Kidney diseases rank second in frequency of exacerbations during pregnancy after cardiovascular diseases. This is not surprising, given the degree of increasing load on the kidneys during this period. The kidneys of a pregnant woman literally work for two, because they remove waste products from both mother and child. And the longer the period, the more intensely they have to work.
In addition, as the period increases, the pressure of the uterus on the kidneys and bladder increases. The growing fetus takes up more and more space in the abdominal cavity, pushing the surrounding organs to the sides and squeezing them. Particularly great pressure is placed on the kidneys and bladder, which cannot pass without leaving a trace.
Decreased immunity and constant hormonal fluctuations lead to worsening kidney diseases during pregnancy. If you previously had any problems with the excretory system, then with a high degree of probability they will make themselves felt now. And in many cases, bacteriuria appears for the first time during pregnancy.
The above suggests that a pregnant woman’s kidneys become quite vulnerable, and their condition must be constantly monitored.
Indications for kidney ultrasound
Ultrasound of the kidneys is not prescribed for all pregnant women without exception. The examination requires certain prerequisites:
- Darkening of urine, presence of blood impurities, signs of sand or stones coming out, and a strong unpleasant odor of urine.
- Increased swelling, which intensifies in the first half of the day.
- Increase in blood pressure indicators.
- Injury (or suspected injury) to the abdomen or lower back.
- Feelings of discomfort (itching, burning), pain when urinating.
- Increased urination.
- Painful sensations in the lumbar region, lower abdomen, back, increased body temperature.
- Signs of symptomatic exacerbations of chronic endocrine diseases.
- Congenital anomalies of the development of the urinary system.
- Tumor processes, chronic diseases affecting the kidneys (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis).
- The presence of protein, blood in the urine, bacterial pathogens, signs of inflammatory processes (identified by the results of laboratory tests).
Increased swelling may be an indication for a kidney ultrasound.
If one or more of the above factors (symptoms) is present, the doctor may refer the patient for an ultrasound examination.
Possible pathology
The most common pathologies detected during pregnancy are hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis.
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis occurs in more than 12% of pregnant women. The ultrasound picture is practically no different from ordinary pyelonephritis. Thickening of the walls of the pelvis and, sometimes, calyces, swelling of the fiber of the renal sinus, blurring and unclearness of its pattern are determined.
Type of kidney in acute pyelonephritis
In the absence of timely treatment, parenchymal involvement may occur, which manifests itself in the appearance of foci of increased echogenicity with reduced blood flow. The changes usually affect only one affected kidney. But both kidneys enlarge, with a predominant increase in the affected one. In addition, there are changes in urine and blood tests, and the clinical picture, which makes it easy to establish a diagnosis.
In addition to newly diagnosed pyelonephritis, an exacerbation of an existing chronic pathology often occurs. With exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis, against the background of increased temperature and pain, changes appear in urine tests.
Sonography reveals a typical deep scar in the parenchyma above the flattened calyx. With a long-term ongoing process, the organ shrinks. When using the color duplex sonography mode, an increase in the final diastolic velocity of blood flow in the renal arteries and an increase in the systole-diastolic ratio are determined.
Signs of pyelonephritis: a round formation lacking blood supply. The rest of the kidney is supplied with blood normally. The diagnosis is pyelonephritis.
In the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment, a kidney abscess may develop against the background of pyelonephritis.
Echographically, it is visualized as a heterogeneous hypoechoic area with a clear echogenic contour of infiltrated parenchyma.
Hydronephrosis is a persistent violation of the outflow of urine in the ureteropelvic segment. This leads to expansion of the pelvis, and as it progresses, the calyces are also involved in the process. It should be remembered that during pregnancy the pelvis is somewhat dilated, which is not a pathology.
So, in the first trimester, sizes are allowed up to 18 mm, and in the second trimester - up to 27 mm.
If borderline indicators are detected, a diagnosis of pyelectasis is made and dynamic observation is necessary. A reliable method for diagnosing hydronephrosis is radiography, but due to the limited use of radiation methods during pregnancy, only ultrasound diagnostics is performed.
The diagnosis of hydronephrosis is made when the pelvis is dilated above acceptable values, the calyces are dilated, and the renal parenchyma is thinned. Determining the degree of hydronephrosis is only indicative; moreover, this pathology is often temporary and the changes gradually disappear after the birth of the child.
Types of kidney ultrasound
Depending on the detected symptoms, echography and Dopplerography (ultrasonography) may be performed.
