disinfection and sterilization department 1981 - 1992. Work as head of the department of especially dangerous infections 1992 - 2010. Teaching activity at the Medical Institute 2010 - 2013
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
How is it diagnosed?
When a patient seeks help and suspects he has salt diathesis, the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination to identify all disorders and establish the causes of the disease. At the first stage, he interviews the person about the presence of pain and urination problems, his lifestyle and diet. This helps to suggest pathology and adjust the study.
, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed :
- Urine tests. Changes in clarity, color, concentration and composition. Increased level of organic acids, pH value below seven, dominance in the composition of salts. The presence of proteins and red blood cells in the urine.
- Blood analysis. Leukocytosis and increased ESR, the presence of urea, nitrogen and creatinine in the composition.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys. Echo-positive inclusions at the initial stages, visualized crystals and sand at later stages. Echo signs of the disease allow us to accurately confirm the presence of this pathology in the kidneys.
- X-ray of the excretory system. Detects obstruction of ducts and stones in organs.
The totality of examination data allows us to create the most detailed picture of the disease and select the necessary treatment in accordance with the patient’s characteristics and the severity of the pathology.
Diagnostics
The main indicator of the development of urate diathesis is the increased content of salts in urine. Therefore, when conducting diagnostics, urine is examined first. Its general and biochemical analyzes are carried out: color, transparency, density, pH, salt content, presence of sugar, protein components are determined, and sediment microscopy is studied. In addition, a general and biochemical blood test is prescribed to determine: the level of urea, creatinine, nitrogen, and the presence of sugar.
Instrumental examination methods are used to clarify the diagnosis: some of the abnormalities found in the examination of urine and blood are also characteristic of other diseases. In addition, ultrasound, sonography or urography make it possible to detect small urinary stones that are not yet causing concern and begin timely treatment of developing urolithiasis.
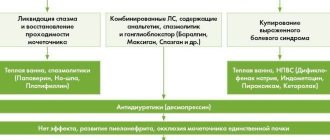
Treatment of diathesis
Before the transition of salt diathesis to urolithiasis, drug therapy is effective . Doctors prescribe groups of drugs whose action is aimed at eliminating certain causes and symptoms of the disease:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs act on the root cause of the pathology – inflammation of the parenchyma.
- Diuretics help remove sand from the kidneys.
- Antibiotics are used when the kidneys are infected by bacteria.
- Uroseptics are complex drugs that have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- General strengthening agents and vitamins.
However, medication alone is not enough. The cause of the disease is poor nutrition, and therefore there is a need to adhere to a special diet.
Why does the disorder develop?
The reasons for the development of salt diathesis include:
- genetic predisposition;
- insufficient fluid intake into the body;
- systematic unhealthy diet (smoked meats, fast foods, sausages, etc.);
- pregnancy (kidneys cannot cope with increased loads);
- metabolic disorders leading to increased levels of uric acid and calcium in the body;
- infectious kidney diseases that cause functional impairment.
Application of traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies should complement drug therapy. Traditional medicine can provide effective help, but its use should also be agreed with the attending physician.
One of the effective methods is the use of madder-based products. They are most effective in the presence of phosphate stones, which they successfully loosen. For treatment, you can use ready-made pharmaceutical drops - take 20 drops twice a day, simultaneously with meals, after diluting them in water. The course of treatment is 30–32 days. If the stones are large in size and pain occurs, it is recommended to purchase madder in powder form. The product is taken 2 times a day with water. If inflammatory reactions are detected, then it is better to prepare a tincture from the plant and consume 1 tsp. after eating (after 30 minutes).
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs containing anthraglycosides are very useful for the treatment of renal diathesis. Among such plants, the following stand out: St. John's wort, senna, rhubarb. The composition is prepared as follows. The crushed plant (1 tablespoon) is poured with boiling water (250 ml) and infused for 25–35 minutes. This portion is drunk during the day, and the general course of treatment is 5 days.
Another direction of alternative medicine is the prescription of herbal products containing saponins. The most famous plants are horse chestnut, licorice root, and horsetail.
With the development of kidney stones, the following folk remedies will undoubtedly be beneficial:
- carrot seed powder;
- parsley infusion using leaves and roots of the plant;
- infusion from a mixture: sweet clover, juniper fruits, shepherd's purse, bearberry, rose hips, nettle;
- heather infusion;
- Birch juice;
- knotweed infusion.
Particularly noteworthy is medicinal tea with the following composition: birch leaf, bearberry, horsetail, dandelion root, juniper fruits, licorice root (all 10 g), lingonberry leaf, flaxseed (20 g each). This drink is taken 3-4 times a day, 150-180 ml.
Salt diathesis can be considered a rather insidious disease that can cause serious kidney problems. This disease cannot be neglected, and at the first manifestations you should consult a doctor, because at an early stage the pathology can be treated quite easily
For preventive purposes, special attention should be paid to proper nutrition and sufficient drinking regime