Echography is a frequently used ultrasound diagnostic method that allows one to make a conclusion about the location, size, structural features, mobility of the organ, the presence of pathological formations, and stones. Echography is based on the ability of objects of different densities (including kidneys) to reflect ultrasonic waves.
There are two types of kidney ultrasound
When performing Doppler sonography, the condition of the blood vessels of the kidneys is analyzed. The ultrasound machine displays a graphic image called a Dopplerogram, from which the doctor can judge the direction of blood flow. The sound signals produced by the ultrasound machine indicate changes in the blood circulation of the kidneys.
Decoding
The results obtained should be deciphered by a doctor who has experience working with pregnant women. Since the parameters of the kidneys in women expecting a child are somewhat different from the sizes of the organs of a non-pregnant woman. Normally, the expectant mother should have the following indicators:
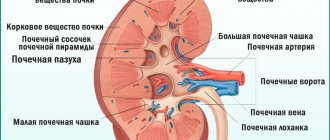
- the kidneys should be located in the retroperitoneal space at the level of the 2nd lumbar and 12th thoracic vertebrae. The location of the right kidney is slightly lower than the left;
- kidney mobility should be limited. Moreover, it should be observed only in a vertical position. The presence of increased mobility is a sign of pathology;
- normal kidney sizes should be no more than 12 cm in length, no more than 6 cm in width, and no more than 5 cm in thickness. These indicators are important because they indicate the presence of a number of diseases. For example, an enlarged organ indicates inflammatory processes and neoplasms. Reduced – about chronic pathologies, dystrophy;
- The thickness of the kidney tissue should be within 2.5 cm with a homogeneous structure. Thickened renal tissue occurs with inflammation, decreased - with pyelonephritis, diabetes mellitus, dystrophy;
- the renal pelvis should be free without the presence of any inclusions that occur with ICD;
- The structure of the fibrous capsule should be smooth.
After the examination, the woman is given a form with the results, which is used to assess the condition of the urinary system. The following changes may be written on the results form:
- microcalculosis, echogenic formation. This indicates the presence of stones;
- heterogeneity of echostructure, presence of echoshadows – tumors;
- hyperechogenicity, homogeneous formation - lipomas;
- anechoic formation, homogeneous anechoic content without the presence of an internal echo - cyst;
- purulent cavities – pyelonephritis, abscess;
- enlarged pelvis - blockage of the urinary tract.
If it is necessary to assess renal blood flow, Doppler ultrasound is performed. This type of diagnosis evaluates the volume and speed of blood flow. This indicator makes it possible to monitor the functionality of the kidneys. If during the diagnosis a decrease in blood flow is detected, then a version of congestion, cystic formation, or an inflammatory process is put forward. An increased blood flow rate is characteristic of a malignant formation.
The dimensions of the fetal renal apparatus are also subject to analysis
Preparing for the examination
An ultrasound examination of the kidneys can be performed regardless of the stage of pregnancy. If you are prone to flatulence, a few days before the procedure, it is recommended to stop consuming carbonated drinks, fresh milk, legumes, and minimize the consumption of sweets, fruit and vegetable dishes and other foods that can increase gas formation, which will ultimately distort the results.
If, despite dietary restrictions, flatulence actively manifests itself, medications (enterosorbents, espumizan) are used in consultation with the doctor.
Preparing for further examination
In order to prevent changes in the tone of the uterus before an ultrasound scan, there is no need to use medications with a laxative effect or enemas that cleanse the intestines.
An hour before the procedure, you need to drink about one liter of non-carbonated liquid, refraining from urinating until the end of the examination.
Before starting the procedure, it is necessary to remove clothing above the waist, jewelry and other items that may complicate the examination process and distort the results.
If an X-ray diagnosis was carried out, during which a contrast agent (for example, barium) was used, then an ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy can be performed no earlier than a few days after the specified examination. Another factor that complicates the procedure is obesity (overweight).
Treatment
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate treatment is prescribed. At the initial stage of development of the pathology, specific therapy is not carried out. In critical cases, surgery is required. One and most important indication is a violation of the organ’s activity.
There are also contraindications to surgical therapy. The first is the development of bilateral hydronephrosis. The second is the presence of a concomitant dangerous disease of an internal organ in the baby in the womb. According to Dr. Komarovsky, the only way out is premature termination of pregnancy.
Full treatment of the disease is carried out after the birth of the child. If after birth the pathology was diagnosed at the initial stage of development, no therapeutic measures are prescribed. To prevent complications, only a systematic control ultrasound examination is required (for the first 3 years - once every 4 months, subsequently - once every 12 months).
It is important to know! At later stages of pathology development, surgical intervention is prescribed. This is especially true in cases where the process of urine excretion in a newborn is significantly impaired, the work of the paired organ is slowed down or completely stopped.
If reflux is detected, diagnosed during fetal development, therapeutic measures are taken to prevent infection of the urinary tract. As a rule, this pathology disappears on its own as the child grows older. If there is no positive dynamics, surgical intervention is prescribed.
In order to determine treatment tactics, pyelectasia is divided into three degrees: mild, moderate and severe. For mild cases, only monitoring is required. With an average degree, the monitoring period increases, the probability of a successful outcome is high. The urethra develops, and the disease goes away on its own. Observation is carried out via ultrasound.
Severe severity requires only surgical intervention. The operation is performed using very small instruments so as not to damage the tissue. The instrument itself is inserted through the baby's urethra. Before surgical treatment, in order to avoid complications, babies are given anti-inflammatory drugs approved for use by newborns. As a result of the operation, the outflow of urine is restored, and the reflux of urine from the ureter into the bladder disappears.
After surgical treatment, a special diet is prescribed with the exclusion of foods that irritate the ureteral mucosa.
Degrees of dilation of the renal pelvis
Treatment with medications is not used, because it is not effective.
The prognosis for such a child does not imply any guarantees; the pathology may make itself known many years later. That is why such young patients need to be monitored very carefully. They are registered at the dispensary all their lives. Such patients are especially carefully monitored during the so-called periods dangerous in terms of relapse.
An anomaly detected in the prenatal period requires observation. The doctor evaluates the enlargement of the fetal pelvis over time and assigns one of three degrees to the pathology. In mild and moderate forms of the pathology, the prognosis is favorable: the pelvis returns to normal during the first year of life as the baby grows. In severe cases of bilateral progressive pyelectasis, surgery is indicated. It is done in 30% of cases.
The intervention is performed under anesthesia using laparoscopy, which eliminates large incisions. Miniature surgical instruments are inserted through the urethra and manipulations are performed under ultrasound guidance. The doctor’s goal is to restore the normal flow of urine and eliminate its backflow into the pelvis. After surgery, the baby is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs.
The operation does not guarantee a 100% recovery, and the little patient must be observed by a urologist until school, and then until puberty. During periods when the child is actively growing, relapse of the pathology is possible.
There are no special measures that can prevent pyeloectasis. Experts recommend that women plan pregnancy, treat genitourinary infections and kidney diseases before conception, and prevent relapses of chronic pathologies. For this purpose, before and after pregnancy you need to follow a diet, drinking regime and personal hygiene.
During pregnancy, it is important to avoid exposure to toxins and stay in environmentally polluted places. As recommended by your doctor, you should take diuretics to improve urine flow and prevent swelling. If a pathology is discovered in the fetus, it is important to adjust the diet and drinking regimen and carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations. Moderate physical activity of the mother in this situation will have a positive effect on the condition of the fetus.
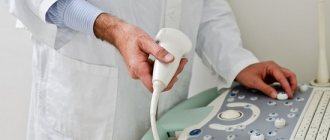
Description of the procedure
The patient, sitting on the couch, should take the position recommended by the diagnostician (lying on her side or on her back, less often - standing). It is not advisable to carry out the procedure while lying on the stomach, since the patient will experience discomfort.
At certain moments, the specialist asks you to hold your breath or inhale. The areas where the sensor touches are treated with a gel-like substance, which is removed from the skin surface after the diagnosis is completed.
Using an ultrasound machine, you can assess the size, structure, mobility, and position of the kidneys
During the examination, the doctor, using special equipment, assesses the size, structure, mobility, position of the kidneys, examines the sections of the ureter, the collecting system, and the bladder (if necessary). After the ultrasound examination, the patient is given the results (conclusion), analyzed by the attending physician and other specialists.
Is it possible to do
Often, expectant mothers wonder whether ultrasound is harmful to the baby, or whether it is dangerous to do ultrasound in the later stages. Scientists claim that during ultrasound, ultrasonic waves do not penetrate so deeply as to harm the health of the embryo. Although no research has been conducted on this issue. But there are no complaints that after diagnosis the child developed any disorders.
The risk of developing complications from undetected kidney pathology is many times more significant and real than the theoretical harm from an ultrasound procedure. Disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys can provoke vasospasm
, which supply blood to the embryo. This negatively affects the development of the fetus. The risk of infection of the baby, placental abruption and death of the child also increases.